ATE Physiology 1, L1
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
the term “milieu interieur” was created by
Claude Bernard
the expression "milieu intérieur" refers to
stable internal conditions maintained by living organisms
components of homeostasis
isovolemia, isoionia, isotonia, isohydria
homeostasis is
the process by which living organisms regulate and maintain a stable internal environment
isovolemia
constant volume
isoionia
constant ion composition
isotonia
constant osmotic pressure
isohydira
constant pH
the interstital space resembles
ancient oceans
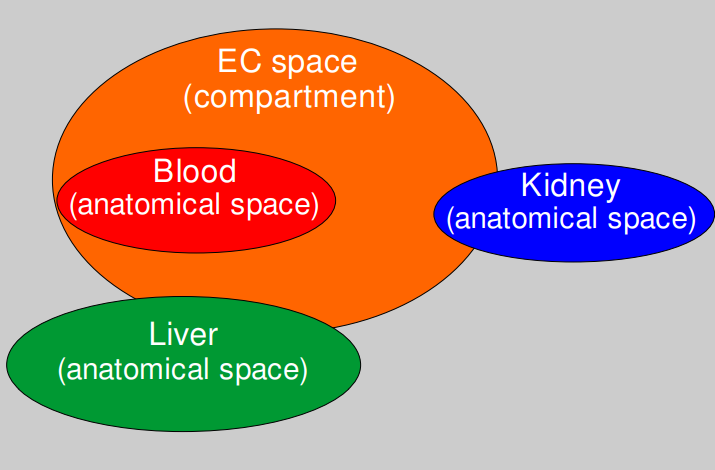
an anatomical space is not the same as a compartment
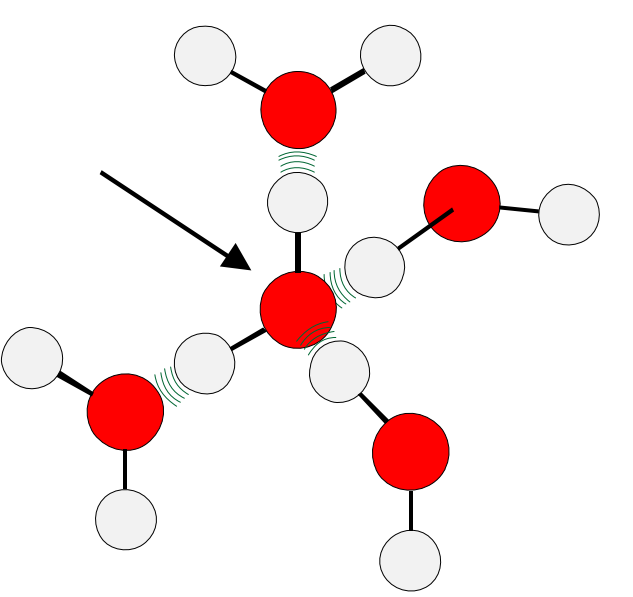
flickering clusters of water molecules
dynamic, short-lived groupings of water molecules that constantly form and break hydrogen bonds with each other
flickering clusters of water molecules are positioned in
quaternary order
water penetrates dividing membranes in the
flickering cluster form
water in the body acts as a
solvent; medium for reactions
water in the body also acts as a
source of osmotic forces
another function of the water in the body is
forming compartments
Water content of blood
90%
Water content of liver, muscle, brain
70-75%
Water content of bone
25%
Water content of fat
10%
Barriers separating compartments (2 types)
cell membranes and capillary walls
the cell membrane is
permeable for water without restriction, but selective for other substances
the capillary walls
retain colloids, permeable for other substances
Parts of the membrane determining transport:
lipid bilayer, complex proteins
what are the complex proteins determining transport through membranes
receptors, enzymes, carriers, channels
types of transport through membranes
passive transport and active transport
types of passive transport require
no ATP
types of passive transport
simple and facilitated diffusion
facilited diffsion
a type of passive transport in which substances move down their concentration gradient with the help of membrane proteins
types of active transport
from direct energy source and from indirect energy source
primary active transport moves substances
against their gradients
Primary active transport (direct use of ATP)
transport protein (pump) uses ATP hydrolysis to move ions/molecules against their gradient
secondary active transport
does not directly use ATP, but depends on gradients created by primary active transport
direction of solutes involved in secondary active transport
either both in the same direction or in opposite directions
Total body Water (TBW)
Extracellular compartment (2/3)+ Intracellular compartment (1/3)
How much is the tbw /bwkg?
