A&P Practicum 1 CBU BIO153L Anatomy & Physiology Lab (Sem 1) (Professor Heyman)
1/174
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
175 Terms
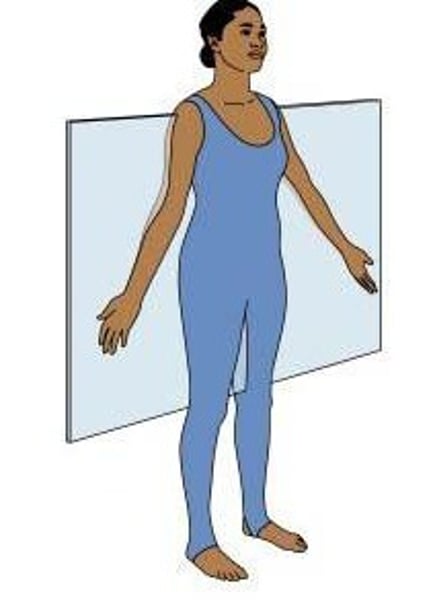
directional terms: median (midsagittal) plane
anterior & posterior
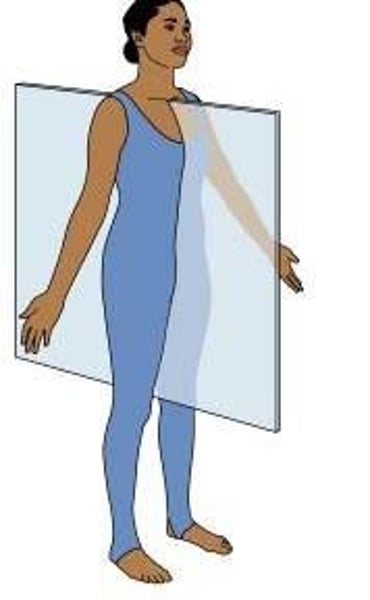
directional terms: frontal plane
medial & lateral
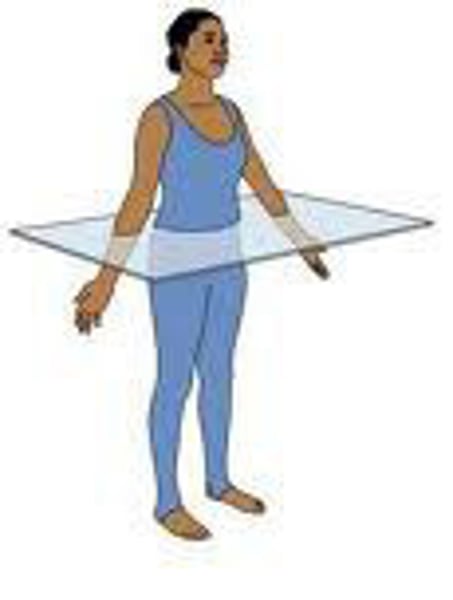
directional terms: transverse plane
superior & inferior
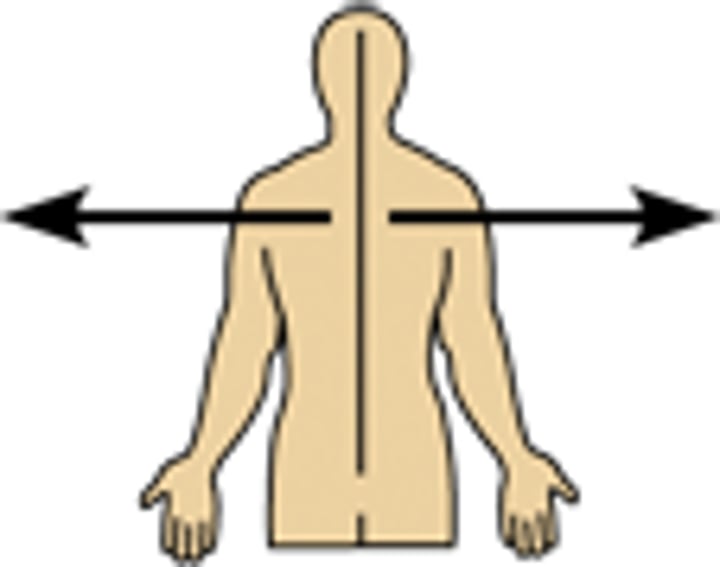
direction terms: lateral
the arms are lateral to the chest
away from the midline of the body; ON THE OUTER SIDE OF
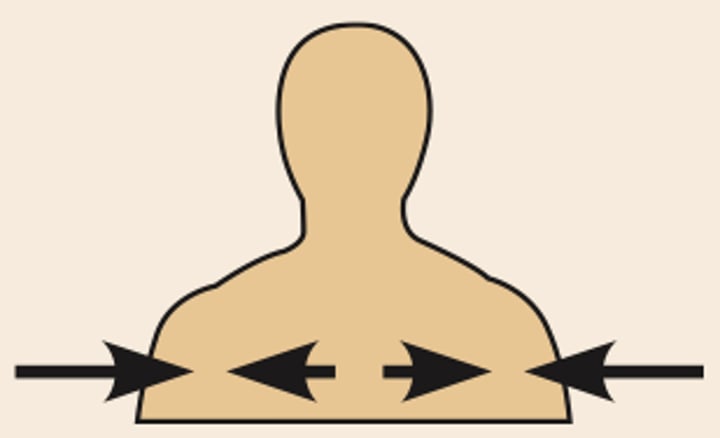
direction terms: intermediate
the collarbone is intermediate between the breastbone and shoulder
between a more medial and a more lateral structure
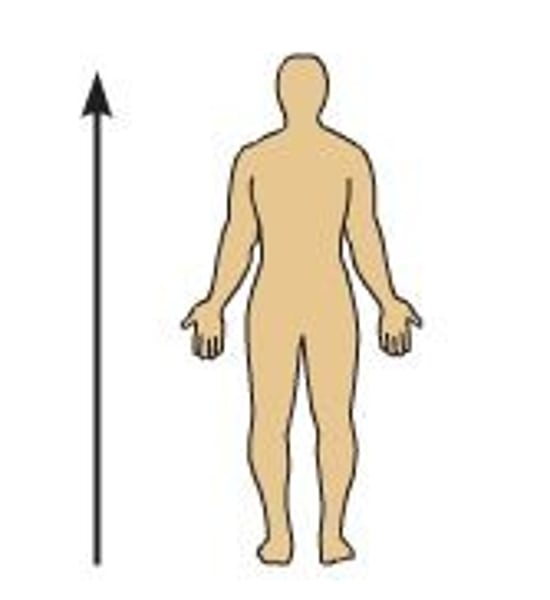
directional terms: superior (cranial/cephalad)
the head is superior to the abdomen
toward the head end or upper part of a structure or the body; ABOVE
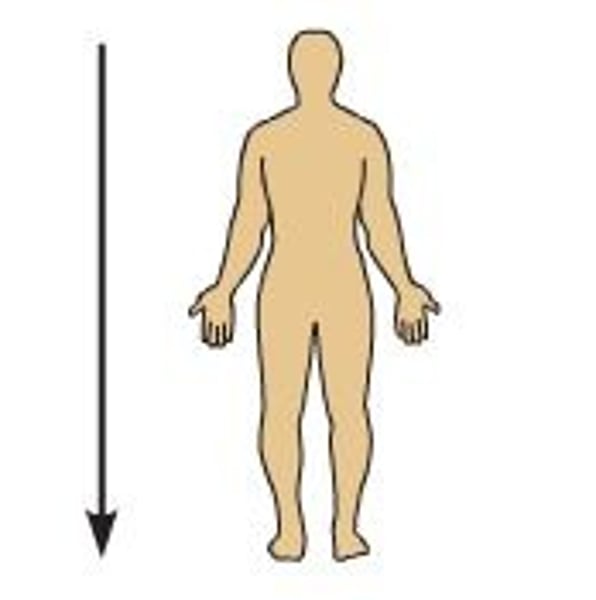
directional terms: inferior (caudal)
the navel is inferior to the chin
away from the head end or toward the lower part of a structure or the body; BELOW
directional terms: ventral (anterior)
