Bio 152 Exam 2
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
Phylogeny
The sequence of events involved in the evolutionary development of a species or taxonomic group of organisms
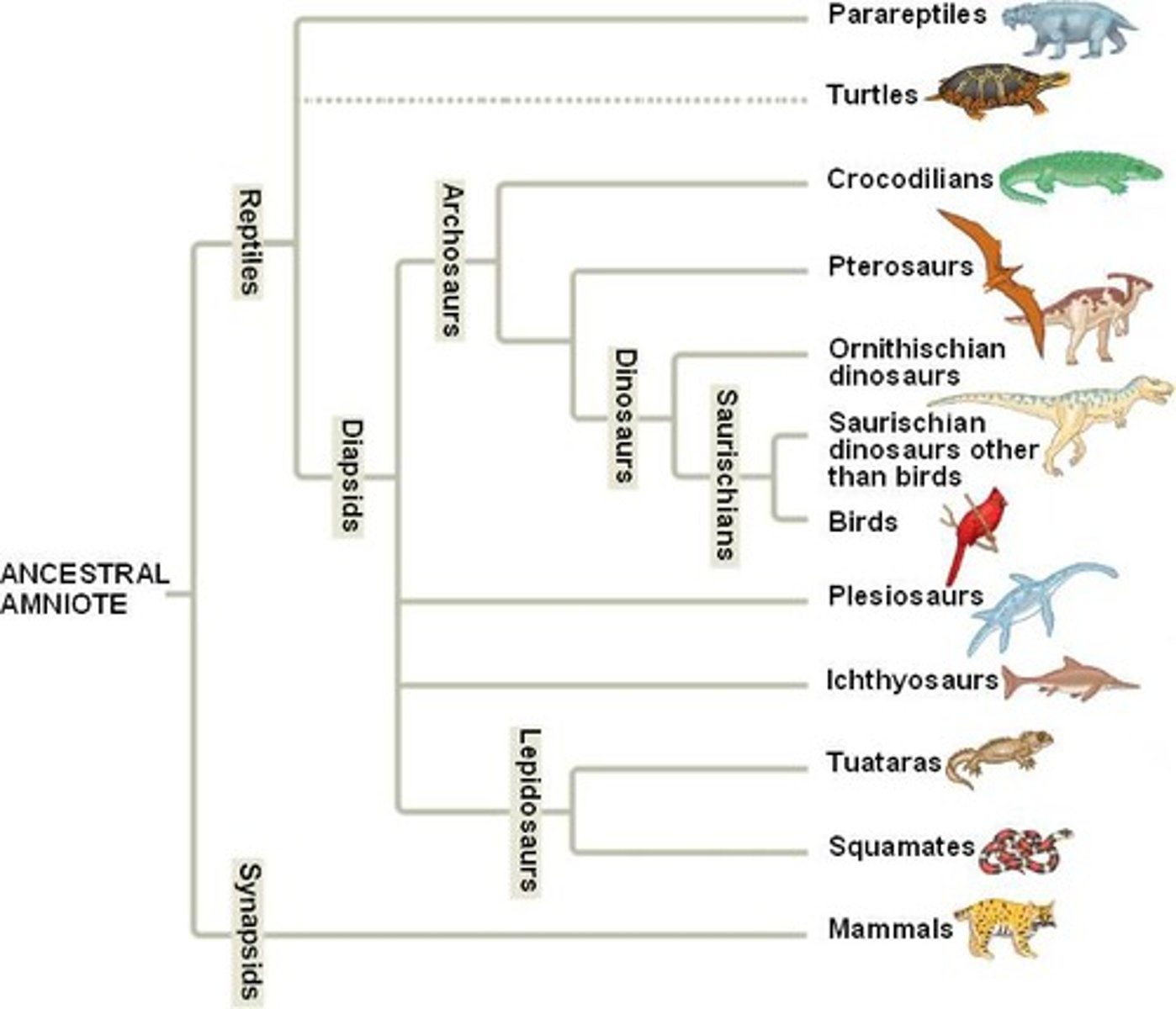
Nodes
Indicates common ancestors in phylogenetic trees
Taxa
Any named group of organisms in phylogenetic trees
Sister Taxa
Two descendants that split from the same node in phylogenetic trees.
Outgroup
a taxon outside the group of interest. All the members of the group of interest are more closely related to each other than they are to this group. Hence, this group stems from the base of the tree.
