org chem fucntional group
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
alkanes
-ane
single bonded chain
CnH2n+2
H-C-C bond angle 109.5
Rotate around single bonds
saturated hydrocarbon (no room for other atoms to bond to C)
alkenes
-ene
double-bonded chain
has cis and trans isomer
CnH2n
H-C=C bond angle 120
canT rotate around double bonds
unsaturated (reactive site for other atoms to bond to C)

cis trans isomers
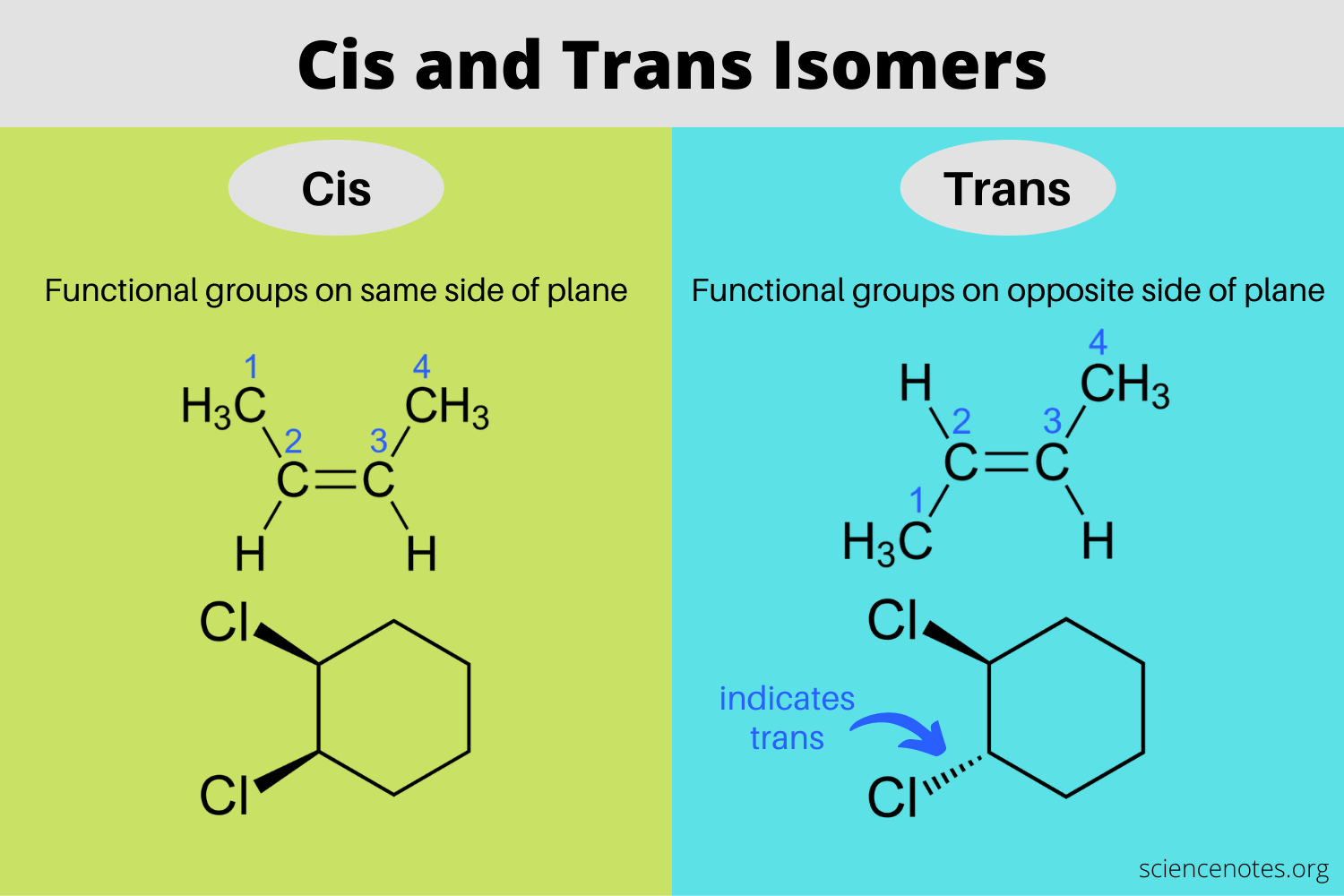
