Muscle intro & axial muscles
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
74 Terms
Where is smooth muscle found in the body?
In the walls of hollow organs and throughout the body, including blood vessels, the gastrointestinal tract, reproductive system, urinary system, and respiratory system
Where is skeletal muscle found?
Primarily attached to bones via tendons
Where is cardiac muscle found?
In the walls of the heart, specifically within the middle layer (myocardium)
Smooth muscle is…
Involuntary
Skeletal muacle is…
Voluntary
Cardiac muscle is…
Involuntary
Levator labii superioris
Elevates the upper lip and
Buccinator
Pulls the cheek inward and plays a crucial role in chewing. “Trumpeter" muscle
Depressor labii inferioris
Contributes to facial expressions like frowning, pouting, and is important for exposing the lower teeth during smiling.
Occipitofrontalis
Wrinkling the forehead, raising the eyebrows, the backward movement of the scalp, and draws the scalp anteriorly
Orbicularis oculi
Plays a role in creating expressions like squinting and frowning, as well as contributing to "crow's feet" wrinkles
Orbicularis oris
Closes the lips to narrow the oral opening
Platysma
Plays a role in facial expressions by contributing to lowering the corners depressing the lower lip the mouth, wrinkling the neck, and tensing the skin of the neck
Zygomaticus
Plays a crucial role in facial expressions, elevates the upper lip for smiling
The attachment site for the temporalis is
The temporal fossa and the temporal fascia, and its tendon inserts on the coronoid process of the mandible
