BMS Unit 5 Exam
1/139
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
140 Terms
Gonads
organs that produce gametes and hormones
Ducts
receive and transport gametes
Accessory glands
secrete fluids into ducts
Path of sperm through male reproductive system
testes, epididymis, vas deferens, urethra
Spermatic cord
- begins at entrance to inguinal canal
- descends into the scrotum
- enclose the vas deferens, blood vessels, nerves, and lymphatic vessels of the testes
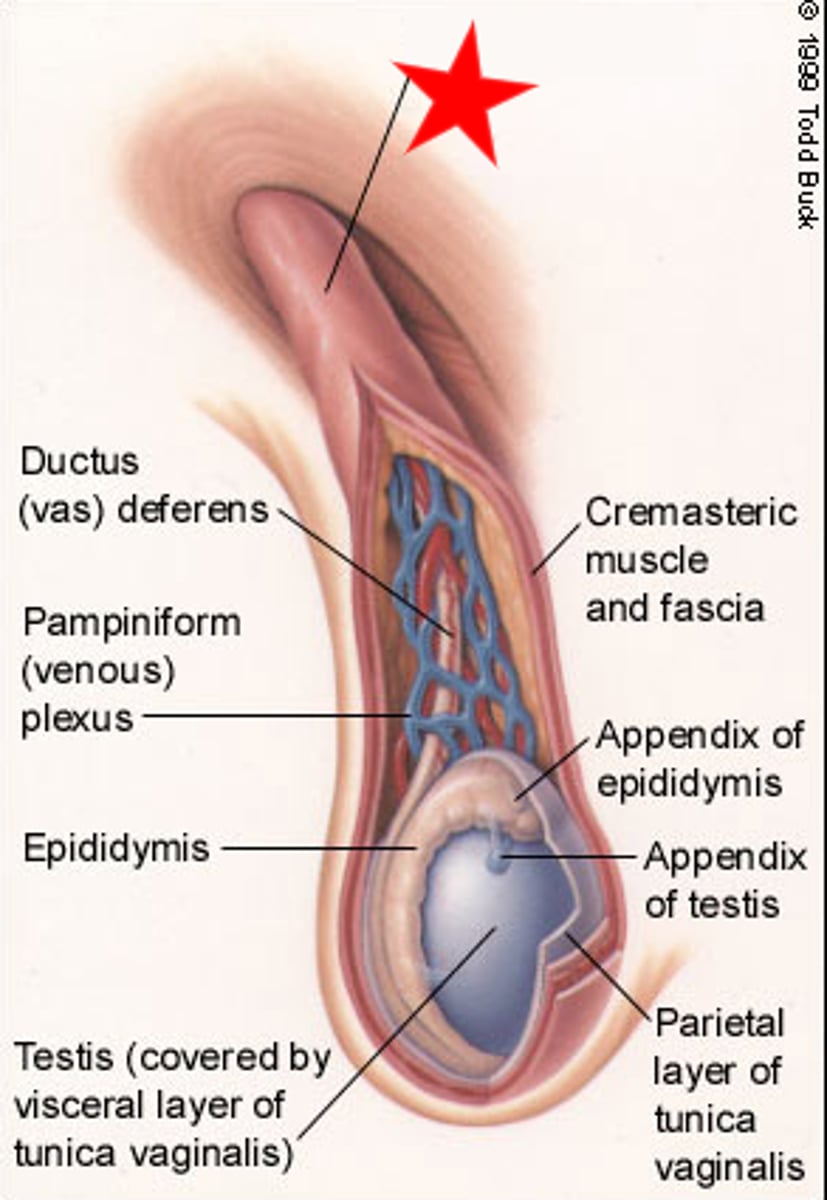
Inguinal hernia
- protrusion of visceral tissues into inguinal canal
- common in males because spermatic cord creates weak point in abdominal wall
Temperature requirement in the testes
- normal sperm development requires temperatures 1.1 C lower than rest of body
Temperature regulation in the testes
when air or body temp increases
- cremaster and dartos muscles relax, moving testes away to keep them cooler
Seminiferous tubules
- slender, tightly coiled tubules in the lobules of the testes
- location of sperm production
the blood-testis barrier is located between the:
spermatogonia and primary spermatocytes
Mitosis
results in 2 identical cells
Meiosis
results in 4 unique cells
After completion of meiosis II, all gametes are....