the breastbone is anterior to the spine
toward or at the front of the body; IN FRONT OF
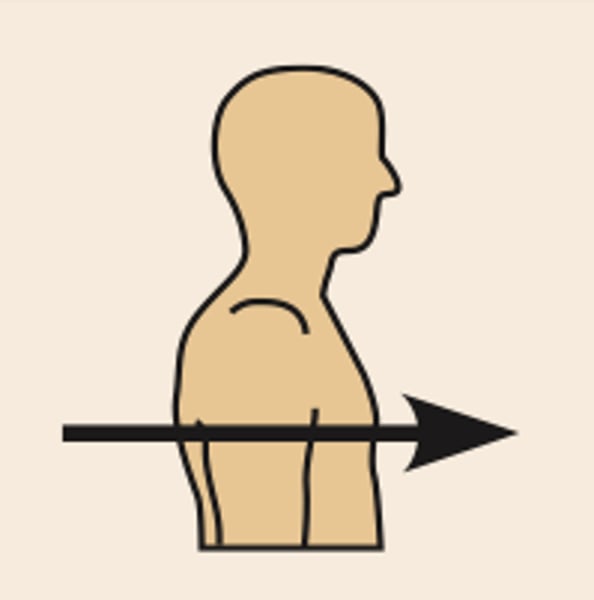
directional terms: dorsal (posterior)
the heart is posterior to the breastbone
toward or at the back of the body; BEHIND
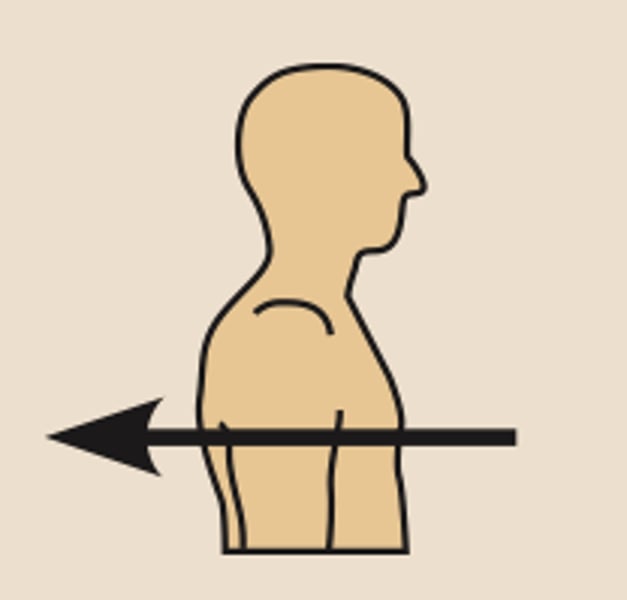
directional terms: medial
the heart is medial to the arm
toward or at the midline of the body; ON THE INNER SIDE OF
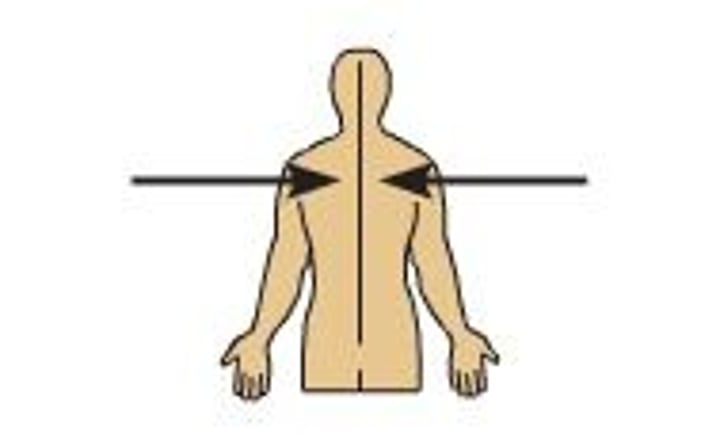
direction terms: proximal
the elbow is proximal to the wrist
closer to the origin of the body part or the point of attachment of a limb to the body trunk
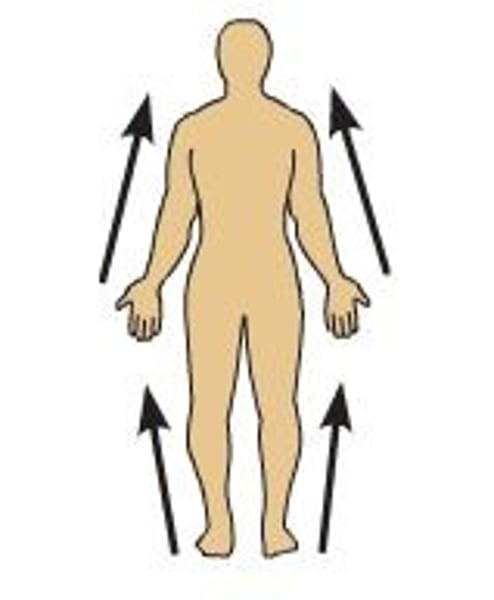
direction terms: distal
the knee is distal to the thigh
farther from the origin of a body part of the point of attachment of a limb to the body trunk
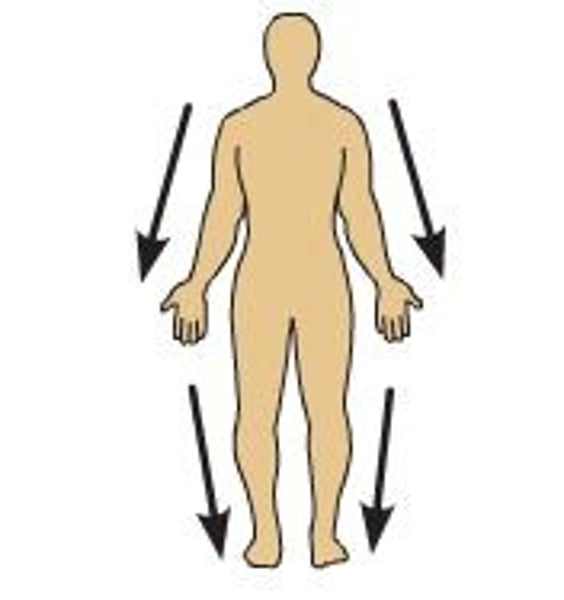
direction terms: superficial (external)
the skin is superficial to the skeletal muscles
toward or at the body surface
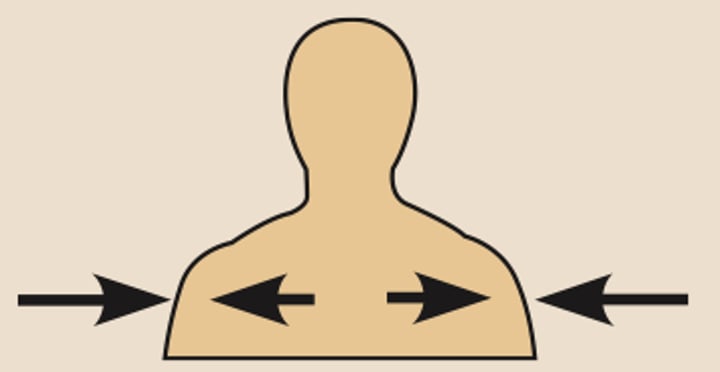
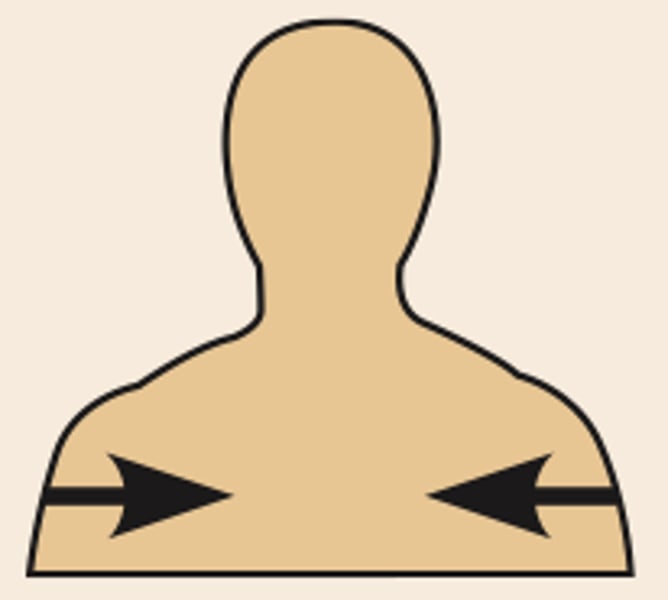
direction terms: deep (internal)
the lungs are deep to the skin
away from the body surface; MORE INTERNAL
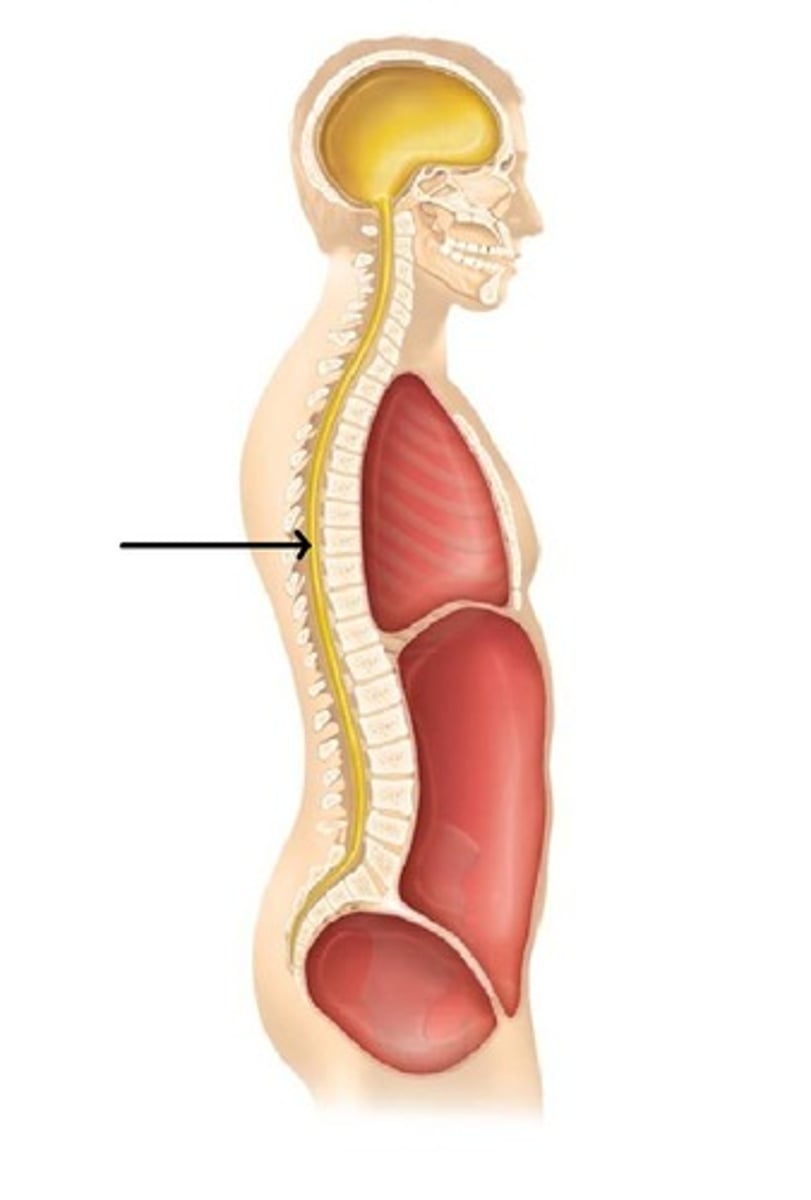
dorsal body cavity
contains cranial cavity & vertebral cavity
