Key Concepts in Cell Biology
1/54
Earn XP
Description and Tags
A comprehensive collection of vocabulary flashcards based on key concepts in cell biology to aid in studying for an exam.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
Cell
The smallest, basic unit of life responsible for all of life's processes.
Cell Theory
All organisms are made up of one or more cells.
The cell is the basic unit of all organisms.
All cells come from existing cells.
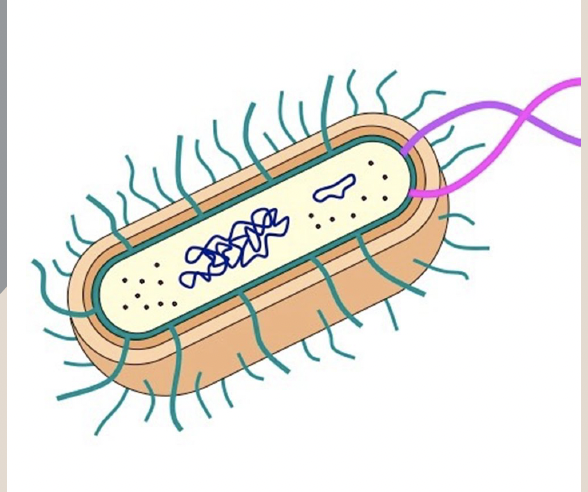
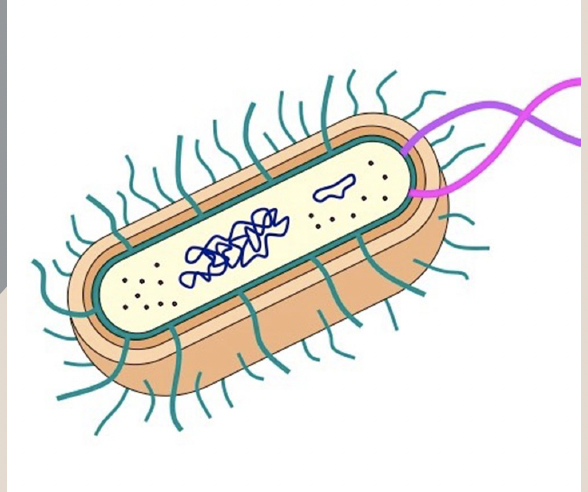
Prokaryote
A type of cell that is single-celled with no nucleus or membrane-bound organelles, DNA located in cytoplasm, ex. bacteria.
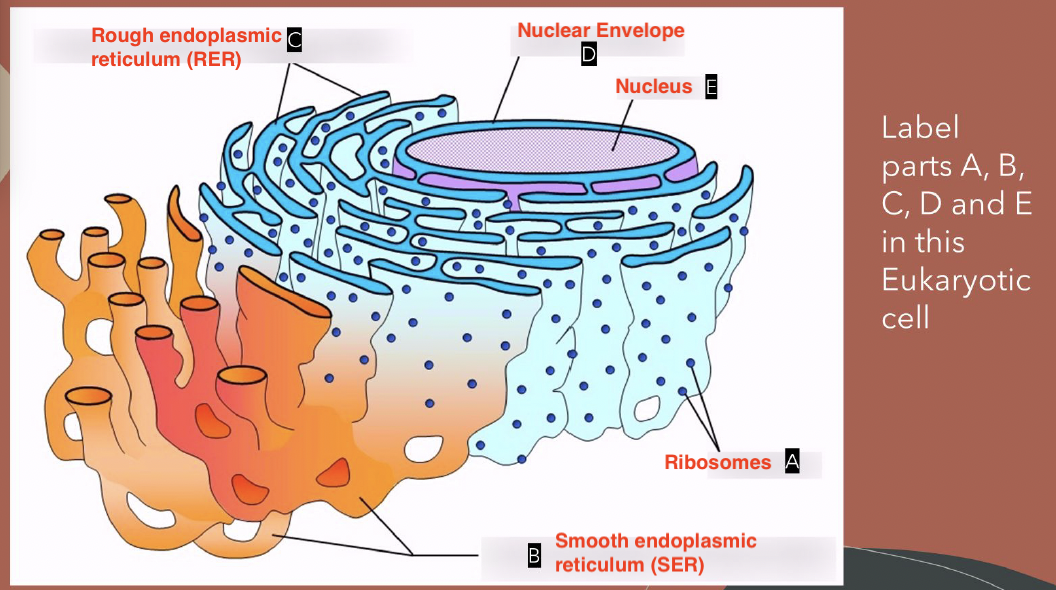
Eukaryote
A type of cell that can be single or multicellular and has membrane-bound organelles with DNA in the nucleus. There are two types of eukaryotic cells: plant cells and animal cells.