haploid
Spermatogenesis
process of sperm production
- begins at puberty
- takes about 64 days
Spermiogenesis
differentiation of a spermatid into a sperm
- approx 24 days
Cell types in testes
- Germ cells
- Leydig cells
- Sertoli cells
Germ cells
produce spermatogonia
Leydig cells
(interstitial cells) synthesize testosterone
Sertoli cells secretions
(nurse cells)
synthesize anti-mullerian hormone, inhibin, androgen binding globulin
Sertoli cell function
- maintain blood-testis barrier (tight junctions)
- secrete androgen-binding protein (keeps testosterone high to support spermatogenesis)
- support spermiogenesis
- support mitosis and meiosis
Epididymis
coiled tube that serves as start of male reproductive tract. Site of:
- sperm storage
- sperm maturation
- recycling of damaged sperm
Structure of epididymis
- Head: largest part that receives sperm produced in seminiferous tubules
- Body: on the posterior surface of each testis
- Tail: begins near inferior border of testis and ascends to connection with the ductus deferens (primary storage location)
Sperm entering the lumen of the seminiferous tubules are:
immature and immotile
Sperm motility post epididymis
sperm leaving epididymis are not capable of coordinated movement or fertilization, must undergo capacitation
Sperm capacitation
- sperm become motile when mixed with secretions of seminal glands
- become capable of fertilization when exposed to the female reproductive tract
Bulbourethral gland
- alkaline mucus to neutralize urinary acids in the urethra
- lubricates tip of penis
Seminal gland
- fructose (nutrient for sperm)
- prostaglandins (stimulates smooth muscle contractions)
- fibrinogen (forms temporary clot in vagina)
- slightly alkaline (neutralize acids in vagina)
- first step in capacitation
Prostate gland
- slightly acidic with enzymes that prevent sperm coagulation in the vagina
Fibrinogen forms a temporary clot in the vagina, and is found in
seminal gland
Exogenous administration of excessive testosterone can eventually lead to male infertility by decreasing the levels of
Gonadotropin-releasing hormone, follicle-stimulating hormone, and luteinizing hormone
In males, you would find receptors for follicle-stimulating hormone on
Sertoli cells
Uterine tubes
- Mucosa consists of ciliated columnar epithelial cells
- Peg cells secrete fluid that completes sperm capacitation
- Nutrient rich for sperm and oocytes
What mechanisms in the fallopian tubes move oocytes to the uterus?
- Ciliary movement
- peristaltic contractions
Uterus
- muscular organ that protects, nourishes, and removes wastes for developing embryos
Cervix
inferior portion of uterus that extends to the vagina
Layers of the uterine wall
- perimetrium
- endometrium
- myometrium
Perimetrium
outer thin layer that covers the surface of the uterus
Endometrium
- inner lining of uterus
- thin, glandular, and vascular
- supports fetus
Myometrium
- thick layer of smooth muscle
- contractions move fetus
Vagina
- highly distensible, muscular tube that extends between cervix and vestibule
Functions of vagina
- passageway for elimination of menstrual fluids
- receives penis
- forms portion of birth canal
- vestibular glands: secrete during sexual arousal
External female genitalia
- clitoris
- labia minora
- labia majora
Clitoris
small projection containing erectile tissue, derived from same embryonic structures as penis
Labia majora
- prominent folds of skin and adipose tissue that encircle and conceal labia minora and adjacent structures
Labia minora
Small folds around vestibule covered with smooth, hairless skin
Mammary glands
- consist of lobes
- each lobe: several secretory lobules separated by dense connective tissue
- mammary gland ducts converge, forming lactiferous duct
Lactiferous sinus
where milk accumulates during nursing
Lactiferous duct
A duct through which milk is secreted and which opens at the nipple
Ovarian follicle
specialized follicle where oocyte grows and matures
Maturation of oocyte in ovary
- Primordial oocytes surrounded by a single layer of squamous cells
- Primary surrounded by simple cuboidal
- Secondary surrounded by stratified cuboidal epithelium
- Tertiary filled with follicular fluid secreted by deeper follicular cells
Oogenesis
- oogonia complete mitotic divisions before birth
- between 3-7 months of fetal development, primary oocytes undergo meiosis but halt at prophase of meiosis I
- during puberty, FSH triggers ovarian cycle
- Meiosis I is completed by LH stimulation
- Fertilization causes Meiosis II completion
Female germ cells enter meiosis I
before birth
Female germ cells complete meiosis II
at fertilization
Menopause
- time that ovulation and menstruation cease
- circulation concentrations of estrogen and progesterone decrease
- increase in GnRH, FSH, LH
Decrease in levels of estrogen during menopause leads to
- reductions in size of uterus and breasts
- thinning of urethral and vaginal epithelia
- reduction in rate of bone deposition
Which uterine phase is marked by the initial buildup of endometrium in response to rising estrogen levels?