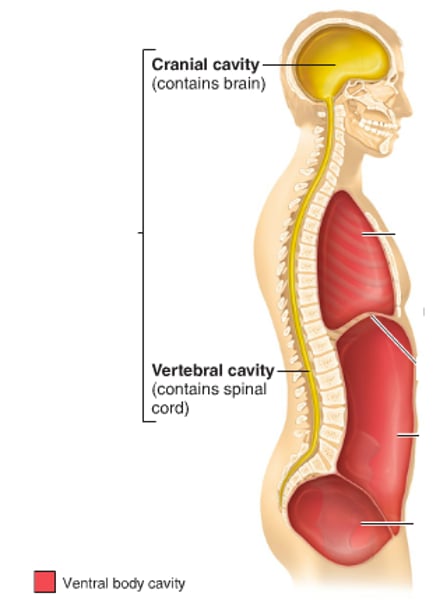
ventral caviry
contains thoracic cavity & abdominopelvic cavity
cranial cavity
(contains brain)
vertebral cavity
contains spinal cord
thoracic cavity
contains heart & lungs
(superior mediastinum, pleural cavity, pericardial cavity within mediastinum)
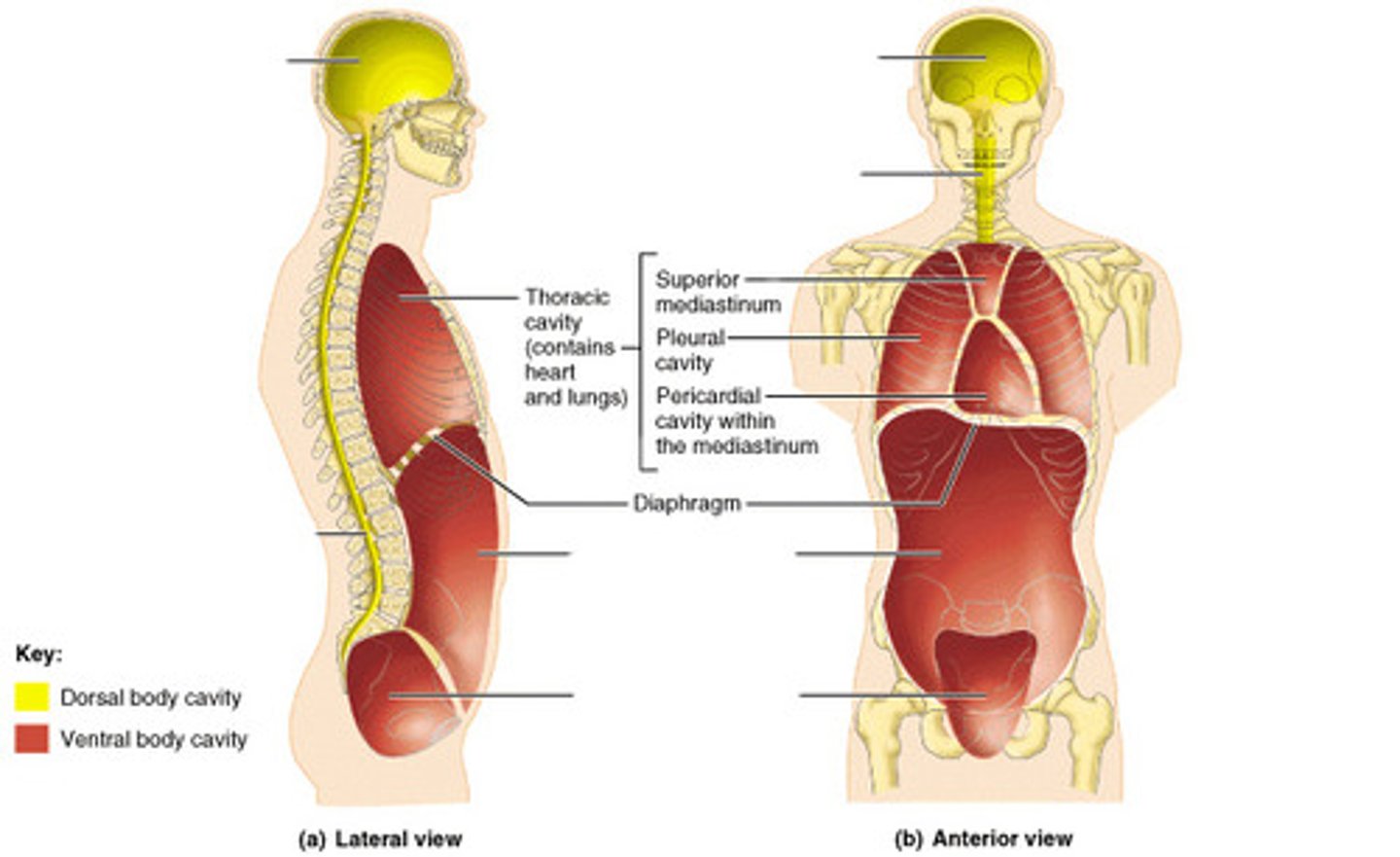
abdominal cavity
contains digestive viscera
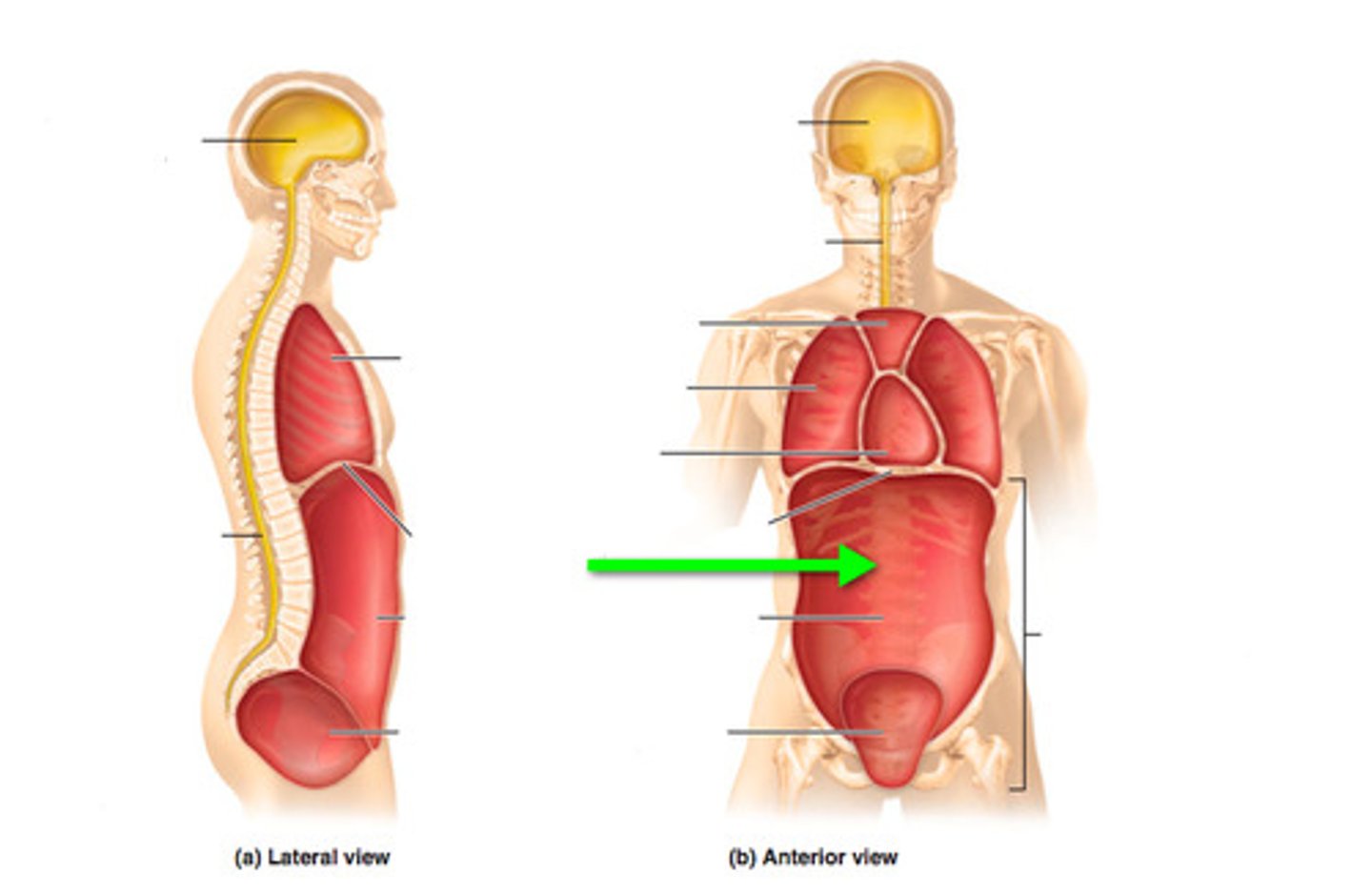
pelvic cavity
contains urinary bladder, reproductive organs, and rectum
four basic tissue types and basic function
epithelial tissue- covering
connective tissue- movement
muscle tissue- movement
nervous tissue- control
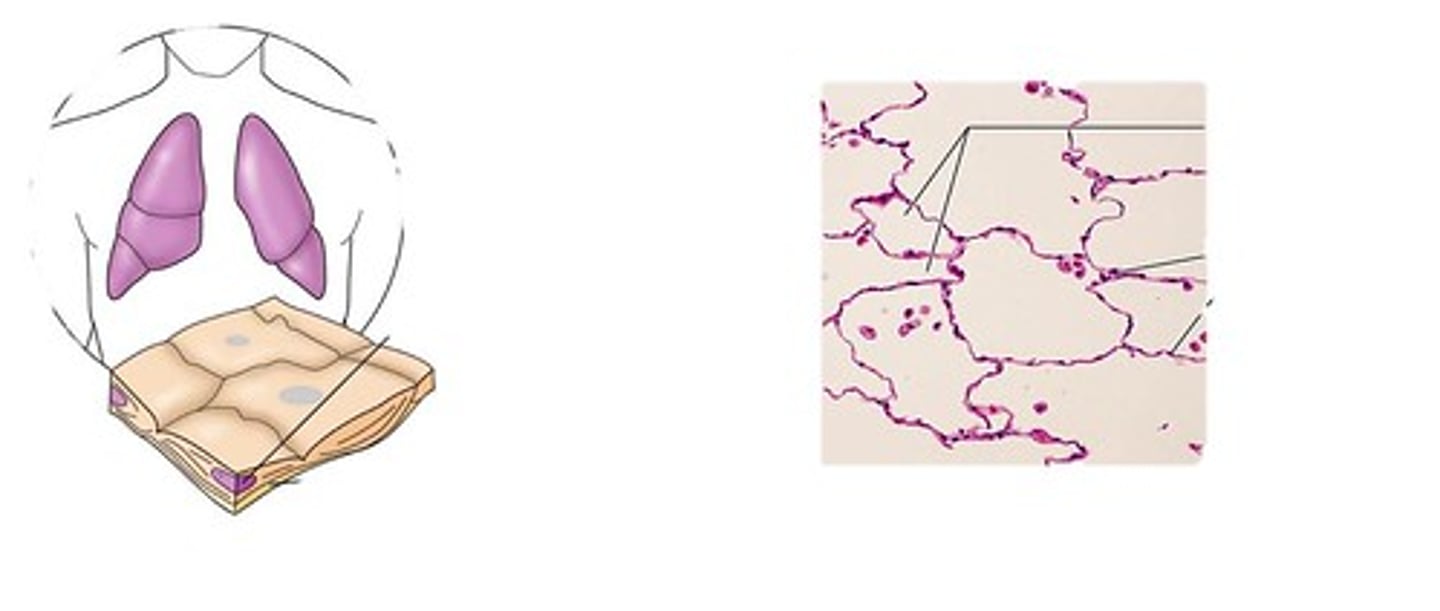
simple squamous epithelium
example: alveoli of lung
function: diffusion and filtration
a single layer thick; flattened and scale like
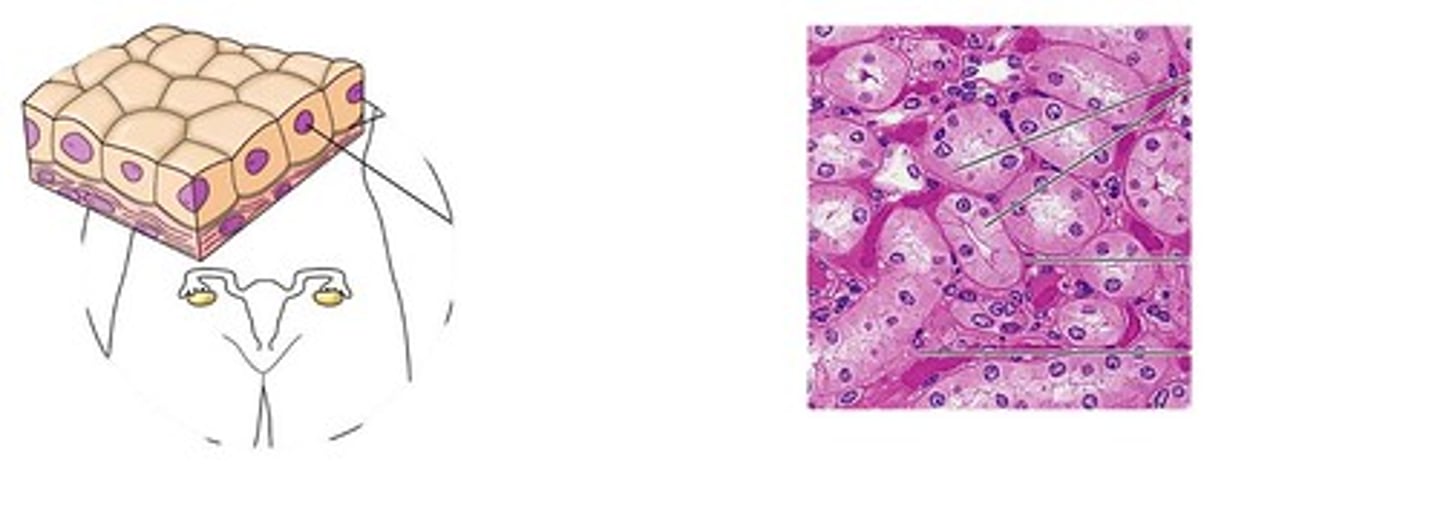
simple cuboidal epithelium
example: kidney tubules
function: secretion and absorption
a single layer thick; box-like, cube
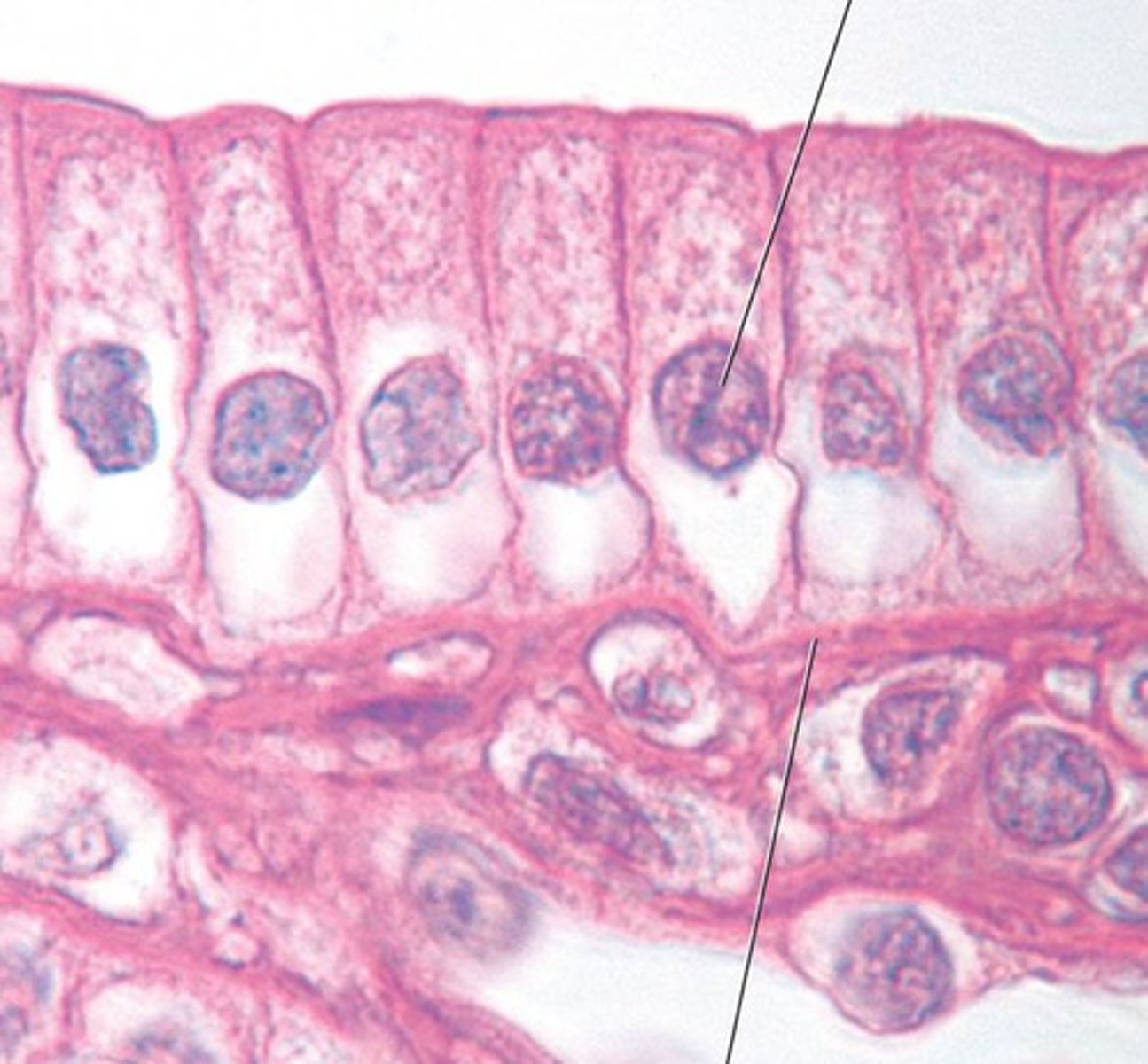
simple columnar epithelium
example: digestive tract
function: secretion of mucous/ absorption
a single layer thick; tall, column-like
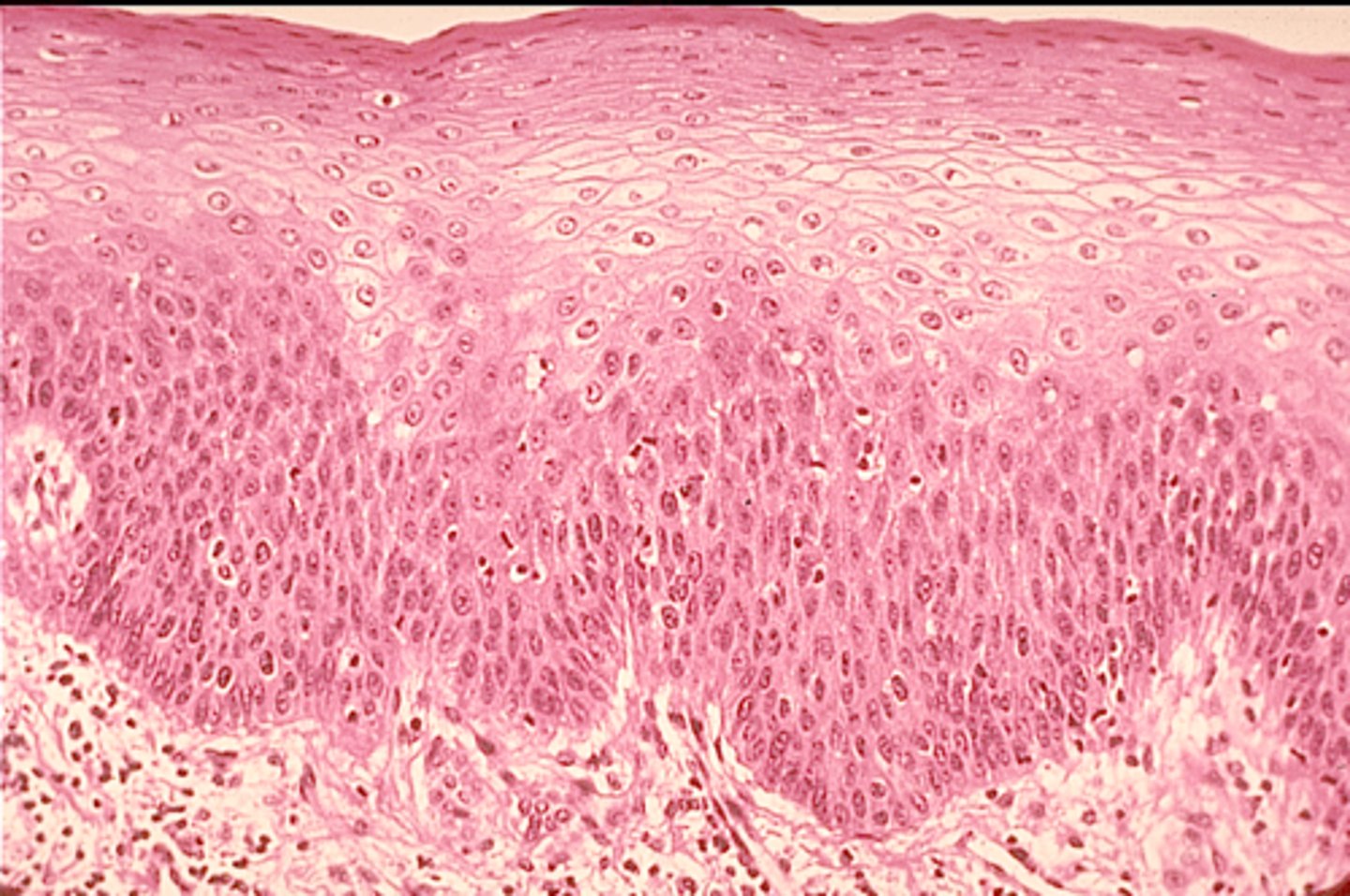
stratified squamous epithelium
example: epidermis of skin
