ECON 2020 Exam 3
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
You run a business growing heirloom tomatoes in a greenhouse. When you employ only yourself and use 10 pounds of fertilizer, you can harvest 50 tomatoes. When you employ both yourself and a friend, and use 20 pounds of fertilizer, you can harvest 120 tomatoes. This is an example of:
A) Coordination problems
B) Constant returns to scale
C) Increasing returns to scale
D) Decreasing returns to scale
C) Increasing returns to scale
You are running a bakery in a perfectly competitive market, and have already determined that your profit-maximizing quantity of bread to bake is 18 loafs every day. When you bake 18 loafs of bread, your average variable cost is $12 and your average total cost is $16. At what market price would a firm choose to NOT shut down in the short-run, but exit in the long-run?
A) $10
B) $14
C) $18
D) $20
B) $14
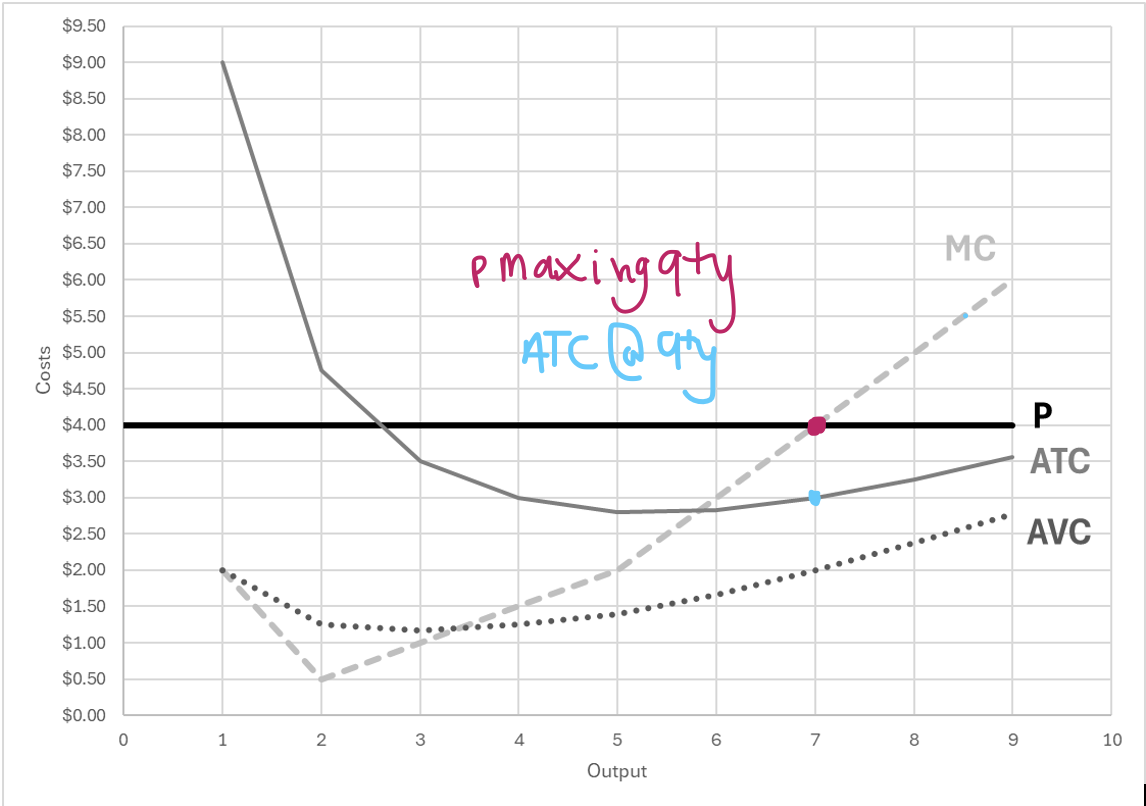
Suppose the above graph is for a firm in perfect competition. Calculate short-run profit.
A) $0
B) $7
C) $14
D) $28
B) $7
Q*(P-ATC)
7*(4-3)
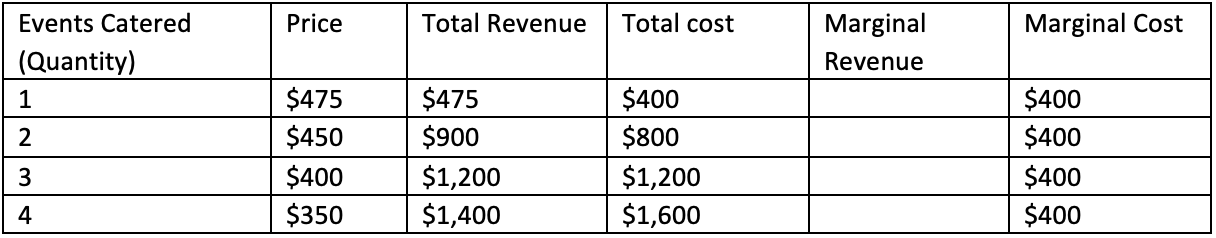
Consider the following table which gives weekly information on a local catering business. There are no other caterers in the area, so the business has market power. What is the business’s profit-maximizing price and quantity?
