adolescent midterm
1/152
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
153 Terms
what is adolescence and what does it describe?
A cultural phenomenon that describes the period when puberty begins and ends at adulthood
what ages is adolescents occurring?
Roughly ages 10-18 years, and perhaps extends to emerging adulthood (ages 18-25 years) as more individuals continue to depend on their parents for financial and/or emotional support

what % of the world’s population account for __% of the world’s income
20% of the world’s population account for 50% of the world’s income
how many children have no access to school (6-18)
235 millon
2019 data about math and literacy
Global literacy and mathematics have been on the decline as of 2019 data
(44% have minimum proficiency in math, 24% can read)
___% of the worlds population has a smartphone, and what does it affect?
69%
ncreasingly adolescents have bicultural identity—one to align with local traditions and practices, and one to align with their preferred online community
where was majority of empirical research on adolescence conducted?
the west, with a minority of adolescents in the world
does puberty began earlier now? why so?
With better prenatal and early years care (healthcare, nutrition, parental awareness), puberty begins earlier than in the previous century

what type of construction is emerging into adulthood considered?
cultural construction
what’s the Criteria for adulthood
Accepting responsibility for oneself
Making independent decisions
Being financially independent
Cultural specifics: military service, supporting a family, supporting parents, marriage
Naturally, “adult” is a cultural contstruct
a scientific method breakdown
A curiosity: “Are smartphones bad for youth?”
Collect the evidence: “Who has smartphones, and how are those youths doing relative to those who don’t have smartphones?”
Fine detail in methodology: do you want to compare those who have vs. have not, spend more time vs. less time, specific apps or just any smart phone activity...
Draw conclusions

2 types of data collection
collecting your own
relying on someone else’s
what do correlations examine?
the relationship between two existing variables

The experimental method
breakdown
hypothesis
testable hypothesis
create 2 groups (experimental and control)
dependant variable
indepdant variable
results
statistics in developed country for education
All adescents obtain secondary education
50% tertiary education
statistics for education in a developing country
20% of adolescents do not complete primary school and only somewhat more than half enrolled in secondary
80% do
Tertiary education are only for the wealthy elite
who adheres most closely to the historical traditions of their culture
Rural areas of developing countries, who tend to adhere more closely to the historical traditions of their culture than people in urban areas

Traditional cultures tend to be more collectivist than other cultures, in part because in rural areas close ties with others are often an economic necessity

what is a majority culture?
Sets most of the norms and standards and holds most of the positions of political, economic, intellectual, and media power
Many minority cultures defined by ethnicity, religion, language, or other characteristics
Asias culture
Filial piety
Children are obligated to respect, obey, and revere their parents, especially their father
Asians are more likely to have a grandparent living in home then other cultures

indias culture
2010 education compulsory for children 6-10 to gain education
Young pople, mainly girls are illiterate
latin americas culture
Unemployment in young people is high, exceeding 25%
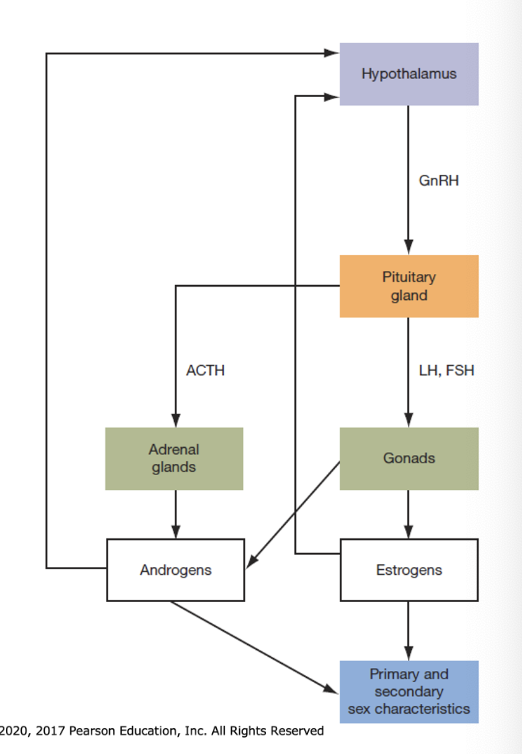
Endocrine system breakdown
Hypothalamus signals hormonal changes
Gonadotropin-releasing hormone production increased (related to body fat)
Fat cells produce protein leptin that provides signal to release GnRH
Pituitary Gland releases gonadotropins
Follicle-stimulating & luteinizing hormones
Poor thyroid functioning related to abnormalities sexual development
feedback loop
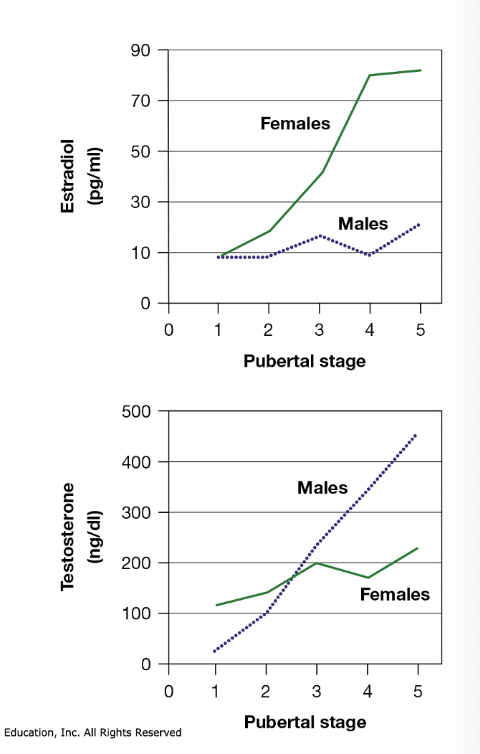
sex differences in esterdil and testororsone
Important to understand that estrogens and androgens exist in both sexes
More sex-specific sex hormones are released as puberty progresses

