Lecture 6 Embryology
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
embryonic development phases
-cleavage
-implantation
-primitive streak formation
-gastrulation
-neurulation
cleavage
-rapid miotic divisions
-immediately follows fertilization
-cells are called blastomeres
-end of phase results in a blastula
patterns of cleavage
determined by amount and distribution of yolk protein and factors in the cytoplasm that influence the angle and formation of the mitotic spindle
yolk rich pole
vegetal pole
low yolk
animal pole
rotational holoblastic cleavage
-mammals
-very small -- human is 100um in diameter
-first cleavage begins about 24 hours after sperm entry and completion of meiosis
-in mice, miRNA from sperm initiates first cell division
-slow, 12-24 hours apart
-blastomeres divide asynchronously
-zygotic gene expression is required for early cleavage
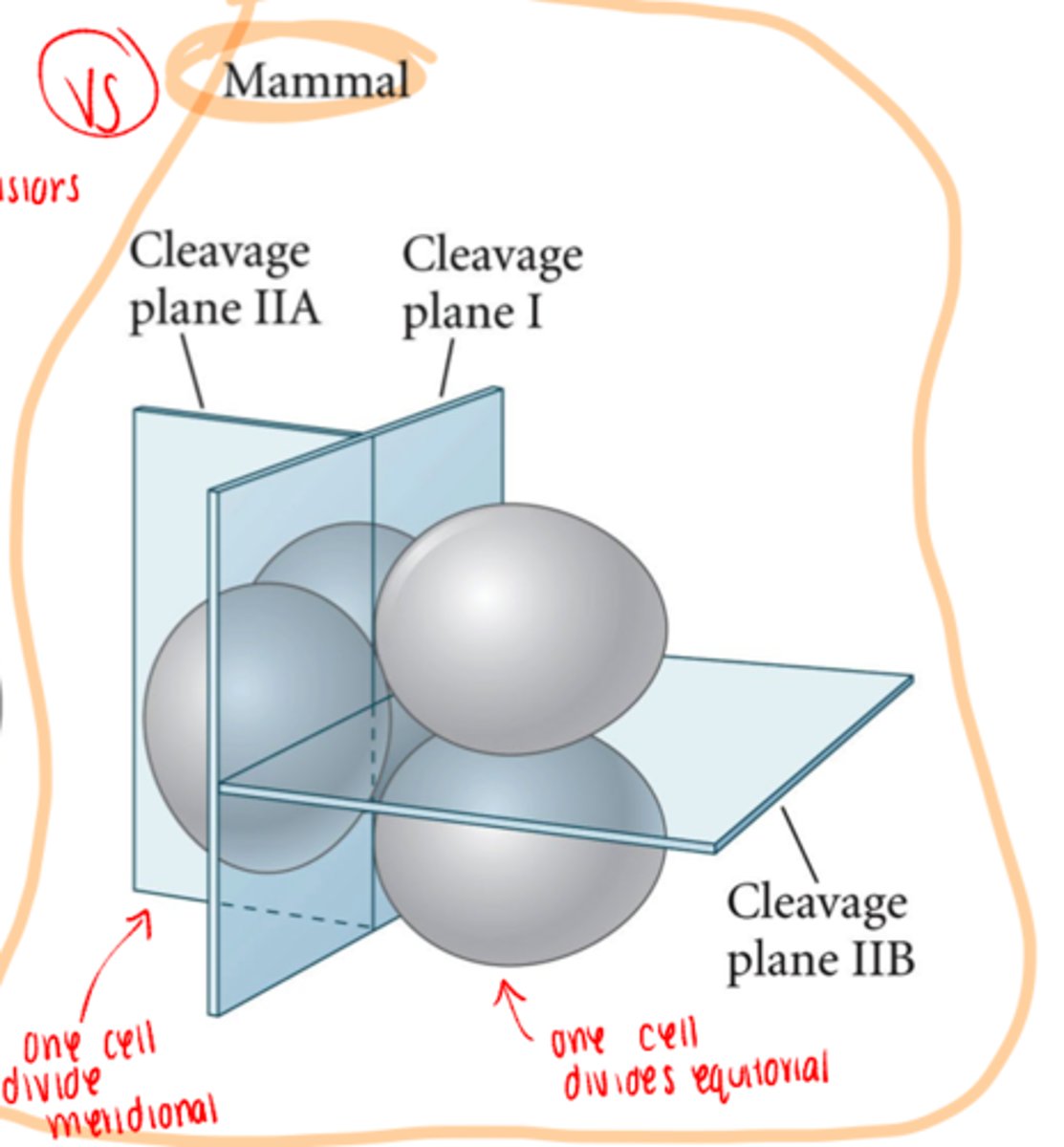
compaction in mammalian cleavage
-up to 8 cell stage blastomeres are loosely arranged
-at third cleavage, blastomeres form a compact ball of cells
-Due to increase in adhesion proteins
