Organic Chemistry pKa Values
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
Alkane (e.g. H3C-CH3)
50+
Alkene (e.g. H2C=CH2)
42-46
Ketone (e.g. CH3COCH3)
18-20
Alkyne (e.g. HC≡CH)
22-26
Amine (e.g. CH3CH2-NH2 )
38-42
Alcohol (e.g. CH3CH2-OH)
16-18
Phenol (e.g. C6H5-OH)
9-11
Ammonium (protonated amine, e.g. NH4+)
9-11
CH3CO2-H (Acetic acid)
4.76
Carboxylic Acid
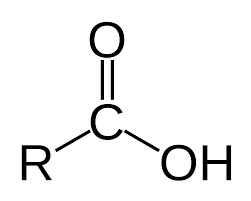
4-5
Hydronium (protonated water, H3O+)
-1.74
Protonated Oxygen (alcohol, ketone, aldehyde, ester)
~ -2
H-Cl
-7
H-I
-9
H2SO4 (Sulffuric Acid)
-10
Large pKa → weak acid
weak acid → strong conjugate base
Strength of Acid
Stronger acid → Weaker CB
Weaker acid → Stronger CB
Acid-base rxns favor the weaker acid and the weaker base
Lewis Bases (Nucleophiles)
Have availiable electrons that can be donated to form a new bond
Lewis Acids (Electrophile)
Accept electrons to form new bonds
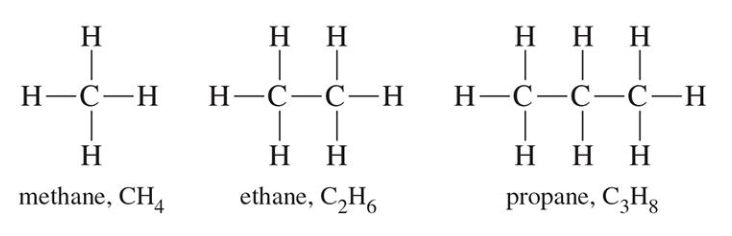
Alkanes
CnH2n+2
Single bonds between the carbons (all carbons are sp3)
Low boiling point → Gases
Constitutional Isomers
Compounds with the same molecular formula but the carbons are connected differently
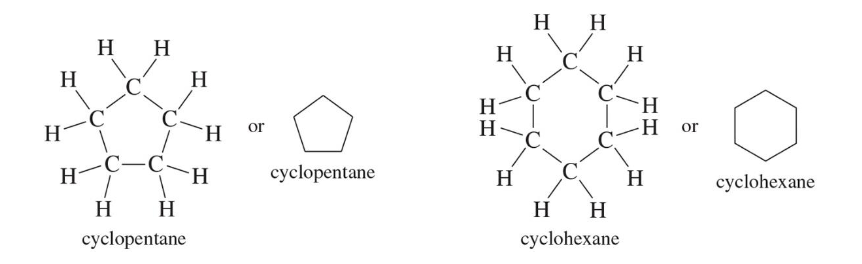
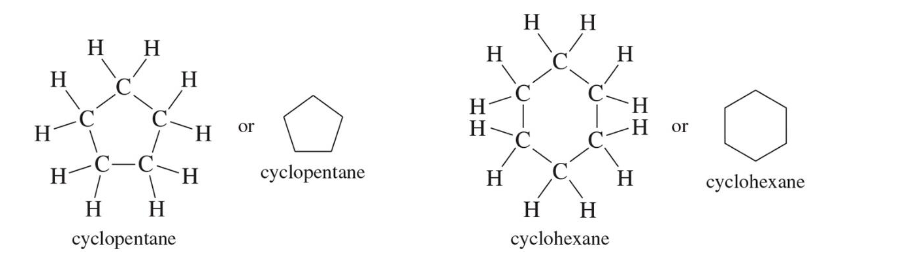
Cycloalkanes
sp3 carbons form a ring
Alkenes
Double bonds are present in the molecule (sp2 carbons)
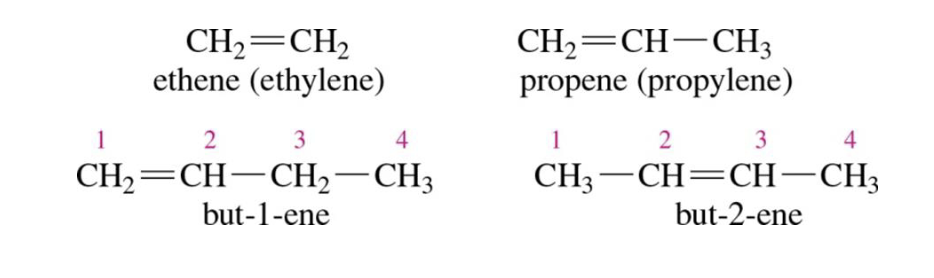
Cycloalkenes
Double bond in ring
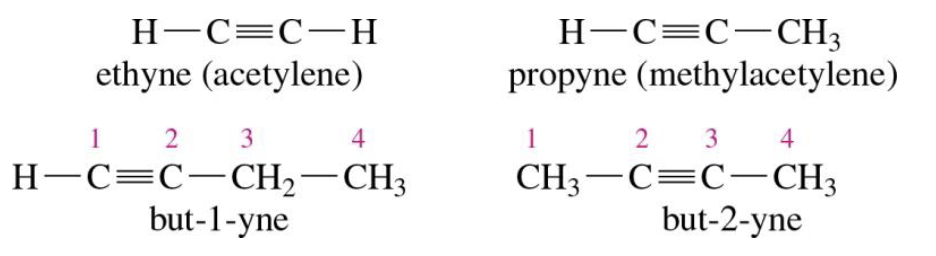
Alkynes
Triple bonds are present (sp carbons)
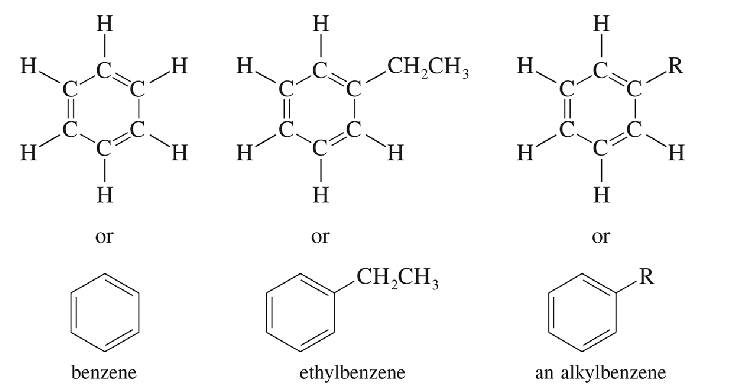
Aromatic Hydrocarbons
Contains a benzene ring
methane
1 Carbon