Unicellular
Organisms made up of one cell that carry out all functions of life.
Multicellular
Organisms made up of more than one cell that perform specialized functions.
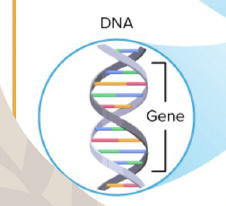
DNA
Deoxyribonucleic Acid; the genetic material that contains the instructions for development, survival, and reproduction.
Atom
The basic building block of chemistry; the smallest unit of matter.
Smallest unit into which matter can be divided.
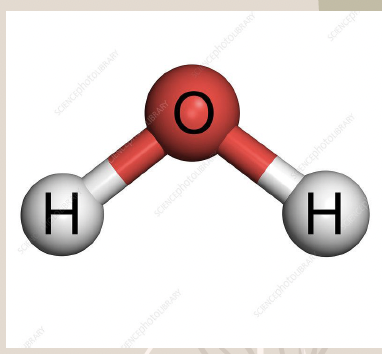
Molecule
A group of atoms joined together by chemical bonds.
Lipid
A hydrophobic (does not mix with water) fat molecule that stores energy in the body.
Protein
A molecule made up of smaller units called amino acids; essential for various body functions.
Amino Acid
The building blocks of proteins that combine to form different proteins.
Carbohydrates
Molecules that are the main source of energy for the body, including sugars, starches, and fiber
Nucleic Acid
Molecules that carry information in cells are made up of nucleotides. DNA is a type of nucleic acid that holds genetic material.
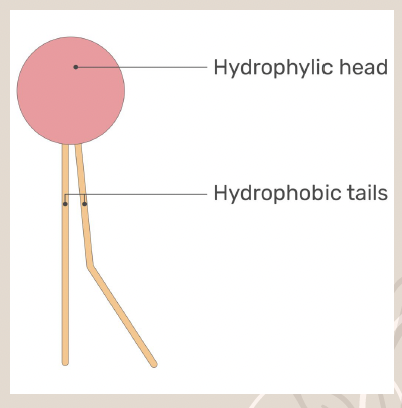
Phospholipid
A lipid that forms the cell membrane, consisting of a hydrophilic head and a hydrophobic tail.
Osmosis
The movement of water across a cell membrane.
Active Transport
Substances moving across the cell membrane with the use of energy (ATP).
Passive Transport
Substances moving across the cell membrane without using energy.
Diffusion
Molecules like to spread out from where there is more of them to where there is less.
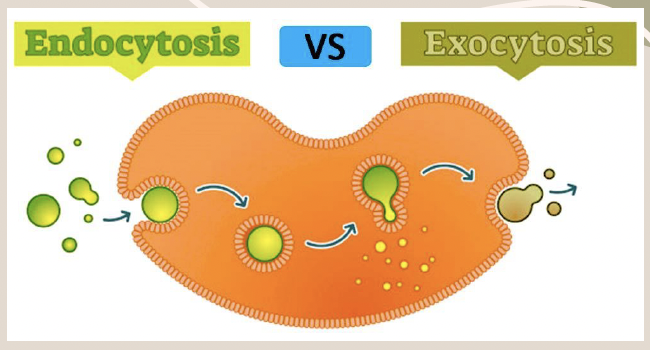
Endocytosis
The process by which a cell takes in large molecules by engulfing them with its membrane.
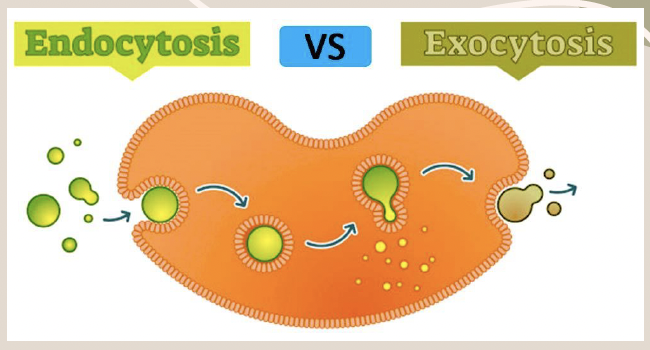
Exocytosis
The process by which a cell releases substances to the outside by using the opposite process of endocytosis.