Proliferative phase
High levels of GnRH will lead to an increase in
FSH, testosterone, inhibin
High levels of estrogen from the dominant follicle cause a _____ feedback to the hypothalamus that leads to ______ levels of luteinizing hormone
positive feedback, increased
Contraceptive types
- short acting
- long acting
- hormonal
- non hormonal
Hormonal contraceptives
- pills
- patch
- ring
- some IUDs
- injection
Combined hormone contraceptives
- contain synthetic estrogen and progesterone
- exposure to estrogen and progestin for 3 wks followed by a 1 wk break
Mechanism of estrogen/progesterone based contraception
- hormones impair folliculogenesis, and inhibit ovulation
- exposure is sufficient to induce endometrial development
- removal of exposure is sufficient to induce menses
Progestin-only contraception
- mini-pill
- injection
Mechanism of progestin-only contraception
- exposure to progestin impacts folliculogenesis
- thicken cervical mucus, blocking sperm
- impair endometrial development
- prevent ovulation (variable between individuals)
Long-term reversible contraceptives
- hormonal IUD (Kyleena, Mirena, etc)
- implant
- copper IUD (Paragard)
Mechanism of IUD (hormonal)
- releases progestin into uterus
- thickens cervical mucus to block sperm
- thins uterine lining
- may prevent ovulation
Mechanism of IUD (copper)
- mechanical barrier that blocks sperm from reaching and fertilizing egg
- prevents implantation
- doesn't inhibit ovulation
Mechanism of implants
- release progestin up to 3 years
- thickens cervical mucus, thins uterine lining, may prevent ovulation
Emergency contraception
- IUD
- morning after pill
Levonorgestrel (LNG)
- synthetic progestin
- blocks LH surge and delays ovulation
- less effective in those > 155lbs
Ulipristal acetate
- progesterone receptor modulator
- blocks LH surge and ovulation
- greater efficacy in those > 155lbs
- lower efficacy in those > 195 lbs
Which of the following acts as a contraceptive by directly inhibiting a hypothalamic hormone?
- FSH
- estrogen
- progesterone
- luteinizing hormone
Progesterone
Trichomoniasis
- protozoan
- antibiotics
Chlamydia
- bacterial
- antibiotics
Syphilis
- bacterial
- antibiotics
- cannot undo damage already done
Genital HPV
- human papillomavirus
- cannot be cured, rather managed and treated
HIV
- human immunodeficiency virus
- if untreated, progress to AIDS
Gonorrhea
- bacterial
- antibiotics
- resistant strains increasing
Which of the following STDs is caused by a bacteria?
- Trichomoniasis
- Syphilis
- Genital HPV
- AIDS
Syphilis
Who is at risk for STDs?
- college age people (chlamydia, gonorrhea, syphilis, HPV)
- elderly (lack of condom bc no pregnancy)
Levels of sex determination
- genetic (XY, XX)
- gonadal (Testes, ovaries)
- phenotypic (external genitalia, glands, tracts)
Genetic sex determination
- Chromosomes (23rd pair, XX or XY)
- autosomes (22 pairs)
- X chromo (need 1)
- Y chromo (SRY gene for males)
Gonadal development is ONLY dependent on ........