The attachment site for the masseter is
The ramus of the mandible
Semispinalis Capitis Muscle movement
Extension, lateral rotation, and lateral flexion
Splenius capitis muscle movement
Neck extension and lateral neck rotation
Trapezius muscle movement
Side bending, rotation of the head, elevating and depressing the shoulders, and internally rotating the arm
Sternocleidomastoid muscle movement
Rotation of the head to the opposite side or obliquely rotate the head
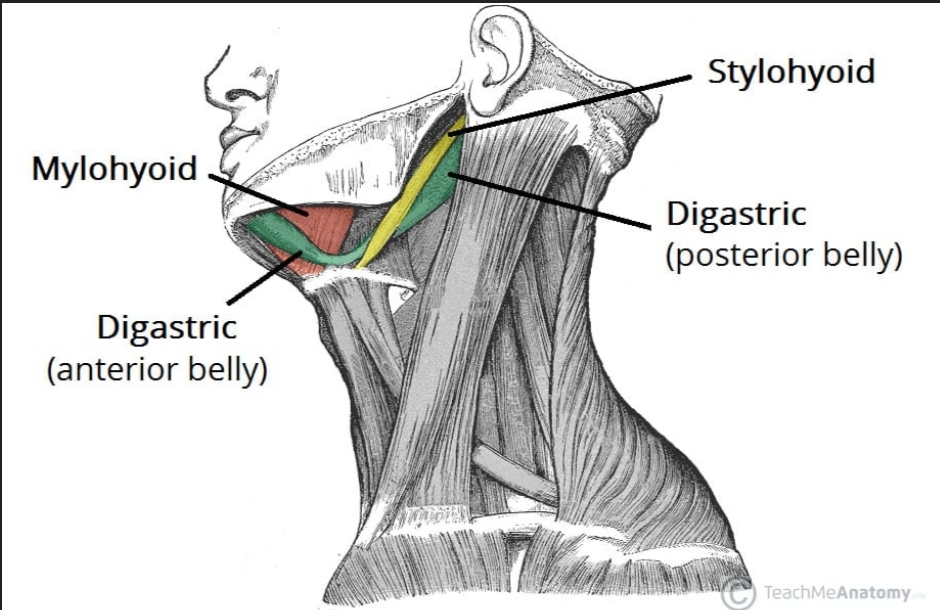
