Investigations Nature of Science
1/96
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
97 Terms
Inference
a conclusion based on evidence, observation, and reasoning
Control Group
a group of specimens in an experiment to which no change is made; does not receive the experimental treatment
Example.
In an experiment investigating the effect of talk therapy on alleviating depression, the group receiving only the medicine would be the control group.
Stratigraphy
the branch of geology that studies the formation and characteristics of rock strata
Democritus
Greek philosopher who believed that atoms were uniform, incompressible, and indestructible; named the building blocks of matter atomos
Gregor Mendel
Austrian biologist known as the father of modern genetics; formulated the three laws of inheritance based on his experiments on pea plants, leading to his terming of dominant and recessive genes.

Dmitri Mendeleev
A chemist (1834-1907) who published the first periodic table with elements arranged by mass

Dmitri Ivanovsky
Russian biologist who proved the existence of an infectious agent causing disease in tobacco plants using the Chamberland filter-candle

Wolfgang Pauli
Austrian physicist who discovered the existence of neutrons and developed the Pauli exclusion principle

Uncertainty Principle
a fundamental property of nature: it is impossible to exactly determine both the position and momentum of a particle at a given time
Ernest Rutherford
New Zealand physicist who discovered that nearly all the mass of an atom is in its nucleus and contributed to the Geiger-Marsden gold foil experiments

Albert Einstein
German physicist who:
Proposed the equivalence of matter and energy based on the constant speed of light in all reference frames
Developed the theory of general relativity stating that an object's gravity is due to the curvature of space
Proposed the existence and size of atoms using Brownian Motion
Explained the photoelectric effect as due to the quantization of light
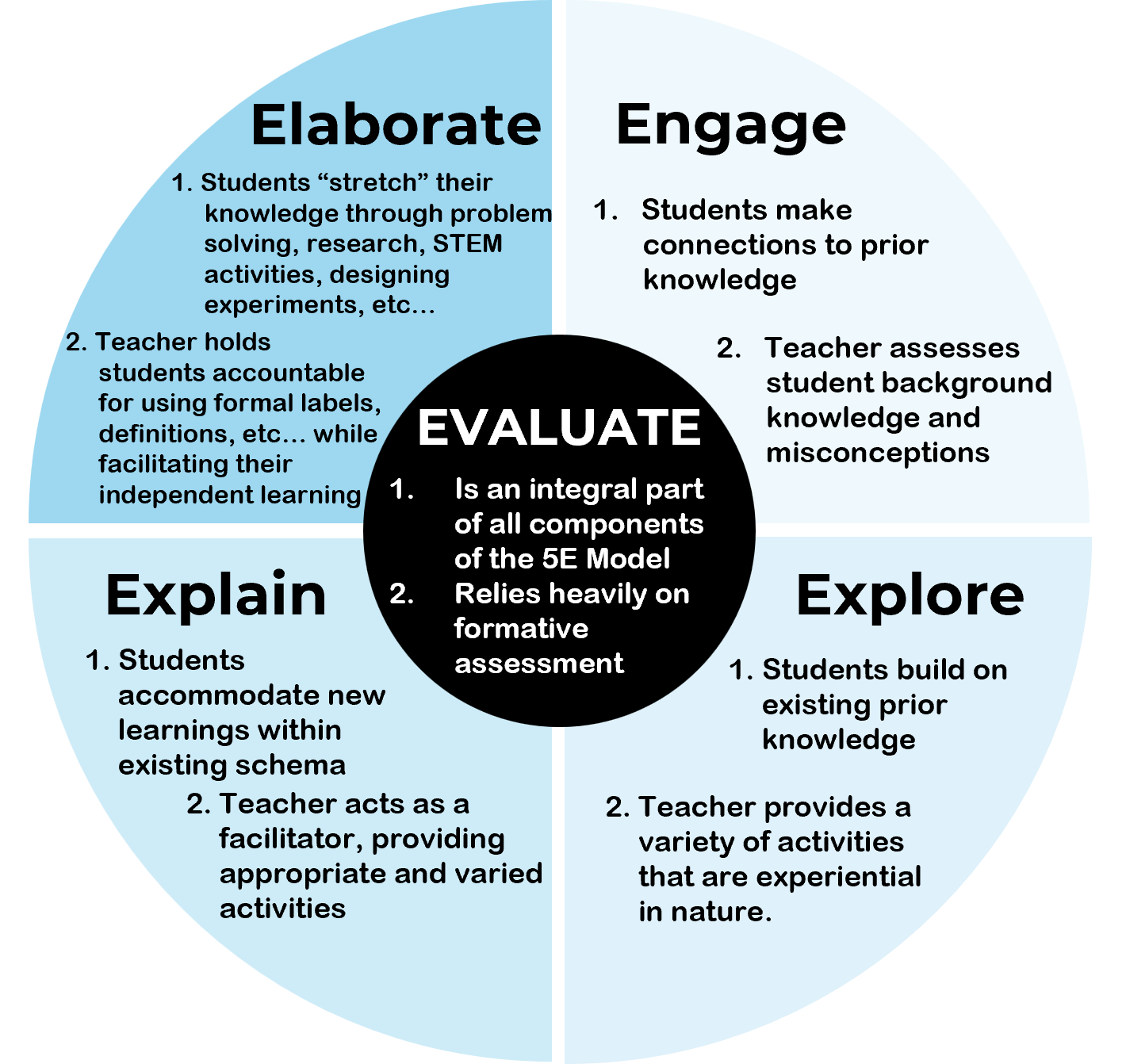
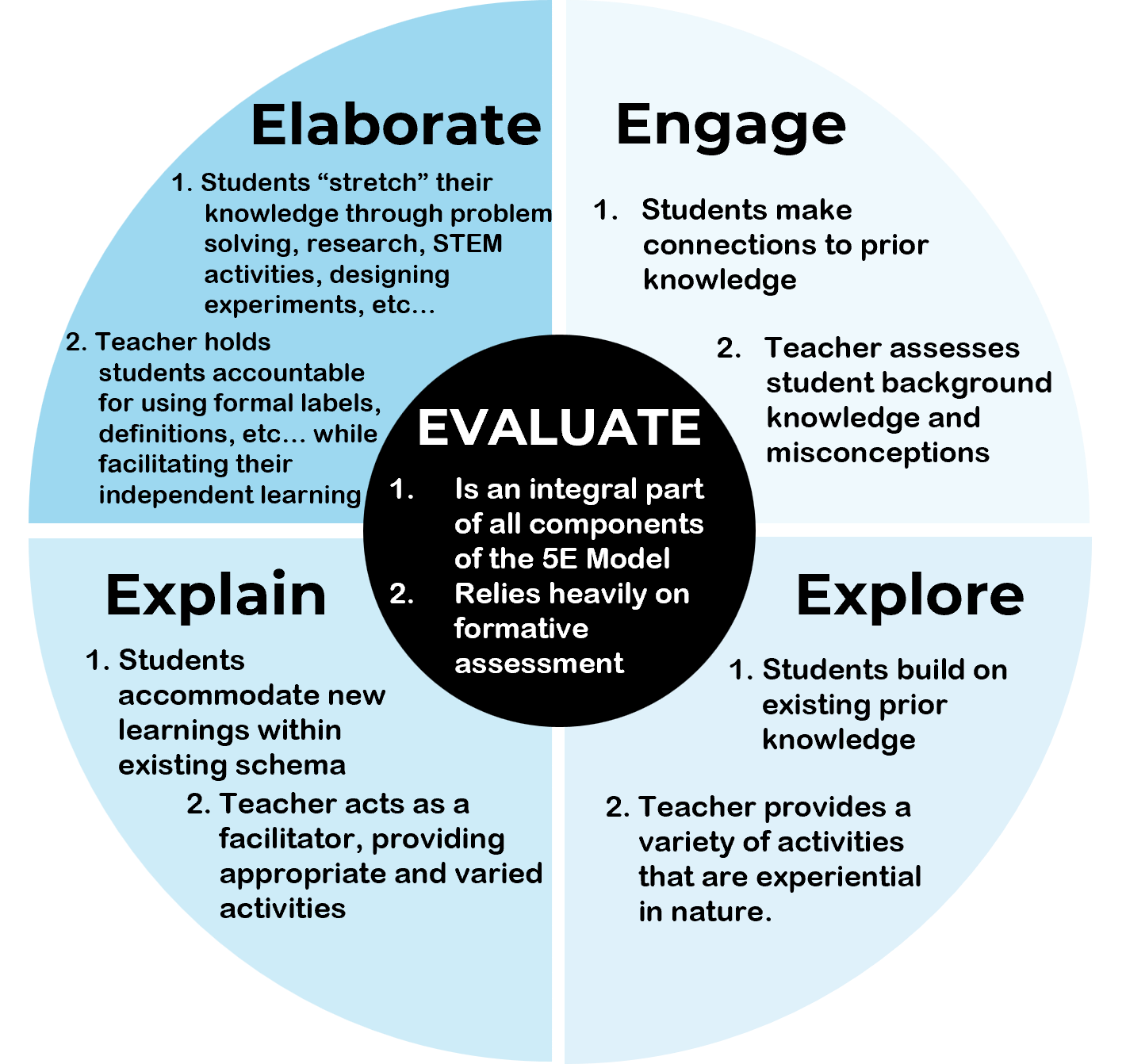
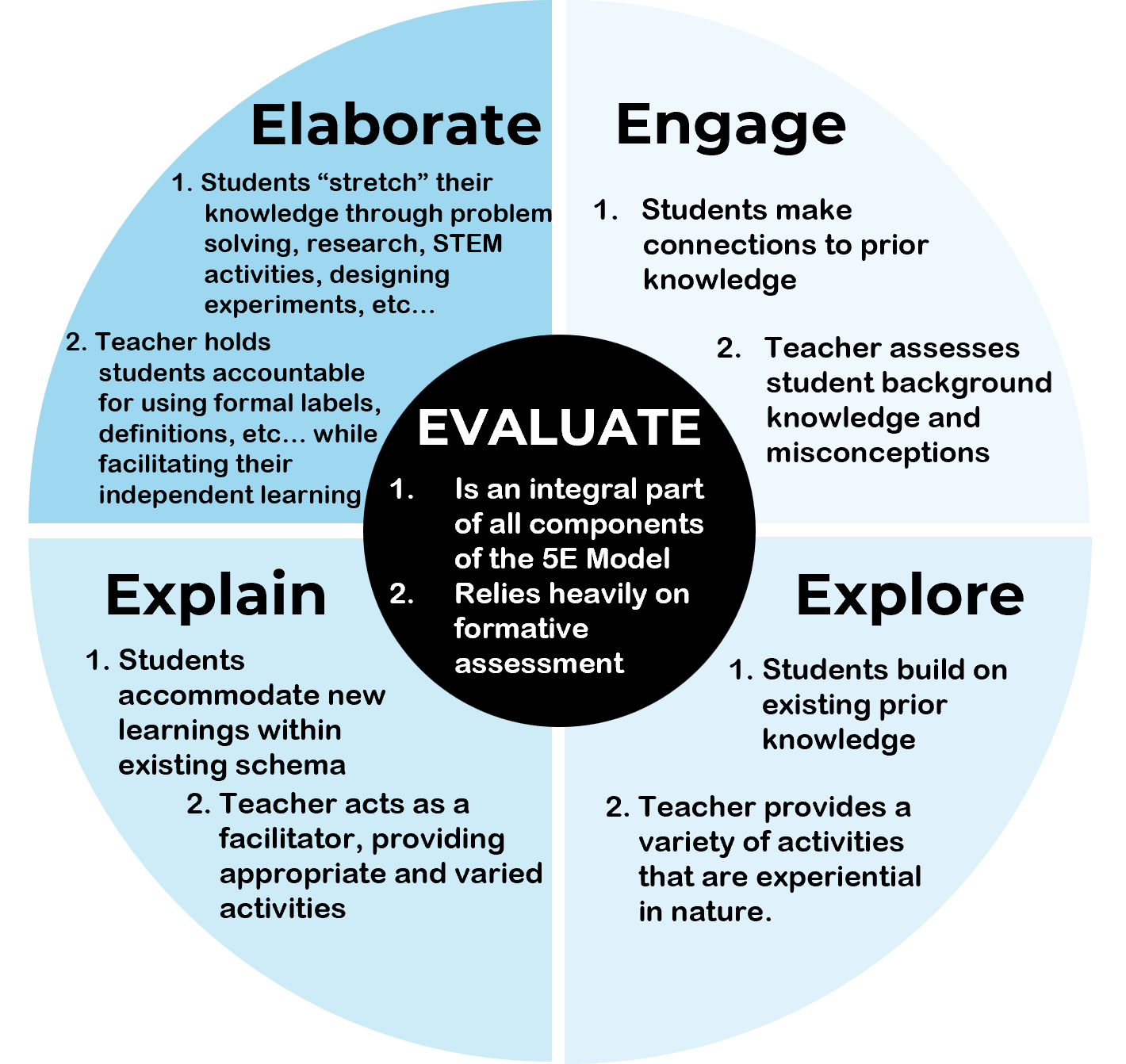
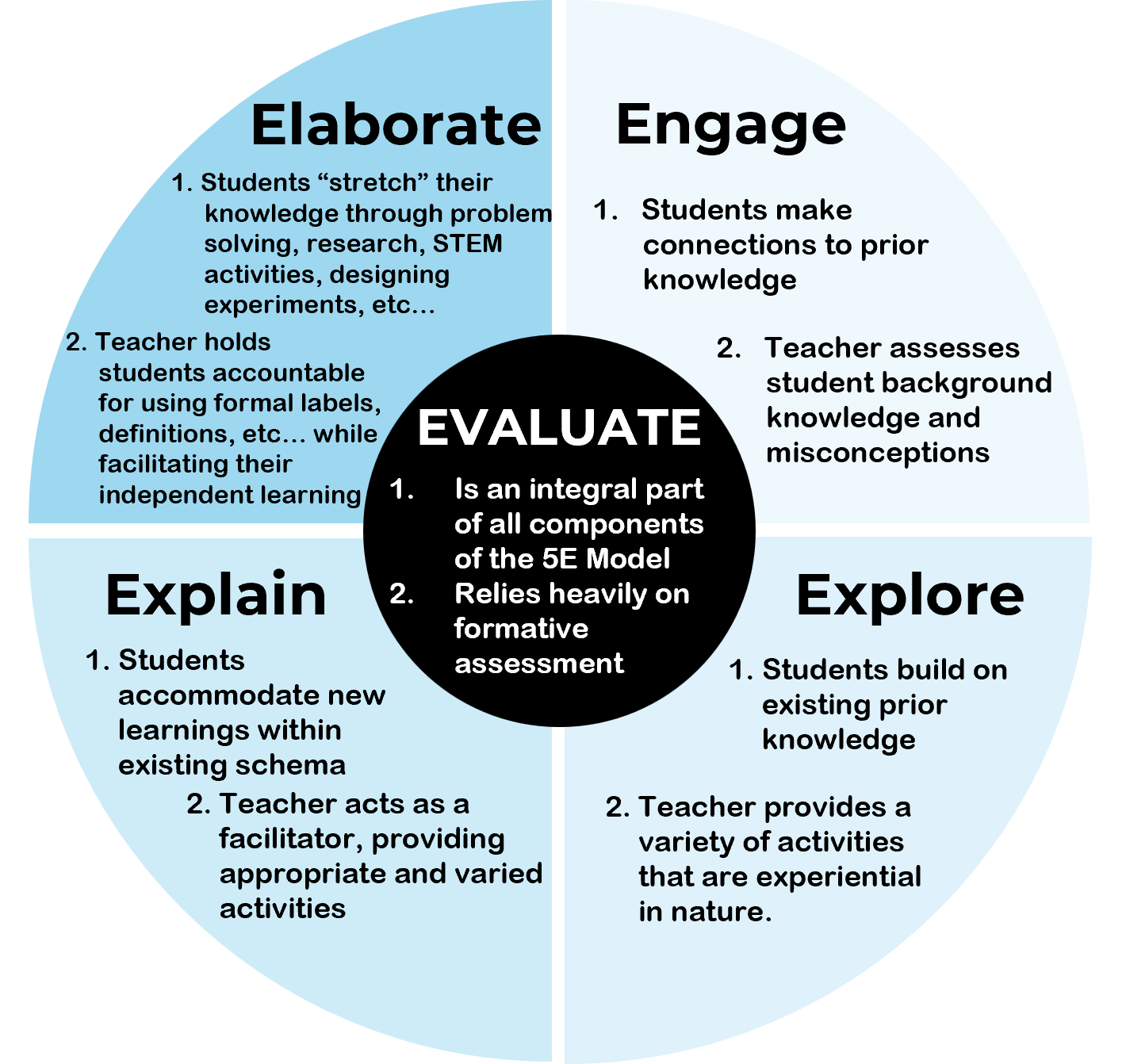
Engage (5E Model)
First phase of 5E model. students become mentally engaged, make connections to previous learning, and think about their own learning outcomes.
Quantitative Data
data which is measured and usually expressed numerically
Example.
distance, time, temperature, test scores
Scientific Knowledge
scientific fact discovered using the scientific method
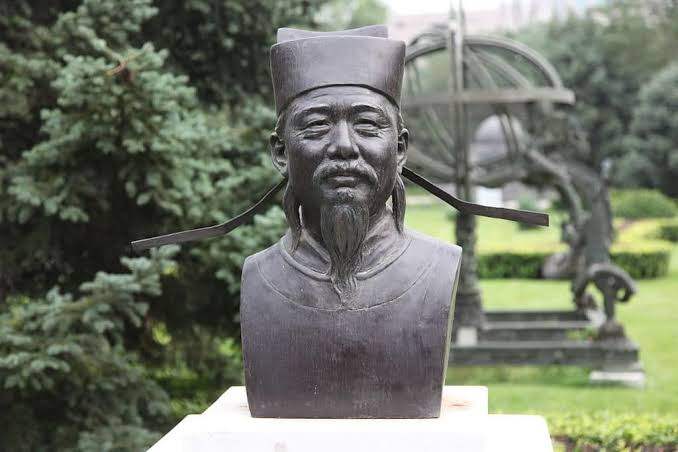
Shen Kuo
Chinese mathematician and scientist who invented the magnetic compass and defined "true north" as magnetic north