function: protects from abrasion
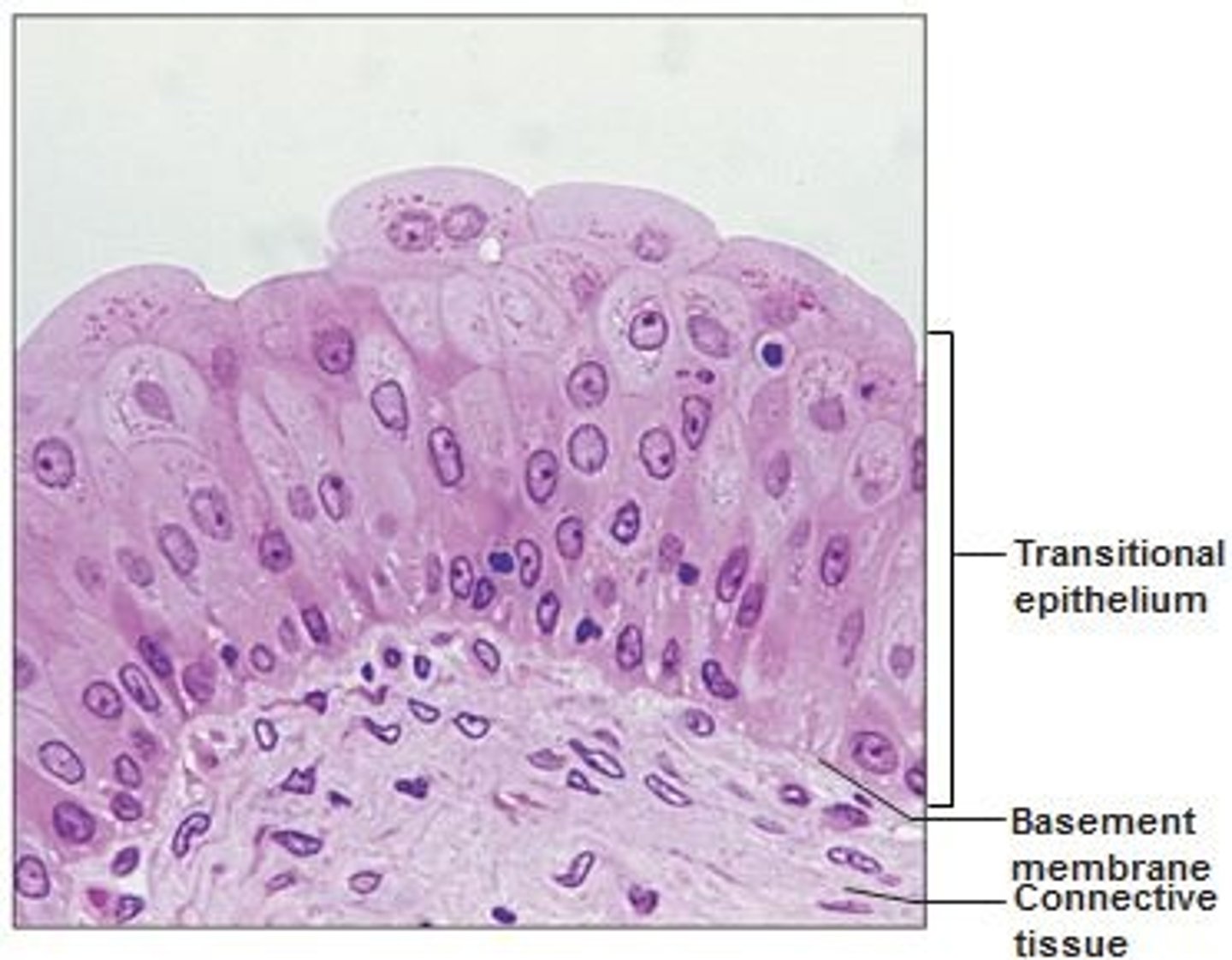
transitional epithelium
example: unitary bladder
function: stretches
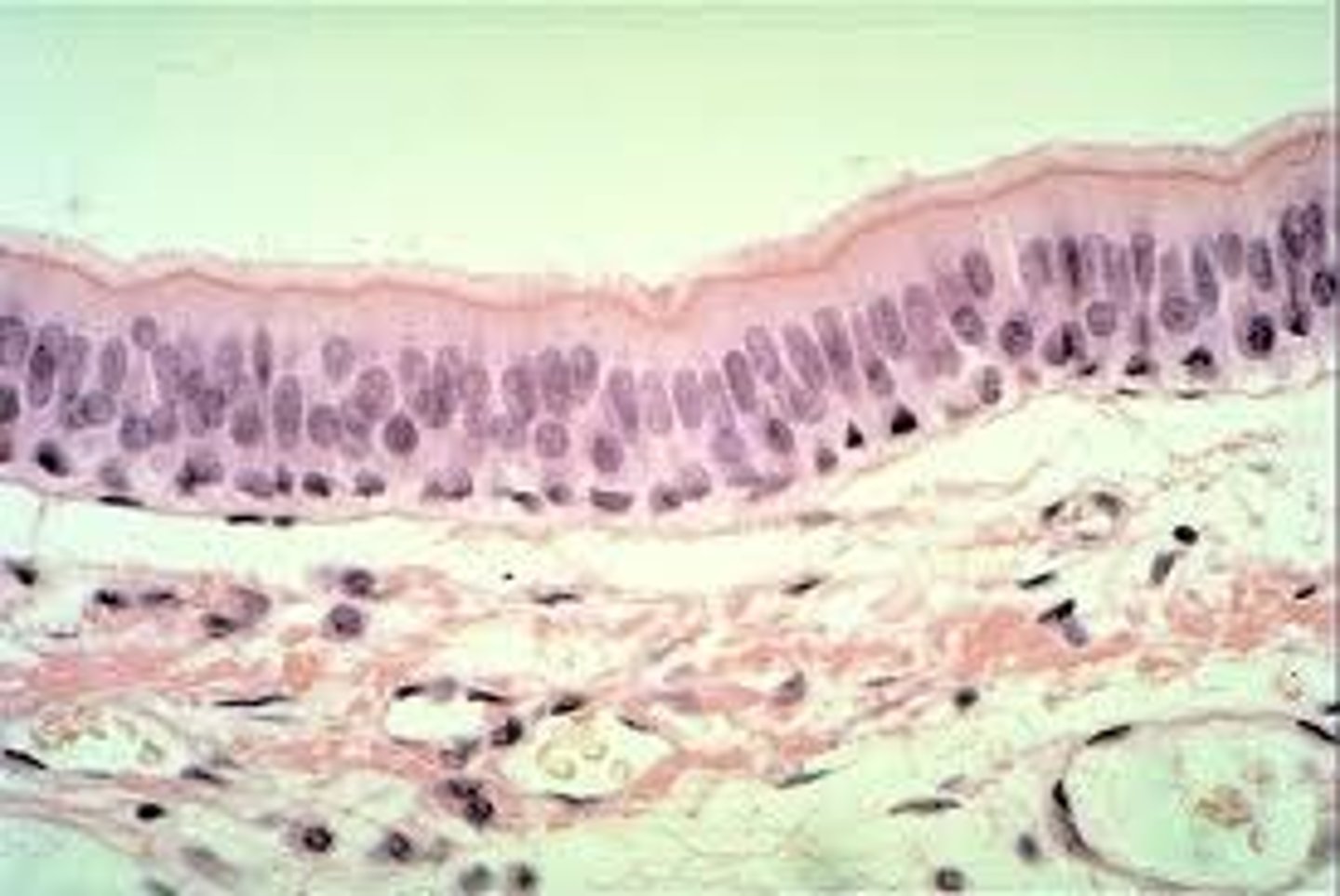
pseudo stratified ciliated columnar epithelium
example: trachea
function: produces and moves mucous
two or more layers thick and involved in protection; tall column-like ciliated
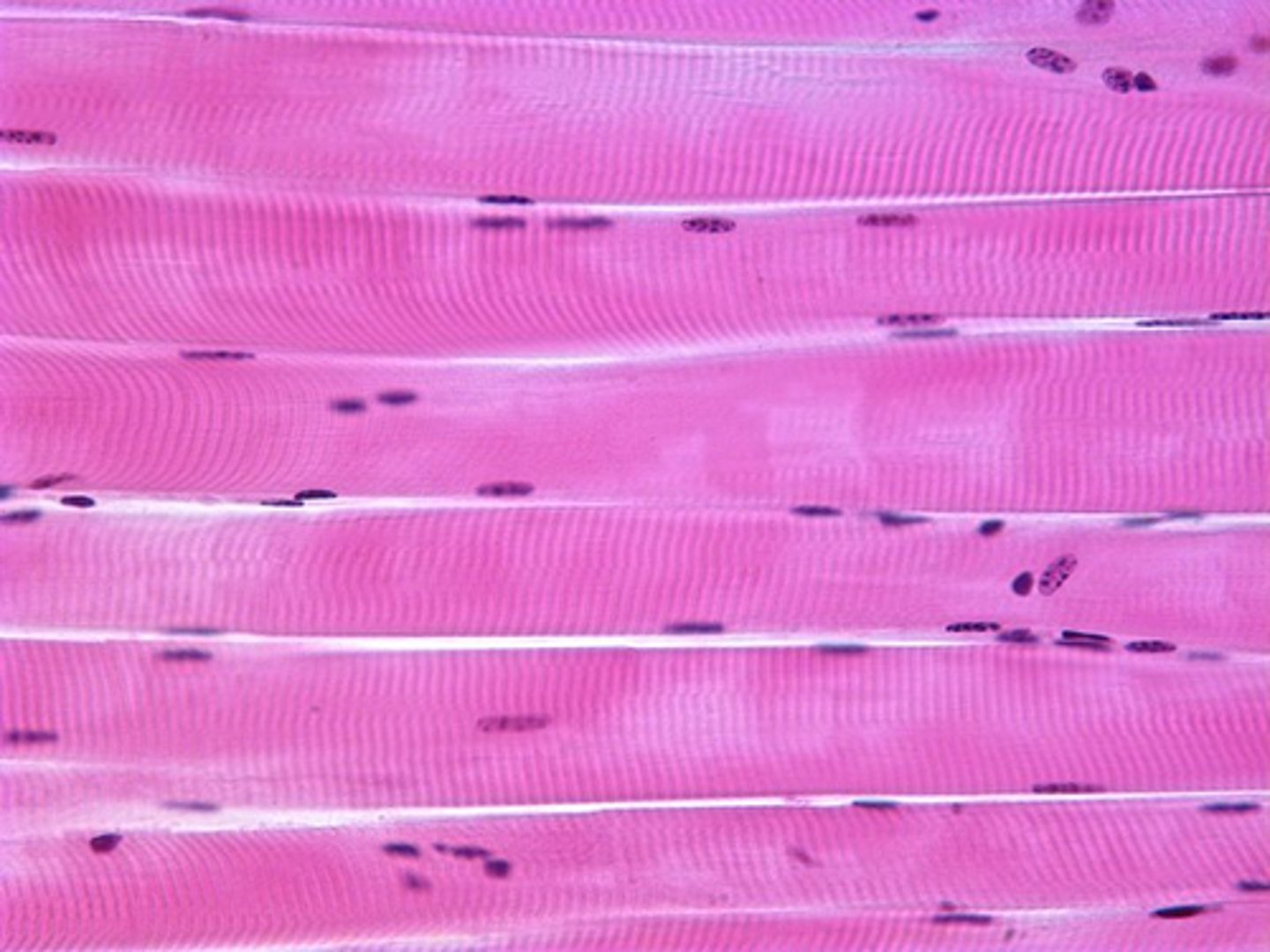
skeletal muscle
example: biceps
function: voluntary movement
cardiac muscle
example: heart
function: pumps blood
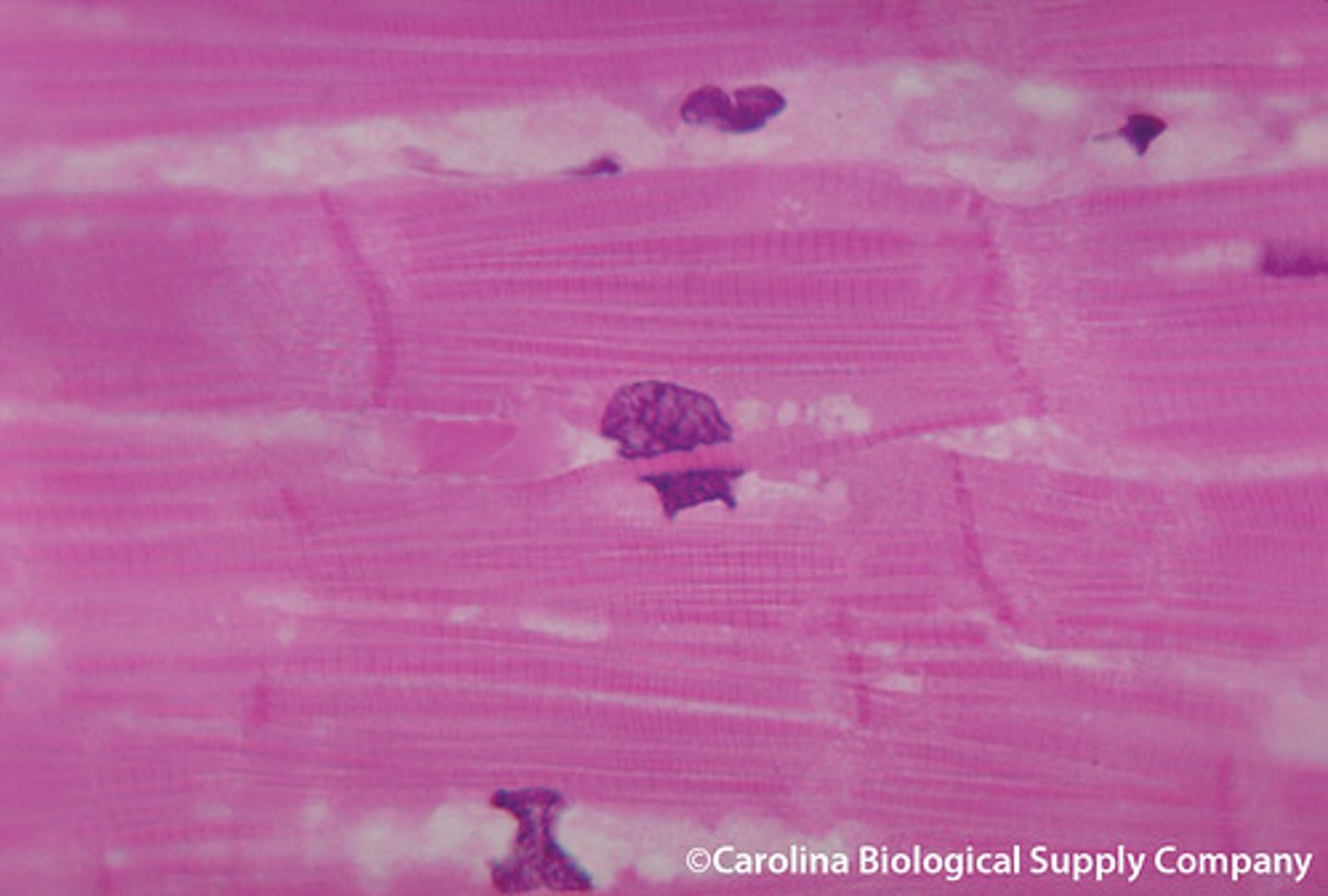
smooth muscle
example: hollow organs (uterus, stomach)
function: involuntary movement of substances
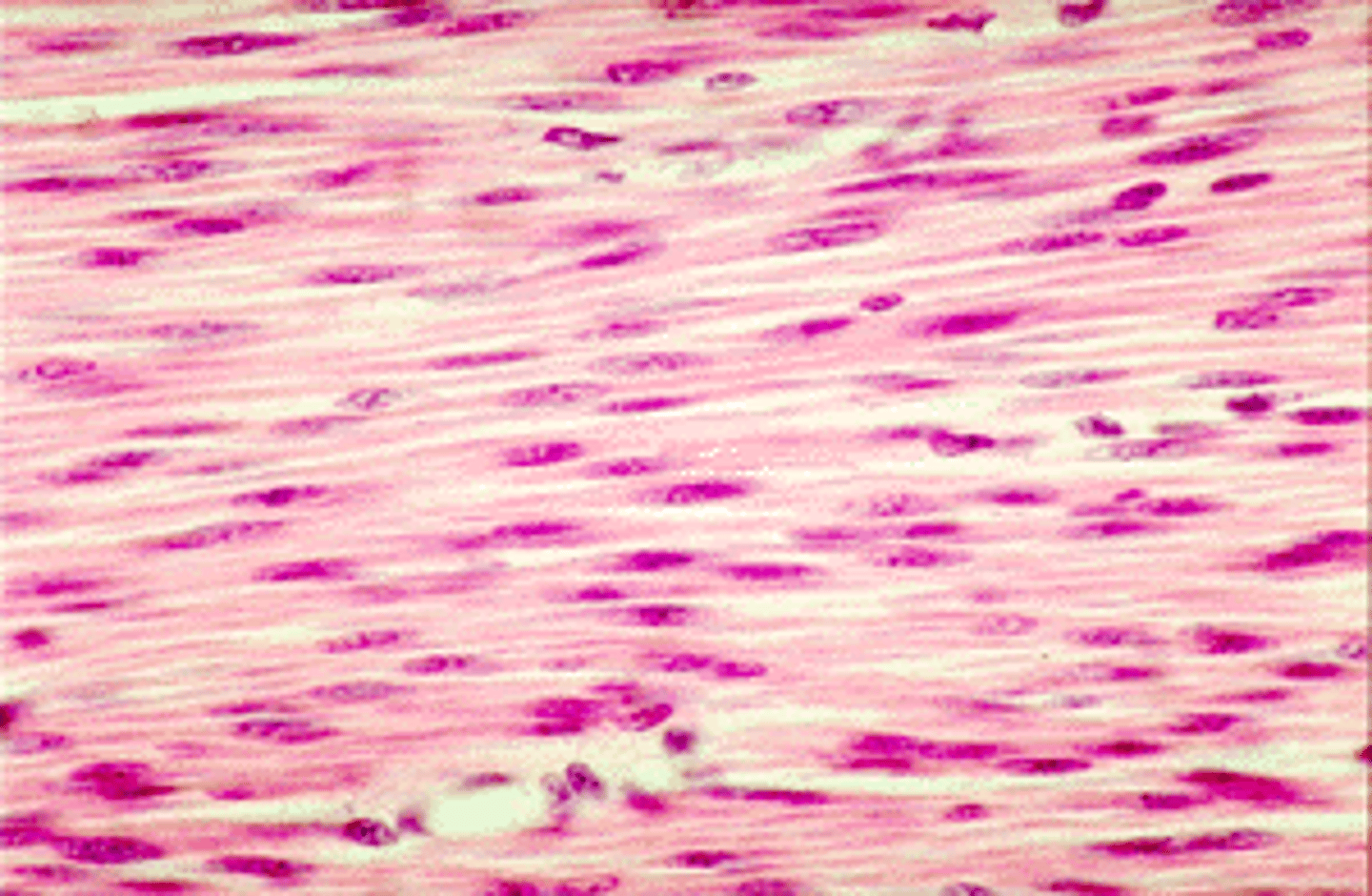
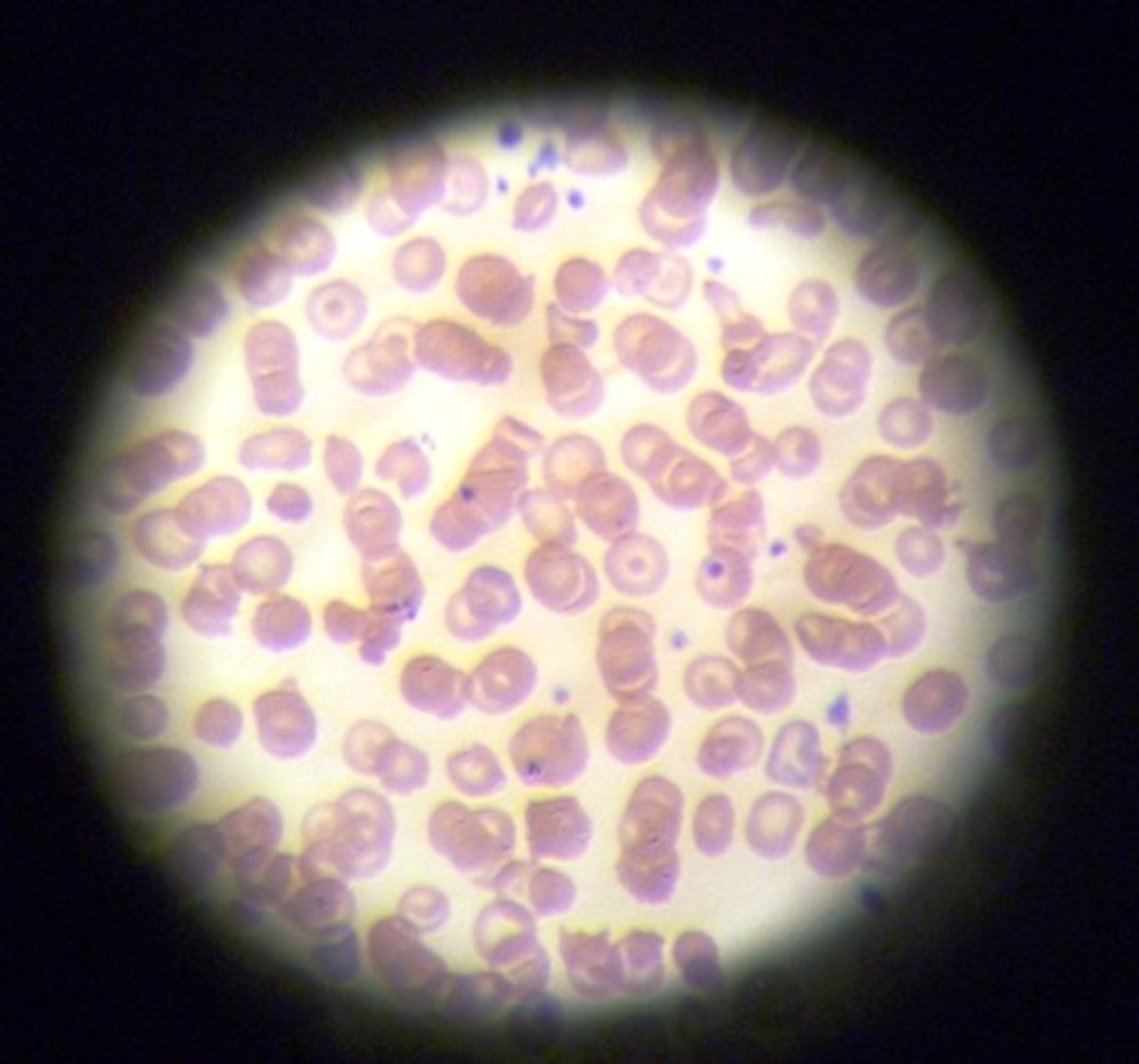
blood (connective)
examples:, blood vessels
function: transports gases and nutrients
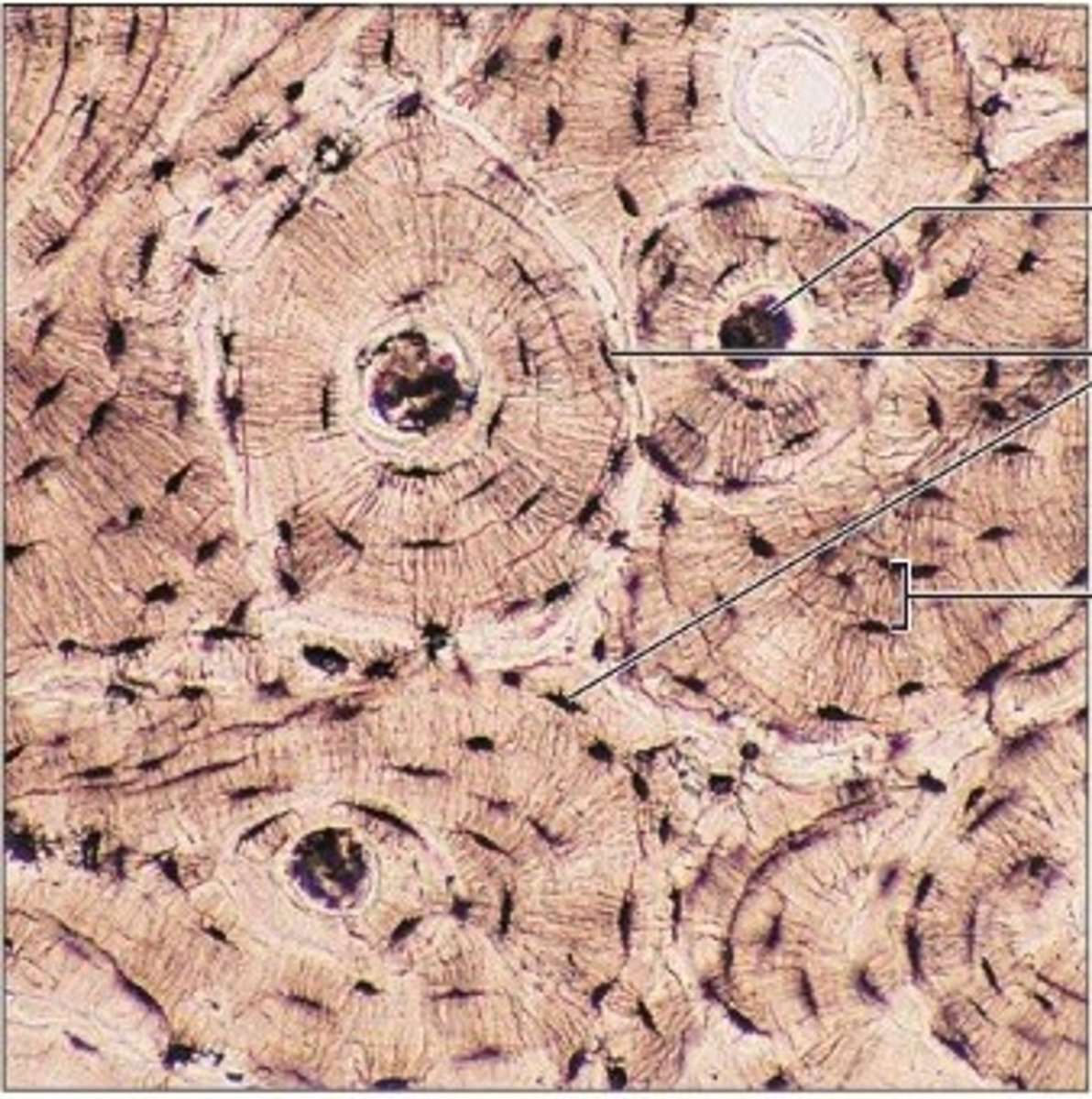
bone (connective)
examples: bones
function: support, protects, allows movement by muscle
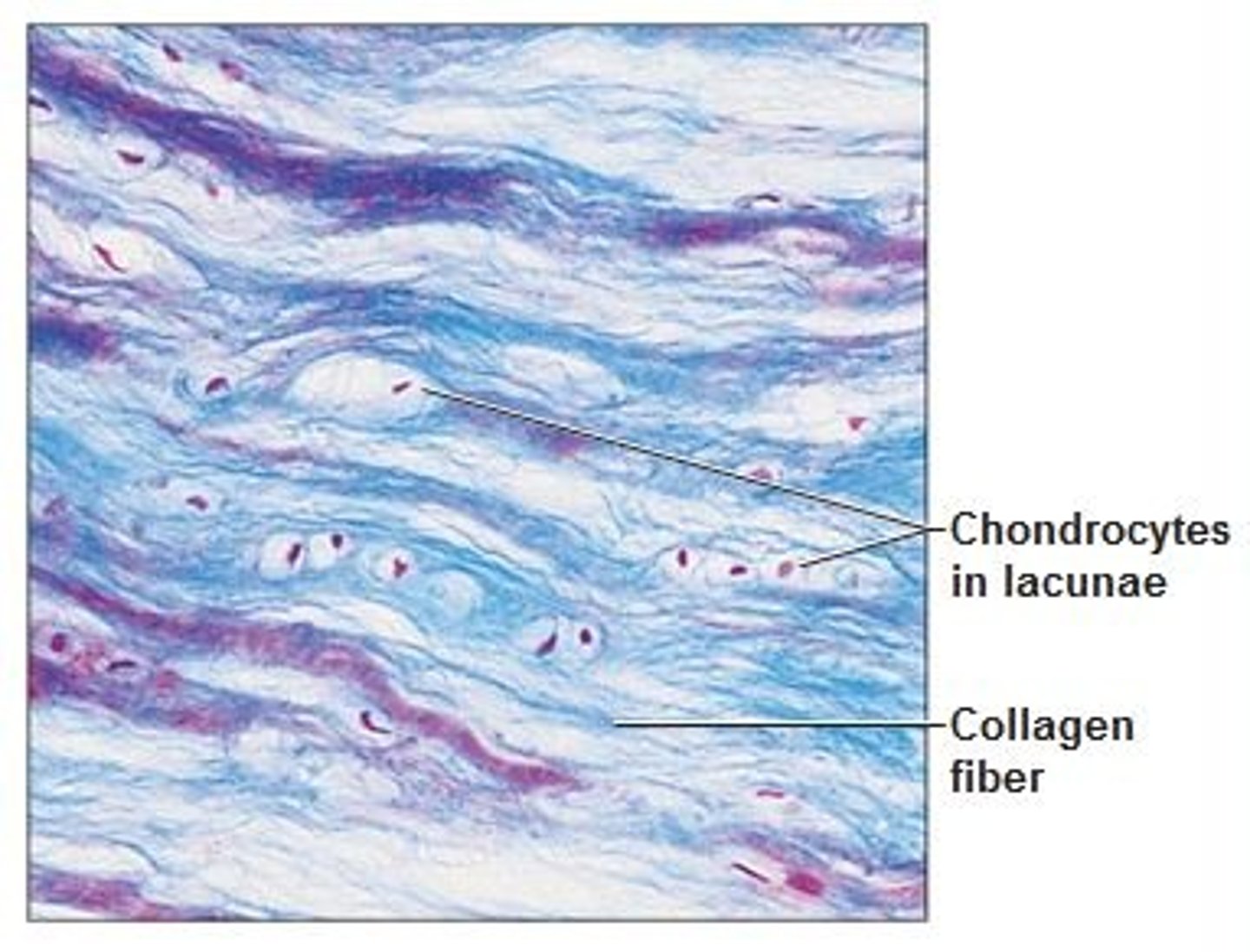
fibrocartilage (connective)
example: intervertebral discs
function: shock absorbers
dense regular (connective)
example: tendons
function: connects muscle to bone

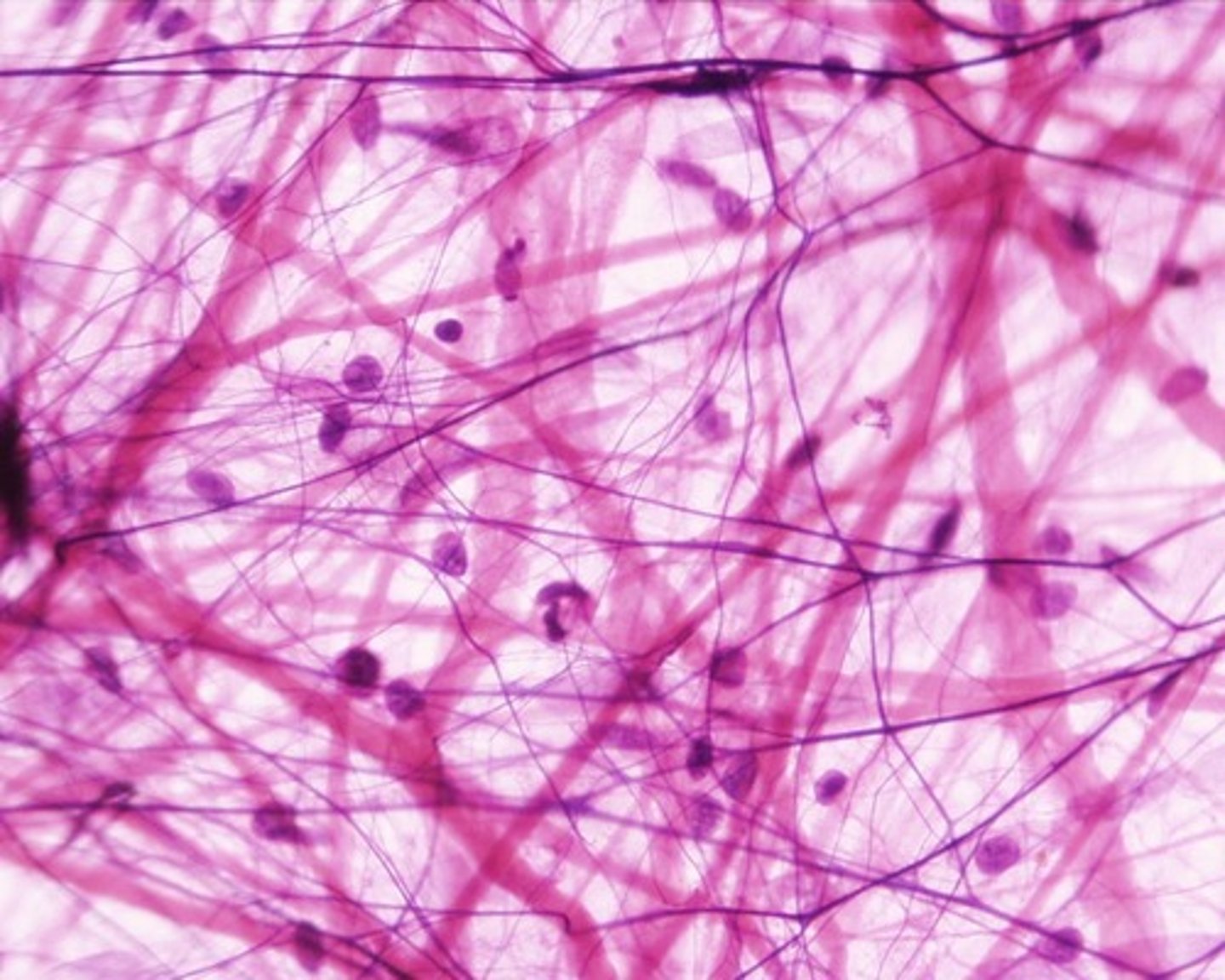
areolar (connective)