-Tight junction and gap junctions add stability and movement of ions between cells
-At 16 cells - mammalian embryo is called a morula
outer cells of morula become
trophoblast, inner cells become inner cell mass
implantaion
trophoblast divide to form the cytotrophoblast (forms vili) and the syncytiotrophoblast (embeds into uterine wall)
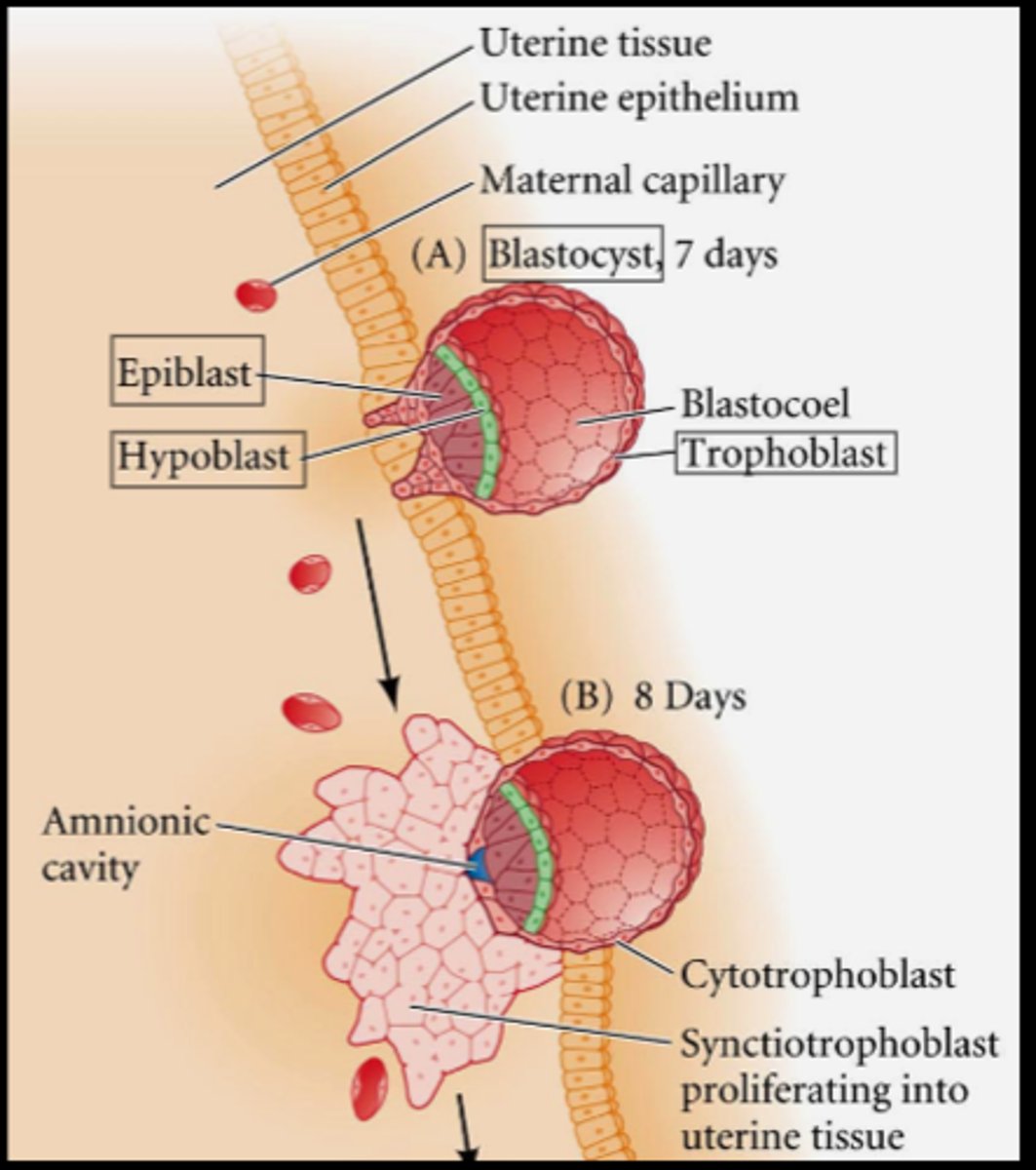
migration through the primitive streak
as cells migrate through the primitive groove, two layers emerge, epiblast and hypoblast (endoderm)
gastrulation
-Bilaminar germ disc- formed from the epiblast layer and endoderm
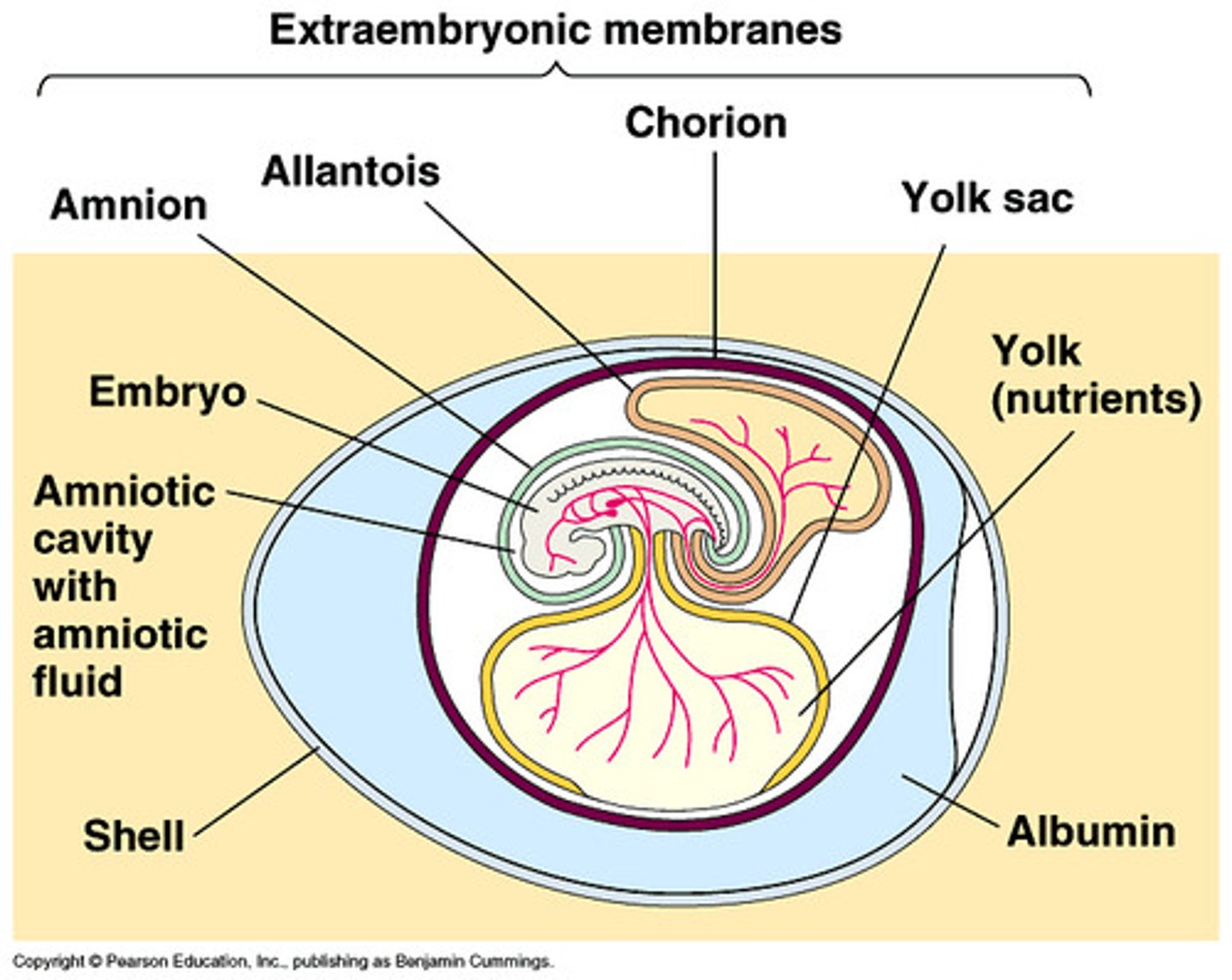
-Epiblast cells split - one group of cells form the amnion, creating the amniotic sac
