Unit 5: Thermal Physics and States of Matter 낱말 카드 | Quizlet
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
80 Terms
What are the four states of matter commonly recognized?
Solid, liquid, gas, and plasma.
What is density and how is it calculated?

What is the formula for pressure in fluids?
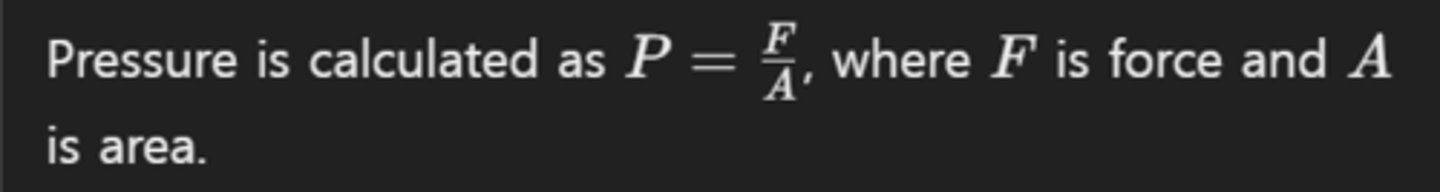
How does pressure vary with depth in a fluid?

What principle describes the transmission of pressure in a fluid?
Pascal's Principle, stating pressure applied to a confined fluid is transmitted undiminished throughout the fluid.
What is Archimedes' Principle regarding buoyancy?
Any object, wholly or partially immersed in a fluid, is buoyed up by a force equal to the weight of the fluid displaced by the object.
What determines whether an object will float or sink in a fluid?
An object floats if its density is less than the fluid's density and sinks if it's greater.
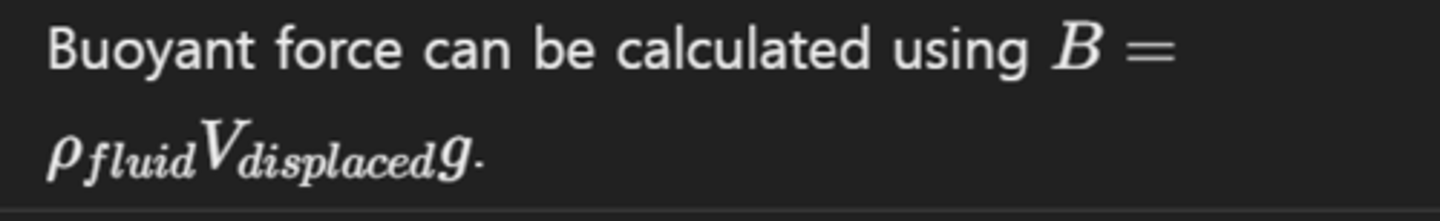
How can you calculate the buoyant force on an object?
How does the depth of immersion affect the buoyant force on a submerged object?
The buoyant force is constant regardless of depth since it depends only on the volume of fluid displaced.
What factors affect the pressure at a specific depth in a fluid?
Pressure at a depth depends on the fluid's density, the acceleration due to gravity, and the depth itself.
Describe the relationship between atmospheric pressure and the pressure at a depth in a body of water.
The total pressure at a depth is the sum of the atmospheric pressure and the pressure due to the water column above the point.
What is meant by the term "gauge pressure"?
Gauge pressure is the pressure relative to atmospheric pressure, excluding atmospheric pressure itself.
How do you convert gauge pressure to absolute pressure?
Add atmospheric pressure to the gauge pressure.
What effect does temperature have on the density of a fluid?
Temperature generally decreases the density of fluids, as most expand when heated.
How is the pressure at the bottom of a container different from the pressure at the top in a fluid?
Pressure at the bottom is higher due to the weight of the fluid above adding to the atmospheric pressure exerted at the top.
In what situation would you use Archimedes' Principle in practical applications?
It is used to determine the buoyancy of boats, ships, and even balloons.
What does it mean if the density of an object is less than the density of water?
The object will float when placed in water.
Explain why ships float in water despite being made of materials denser than water.
Ships float due to their shape and size, which allows them to displace a volume of water equivalent to their weight before being completely submerged.
How do divers adjust their buoyancy underwater?
Divers adjust their buoyancy by controlling the volume of air in their buoyancy compensators, affecting how much water they displace.
What is the principle behind a submarine's ability to dive and resurface?
Submarines control their buoyancy by adjusting the amount of water and air in their ballast tanks.
What is the Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics?
If two systems are in thermal equilibrium independently with a third system, they are in thermal equilibrium with each other.
How is temperature fundamentally measured?
Temperature is measured using a thermometer which equilibrates thermally with another object, indicating thermal equilibrium.
What are thermometers and how do they work?
Thermometers measure temperature based on physical properties that change with temperature, like the expansion of liquids or gases.
What is thermal expansion?
Thermal expansion is the increase in volume of materials as they are heated, due to increased motion of atoms.
What is the coefficient of linear expansion?
It quantifies how much a material's length changes per degree change in temperature.
How does the ideal gas law relate pressure and temperature?

