Medical Terminology Dermatology
1/104
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
105 Terms
Dermatologist
med specialists who use lab & and diagnostic tests, medical & and surgical procedures, and drugs to treat integumentary diseases
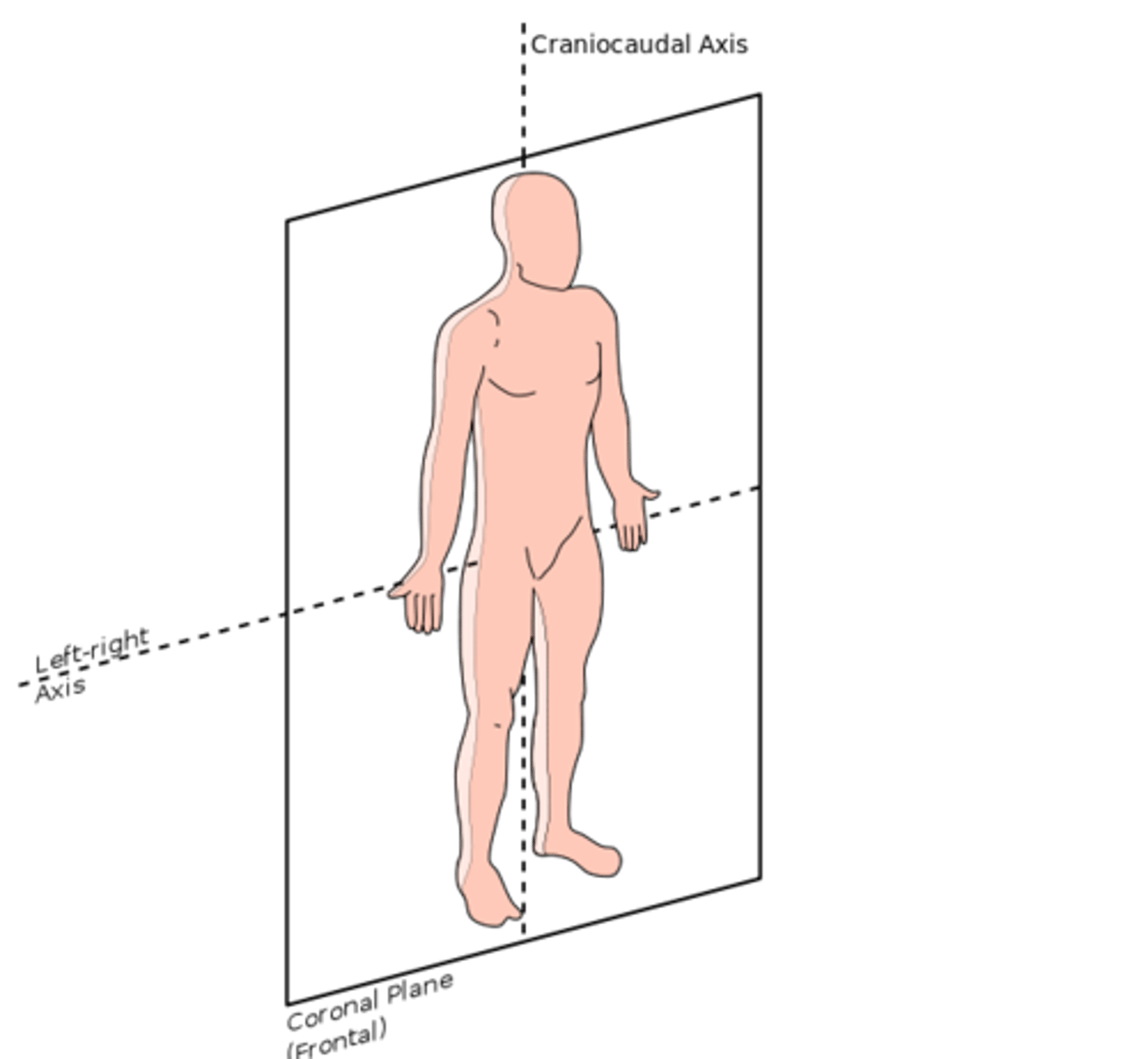
Integumentary System
Large flexible body system that covers the body
Consists of:
skin
hair and glands
nails
subcutaneous tissue
What is the purpose of the integumentary system?
1) Barrier to protect from the outside world
2) First line of defense against invading micro-organisms
3) Sense of touch
4) retain body fluid
5) Regulate body temperature
6) eliminate waste products (sweat)
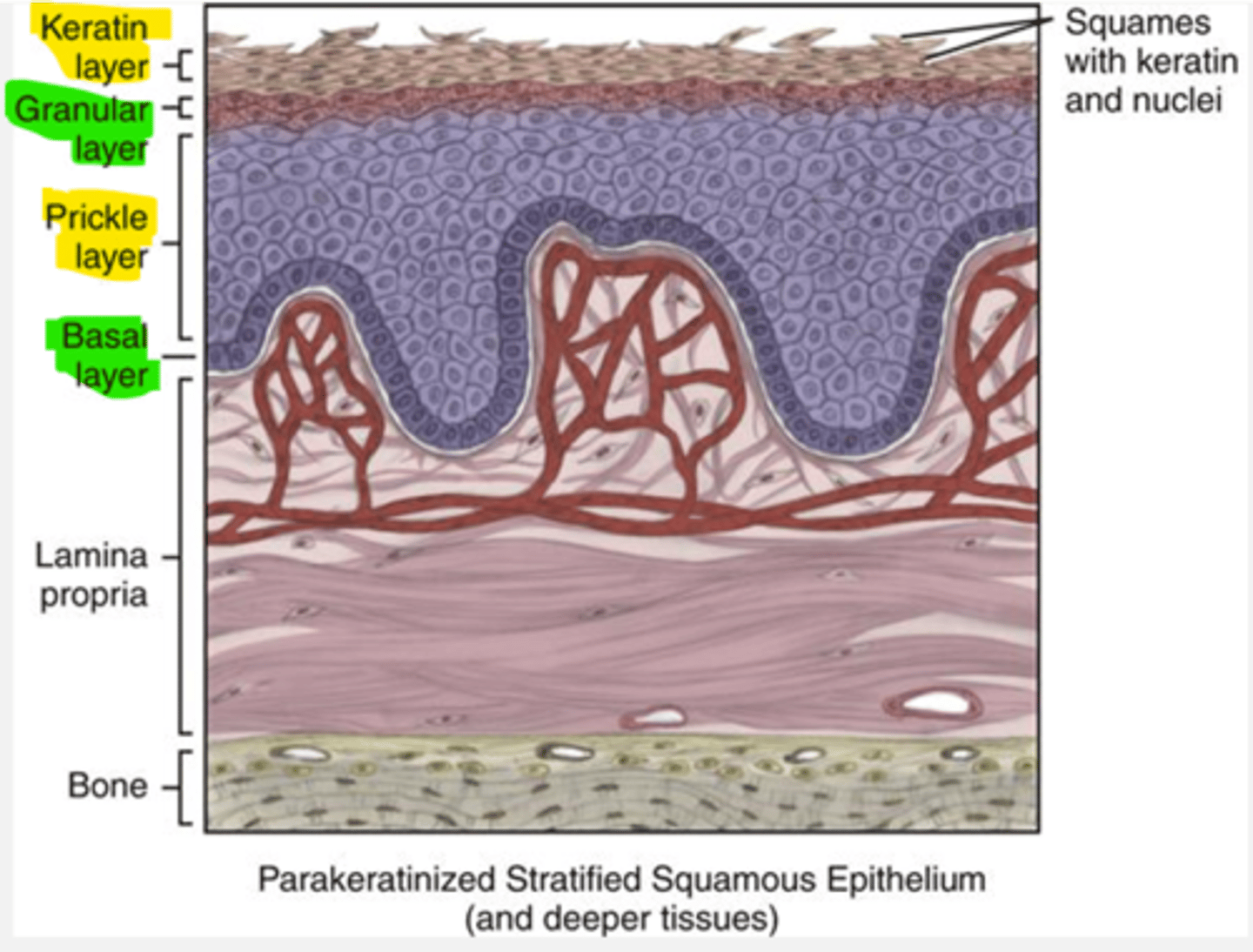
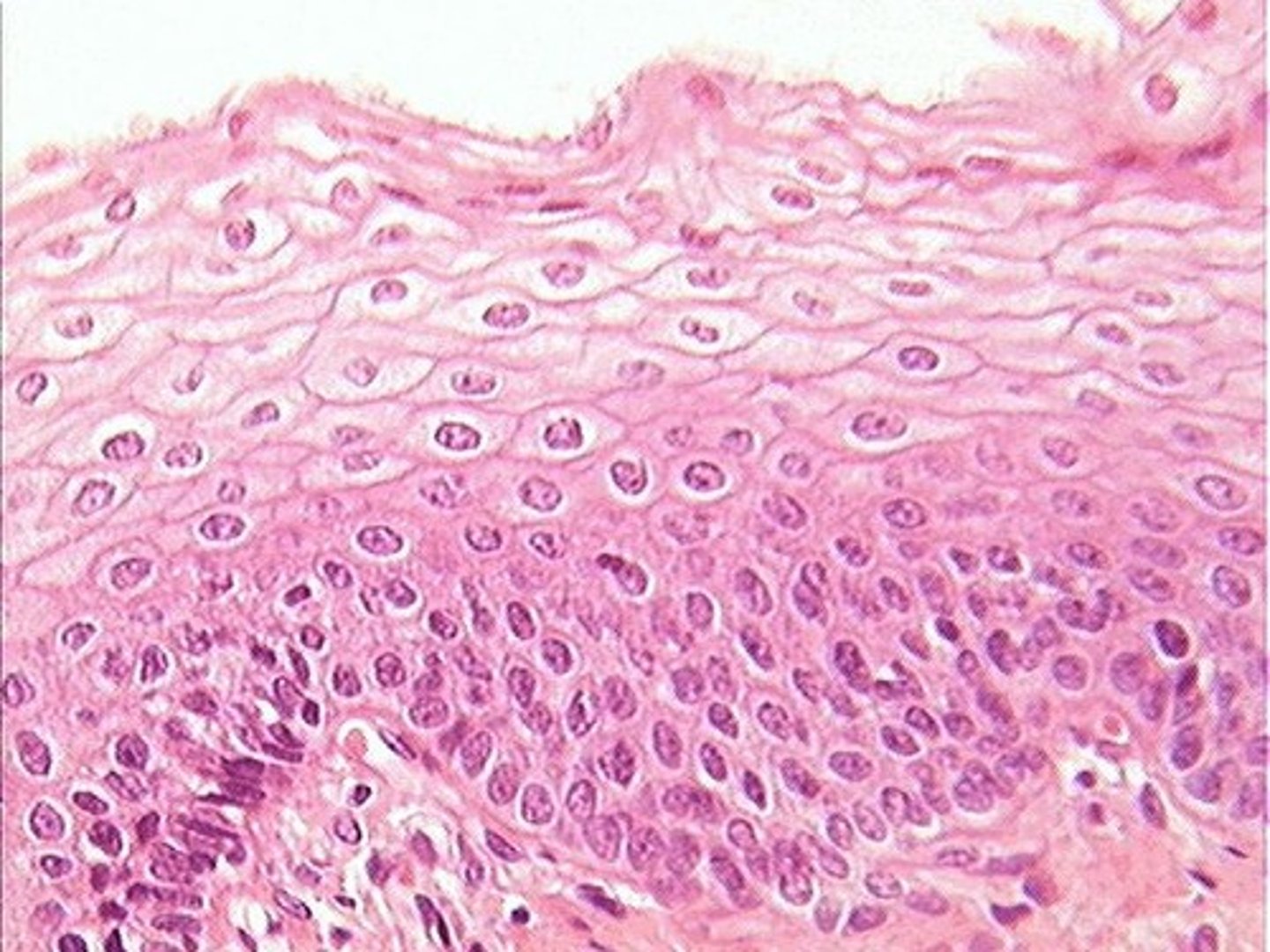
Epidermis
Epithelium
thin outermost layer of the skin
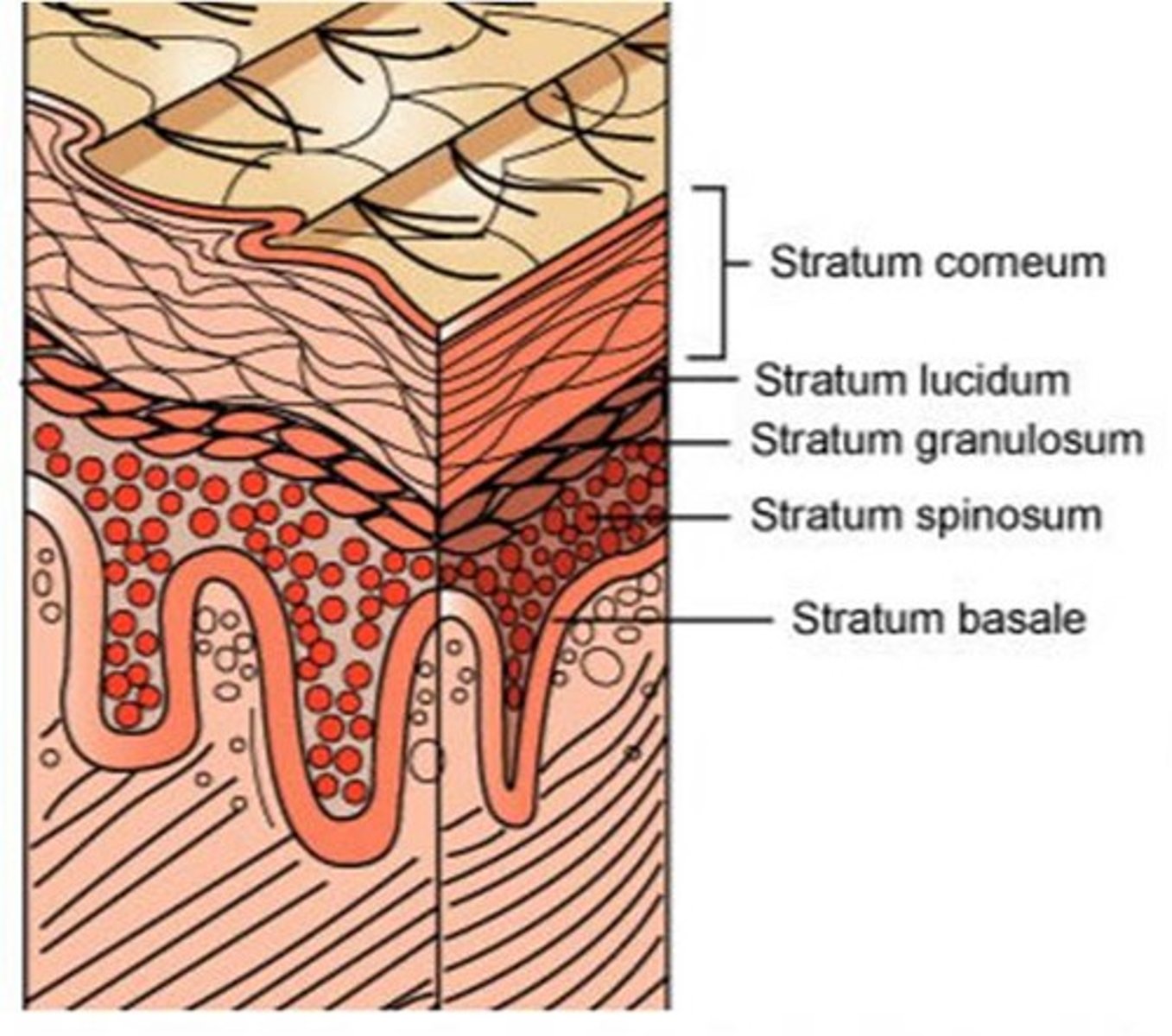
Dermis
Thicker layer of skin below the epidermis
Contains
collagen fibers and elastin fibers
arteries and veins
nerves
hair follicles
sebaceous and sweat glands
Collagen Fibers
provides flexibility and strength
Firm white protein
Elastin Fibers
provide some elasticity to the skin, enabling movement
Elastic yellow protein
Adipose Tissue
fatty tissue
Adipose tissue is the loose connective tissue composed primarily of fat cells, called adipocytes, which store energy as fat
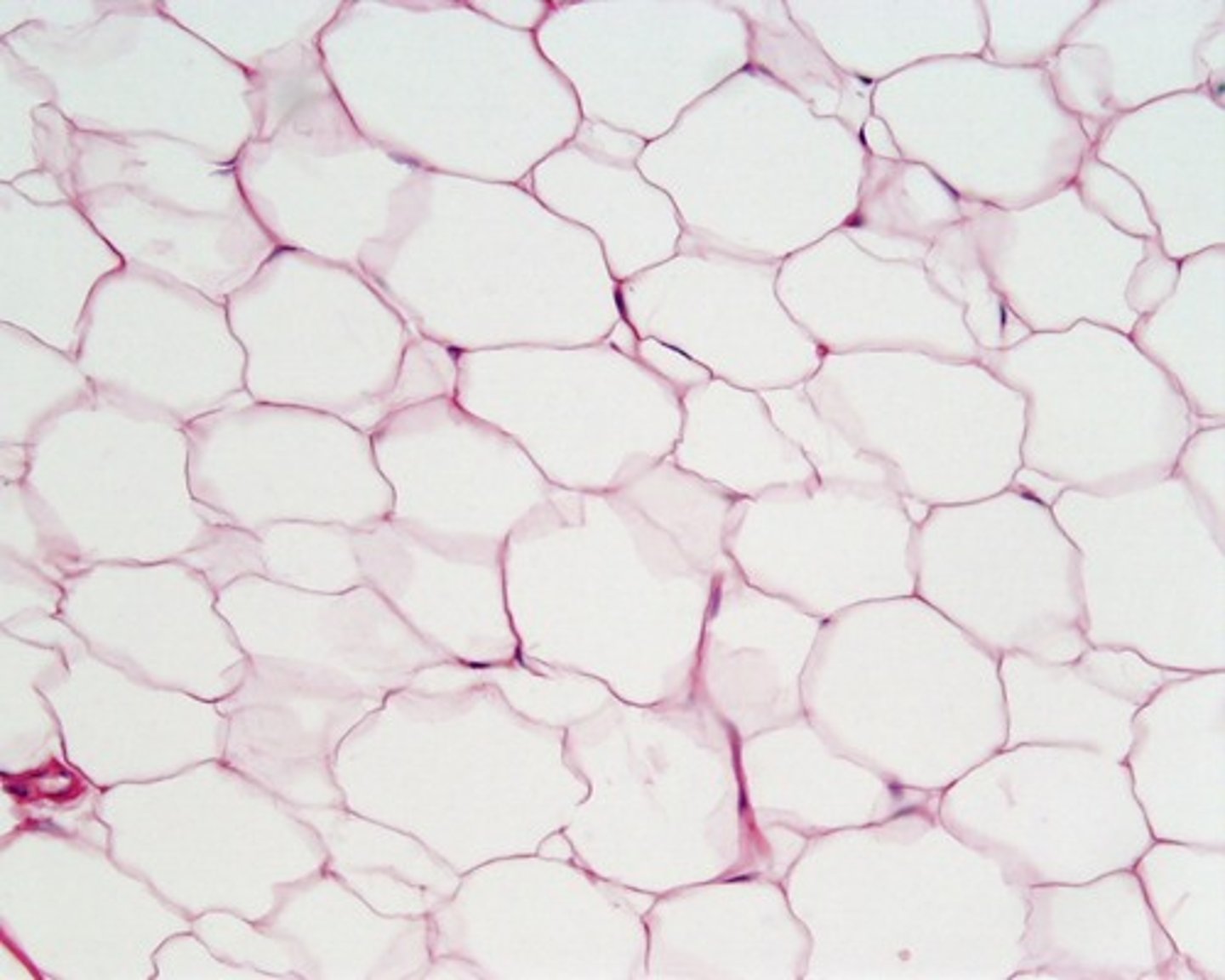
Lipocytes
Fat storing cells
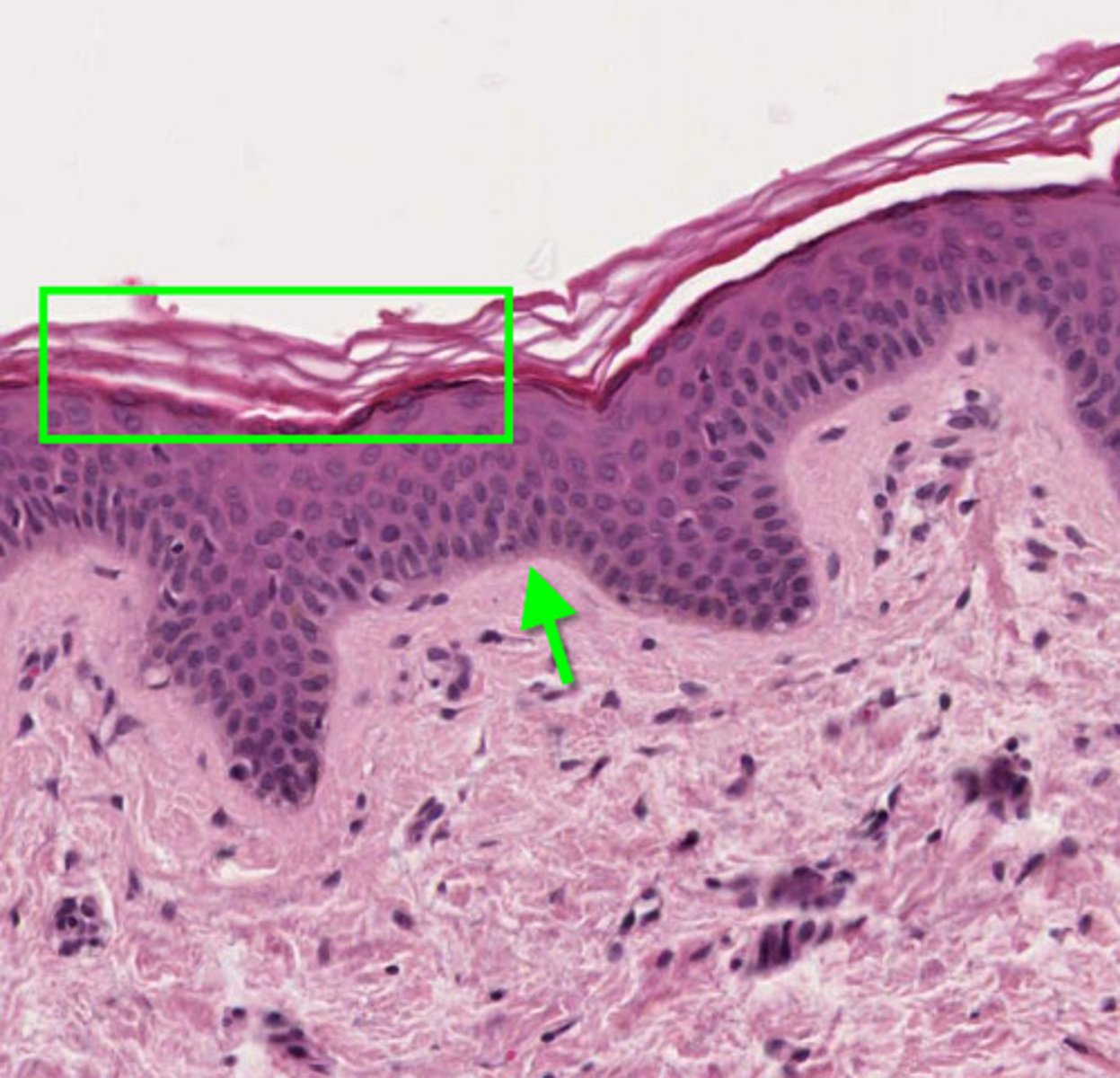
Keratin
Most superficial part of skin containing dead cells
Full of hard, fibrous protein