genes
Ovary development
RSPO1, beta-catenin, and WNT4 are active and block SOX9
Testis development
SRY upregulates SOX9, which blocks RSPO1, B-catenin, and WNT4
Gonadal sex determination
- undifferentiated until 6th week of development
- bipotential (can be ovary or testis)
- RSPO1, B-catenin, WNT4, and SOX9 are autosomal factors on every cell
RSPO1/WNT4 is responsible for:
a. initiating puberty
b.triggering ovulation
c. development of an ovary
d.maintenance of the corpus luteum
Development of an ovary
Mullerian duct
- female reproductive tract progenitor
- differentiates into oviduct, uterus, cervix, and vagina
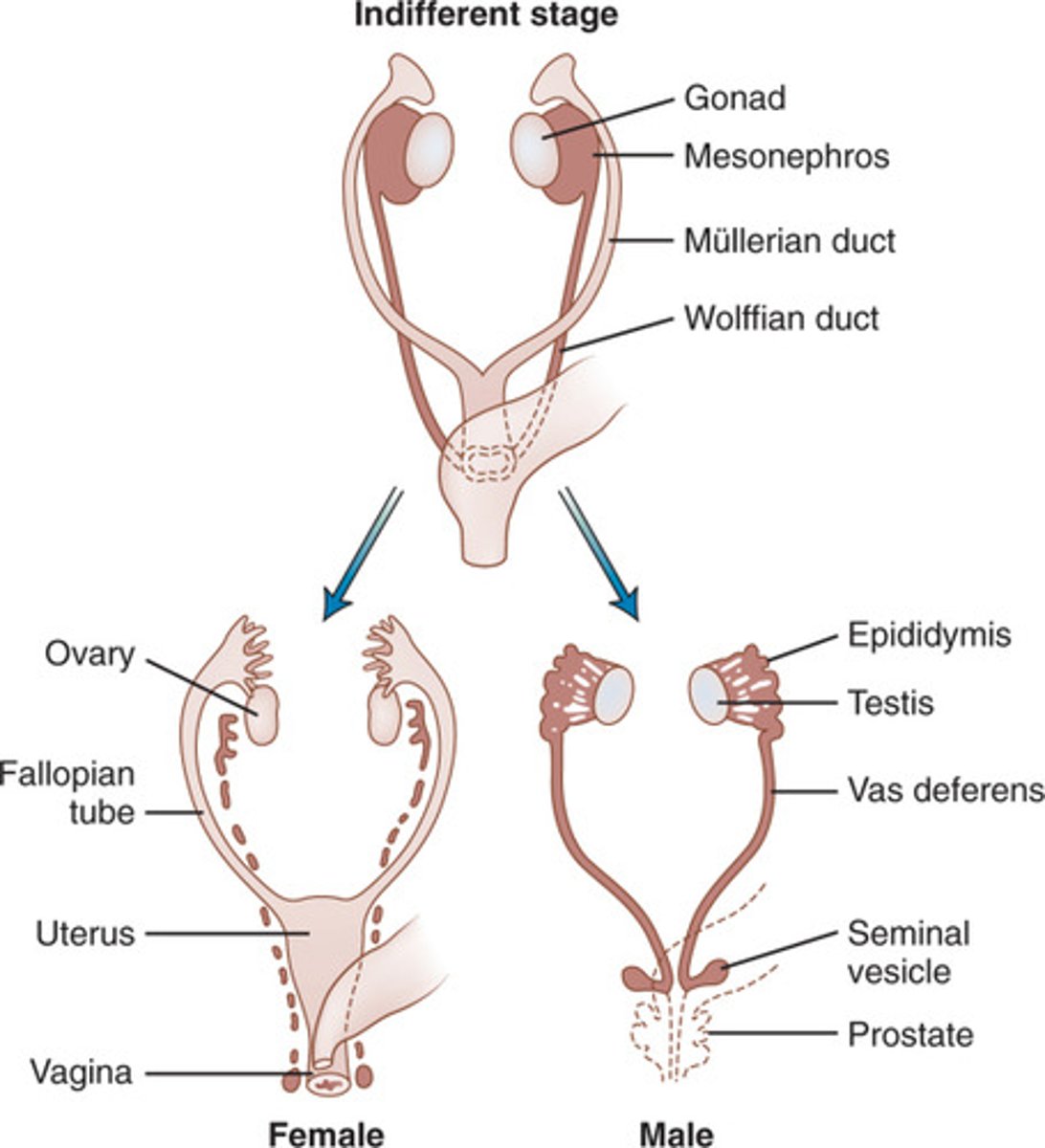
Wolffian duct
- male reproductive tract progenitor
- differentiates into epididymis, vas deferens, seminal vesicle
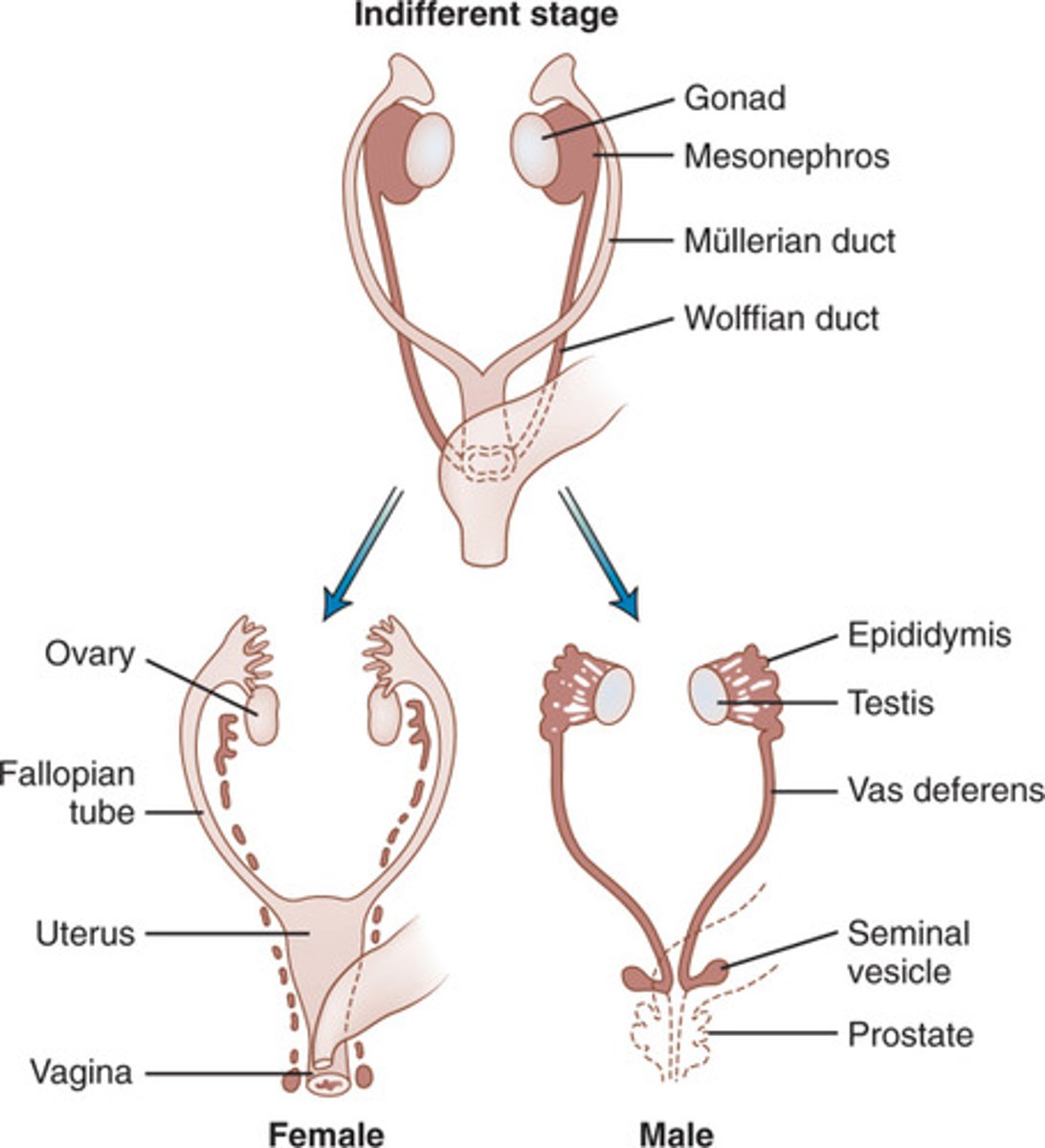
Alfred Jost experiments
- embryos without gonads (regardless of genetic sex) acquired a female phenotype
- regression of Wolffian ducts and maintenance of Mullerian ducts
What maintains the Wolffian ducts?
testosterone
What is required to maintain the Mullerian ducts?
nothing
What is released by the testes for the regression of the mullerian ducts?
Anti-Mullerian hormone (AMH)
Which of the following is TRUE?
a. Anti-Mullerian hormone (AMH) is necessary for the development of the Mullerian duct
b. Estrogen is necessary for the development of an ovary
c. Testosterone is necessary for the development of a testis
d. Chromosomal sex determines gonadal sex, which then determines phenotypic sex
Chromosomal sex determines gonadal sex, which then determines phenotypic sex
Phenotypic sex determination
- ovaries secrete estrogen and progesterone, leading to development of the breasts, uterus, vagina, and ovaries
- testes secrete testosterone and AMH
How does external genitalia differentiate?