amnion
closest to the embryo
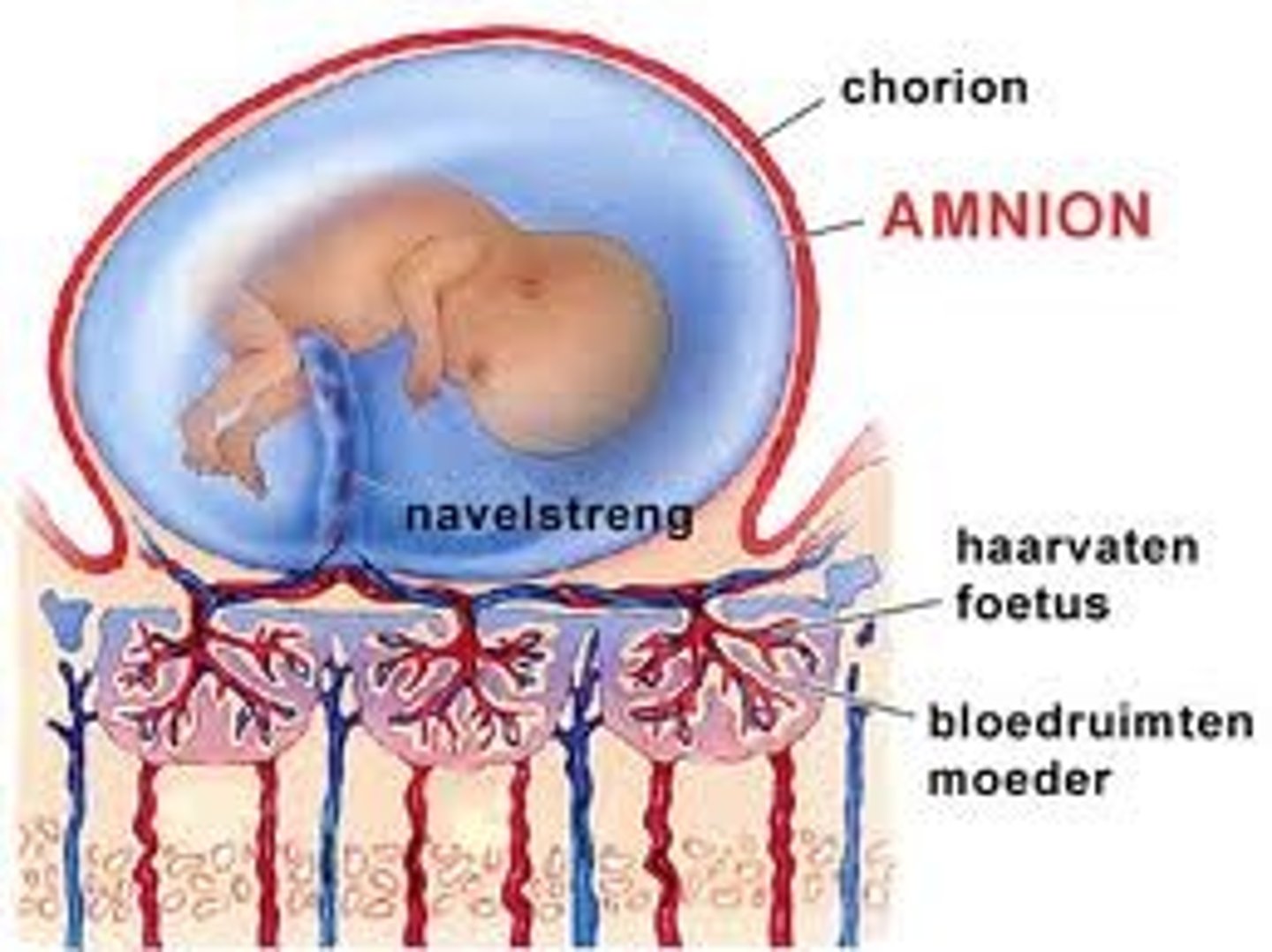
chorion
superficial to amnion, contributes to placenta
placenta
A structure that allows an embryo to be nourished with the mother's blood supply
-produces hormones to retain the pregnancy
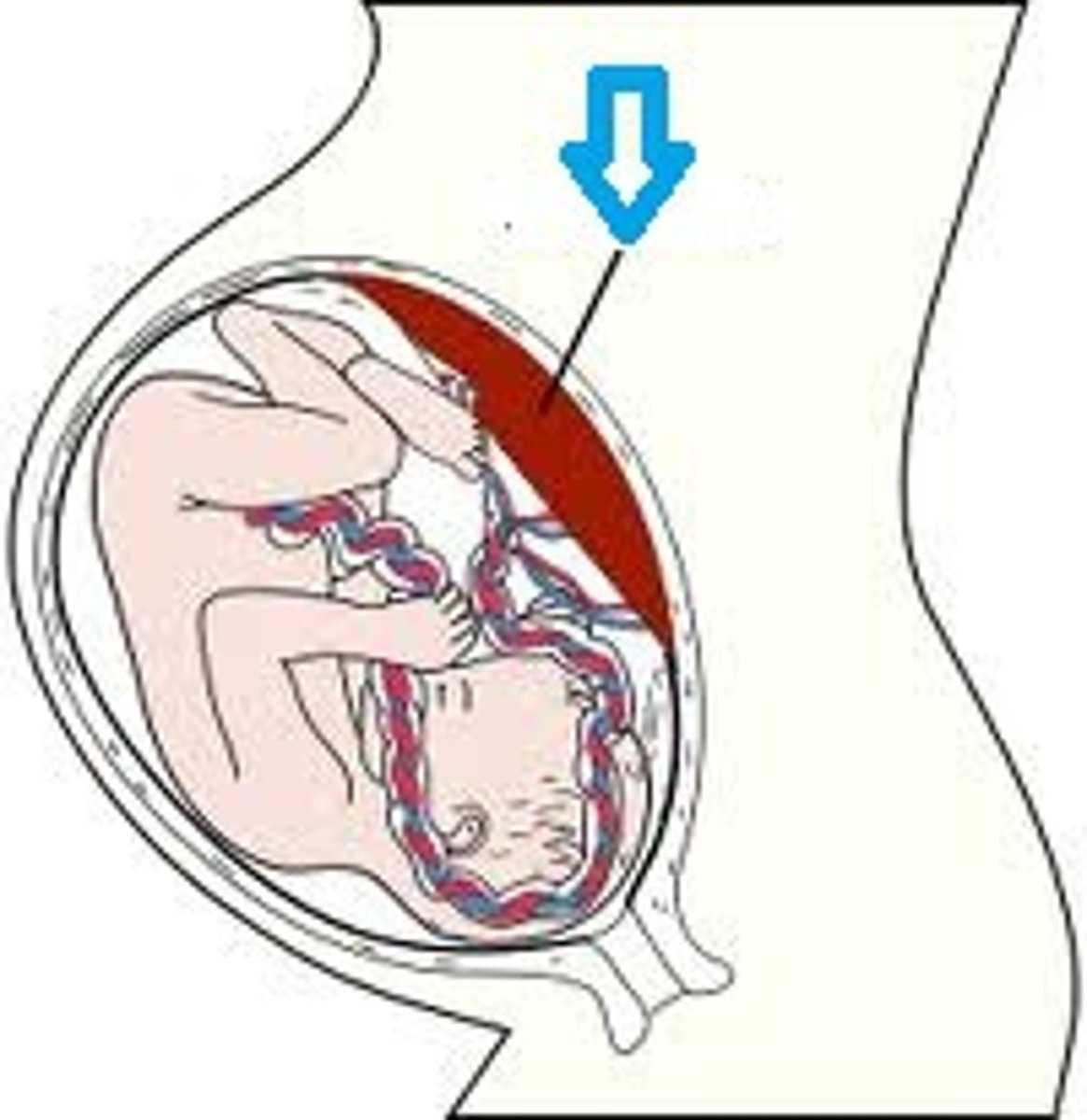
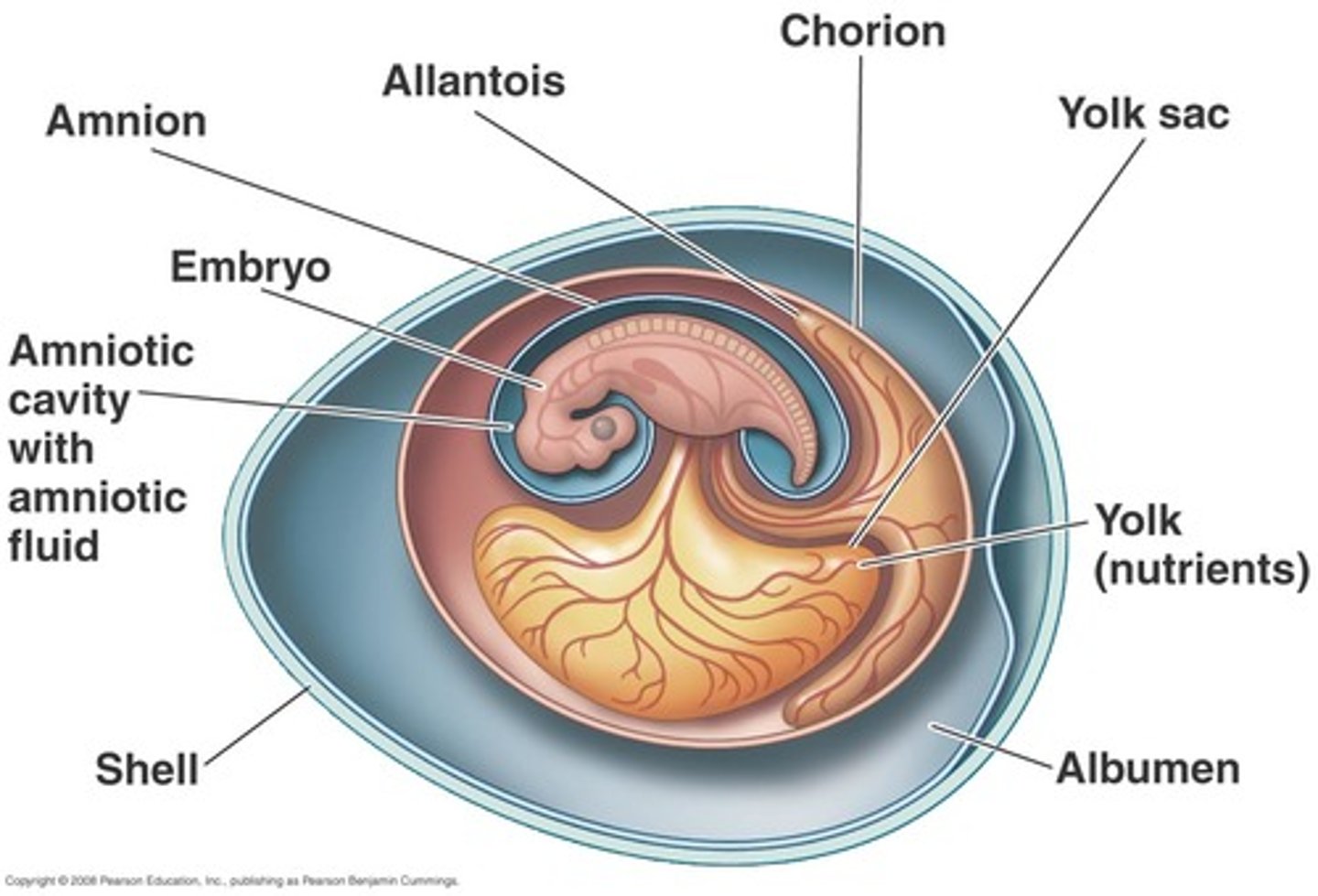
yolk sac and allantois
