Carbocation Rearrangements
1/5
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
6 Terms
What is a Carbocation?
an ion where a carbon atom carries a positive charge
What kind of reactions can have Carbocation Rearrangements?
Sn1 and E1 Reactions. Secondary or Tertiary substrates.
What kind of Carbocation Rearrangements can occur?
Alkyl or Hydride Shifts.
How are carbocation arrangements stabilized and why do they occur?
Hyperconjugation (sp3 - p overlap (C w/ 3 bonds — C w/ 1 bond). Make a more stable carbocation.
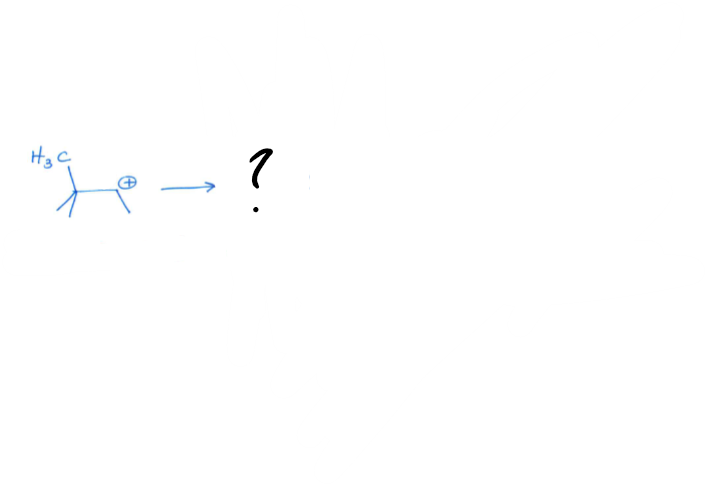
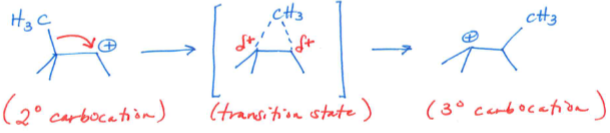
Alkyl Shift
a reaction that occurs when a C-C bond breaks and a new C-C bond forms, shifting the carbocation to an adjacent carbon.
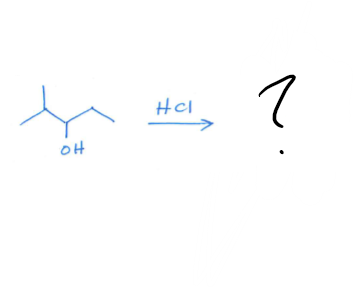
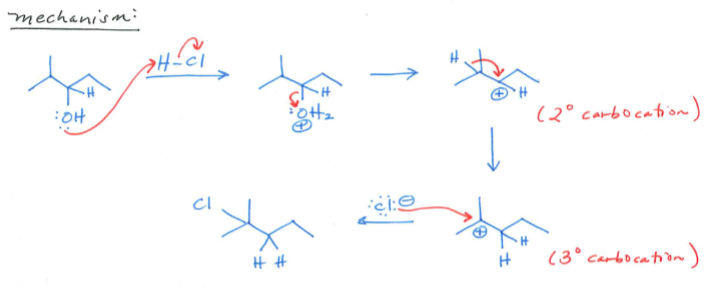
Define Hydride Shift. What’s the mechanism and product?
a rearrangement reaction that occurs when a hydrogen atom in a carbocation moves from one carbon atom to another, making the carbocation more stable. You want the Halide to go to the spot with the most substituents.