Ethane
2 Carbons
Propane
3 Carbons
Butane
4 Carbons
Pentane
5 Carbons
Hexane
6 Carbons
Heptane
7 Carbons
Octane
8 Carbons
Nonane
9 Carbons
Decane
10 Carbons
Alcohols
Hydroxyl Group is the main functional group
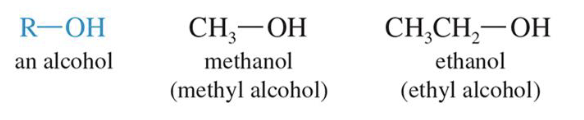
Ethers
Contain 2 alkyl groups bonded to an oxygen
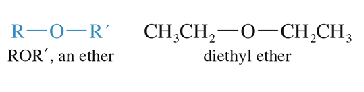
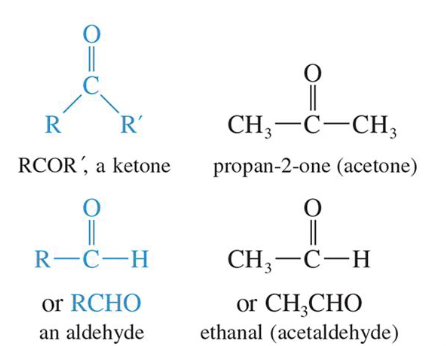
Aldehydes and Ketone
Contain carbonyl group (C==O)
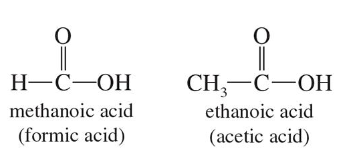
Carboxylic Acids
Contain the Carboxyl Group (-COOH)
Amines
Alkylated derivatives of ammonia
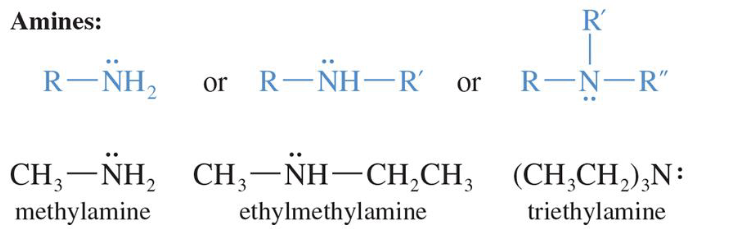
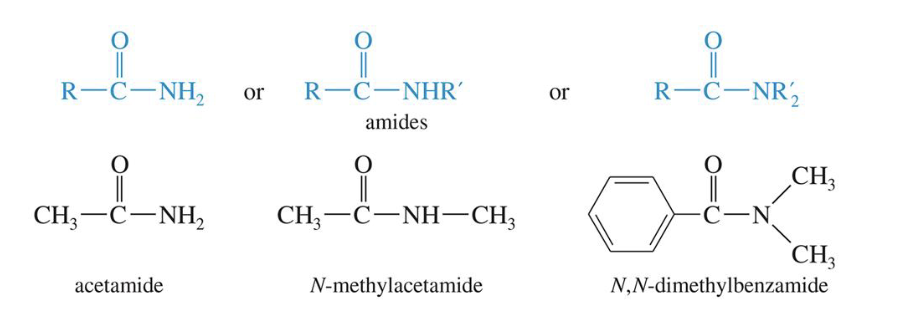
Amides
Derivatives that result from a combination of an acid with ammonia or an amine
Nitriles
Contain the cyano group (C≡N)
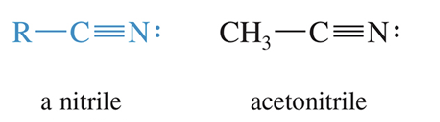
