Acoustic Properties of Sound
1/24
Earn XP
Description and Tags
These flashcards cover key terms and concepts discussed in the lecture on the acoustic properties of sound.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
Articulatory phonetics:
analyses organs and muscles used to produce speech
Acoustic phonetics:
physical properties of speech sounds as they travel in the air from speaker to listener
Auditory phonetics:
effects of sounds when they reach listener’s ear
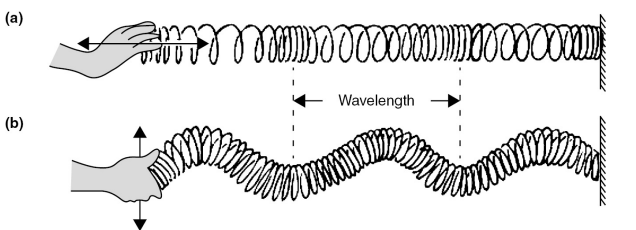
There are three types of mechanical waves:
transverse waves, longitudinal waves, and surface waves. Sound waves are longitudinal waves.
transverse waves
Longitudinal Wave
Sound waves are an example of longitudinal waves where air particles move parallel to the direction of the wave.
Waveform
visible representation of the sound waves of recorded sounds. In Praat, the waveform appears in the upper panel.
Wave Types
Three types of mechanical waves are transverse waves, longitudinal waves, and surface waves.
Intensity
acoustic correlate of what we perceive as loudness
– Amplitude over time over an area
– Measured in dB
– Varies with some linguistic factors (manner of articulation, stress)
– Varies with non-linguistic factors (relative loudness of individual speaker, sex, distance from the microphone)
Intensity
The acoustic correlate of what we perceive as loudness; measured in decibels (dB).
– Intensity > Show Intensity
– Select a portion of a sound.
– Intensity > Get intensity (gives you a mean)
– . . . or Get maximum intensity
– . . . or Get minimum intensity
Different articulatory configurations produce
different air pressure variations.
Voiceless sounds
have an aperiodic waveform: no regular pattern.
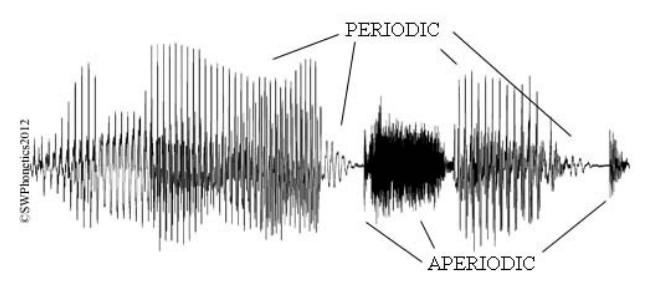
Voiced sounds
Vibrating vocal folds chop up airstream into regular pulses of low and high pressure. They have periodic waveforms: very regularly patterned.
frequency
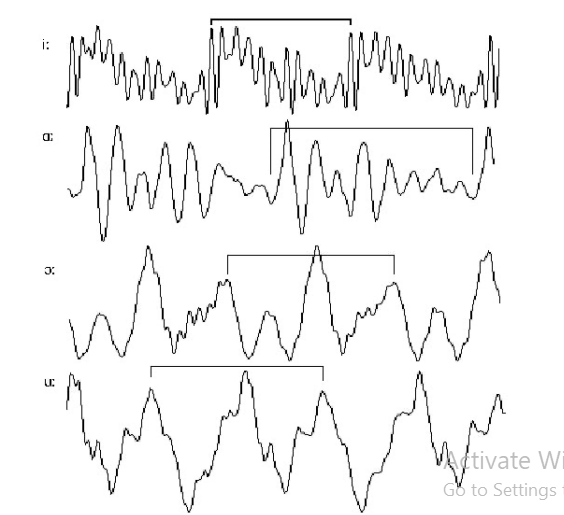
We can measure how many cycles occur per second (equals to number of vibrations per second of vocal cords) – that’s the frequency of a sound. We measure it in Hertz (Hz).
Sine vs. complex waves:
The waveforms of voiced sounds are complex waveforms. They consist of combinations of several simple periodic waves / sine waves.
Sine waves
have only one frequency. They can differ in frequency, e.g. 150Hz or 300Hz or 450Hz, and phase (the relative beginning of each cycle of the wave). They do not occur in speech.
Complex waves
have more than one frequency because they consist of combinations of sine waves. When a complex wave leaves the larynx it is significantly modified in the vocal tract. This is because the position of the tongue, velum and other articulators changes the way the vocal tract resonates.
Spectrograms
are a way to visualise the intensity and different frequencies of voiced speech sounds.

Formants
frequency areas with high intensity
Periodic Waveform
A waveform with a regular pattern, typically produced by voiced sounds.
Aperiodic Waveform
A waveform with no regular pattern, typically produced by voiceless sounds.
Complex Waves
Waves that consist of combinations of several simple periodic waves, such as voiced sounds.
Sine Wave
A wave with only one frequency; does not occur in speech.
Acoustic Properties
Physical properties of speech sounds as they travel through the air from speaker to listener.
Speech Synthesis
The artificial production of human speech, applying principles of acoustic properties.