A&P Chapter 6 - Integumentary System
1/27
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards notes include: Epidermis, Dermis, Hypodermis, Clinical pathologies, and the chapter recap questions.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
Integument
Cutaneous membrane
Dermatology
Study of the skin
Epidermis
Layer of the integument: Stratified squamous epithelium.
Dermis
Layer of the integument: Deeper layer that is primarily dense irregular connective tissue.
Hypodermis
Subcutaneous layer of the skin
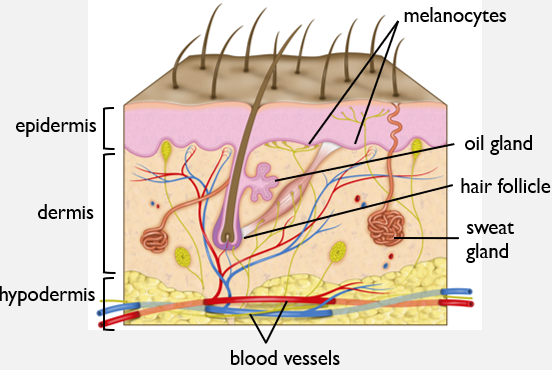
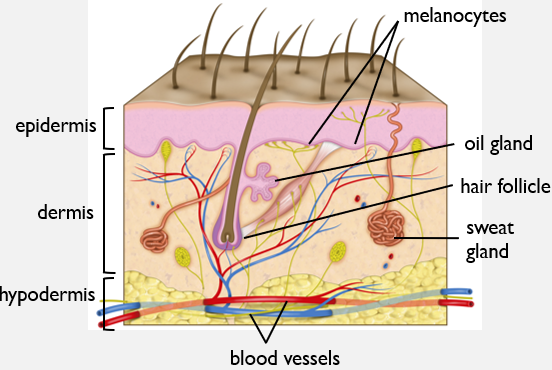
What are the functions of the integumentary system?
Protection
Sensation
Vitamin D production
Immunity
Body Temperature
Excretion
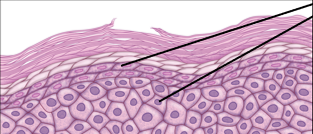
Characteristics of Keratinocytes?
Main cell type of epidermis.
Provide keratin intermediate filaments.
Provide structure to skin hair, and nails.
Water-proofing protective function.
Keratinized tissue = dry
Non-Keratinized tissue = wet
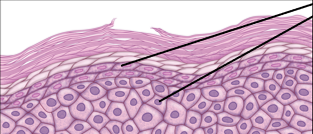
Characteristics of Melanocytes?
Produce pigments eumelanin/pheomelanin, giving skin and hair its color.
Protects from harmful UV rays.
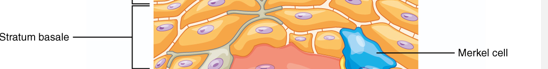
Characteristics of Tactile cells - Stratum basale?
Merkel Cells
Few in number
Sensitive to touch
When compressed, release chemicals, stimulate sensory nerve endings.
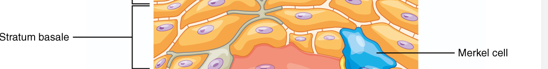
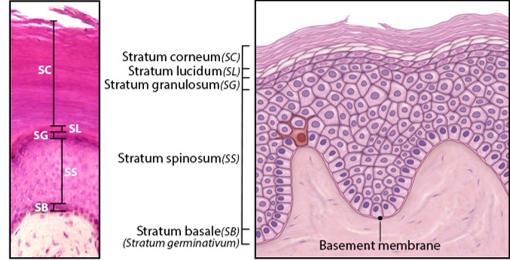
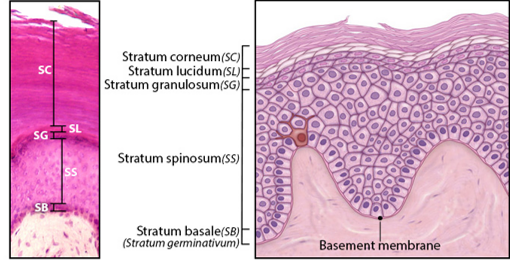
Stratum Basale
Single layer of newly-produced cuboidal cells.
Contains melanocytes and epidermal ridges.
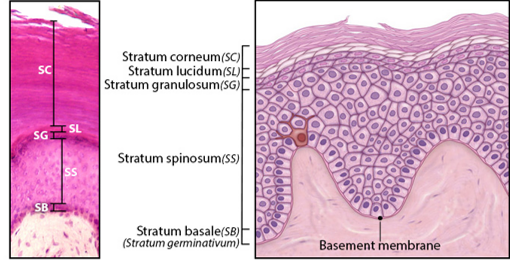
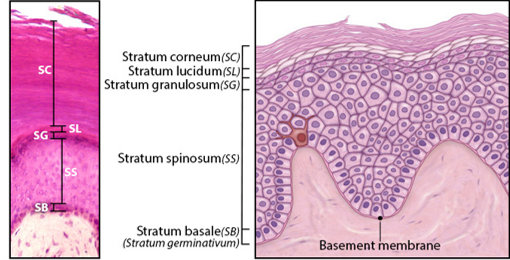
Stratum Spinosum
8-10 rows of keratinocytes.
Accumulation of keratohyalin, lamellar bodies.