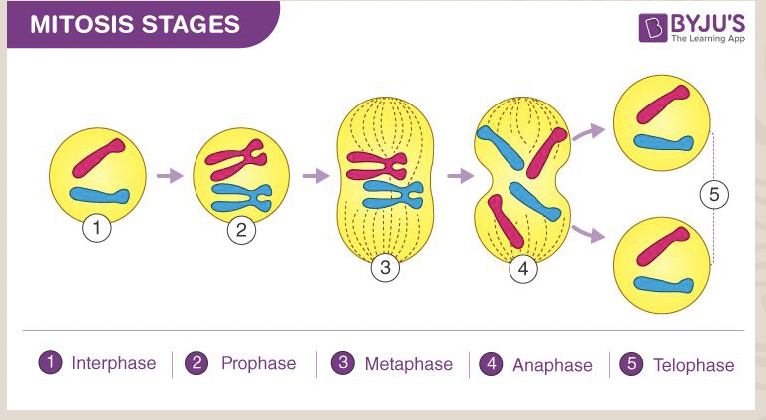
Mitosis
The process of cell replication where one cell divides to produce two identical cells.
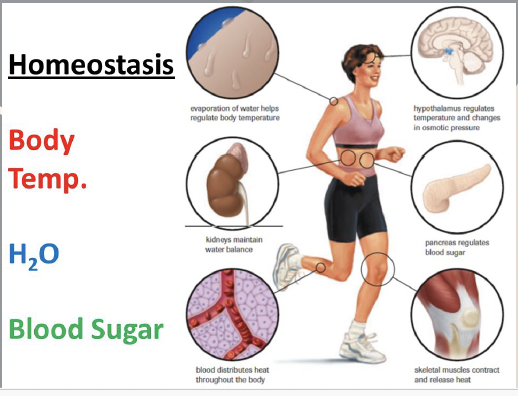
Homeostasis
Constant maintenance of internal conditions in a cell or organism despite changes in the external environment.
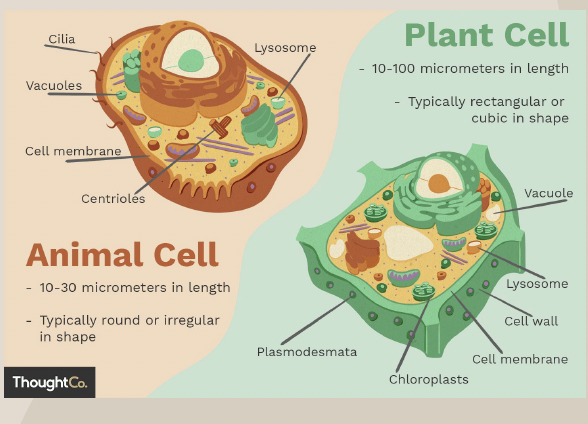
Cell Membrane
A protective layer that covers a cell's surface and controls the movement of substances in and out of the cell. It is semi-permeable: only allows certain materials to cross in or out.
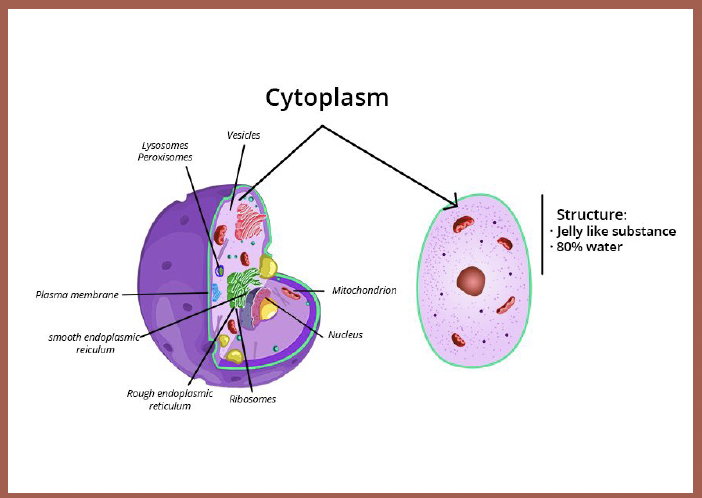
Cytoplasm
The fluid that fills the cell, containing water, salts, and various organic molecules.
Golgi Complex
Oganelle that prepares proteins and lipids for use inside and outside of the cell.
Mitochondria
Organelles known as the powerhouse of the cell, where cellular respiration occurs. Convert chemical energy from food into usable energy for the body.