The anterior belly of the digastric muscle
Originates from the digastric fossa on the mandible
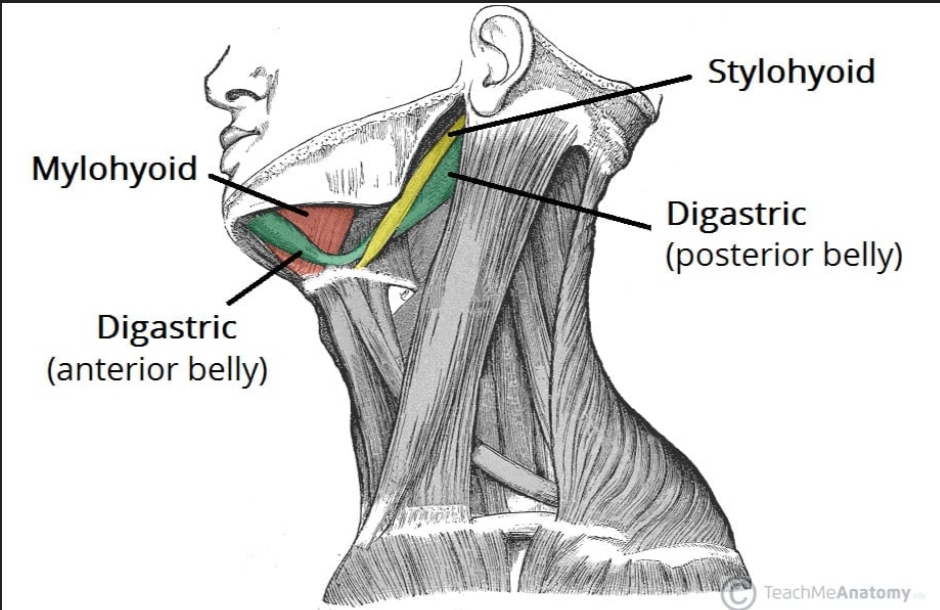
The posterior belly of the digastric muscle
Originates from the mastoid notch of the temporal bone
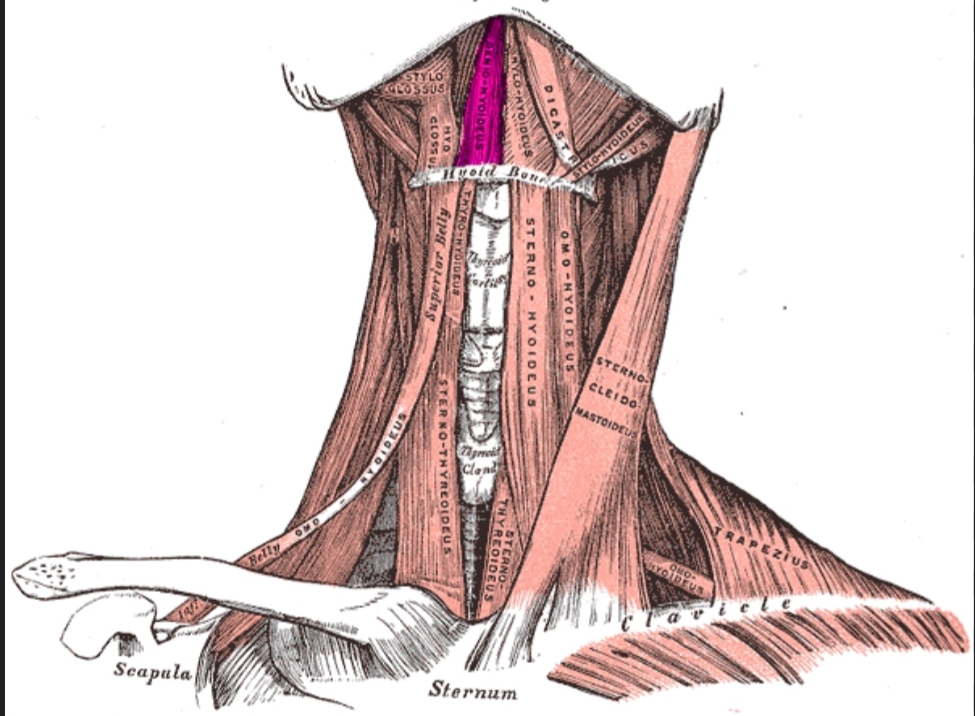
Genohyoid
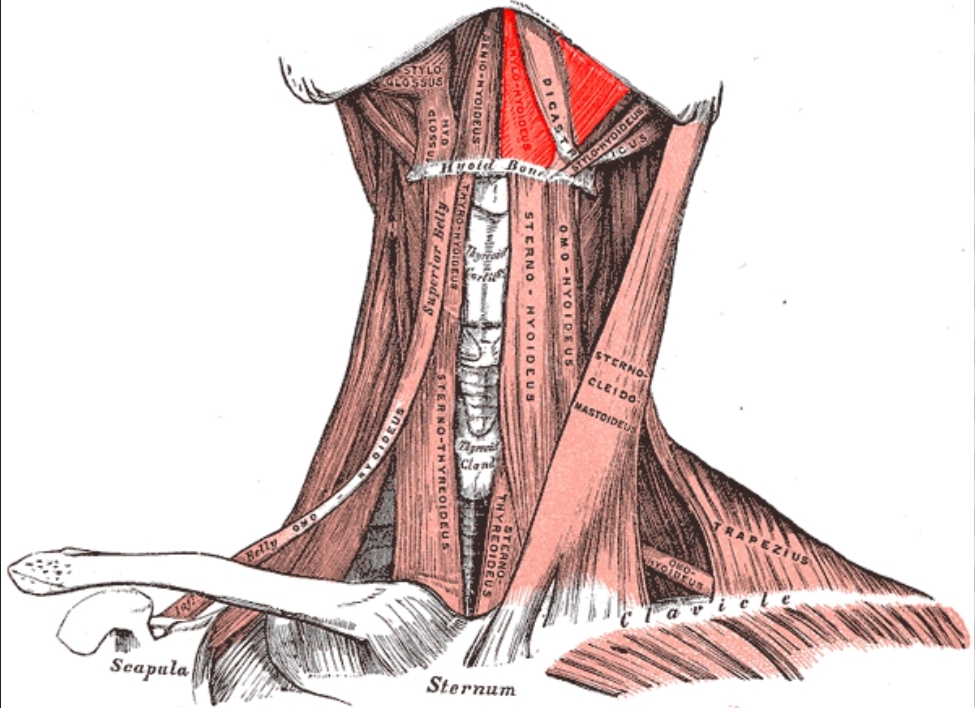
Mylohyoid
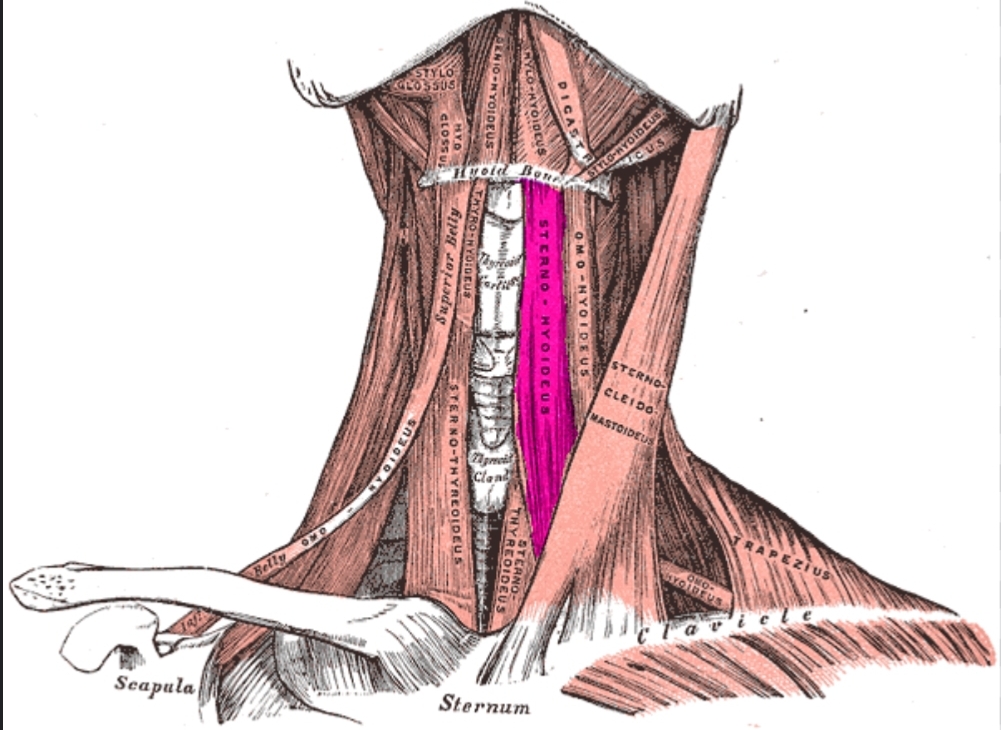
Sternohyoid
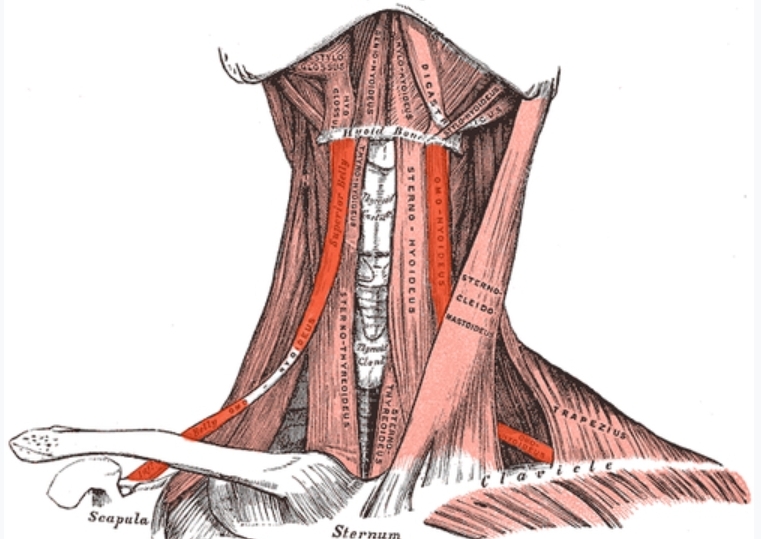
Omohyoid
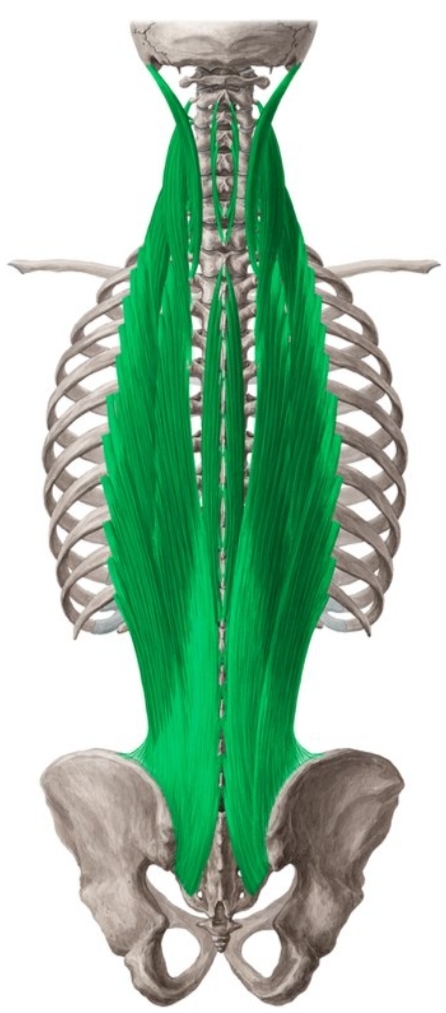

Erector spinae
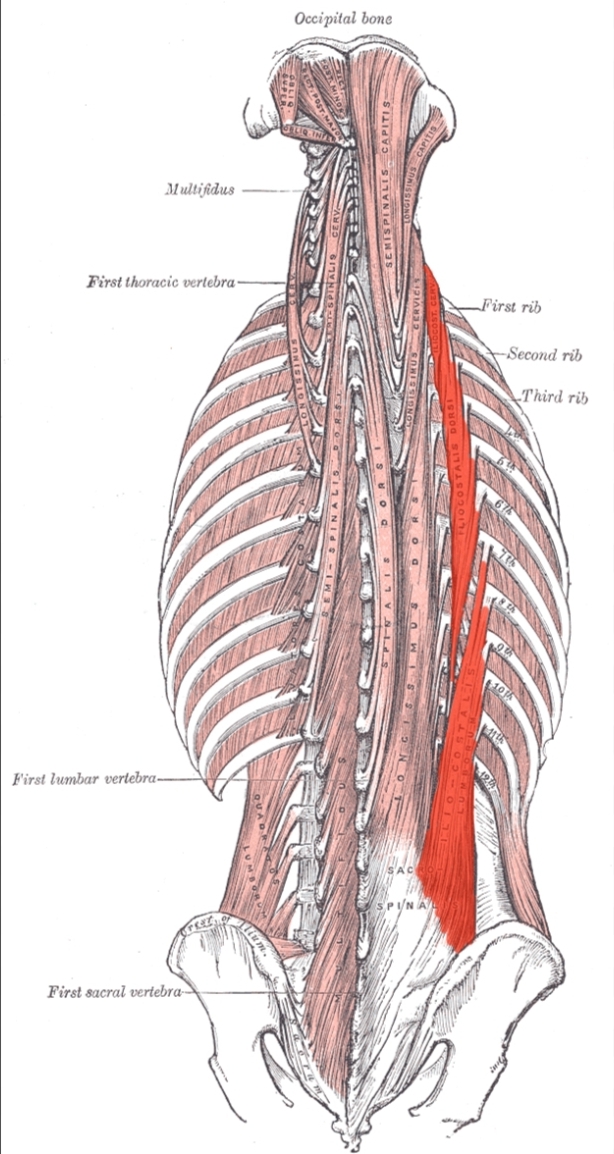
