Biology 1113 Lab Final
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
What should the microscope be cleaned with?
Lens wipes not kim wipes
How does the dissecting microscope magnification work?
The number on the dial is the total amount of magnification
How does the compound microscope magnification work?
Times the amount on the actual microscope by 10
What are the steps for putting the microscope away?
1. After it is cleaned put the cover on it
2. Put it in the cabinet with the arm facing out
What does hypertonic look in an animal and plant cells?
Hypertonic is when water leaves the cell due to solute count being higher in the cell
Animal- The cells shrivels (crenation)
Plant- the membrane shrinks away from the cell wall
What does isotonic look like in plant and animal cells?
Isotonic is when the solute count is even inside and outside of the cell
Animal- circular cells
Plant- Rigid cell wall with green distributed evenly
What does hypotonic look like in plant and animal cells?
Hypotonic is when the solute count is lower inside the cell so water comes into the cell
Animal- the cell bursts (lysing)
Plant- The plant cells
What is the substrate in the enzyme lab?
Hydrogen peroxide
What is the color of the oxidized guiacol?
Brown
What is the maximum slope of the line?
The highest rate
What color is DCPIP in its oxidized state?
Oxidized is blue
Why do some pigments move farther than other on chromatography paper?
They are more soluble/nonpolar
What are the products of the light reactions?
ATP and NADPH
What are the products of dark reactions?
ADP, NADP+ and one molecule for making the glucose needed for cellular respiration
What shows cytokenesis in plant and animal cells?
Animal - cells cleave together forming a figure 8
Plant- cell wall forms in the middle of the two nuclei
How do you know if a dangerous chemical is being used in the lab?
The TA will tell us and it is in the lab manual
What is the procedure if a fire alarm goes off during lab?
Immediately stop working and proceed to the exit in an orderly manner
What items can go in the trashcan?
General trash and paper towels from hand washing
What items go in the biohazard box?
Used coverslips, used pipets, discarded tissue, paper towels with chemicals, live microorganisms, blood waste, etc.
Where should liquid chemical waste go?
Chemical waste container in the fume hood
What happens if there is a spill?
Notify the TA, where gloves and clean it up with soap, water and paper towels
Where should broken glass go?
It goes in the uncontaminated broken glass box if there is nothing on it. If it has been used it goes in the biohazard box
What are the components of the microscope?
Base- part that all components rest on
Arm- part that supports the lenses and stage
Stage- flat surface where slides are placed
Mechanical stage- part that moves the slide up and down
Clip- thing that holds the slide in place
Condenser- The lens positioned immediately below the stage
Light source- The bulb
Rheostat- knob that adjusts the amount of light coming in
Objectives- set of lenses (4, 10, 40 and 100)
Nose Piece- Revolving component that objectives are on
What is parfocality?
The ability to move objectives while staying in focus
Why is dialysis tubing used to show diffusion?
Its semi-permeable; only some particles can get through
What happens when salt is added to the bag?
When the TA added the silver nitrate a precipitate should form
What happens if glucose was added?
Blue means there are no sugars; green means there are some sugars and orange means a high concentration of sugars
What happens if starch was added?
If iodine was used a black/blue color would form if they diffused through the membrane
What happens if iodine was added?
A black/blue color would form if starch was used
Does iodine or starch pass through the membrane?
Iodine passes because it is small while starch does not because it is a bigger molecule
What does DCPIP do in the photosynthesis?
Can measure photosynthetic activity due to being reduced by the light reactions instead of NADP+. Becomes clearer as the activity increases
Why are pigments different colors?
They accept different wavelengths and reflect certain ones giving them their color
Is starch present if a leaf is grown in the dark?
No it is only done where light reactions can take place.
What is a characteristic of a meristem in a plant root?