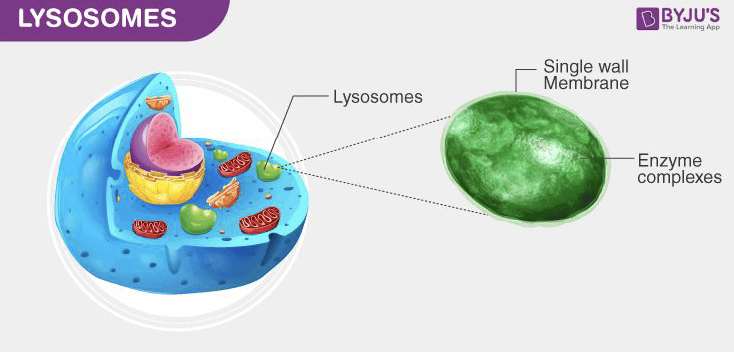
Lysosome
An organelle that contains digestive enzymes for breaking down damaged organelles, waste materials, and foreign invaders in the cell.
Nucleus
The control center of the cell that stores DNA, DNA replication, and controls metabolism.
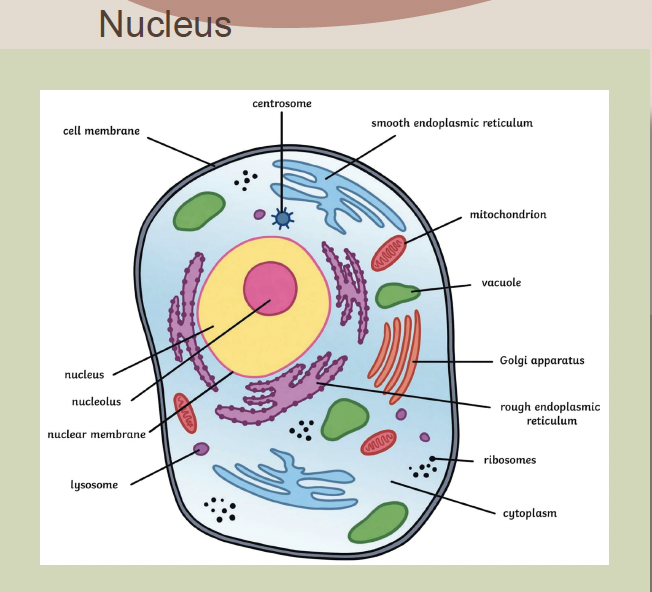
Rough ER
Ribosomes attached to its membrane (makes proteins)
Smooth ER
No ribosomes attached to its membrane, (make lipids)
Cell Wall (Plant Cells Only)
A rigid structure that provides support and protection to plant cells.
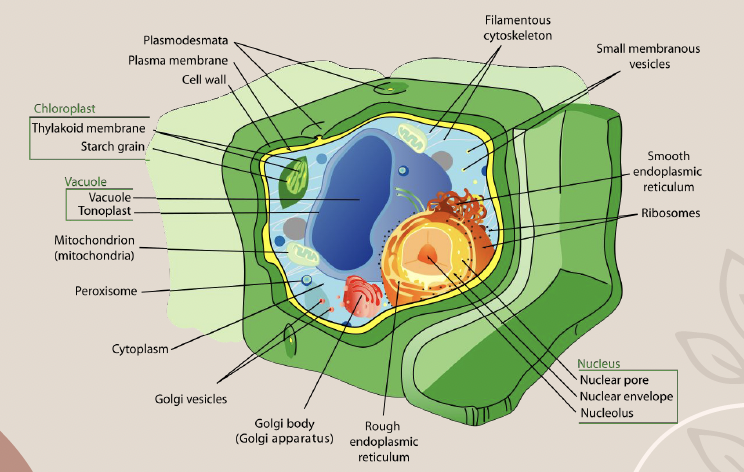
Vacuole
An organelle that stores water and other substances, particularly in plant cells.
Chloroplast
Organelles in plant cells that contain the green pigment called chlorophyll for photosynthesis.
Flagella
Hairlike structures that help PROKARYOTE move
Protein ENZYMES
Chemical aid in digesting food
Tissue
Groups of similar cells that work together to perform a specific function.
What are the 4 types of tissues.