protective layer
cell have no nucleus
constantly being shed
Exfoliation
The removal of excess dead cells from the skin surface.
Basal Cells (Basal Layer)
The deepest layer of the epidermis
Composed of:
living cells that are constantly dividing & forced to the surface
before moving to surface they loose their nucleus and die
Melanocyte
pigment cells that produce melanin
Melanin
pigment that absorbs UV light to protect DNA from mutations
Squamous cells
flattened and scale-like
make up most of the cells in epidermis
composed of dead and living cells
Sebaceous glands
type of exocrine gland in the dermis
secrete sebum through a duct (hair follicle)
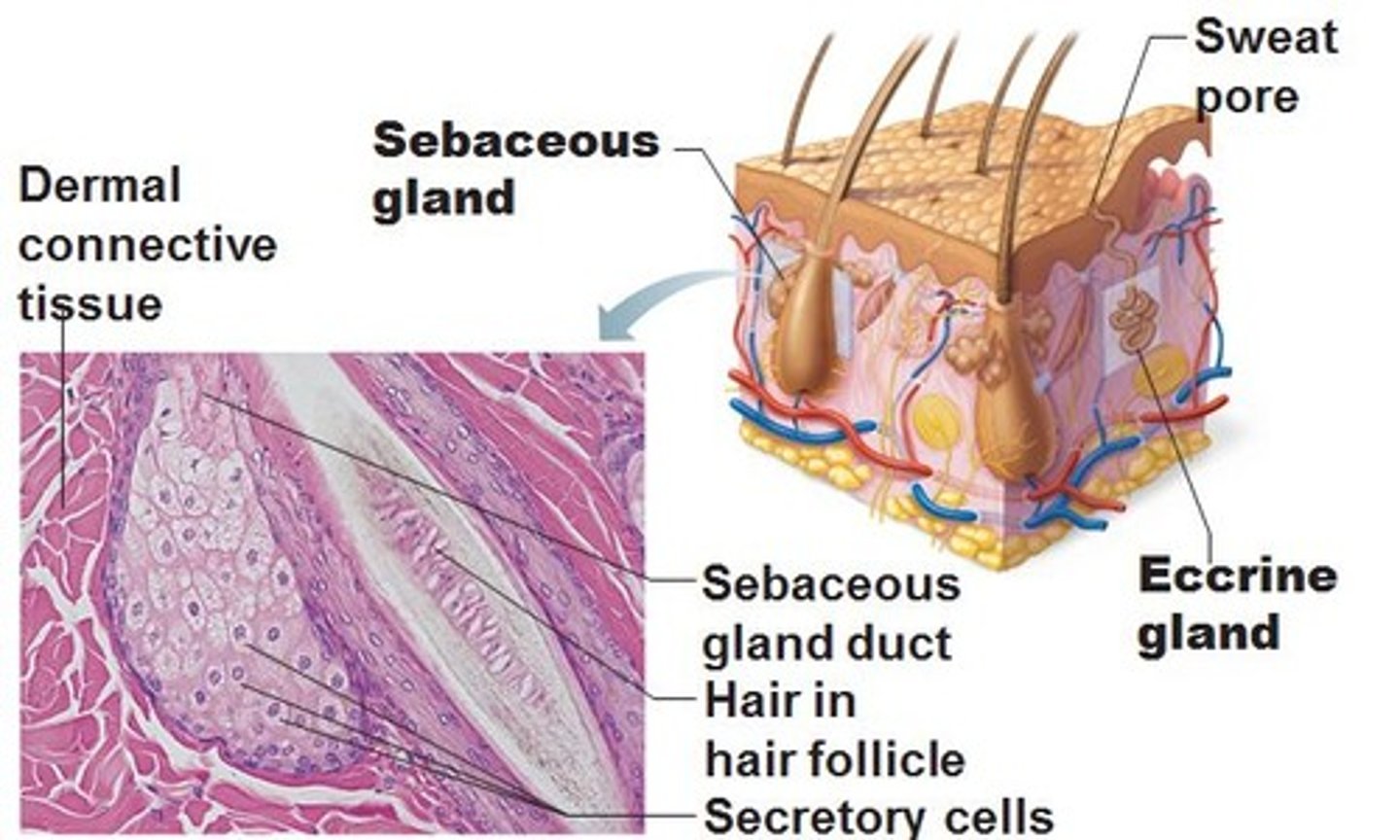
Sebum
the oily secretion of the sebaceous glands
Sudoriferous glands
exocrine gland in dermis that secrete sweat through a duct that ends at a pore
also known as sweat glands
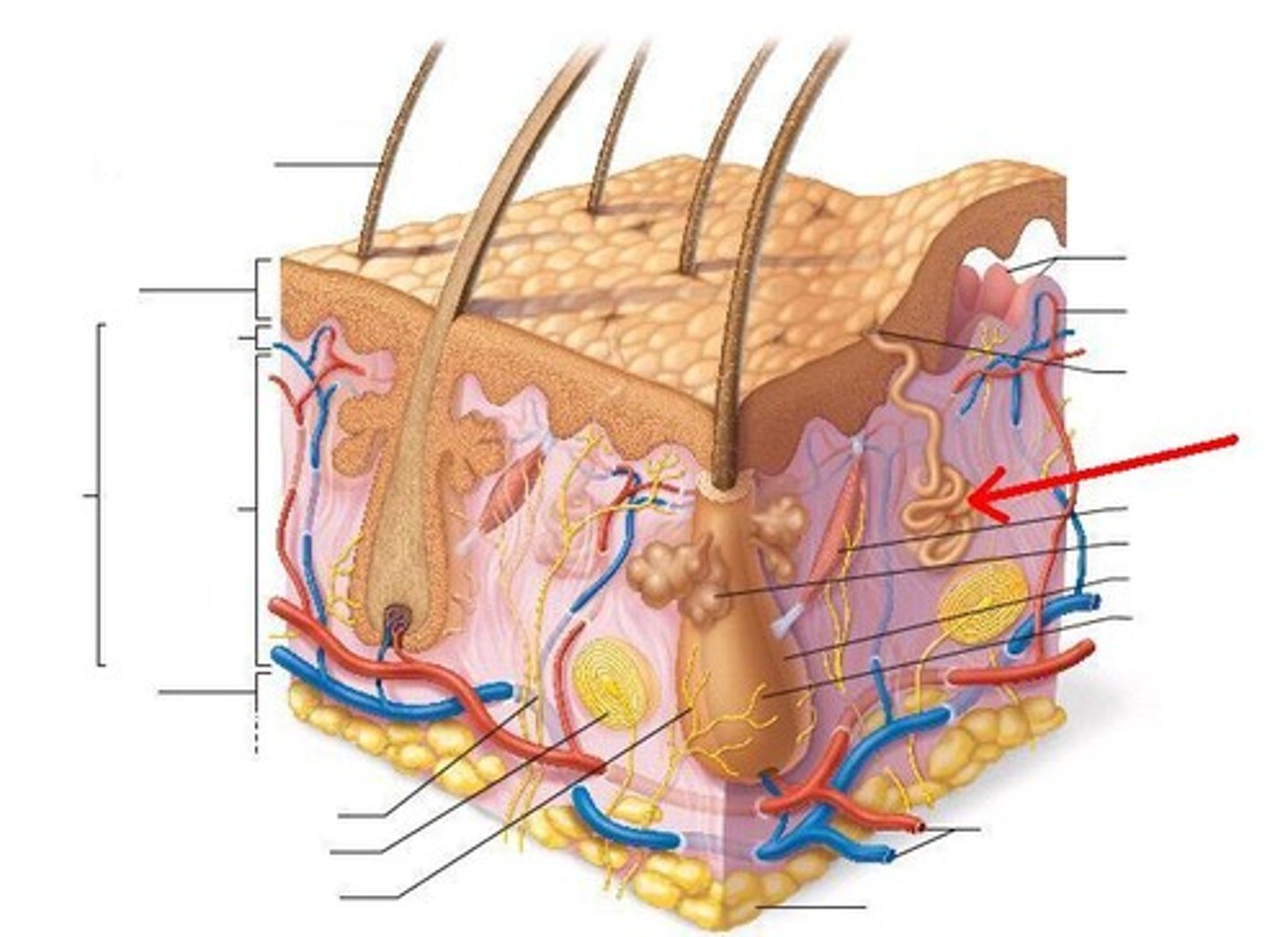
perspiration
sweat
Piloerection
Small muscle at base of hair follicle contracts and causes hair to stand up
functions of integumentary system
First-line defense against injury
acidic epidermis discouragesmicro-organisms's growth
keratin in the epidermis makes skin waterproof
sweat & and sebum contains antibodies and enzymes that kill bacteria
Sensation
UV rays convert epidermal cholesterol into vitamin D (help absorb calcium)
Thermoregulation
Homeostasis
Dermatitis
inflammation of the skin
Involves rash on swollen red skin
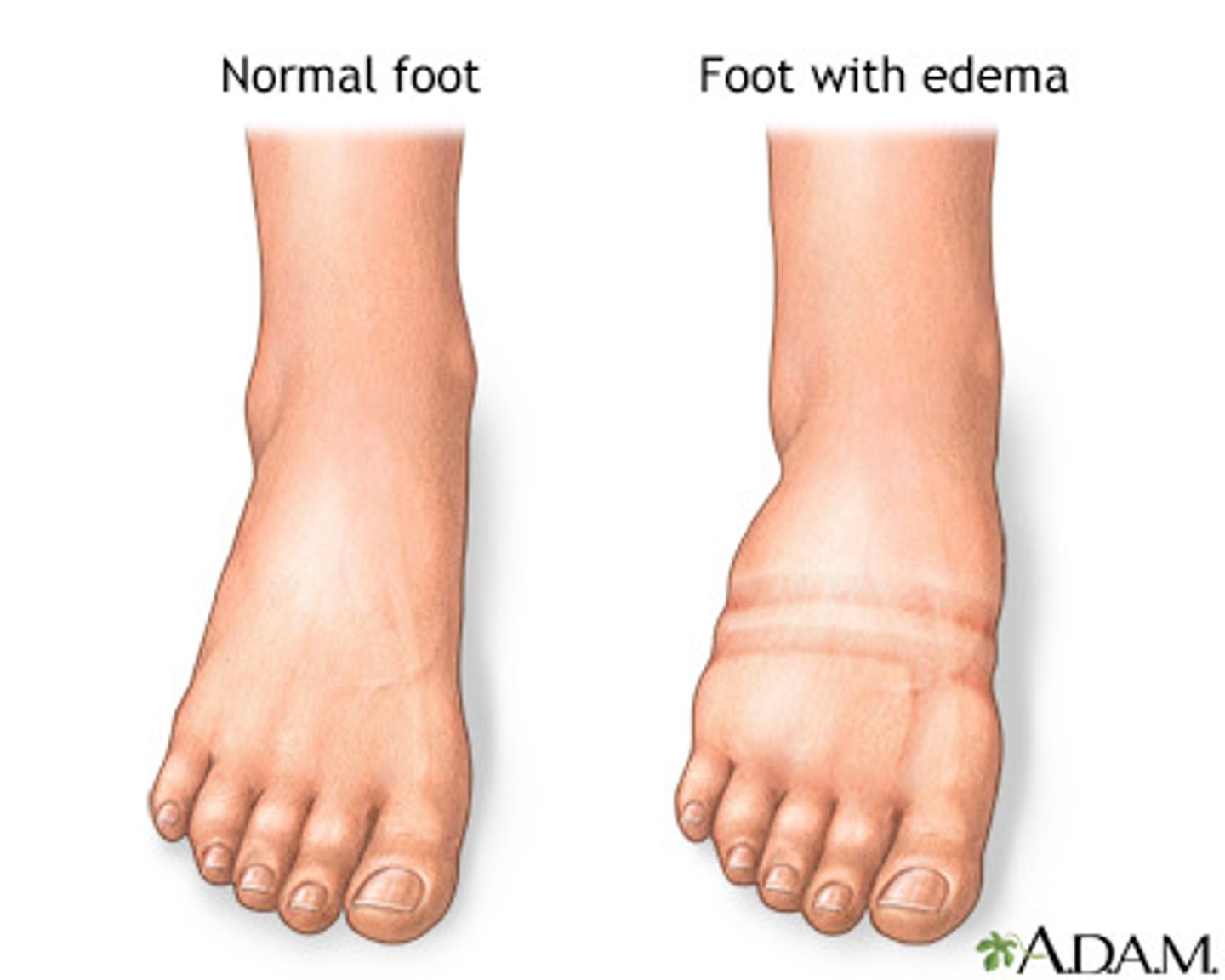
Edema