A) 1 event catered at $475
B) 2 events catered at $450
C) 3 events catered at $400
D) 4 events catered at $350
B) 2 events catered at $450
Compared to perfect competition, a setting in which firms have market power is inefficient due to:
A) Higher prices
B) An insufficient number of consumers in the market
C) Large producer profits
D) Underproduction
D) Underproduction
For identical firms, compared to prices in perfect competition, prices in monopolistic competition are:
A) Always higher
B) Always lower
C) The same
D) Sometimes higher and sometimes lower
A) Always higher
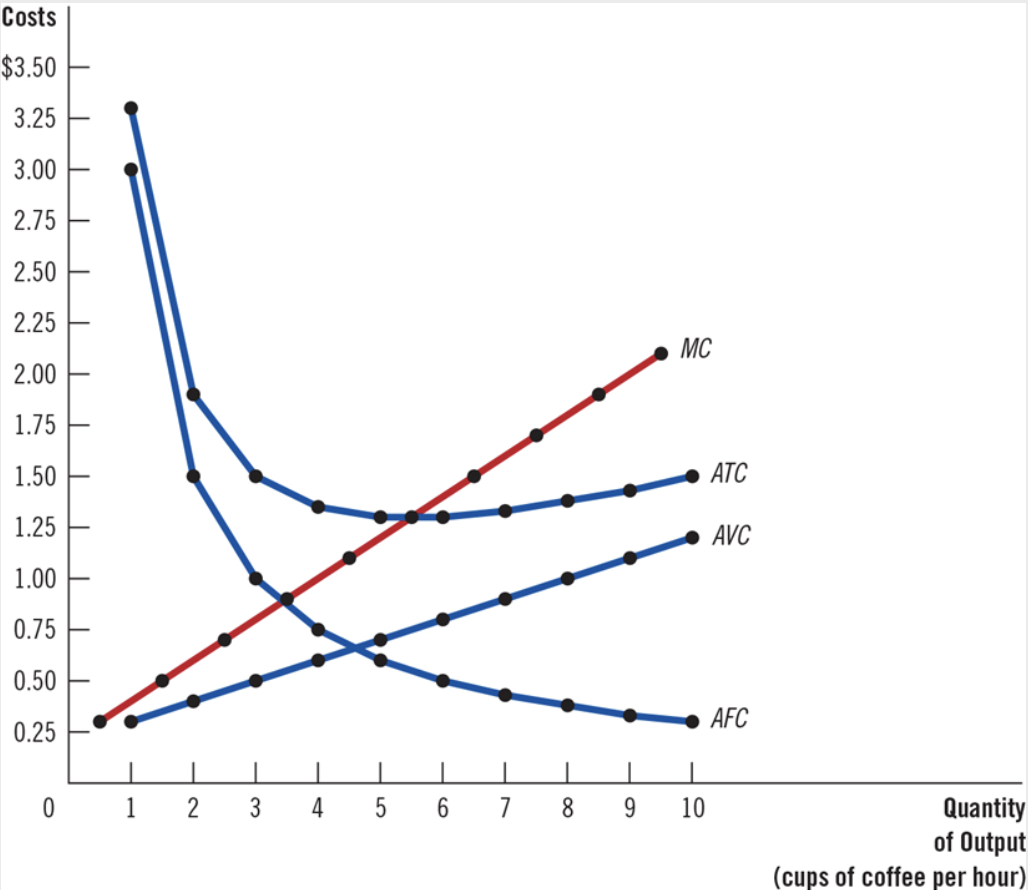
Approximate the efficient scale of production for this firm.
A) 5.5 cups of coffee
B) 1.25 cups of coffee
C) 3.5 cups of coffee
D) 4.5 cups of coffee
A) 5.5 cups of coffee
In the long-run, fixed costs:
A) Are 0.
B) Are decreasing.
C) Are increasing.
D) Are graphically a flat U shape.
A) Are 0.
A firm in a perfectly competitive market earned $1,000 in total revenue. The marginal revenue on its last unit sold is $10. What is the market price and how many units were sold?
A) P = $50, Q = 20
B) P = $100, Q = 10
C) P = $5, Q = 200
D) P = $10, Q = 100
D) P = $10, Q = 100
Select the statement that is true of perfect competition.
A) In the long-run, firms produce at the efficient scale.
B) Perfect competition does not maximize total surplus.
C) Firms in perfect competition face individual demand curves that are downward sloping.
D) In the short-run, firms always make negative profit.
A) In the long-run, firms produce at the efficient scale.
At the profit maximizing quantity for a monopolist:
A) P=MR=MC
B) P>MR=MC
C) P=MR>MC
D) P<MR=MC
B) P>MR=MC
Suppose that Louise is the only person licensed to rent out tandem bicycles on the boardwalk in her small hometown. When she increases her rentals from 15 tandem bicycles to 16 tandem bicycles, the market rental price declines from $35 per rental to $34 per rental. The marginal revenue of the 16th tandem bicycle is:
A) $19
B) $9
C) $29
D) $1
A) $19
The prisoner's dilemma shows that a Nash equilibrium:
A) Generally causes cooperation.
B) Is rational but can be inefficient.
C) Does not always exist.
D) Always delivers the best possible outcome.
B) Is rational but can be inefficient.
You would like to buy a new personal computer. You can get a discount on it if you buy the personal computer along with a monitor, keyboard, and mouse. This is an example of:
A) Bargaining power
B) Price competition
C) The hurdle method
D) Bundling
D) Bundling
Marginal Product of an Input
Increase in output after adding one or more of that input
Total product ______ in the number of inputs, and marginal product to be ______ in the number of inputs.
Increases; decreases