Guiding Questions
questions that lead to a deeper understanding by arousing curiosity and interest
Example.
"What do plants need for optimal growth?" might be the guiding question for the hypothesis "If plants are given twice the water they will grow twice as fast".
Inquiry-Based Activities
activities that allow students to participate in the scientific method with little guidance from the teacher
Example.
experiments, discussions
Accommodation
occurs when existing schemas cannot be applied to new objects or situations, and must therefore be adapted and revised
Example.
An infant develops the use of fine motor skills and is now able to pick up blocks. The child changes their reflex and begins to bite on blocks rather than sucking their thumb - accommodating the new reality.
Natural Selection
the process by which, over time, the population as a whole contains more individuals who are better suited to that environment.
Example.
faster antelopes survive to pass down traits
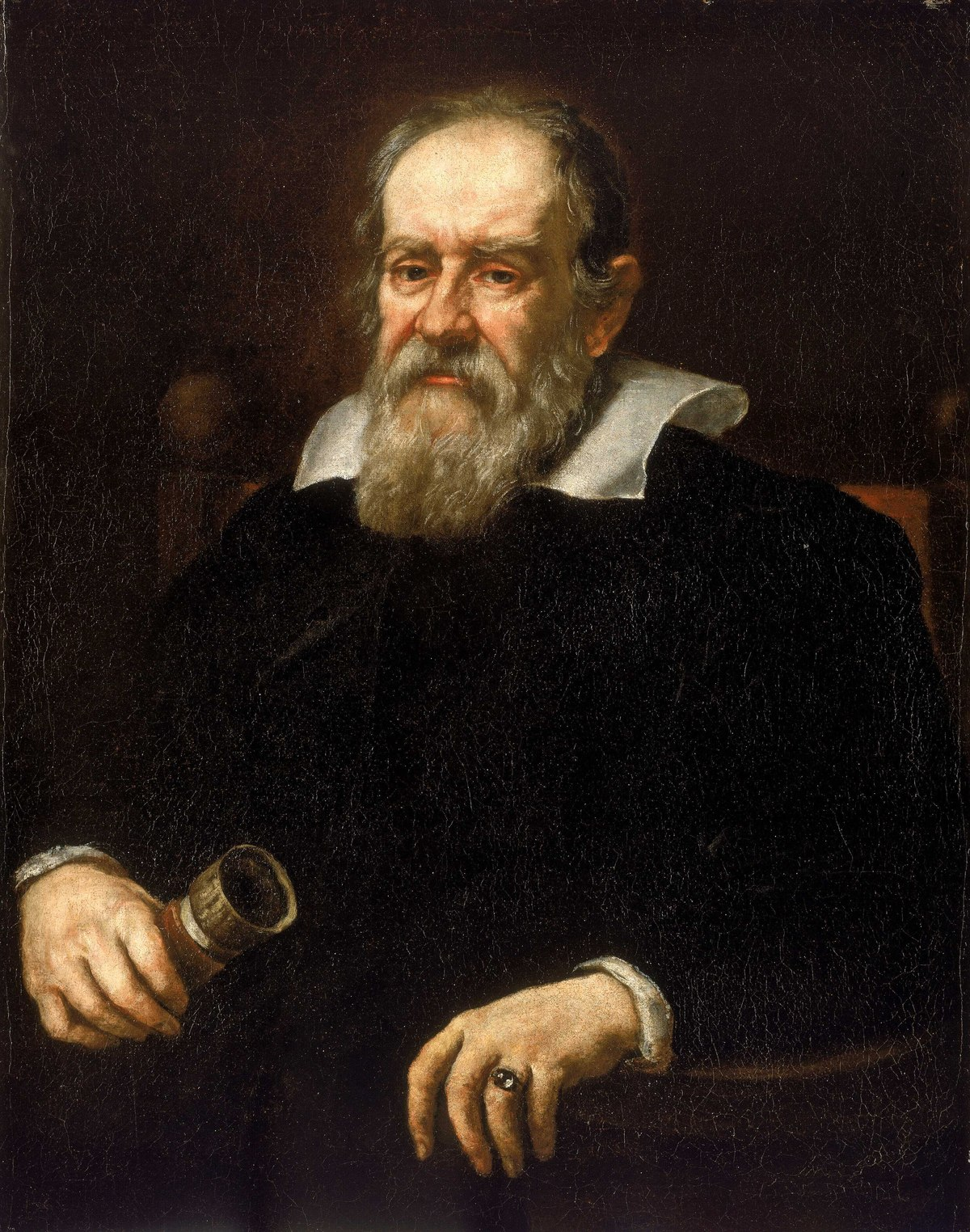
Galileo Galilei
GaliItalian mathematician and scientist who furthered Copernicus' idea of heliocentricism, discovered Jupiter's moons, and was credited with the scientific methodeo Galilei