Clade
A group of organisms that includes all the descendants of a common ancestor and that common ancestor.
Ancestral Trait
The trait originally present in the ancestor of a given group; may be retained or changed in the descendants of that ancestor.
Derived Trait
A trait that differs from the ancestral trait.
Synapomorphy
A trait that arose in the ancestor of a phylogenetic group and is present (sometimes in modified form) in all of its members, thus helping to delimit and identify that group. Also called a shared derived trait and describes a monophyletic group.
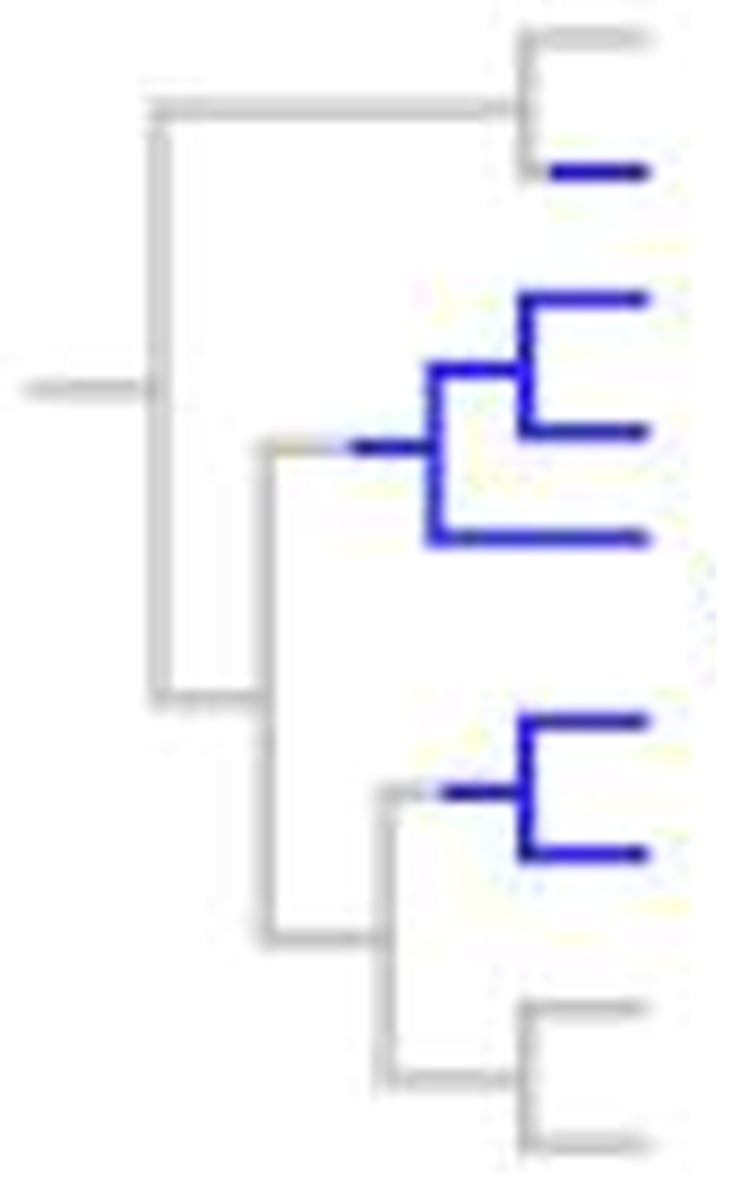
Monophyletic Group
group that consists of a single ancestral species and all its descendants and excludes any organisms that are not descended from that common ancestor
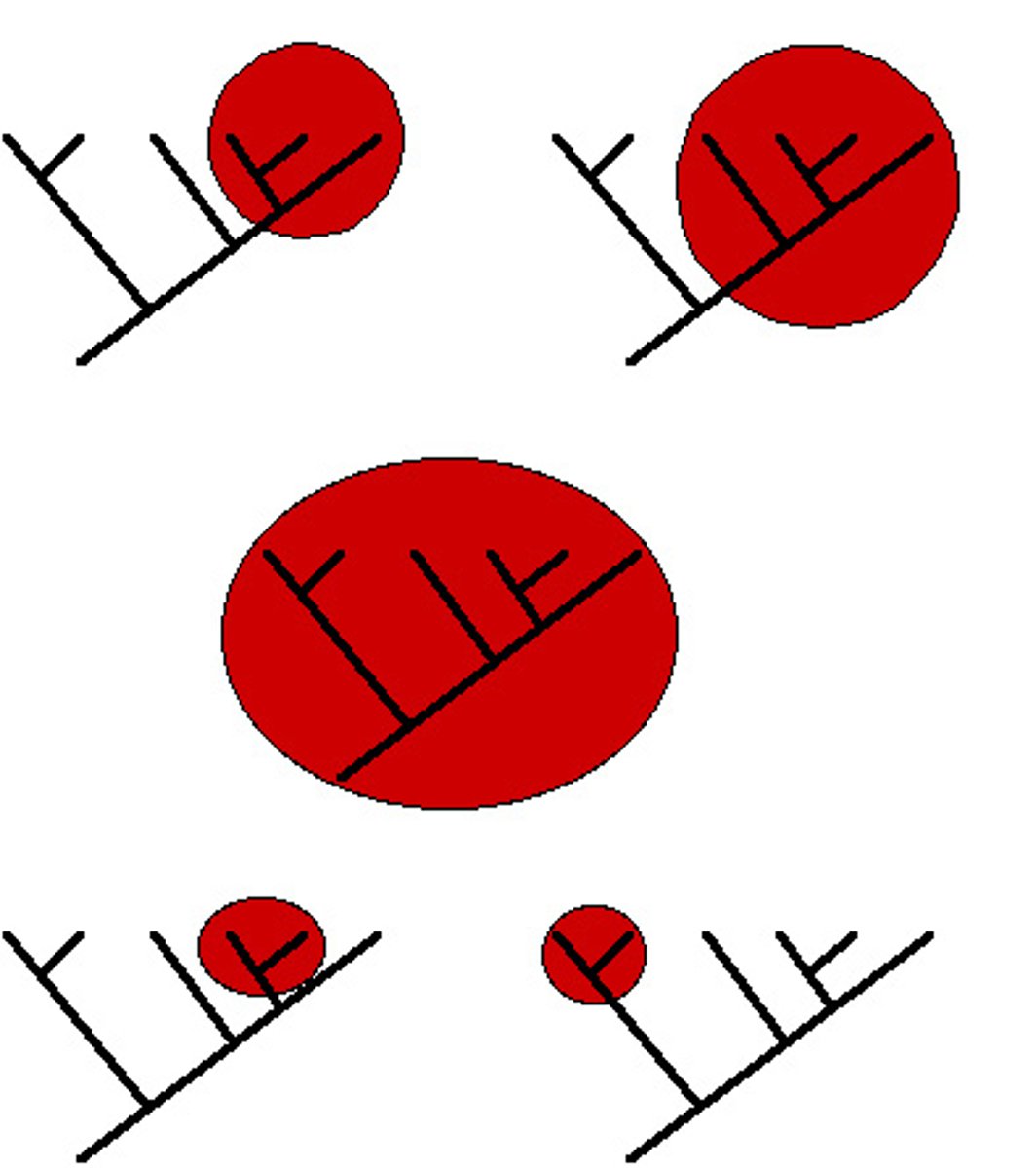
Paraphyletic Group
Composed of some, but not all, members descending from a common ancestor.
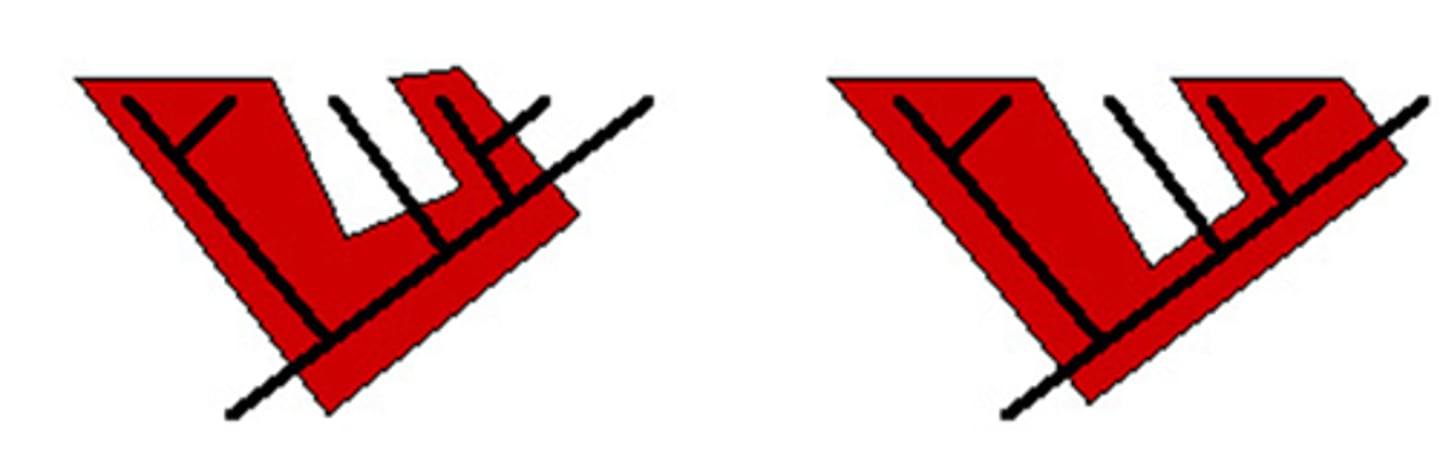
Polyphyletic Group
A taxonomic grouping consisting of several species that lack a common ancestor (more work is needed to uncover species that tie them together into a monophyletic clade).