Llicocostalis
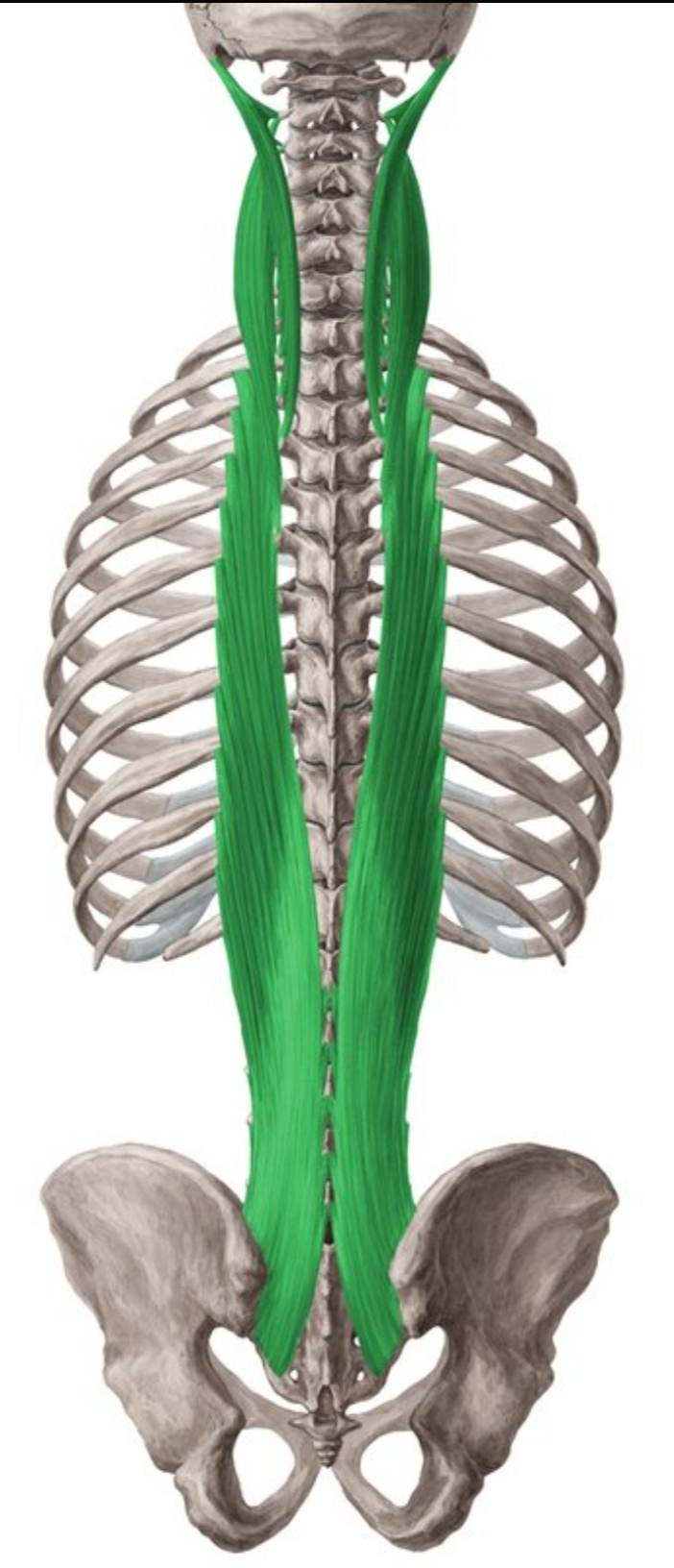
Longissimus
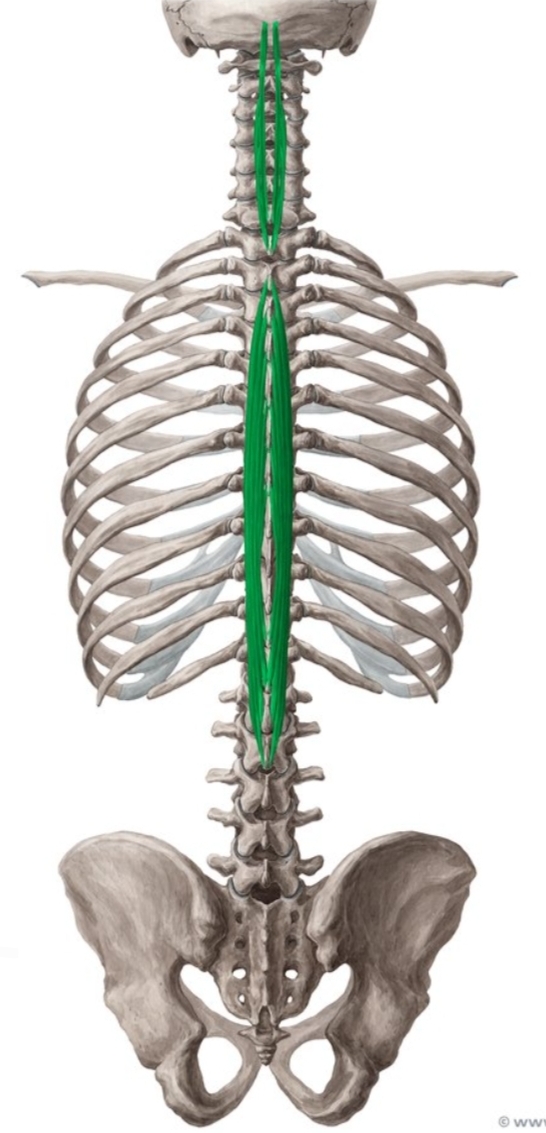
Spinalis
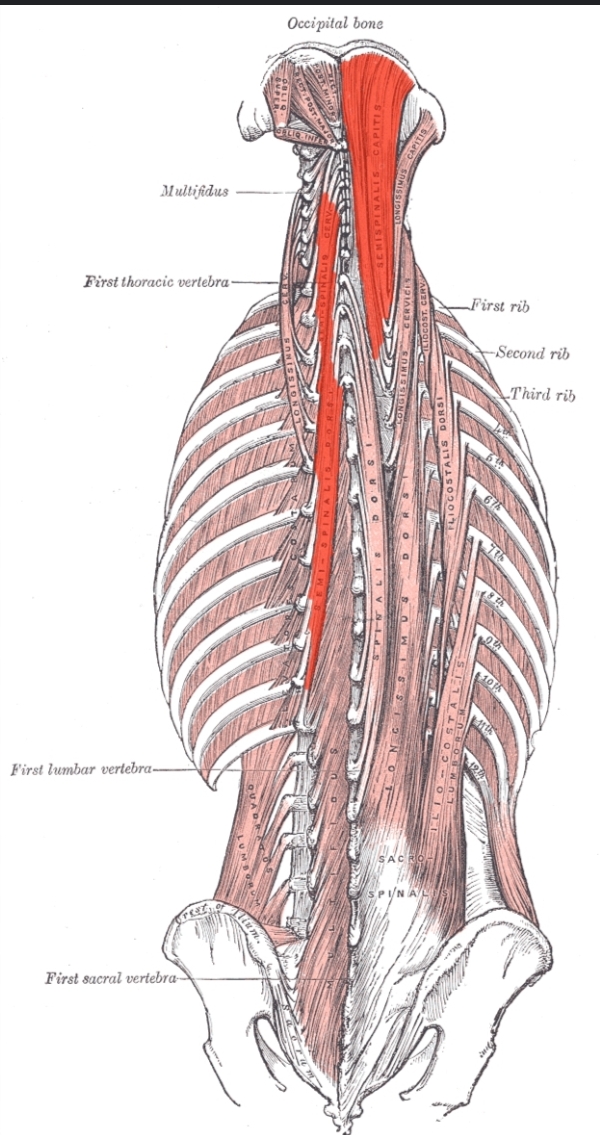
Semispinalis
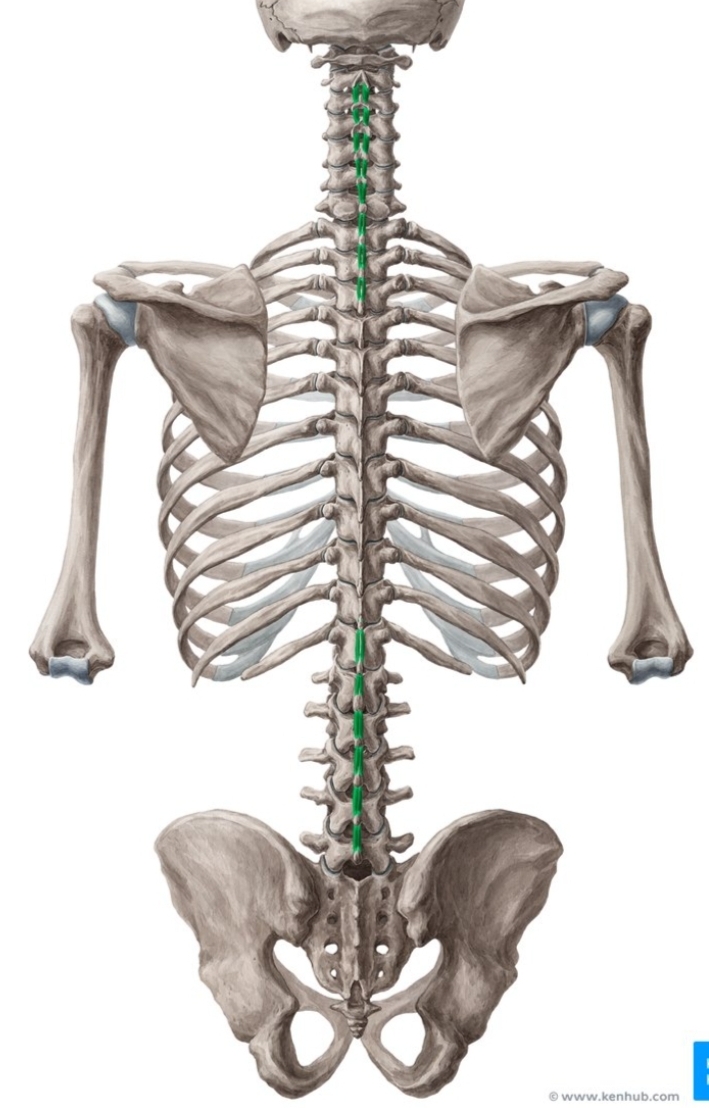
Interspinales
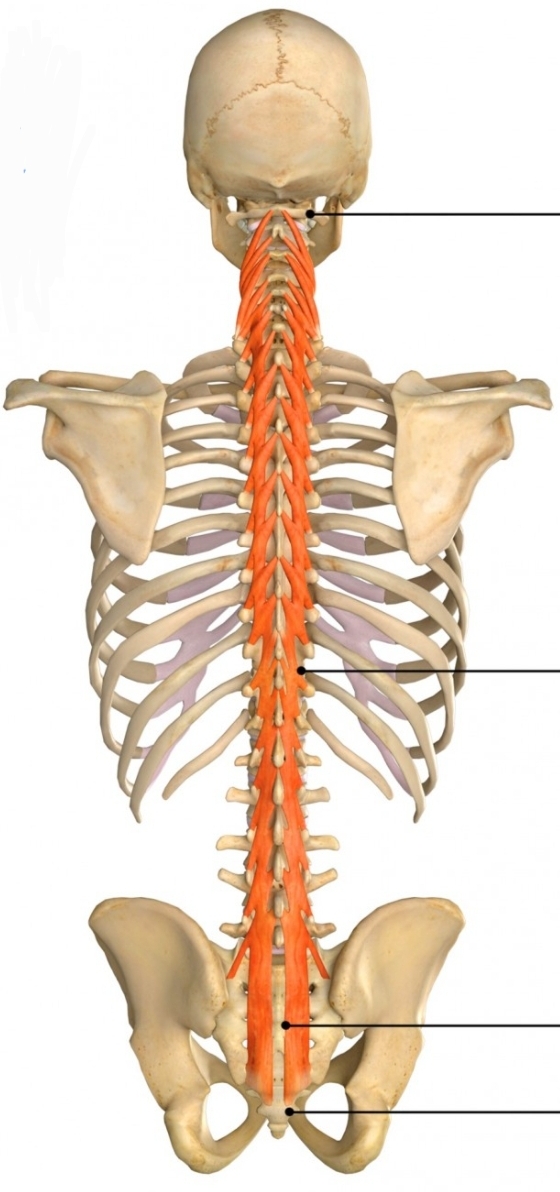
Multifidus
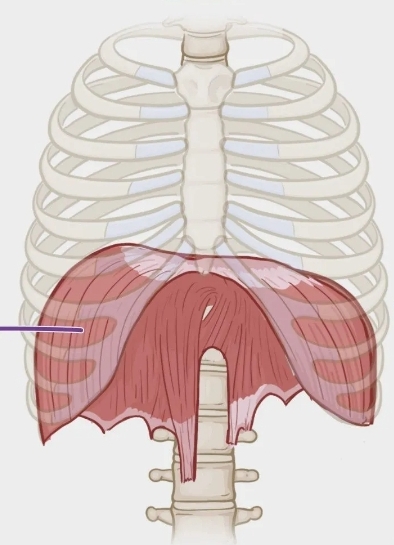
Diaphragm
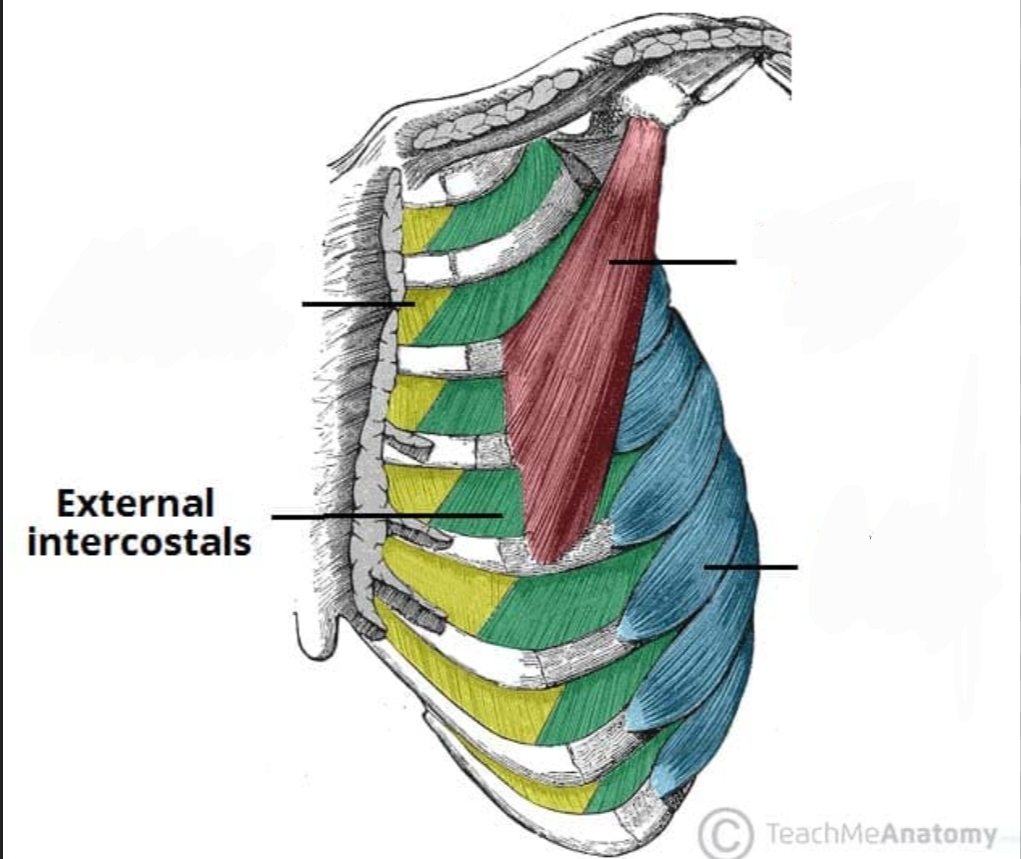
External Intercostals
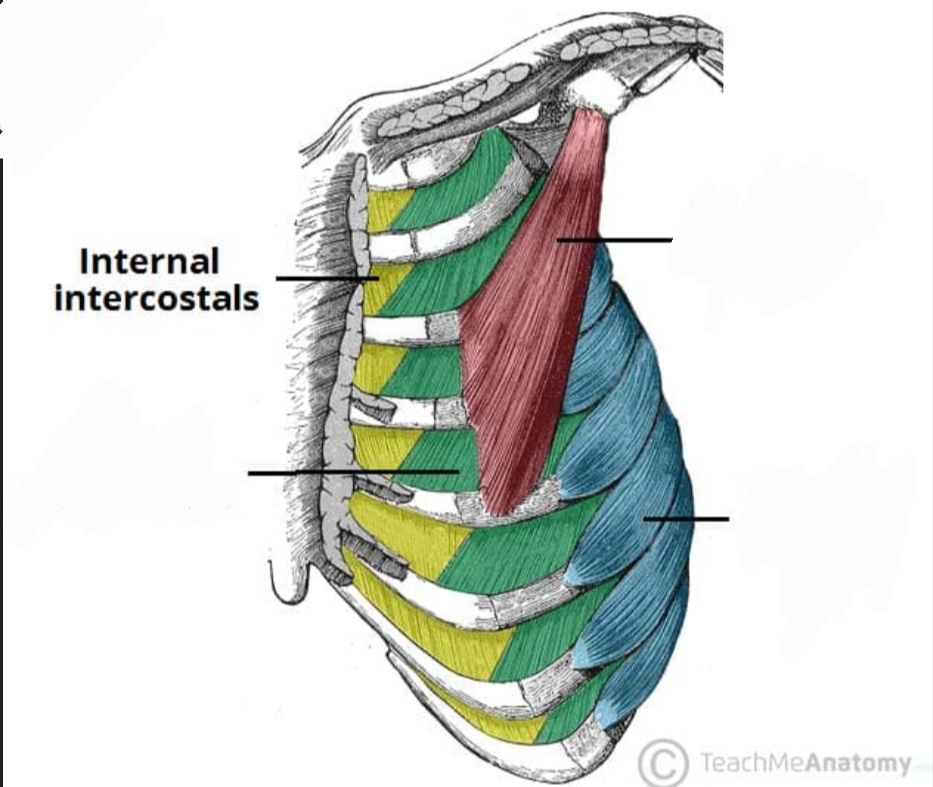
Internal intercostals
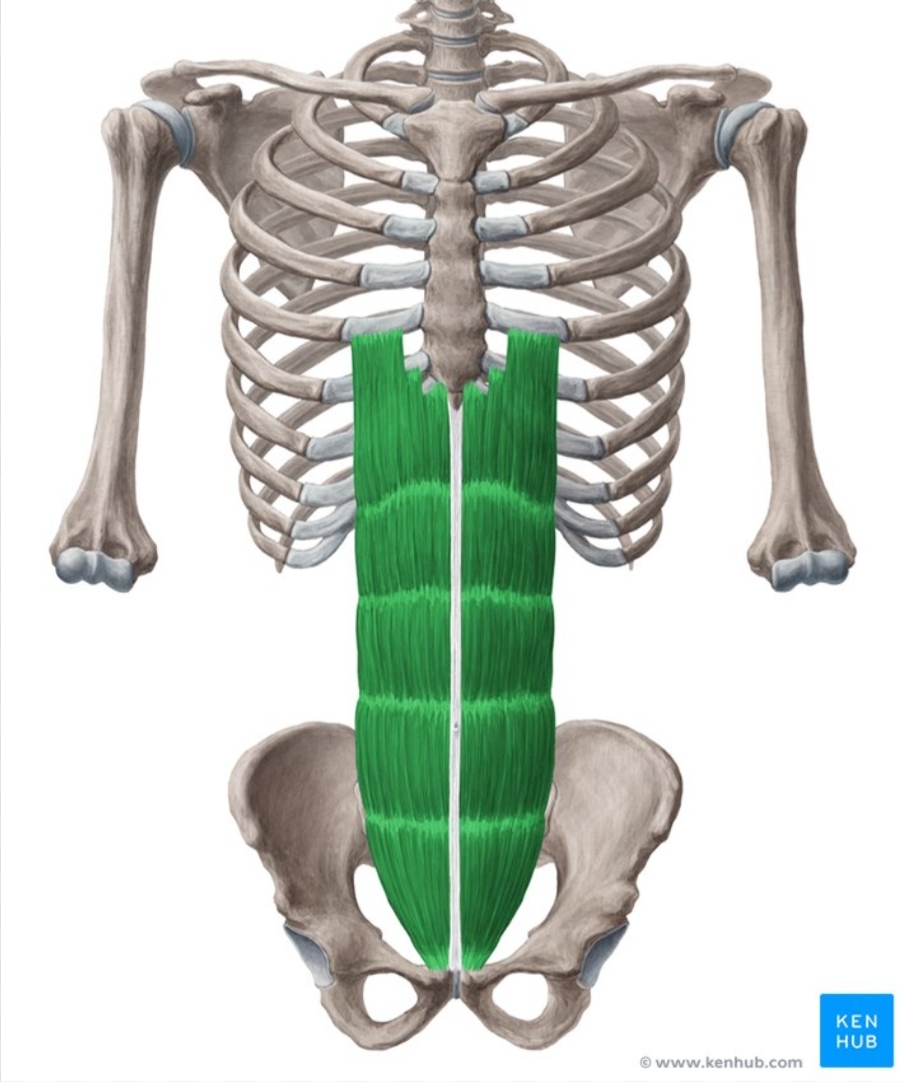
Rectus abdominis