excess amounts of fluid move from the blood into the dermis or subcutaneous layer and causes swelling
Local areas of edema on the skin caused by inflammation due to allergic reaction or infection
Large areas of edema on skin are associated with diseases of cardiovascular or urinary system
Lesion
any visible damage or variation from normal skin whether from disease or injury
Hematoma
elevated localized collection of blood under the skin
Pruritus
itching
causes by the release of histamine as part of an allergic reaction of the skin
Treatment: topical or oral drugs
Rash
Any type of skin lesion that is pink to red, plat to raise or pruritic or not pruritic
Wound
Any area of visible damage to the skin
Xeroderma (zee·row·dur·muh)
Excessive dryness of the skin
Caused by age, weather, vitamin A deficiency, dehydration
Xer/o-
dry
Albinism
Genetic mutation that causes lack of pigment in the skin, iris, hair
There is normal amount of melanocytes but they don't produce enough or no pigment
Hereditary disease
Cyanosis
Bluish-purple discoloration of the skin and nails due to a decreased level of oxygen in the blood
Erythema (eh·ruh·thee·muh)
Reddish discoloration of the skin
can be confined to a local area of infection or inflammation or large areas such as a sunburn
Area is said to be erythematous
Erythr/o-
red
Jaundice
Yellowish discoloration of the skin and mucous members and whites of the eyes
occurs when the liver can't process bilirubin so it moves from the blood to the tissue
Jaund/o-
yellow
Necrosis