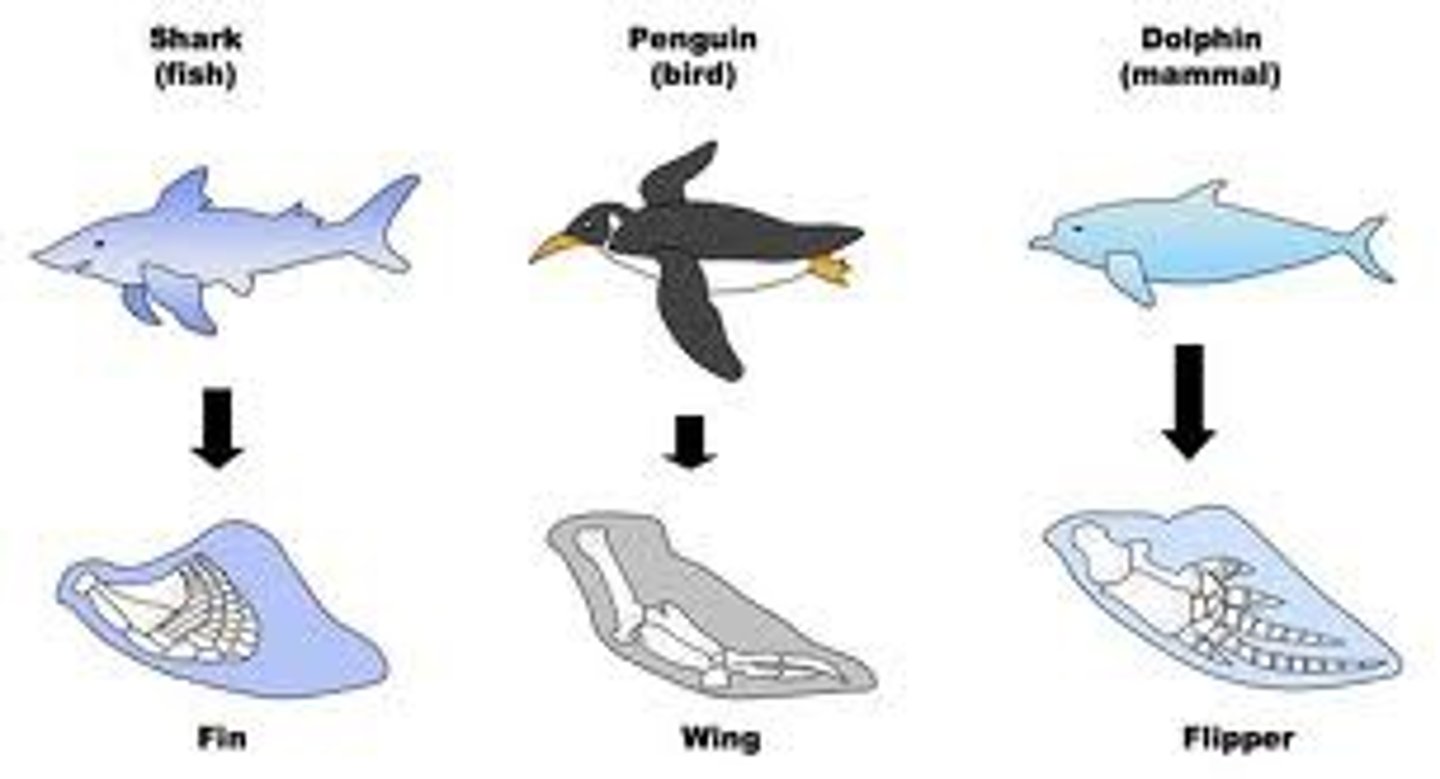
Analogous Traits
arise when groups independently adapt to similar environments in similar ways; evidence of convergent evolution.