- initially undifferentiated
- feminization is default (forms vaginal opening, labia minora/majora, and clitoris)
- Masculinization requires dihydrotestosterone (DHT) which forms penis, urethra, and scrotum
Which of the following does not develop from the Mullerian duct?
- uterus
- uterine tubes
- cervix
- lower vagina
lower vagina
A mutated Y chromosome that lacked an SRY gene would lead to the:
- degradation of the Wolffian duct
- development of testes
- activation of SOX9
- masculinization of external genitalia
degradation of the Wolffian duct
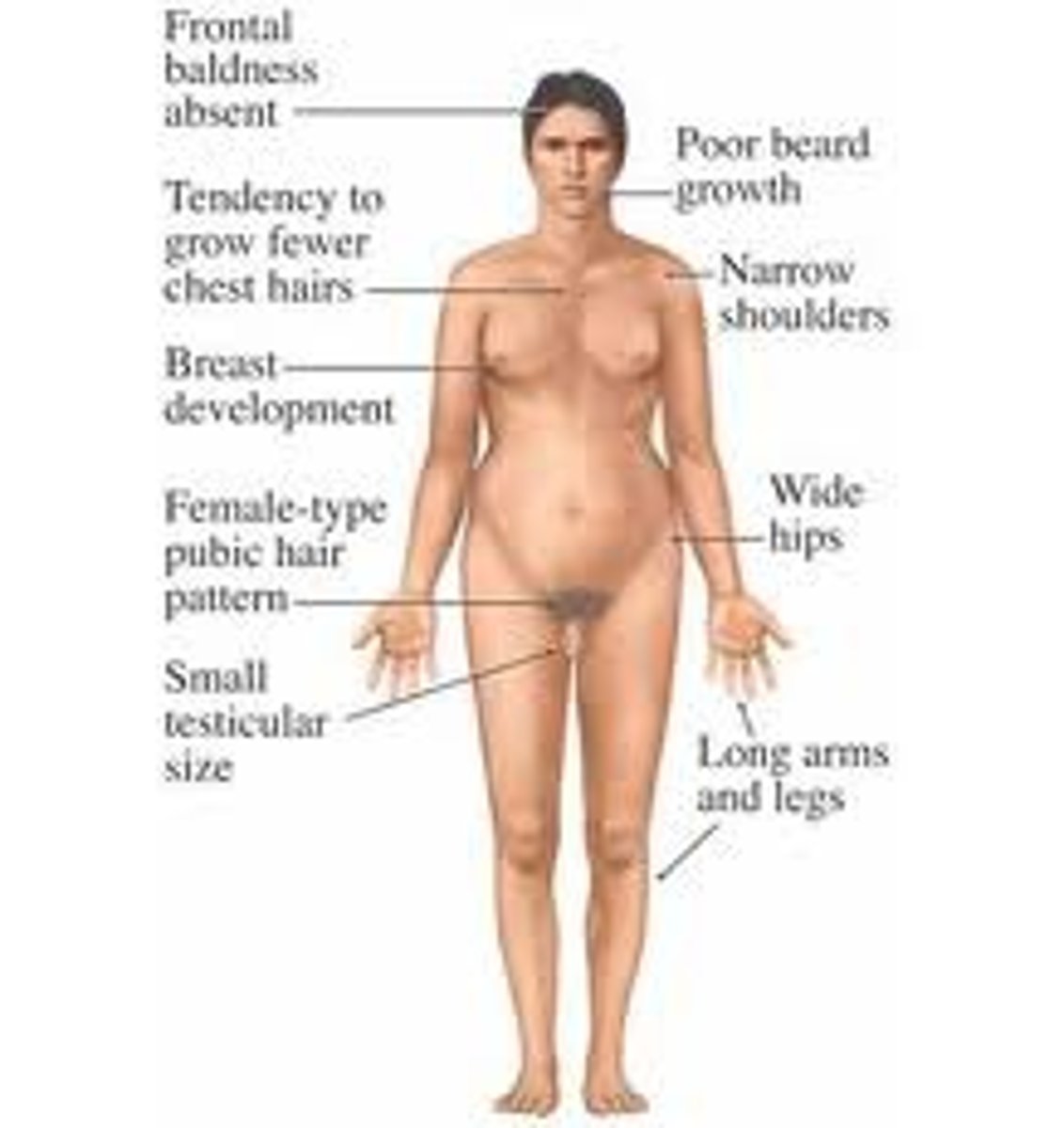
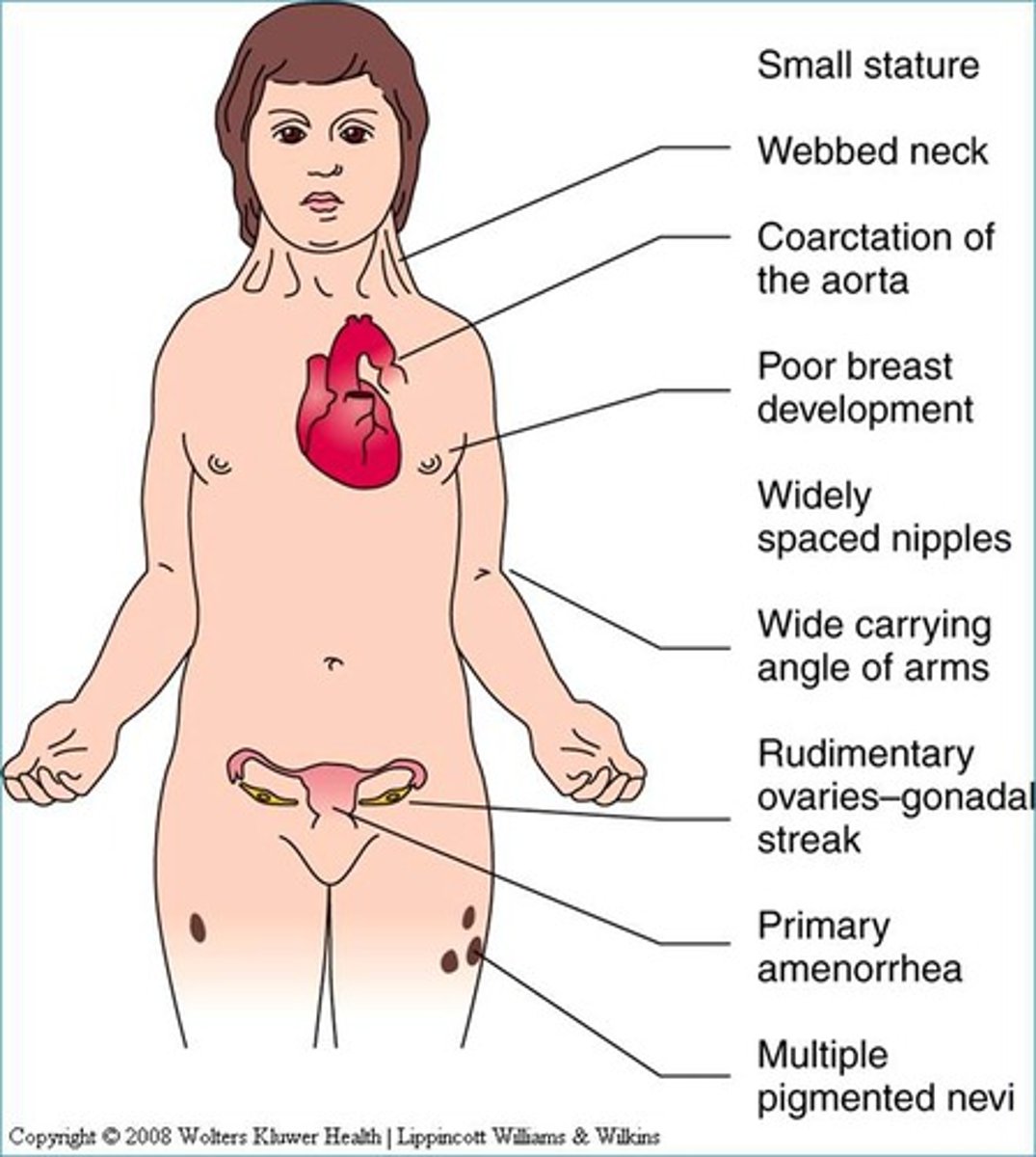
Turner Syndrome
- XO
- Ovaries
- Internal: Mullerian (no AMH or T)
- External: feminization (no DHT)
Klinefelter Syndrome
- XXY
- Testes
- Internal: Wolffian duct (AMH + T)
- External: masculinization (DHT)