higher biology - unit 3.1: food supply, plant growth + productivity
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
food supply
the availability of food to individuals
food security
the ability of human populations to access food of sufficient quality and quantity
three things needed for food security
quality, quantity, access
increase in human population leads to...
concerns for food security and a demand for food production
food production must be...
sustainable and not degrade the natural resources on which agriculture depends
agricultural production depends on...
factors that control photosynthesis and plant growth
food production is limited by...
the area of land available to grow crops
increased food production will depend on...
factors that control plant growth and photosynthesis, e.g. light intensity, temperature and carbon dioxide concentration
increased food production will depend on...
breeding of higher yield cultivars
increased food production will depend on...
use of fertiliser or water to remove factors which may limit plant growth
increased food production will depend on...
protection of crops from damage and diseases and competition from weeds using pesticides, fungicides and herbicides
increased food production will depend on...
breeders seeking to develop crops with higher nutritional values and suited physical characteristics
livestock produce less food per unit area than plant crops due to...
loss of energy between trophic levels
livestock production is often possible in habitats...
unsuitable for plant growth
light energy is absorbed by photosynthetic pigments to generate....
ATP for photolysis
what happens to light energy that is not absorbed?
it is transmitted or reflected
what to carotenoids do in photosynthesis?
extend the range of wavelengths absorbed and pass the energy to chlorophyll
each pigment absorbs a different...
range of wavelengths of light
what does absorbed light energy do to electrons in photosynthesis?
excites them in the pigment molecule
transfer of electrons in through the electron transport chain releases...
energy to generate ATP by ATP synthase
energy is also used for photolysis, in which water is split into...
oxygen, which is evolved, and hydrogen, which is transferred to the coenzyme NADP
first stage of photosynthesis?
photolysis
second stage of photosynthesis?
carbon fixation
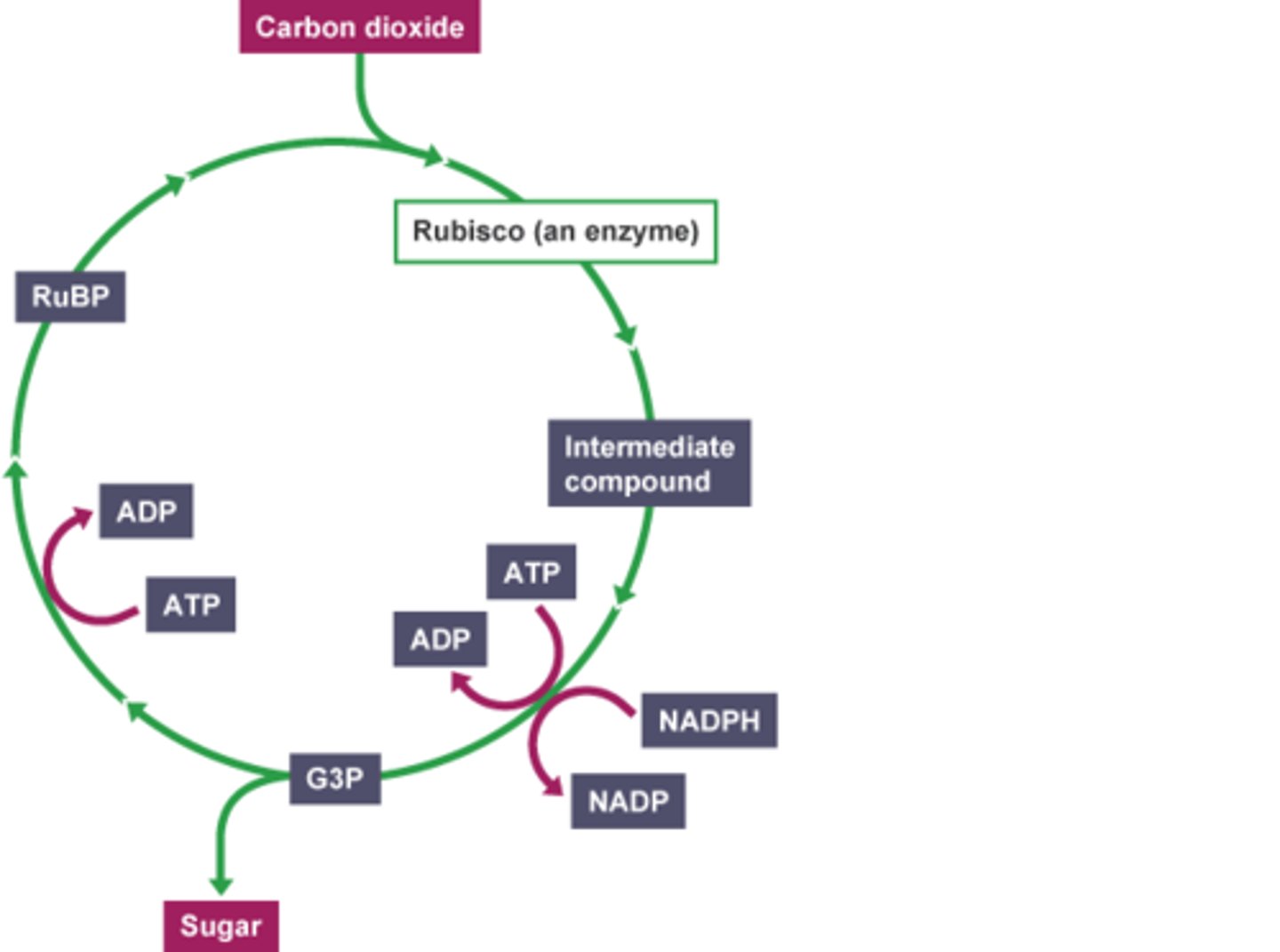
in the carbon fixation stage, the enzyme RuBisCo fixes carbon dioxide by attaching it to...
ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP)
the 3-phosphoglycerate (3PG) produced is phosphorylated by ATP and combined with hydrogen from NADPH to form...
glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate (G3P)
G3P is used to regenerate RuBP...
and for the synthesis of glucose
Glucose may be used as...
respiratory substrate, synthesised into starch or cellulose or passed to other biosynthetic pathways
these biosynthetic pathways can lead to the formation of a variety of metabolites such as...
DNA, protein and fat
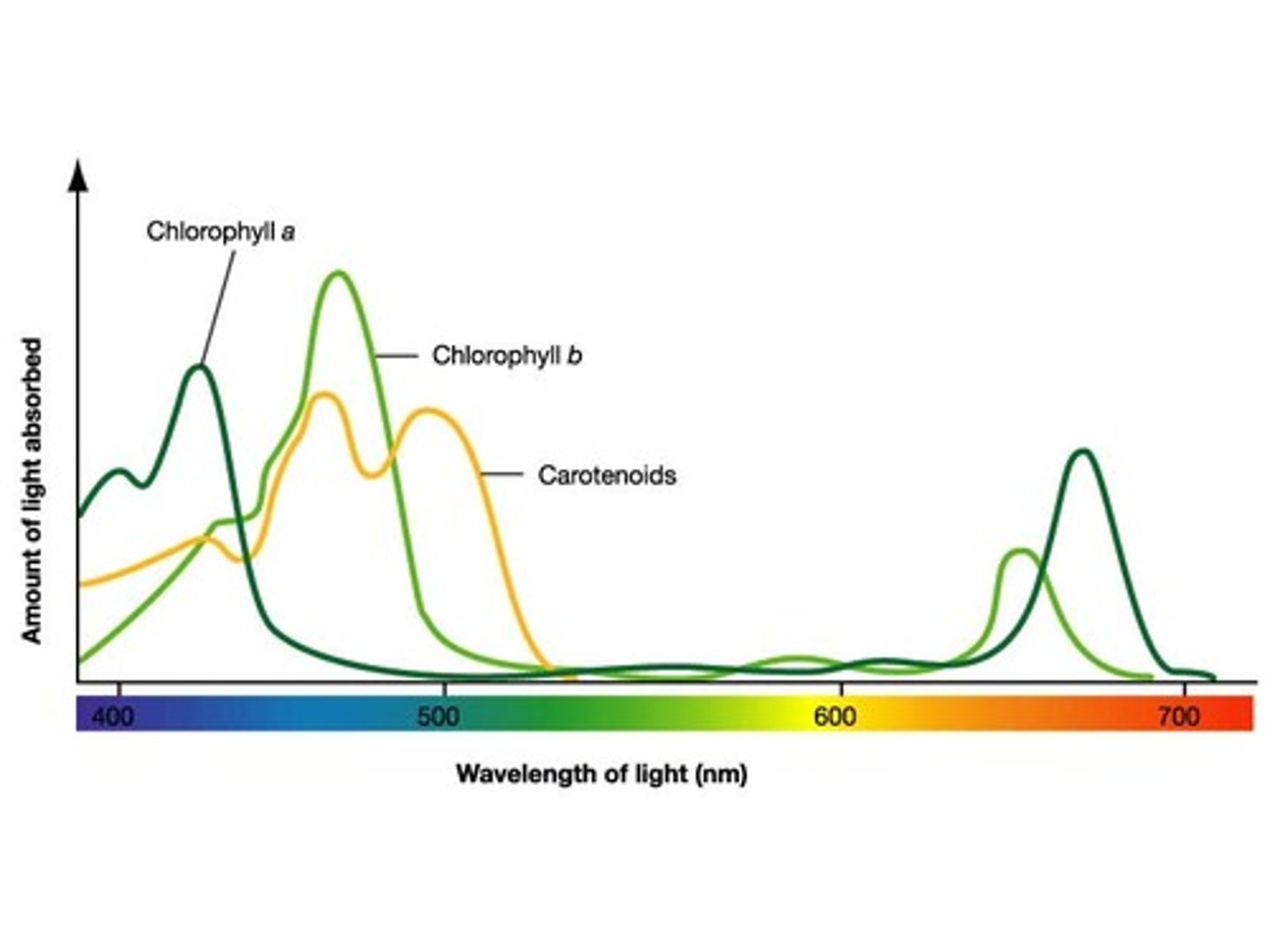
absorption spectrum
shows the different wavelengths of light absorbed by photosynthetic pigments
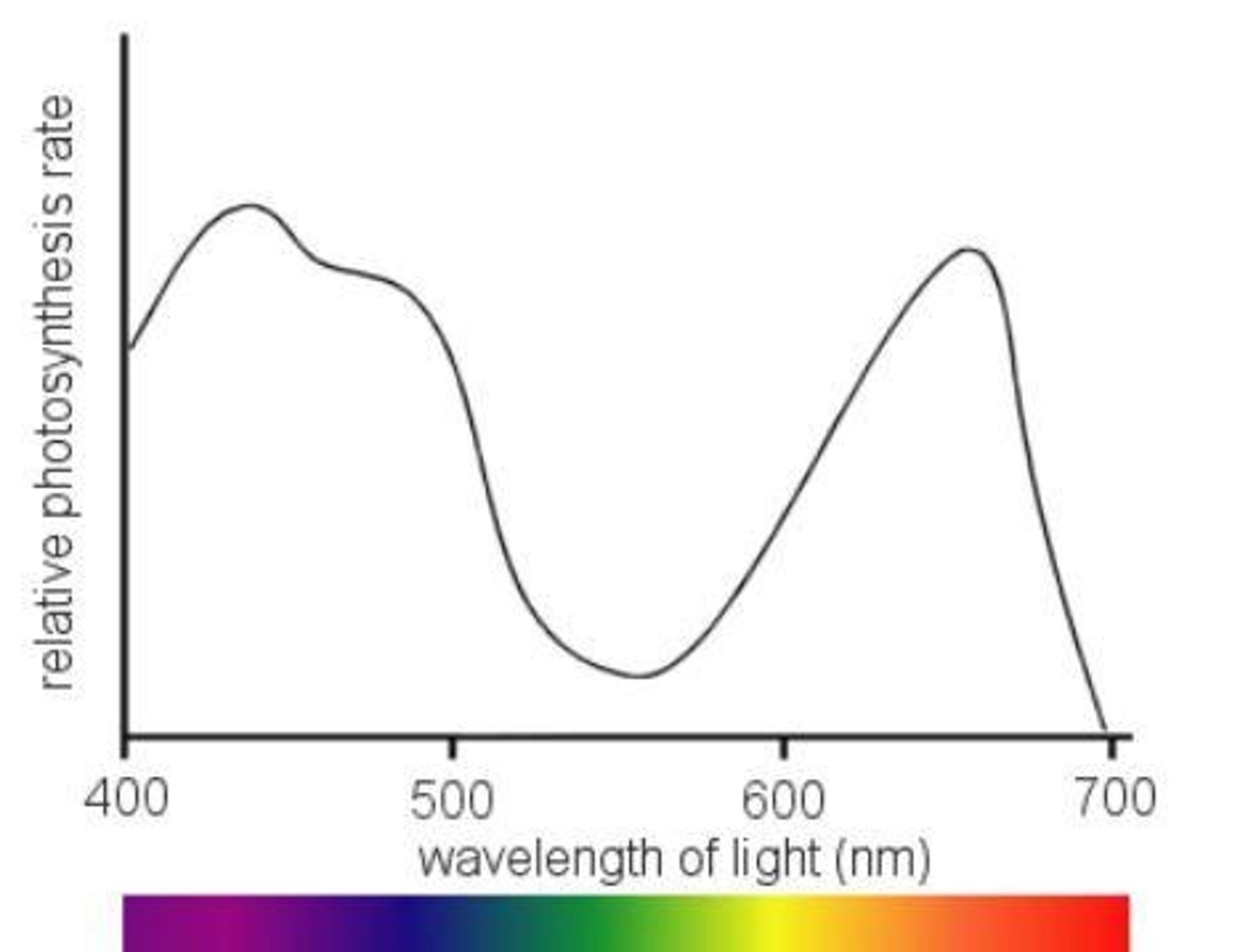
action spectrum
shows the rate of photosynthesis at each wavelength
chromatography
a technique used to separate the photosynthetic pigments. The most soluble travel the furthest