growth spurts
Typically not much difference in first years of life
Fastest you grow at one
Increase at puberty
Difference plays a big role in difference of body image
Natural reason girls pay attention to physical appearance earlier
And throughout puberty

what many years ahead do girls start showing puberty signs
~2 years
male vs female wight gain?
males: major body muscle
females: fat
name primary sex characteristics
menarche: first period
spermarche: first production of sperm
menarche and ovulation
first menstrual period (mature egg released ~28 days; ~400 ova over lifetime, first 4 years ovulation is unpredictable)
Bleeding doesn’t always mean ovulation for the first 4 years

secondary sex charcteristics
skin oil and sweat
underarm hair
change in voice
growth spurt
pubic hair
breast development
what changes first in a females body
breasts
noticeable feature to all
classic BMI guidelines
Canadian Guidelines (canada.ca)
Underweight: BMI < 18.5
Normal weight: 18.5-24.9
Overweight: 25-29.9
Obese: BMI ≧ 30
Issues with BMI index
Not a direct measure of body fat, does not indicate body fat distribution, does not account for muscle mass (e.g., weightlifters will be considered to have too much fat when using BMI)
BMI does not distinguish between men, women, nor different ethnicities (less accurate for non-White individuals)
define obesity
Chronic, progressive, and relapsing disease, characterized by the presence of abnormal or excess adiposity that impairs health and social wellbeing
what is the prevalence of obesity in 1975 and 2016
1% in 1975, 7% in 2016 (5-19 years of age; WHO))
is weight in youth increasing? both in developed and devilling countries?
yes
health risk of weight on adolescents
Health risk: breathing, fractures, hypertension, insulin resistance
Insulin: hormone in pancreas that helps glucose in the blood to be metabolized as energy in muscle, fat, and the liver
what percent of adolescents in the US eat fast food daily
36%
gene and envoirnemtn role in obesity
Hereditary and family concordance in obesity
E.g., correlation coefficients between husband & wife = 0.10-0.19; among siblings =0.24-0.34, DZ twins = 0.15-0.42, MZ twins = 0.70-0.88
Different genes control protein synthesis and function involved in appetite, energy expenditure, metabolism, and adipogenesis
Genes respond to the environment
May burn more calories running then someone else
Controls hunger
If you enjoy exercise
Impact of dietary fat on obesity prevalence is controversial (i.e., may impact carbohydrate & protein consumption, depends on genetic predisposition and physical activity)

environnemental impacts
Possible that environmental factors have the most impact during growth than after growth

puberty secular trends
Menarche in Western countries has decreased in past 150 years
Puberty begins earlier with good nutrition and medical care
US = 12 years, some African countries could be 16 or 17
Environment where you live effects the time of puberty