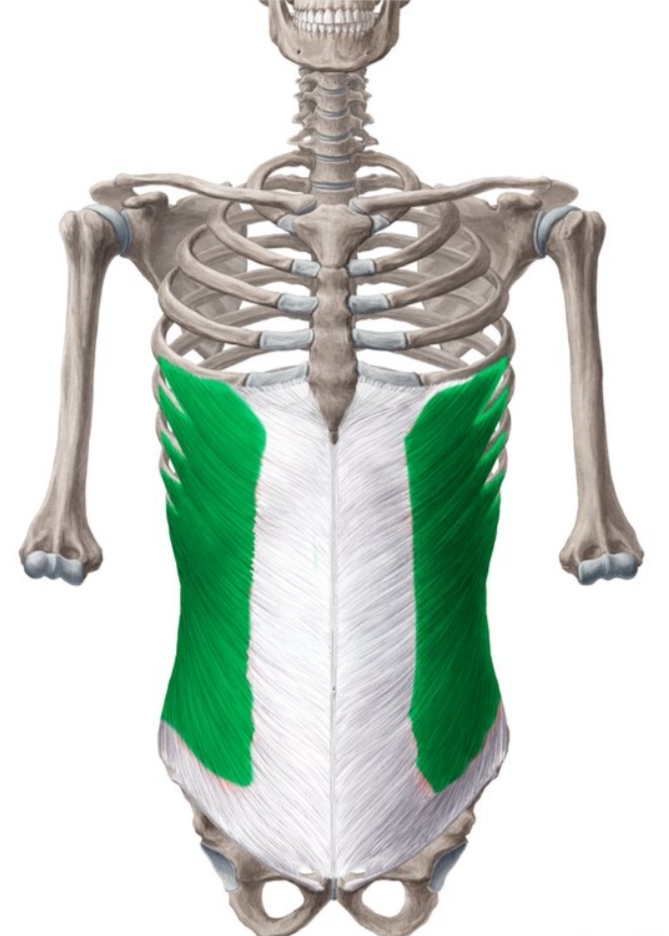
External oblique
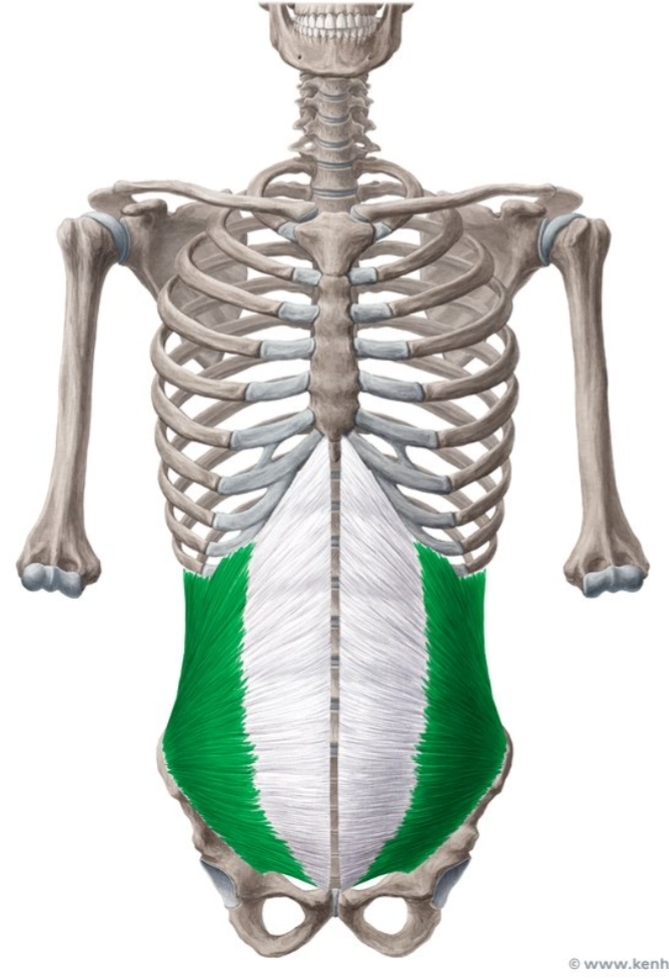
Internal oblique
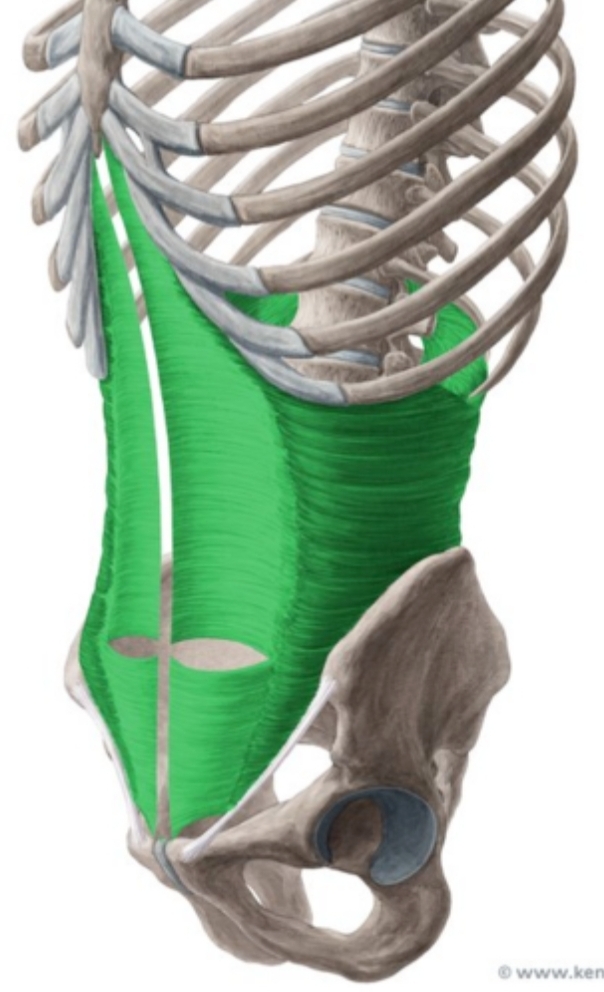
Transversus abdominis
Smooth muscle has…
Non striated contractions and are spindle shaped
Skeletal muscle has…
Excitability, contractility, extensibility, elasticity, thermal generation, and stations
Cardiac muscle has…
Contractilit, conductivity, excitability, automaticity, and intercalated disks
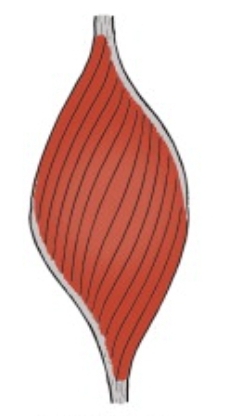
Digital extensor is an example of what muscle shape?