groups cant be bonded to the same carbon
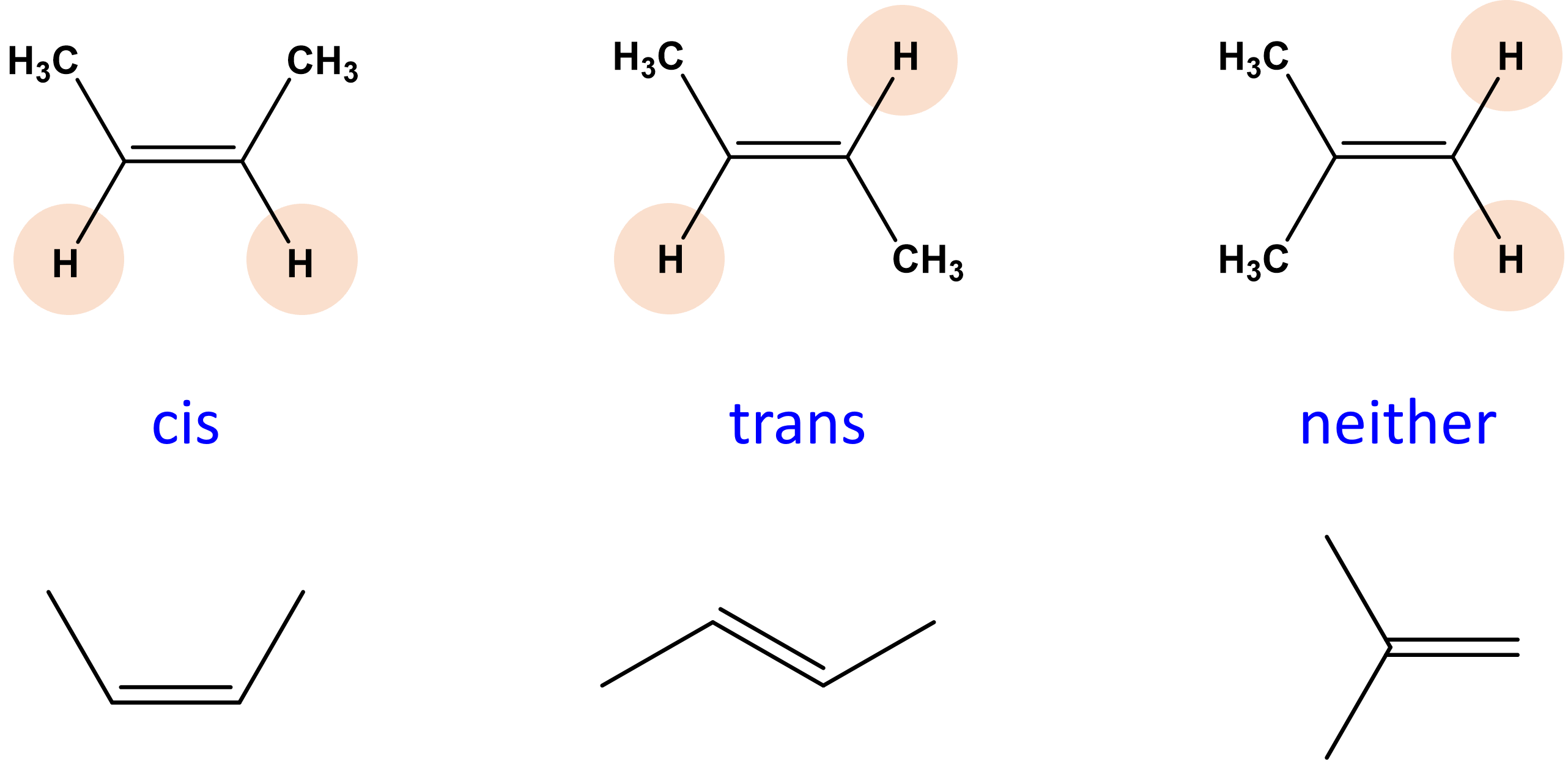
isomers
prop suffix and beyond
same chemical formula but diff structures
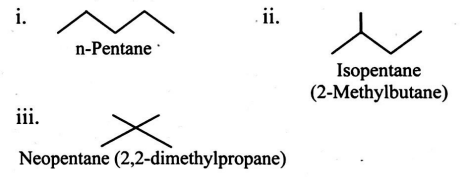
n- normal (straight chain)
iso - branched
CH3
|
CH3– C
ISOPROPYL
alkynes
-yne
triple bonded chain
CnH2n-2
H-C≡C bond angle 180
canT rotate around triple bonds
unsaturated
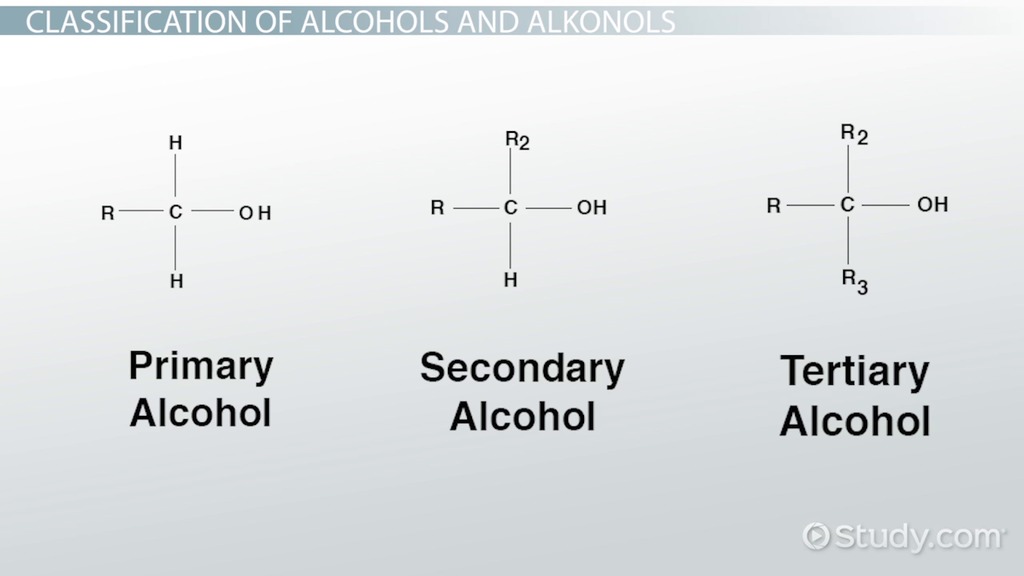
alcohol
-ol
R-O-H
EDGE
alcohol is priority
dont number up to ethanol