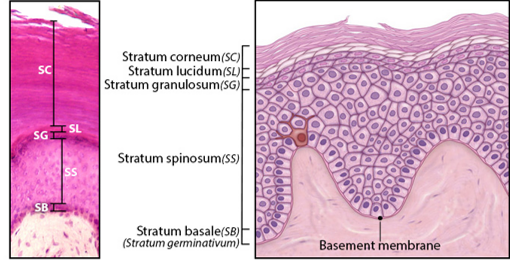
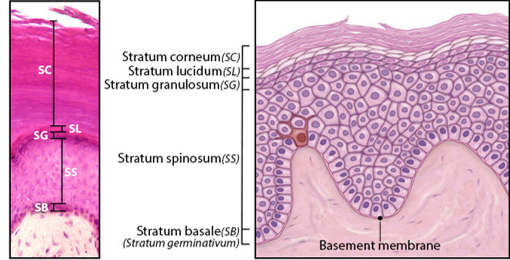
Stratum Granulosum
3-5 rows keratinocytes
Large amounts of keratohyalin are produced.
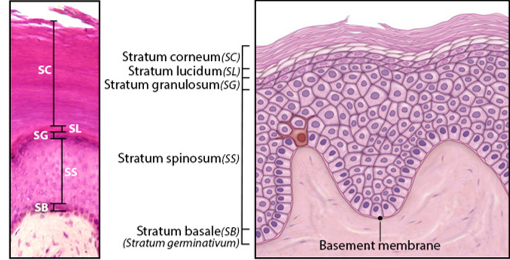
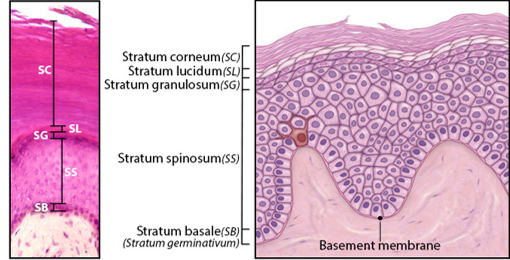
Stratum Lucidum
Layer of dead keratinocytes, only in thick skin.
Contains translucent protein eleidin.
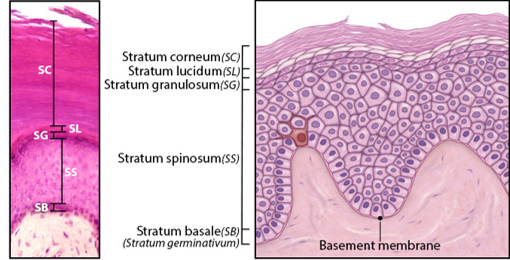
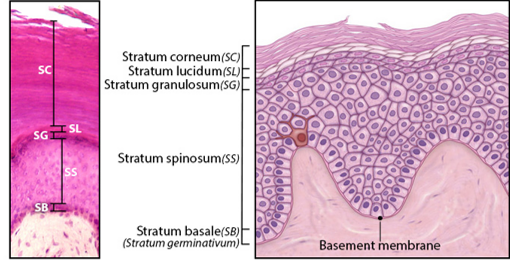
Stratum Corneum
15-30 layers of dead keratinocytes.
Lipid coating forms water-resistant layer.
What are the variations of the epidermis?
Thickness
Color
Skin markings
Characteristics of Thick Skin?
Location: Palms of hands, soles of feet.
Contains all five layers of epidermal strata.
Sweat glands but no hair follicles or sebaceous glands.
Characteristics of Thin Skin?
Covers most of the body.
Lacks a stratum lucidum.
Sweat glands, hair follicles, and sebaceous glands.
Which layer of the Epidermis connects to the Dermis?
A. Stratum basale
B. Stratum lucidum
C. Stratum spinosum
D. Stratum granulosum
D. Stratum basale
What is the function of the Epidermis?
Protection: The epidermis is the first line of defense against microorganisms.
What are the characteristics of the Epidermis?
Dry surface is unacceptable for the growth of most microorganisms.
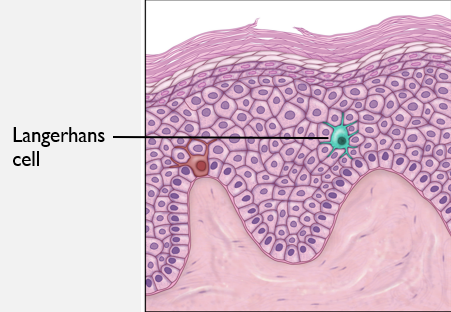
Langerhans cells are found in all but stratum corneum.
Antigen-presenting cells, first line of defense.
Hemoglobin
Oxygen-binding protein in red blood cells.
Bright red color upon binding oxygen.
Melanin
Dark pigment produced in melanocytes, transferred to keratinocytes.
Amount in skin varies (heredity, UV exposure)
Carotene
Yellow-orange pigment acquired from some vegetables.
What are the functions of the epidermis in regard to skin color and protection from UV rays?
Melanocytes produce melanin from tyrosine in specialized organelles (melanosomes).
Melanosomes are transferred to keratinocytes upon stimulation.
Melanosomes in keratinocytes contribute to skin’s pigmentation.
What are the factors affecting pigmentation?
Type of melanin produced.
How much the melanosomes are filled with melanin granules prior to transfer.
Number and size of melanosomes produced.
How long the melanosomes persist in the keratinocytes.
Degree of transfer within the dermis.
What are the mechanisms of skin pigmentation?
By exposure of UV rays, reactive oxygen is generated.
Melanin is excessively produced by melanocytes.
Skin pigmentations are generated.
What is carcinogenesis, in relation to UV radiation, immune-suppression, DNA damage, and