47 & 48 - surfactants, micelles and liposomes
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
What are surfactants
Surfactants are chemical compounds that decrease the surface tension or interfacial tension between two liquids, a liquid and a gas, or a liquid and a solid
Eg. Polysorbates, benzalkonium chloride, SDS/SLS, polymers
What is surface tension
Surface tension is the tendency of liquid surfaces at rest to shrink into the minimum surface area possible. Surface tension is what allows objects with a higher density than water such as razor blades and insects to float on a water surface without becoming even partly submerged.
What is the formula for surface tension

What is interfacial tension
Minimisation of surface free energy
What is surface free energy
Surface free energy is the work required to increase the area by 1m² (under standard temp, pressure), units mJ/m² (J=Nm).
What are factors affecting surface tension
Type of liquid
Temperature
Solute
(There is also vapour pressure and time - for solute to equilibrate and arrange at the surface)
Why does surface tension depend on the type of liquid
The surface tension of a substance depends on the cohesive forces between the molecules
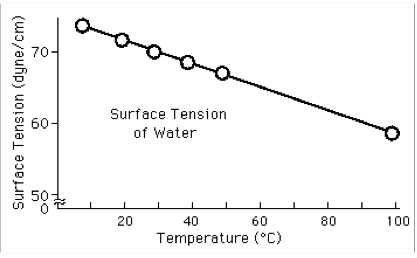
How does temperature affect surface tension
Surface tension decreases with an increase in temp, because KE increases (which disrupts and reduces IMF)
Relationship is linear over a wide range of temperatures
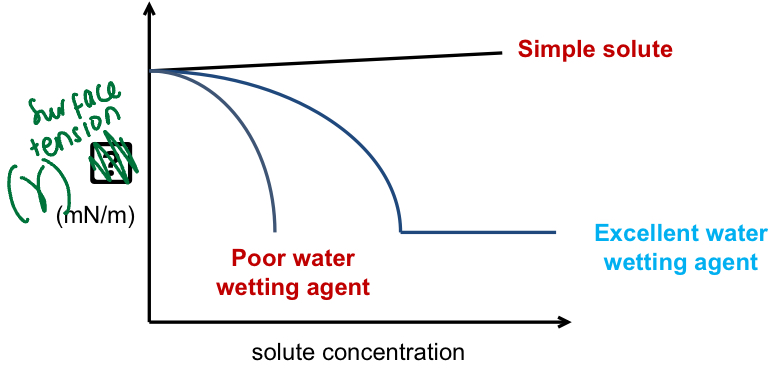
How does the type of solute affect surface tension
Surface tension of a solution (in water) varies with the nature and concentration of the solute added - three types of behaviour are observed ^
Why do surface active molecules decrease the surface tension of water
At low concentrations, the only way both the polar and non polar regions are satisfied is by adsorbing on the surface of water, so that the polar hydrophilic head is in contact with water, and the hydrophobic part is away from water
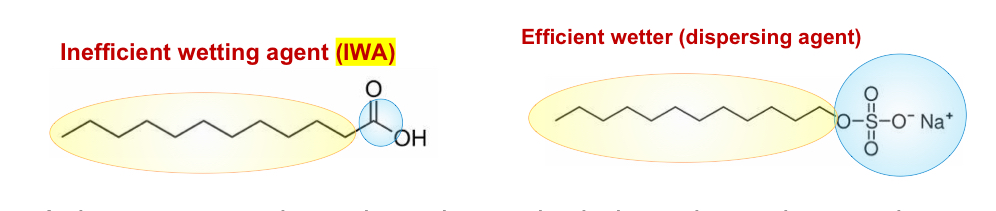
How does the presence of wetting agent molecules affect surface tension
Presence of wetting agent molecules on the surface disrupts binding between water molecules resulting in a reduction in surface tension
What are amphiphiles
An amphiphile, or amphipath, is a chemical compound possessing both hydrophilic and lipophilic properties. Such a compound is called amphiphilic or amphipathic. Amphiphilic compounds include surfactants. The phospholipid amphiphiles are the major structural component of cell membranes.
These types of molecules are typically referred to as co-surfactants
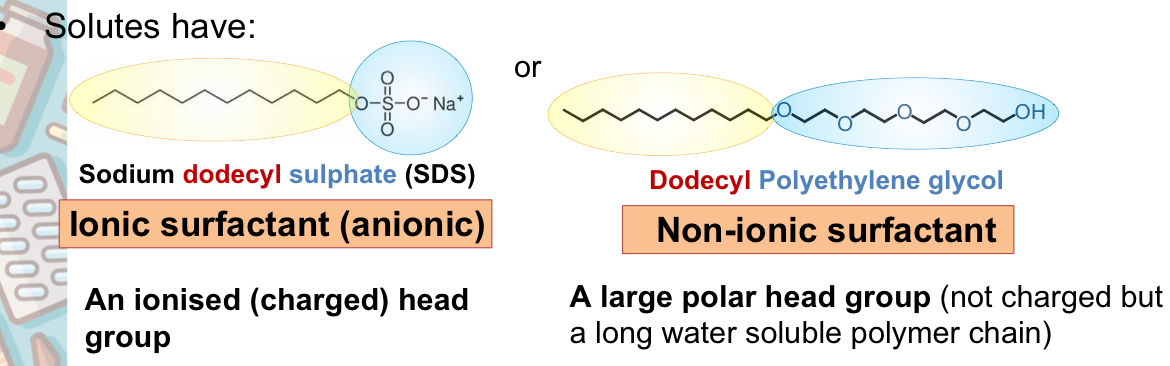
What types of head will a solute have
How do surfactant solutes reduce surface tension
Surfactant solutes initially cause a lowering in surface tension with increasing concentration
At a critical concentration, surface tension levels off with increasing surfactant solute concentration, without causing any more lowering in surface tension
This is because:
at low surfactant concentration the molecules adsorb on the surface, lowering the surface tension
As concentration increases, no more monomers can fit on the surface, so surface tension doesn’t change
Now the monomers can only shield their hydrophobic groups by aggregating to form micelles or other structures
The concentration at which micelles start to form is called the critical micelles concentration
How does micellesation cause an increase in entropy?
Micelles form because of a minimisation of free energy (G). The change in water structure around the hydrophobic part of the surfactant is associated with a decrease in entropy (S; most influential contribution to overall thermodynamics). Micellisation thus causes a favourable increase in entropy (disorder).
What factors influence the spreading (in terms of wetting) of a solvent droplet on a drug particle or other surface?
surface roughness
The surface energy (or hydrophobicity) of the surface
The presence of surfactants
Temperature as this influences viscosity
What is the spreading coefficient
It gives an idea of the ability of a liquid to spread on a surface eg. on a drug particle or eye drops on the eye surface or liquids on the skin

What are some surfactant types
anionic
Cationic
Non-ionic
Ampholytic
These molecules concentrate at an interface and lower the surface tension therefore they find value as solubilises, wetting aids and detergents
What is a colloid
A colloid is a mixture in which one substance consisting of microscopically dispersed insoluble particles is suspended throughout another substance. Some definitions specify that the particles must be dispersed in a liquid, while others extend the definition to include substances like aerosols and gels.
What are disperse systems
They are systems where one component is dispersed as particles or droplets through another component
Dispersions in the size 1nm are also termed colloids
What are course dispersions
These are not colloids but may have a colloidal component eg surface adsorbed amphiphile
Thermodynamically unstable, high surface free energy, cannot be reconsituted