What is the constant-volume gas thermometer?
A device measuring temperature by observing the pressure change at constant volume of a gas.
How is temperature related to internal energy?
Temperature is a measure of the average kinetic energy of the particles in a substance.
What is absolute zero?
he lowest possible temperature, -273.15°C or 0K, where no more thermal energy can be removed from a system.
How do different thermometers (e.g., mercury, alcohol) differ in practical use?
Different substances used in thermometers expand differently, affecting their precision and range.
What is the Kelvin scale based on?
The Kelvin scale starts at absolute zero and increments are equivalent to those on the Celsius scale.
Describe how a constant-volume gas thermometer is used to measure temperature.
It measures temperature by the pressure of a gas at constant volume, calibrated against fixed points like the triple point of water.
How does thermal expansion affect engineering structures?
Structures must account for expansion due to temperature changes to avoid stress and potential failure.
What role does thermal expansion play in everyday appliances, like a refrigerator or oven?
Components must be designed to handle expansion and contraction to maintain seals and prevent warping.
How is the Fahrenheit scale defined relative to the Celsius scale?
Water freezes at 32°F and boils at 212°F, compared to 0°C and 100°C on the Celsius scale.
What practical steps are taken to calibrate a thermometer?
Thermometers are often calibrated against known fixed points, such as the freezing and boiling points of water.
How do altitude and atmospheric pressure affect boiling points?
Higher altitudes have lower atmospheric pressure, lowering the boiling point of water.
What is the role of the coefficient of volume expansion in thermodynamics?
It quantifies the change in volume of a substance per unit temperature change.
How does the thermal expansion of solids compare to that of liquids?
Solids generally have lower coefficients of expansion compared to liquids.
Why is it important to understand the properties of thermal expansion in material science?
It helps in selecting materials for specific applications where temperature changes are critical.
Explain the relationship between thermal expansion and thermal stress.
As materials expand or contract with temperature changes, they can induce stresses that may lead to structural failure.
How can temperature affect the performance of electronic devices?
Expansion and contraction from temperature changes can affect electrical connections and material properties.
What is the significance of standard temperature and pressure in experiments?
It provides a reference for conditions under which many gas-related experiments are conducted.
How do materials like Pyrex handle thermal stress better than ordinary glass?
Pyrex has a lower coefficient of thermal expansion, reducing stress under temperature changes.
What happens at the triple point of water?
It is the unique temperature and pressure at which water can coexist in solid, liquid, and gas phases.
How does thermal expansion relate to the design of composite materials?
Different materials' expansion rates must be compatible to avoid internal stresses.
What are bimetallic strips and how do they work?
They consist of two metals with different expansion rates, bending with temperature changes, often used in thermostats.
Why do metals generally have higher thermal conductivities than other materials?
Metals have free electrons that transfer kinetic energy quickly through the material.
What is a thermocouple and how does it measure temperature?
It measures temperature based on voltage generated by junctions of two different metals at different temperatures.
How does the ideal gas law apply to weather forecasting?
It helps in understanding atmospheric conditions by relating temperature, pressure, volume, and amount of gases in the air.
What is internal energy?
Internal energy is the total energy stored within a system, including the kinetic and potential energy of all its molecules.
How is heat defined?
Heat is the transfer of energy between a system and its surroundings because of a temperature difference.
What is the mechanical equivalent of heat?
The mechanical equivalent of heat is the amount of mechanical work needed to produce the same amount of heat, specifically 1 calorie equals 4.186 Joules.
How is specific heat defined?
Specific heat is the amount of heat per unit mass required to raise the temperature by one degree Celsius.
What is the formula to calculate heat transfer using specific heat?

