Chapter 11: Factorial Design
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
factor (independent variables)
something that can influence an outcome or dependent variable
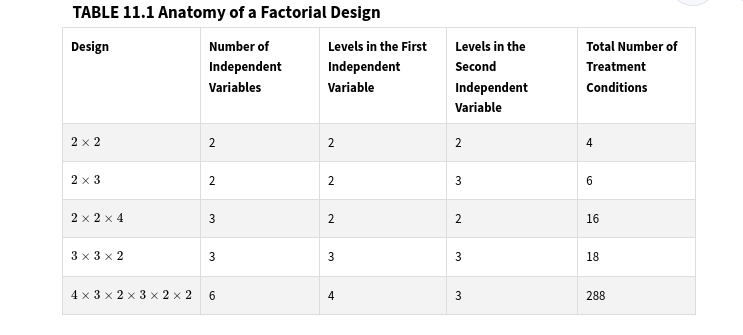
factorial design
an experimental design that has more than one independent variable
anatomy of a factorial design
hybrid-design
only factorial design that has at least one quasi-independent variable (something that can not be manipulated)
benefits of factorial designs
being able to establish cause and effect and the ability to examine how the combination of independent variables affects dependent variables
interaction
when one independent variables influence on the dependent variable changes depending on the level of the other independent variable(s)
main effect hypothesis
focuses solely on the effect of a single IV on the DV, ignoring all other IV
interaction effect hypothesis
a prediction about how the levels of one IV will combine with another IV to impact the DV in a way that extends beyond the sum of the 2 separate main effects.
crossover interaction (or disordinal interaction )
when the influence of one independent variable on the other reverses across levels of the two other IVs
ordinal interaction
where one independent variable has an influence on a particular level of the other independent variable but not on all of its levels
vignette
a description of a hypothetical situation, event or scenerio to which participants react.
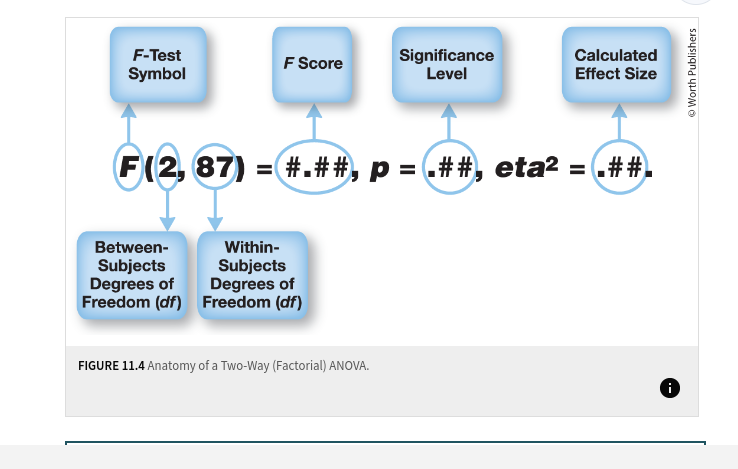
two-way analysis of variance (two way ANOVA or factorial ANOVA)
a statistical test that allows us to simultaneously test how two seperate nominal or categorical independent variables (or factors) influence the dependent variables interact to influence the dependent variable
two-way ANOVA test for any main or interaction effects
cell mean
the average on the dependent variable for participants with a combination of the levels of the IVs
marginal means
the averages of all participants on each level of the independent variables, ignoring the other independent variables
Anatomy of a Two-Way (factorial ANOVA)