Homologous Traits
Features that are inherited from a common ancestor.
Convergent Evolution
Process by which unrelated organisms independently evolve similarities when adapting to similar environments.
Parsimony
Preferring the simplest among a set of plausible explanations of any phenomenon.
Molecular Clock
The approximately constant rate of divergence of macromolecules from one another over evolutionary time; used to date past events in evolutionary history.
LUCA
Scientists think one early cell gave rise to all subsequent life on Earth. That one cell is called the ________.
Simple Multicellularity
1. Have cell-to-cell adhesion molecules.
2. They have no, to few, specialized cells.
3. They rely on diffusion for nutrient transfer.
4. They do not have genetic regulation of development.
Complex Multicellularity
1. Different cell types
2. Different tissues
3. Organs
4. Reproductive cells
5. Bulk-flow system
6. Cell-to-cell communication
7. Genetic regulation of development
8. Cell-to-cell adhesion
Challenges a Multicellular Organism must Overcome
1. Diffusion
2. Sticking together
3. Cell-to-Cell communication
4. Regulate growth & development
Diffusion
The net passive movement of particles (atoms, ions or molecules) from a region in which they are in higher concentration to regions of lower concentration. It continues until the concentration of substances is uniform throughout.
Bulk-flow System
This process uses vessels and pressure to move nutrients around the organism. All complex-multicellular organisms large enough have this.
Hierarchical Control of Development
Once anterior/posterior polarity is established, different genes control the segmentation in this process. Each set in the hierarchy is a transcription factor that leads to transcription of proteins but also transcription of the next layer of regulation.
1. Maternal effect genes
2. Gap Genes
3. Pair-rule genes
4. Segment Polarity genes
Hox clusters show up throughout.
Maternal Effect Genes
Deals with anterior & posterior determination (bicoid & nanos genes).
Gap Genes
Controls the broad sections of the embryo (middle region & head region).
Pair-rule Genes
Defines segment pairs.
Segment Polarity Genes
Determines anterior and posterior of each segment.
HOX Clusters
Groups of homeobox genes. More complex organisms have more such groups, probably due to a mutation that duplicated them.
HOX Genes
They code for transcription factor that regulate gene expression in the embryo. They determine the basic structure and orientation of an organism. It goes and turns on a bunch of other genes that turn on development of body parts.
Ectopic Expression
Expressed at the wrong place and time.
Knocked-Out Expression
No particular segment formation as a result of no expression of that gene, where there should be expression of that gene normally.
Combinatorial Control of Development
Different transcription factors acting together to lead to different cellular outcomes.
Carpel
the female reproductive organ of flowering plants. It contains the egg.
Stamen
The male reproductive organ of flowering plants. Produces the pollen.
Petal
One of the often colored segments of a flower.
Sepal
One of the individual leaves of a flower.
Whorl
A circular arrangement of like parts, as leaves or flowers, around a point on an axis.
MADS Box Genes
In plants, these are involved in controlling all major aspects of development, including male and female gametophyte development, embryo and seed development, as well as root, flower and fruit development. Counterpart to HOX genes.
Charophytes
A division of freshwater green algae.
1. Didn't have to support themselves
2. They didn't need roots
3. They didn't desiccate (dry out)
4. They have motile sperm
Challenges that a Multicellular Organism Must Overcome
1. Limits of diffusion/distribution
2. Must stick together/support organism (in part)
3. Cell-to-cell communication
4. Regulate cell division and cell fate (development & reproduction)
5. Defense
Important Innovations for Plant Life on Land
1. Waxy Cuticle
2. Vasculature
3. Stomata
4. Seeds
Challenges of Plants Trying to get on Land
1. CO₂ use
2. Pressure Change
3. Moving from a salt-water environment
4. Change in light (are not shielded with water as much anymore)
Vasculature
In plants, assemblage of conducting tissues and associated supportive fibers.
Stoma
Plants use these structures and open or close them with guard cells for the transfer of storing of water and CO₂. Light and hormones are also ways to open and close these structures
Guard Cells
Each of a pair of curved cells that surround a stoma, becoming larger or smaller according to the pressure within the cells. Help open up or close the stoma opening.