What is calorimetry?
Calorimetry is the process of measuring the amount of heat released or absorbed during a chemical reaction, physical change, or heat capacity.
How does a calorimeter work?
A calorimeter measures the heat of chemical reactions or physical changes as well as heat capacity by ensuring the heat transfer is contained within the device.
What is latent heat?
Latent heat is the heat required to convert a solid into a liquid or vapor, or a liquid into a vapor, without change of temperature.
What are the latent heats of fusion and vaporization?
The latent heat of fusion is the energy required to change a substance from solid to liquid at its melting point. The latent heat of vaporization is the energy needed to convert a liquid into a gas at its boiling point.
How does phase change occur without temperature change?
During a phase change, the system absorbs or releases a specific amount of heat, but the temperature remains constant as the energy is used to alter the state rather than the temperature.
What is the relationship between heat transfer and temperature change in calorimetry?
In calorimetry, heat transfer results in a change in temperature unless a phase change occurs, in which case temperature remains constant during the transition.
What is the equation for heat transfer in substances undergoing a phase change?

How is specific heat capacity used in practical situations?
Specific heat capacity is used to design systems where temperature control is crucial, such as cooling systems and cooking appliances.
What is the effect of specific heat on climate?
Substances with high specific heat, such as water, can moderate climate by absorbing and releasing large amounts of heat without a significant change in temperature.
How does the specific heat of water compare to that of land?
Water has a higher specific heat than land, meaning it can absorb more heat without getting as hot, which influences coastal climates.
What is the primary method for measuring specific heat experimentally?
Specific heat is most commonly measured by calorimetry, which involves measuring temperature changes under controlled heat transfer conditions.
Describe how the concept of heat transfer is applied in everyday cooking.
Heat transfer in cooking involves raising the temperature of food until its chemical components react to produce edible or more palatable food, which relies on the specific heat capacities of different food components.
How do materials with different specific heats affect building design?
Materials with lower specific heats heat up and cool down more rapidly, affecting the thermal comfort inside buildings and the energy efficiency of heating and cooling systems.
Why is water considered an effective coolant?
Due to its high specific heat, water can absorb a lot of heat with little change in temperature, making it effective for regulating temperatures in processes or environments.
What role does specific heat play in thermal management technologies?
Specific heat is crucial in thermal management to ensure materials can handle the thermal energy during operation without overheating.
How does specific heat contribute to thermal inertia?
Materials with high specific heat can store heat energy, which contributes to thermal inertia, affecting how quickly an object responds to temperature changes.
Why is it important to consider specific heat in material selection for heat exchangers?
Selecting materials with appropriate specific heat capacities ensures that heat exchangers operate efficiently by maximizing energy transfer without excessive temperature changes.
How do phase changes relate to energy conservation in closed systems?
In closed systems, energy conservation during phase changes means that all heat absorbed or released is accounted for in the system's energy budget, ensuring no net loss or gain.
What practical applications utilize the concept of latent heat?
Applications include refrigeration, where latent heat is used to absorb heat during the refrigeration cycle, and climate engineering, exploiting water's latent heat for temperature regulation.
How is latent heat used in meteorology?
Latent heat is important in meteorology for understanding processes like evaporation and condensation that drive weather patterns and influence climate.
Describe how latent heat is involved in the water cycle.
Latent heat is absorbed when water evaporates, carried aloft in the atmosphere, and then released as heat when water condenses to form precipitation, driving weather systems.
How does the concept of latent heat impact environmental engineering?
Environmental engineering uses latent heat in the design of systems that manage or mitigate the effects of heat in the environment, such as cooling ponds and thermal pollution controls.
What role does latent heat play in industrial processes?
In industries, latent heat is critical for processes like distillation and other phase change operations, where control of energy transfer is essential for efficiency and safety.
How do changes in latent heat affect phase change materials (PCMs) in energy storage systems?
PCMs utilize latent heat for thermal energy storage, releasing or absorbing heat as they cycle between phases, which is key for applications like solar energy storage and thermal regulation.
What is the significance of measuring latent heat in materials science?
Measuring latent heat in materials science helps characterize materials' thermal properties, which are crucial for applications requiring precise temperature control during manufacturing processes.