Small cells that are not as big as the others
Flip it over to see the image
Identify what is happening in each of these steps
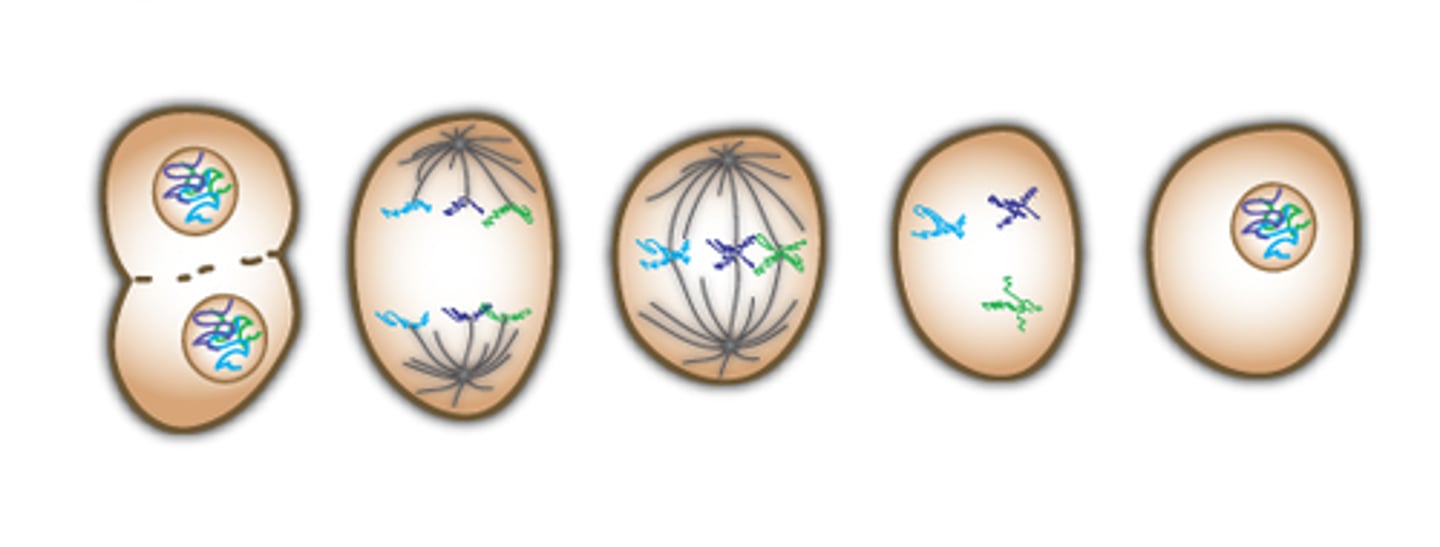
Does the process of mitosis take up a majority of the cell cycle?
NO!
What does asexual reproduction look like?
Budding- like a stem off the main plant
Fission- elongation of cells into torpedo shape before they split
How do scientists use karyotypes?
To identify mutations or see how chromosomes compliment each other
What is the law of segregation?
Alleles seperate to end up in seperate gametes
What is the law of independent assortment?
Alleles seperate without any influence from the other ones
What is a null hypothesis?
A hypothesis that states that nothing will happen and if it does it is just random error
What is an alternative hypothesis?
Just states that something will happen not due to random error
What factor can affect the phenotype?
The environment
Steps to a chi-squared test
1. Take the observed minus the expected (deviation)
2. Square the deviation
3. Divide deviation squared by expected
4. Add up for each class
Where do we get the degrees of freedom for the Chi-squared test?
Its the classes minus one
What is the convential p-value?
0.05
Should you reject the null hypothesis if it is greater or less than the value on the table?
If it is greater, reject the null
What did Griffith learn in his experiment?
That even if a virus was killed with heat, it would somehow transfer its genetic material to a non-virulent strain in order to kill the host
What makes up a nucleic acid?
The phosphates, the sugars and the nitrogenous bases
Is the phosphate on the 5 prime or 3 prime end of a nucleotide
The 5 prime, the sugar is on the 3 prime and the base is on the 1 prime
What element was important for finding the real source of heredity?
Phosphate which is found in nucleic acids and not proteins
What was the basis of the argument that proteins were the source of heredity?
The variety of amino acids
What led to the discovery of the semi-conservative type of replication?
Mendelson and Stahl's experiment about light and heavy nitrogen bases
How does conservative replication work?
The strand splits, and replicated and the original strand comes back together and the new strand is formed
How does semi-conservative replication work?
Each strand is split in half and replicating resulting in strands with half the old and half the new DNA
How does dispersive replication work?
The old DNA is broken up into segments and each strand has bits of old and new DNA
What does PCR stand for?
Polymerase chain reaction
Why is taq polymerase used in the experiment?
It can withstand the high heat needed
What is the process of PCR?
1. Heating to denature
2. Annealing (cooling to allow promoter to bind)
3. Extension (polymerase replicates)
What was used to break down the barrier of the cell?
Salt and a blender
What is Instagene?
Prevents DNAses from breaking down the DNA in the tube
How does gel electrophoresis work?
The more negatively charged/smaller parts separate out further to create distinct lines that can be compared to a known sample
Where was CRISPR discovered?
In bacteria as a way to fight off viruses?
What makes up the complex for CRISPR?
The cas 9 protein and guide RNA
What eventually stopped the end of the hand washing problems?
The pictures of the bacteria on their hands
Why is the scientific method considered a nonlinear process?
Because you can start at any step or go back if you need to
What is a precaution that must be taken while setting up PCR?
Preventing sample exposure to DNAses
What things are true about a Chi-squared test?
Increasing sample size decreases Chi-squared
An increase in deviation increases the Chi-squared value
An increase in the number of classes increases the chi-squared value
In what order do you clean the lenses after oil has been used?
4, 10, 40 then 100
How do enzynes catalyze chemical reactions?
Decreasing the activation energy of a reaction