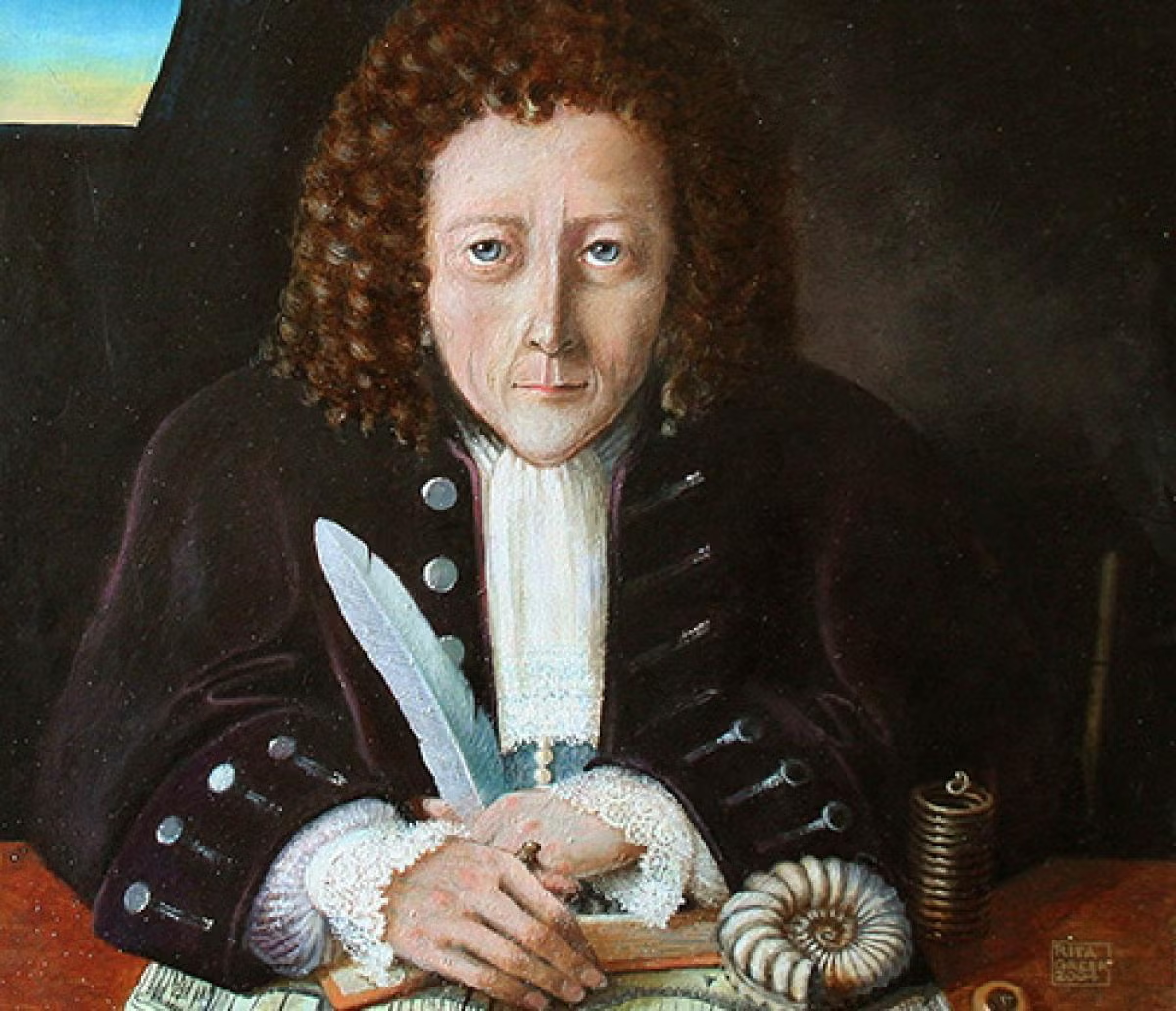
Robert Hooke
English scientist who developed Hooke's law for springs (elasticity) and described the expansion of matter when heated

Data
information gathered through measurement and observations; used as a basis for calculations, reasoning, discussion, and conclusions
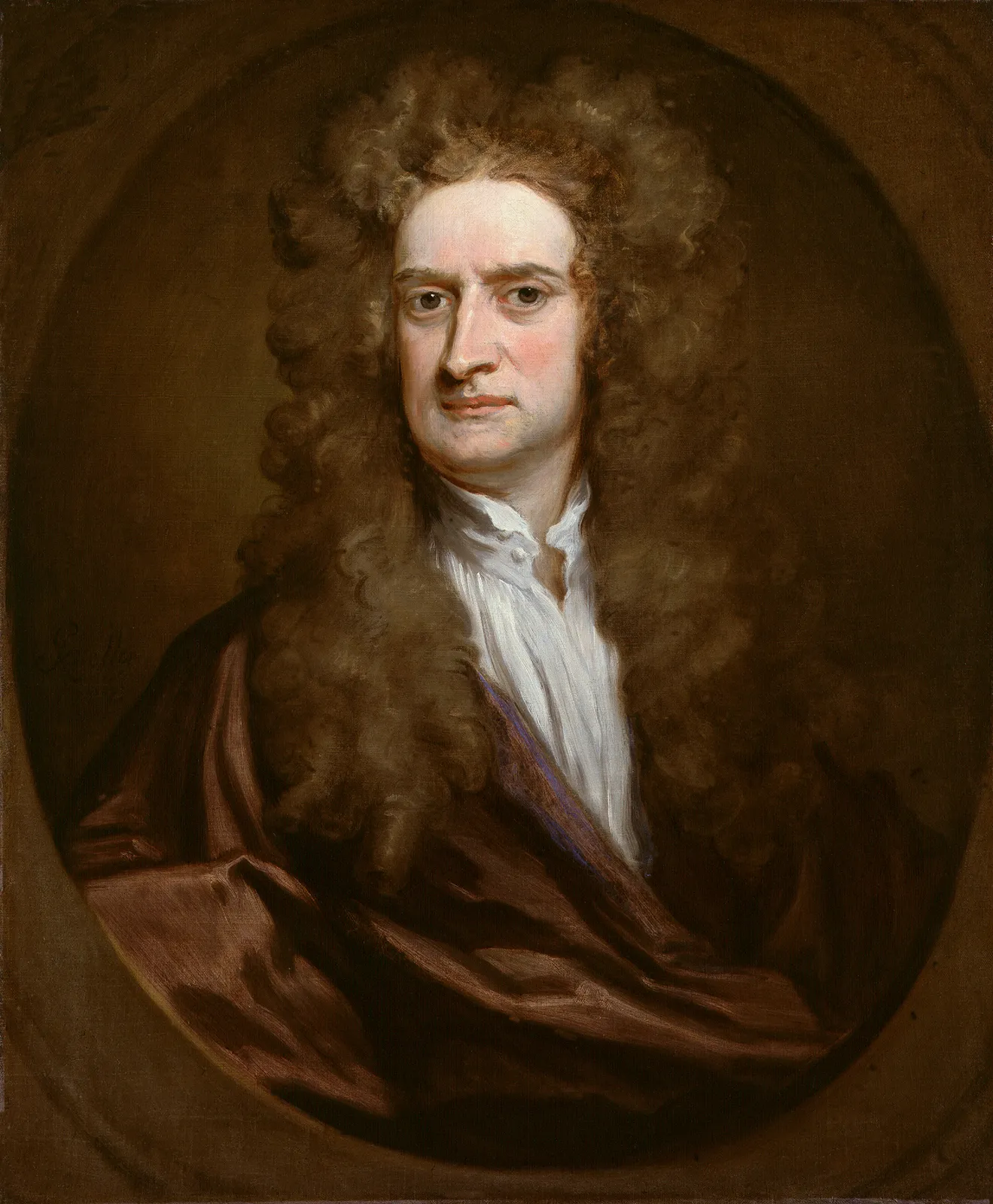
Isaac Newton
English mathematician and scientist who formulated the Laws of Motion and the Law of Universal Gravitation

Harry Hess
American geologist who discovered seafloor spreading
Measure
using an instrument/device to determine the size, amount, or degree of (something)
Example.
The student measured the liquid before pouring it into the test tube.
Scientific Theory
a proposed explanation for a phenomenon which may not be testable
Example.
Darwin's Theory of evolution
Niels Bohr
Danish physicist who developed the quantum model of the atom showing that only certain electron orbitals exist

Experimental Investigation
Researchers assign subjects in the sample to certain treatments, then observe the effects of the treatment. Can show causation (cause and effect).
Example.
Does using algebra tiles during instruction help freshman students learn how to solve equations?
Inge Lehmann
Danish seismologist and geophysicist who discovered Earth's inner core

Principle of Uniformitarianism
the belief that physical laws, and therefore geologic processes, are constant; these processes have always occurred in the same manner at the same rate and will continue to do so
Independent Variable
Term definition.
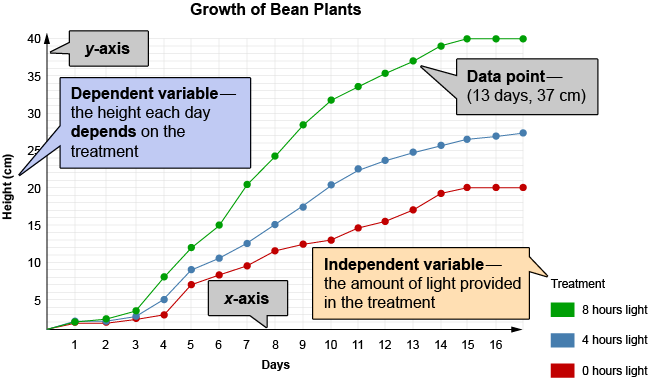
the variable manipulated by the scientist conducting the experiment to observe the effect on the dependent variable
Example.
In an experiment investigating the effect of the amount of light on plant growth, the amount of light is the independent variable since it affects the amount of growth.
Werner Heisenberg
German physicist who developed the uncertainty principle

Eratosthenes
Greek mathematician and geographer who founded the science of geography and accurately calculated Earth's size

Matthias Jakob Schleiden
German botanist; co-founder of cell theory (with Theodor Schwann); proposed that all structural plant parts are made of cells
Aristotle
Greek philosopher; created the first taxonomy of organisms by grouping animals with similar characteristics

Marie Curie
Polish-French physicist and chemist who defined radioactivity as a property of atoms (uranium/thorium experiment) and helped discover radium and polonium; wife of Pierre Curie

Stephen Jay Gould
American paleontologist who developed the evolutionary theory of punctuated equilibrium

Communicate
share or exchange information
Example.
Students must be able to communicate the results of their experiments in a written or oral report.
Carl Linnaeus
Swedish biologist known as the father of taxonomy; developed the modern system of classification used to name, identify, and classify living things

J.J. Thomson
British physicist who conducted cathode-ray experiments to discover the electron and proposed the "plum pudding model of an atom"

James Watson
American biologist who proposed that the structure of DNA is a double helix (with James Watson and Rosalind Franklin)

Antonie van Leeuwenhoek
Dutch microbiologist; founded the science of microscopy by describing microscopic organisms
Erwin Schrödinger
Austrian physicist who developed the main equation for quantum physics and proposed the electron cloud model of the atom
Explore (5E Model)
Second phase of 5E model. students work with the material, developing their knowledge, and usually actively manipulating materials or interactive content.
Qualitative Data
data which is described rather than measured
Example.
color, shape, smell, opinions
Rudolf Virchow
German physician and scientist who was the pioneer of modern pathology; proposed that diseases arose from their individual cells

Rosalind Franklin
British chemist who used X-ray crystallography to research the DNA molecule's density and helical shape