what factors predicted early menarche
Later born, urban residency (urbanization increasing, 1985: 24%, 1995: 29%, 2010: 50%), high BMI (predicted based on the role of fat on triggering hypothalamus activity)
Hypothalamus is reaching a set point of adipose tissue on your body
High carbohydrate intake predicted later menarche
SES, household income, parental education, fat intake, exercise not correlated to early vs. late menarche
Dietary fat consumption - not correlated to early or late menarche

difference between rural and urban areas in puberty
Some criss cross but overall city living more likely more earlier age than rural areas
Less difference now than the 70s

what are endocrine disrupting chemicals?
Synthetic chemicals in the environment that could impact the endocrine system and reproductive health
Impacts adults as well, but adolescents is particularly prone as its changing to be sexually mature
May mimic hormones, disrupt hormone synthesis or breakdown, alter development of hormone receptors, act as hormone antagonists, or alter hormone binding
Now working against it and body does not benefit
Most common sources: pesticides, plastics, electronic wastes, flame- retardants, metals, food additives, personal care products

what is the evidence for exogenous chemicals onsetting early puberty?
Evidence is mixed: varying degrees of exposure, timing of exposure, and non-linear dose-response patterns (i.e., incremental increase in exposure does not mean incremental earlier puberty)

oskihan
(red bean rice) is often cooked for any celebratory meal in Japan (e.g., accepted into university, first job, etc.)
Historically, the mother cooked it for dinner when the daughter experienced menarche
Not as common today

puberty rituals
Most cultures have a ritual to celebrate the beginning of puberty
For girls, menarche is usually the event that is celebrated
For some cultures menstruation is taboo and associated with restricting the woman’s behaviours, whereas in other cultures it is celebrated, and in some cultures there are ambivalent responses
For boys, typically associated with age, and involves rituals that display courage, strength, and endurance
Many cultures traditionally had rituals that involved pain, as initiation into adulthood and preparation for life’s challenges as an adult (e.g., Samoan tattooing especially painful for boys)


parent adolescent relations
Relations between parents and adolescents become cooler when pubertal changes become evident

what happens to self esteem in adolescents
declines
what did teens report for days with they experience maternal warmth and not conflict
higher self esteem
does maternal warmth effect long term
Maternal warmth also associated with better self-esteem the next day (more long-lasting effects with warmth)

is puberty a taboo?
Menstruation and ejaculation (masturbation) have been taboo topics in many cultures, including North American culture
The better informed the adolescents are, the more positive their experience towards the physical changes associated with puberty


what percent of girls have no knowledge of menarche before occurring?
60%
why is puberty a taboo to girls? and how to rural learn?
Effort to keep girls “pure” and away from sexuality (rural girls learned about sex and reproduction through taking care of farm animals, but urban girls more sheltered)

spermachre and semanarche
permarche: first production of sperm (no way to know yourself when)
Semenarche: first ejaculation
Cultural differences in whether this is to be experienced privately or celebrated with others
No one measures when this happens

does the effect of enviornemtn increase or decrease with age?
The effect of environment increases with age, such that adolescents and adults are less determined by their parental environment than infants and children
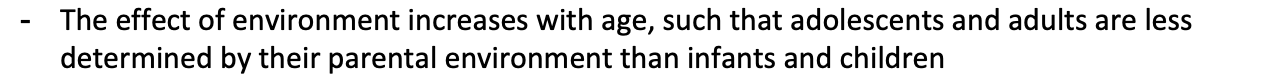
early studies reveal intelligence, specific cognitive abilities (e.g., memory), personality, and psychopathology, vary HOW much between and within families?
vary as much within families as between families

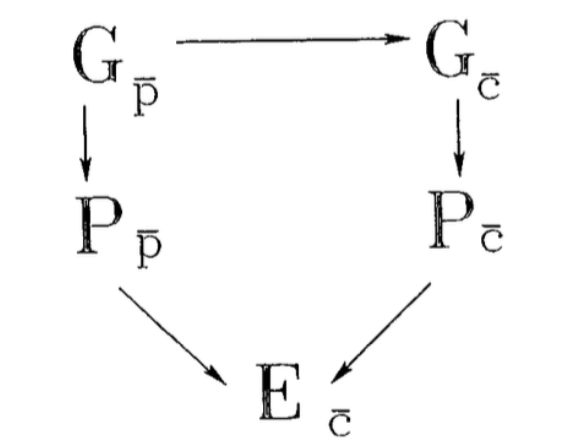
the better model for experience environment and genetics
Genotype of parents —> Phenotype of parents —> Environment of child
Genotype of parents —> Genotype of child —> Phenotype of child —> Environment of child