grey to black discoloration of the skin in areas where the tissue has died
Can develop in a burn pressure injury, wound, or tissue with poo blood supply
Necr/o-
dead body; dead tissue
Necrotic tissue
dead tissue
Gangrene
necrosis with subsequent bacterial invasion and decay
Gangerous tissue
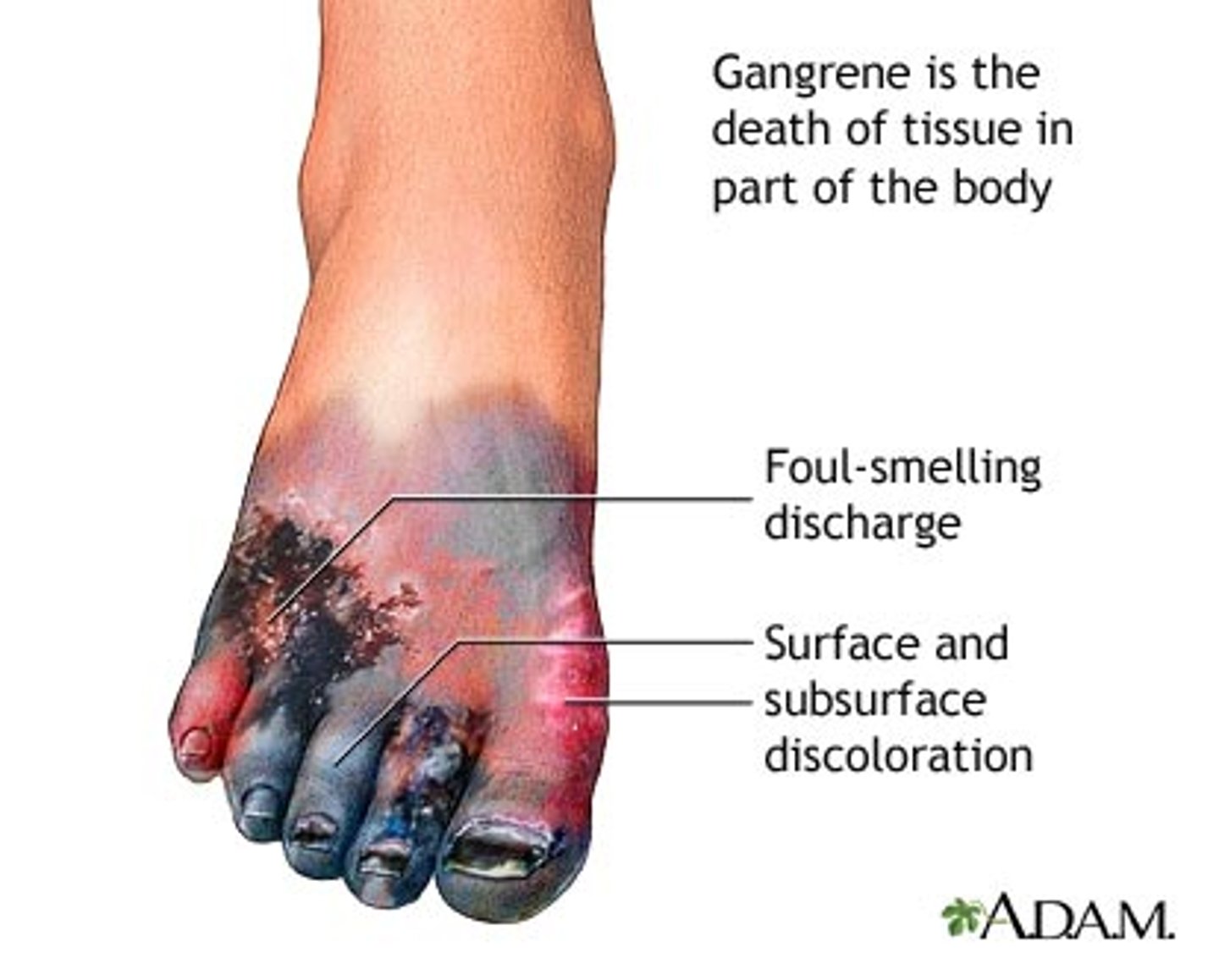
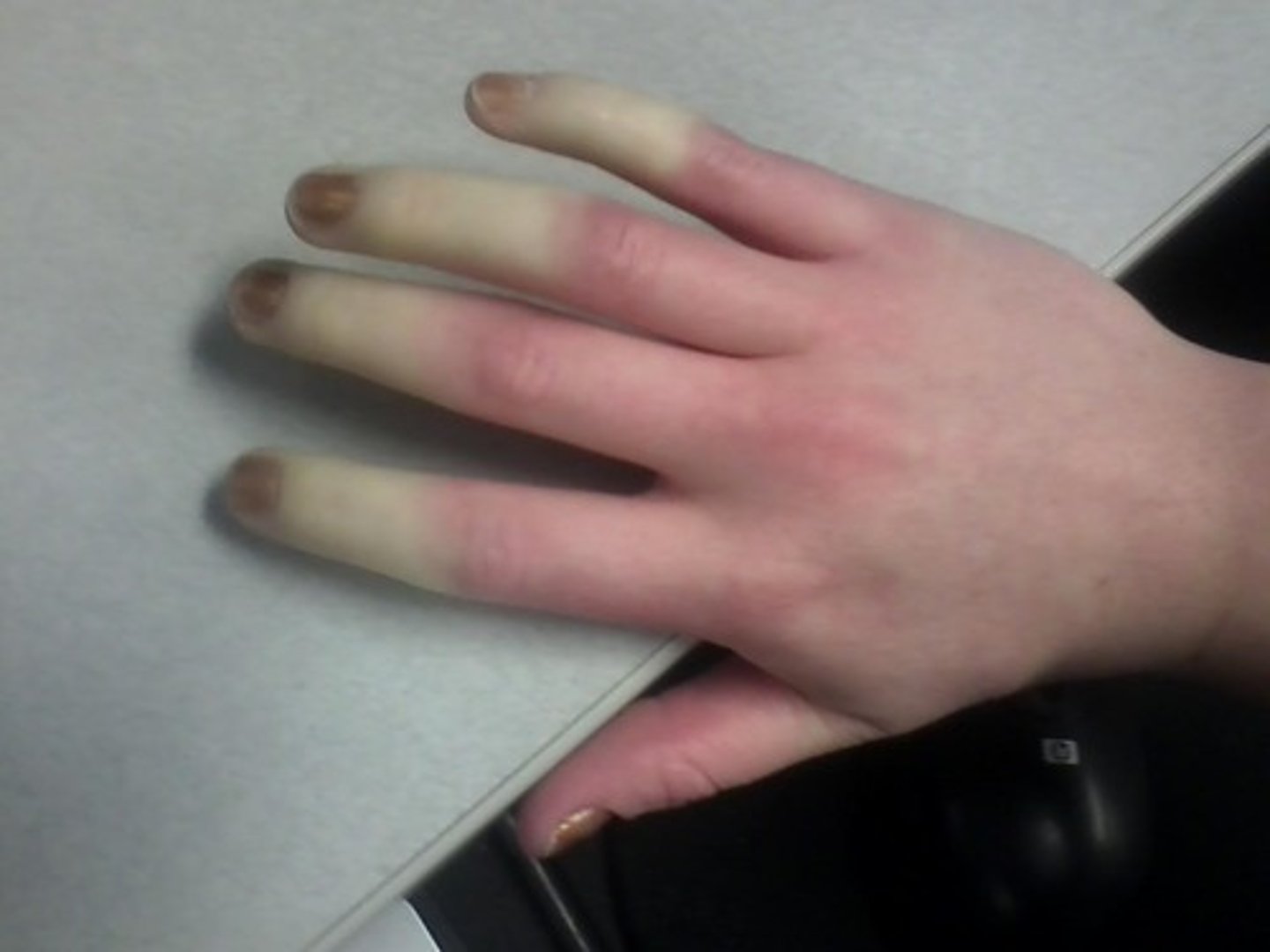
Pallor
Unnatural paleness due to a lack of blood supply to the tissue
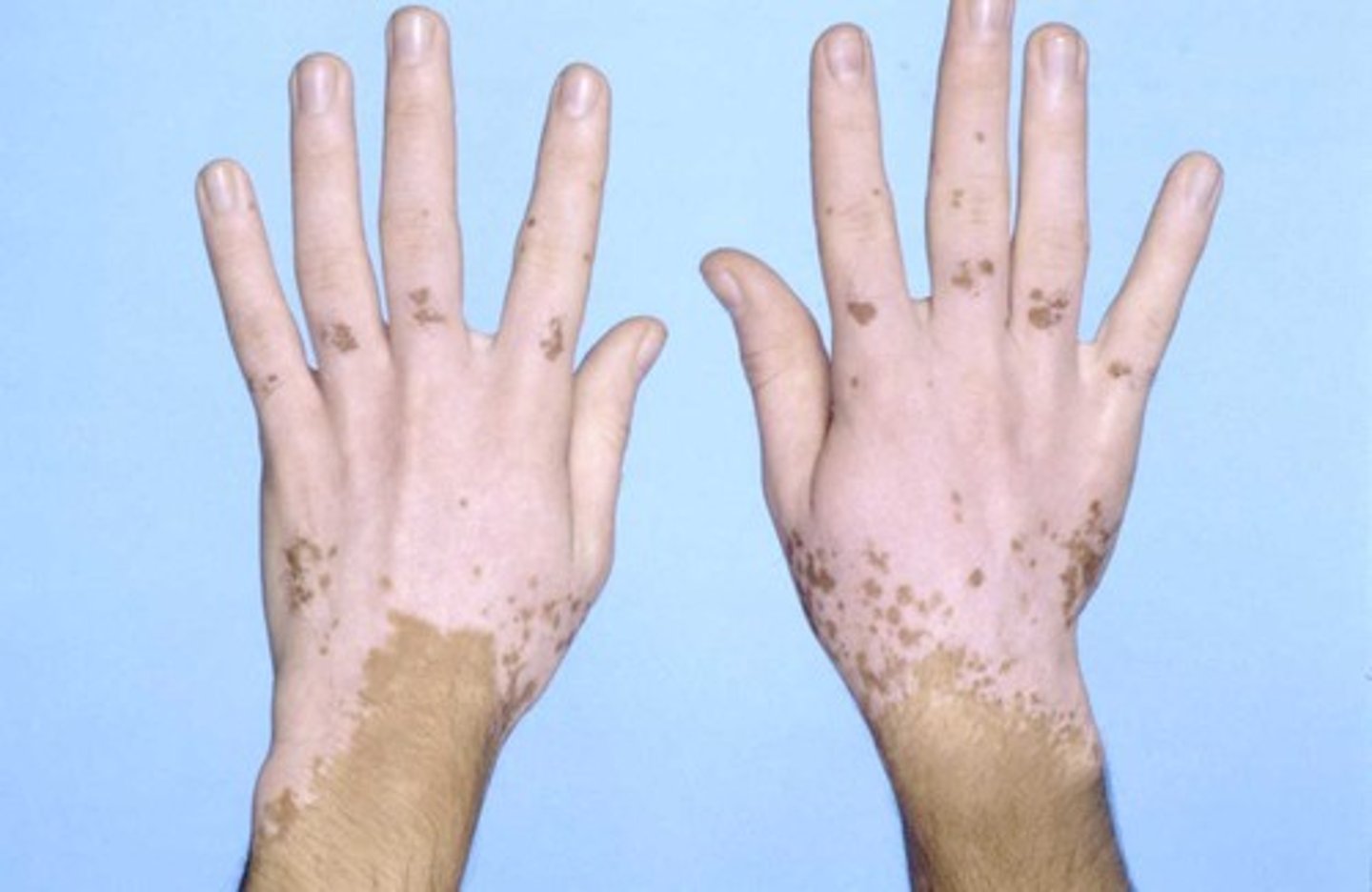
Vitiligo
Autoimmune disorder where melanocytes are destroyed
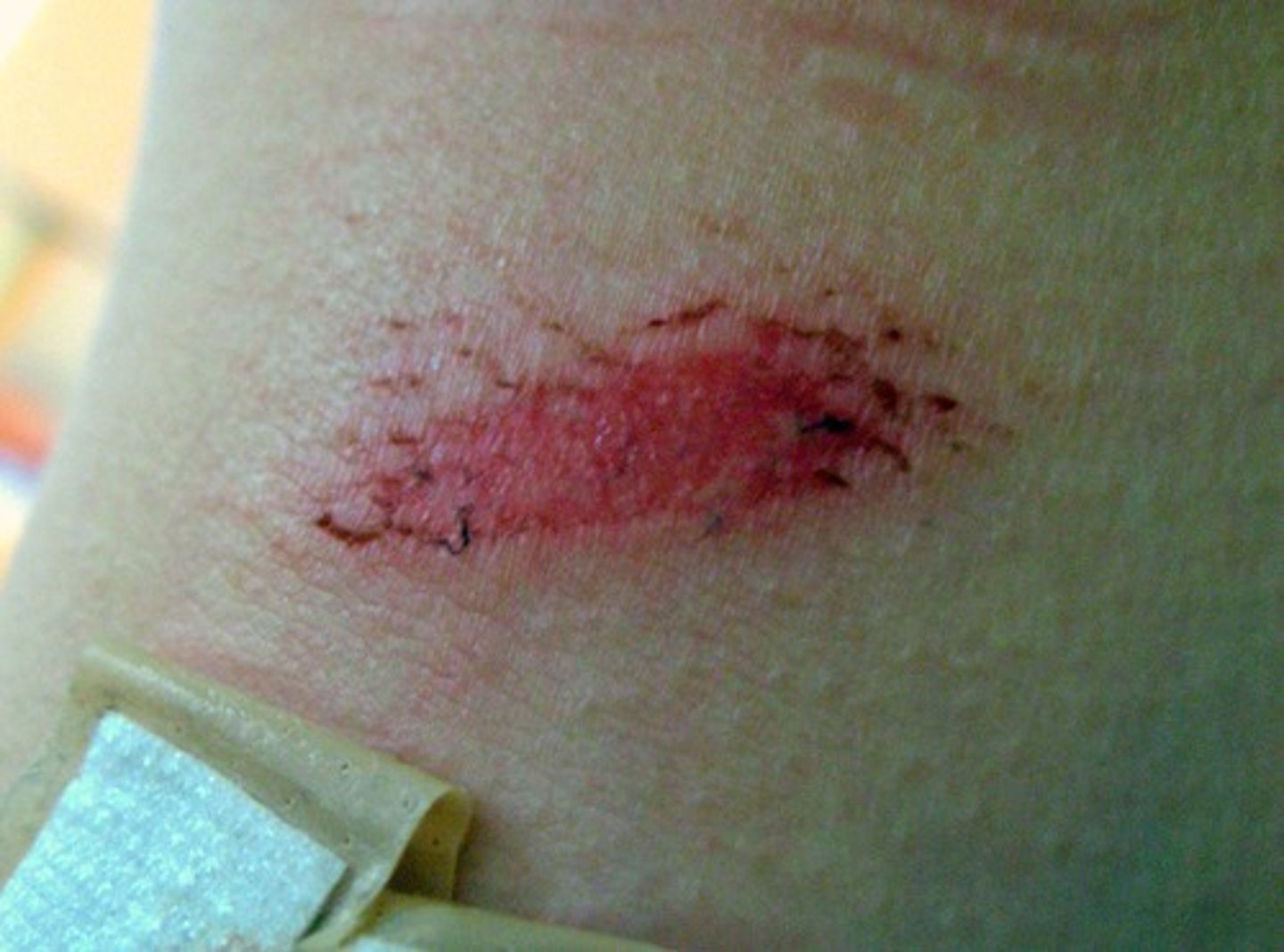
Abrasion
sliding or scraping injury that mechanically removes the epidermis
Blister
Fluid-filled sac with tin transparent covering of epidermal cells
Occurs when repetitive rubbing separates epidermis from the dermis
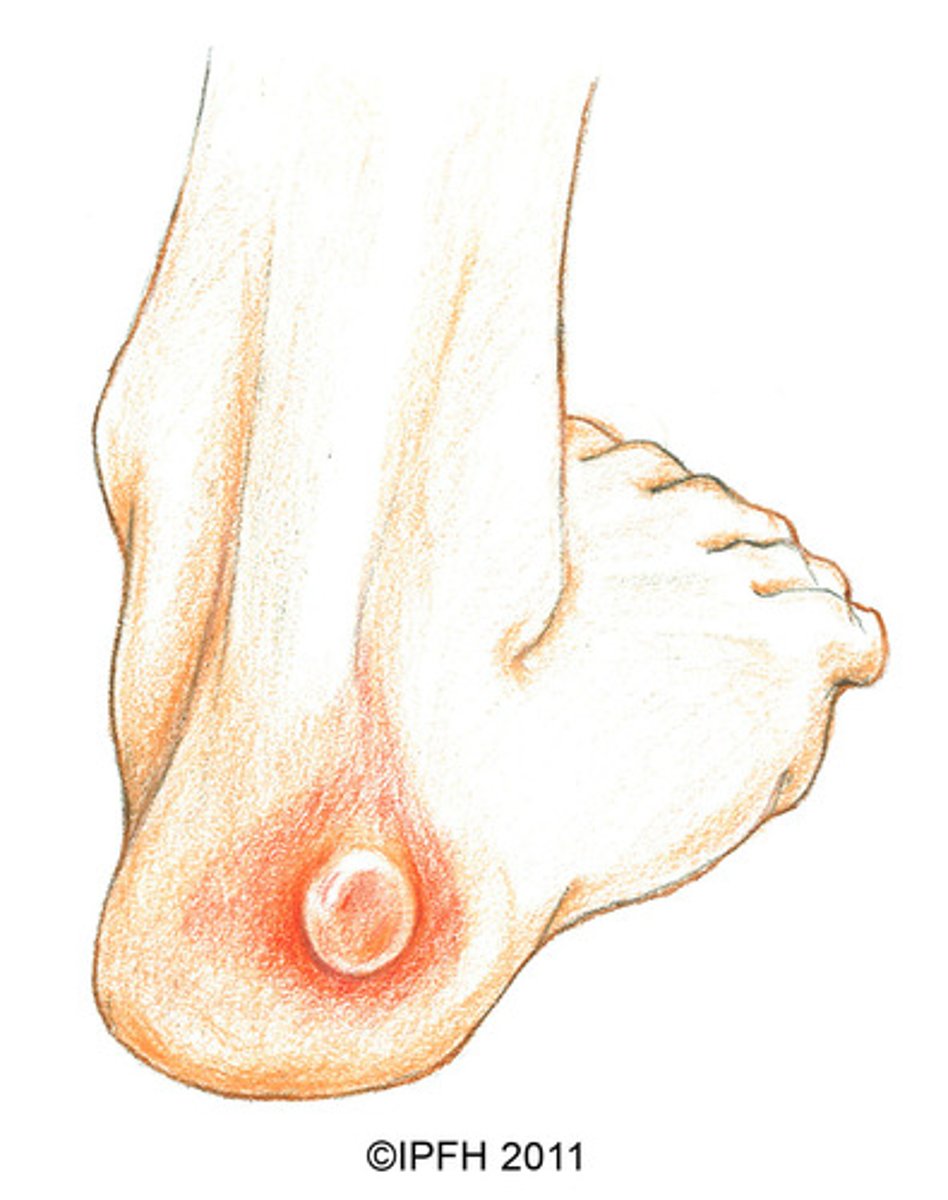
What causes burns
Heat, electric currents, chemicals, radiation causes burns
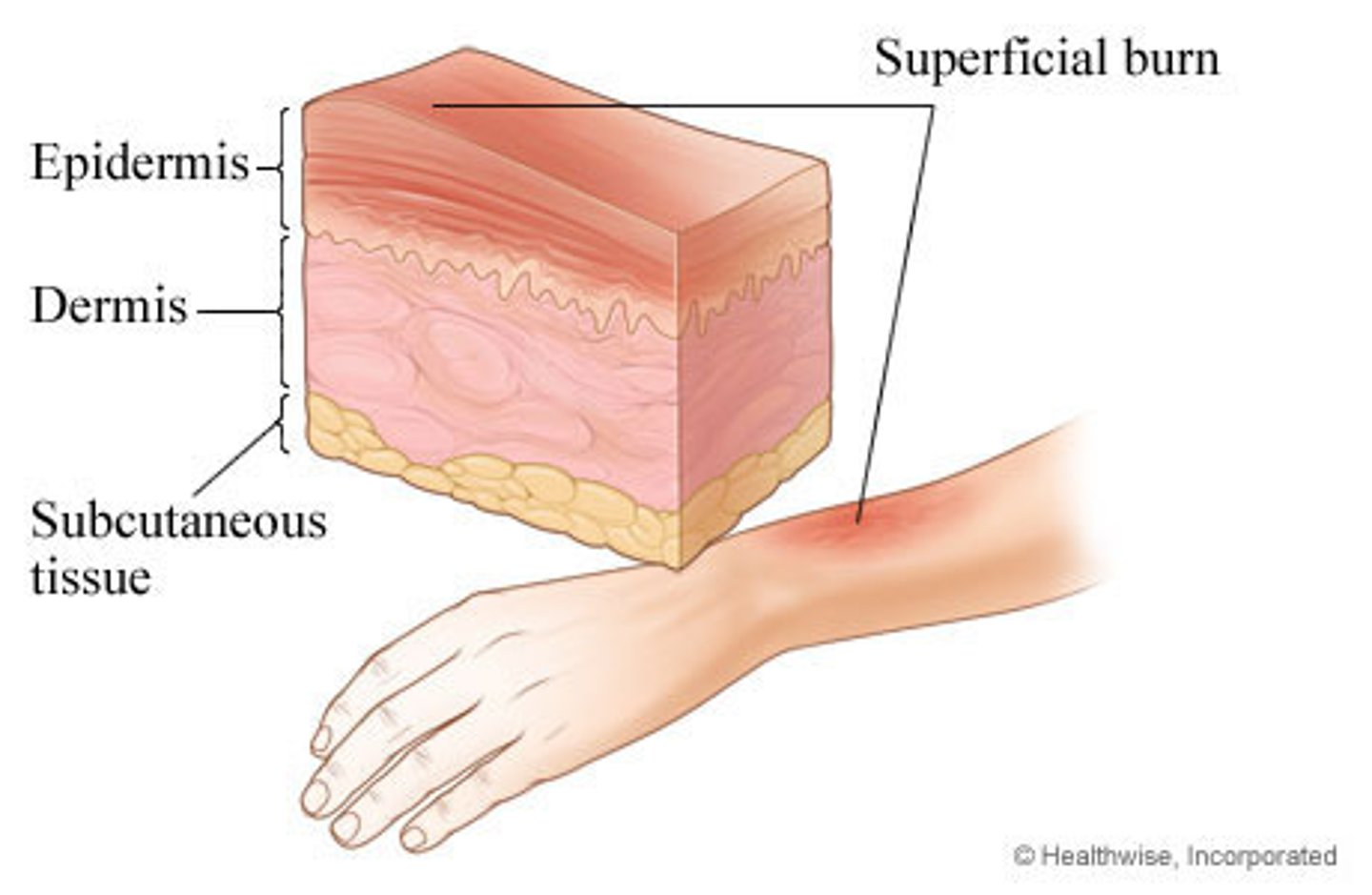
First degree burns
Involves only the epidermis
Erythema, pain, and swelling
no blisters
AKA: superficial burns
Second degree burn
Involves epidermis and UPPER part of dermis
Erythema, pain, swelling
HAVE blisters or bulla (bullae)
AKA: Partial thickness burn
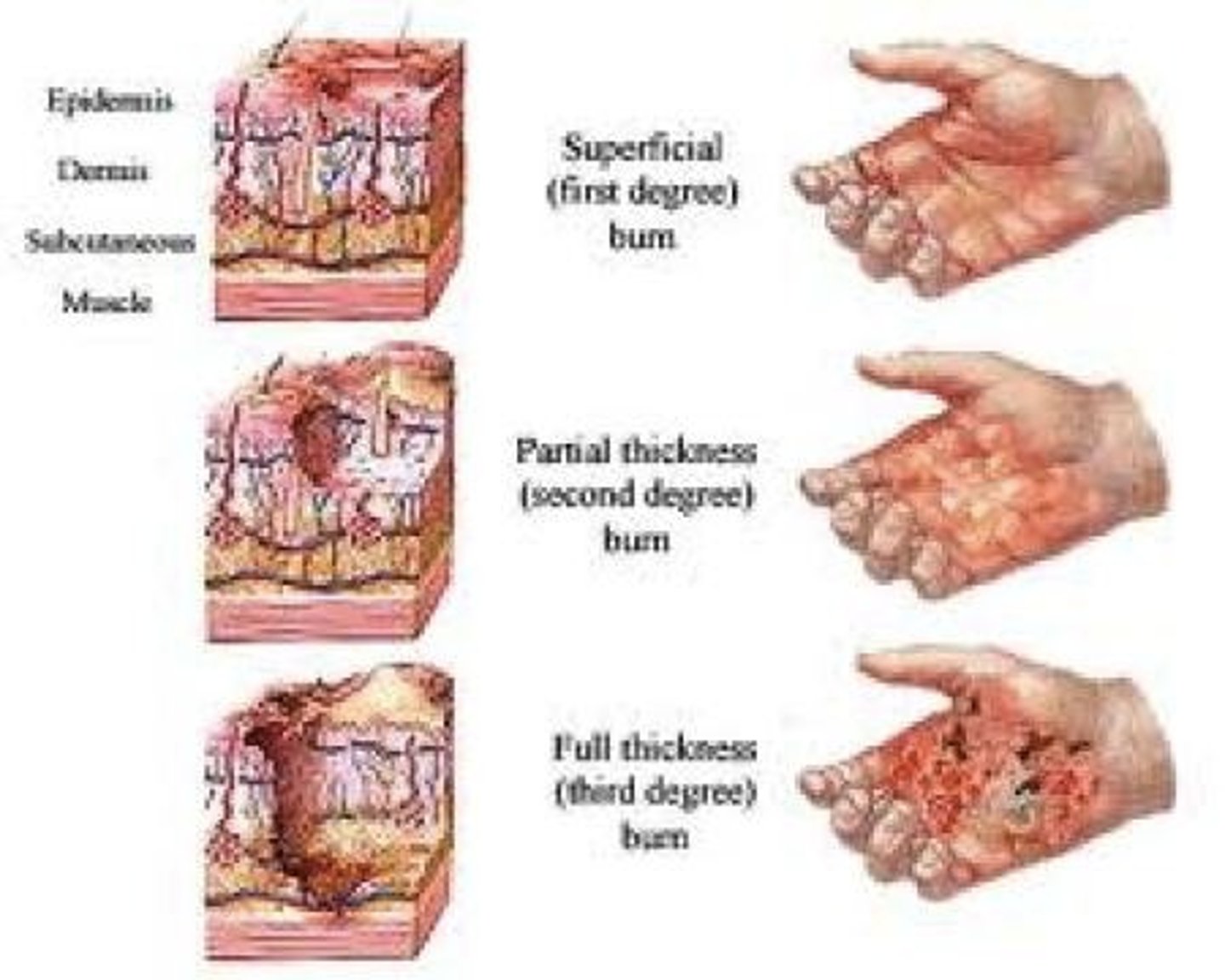
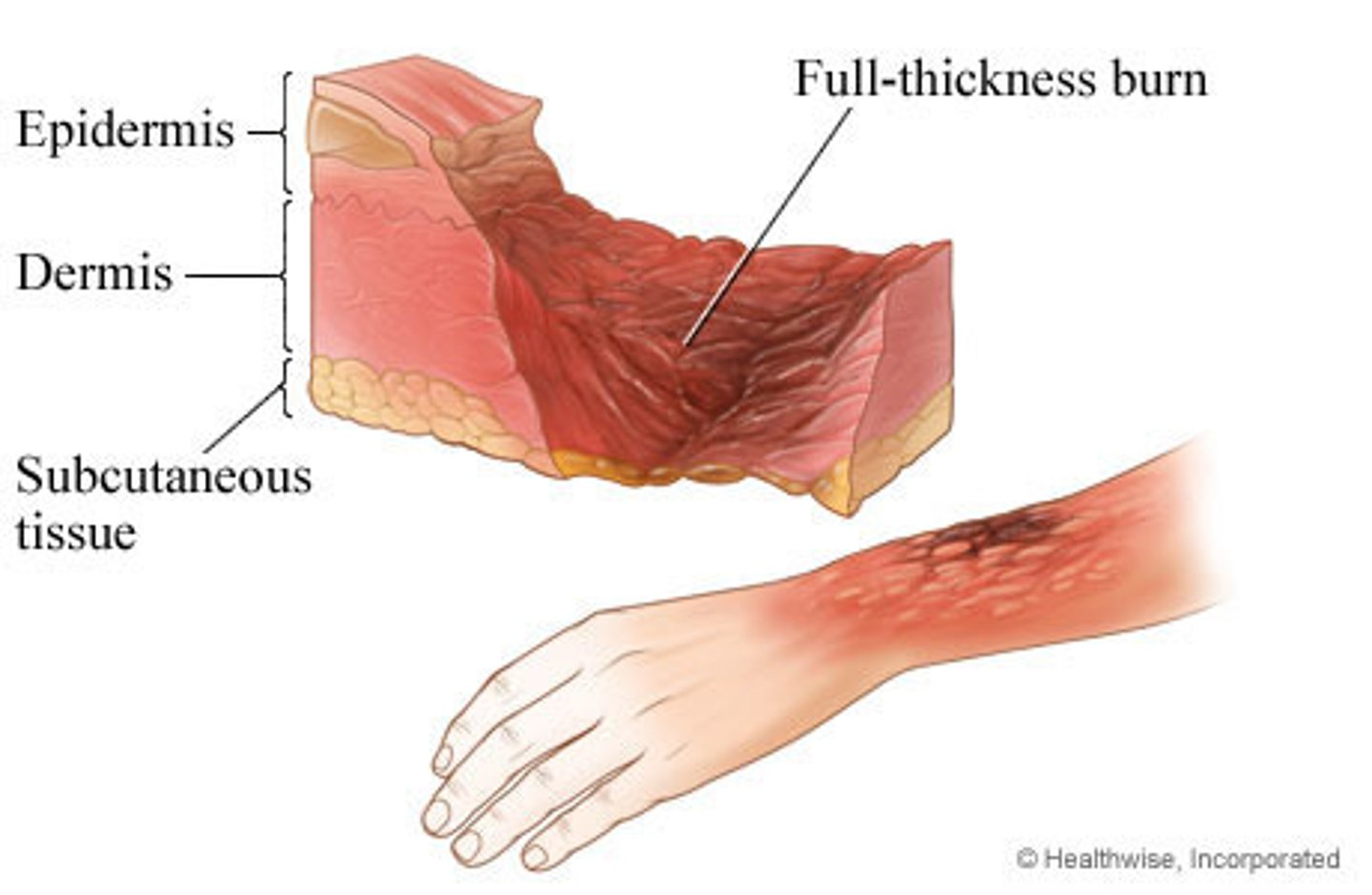
Third degree burn
Involves the epidermis, the dermis, and sometimes subcutaneous tissue and muscle
Nerves in the dermis are destroyed leading to local anesthesia
AKA: Full-thickness burn, requires skin grafting
Bulla