double bond + H2O → alcohol
ether
[alkyl][alkyl]ether
R-O-R1
MIDDLE
R (2 C’s or less)
2+, [alkoxy]alkane
alkoxy is shorter chain
alcohol (→ strong base/R-Cl) R-O-R
aldehyde
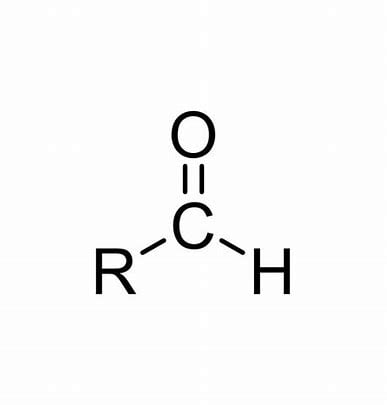
-al
No numbering
also remember methanal
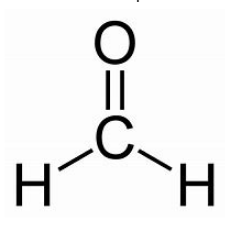
EDGE
oxidation of primary alcohol → aldehyde + h2
ketone
-one
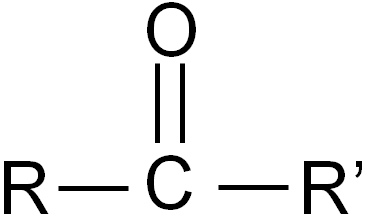
MIDDLE
propanone only doesnt have number
(meth and eth don’t exist)