provides nutrients to embryo
allantois becomes umbilical cord
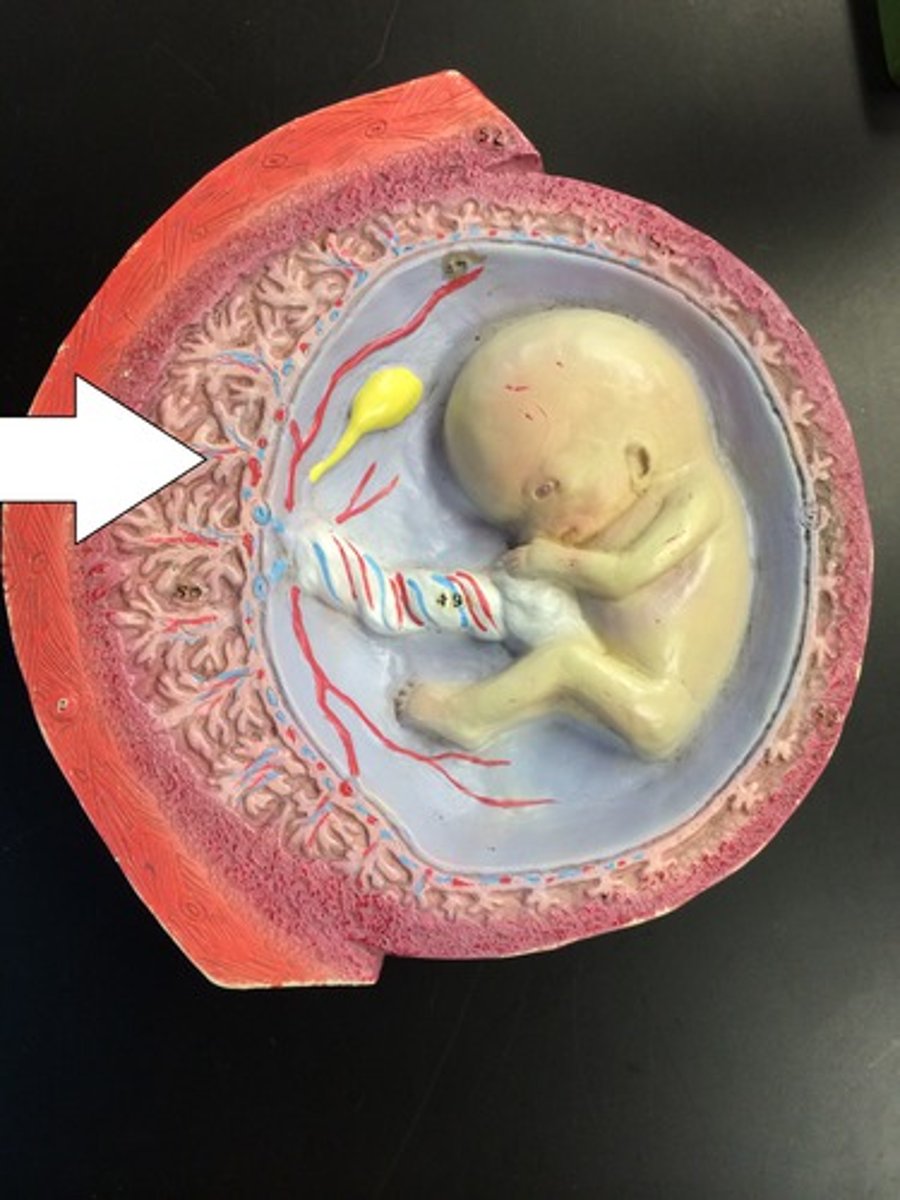
chorionic villi
allow diffusion of substances between maternal and fetal blood supply
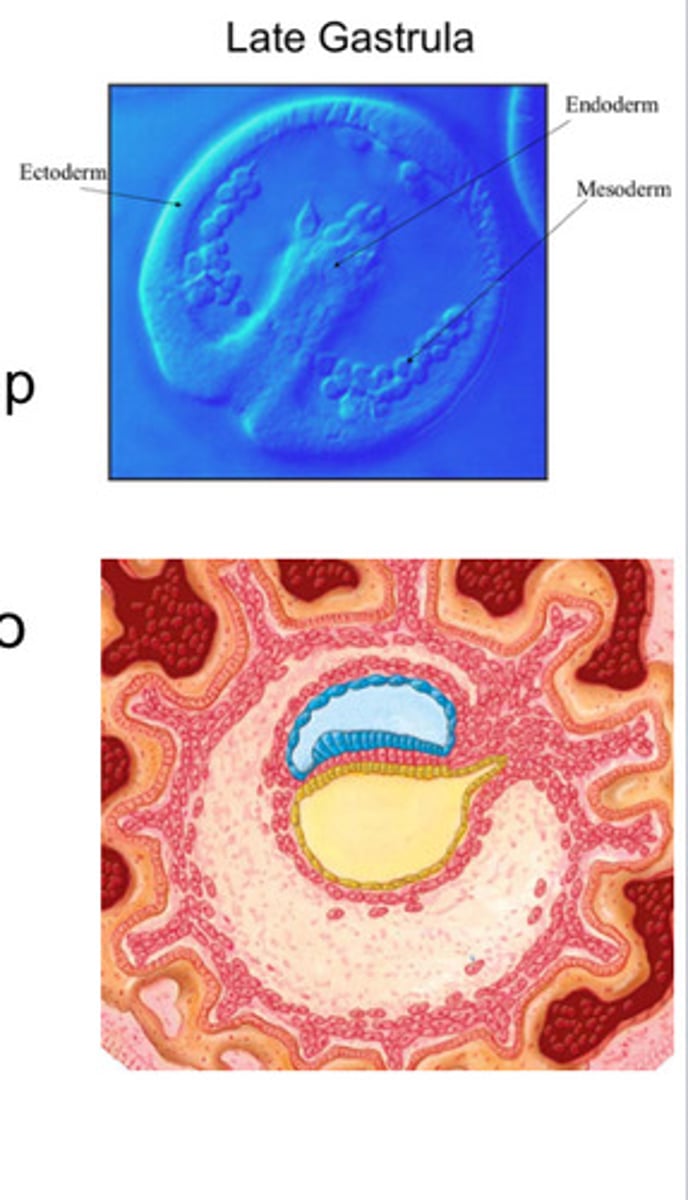
development of 3 layer germ disc
-happens during week 3
-part of the establishment of body axes in humans
-anteroposterior, dorsoventral, and left-right axis formation takes place before and during the period of gastrulation
development of the notochord
invagination at the primitive pit
-required for development of nervous system
twins
defined by what extraembryonic tissues they share
-2 chorions, 2 amnions
-1 chorion, 2 amnions
-1 chorion, 1 amnion (most rare, can lead to conjoined)