Nervous
Epithelial
Connective
Muscle
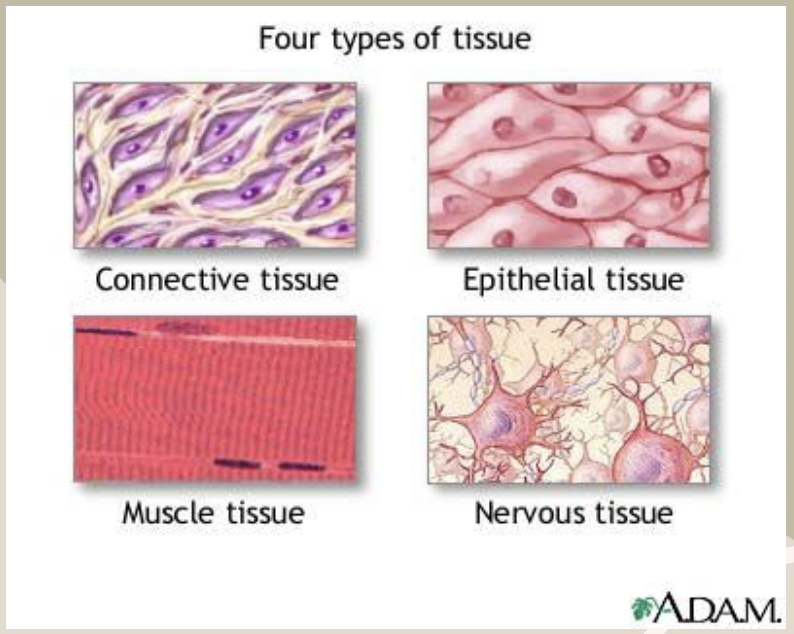
Nervous Tissue
Made up of nerve cells and is used to carry messages throughout
the body
Epithelial
Protective tissue; provides a covering
Connective
Supports other tissues and binds them together
Muscle
Responsible for the movement of the body and organs through contraction.
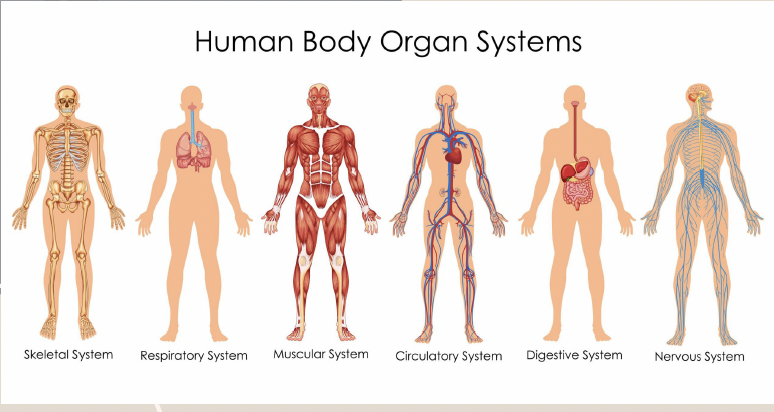
Organ System
Group of organs that work together to perform specific body functions.
Photosynthesis
Plants use sunlight to change carbon dioxide and water into sugar and oxygen
Species
a group of organisms that are
very closely related.
Taxonomy