oxidation of secondary alcohol → ketone + h2
alkyl halide
H’s replaced by halogens
F: fluro
Cl:chloro
br: bromo
i: iodo
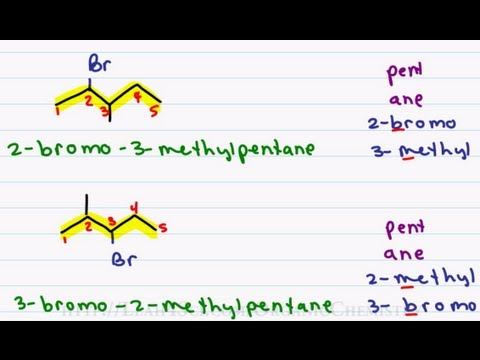
carboxylic acid
-oic acid
EDGE
carboxylic ion: H+ [Carboxylate]-
oxidation of primary alcohol → acid + h2O
![<p>-oic acid</p><p>EDGE</p><p>carboxylic ion: H+ [Carboxylate]-</p><p></p><p>oxidation of primary alcohol → acid + h2O</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/acbfb6e6-8a2a-4b08-9cc0-5fdb1bcda54f.png)
ester
[alkyl][carboxyl]ate
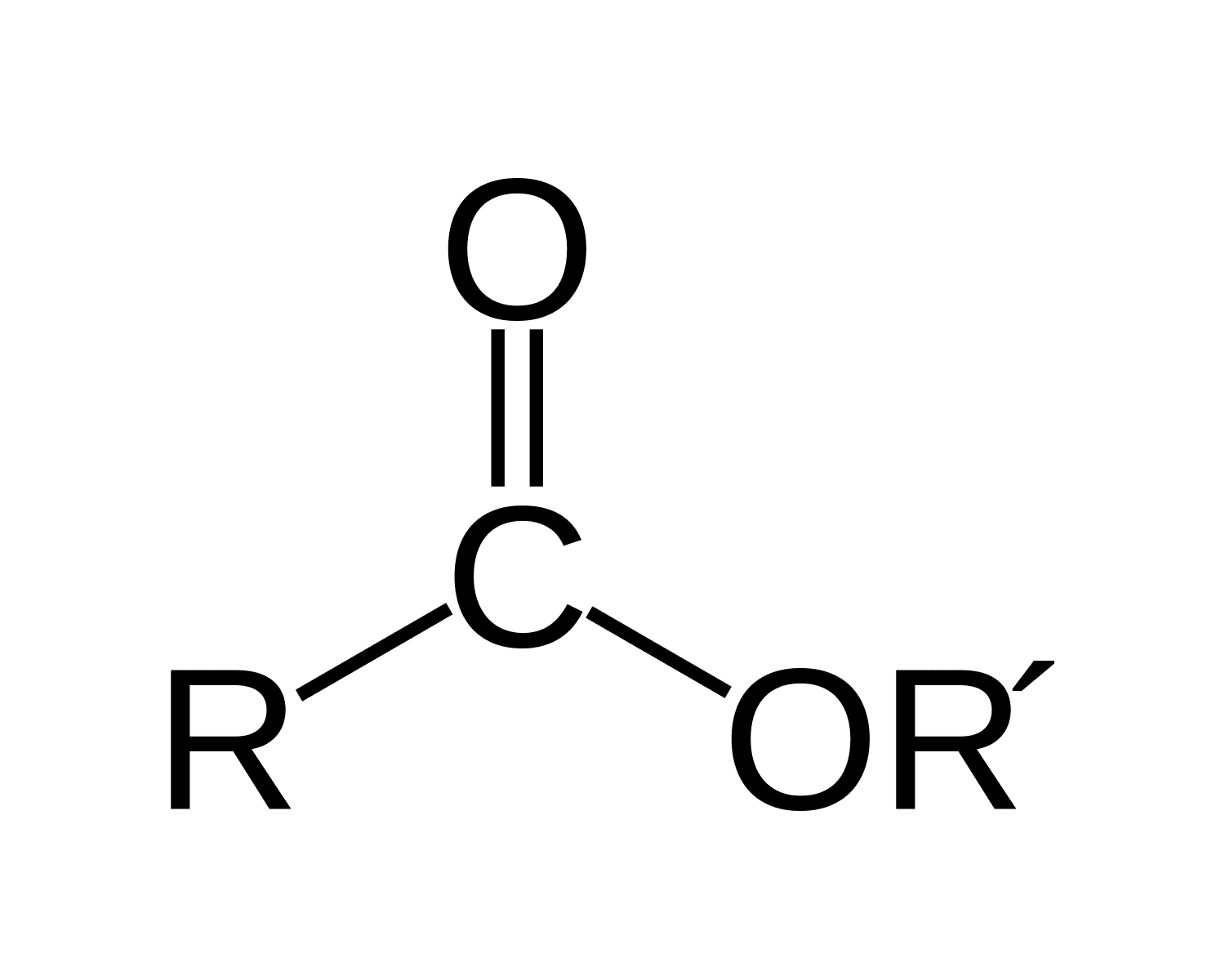
MIDDLE
carboxylic acid + alcohol → ester + H2o
amine
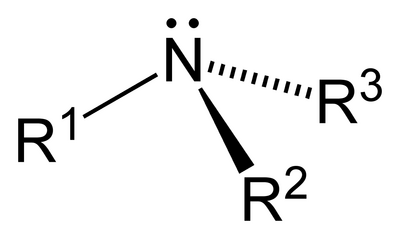
-amine
EDGE
what are these as branches
no2, oh, and benzene
nitro, hydroxy, phenyl
UNBRANCHABLES are always prioritized
cycloalkanes
ring shape
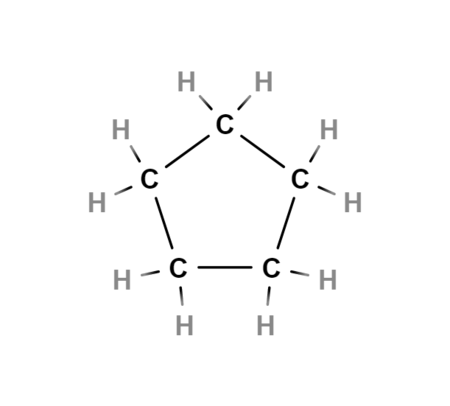
cyclo[alkane]
functional groups
c=o carbonyl
aldehydes, ketones, carboxylic acids, esters, and amides.