passive
evocative
active
Passive: Biological parents provide your environment
Evocative: Individual’s genes evoke specific responses
Active: Individual’s genes seek out environments that match predispositions/tendencies

do people make their own expierences?
people make their own environments, based on their own heritable characteristics

difference with moms to first and second borns
Firstborn infants looked at their mothers and smiled more, and engaged in more exploration with objects than second born infants
Mothers engaged in more physical encouragement, social exchange, didactic interaction, material provisioning, and language with firstborns than second borns
Only feeding & holding did not differ between two infants

time with older and younger siblings??
“time” is determined by age of older child (older child, less time), and then parent “splits” the time equally between two children
Time is determined by the age of the older child
Older child is 3 needing a lot of moms time
If there 12 there expected to play alone
First-born child receives 20-30 minutes of quality time each day more than second-born child of same age

what personality trait is affected by birth order?
onfirmed birth-order effects on intelligence: 1.5 points decline with increasing birth-order
No birth order effects on extraversion, emotional stability, agreeableness, conscientiousness, imagination

Behavioural genetics research reveals that the environment impacts
traits more than _____

Behavioural genetics research reveals that the environment impacts psychological traits more than genetics

behavioural genetics 101
Covariance among relatives on normally distributed traits allows us to estimate the role of heredity
People can differ in terms of genetics or non-genetics
To the extent that a phenotype is different among individuals, to what extent is this difference attributable to genetic variation or non-genetic variation among individuals?
If heredity is important for X (e.g., height), then 2 people who are related should be more similar in height than 2 people not related

Genetic variance explains___of individual variance at age 15 observed in rule-breaking behaviour (e.g., property crime) but only____ at age 10
Genetic variance explains 80% of individual variance at age 15 observed in rule-breaking behaviour (e.g., property crime) but only 20% at age 10
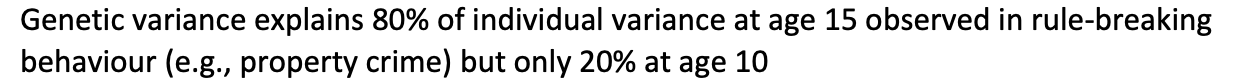
are genetic influences mediated by peers?
Genetic influences are mediated by sensation-seeking, and exacerbated by deviant peers

adolescents brain and peer breakdowns
Ventral striatum (incentive-processing system) responds increasingly to rewards in adolescence, especially when peers are involved
Individual differences (e.g., hormones during puberty) in reward- responsive brain regions may mediate genetic risk for problem behaviours
Higher testosterone (endogenous and exogenous) correlates with more reward seeking, greater VS activation

alcohol and tobacco use in the brain and peer influences
Genetic factors (own or sibling’s use) correlated with increased exposure to best friends with heavy substance use
Adolescents who were genetically liable to substance use were more vulnerable to adverse influence of best friends
Not just if genetically suspectable but also more vulnerable to the influence of best friends who use

white and grey matter?
White matter = fatty tissue
myelin
Grey = dendrites and cell bodies

Grey matter volume in childhood
Postmortem studies suggest changes in grey matter volume reflect synaptic proliferation followed by synaptic pruning
Grey matter seems to peak 1-3 years earlier in female brains
Increase in functional and structural connectivity, changing balance between limbic-frontal function, extends into adulthood

how does testostoronce affect white matter
Using a voxel-wise approach in neuroimaging (as opposed to whole brain or ROI) reveals increase in density between ages 4-17 years, although in male brains testosterone appears to decrease white matter
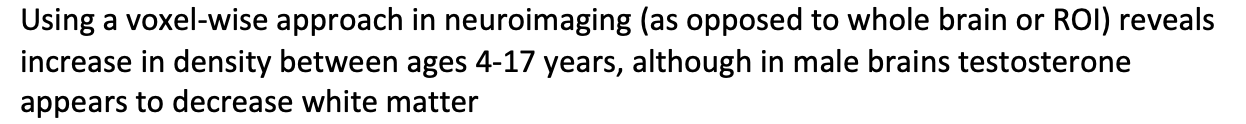
sex difference in white matter
white matter density across age in cortico-spinal tract as a function of age
Increased with age in girls
Decreases with boys
Testosorone decreases it
Androgens and estrogens may play differential roles during puberty in terms of white matter maturation

