Phys Lecture 12 Nerve Cells and Neurotransmitters
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
Nervous system
Rapid (milliseconds-seconds)
Voluntary and involuntary control
NEUROTRANSMITTERS (close to cell)
Neurotransmitters
close cell to cell
Exocytosis of all neurotransmitters
All have extracellular receptors
Excitatory and Inhibitory Neurotransmitters
Endocrine system
Slow and long lasting (minutes-hours)
Involuntary
HORMONES (cells very far apart)
Transported in blood vessels and lymph vessels
Nervous system controls
The nervous system controls a lot of the endocrine system
Both nervous and endocrine systems
are long distance signaling systems
Cell to cell chemical signaling
1) Chemical signal is released outside of cell
2) Receptor for signal is
on the plasma membrane (extracellular)
In the cytoplasm (intracellular)
Autocrine
Chemicals that exert effects on the SAME cells that secrete them (self signaling)
Paracrine
Chemicals released by cells that effect OTHER nearby cells (next door signaling)
Endocrine
Secretion into the blood for signaling with cells far away (far away signaling)
Exocrine
Secretion into the external environment through a duct usually in an epithelium (not signaling)
1) Sensory input
Sensory receptors (millions) detect changes inside and outside of body (stimuli)
2) Integration
Processing and interpretation of sensory input (what to do)
3) Motor output
Response caused by activation of effector organs (muscles or glands)
Central nervous system (CNS)
Brain and spinal chord
integration and command center
Peripheral nervous system (PNS)
OUTSIDE CNS: links all the body to the CNS via spinal nerves and cranial nerves
Sensory input
Motor output
Neuronal signaling
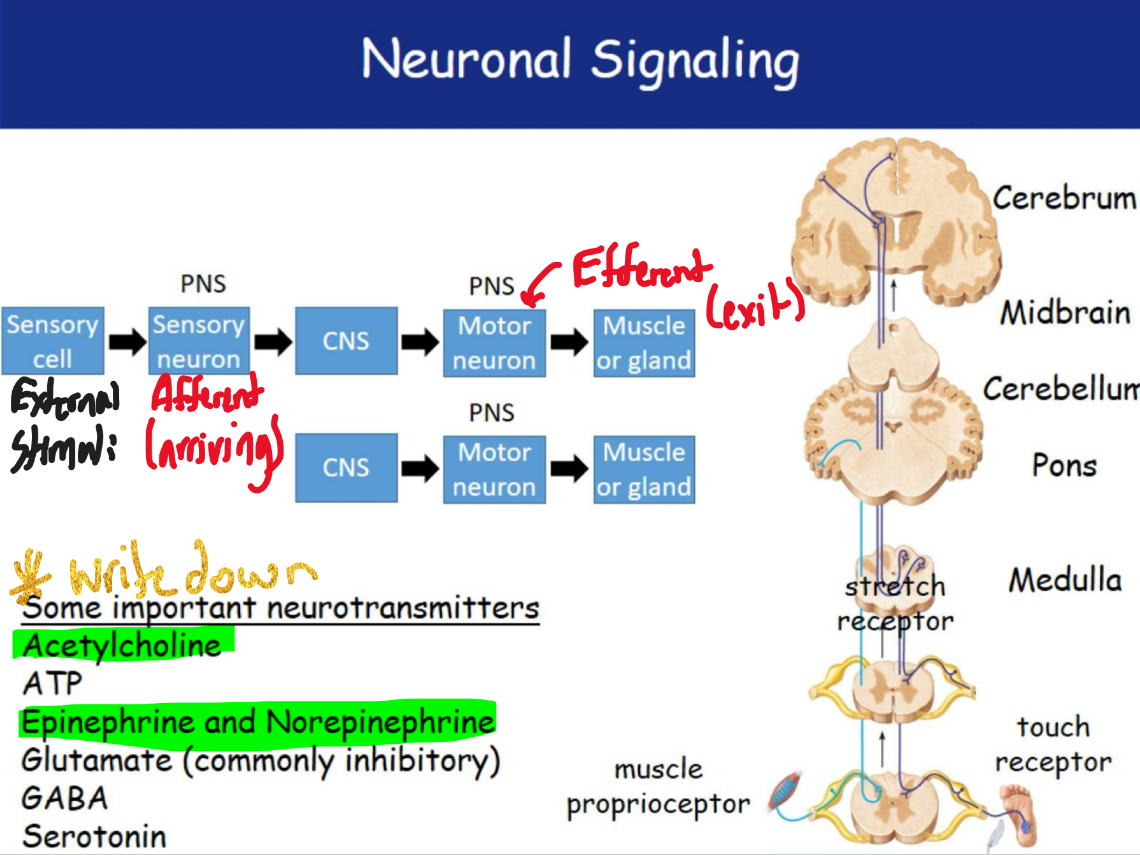
Acetylcholine
neurotransmitter—a chemical messenger that nerve cells use to communicate with other cells, such as muscles, glands, or other nerves.