Predict
say or estimate that an event will occur in the future
Example.
Before performing the experiment, students predict that the plant in the direct sunlight will grow the tallest.
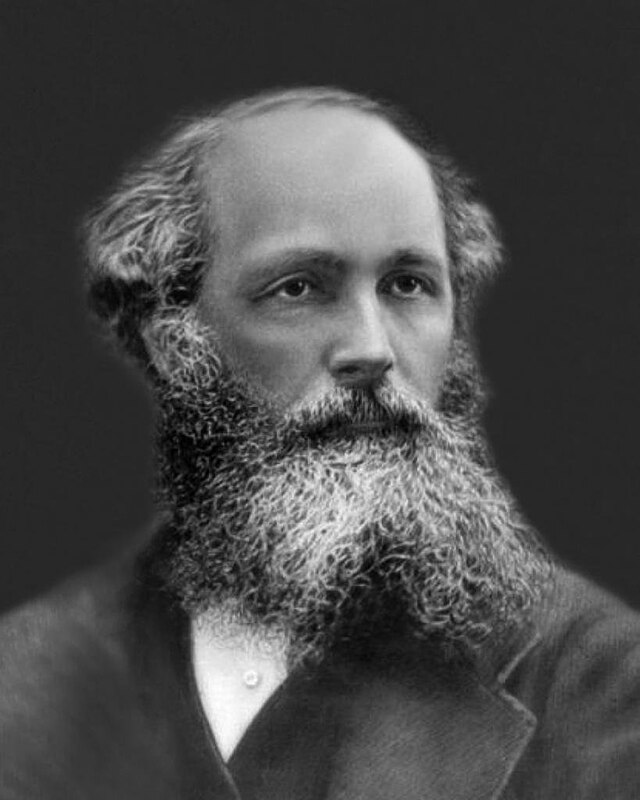
James Clerk Maxwell
Scottish physicist who developed the theory of electromagnetism; showed that electricity, magnetism, and light are all manifestations of the electric field

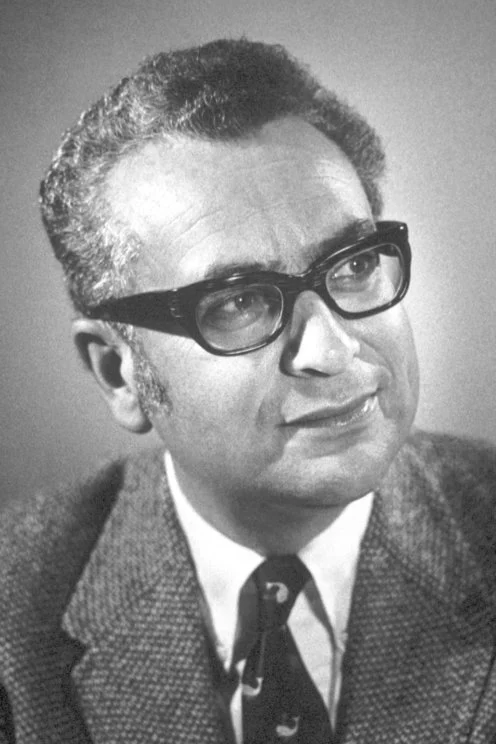
Murray Gell-Mann
American physicist who proposed that matter is made of quarks

Scientific Method
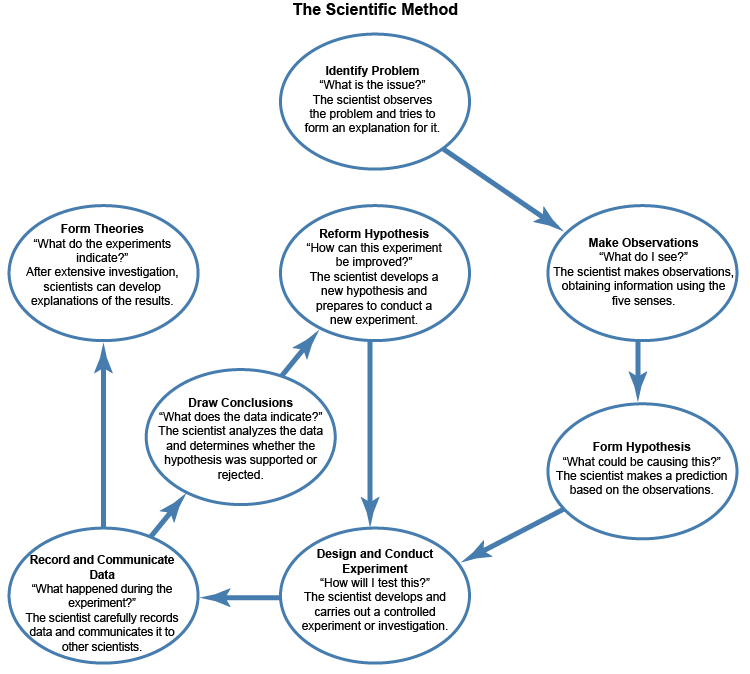
a series of deliberate steps by which scientists observe, hypothesize, test, analyze data, and communicate results
Assimilation
a process in which existing schemas are applied to new objects or situations
Feedback Loop
a series of experiments in which the results lead to more possible hypotheses and subsequently more testing
Controlled Variable
a variable that is kept stable throughout the experiment, across control and experimental groups, to ensure that any difference in the dependent variable is because of the independent variable.
Example.
In an experiment investigating the effect of amount of light on plant growth, the amount of water would be a controlled variable since it is not being studied.
Activate Prior Knowledge
helping students remember what they already know about the topic
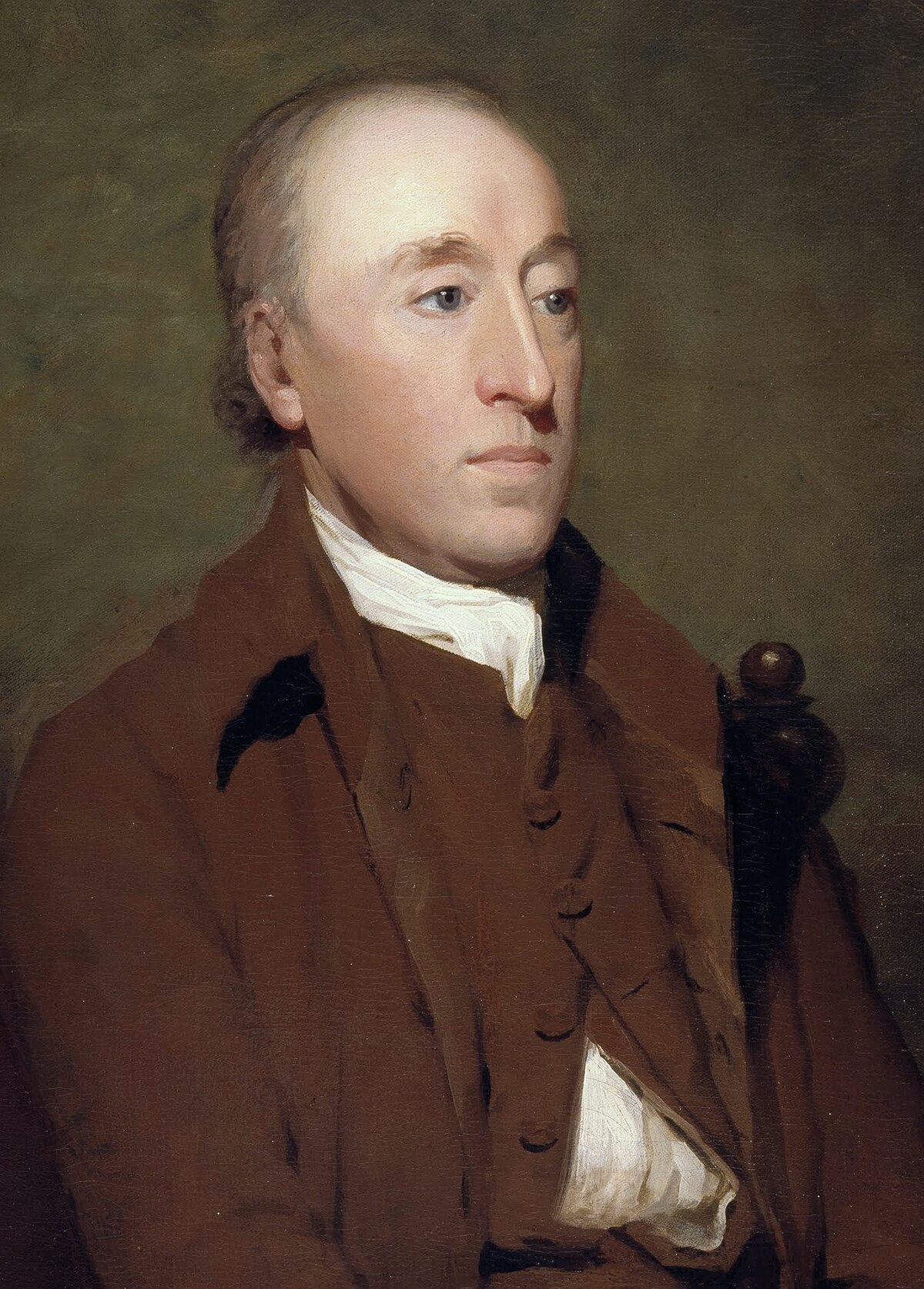
James Hutton
Swedish geologist who developed the theory of uniformitarianism, explaining that Earth is continuously being formed

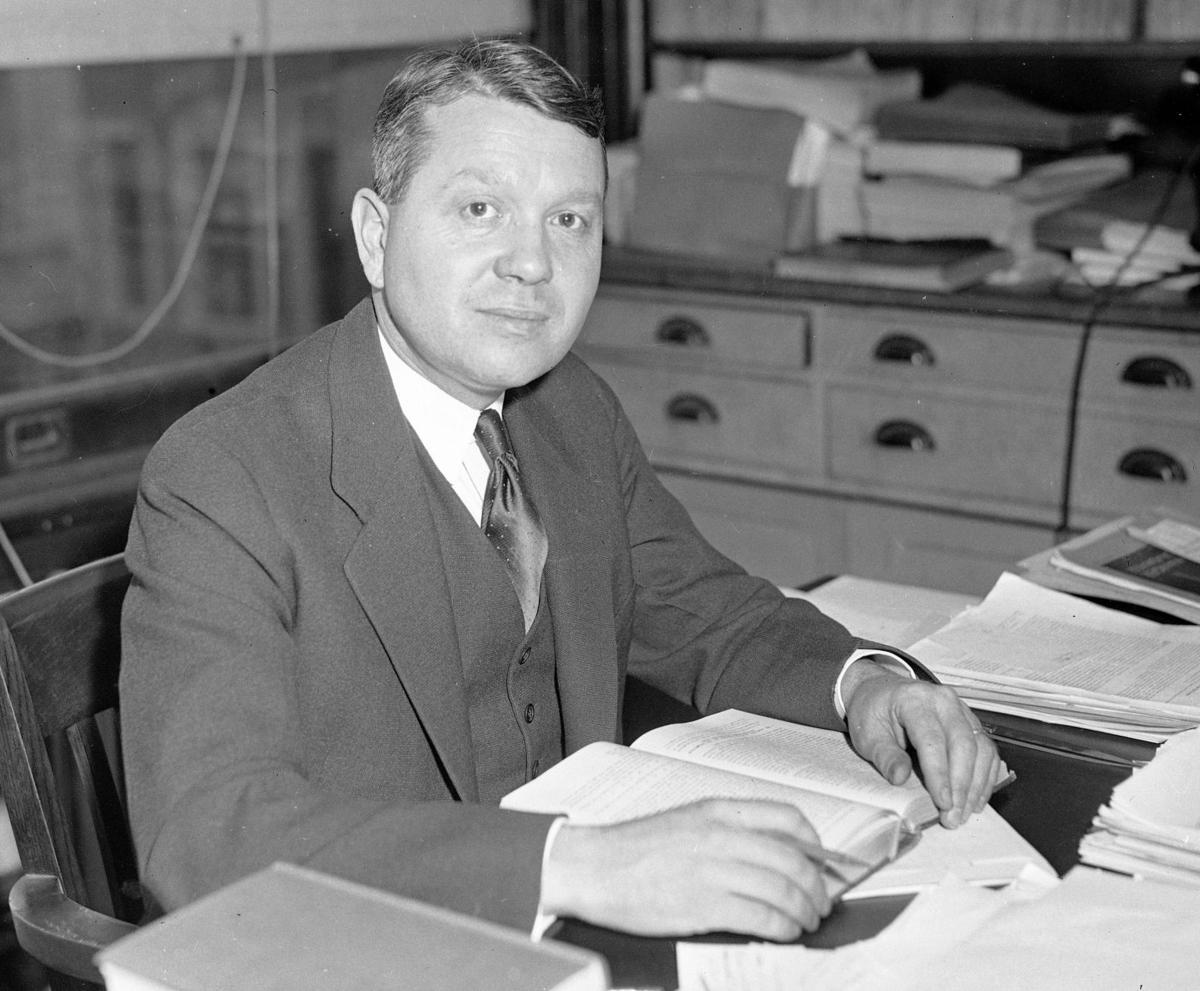
Harold Urey
American chemist who discovered deuterium, a radioactive molecule of hydrogen, and collaborated on the Urey-Miller abiogenesis experiment showing a possible origin of life on Earth