Bronsted-Lowry Acids
Donate a proton
Brownster-Lowry Bases
Accept a proton
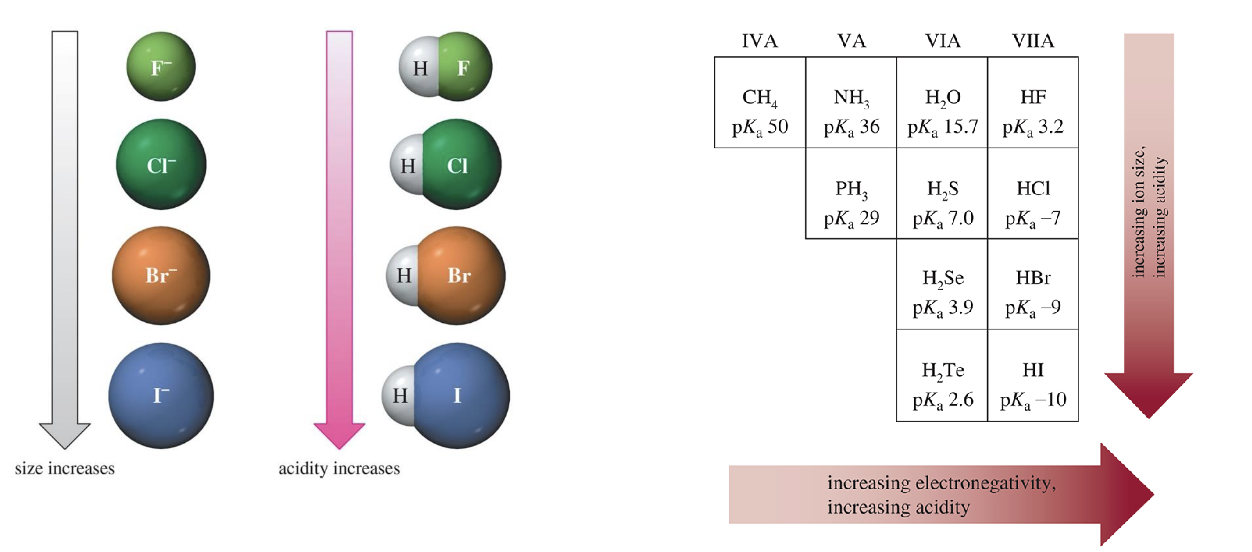
Effect of Electronegativity on pKa
More electronegative element bears a negative charge more easily, giving a more stable conjugate base and stronger acid
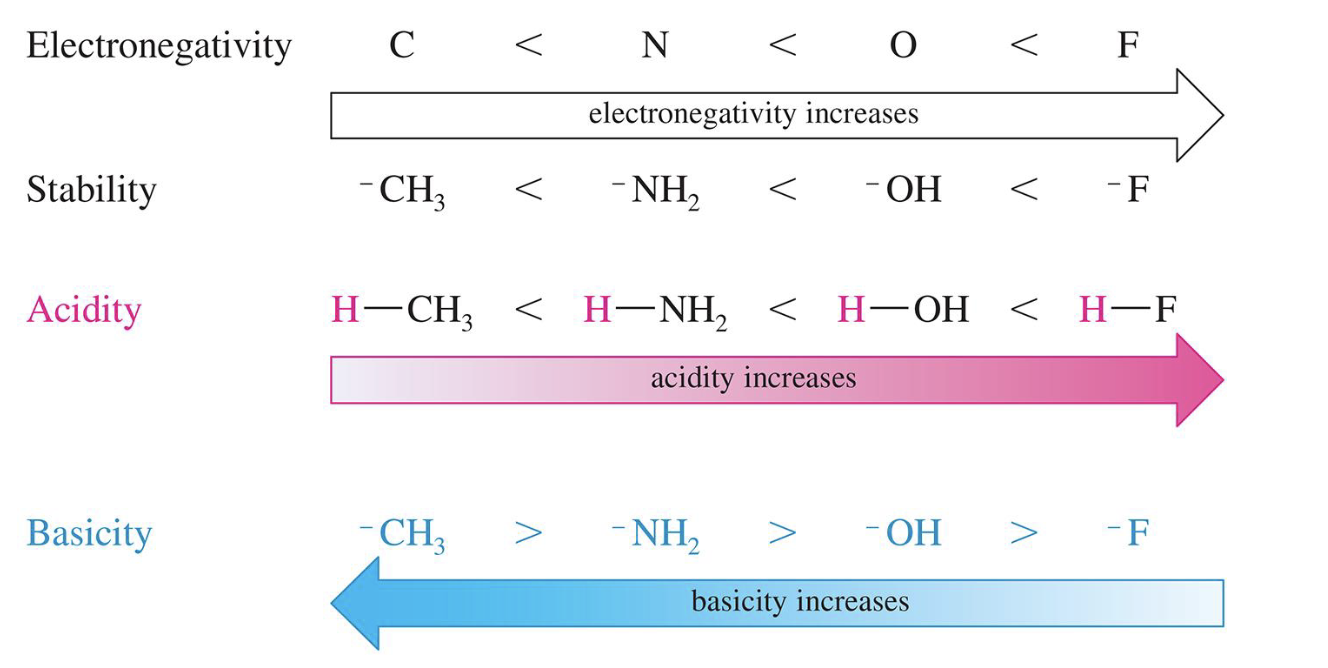
Atom Effect on pKa
Negative charges of an anion are more stable on larger atoms
Acidity increases down the column on periodic table
Aufbau Principle
Fill the lowest energy orbitals first
Hund’s Rule
When there are two or more orbitals of the same energy (degerate), electrons will go into different orbitals rather than pairing up in the same orbital
Bond Formation
Conbining orbitals between two different atoms
Hybridization
Combining orbitals on the same atom