ATP
ATP: adenosine triphosphate) is the main energy currency of the cell. (movement, transport, and chemical reactions.)
Epinephrine
Epinephrine (adrenaline): A hormone and neurotransmitter. It increases heart rate, blood pressure, and energy supply—part of the “fight or flight” response.
Norepinephrine
Norepinephrine (noradrenaline): Similar but also acts more as a neurotransmitter. It increases alertness, focuses attention, and helps regulate blood pressure.
Glutamate
main excitatory neurotransmitter in the nervous system. It sends signals between nerve cells and plays a key role in learning, memory, and brain function.
GABA
gamma-aminobutyric acid) is the main inhibitory neurotransmitter in the brain. It reduces nerve activity, helps prevent overstimulation, and promotes calmness, relaxation, and sleep.
Serotonin
neurotransmitter that helps regulate mood, sleep, appetite, and digestion
Peripheral Nervous System Organization
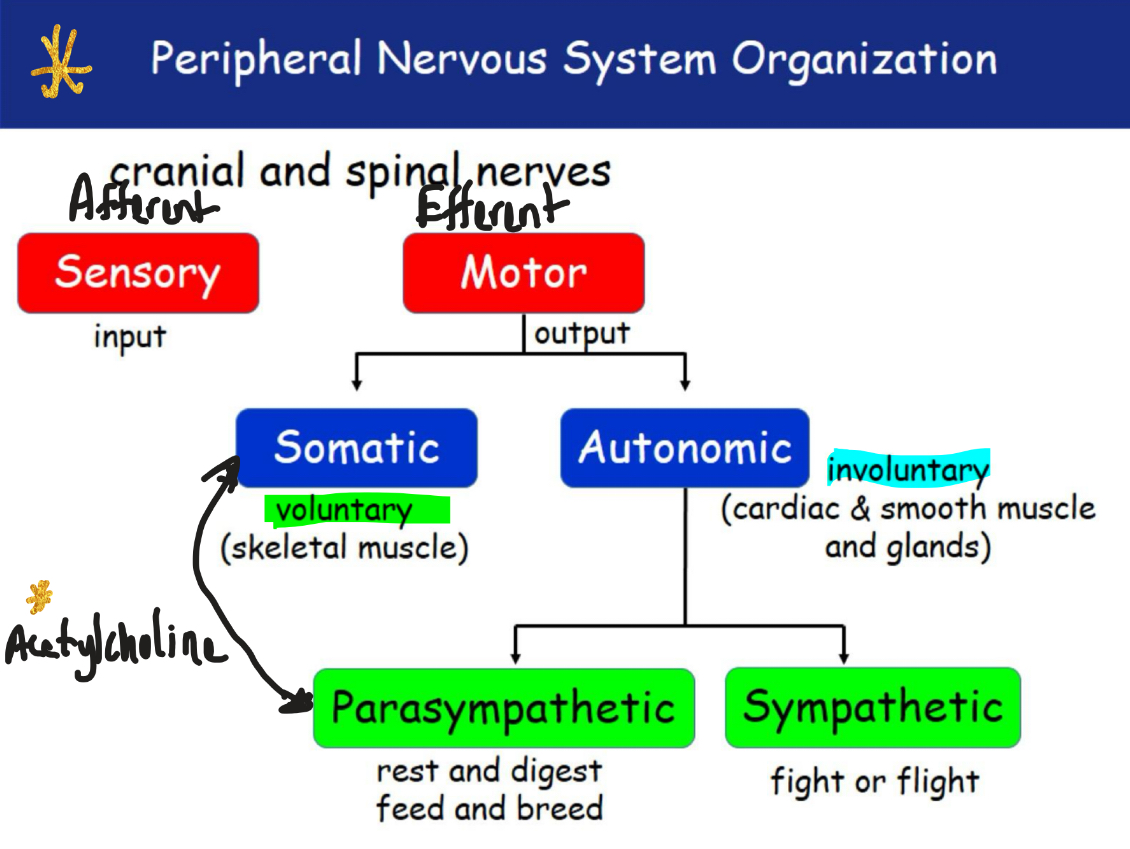
Sensory input
Collect and relay information to sensory neurons
Sensory receptors
Are commonly proteins that are ion channels or G- protein coupled receptors (transplasma membrane)
Sensory receptors include
Mechanoreceptors – detect touch, pressure, vibration (skin, ears).
Photoreceptors – detect light (eyes).
Thermoreceptors – detect temperature.
Chemoreceptors – detect chemicals (taste, smell, blood pH).
Nociceptors – detect pain.