when is the intercrinaial myelin peak?
age 50
non human primate synaptic pruning
Non-human primate brains demonstrate synaptic density that increases around 3 months, then declines by 10% by age 2 years, and 40% declining between 3-5 years (analogous to human adulthood)

human synaptic pruning
In humans, synaptic density reaches its peak in childhood, followed by synaptic pruning in early (auditory cortex) to mid-adolescence (prefrontal cortex), but continues at a slower rate into adulthood

egray matter _____ in frontal lobes to improve what things?
Gray matter thinning in frontal lobes correlates with improved cognitive performance, such as verbal and spatial memory

alcohol abuse on the brain memory and grey matter?
Detrimental effects of alcohol are magnified during adolescence
Memory impairment worse for ages 21-24 than 25-29
In adult brain, chronic alcohol abuse associated with cortical gray matter thinning in PFC

Mechanisms for neural plasticity

long-term potentiation (synaptic efficiency), synaptogenesis, axonal sprouting, dendritic remodeling, neurogenesis, recruitment.
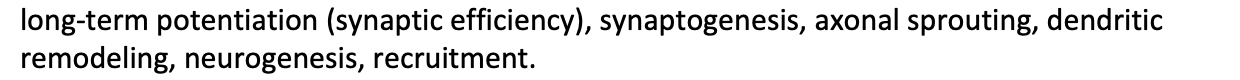
During adolescence, _____, _____, and ____ alter structure and function of neural networks

Tourette syndrome theory
Theory that tics are the result of abnormal motor pathways in the networks connecting cortex to basal ganglia and thalamus
certain areas and cortical thinning with toureetes syndrome
Some regions are significantly thinner than control children (sensorimotor cortex and Broca’s areas), and more severe tic symptoms associated with more extensive cortical thinning

what happens in adolescents leadingg to more severe toureetes symptoms
In some individuals, plasticity is reduced during adolescence, leading to more severe symptoms, greater activation of neural systems that support inhibitory control to maintain task performance, and relative persistence of tics into adulthood.
unmedicated depressed adults brains
in unmedicated depressed adults, cortex is thicker than healthy controls.
antidepressant treatment changes what in the brain ?
Successful antidepressant treatment reduces cortical thickness to normal levels
developmental systems theory
experience drives neural changes and neural changes support development
Piagets theory
constructivist approach
Stage theory
Sensorimotor, preoperational, concreate operational, formal operation

what did Piagets emphasis on
Emphasis on maturation: active processes triggered by children’s desire to learn and solve problems
Thinking is organized into schemes: assimilation & accommodation
formal operations
Ability to reason about complex problems
Can hold in working memory multiple variables at once

abstract thinking: formal logic
if A = B, and B = C, then A = C
If C is the same as A, you dont need to compare a and b bc we can infer it is the same
Children think it depends on what A, B, and C represent

abstract thinking: complex thinking
considering simultaneously multiple connections and interpretations (e.g., metaphors: literal & abstract meanings; sarcasm

define Metacognition
ability to think about own thoughts
Inherent assumption that your own assessment is accurate. Children can think they know a lot, even when they don’t

how do students with high metacognition perform academically
Students who have high metacognition perform better academically
Who can accurately assume their own assessment

do grades promote metacognitive awareness
Metacognition is you assessing your own performance
Grades exogenous = something from the outside
what are the limitation of Piaget's theory
More criticism for formal operations than other stages
Individual differences
Cultural influences
Beyond adolescence
individual differences in Paiget theory
Because the natural environment is similar for all individuals, Piaget expected the typical experiences to be sufficient to drive maturation through the four cognitive stages
Success rate in completing Piagetian formal operations tasks is 40-60%, even among late adolescents and adults
Individuals also do not always apply formal logic in all contexts
Easier in situations with which there is expertise; easier among individuals who enjoy math & science

cultural differences in Piaget theory
Performance on Piagetian tasks likely depends on extent to which formal schooling is a normal cultural experience
Even in cultures without formal schooling, adolescents are better able to solve complex tasks than children
Requires the ability to take multiple perspectives, consider multiple facts/ideas at once, and think beyond the concrete world

emerging adulthood: Postformal thought
ability to think about the complexities of everyday life
emerging adulthood: pragmatism:
adapt logical thinking to the practical constraints of real- life situations (e.g., use permutations than working through every possible outcome)