Cell Culture and Cell Growth (Flashcards)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 11:58 PM on 3/11/25
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
78 Terms
1
New cards
Bacteria (E. coli)
Binary fission.
2
New cards
Yeast (S. cerevisiae)
Budding.
3
New cards
Mold (A. niger)
Spore formation (conidia).
4
New cards
Plant & Animal Cells
Mitosis.
5
New cards
Mitotic Division in Plants
Involves interphase, preprophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase, and cell plate formation.
6
New cards
Mitotic Division in Animal Cells
Involves prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase, and cytokinesis.
7
New cards
Cell Culture
Growing cells under controlled conditions outside their natural environment.
8
New cards
Adherent Culture
Cells grow freely in the culture medium without requiring attachment.
9
New cards
Examples of Adherent Culture
Bacteria, yeast, plant cells, hematopoietic cells.
10
New cards
Suspension Culture
Cells require cell-cell adhesion or attachment to a surface to grow.
11
New cards
Examples of Suspension Culture
Mammalian cells, plant cells.
12
New cards
Cell Passaging (Subculturing)
Process to transfer a portion of cells from an existing culture to fresh medium.
13
New cards
Detachment
Using enzymes (trypsin, collagenase) or mechanical methods.
14
New cards
Neutralization/Washing
Remove enzymes using serum-containing medium.
15
New cards
Resuspension & Seeding
Cells are diluted and placed into fresh vessels.
16
New cards
Culture Medium
A nutrient-rich gel or solution used to support the growth, survival, and proliferation of cells.
17
New cards
Nutrients & Salts
Amino acids, vitamins, Na⁺, K⁺, Ca²⁺, etc.
18
New cards
Energy Source
Carbohydrates, lipids, amino acids.
19
New cards
Carbon and Nitrogen Sources
Essential for cell growth and metabolism.
20
New cards
pH Buffers
Bicarbonate, HEPES, phosphate buffers.
21
New cards
Growth Factors
Varies by cell type.
22
New cards
Types of Culture Media
Solid (agar-based), liquid (broth-based).
23
New cards
Defined Media
Exact composition is known.
24
New cards
Undefined Media
Contains complex components like yeast extract.
25
New cards
Specialized Media
Designed for differentiation or regulatory compliance.
26
New cards
Biological Contaminants
Bacteria, fungi, viruses, mycoplasma.
27
New cards
Chemical Contaminants
Endotoxins, heavy metals.
28
New cards
Physical Contaminants
Dust, fibers, glass particles.
29
New cards
Antibiotics in Cell Culture
Used to prevent microbial contamination and maintain plasmid-bearing cultures.
30
New cards
Aseptic Techniques
Methods used to maintain a sterile environment in cell culture.
31
New cards
Sterile Workspace
HEPA-filtered laminar flow hoods.
32
New cards
Sterilization Methods
Autoclaving, ethanol disinfection.
33
New cards
Good Lab Practices
Standard protocols to prevent contamination.
34
New cards
Monitoring Techniques
Microscopy, contamination checks.
35
New cards
Microbial Cell Culture
Growing bacteria, yeasts, or fungi in a controlled environment using solid or liquid nutrient-rich media.
36
New cards
Streak Plate
Used to isolate individual colonies.
37
New cards
Spread Plate
Used to evenly distribute bacteria for counting.
38
New cards
Plant Suspension Culture
Growth of free-floating plant cells used for metabolite secondary metabolite production.
39
New cards
Mammalian Cell Culture
The growth of cells in controlled conditions using a nutrient-rich medium.
40
New cards
Freezing Temperature for Cell Preservation
-80°C.
41
New cards
Long-Term Storage for Cell Preservation
-150°C to -196°C in liquid nitrogen.
42
New cards
Thawing Temperature for Cell Recovery
25-37°C.
43
New cards
Factors Affecting Cell Growth
Temperature, pH, osmolarity, oxygen levels.
44
New cards
Optimal Temperature for Mammalian Cells
37°C.
45
New cards
Optimal pH Range for Mammalian Cells
7.2-7.4.
46
New cards
Impact of pH on Protein Structure and Enzyme Activity
Disrupts hydrogen bonds and ionic interactions.