a large blister that is usually more than 0.5 cm in diameter
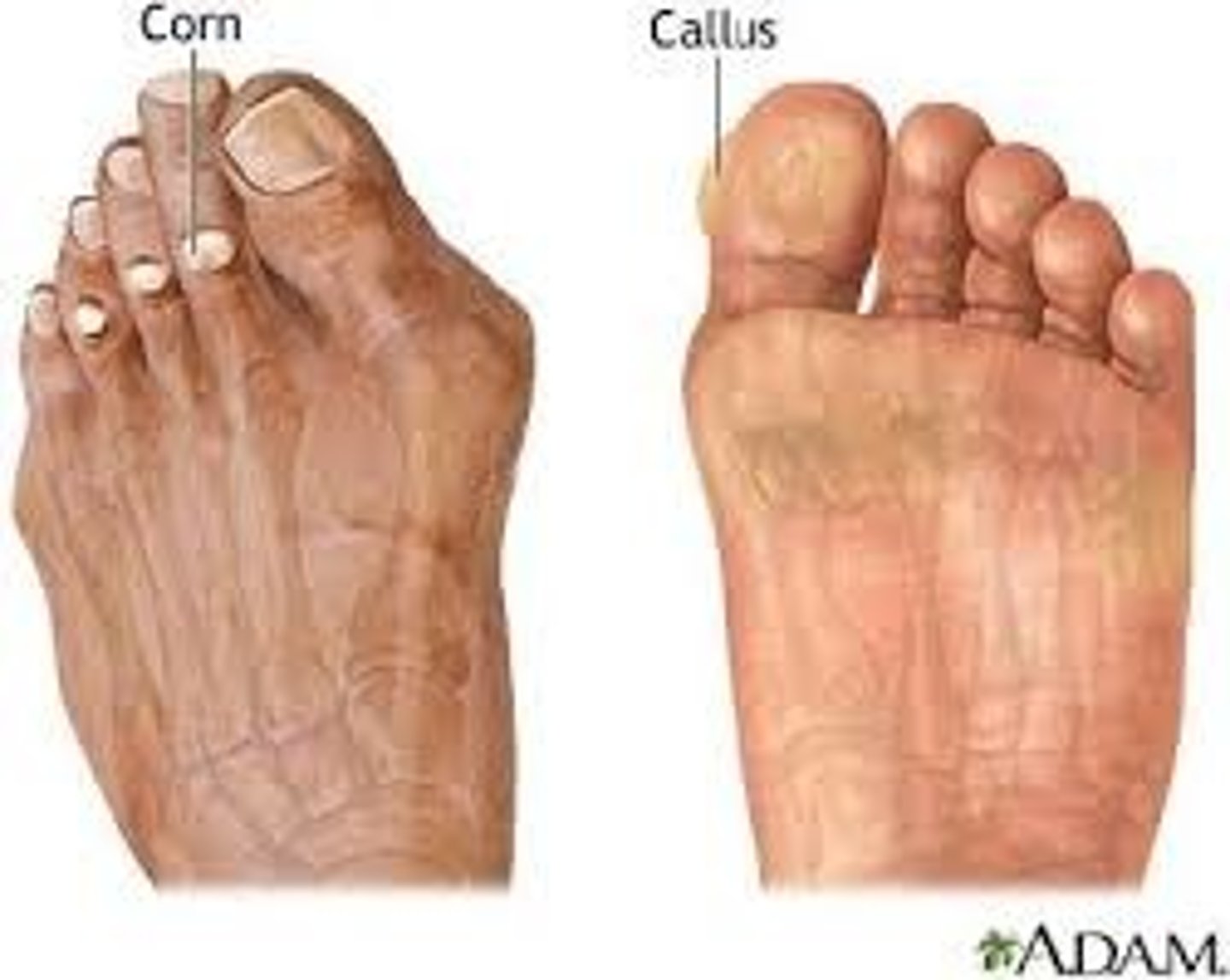
Callus
Repetitive rubbing injury causes epidermis to gradually thicken into wide elevated pad
Corn
Callus with a hard central area and pointed tip that causes pain and inflammation
Keloid
Firm abnormally large scar that grows larger than the original injury due to over production of collagen as it heals
Doesn't decrease overtime like regular scar
Can be surgically removed but often grows back
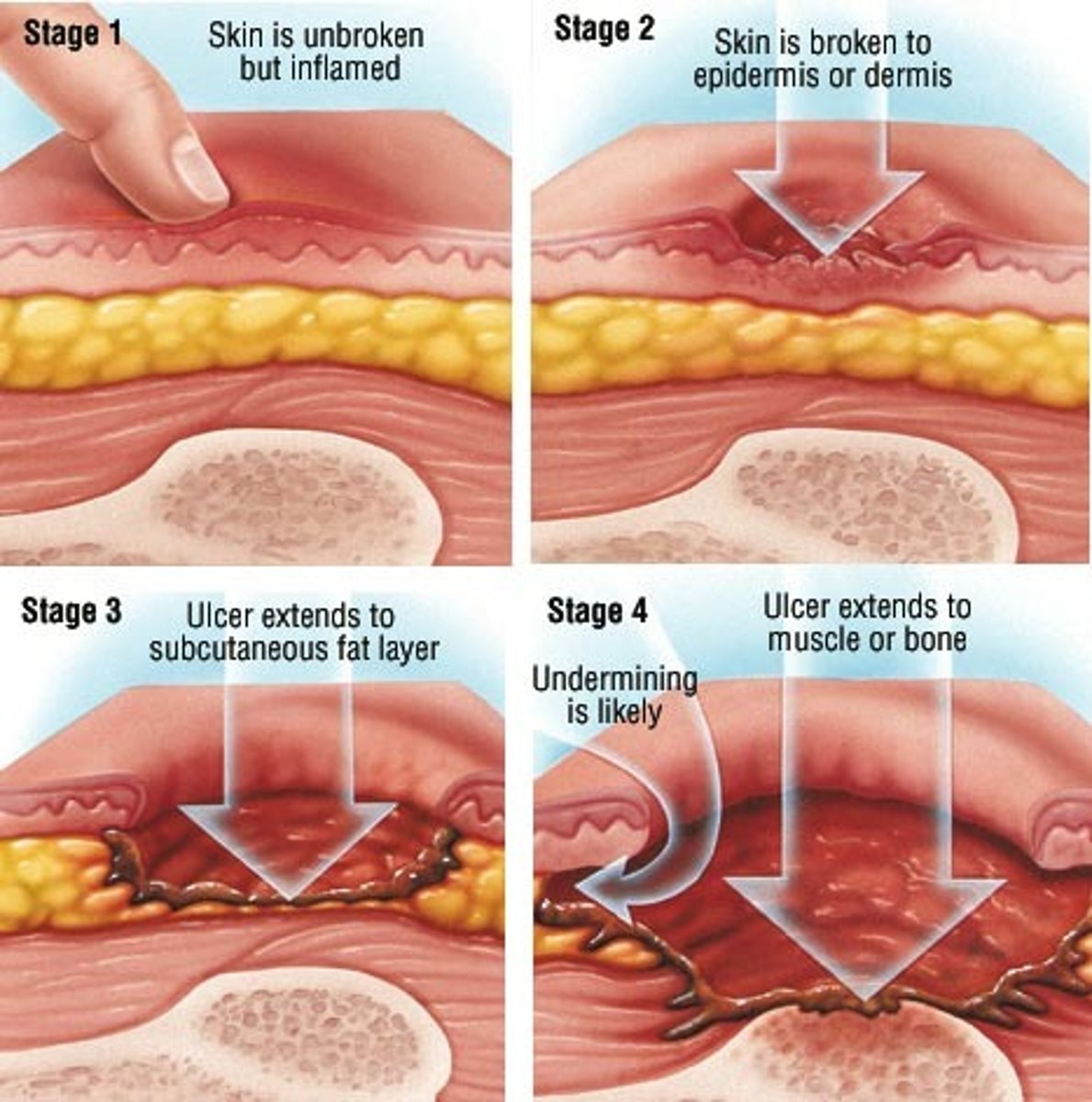
Decubitus Ulcer
constant pressure on the skin decreases blood flow to that area
The epidermis an dermis break down resulting in shallow deep ulcer
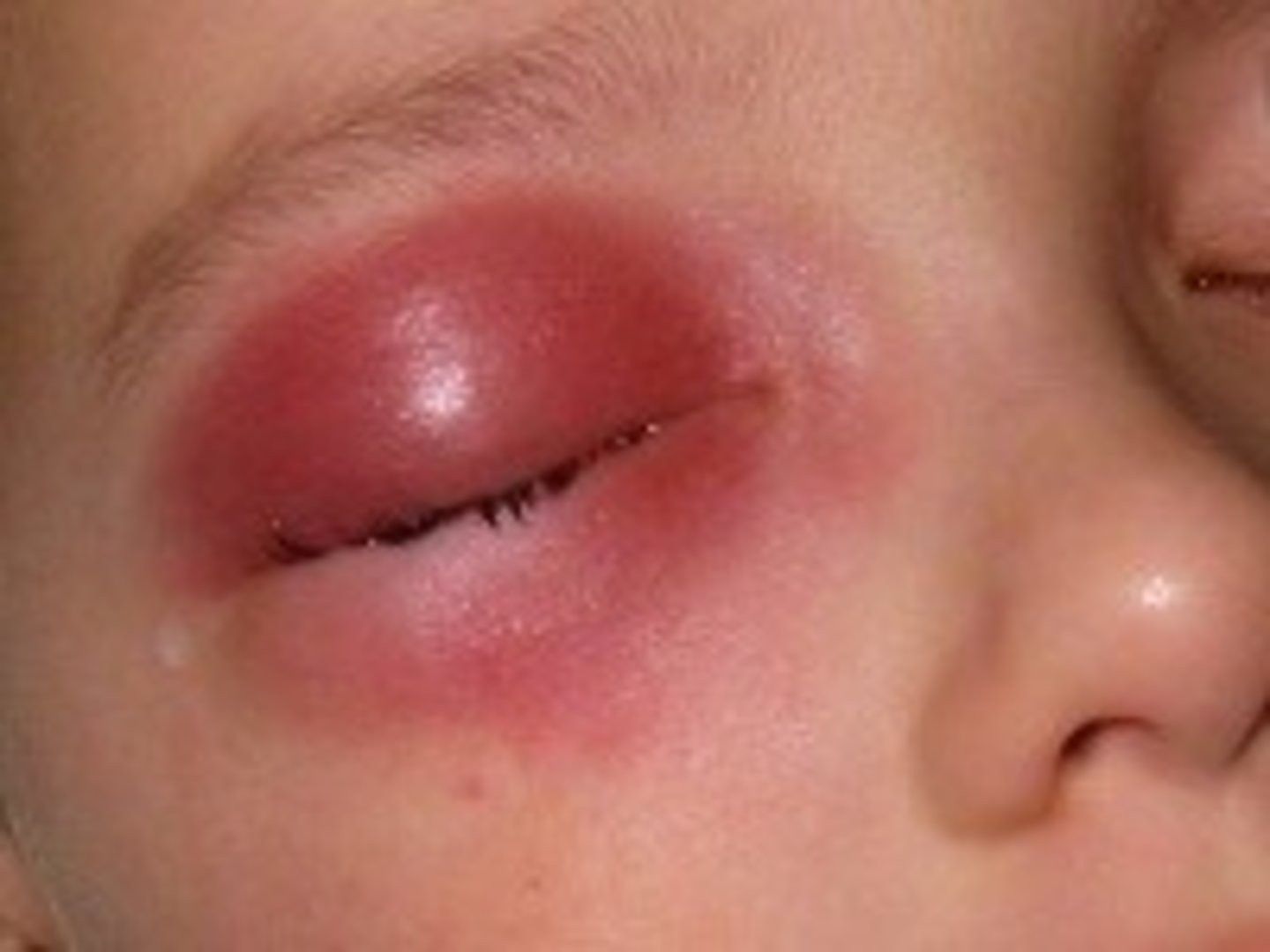
Cellulitis
Infection and inflammation that spreads through the skin, subcutaneous tissue and muscle
Develops from superficial scratch, insect bite, blister, or splinter that becomes in infected
Spreading bacteria produces enzymes that allow the infection to spread between tissue layers
Herpes
Infection caused by herpes virus
Causes vesicles, erythema, edema, pain
Vesicles rupture and release clear fluid that forms crust
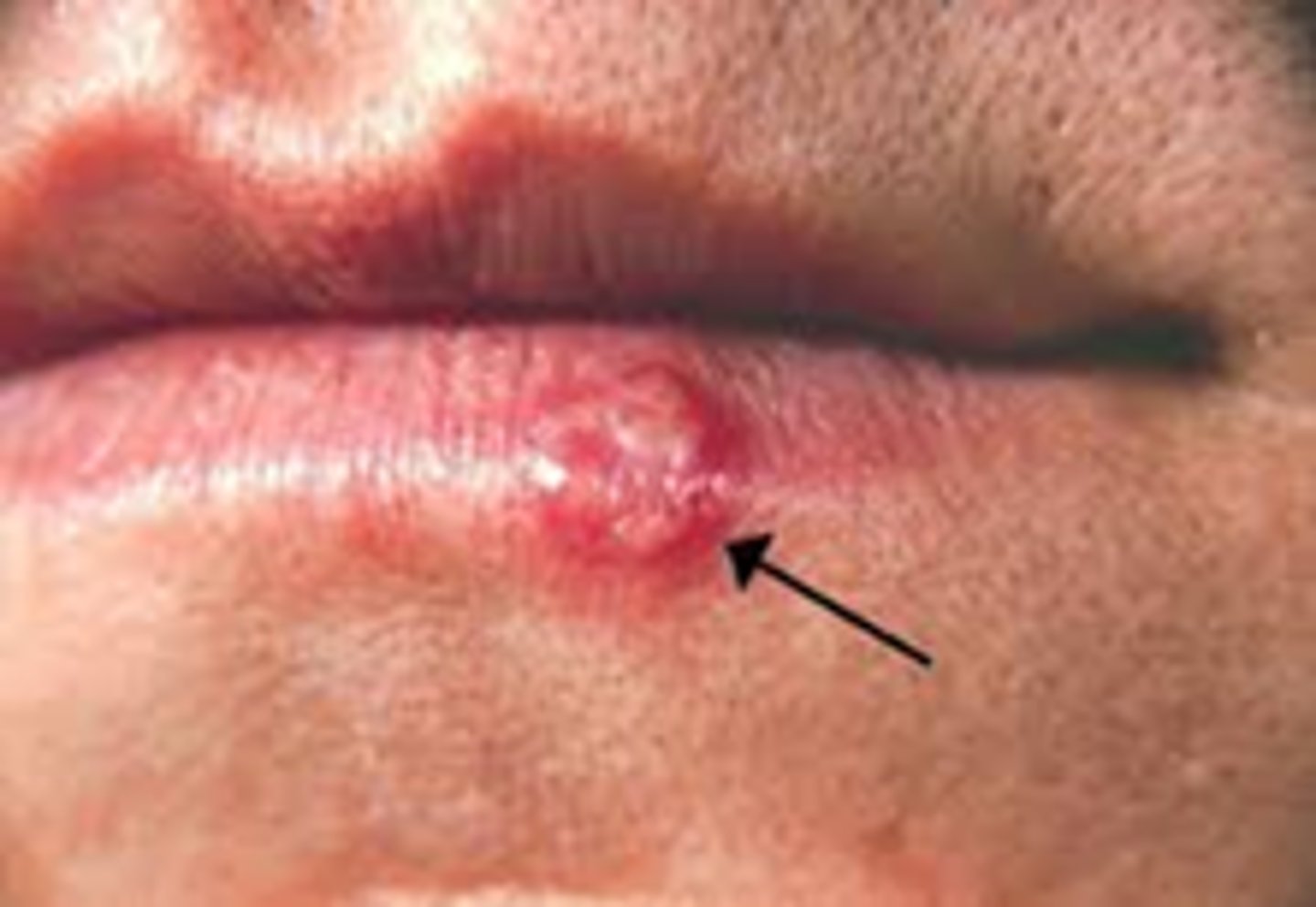
Herpes Simplex Virus (HSV) Type 1
Causes vesicles on lips (cold sores/ fever blisters)
Tend to recur during illness and stress, stays dormant in body
Herpes Simplex Virus (HSV) Type 2
Sexually transmitted diseases cause vesicles in genitals (genital herpes)
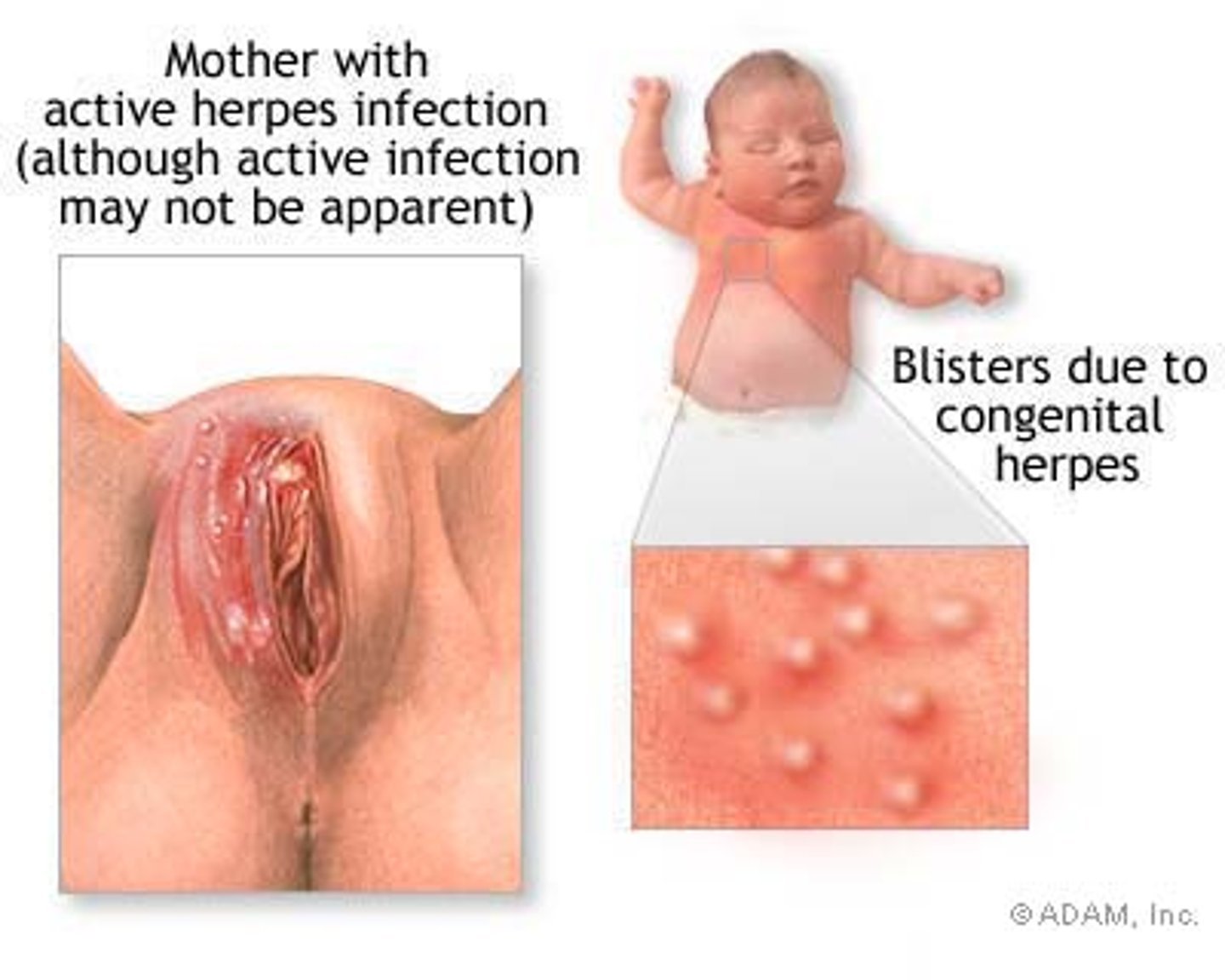
Herpes Whitlow
Infection at distal fingernail bc contact with Herpes Simplex Type 1 or 2