Science of describing, classifying and naming living things.
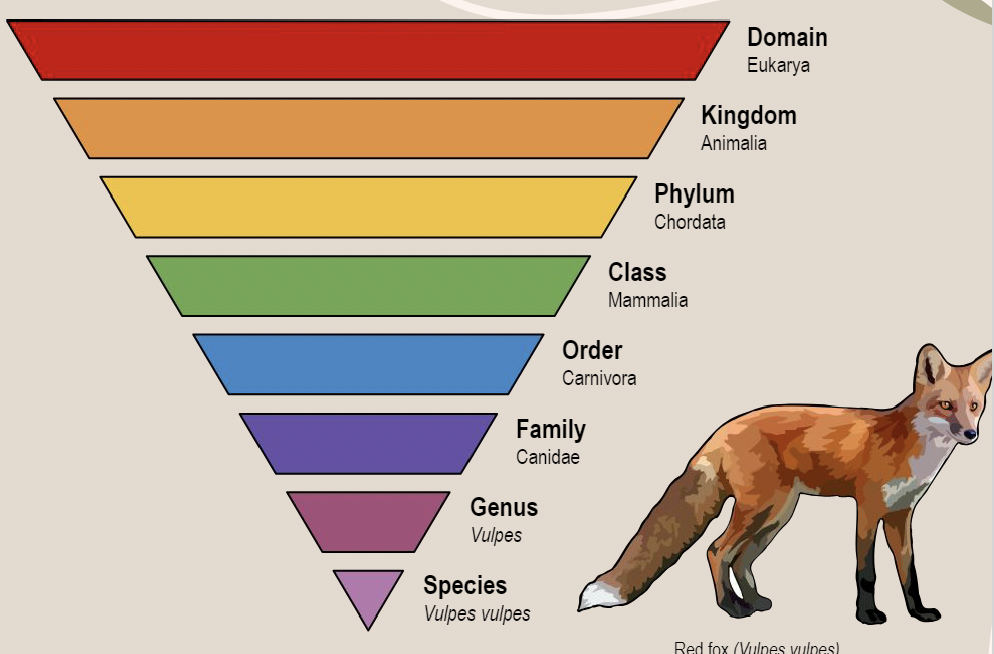
Domain
Domain represents the largest level of classification of organisms
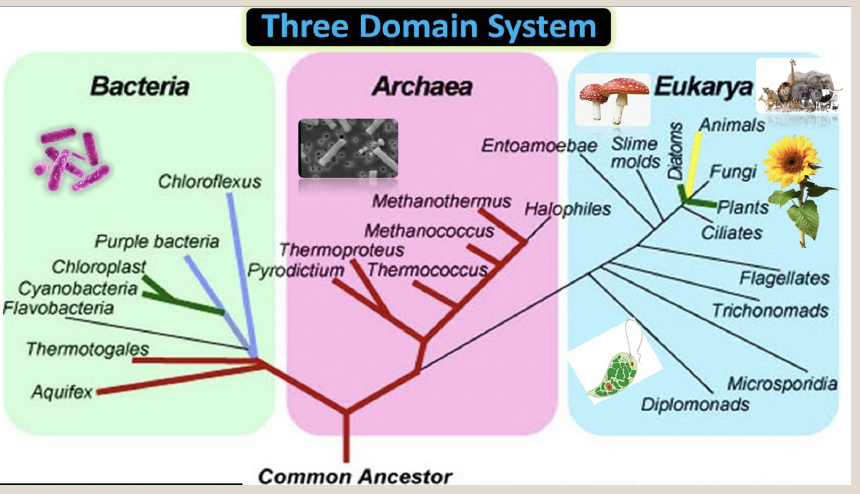
Fungi
Yeasts, molds, and mushrooms.
Animalia
Birds, fish, reptiles, mammals.
Protista
Protists such as algae and slime molds
Autotroph
Make their own food
Heterotroph
Eat other organisms
Plantae
Plants and trees
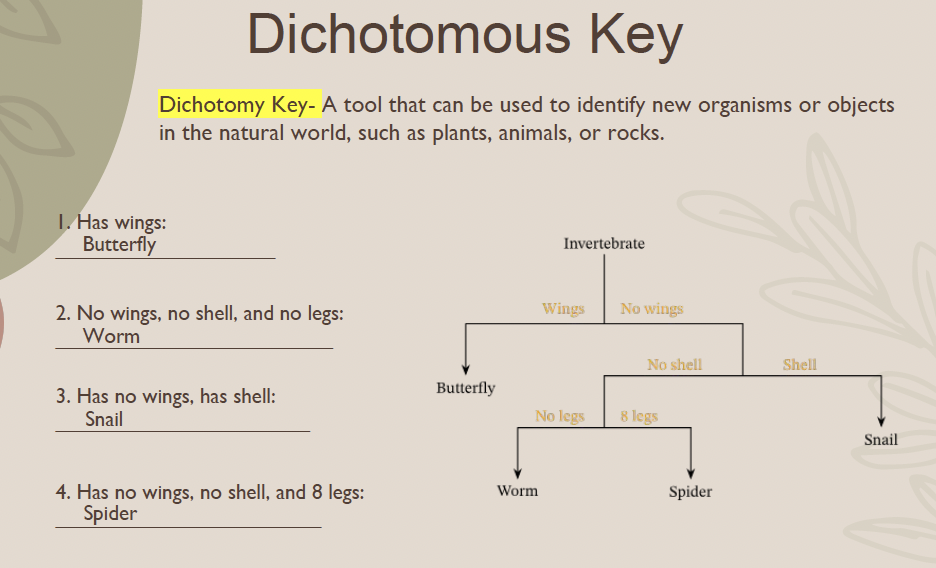
Dichotomy Key
A tool that can be used to identify new organisms or objects in the natural world, such as plants, animals, or rocks.
Ribosomes
Makes protein by chains of amino acids (protein synthesis)