Hypothesis
an informed prediction (made based on previous observations) for a phenomena. Should be testable.
Example.
If we give plants more fertilizer, they will grow taller.
Michael Faraday
English scientist who discovered electromagnetic induction

Theodor Schwann
German physicist and physiologist who extended cell theory to include animal cells
Scientific Law
a proven explanation for a phenomenon
Example.
Newton's Laws of Motion
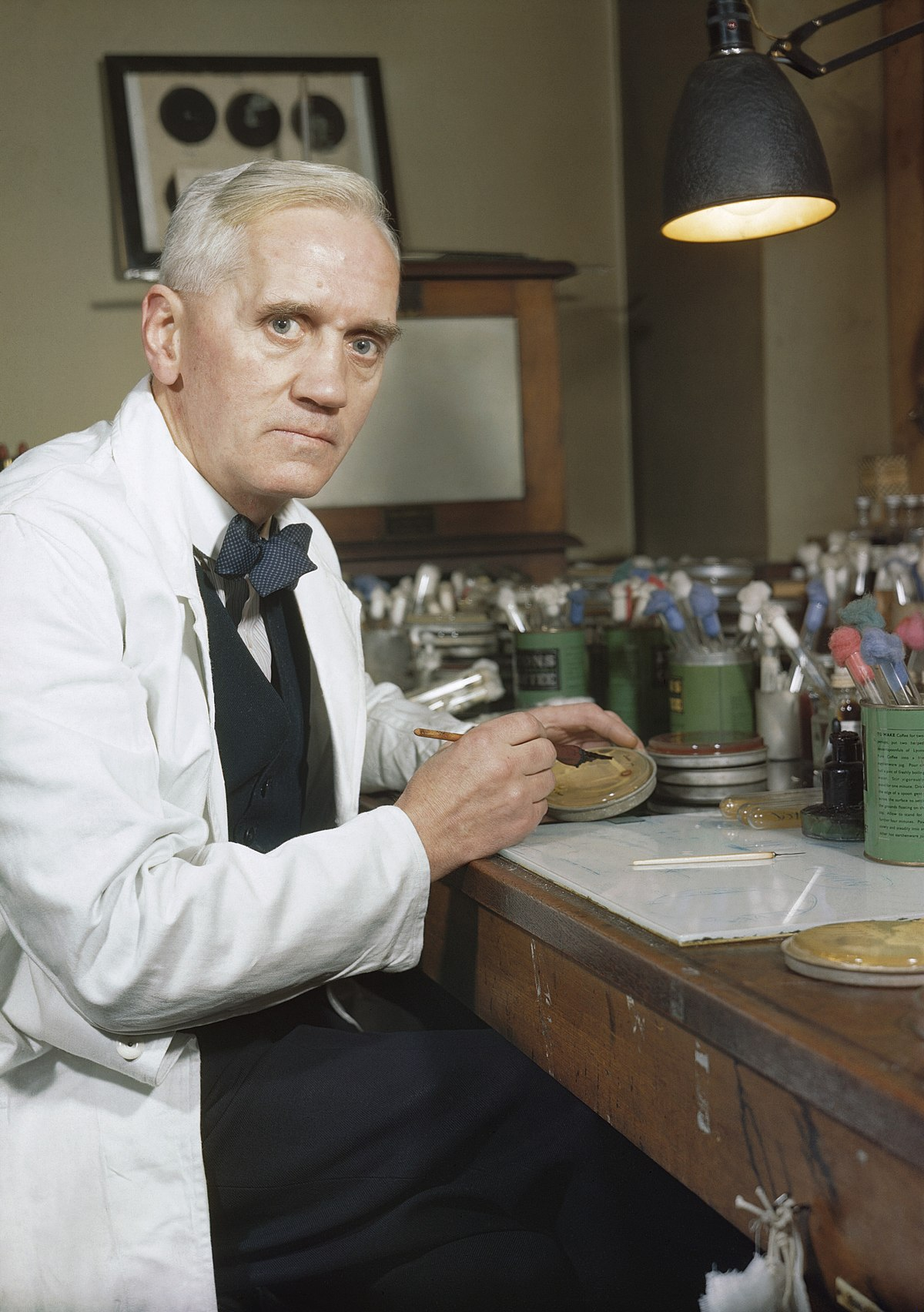
Alexander Fleming
Scottish physician and microbiologist who discovered the first antibiotic (penicillin)

Peer Review
evaluation of work by others in the same field
Example.
students reviewing each other's essays for feedback
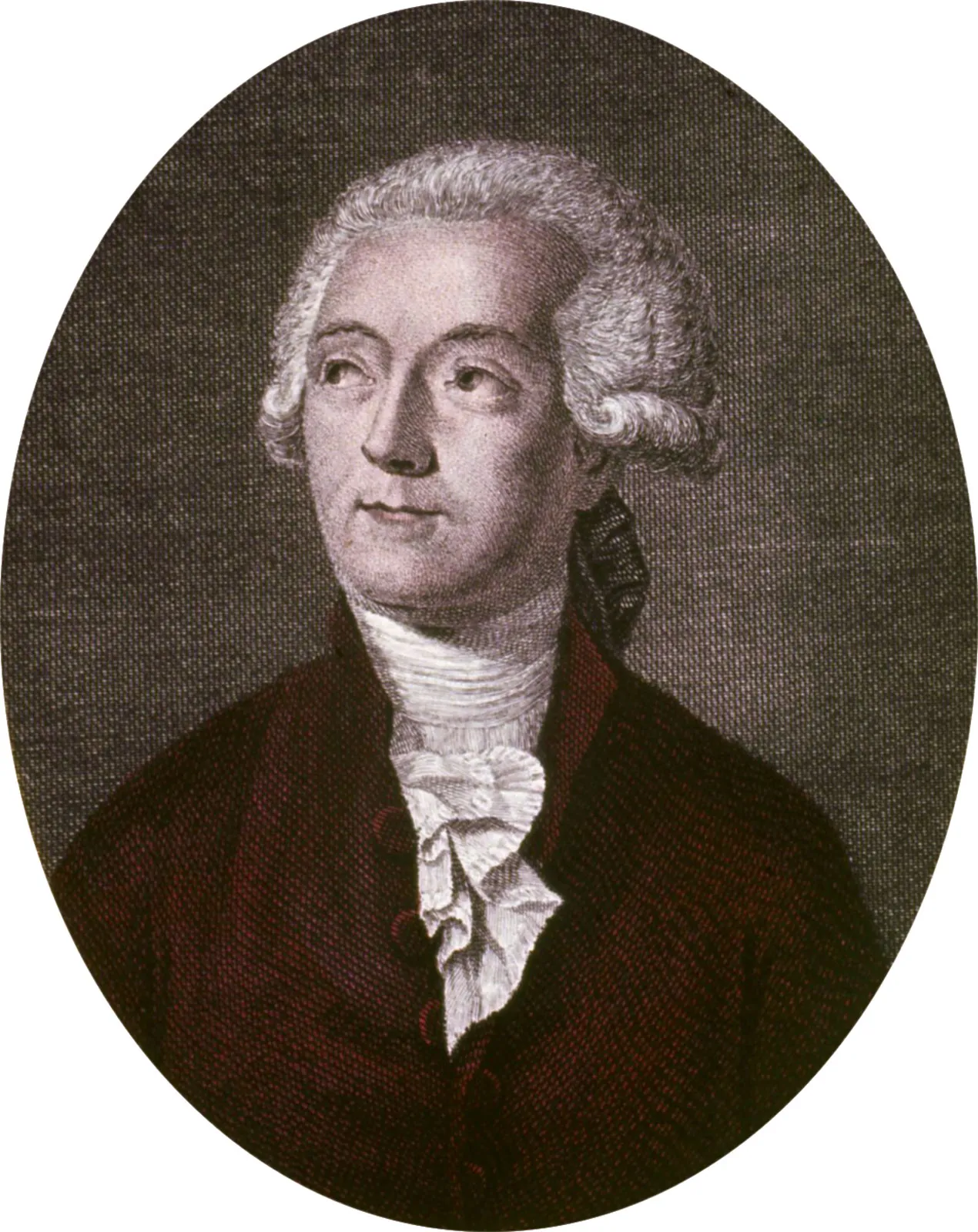
Antoine Lavoisier
French chemist who contributed to the chemical naming system

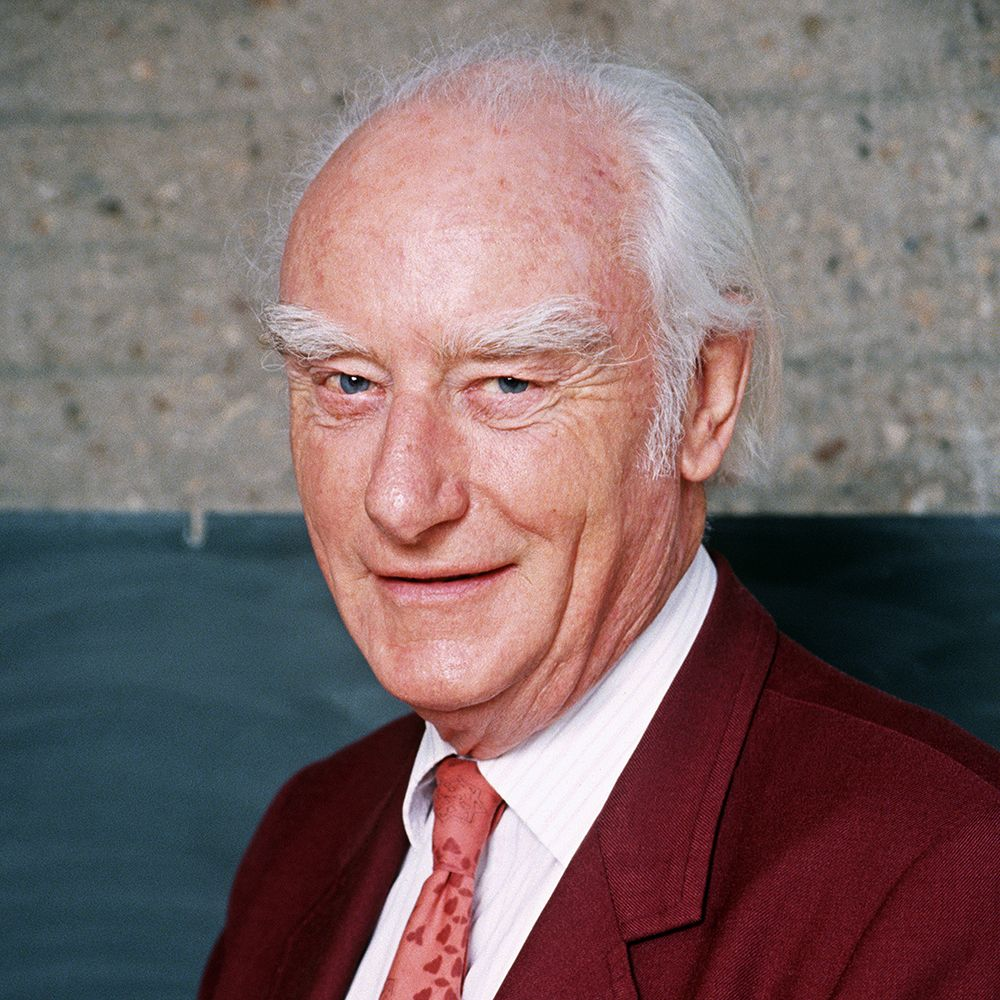
Francis Crick
English biologist who proposed that the structure of DNA is a double helix (with James Watson and Rosalind Franklin)