Unipennate
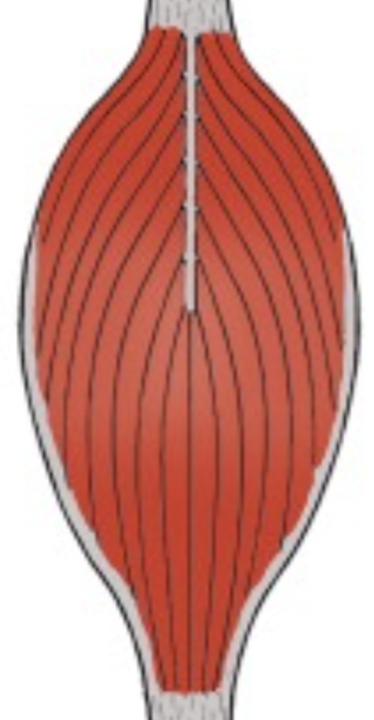
Rectus femoral is an example of what muscle shape?
Bipennate

Deltoid is an example of what muscle shape?
Multipennate

Abdominal muscles are an example of what muscle shape?
Parallel
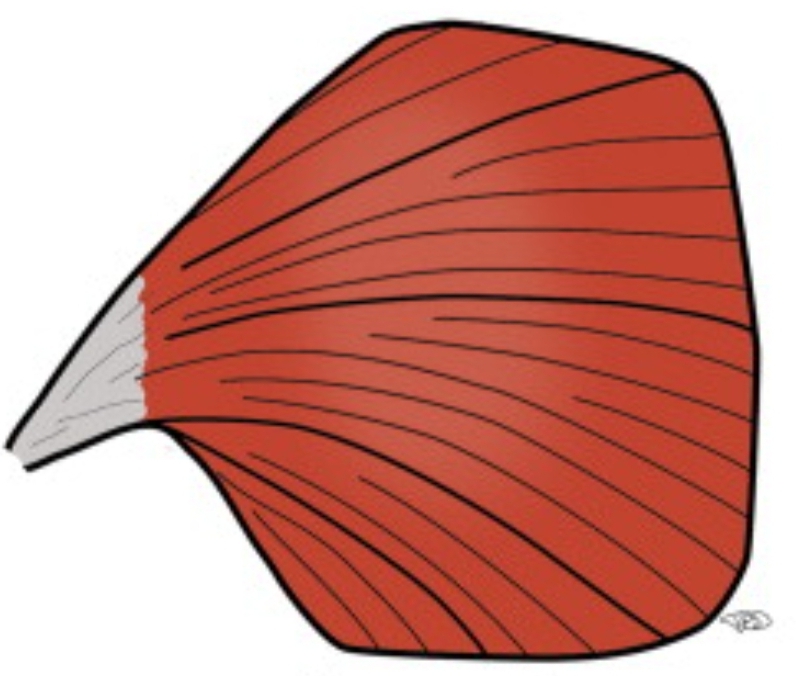
Pectoralis is an example of what muscle shape?
Convergent

Orbicularis oris/ oculi is an example of what muscle shape?
Circular
Agonist
Rhe primary muscle responsible for initiating and controlling a specific movement at a joint by contracting
Antagonist
A muscle that opposes or reverses the action of another muscle
Synergists
Muscles that work together to produce a specific movement
Fixators
Muscles that help stabilize a joint or body part during movement
Aponeurosis
Flat sheets of connective tissue in your body that are similar to tendons
Contractility
The inherent ability of muscle, particularly cardiac muscle, to contract and generate force, independent of preload and afterload
Excitability
A cell's ability to respond to stimuli, particularly neurons, through rapid changes in membrane potential
Extensibility
The ability of a muscle or other tissue to be stretched or elongated without sustaining damage
Elasticity
A tissue's ability to return to its original shape and size after being stretched or deformed
The property of muscle that allows it to return to its original shape after contration is
Elasticity
A muscle that would hold a bone in place during a particular action is called a…
Fixator
What actions are produced by the muscles that attach to the mandible
Elevation, depression, adduction, and retraction
The facial nerve innervation (contracts muscle fiber) of…
Most facial muscles
The muscle that aids in chewing, but does not move the mandible is the…
Buccinator
What muscle doesn’t act on the vertebral column?
External intercostals
What muscles act on the vertebral column?
Interspinalis, longissimus, multifidus, and semispinalis
Depression of the ribs during forced exhalation is due to contrsction of the…
Internal intercostals
The___muscle, named for its two bellies, opens the mouth
Digastric
One of the distinguishing features of mammals is the ability to suckle. This action is due to contraction of the___muscle
Buccinators
When you bow your head, for example during prayer, it is due to contraction of the___muscle
Sternocleidomastoid
A circular muscle that controls the size of an opening or passage is a/an___
Sphintor
Rectus abdominis
Compresses abdomen and flexes vertebral column
Iliocostalis
Flexes laterally, extends and rotates vertebral column
Shaking the head consists of what muscles?
Sternocleidomastoid, semispinalis capitis, and splenius capitis
Whistling consists of what muscles?
Buccinator & orbicularis oris