example: under epithelial tissue throughout body
function: wraps and cushions organs
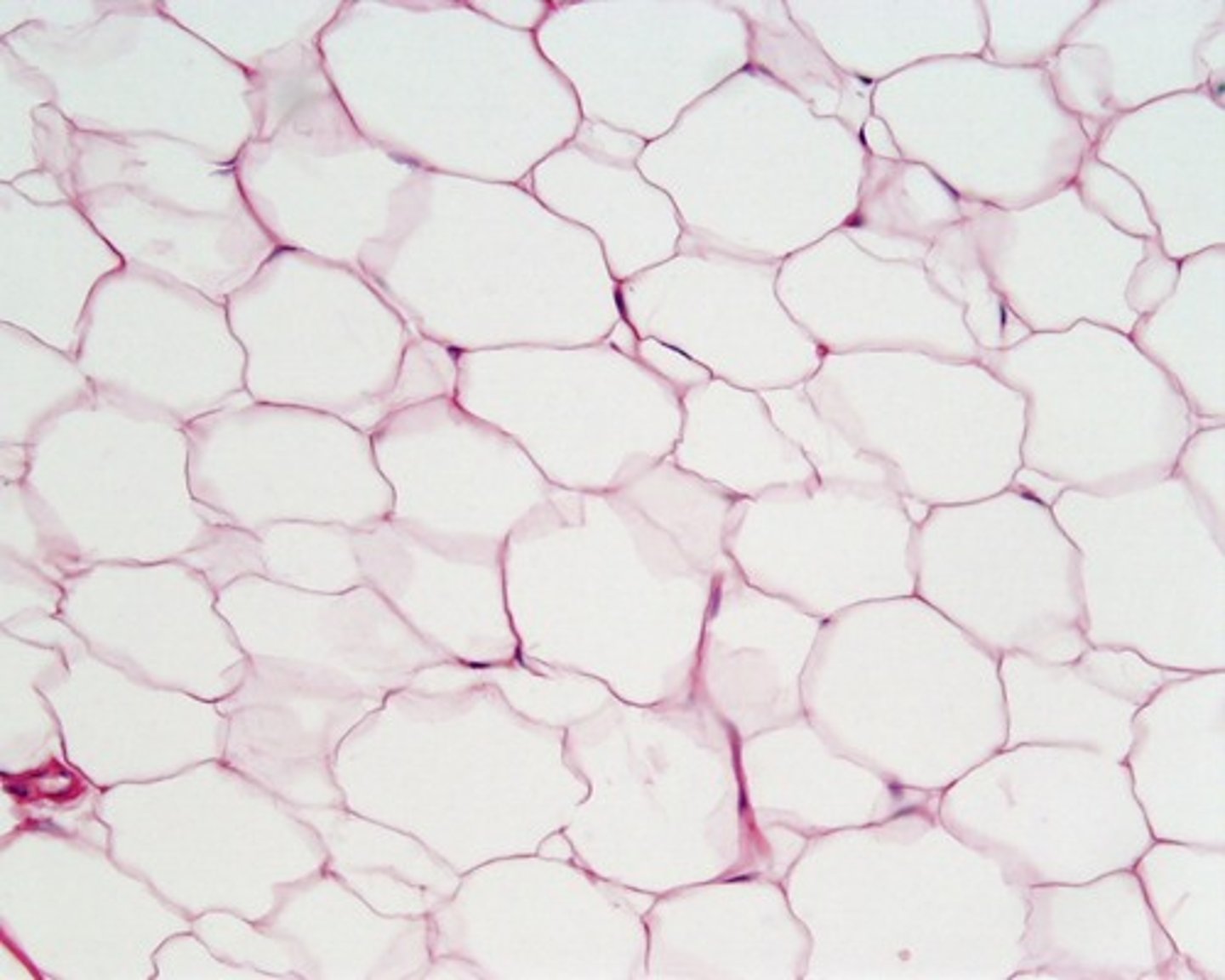
adipose (connective)
example: fat
function: energy storage, insulation and protection
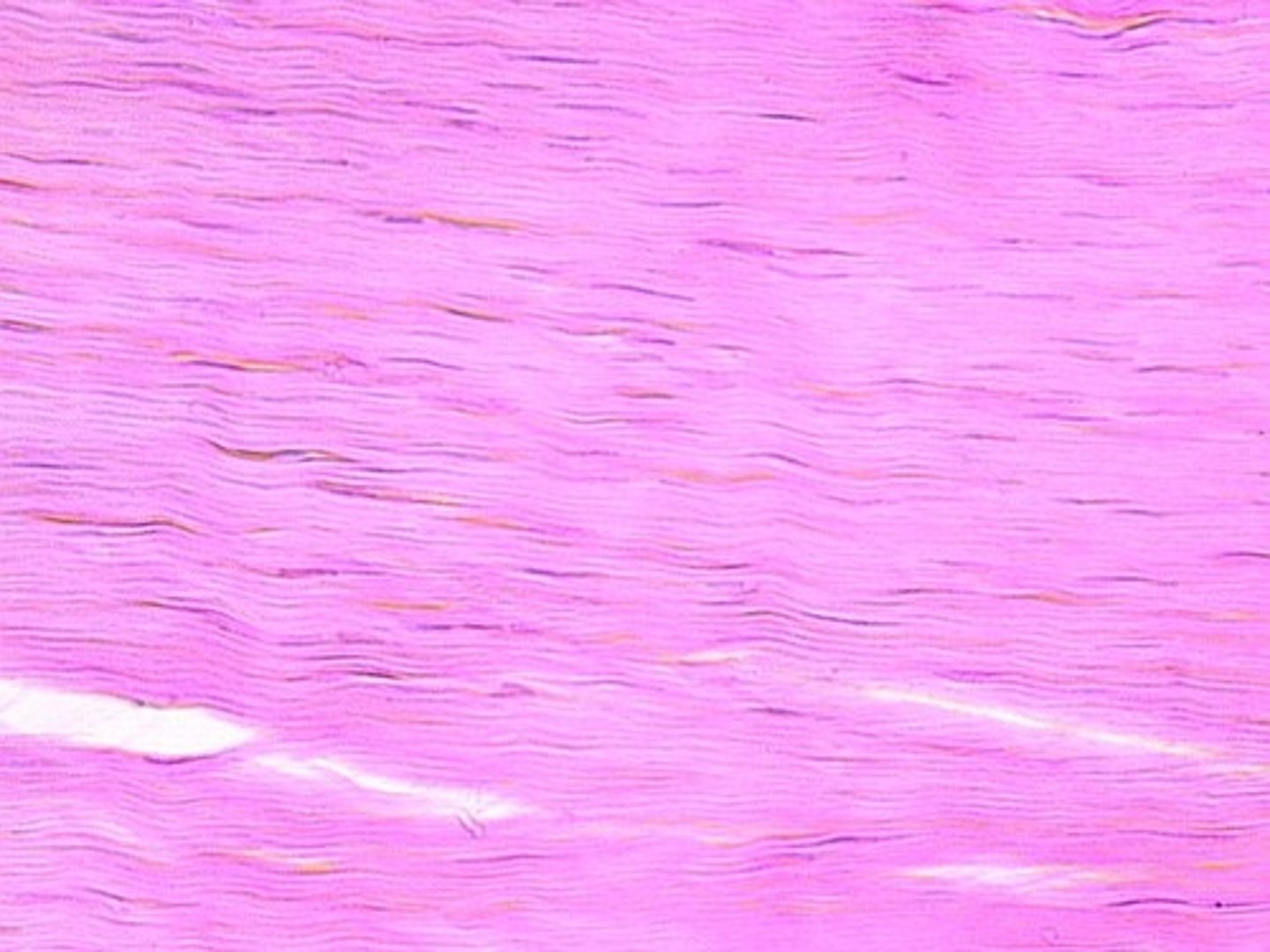
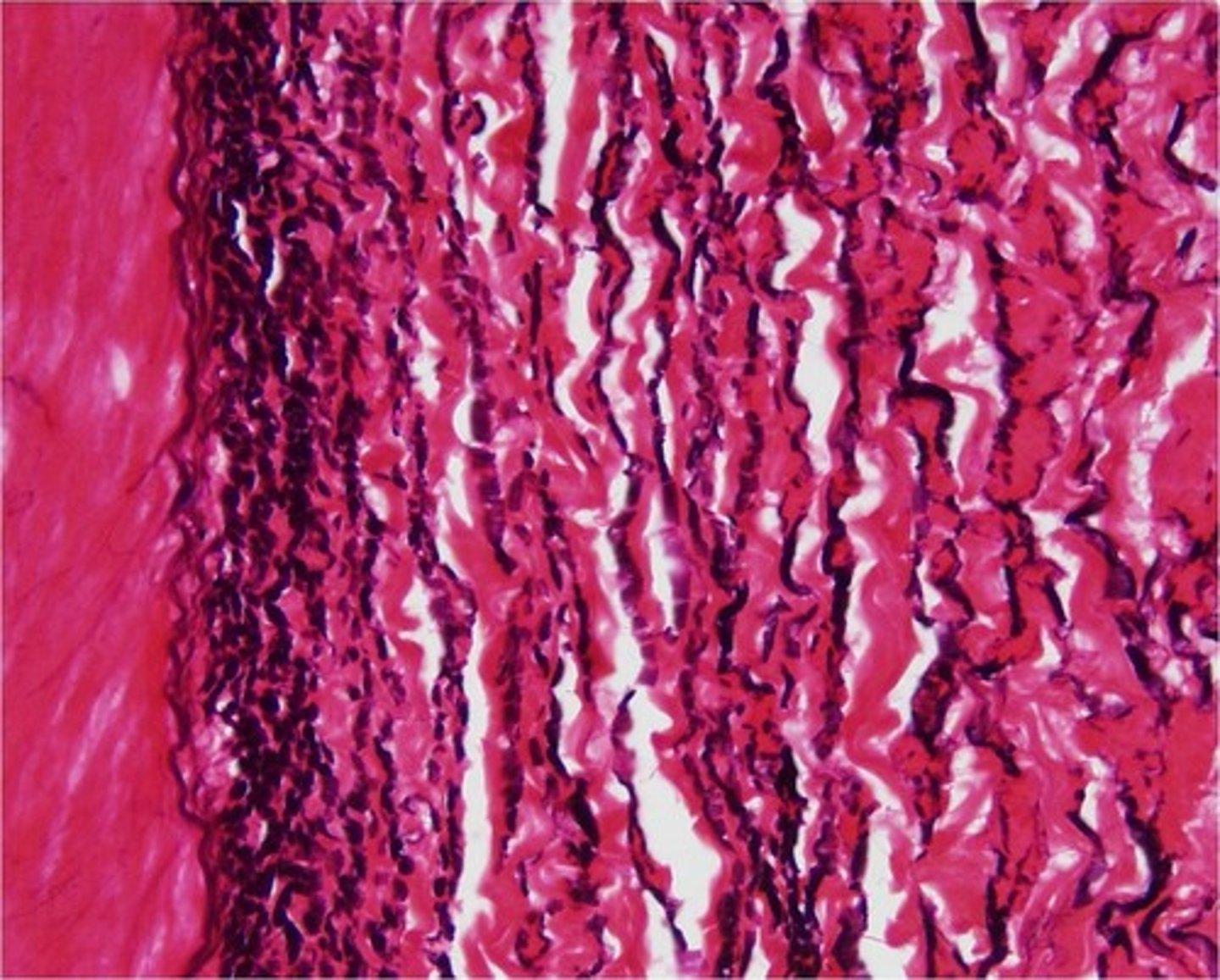
elastic (connective)
example: aorta
function: recoils if stretched
nervous tissue (neurons)
example: brain, spinal cord and nerves
function: transmits electrical signals from sensory receptors and to effectors
Interphase
perfect circle- DNA is replicated, cell prepares for mitosis
Prophase
cloudy circle- chromatin condenses making the chromosomes visible
Cytokinesis
two identical daughter cells
Telophase
goggles- daughter chromosomes reach the poles and form two new nuclei
Anaphase
oval- sister chromatids desperate and resultant daughter chromosomes move toward poles
Metaphase
middle- chromosomes become aligned at the equatorial plane
the cell: ribosomes
composed of RNA and protein
attached to the rough ER or floating freely
sites of protein synthesis
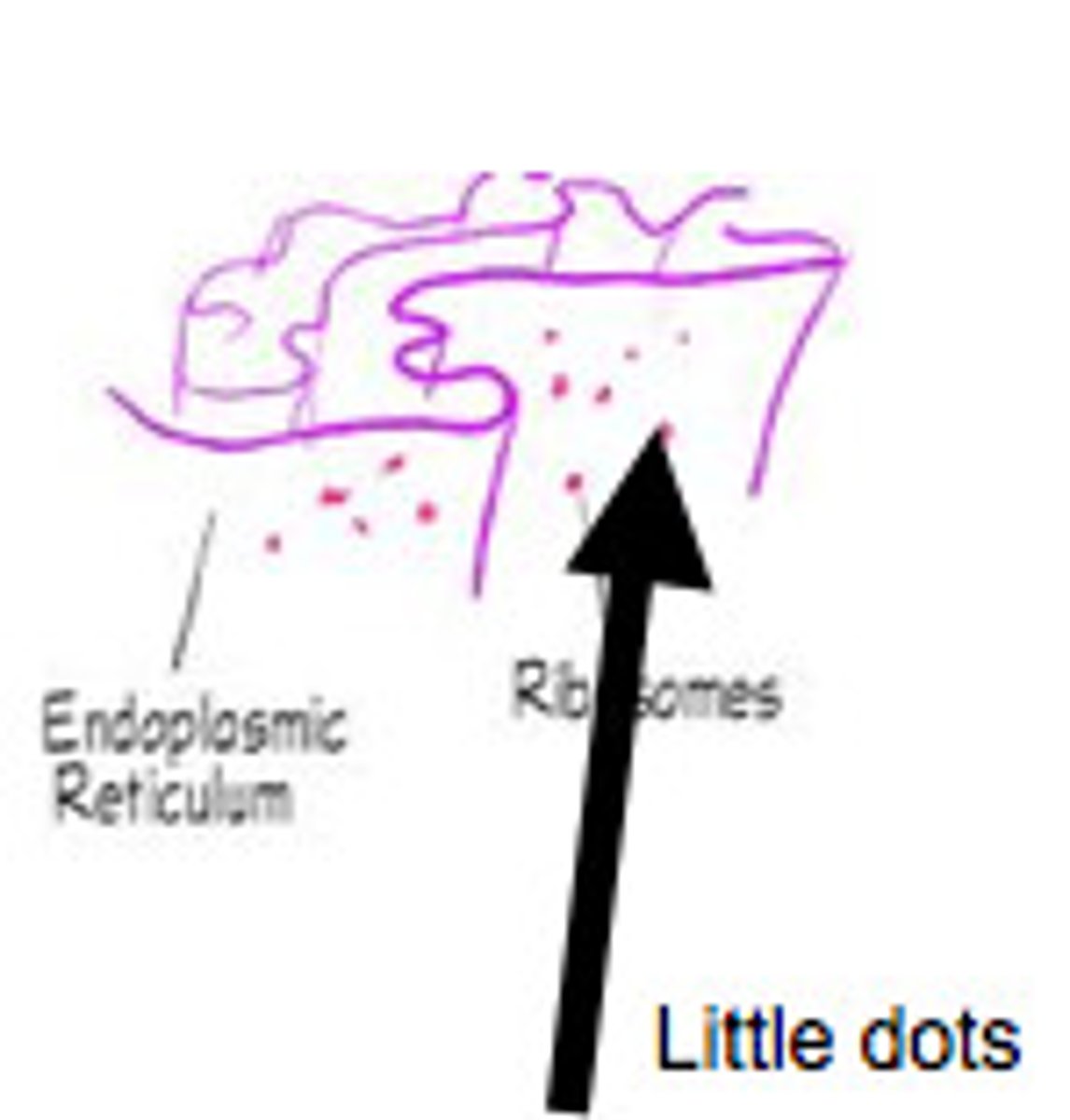
the cell: ER (endoplasmic reticulum)
rough ER: provide area for storage and transport of the proteins made on ribosomes to other cell areas.