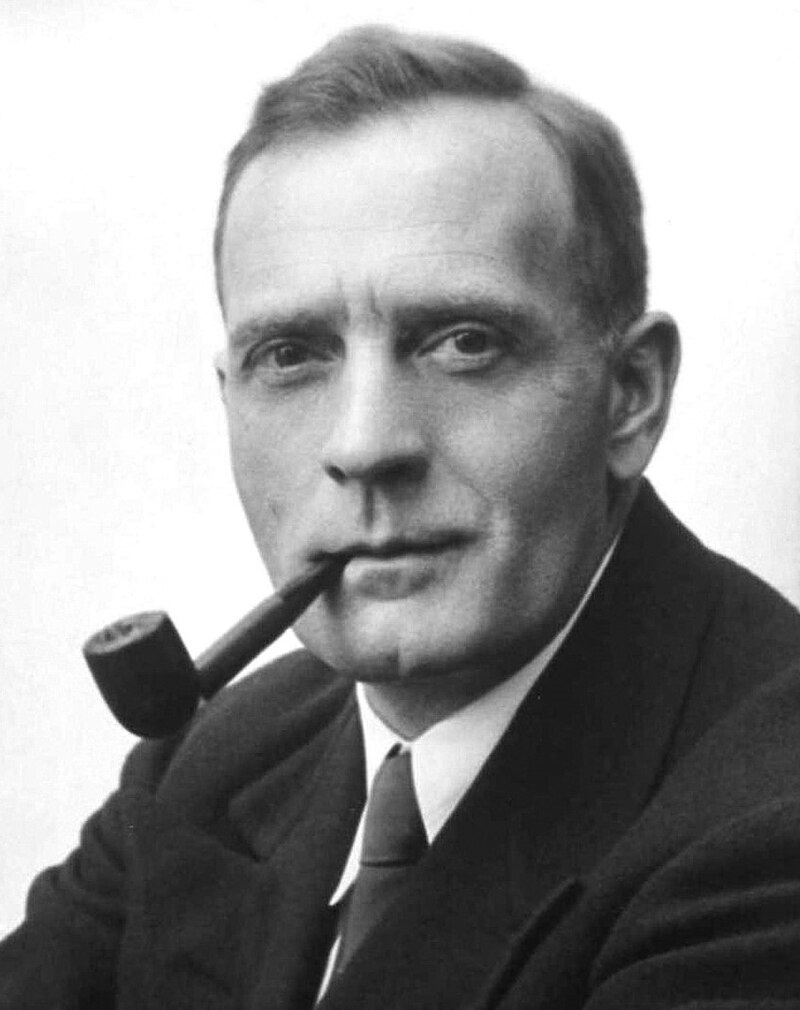
Edwin Hubble
American astronomer who developed Hubble's Law, providing insight into the expanding universe

Elaborate (5E Model)
Fourth phase of 5E model. students extend their thinking and practice new skills.
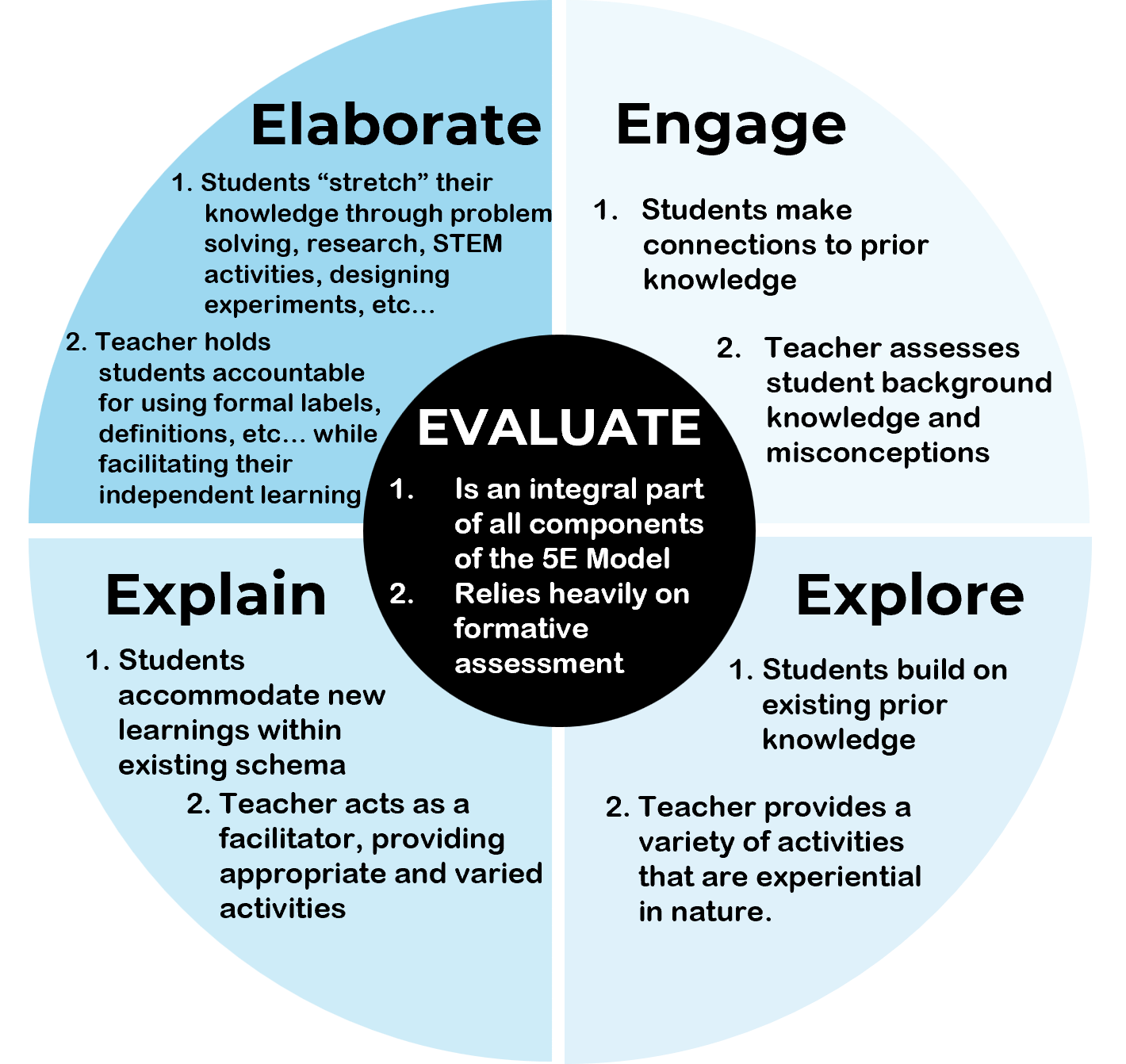
Evaluate (5E Model)
Final (fifth) phase of 5E model. students are assessed on their understanding and teachers evaluate learning to inform their next lesson.
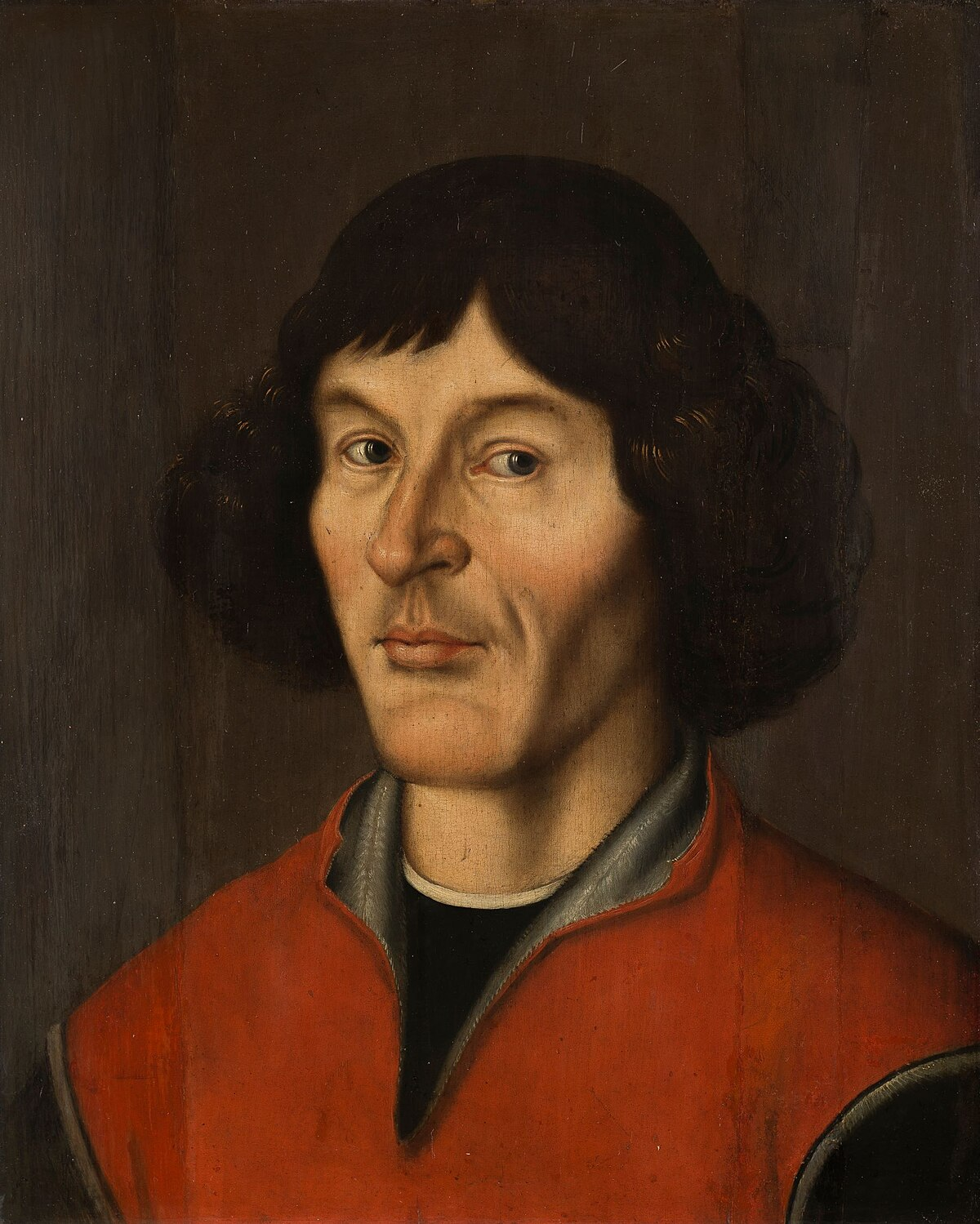
Nicolaus Copernicus
Polish mathematician and scientist who discovered heliocentricity, which explains that the Sun, not the Earth, is the center of the solar system