Virus enters through small tear in cuticle
Herpes Varicella-Zoster
Causes and shingles chickenpox then remains dormant until activated due to stress the
Forms vesicles and crusts along dermatome
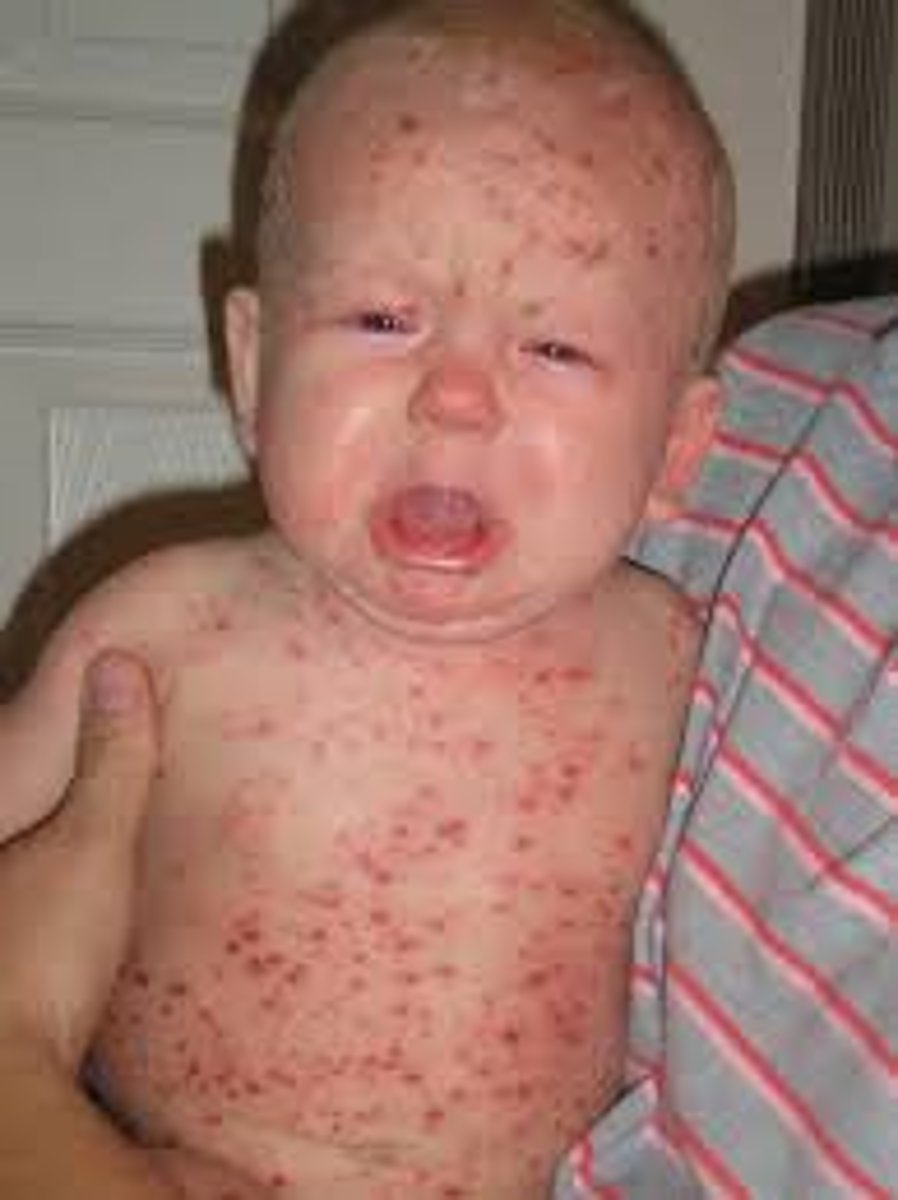
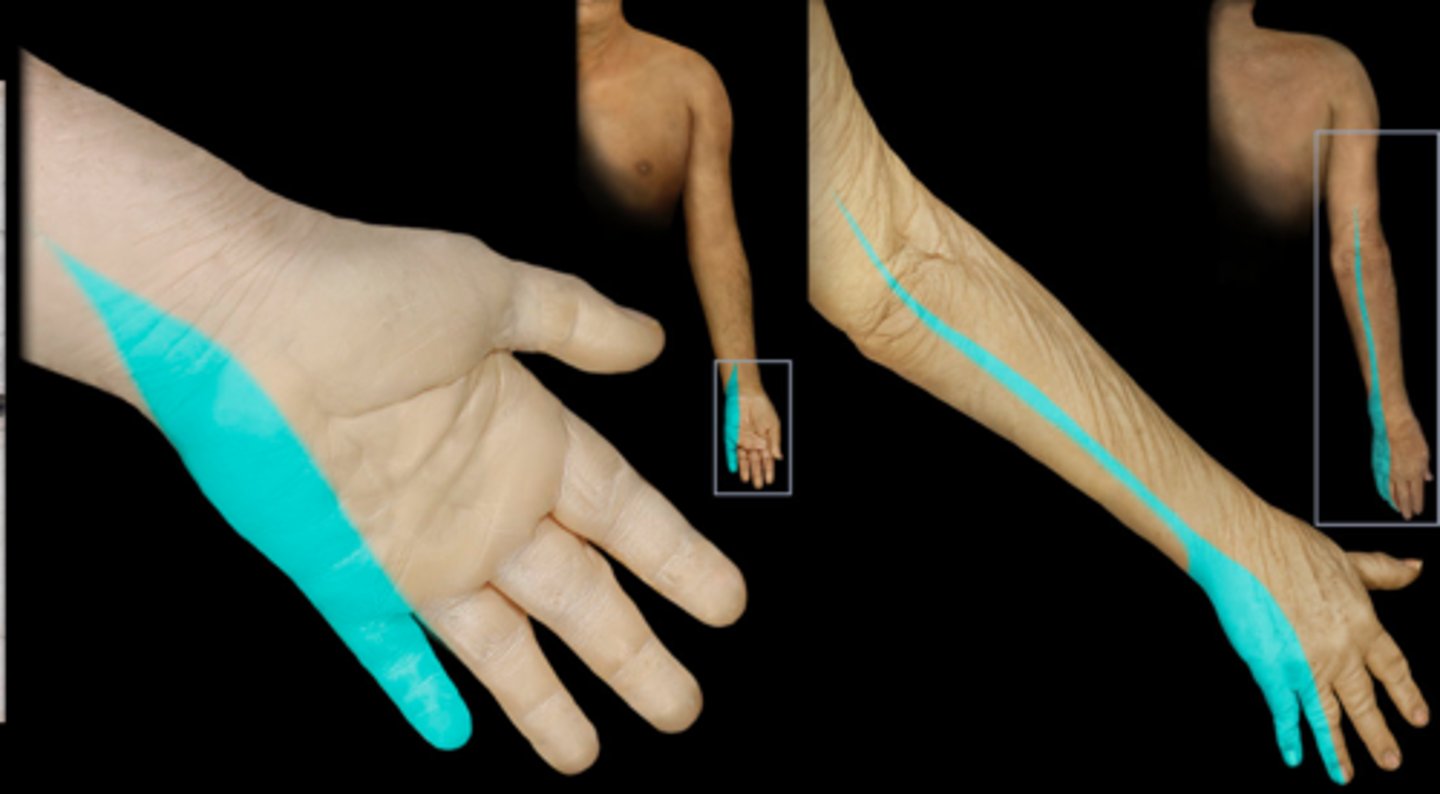
Dermatome
Area of skin supplied by nerves from a single spinal nerve
Tinea
Skin infection caused by fungus that feeds on epidermal cells
Causes severe itching and burning w/ red scaly lesions
AKA: ringworm
Tinea Capitis
fungal infection of the head
Tinea Corporis
ringworm of the body
Tinea Cruris
known as Jock itch. it is found in the groin area
brownish-red lesions in groin area, pruritus, skin excoriation
Tinea Pedis
fungal infection of the foot; athlete's foot
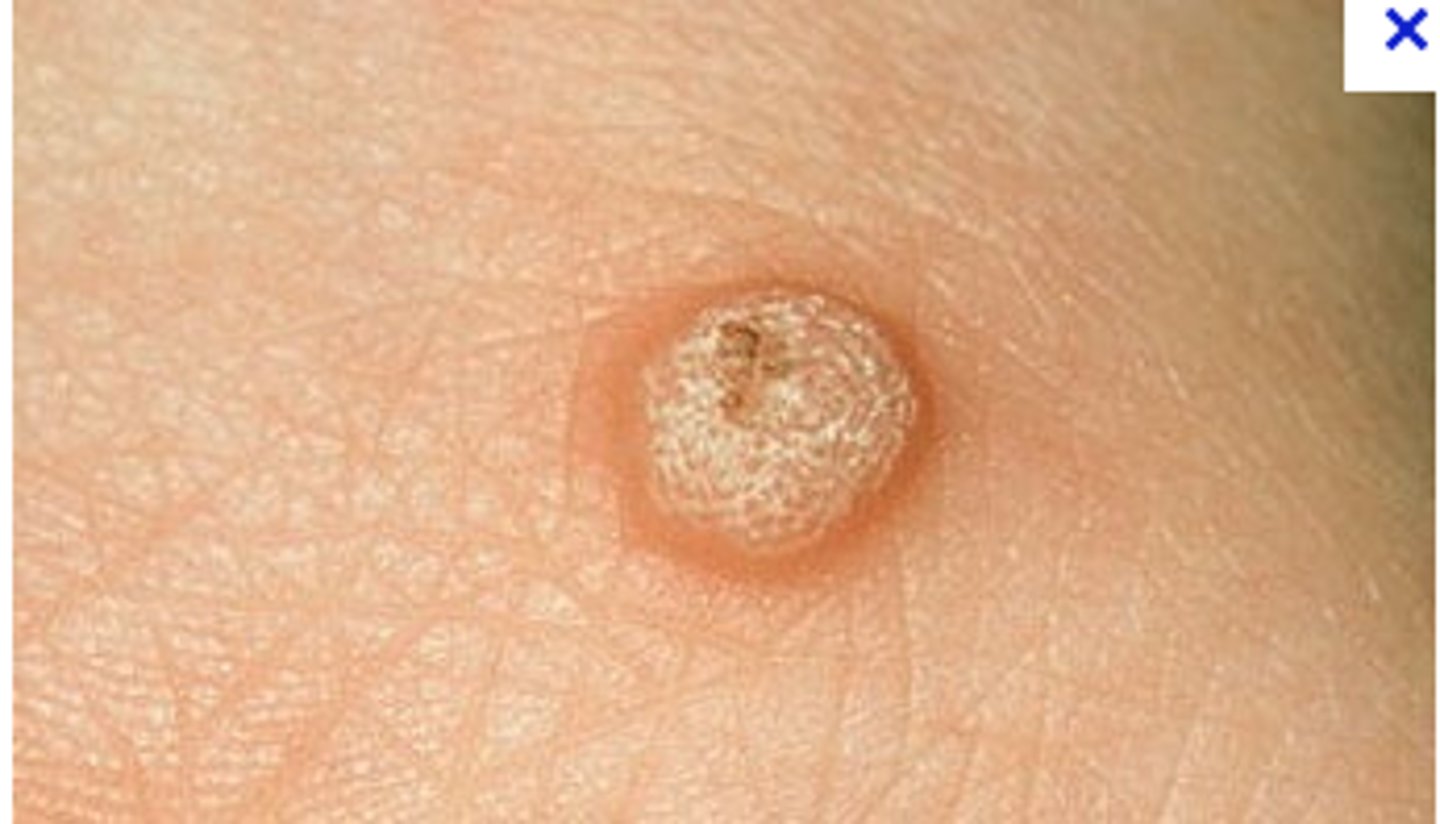
Verruca (vr·oo·kuh)
Irregular, rough skin lesions caused by HPV
Occurs on hands, fingers, or soles of feet (plantar warts)
AKA: warts
Pediculosis
infestation with lice
Scabies
Infestation of parasitic mites that tunnel under the skin and produce vesicles
Urticaria
AKA: Hives
Raised areas of redness and edema
Caused by local allergic reaction to food, plants, animals, bites, or drugs
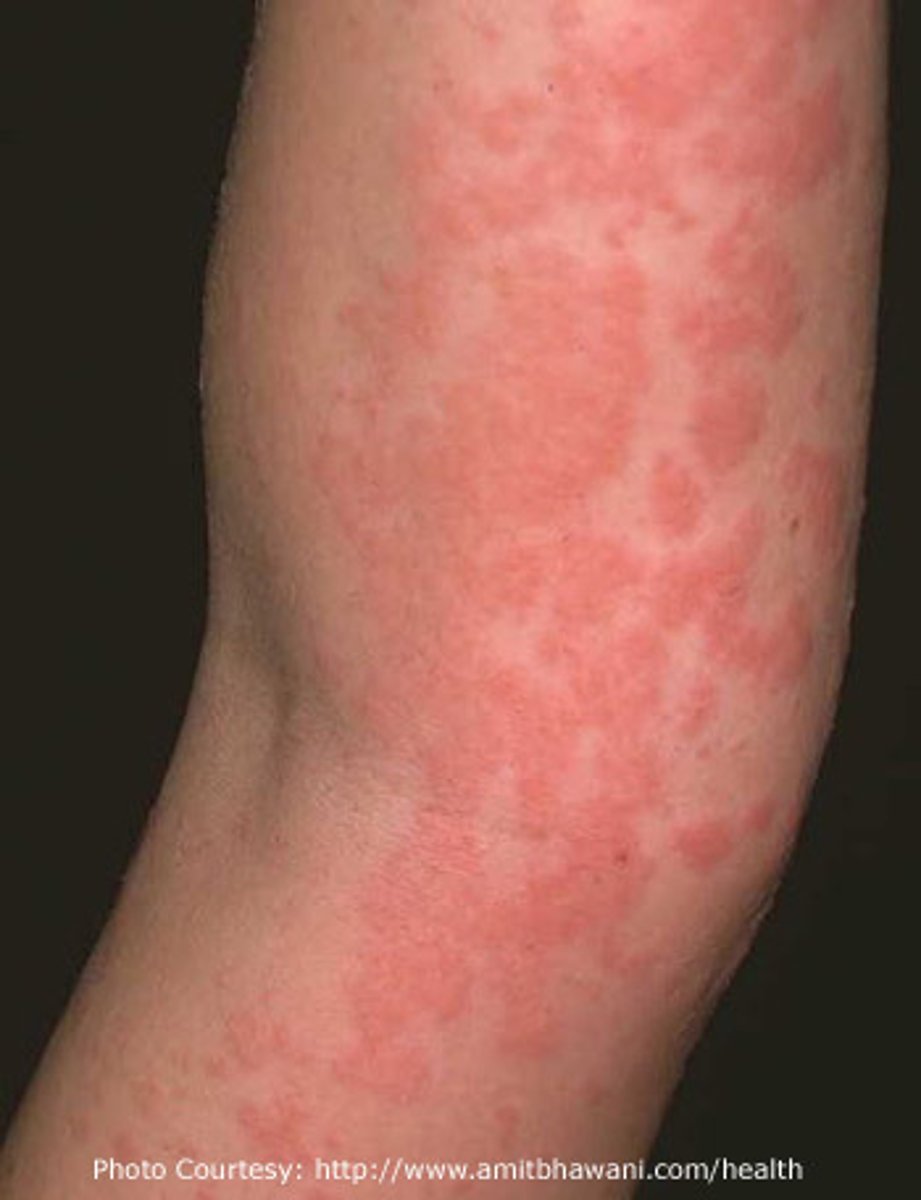
Hemangioma (hee·man·jee·ow·muh)
Benign mass of superficial, dilated blood vessels present at birth
Most disappear by age 3
Angi/o-
blood or lymphatic vessel
Lipoma
Benign growth of adipose tissue in the subcutaneous layer
Lip/o-
Fat
Neoplasm
new growth on or in the skin