smooth ER: no function in protein synthesis. site of steroid and lipid synthesis
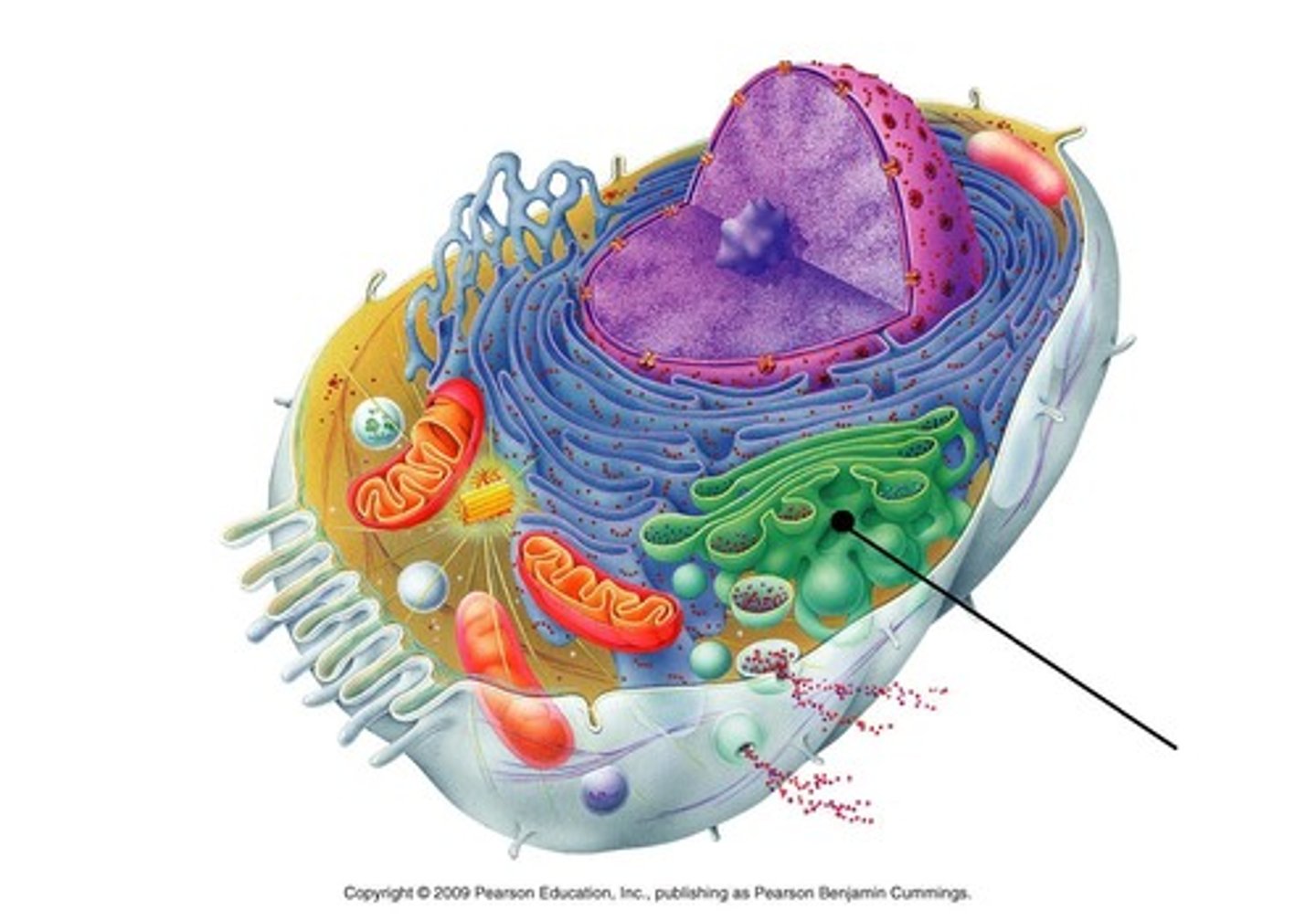
the cell: Golgi appartatus
found close to the nucleus
packaging proteins
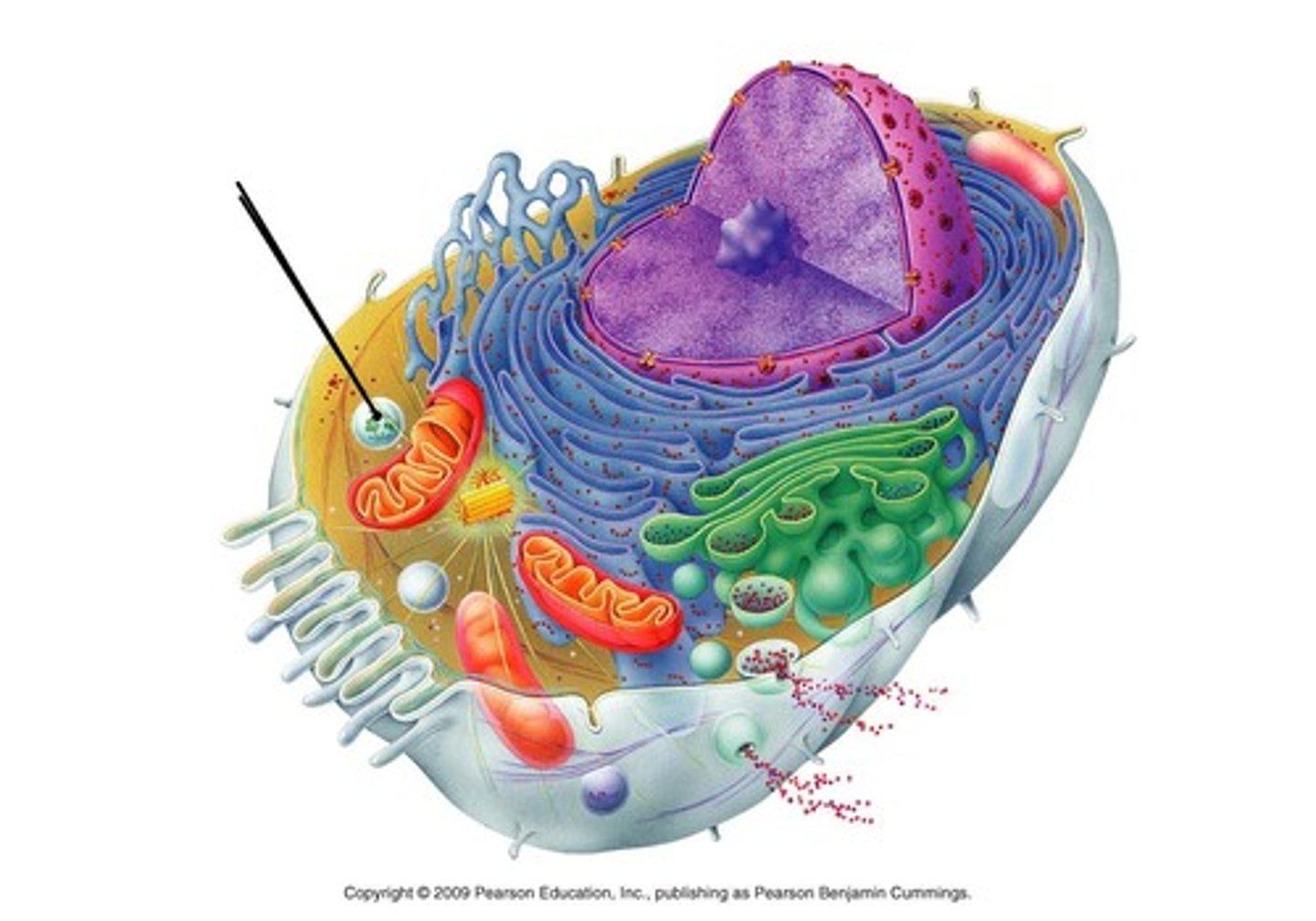
the cell: lysosomes
digestive enzymes
the cell: peroxisomes
contains oxidase enzymes that detoxify (alcohol, hydrogen peroxide and other harmful chemicals)
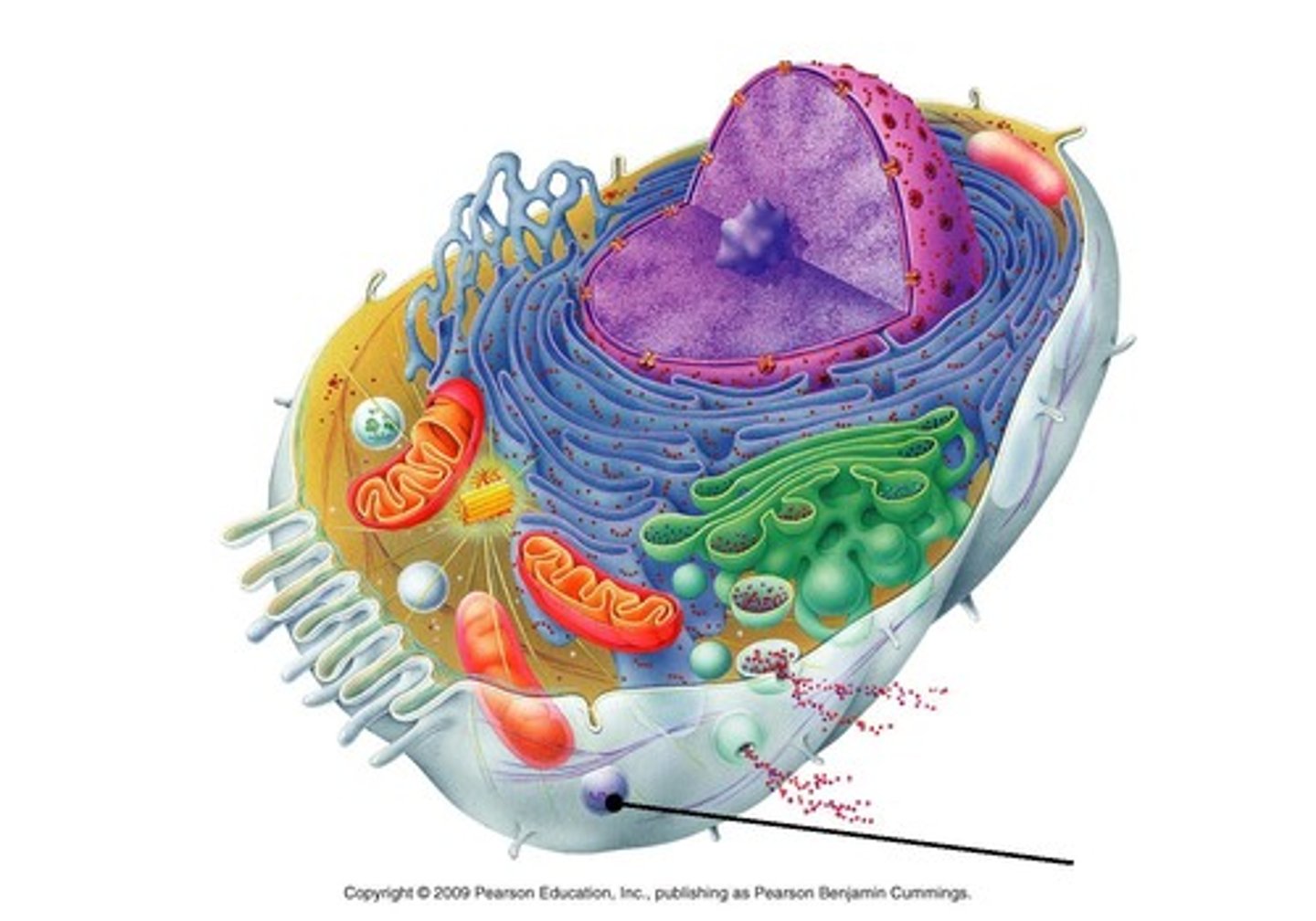
the cell: mitochondria
"the powerhouse of the cell"
produce cellular energy (ATP)
the cell: centrioles
direct the formation of the mitotic spindle during cell division: form the bases of cilia and flagella
close to the nucleus
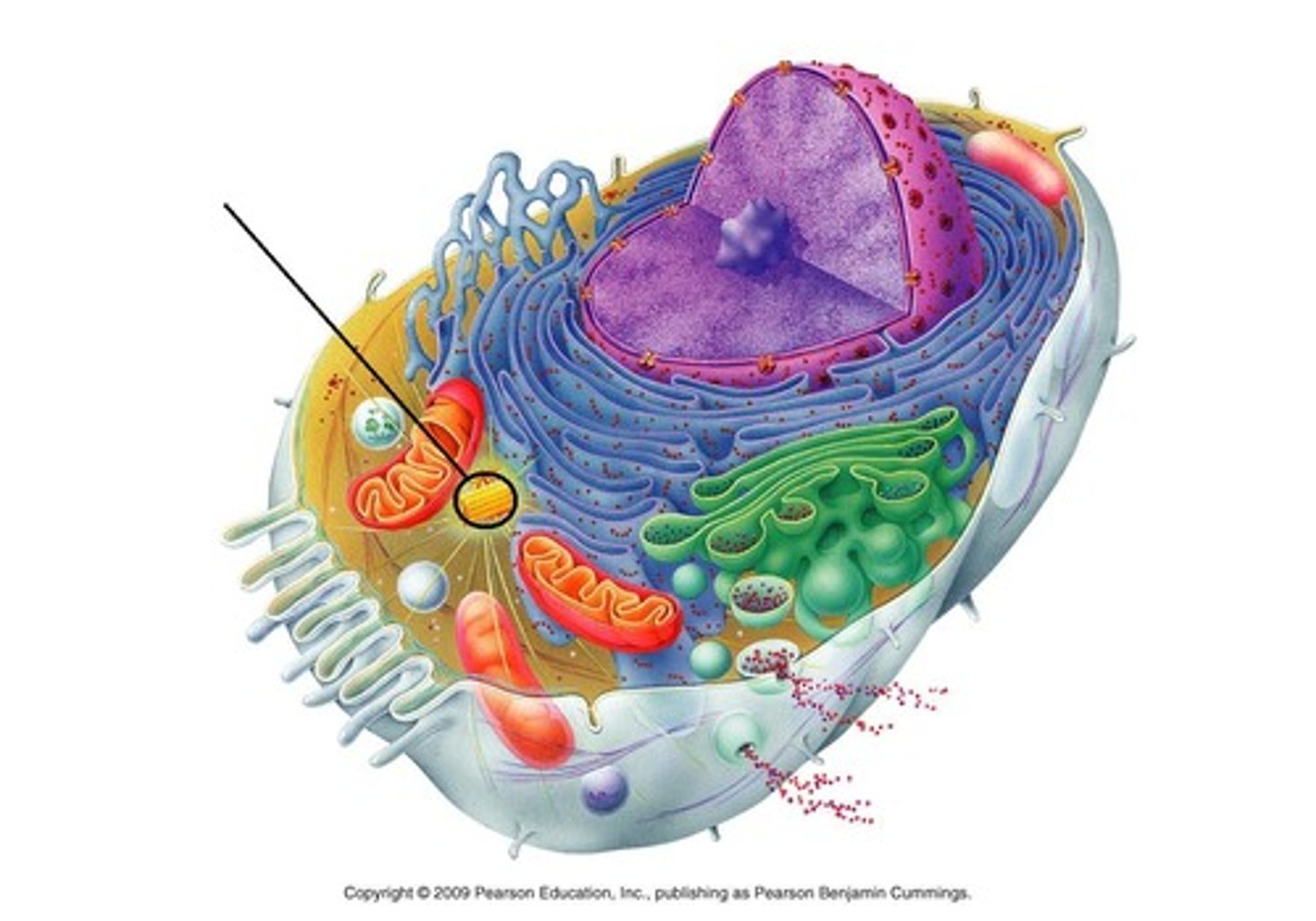
the cell: cytoskeletal elements (microfilaments, intermediate filaments and microtubules)
provide cellular support (function in intracellular transport)
microfilaments made up of actin (IMPORTANT IN CELL MOBILITY)