Daniel Bernoulli
Swiss mathematician and physicist who developed the Bernoulli Principle to explain the relationship between the speed and pressure of a fluid
Heliocentricity
the accepted astronomical model that the sun is at the center of our solar system; theory was put forth by Copernicus in 1543 and expanded upon by Galileo in 1632
Disequilibrium
occurs when a child cannot use existing schemas to comprehend new information
Example.
A child moves to a new country. The new classroom rules are difficult to assimilate on top of the previous classroom rules.
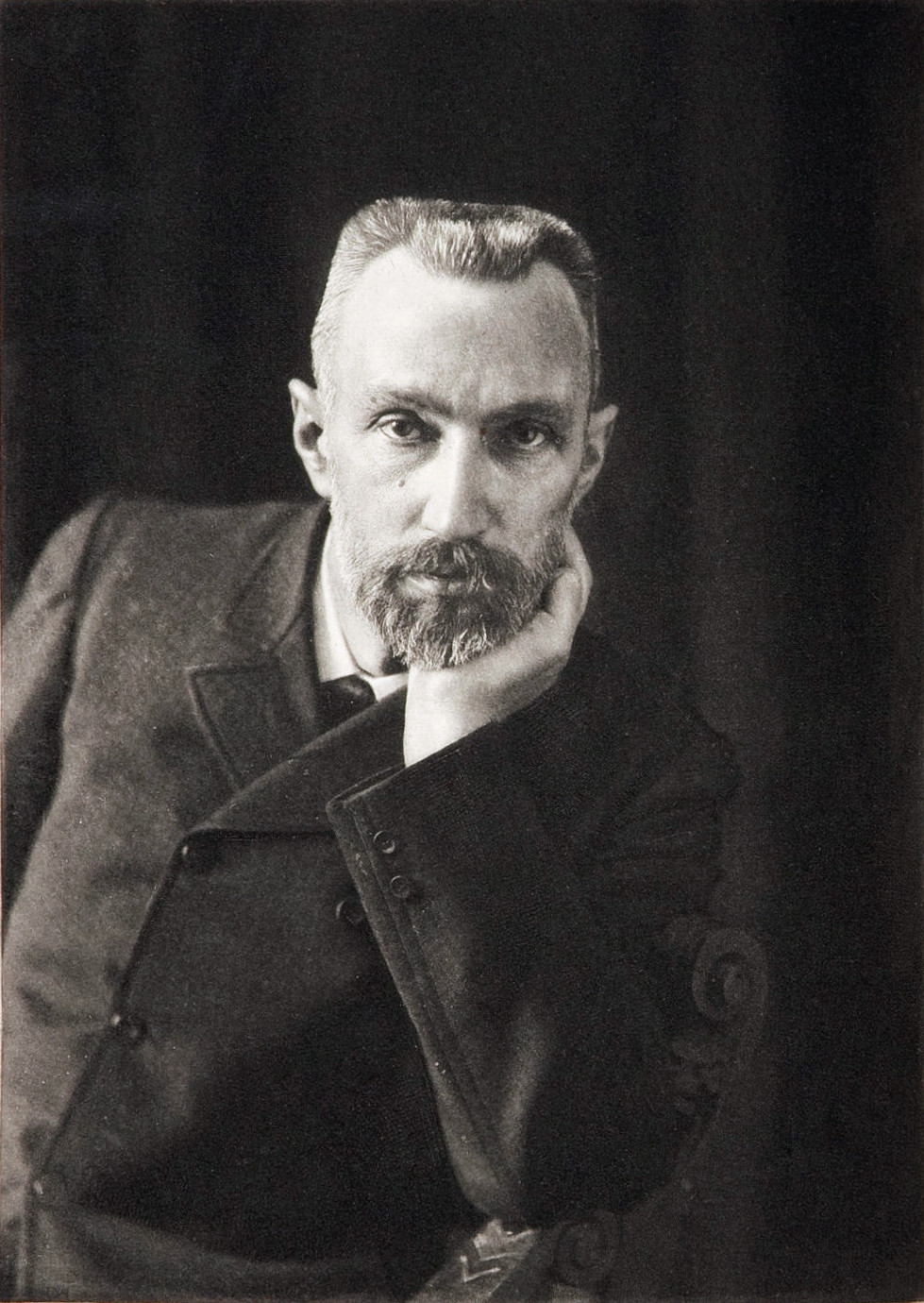
Pierre Curie
French physicist who helped discover radium and polonium; husband of Marie Curie

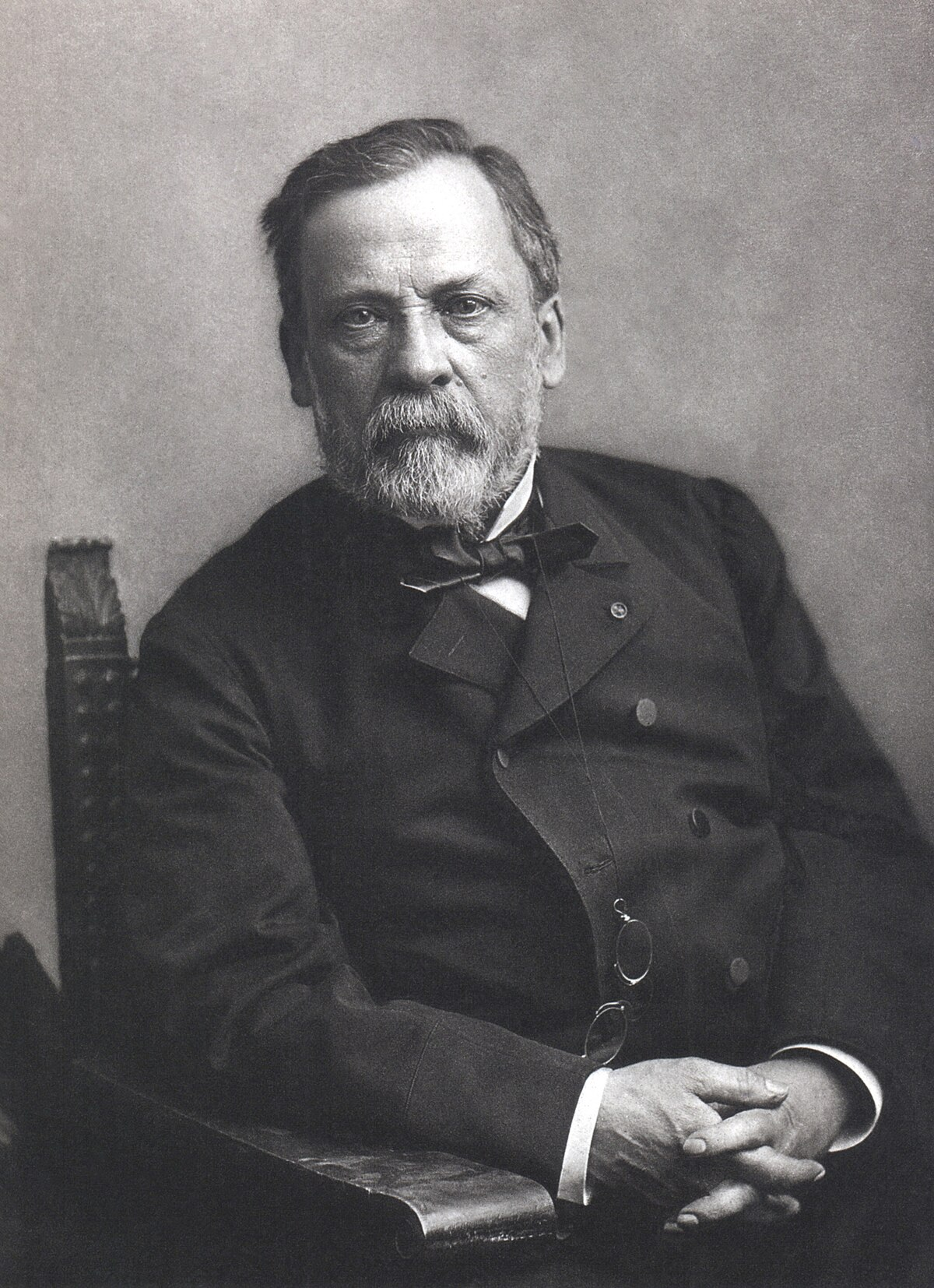
Louis Pasteur
French biologist, chemist, and pharmacist known as the father of germ theory; created the first vaccinations for rabies and anthrax, discovered airborne illnesses, disprove the theory of spontaneous generation using the swan neck flask

Explain (5E Model)
Third phase of 5E model. students explain what they know and verbalize their understanding. Teachers use this phase to formally define terms and explain processes.
Johannes Kepler
German astrologer and mathematician who proposed three laws of planetary motion that describe the orbits of the planets as ellipses

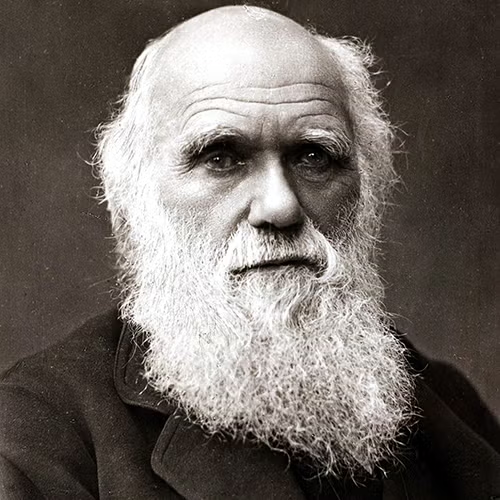
Charles Darwin
an English naturalist who developed the idea of natural selection and the theory of evolution; these ideas were published in the book On the Origin of Species