-plasm
formed substance; growth
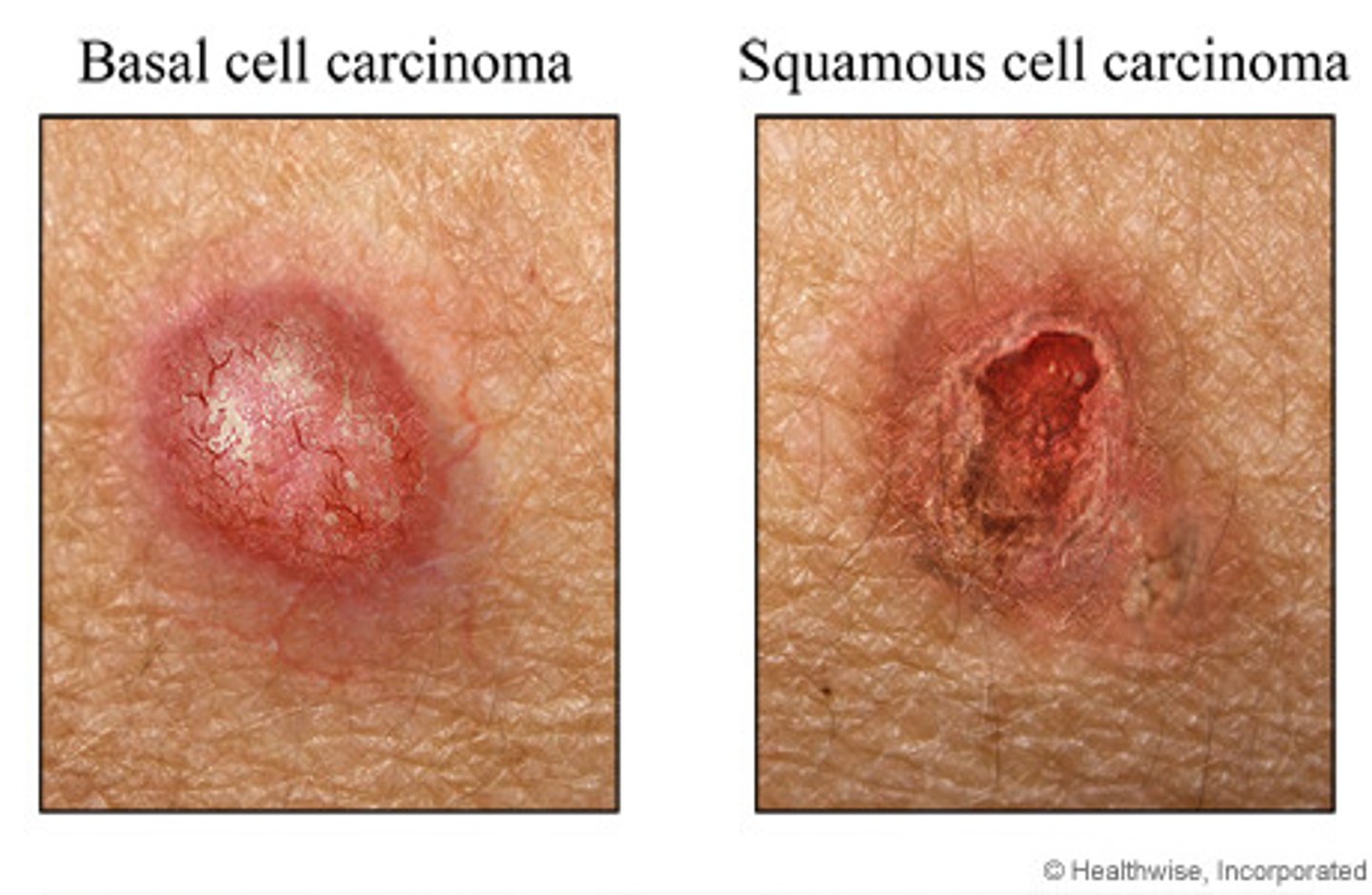
Basal cell carcinoma
Begins in the basal layer of the epidermis
Most common, slow-growing, non metastatic
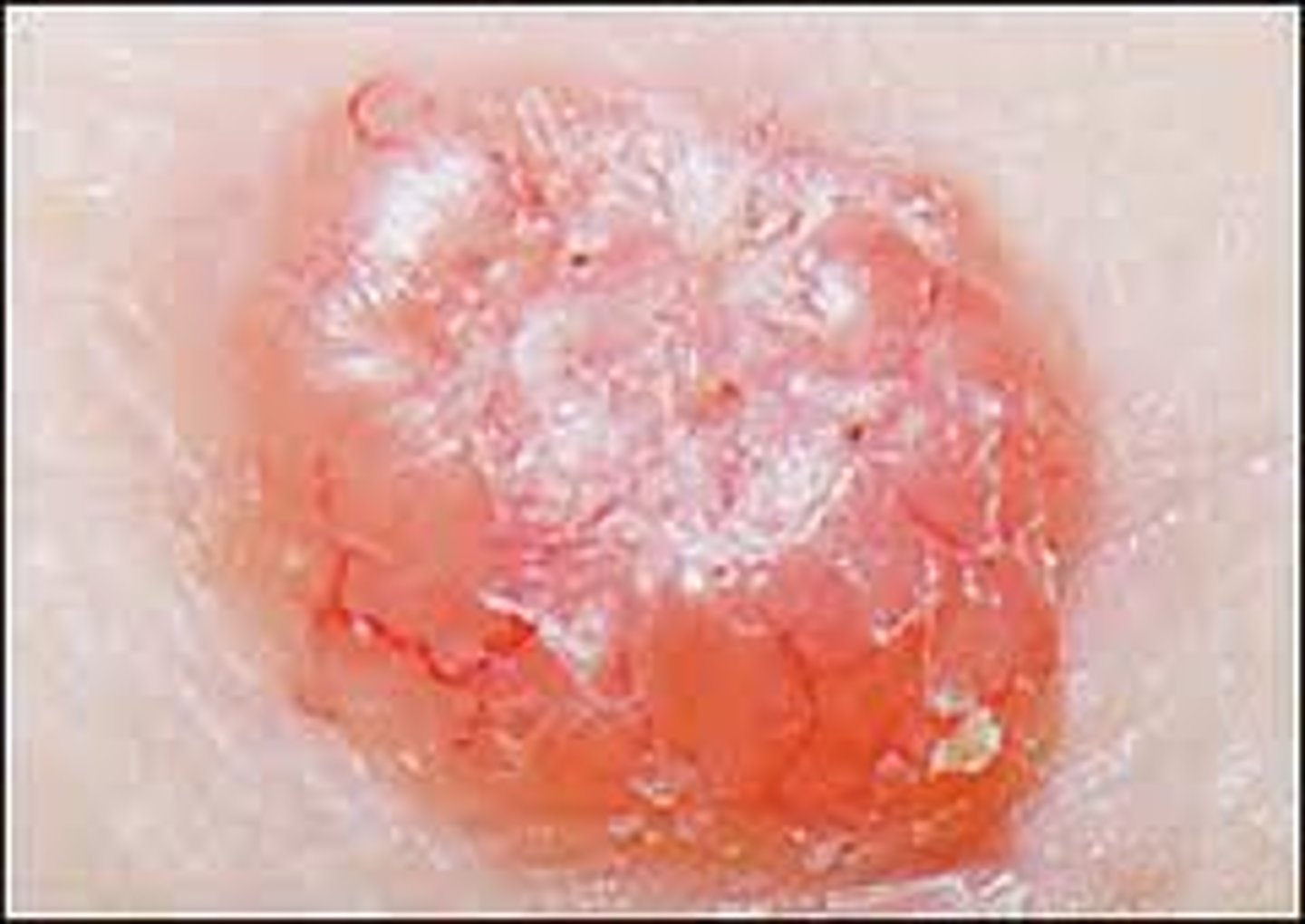
Metastatic
moves from site of origin to secondary site in body
squamous cell carcinoma
Begins in flat squamous cells of superficial layer of epidermis
Melanoma
The most serious form of skin cancer
Begins in the melanocytes in the epidermis
grows quickly and metastasizes to other parts of the body
ABCDE
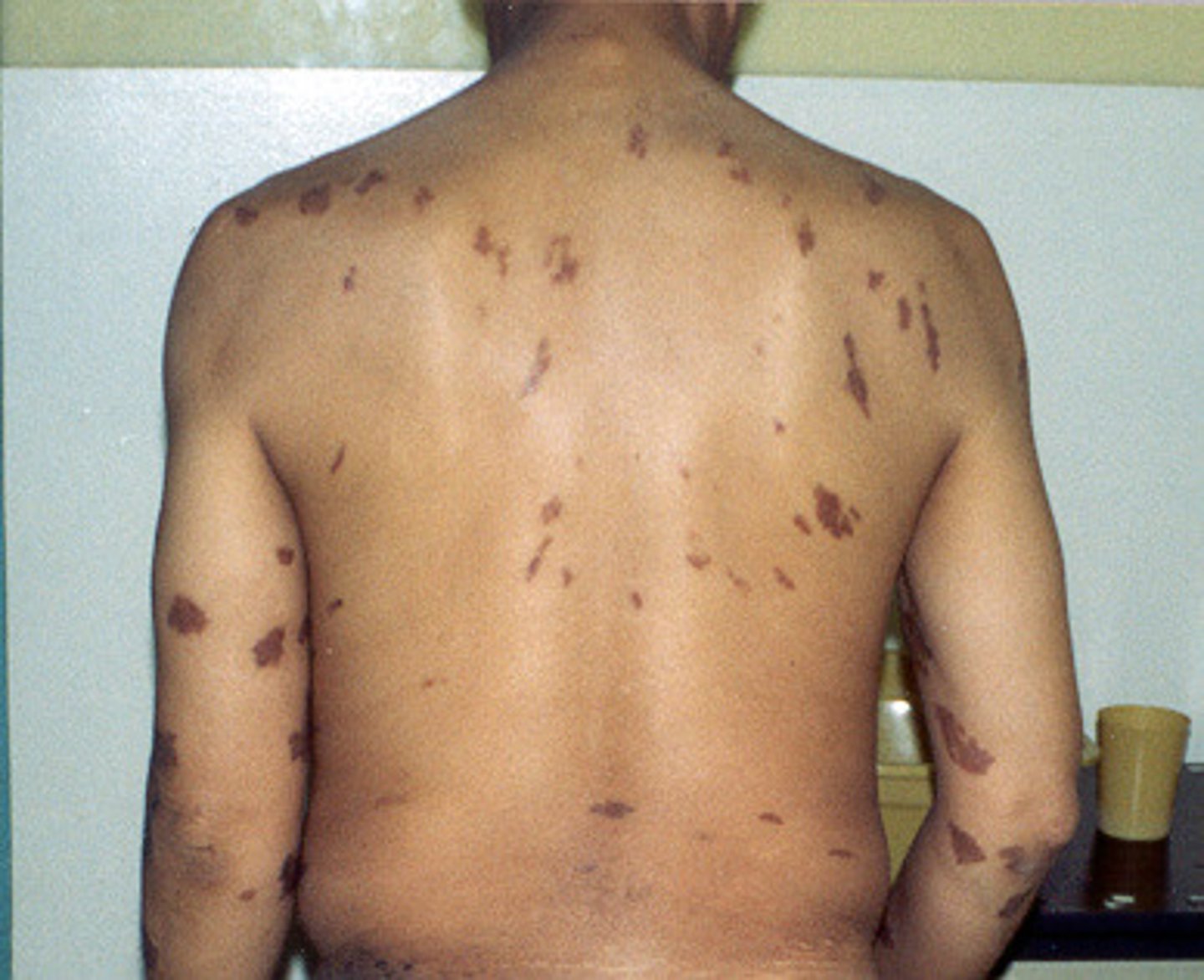
Kaposi's sarcoma
skin cancer that begins in connective tissue or lymph nodes, common in AIDS patients
Tumors on skin are elevated, irregular and dark reddish-blue
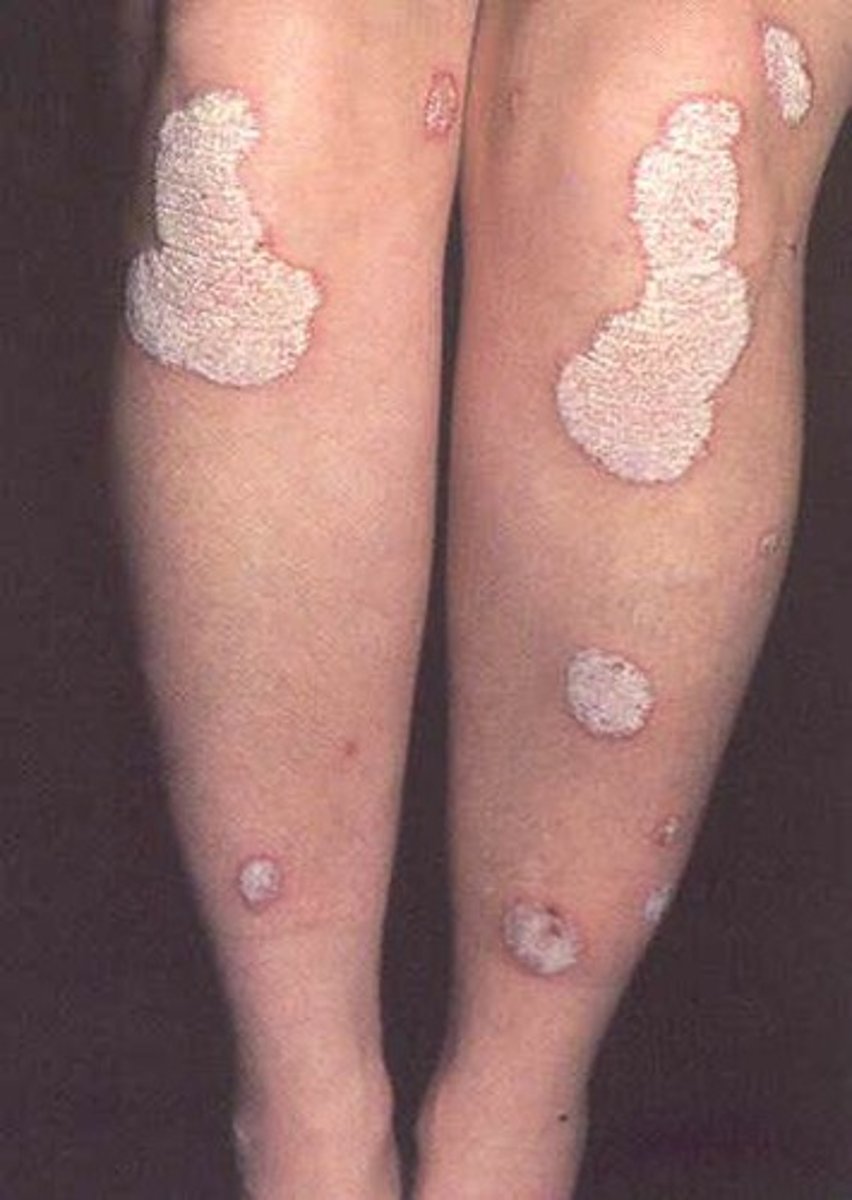
Psoriasis
An autoimmune disorder that produces an excessive number of epidermal cells
Skin lesions are itchy, red, and covered in silvery scales and plaques
HEREDITARY
Acne
Sebaceous glands secrete excessive amounts of amounts of sebum
Excess sebum enlarges pores and turns black as the oil is exposed to the air and becomes a blackhead
Excess sebum blocks the pore and causes red raised plaque Draws white blood cells to area forming pus or whiteheads
Rosacea
Sebaceous glands secrete excessive amounts of sebum
Blotchy erythema and dilated superficial blood vessels
anhidrosis
Absence of sudoriferous glands and inability to sweat and tolerate heat
Diaphoresis
Excessive sweating point to underlying serious condition
patient is diaphoretic