intermediate filaments made up of a variety of proteins and resist mechanical forces acting upon the cell
microtubules form the internal structure of the centrioles and help determine cell shape
axial skeleton
the "axis"
skull, vertebral column and thoracic cage
appendicular skeleton
the "appendages"
arms, legs (and shoulders and hips)
foramen
hole or opening in a bone
fossae
basin-like depression in bone
Condyle
a smooth round projection on bone
concha
bone curled like a sea shell
Fossa
depression or hollow in a bone or other part of the body
Meatus
Canal in a bone
ramus
bony projection
Fossae
basin-like depressions in bone
suture
an immovable fibrous joint
articulation
joint between bones
articulate
to form a joint
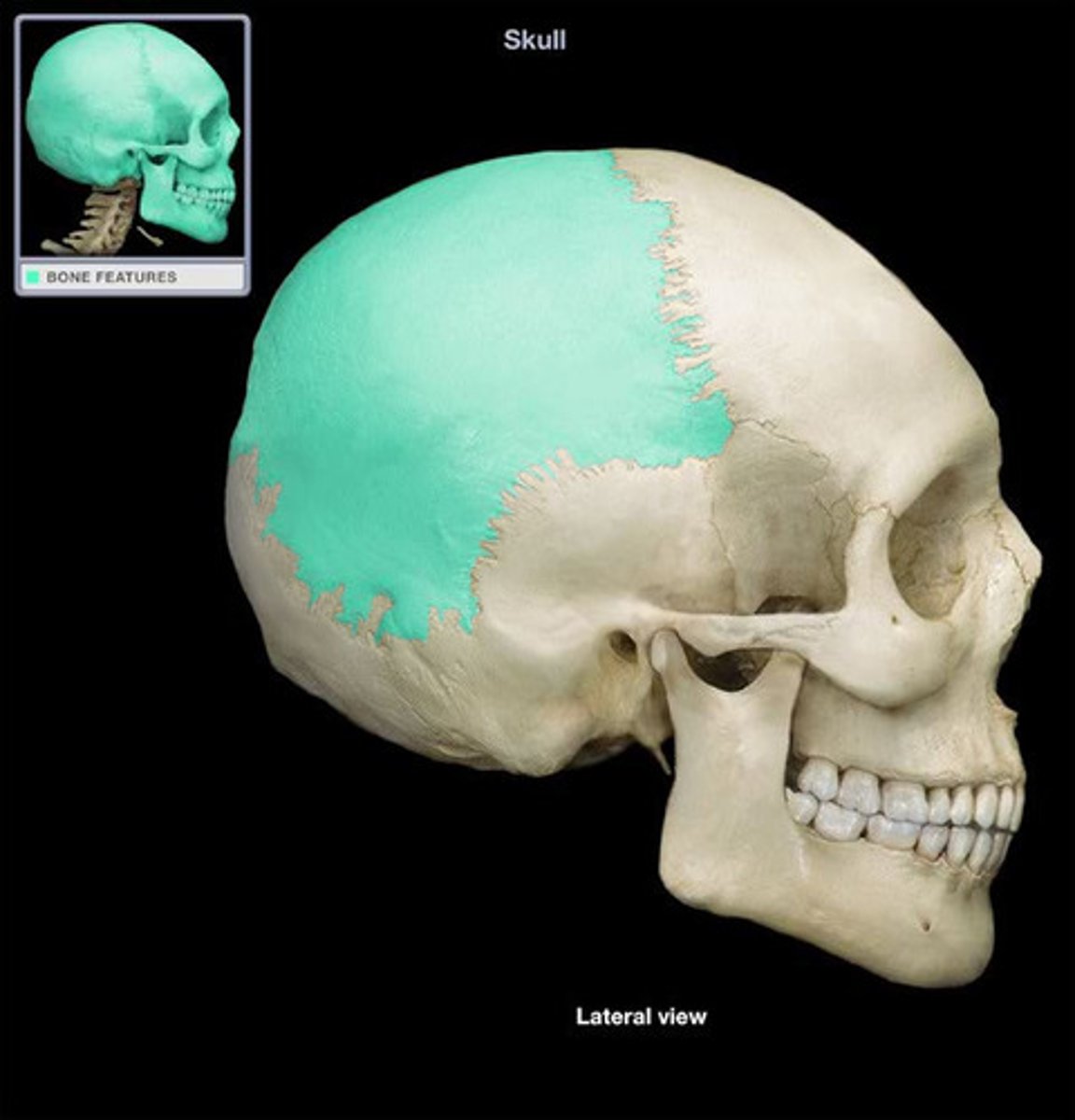
frontal bone
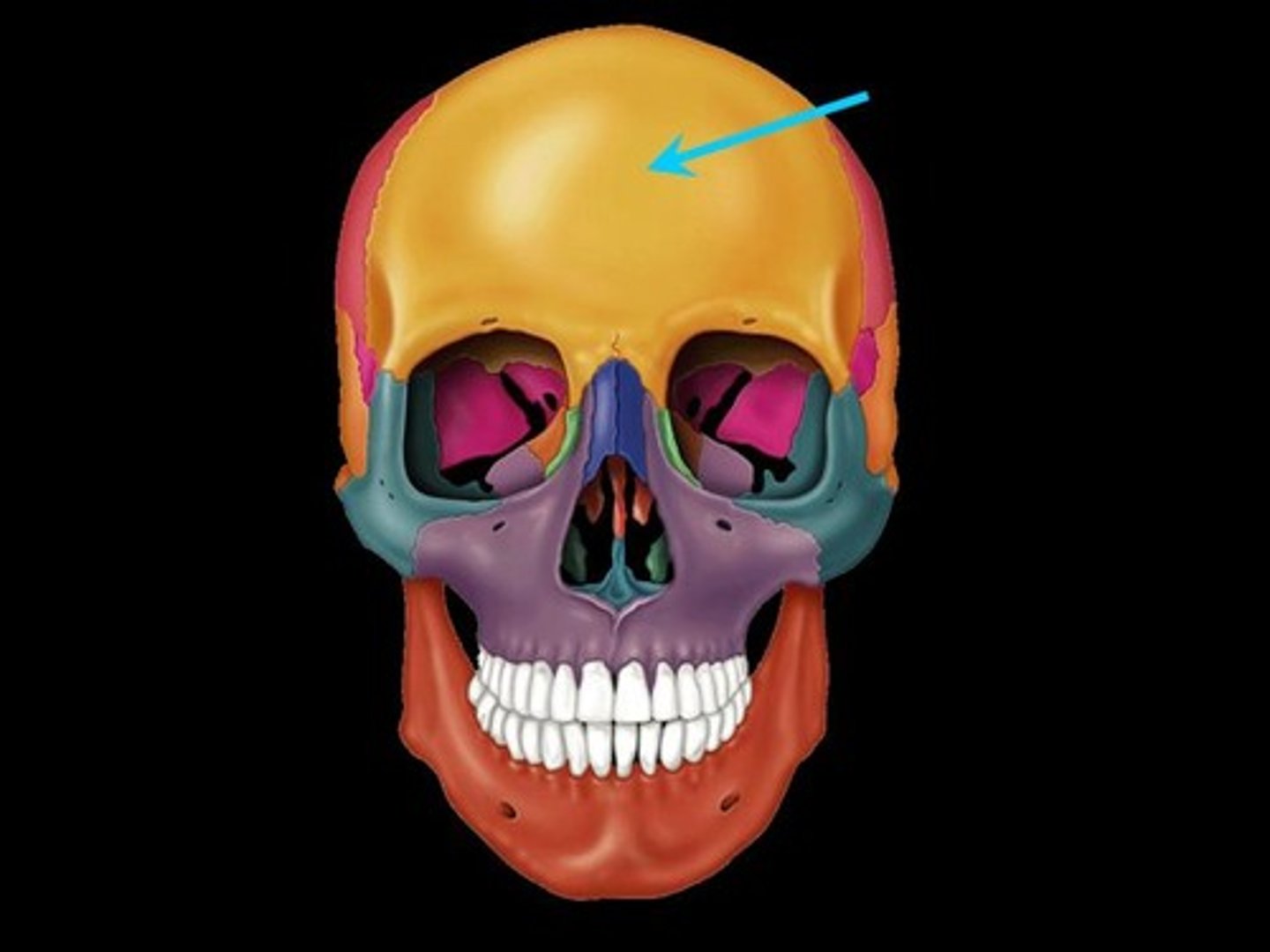
supraorbital notch
parietal bone