600-650 ml/bwkg
parts of the EC body fluid
intravasal, (in the circul.) interstitial in the tissues
the EC compartment has subcompartments
intravascular, interstitial, transcellular
transcellular subcompartment
separated from the other compartments of the body by epithelial cell layers!!!
examples of transcellular subcompartments
synovial fluid, aqueous humour, glandular discharges, content of the urinary bladder, gastrointestinal tract
measuring the EC compartment by the dilution principle
quickly and slowly equilibrating spaces
quickly equilibrating space
substance flow is fast, it equilibrates within the 0.5 -1 hour
examples of quickly equilibrating spaces
blood plasma, interstitium of soft tissues, lymph
slowly equilibrating space
uniform distribution develops only 8-10 hours later
examples of slowly equilibrating spaces
bone, transcellular space
the intracellular compartment is considered to be
uniform
Stewart Dilution Principle
a method used in physiology to measure the volume of a fluid compartment in the body
Stewart-principle in living organisms
In the living organism the concentration of the indicator decreases constantly
Why does the C decrease contantly in a living organism
permeates barrieres, metabolized, excreted by the kidney, lung or the skin
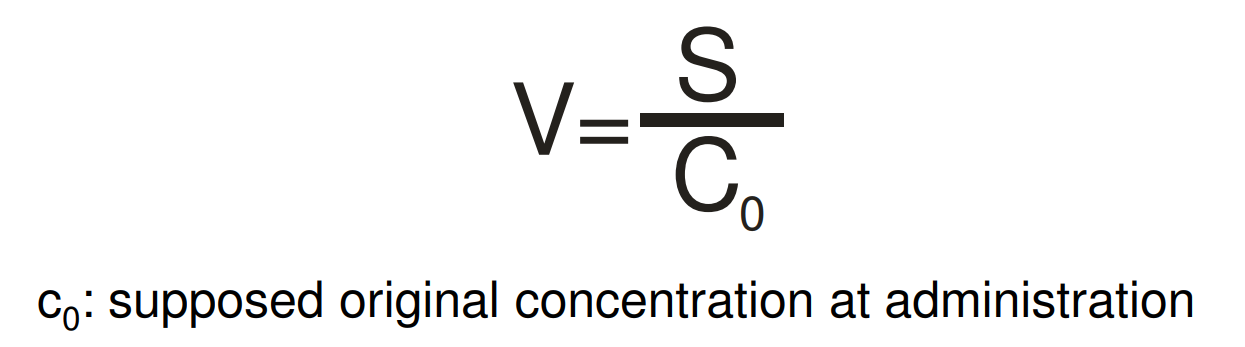
Stewart-principle in living organisms
indicator concentration should be calculated at administration
When does the indicator start to get eliminated?
immediately after administration
substances used for the assessment of total body water
3H2O, 2H2O antipirin, urea, tiourea
exsiccation
desiccation till constant mass at a temperature of 105 ºC
assessing body density
weigh the mass, quantify volume, calculate density (m/V)
densities of some tissues
bone: 1.56, soft tissue: 1.06, fat: 0.94
What is the constant water content of lean body mass?
73% water content
What is the constant water content of fat?
10% water content
calculating density: suitable for estimating the
composition of the body (fat content)
TOBEC (Total Body Electrical Conductance)
measures the fat content of the body with high precision
fat content can be measured by
measuring density experimentally, or calculating it from TBW%
substances used for the uantification of the EC compartment
diffuse across capillary walls, but cannot cross cell membranes
example substances used for the uantification of the EC compartment
inulin, mannitol, sacharose
EC space – Stewart-principle
3 types of distributions; fast, slow and late distribution
EC space – Stewart-principle: Fast distribution:
shows the volume of the soft tissues
EC space – Stewart-principle: Slow distribution:
shows the volume of the soft plus the fibrous tissues
EC space – Stewart-principle: Late distribution:
shows the volume of bone, fibrous and soft tissues