Dependent Variable

a variable measured by the scientist conducting the experiment
Example.
In an experiment investigating the effect of amount of light on plant growth, the plant growth would be the dependent variable since it depends on the amount of light.
John Dalton
English chemist and physicist who developed the fixed orbital model of the atom using gas phase experiments
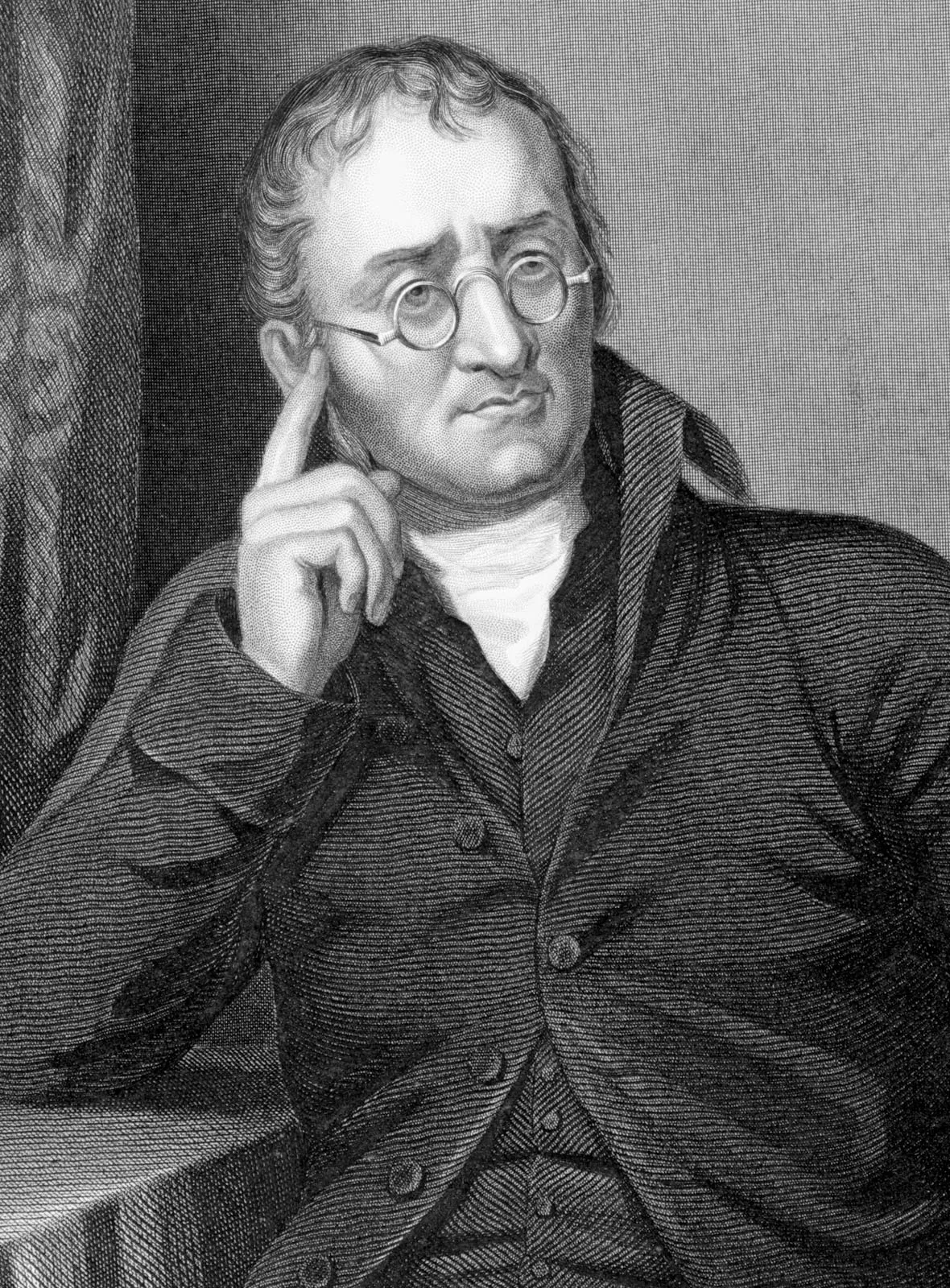

John Michell
English philosopher who:
Described the cause of earthquakes
Described earthquakes as waves
Invented the torsion balance to measure the mass of the Earth

Classify
to arrange or group things into categories (classes) based on shared characteristics
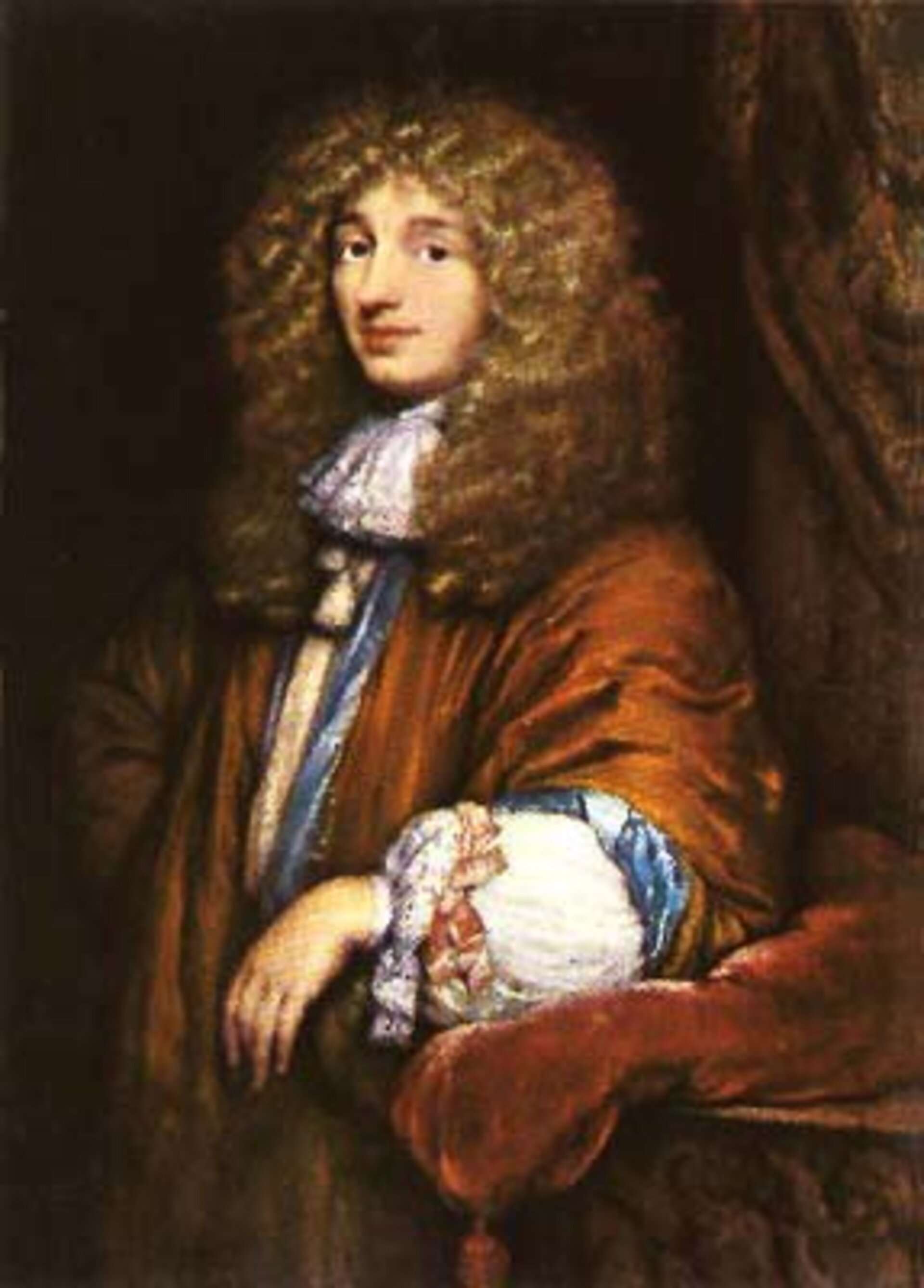
Christiaan Huygens
Dutch mathematician and physicist who supported the wave nature of light

Experimental Group
a group of specimens in an experiment to which a change is made; receives the experimental treatment
Example.
In an experiment investigating the effect of talk therapy on alleviating depression, the group receiving the medicine and the therapy would be the experimental group.
Thomas Hunt Morgan
American biologist who advanced the theory of genetics by studying fruit flies
Conclusion
a summary of the results of an experiment; states whether the initial hypothesis was rejected or supported
Scaffolding
providing support to students to achieve a task
Example.
guiding students step-by-step in solving a math problem
Alfred Wegener
German geologist who developed the theory of continental drift
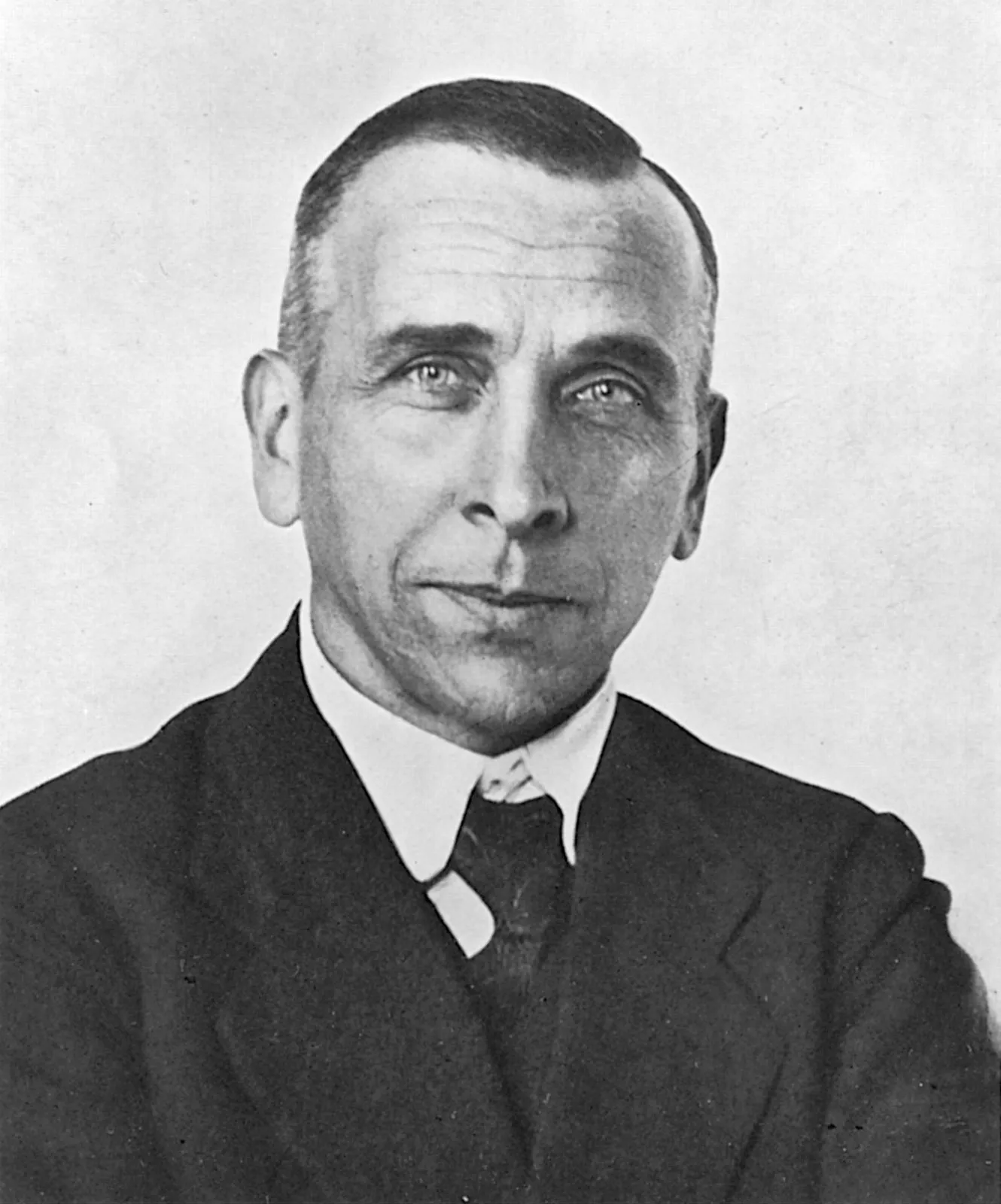

Max Planck
German physicist who discovered the photoelectric effect leading to the principle of quantum mechanics
Nicolas Steno
Danish scientist who developed stratigraphy, the study of Earth's layers

Stanley Miller
American chemist who discovered that organic amino acids could be made from inorganic molecules; performed the Urey-Miller abiogenesis experiment showing a possible origin of life on Earth (with Harold Urey)

Variables
factors that can change or vary in an experiment
Example.
changing temperature to see its effect on plant growth
Continental Drift
the movement of continents due to the activity of the tectonic plates beneath them
Discrepant Events
events with unexpected outcomes
Example.
A teacher starts a lesson on gravity by dropping two objects with different masses. Students are surprised when the objects hit the ground at the same time.
Organization
students store new information and relate it to what they already know and understand about the world
Example.
Students organize their data and analysis into a class presentation that makes sense of their learning.
Radioactivity
when an atom changes the number of protons in the nucleus and releases radiation
Questioning Strategies
techniques used to ask questions in a way that requires students to use the thinking that the teacher is trying to develop
Example.
Different questioning strategies can be used to encourage student curiosity and creativity by asking students to observe, infer explanations, predict expected experimental outcomes, and elaborate on their reasoning.
Observation
information gathered using the five senses
Example.
smell, color