Cells of the nervous system (Glia)
supporting cells
1-5:1 glia:neuron ratio
Most glia maintain MITOTIC ability- (can form tumors)
Cells of the nervous system (Neurons)
transmit signals
Extreme longevity: >100 years
Amitotic: most do not divide and are not replaced if destroyed
High metabolic rate: requires continuous supply of O2 and glucose - (brain is 2% of body mass but uses 20% of O2)
Supporting cells (Glia) of CNS
Astrocytes: most abundant
Help regulate composition of extracellular fluid (remove K+ and neurotransmitters) (CLEAN UP)
Microglia: macrophages:
scavengers that phagocytize debris and remodel synapses (BODY GUARDS)
BOTH CELLS FORM BLOOD BRAIN BARRIER
Supporting cells (Glia) of CNS
Oligodendrocytes: Electrical insulation
wrap axons in myelin sheaths around axons
Ependymal cells:
Line cavities where cilia circulate cerebral spinal fluid (CSF) to cushion and nourish CNS (ventricles)
Supporting cells (Glia) of PNS
Schwann cells: surround and form myelin sheaths around axions (oligodendrocytes in CNS)
Satellite cells: surround neuron cell body, regulate external chemical environment (CLEAN UP)
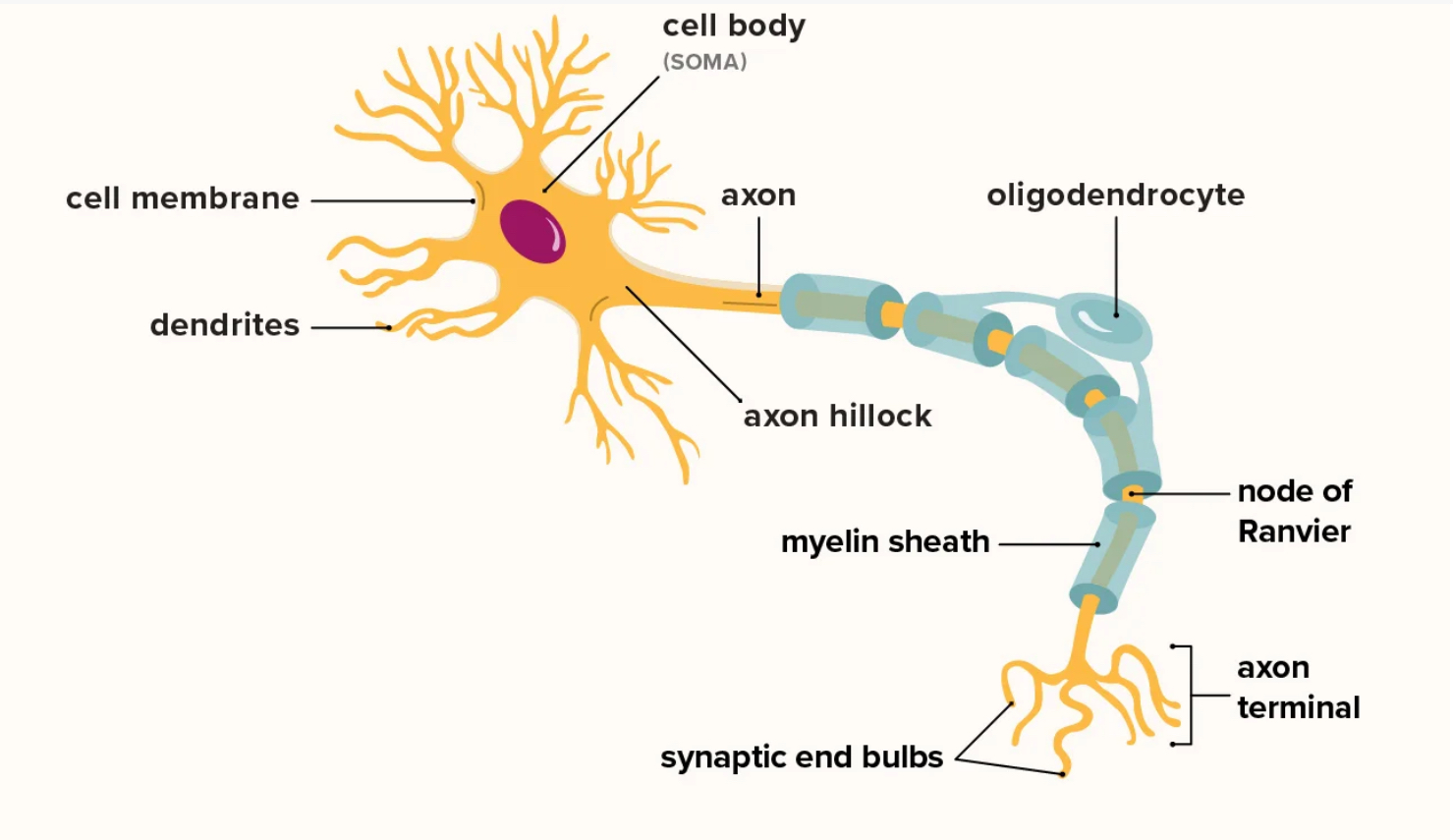
Myelination
Lipid bilayer of plasma membrane - like electrical tape around a wire
Myelin sheath
Protects/insulates axons
Increases action potential conduction speed
Myelinated fibers
Axons w/ myelin sheath
Nodes of ranvier
Nerofiberal nodes (gaps on axon between myelin sheaths)
Neuronal cell body (soma)
Cell body (soma): biosynthetic center
Contains: nucleus (mitochondria, golgi, vesicles)
Rough ER (Nissan bodies) most active in cell body
neurofilaments (intermediate filaments): maintain cell shape
Multipolar neurons are the most common
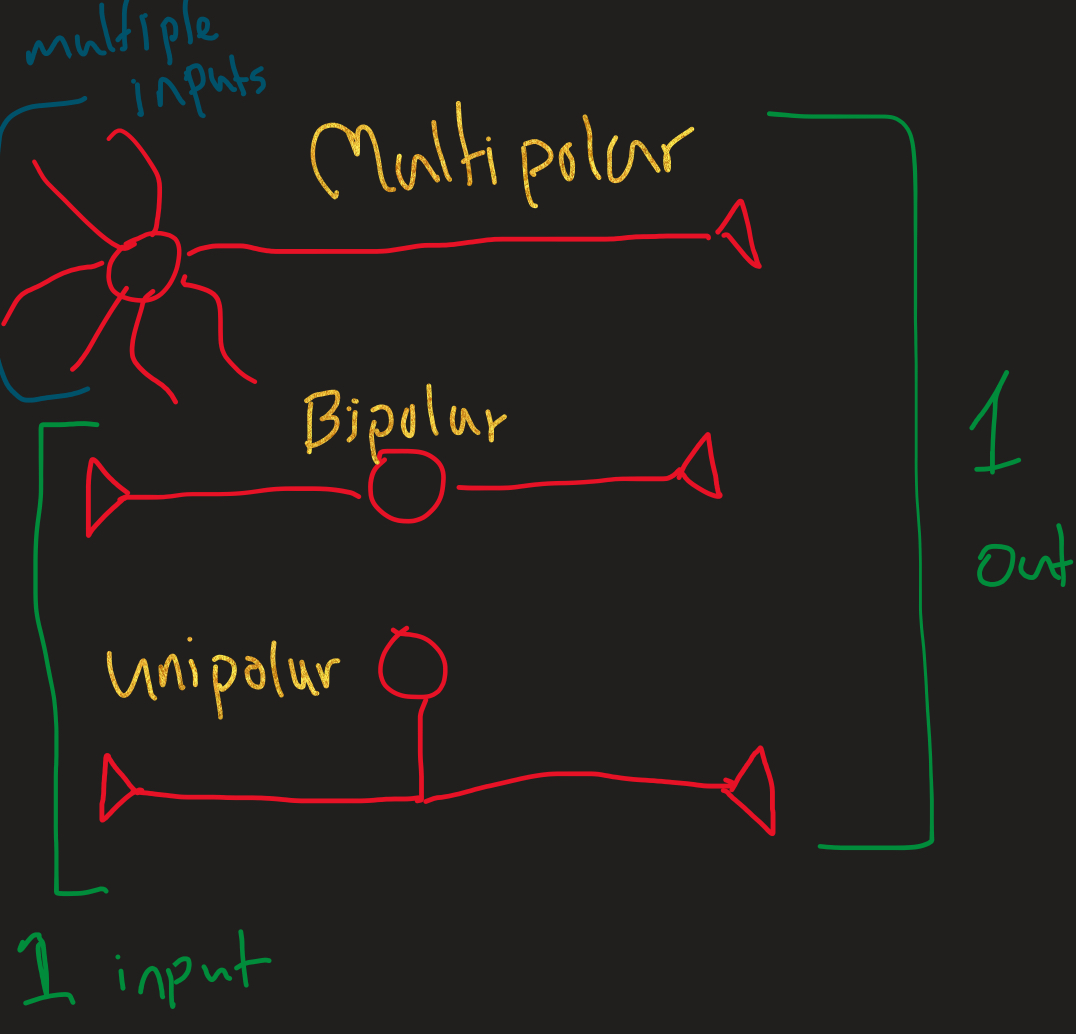
Neuronal processes (input)
Dendrites Receive INPUT
Short branching: large surface area
Convey incoming messages to cell body
Short distance signals= graded potentials (integration)
Neuronal processes (output)
Axon: send OUTPUT -(some do/don’t have myelin insulation)
Vary in size: (short- one meter)
Only one per neuron
Axon hillock: copse shaped area from which axion arises
What a nerve looks like