47
New cards
Impact of pH on DNA/RNA
Causes depurination and hydrolysis of phosphodiester bonds.
48
New cards
Impact of pH on Cell Survival and Proliferation
Increases ROS levels, leading to cell death.
49
New cards
Impact of pH on Membrane Integrity
Collapses proton gradients, affecting energy generation.
50
New cards
Effect of High Osmolarity
Causes cell shrinkage.
51
New cards
Effect of Low Osmolarity
Causes cell swelling.
52
New cards
Obligate Aerobes
Require oxygen for survival.
53
New cards
Obligate Anaerobes
Cannot survive in the presence of oxygen.
54
New cards
Facultative Anaerobes
Can grow with or without oxygen but prefer oxygenated environments.
55
New cards
Microaerophiles
Require oxygen but at lower concentrations than atmospheric levels.
56
New cards
Aerotolerant Anaerobes
Do not use oxygen but can tolerate its presence.
57
New cards
Batch Growth
A closed system where a fixed volume of medium is inoculated with cells, and no additional nutrients are added.
58
New cards
Phases of Batch Growth
Lag, log, stationary, death.
59
New cards
Net Growth Equation
Mu (net) = mu (gross) - k(death).
60
New cards
Growth Rate
The absolute increase in biomass in a system or cell over time (dX/dt).
61
New cards
Specific Growth Rate
The rate of biomass increase of a cell population per unit of biomass concentration.
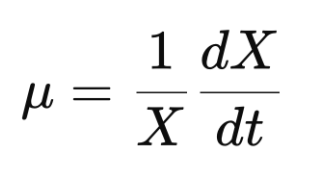
62
New cards
Continuous Exponential Growth
Assumes cell division and biomass accumulation occur at every instant of time.
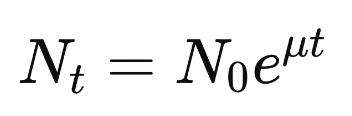
63
New cards
Discrete exponential growth
cell division as occurrs at specific intervals, rather than continuously
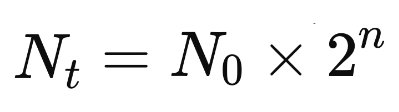
64
New cards
Monod Model
Describes microbial growth based on substrate concentration.
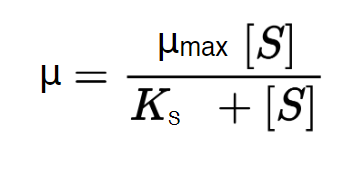
65
New cards
Monod Kinetics Assumptions
Single substrate, homogenous environment, no inhibition, steady state, cell uniformity, negligible cell death.
66
New cards
Zero-Growth Bioprocesses
Maintain cells in a non-growing state while still producing useful products.
67
New cards
Luedeking-Piret Equation
Describes product formation in zero growth systems (dP/dt = BX, B = beta).
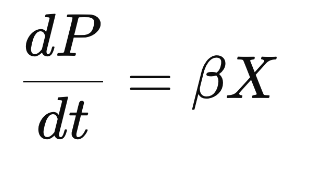
68
New cards
Biomass Yield (Yx/S)
Grams of cells per gram of substrate consumed.
69
New cards
Product Yield (Yp/S)
Grams of product per gram of substrate consumed.
70
New cards
Inoculum
A population of cells introduced into a medium to initiate a cell growth or fermentation process.
71
New cards
Direct Growth Monitoring Methods
Hemocytometer, automated cell counters, plate counting, flow cytometry.
72
New cards
Indirect Growth Monitoring Methods
Spectrophotometry (optical density), metabolic activity, dry weight.
73
New cards
Cell Immobilization
Trapping cells on a solid surface or within a matrix for reusability.
74
New cards
Adsorption
Cells adhere to a surface.
75
New cards
Ionic/Covalent Binding
Cells attached via chemical interactions.
76
New cards
Entrapment
Cells enclosed in a semi-permeable membrane.
77
New cards
Advantages of Cell Immobilization
Simplifies purification, reusability, protection from stress.
78
New cards
Disadvantages of Cell Immobilization
Mass transfer limitations, potential activity loss, cost.