Alopecia
Loss of hair
Autoimmune, side effect of chemo, can happen as we age
Hirsutism
Condition in women, results in excessive hair growth of dark or course hair
onychomycosis
Fungal infection of the nails
What is a culture and sensitivity used for?
To identify the bacteria casing infection and the sensitivity to specific antibiotic drugs
Wheal
small, round, raised area on the skin that may be accompanied by itching; usually seen in allergic reactions
Botox injections
Drug Botox is injected into the muscle to release deep wrinkle lines
Drug keeps the muscle from contracting and creating wrinkles
Last couple months depending on how fast u metabolize the drug
Collagen injections
Liquid containing collagen is injected into wrinkles or acne scars, plumps the skin
Biopsy
Removal all or part of a lesion or tumor for examination under microscope to obtain diagnosis
-opsy
Process of viewing
biopsy, excisional
Uses scalpel to remove denture skin lesion or tumor
Biopsy Incision
Uses scalar to make incision to remove a portion of the lesion or tumor
Biopsy punch
Uses circular metal cutter to remove a core of tissue from the skin lesion or tumor
Biopsy shave
Uses scalpel or derma blade to shave off superficial skin lesion in epidermis
Liposuction
Procedure to remove excessive adipose tissue
Cannula is inserted through small incision to remove fat
Mohs surgery
technique uses to treat skin cancer
Thin layers are removed and examined under microscope until only cancer free tissue remain
Mohsmicrographic surgery