c-oh hydroxyl
o=c-oh carboxyl
c-n amine
o=c-n amide
c-o alcohol/ethers
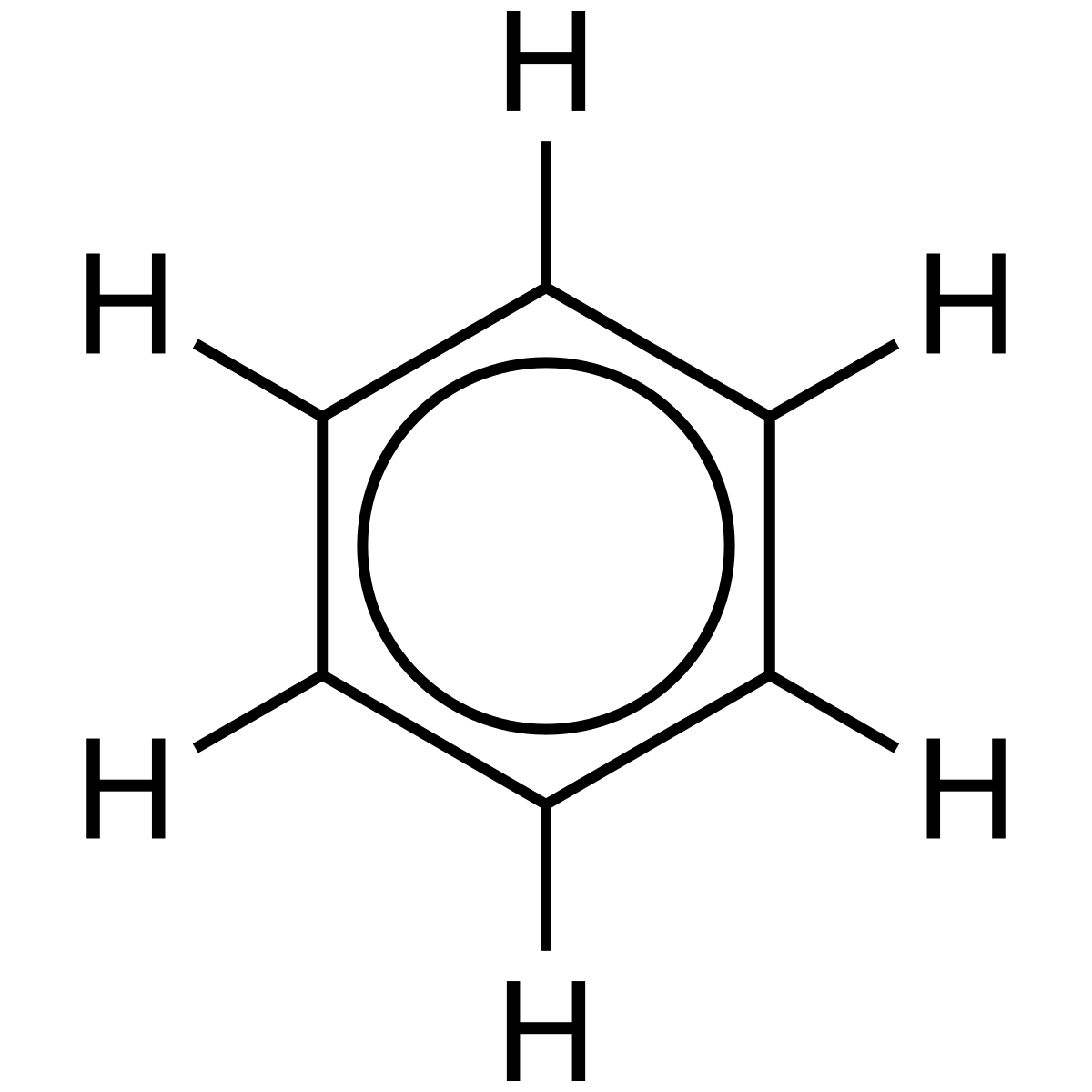
benzene
C6H6
phenyl if branch
amide
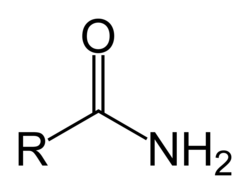
-amide
ester + NH3/amine → amides
benzene suffixes
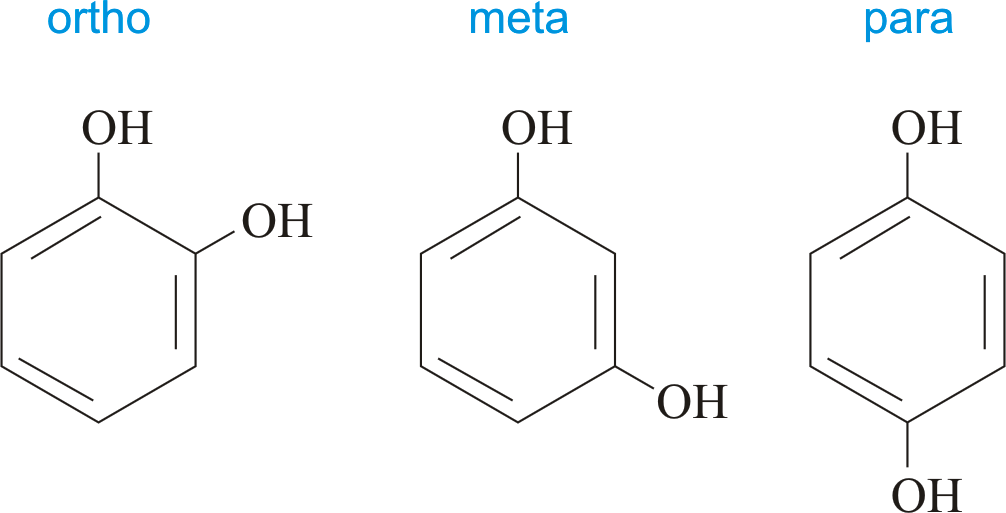
ortho - 1,2-di___benzene
meta - 1,3 - di____benzene
para - 1,4 - di____benzene
priority
carboxylic acid
ester
amide
aldehyde
ketone
alcohol
amine
alkene/alkyne
ether
halides