RADT W14 L1 Imaging Pt w Special Needs; Descriptive Terminology
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
Which area in the mouth elicits the gag reflex?
Soft palate and lateral posterior third of the tongue
T or F - The lack of confidence may act as a psychogenic stimulus and elicit the pharyngeal reflex (gag reflex).
T
What are some tips for reducing a client’s gag reflex?
limit the amount of time the dental film is intraorally → be quick with it; longer its in the mouth, the more likely client with gag
place film and expose film as quickly as possible
use extraoral films in cases where client has extreme gag reflexes.

What exposure sequence should you use to reduce triggering the gag reflex?
Start with Anterior
Premolars to molars
Maxillary molars LAST
When placing films in the maxillary posterior areas, what should you NOT do? What SHOULD you do to prevent triggering the gag reflex?
DO NOT: slide the film along the palate
DO: position film lingual to the teeth and bring film into contact with the palate in one swift motion.
Why are radiographs useful for pediatric clients?
detecting lesions and conditions of teeth/bones
showing changes secondary to caries and trauma
evaluating growth and development
Rx for peds radiographs depends on: (3)
Child’s individual needs
Child’s age
Child’s co-operation
Why do we still take radiographs on edentulous clients?
To detect any root tips, impacted teeth, cysts, tumours
to identify objects, embedded in alveolar bone
to establish position of normal anatomic landmarks
to observe quantity and quality of existing bone
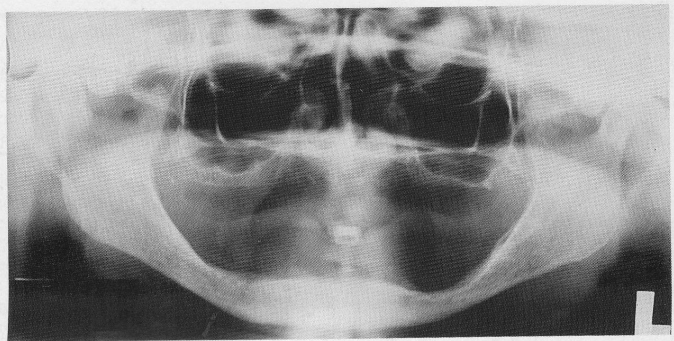
What is this ?
PAN bite block for Edentulous clients → no teeth to bite down.
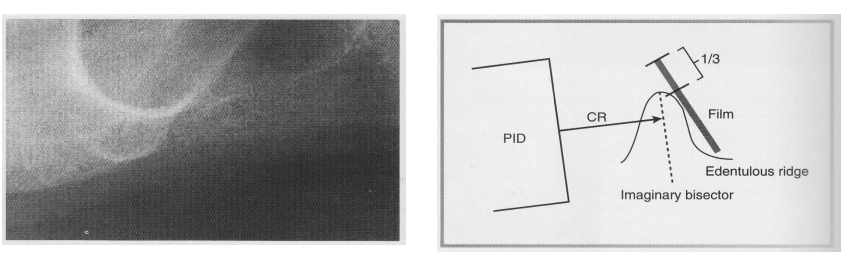
What are some technical adjustments that need to be made when using Paralleling or Bisecting technique to radiograph edentulous clients?
Paralleling → cotton rolls must be placed on BOTH sides of the BB to substitute missing teeth
Bisecting
Edentulous ridge and film form the angle to be bisected
a third of the edge of the film should extend beyond the edentulous ridge
Bisecting is recommended if alveolar ridges of the client are severely resorbed.
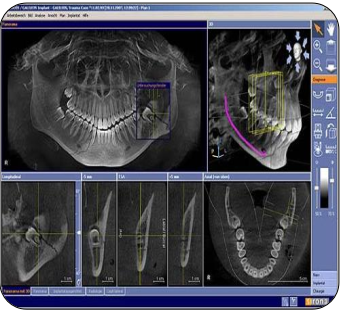
What is cone beam computer tomography? (CBCT)
Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT):
A 3D imaging technique using a cone-shaped X-ray beam and a digital detector that rotates around the patient.
Produces detailed three-dimensional images of teeth, bone, and surrounding structures.
Used for:
Implant planning
Endodontic assessment (root morphology, resorption, fractures)
Orthodontic evaluation
TMJ and airway analysis
Pathology detection
Advantages:
Lower radiation dose than medical CT.
High-resolution, accurate spatial representation.
Allows precise measurements and cross-sectional views.
What is Dicom data?
The universal format for handling, storingm and transmitting 3D images.