Protoplasts
A plant, bacterial or fungal cell that had its cell wall completely or partially removed using either mechanical or enzymatic means.
Opening/Closing of Stoma
More solutes entered - more water rushes after to create equilibrium - means stoma is open (guard cells more curved).
Solutes rush out of stoma - water follows to create equilibrium through osmosis - means stoma is closed (guard cells straighter and closer together/no opening).
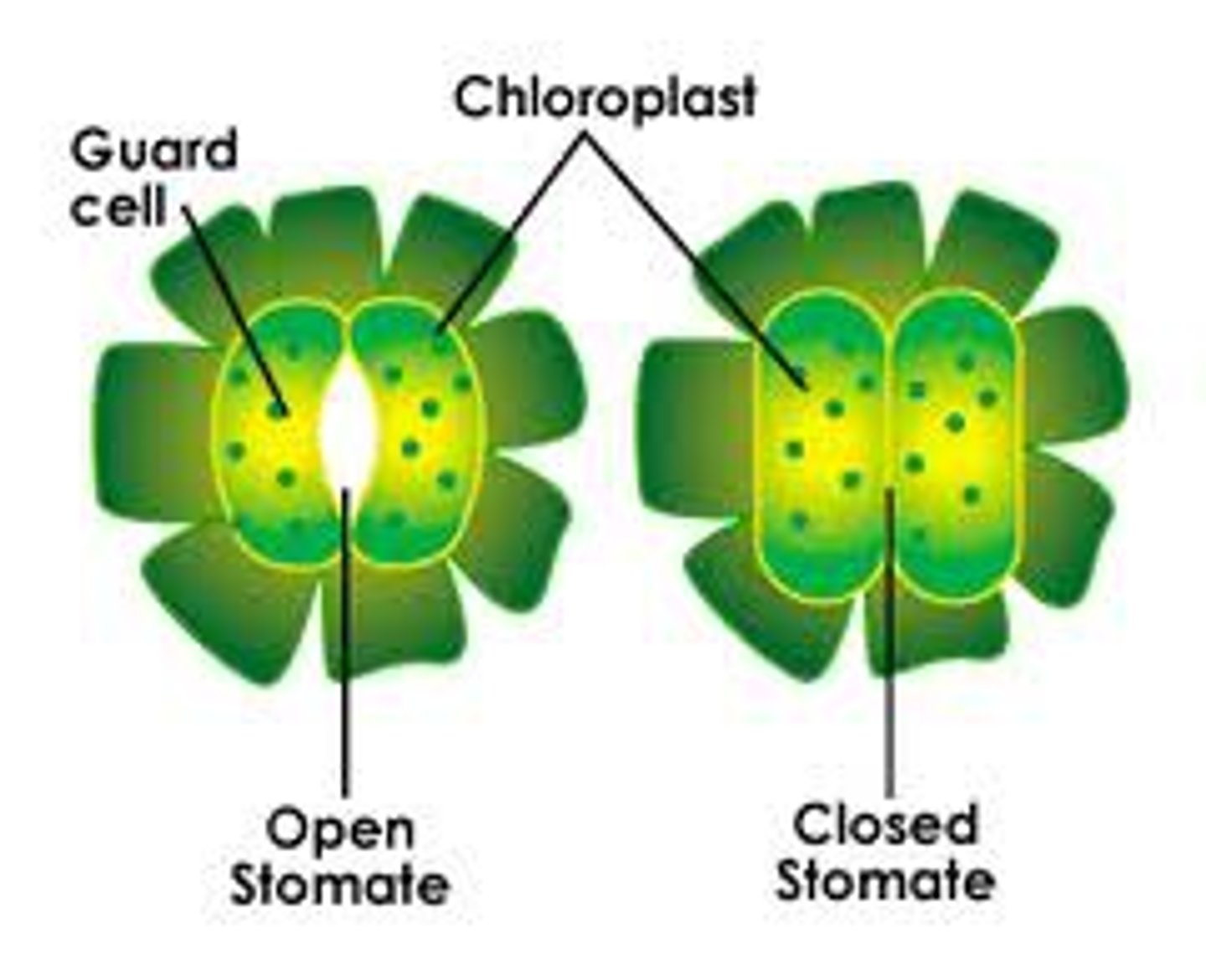
When should Stomates be open?
a. Day
b. Night
c. Winter
d. Summer
Day