temporal bone (exterior)
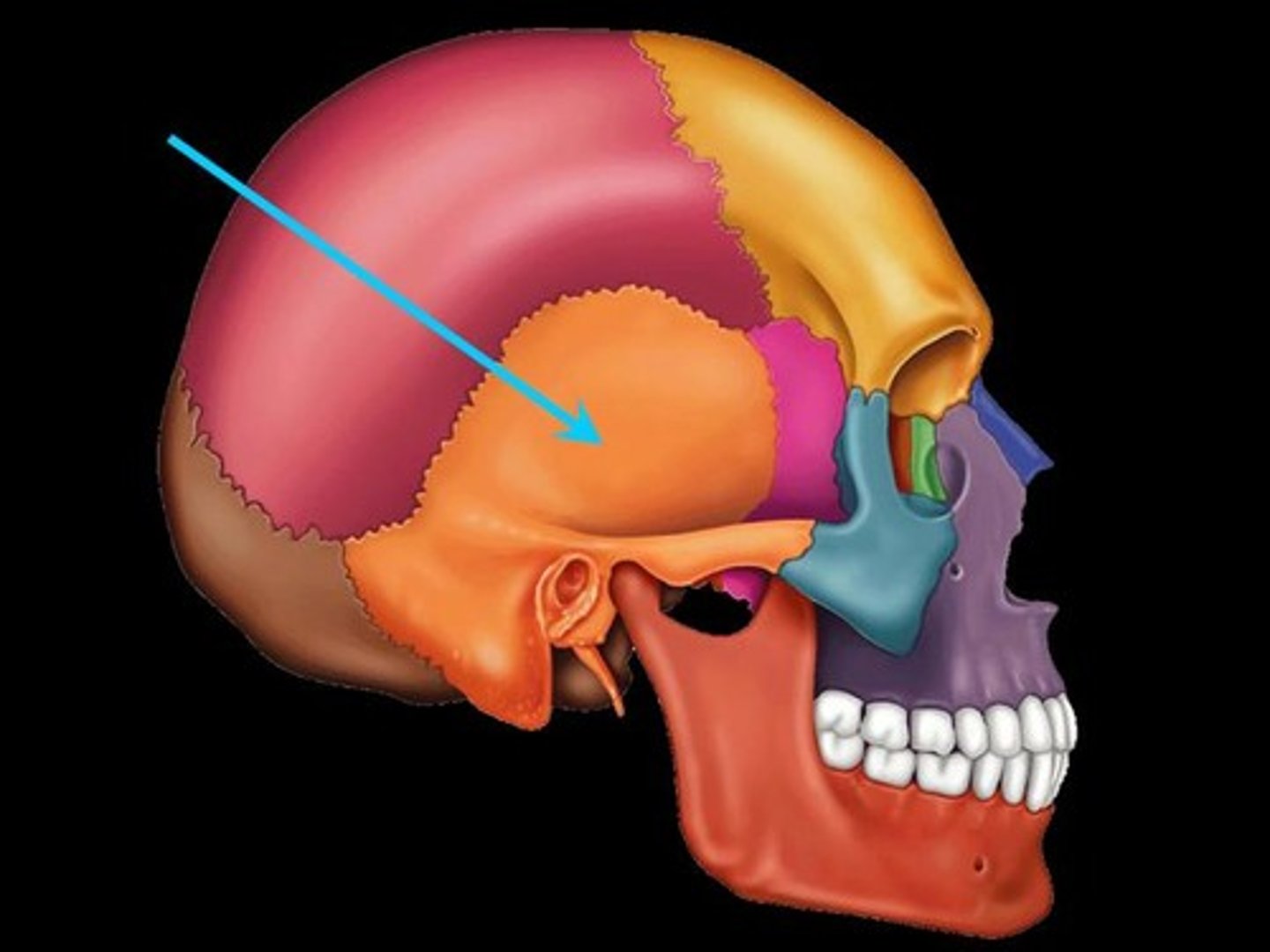
temporal bone (interior)
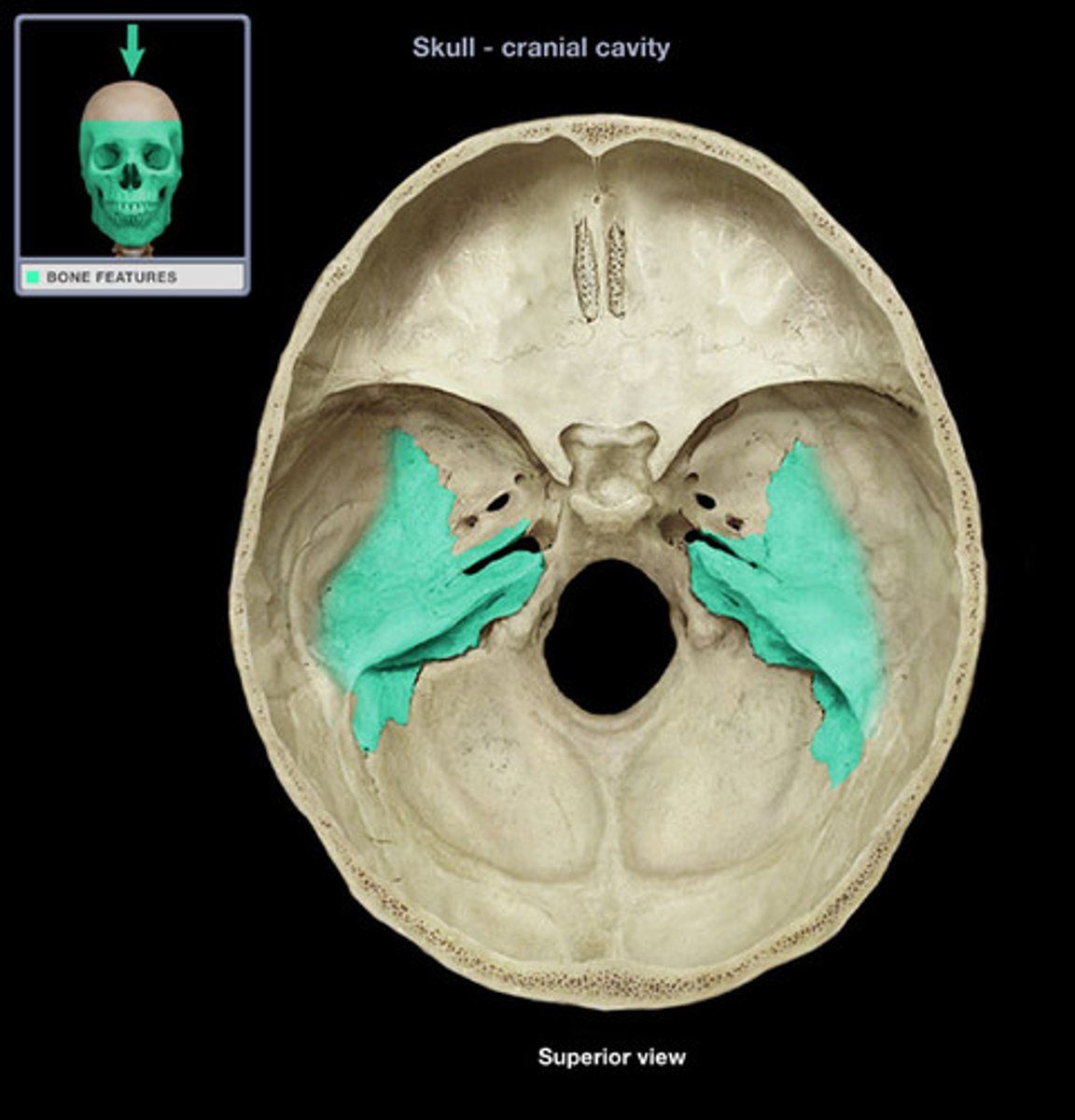
internal acoustic meatus
internal acoustic meatus
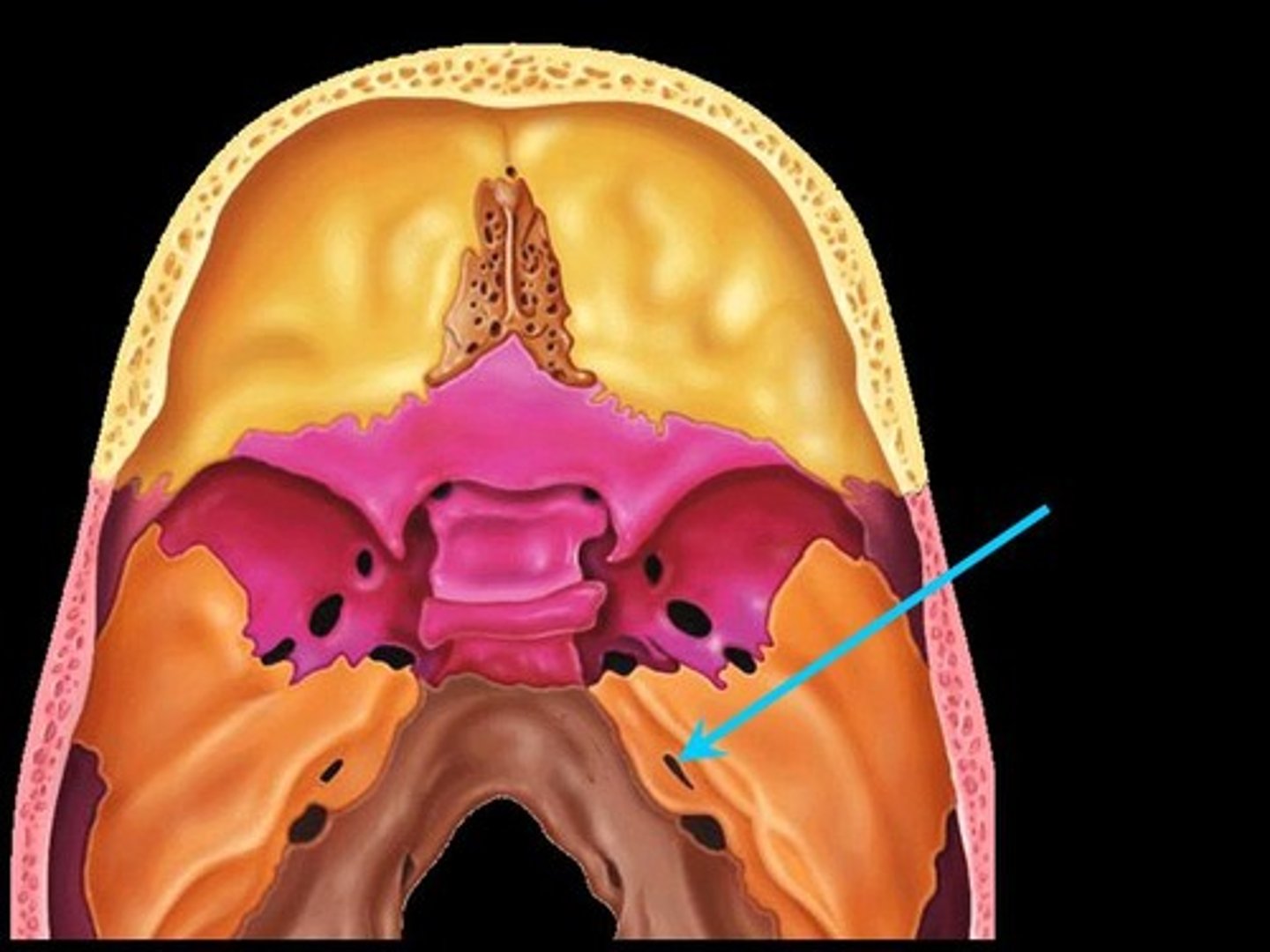
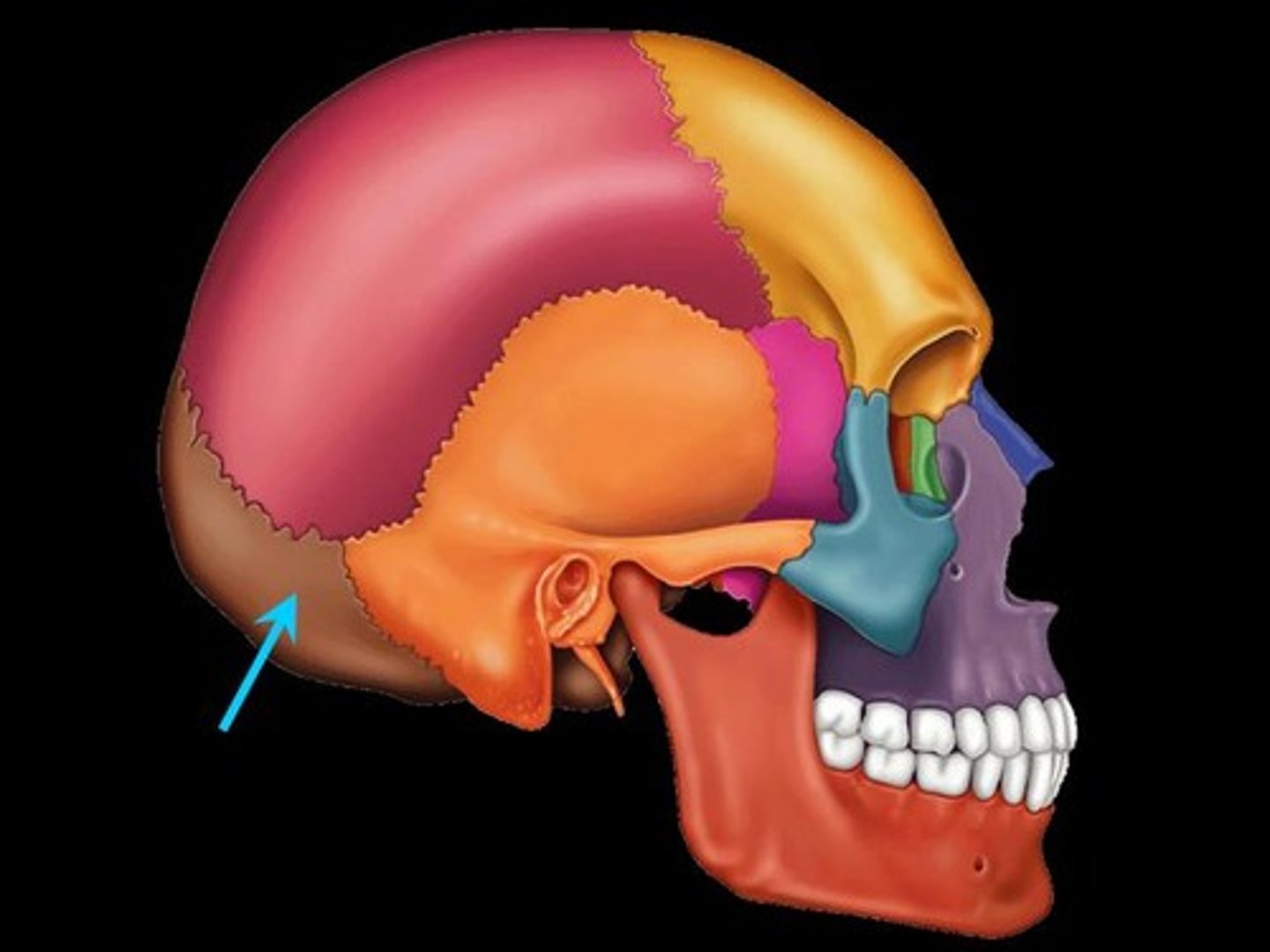
occipital bone
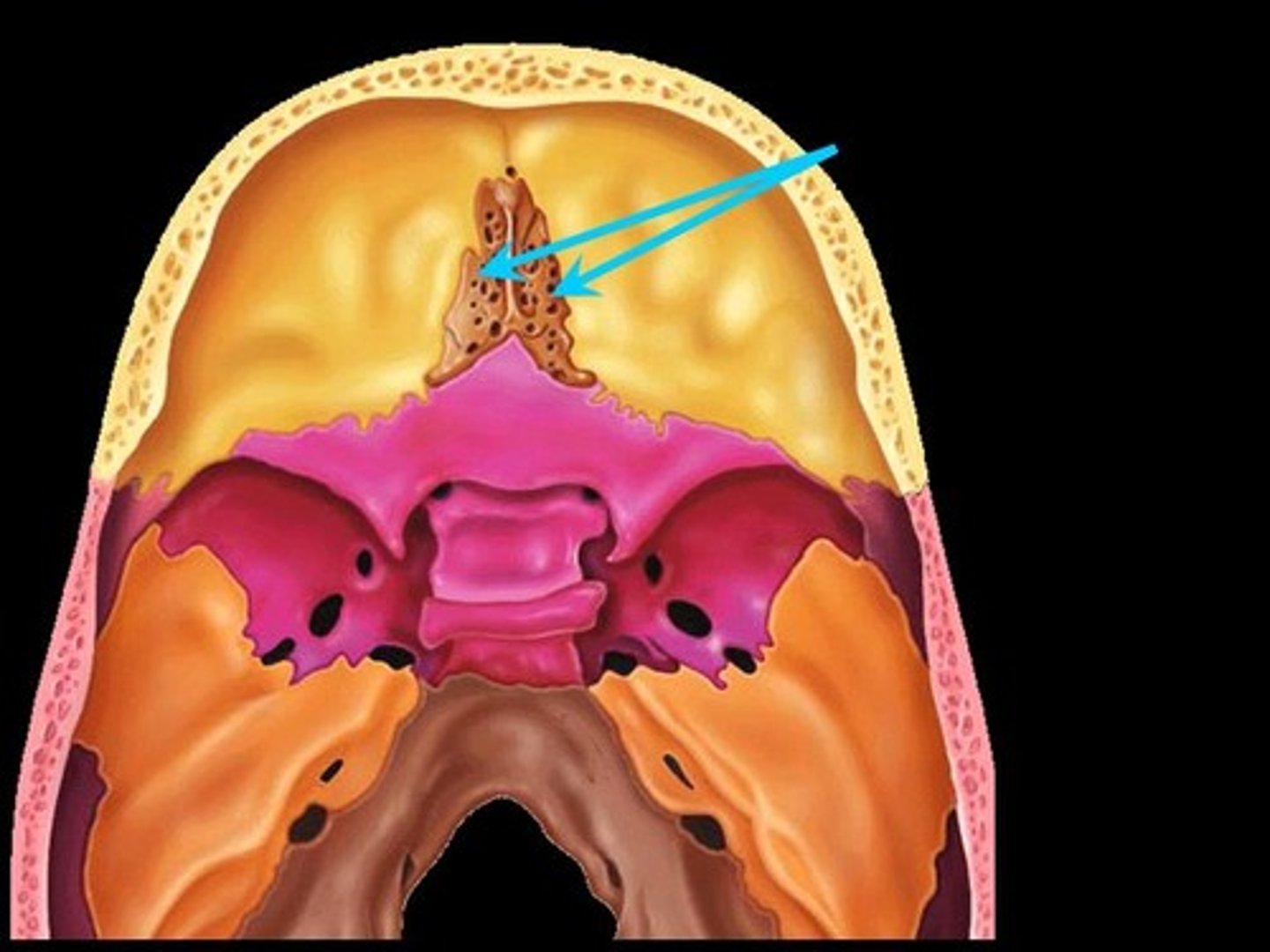
ethmoid bone
(crista galli, cribiform plate, middle nasal conchae, perpendicular plate)
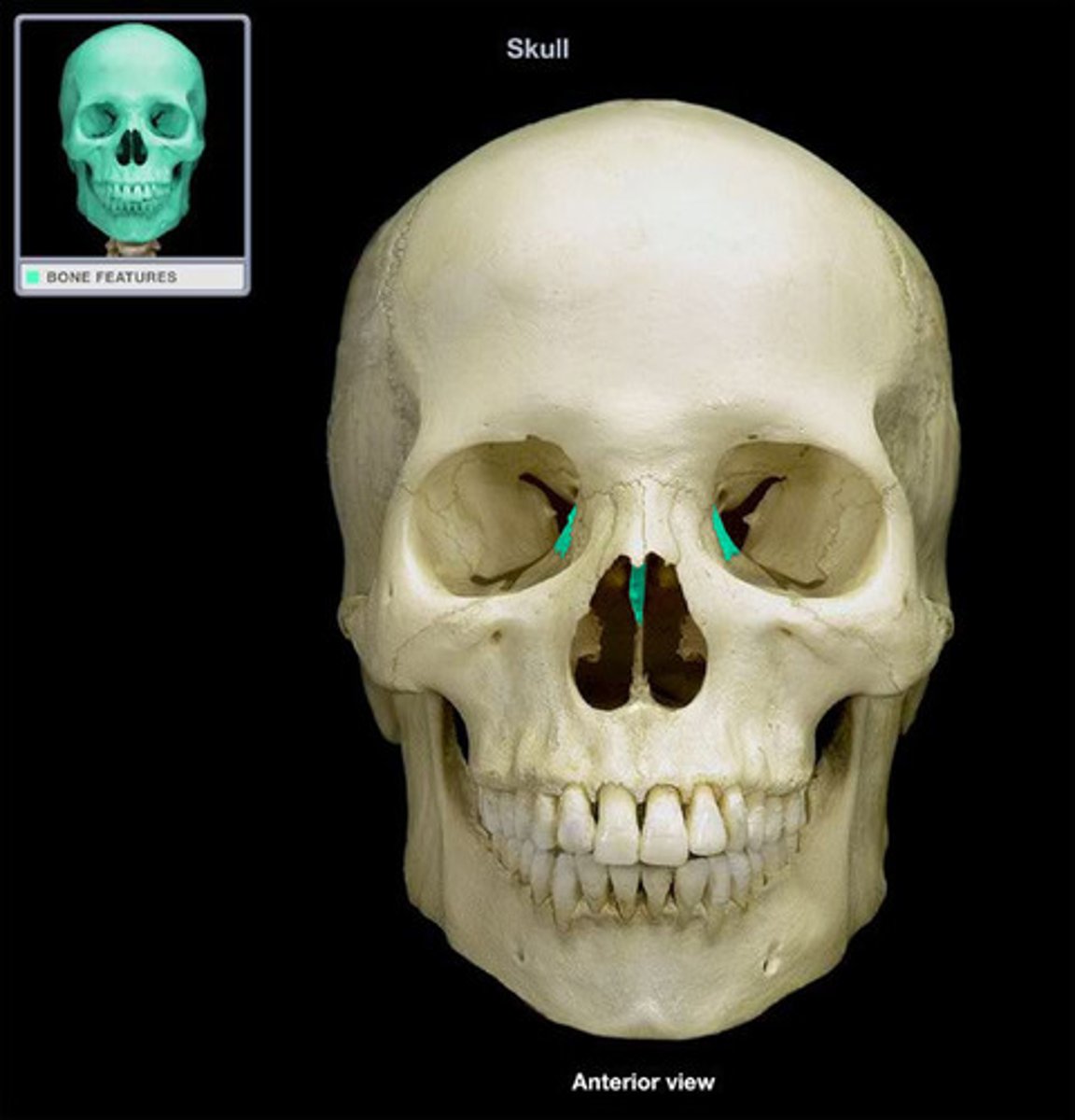
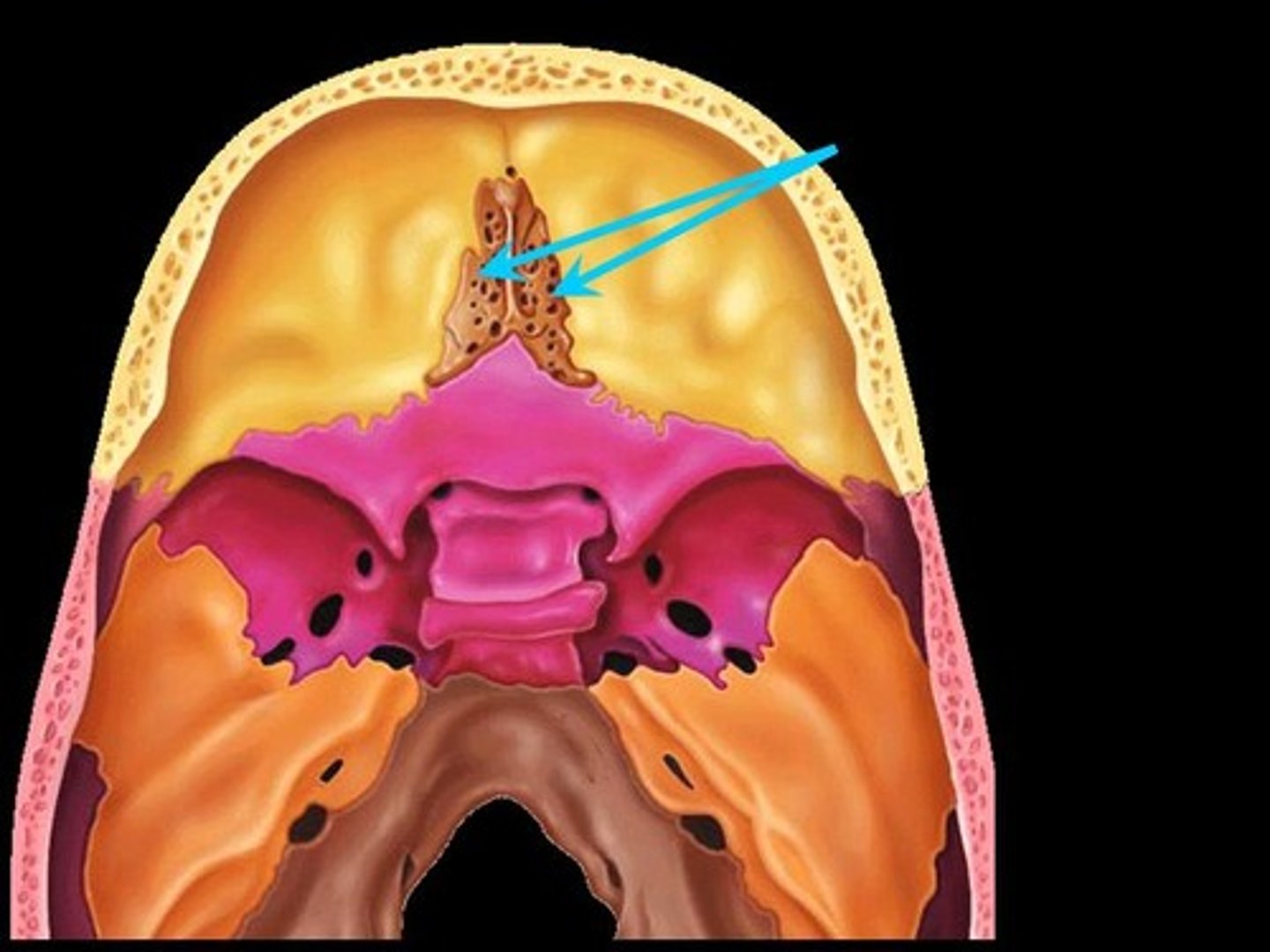
cribriform plate
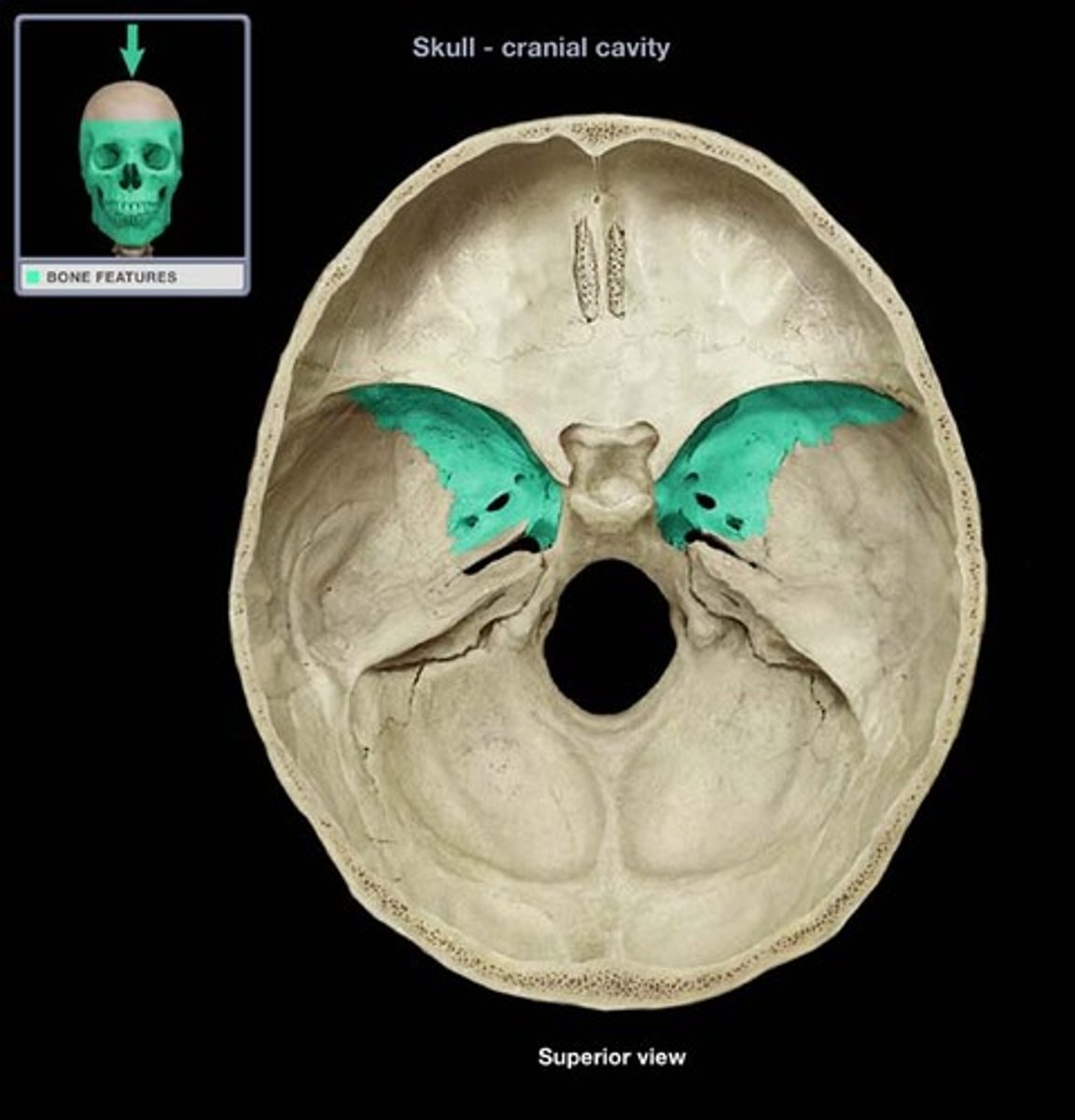
sphenoid bone
(greater wing)
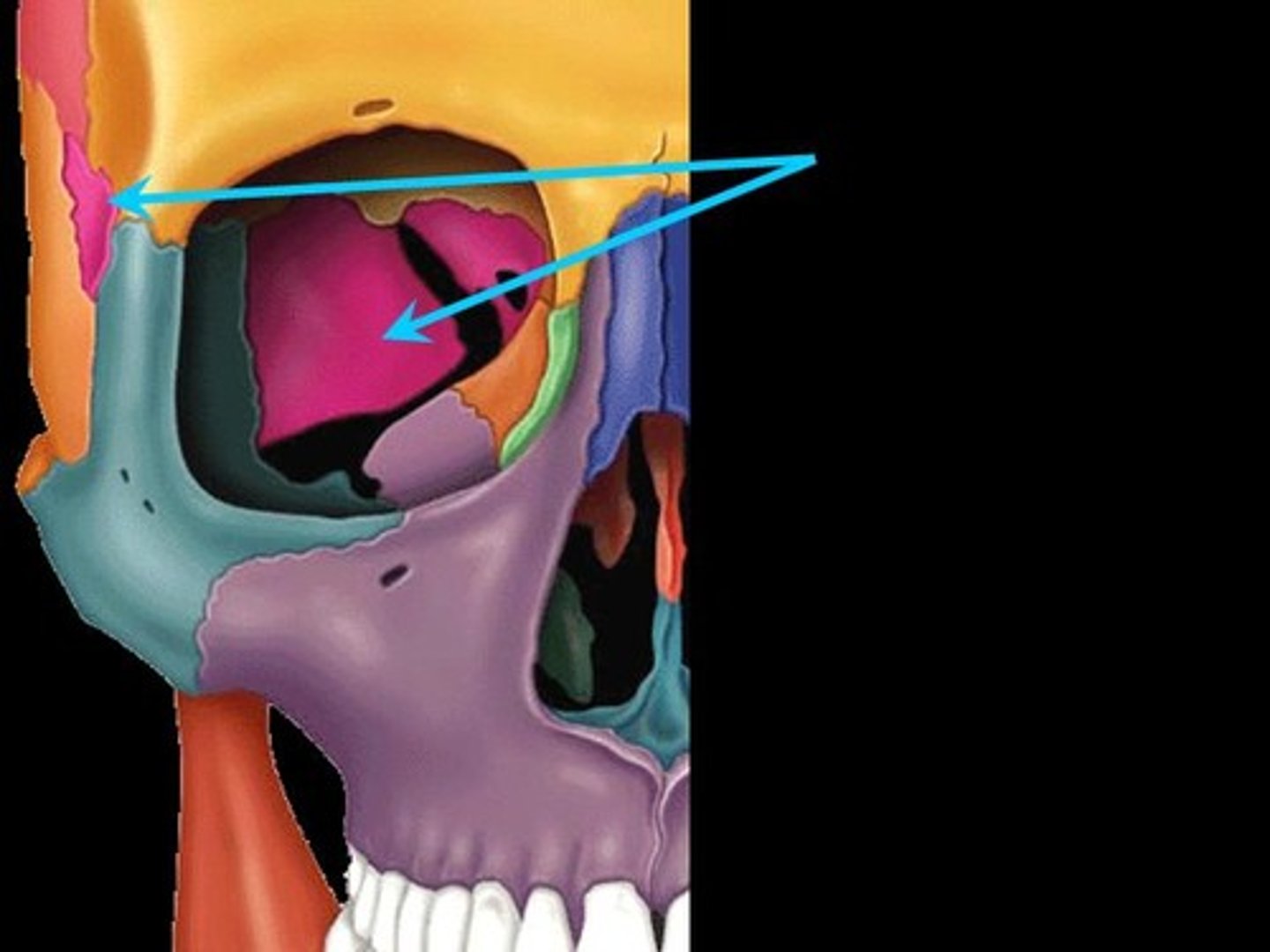
ramus
a bony projection
condyle
a smooth prominence (rounded projection) on a bone
concha
bone curled like a sea shell
fossa
a depression or hollow in a bone or other part of the body
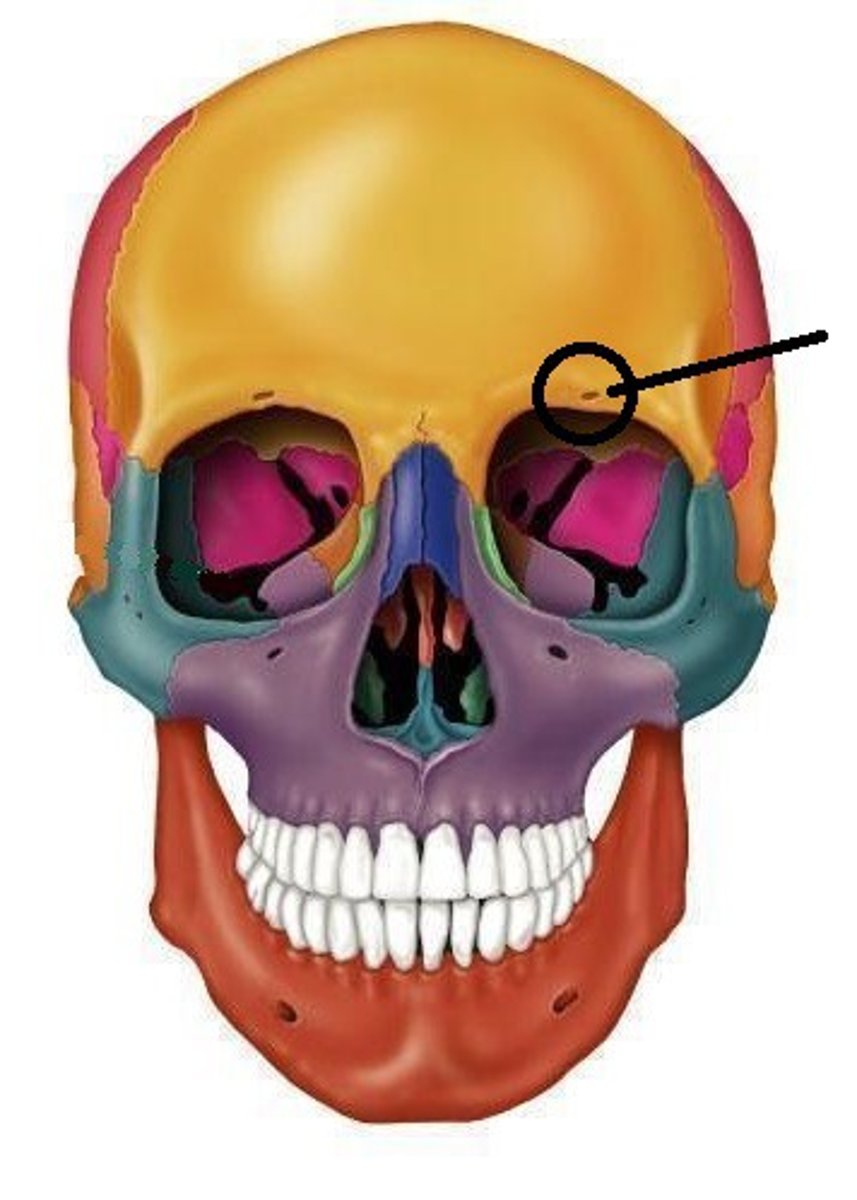
supraorbital foramen (notch)
(greater wings, and lesser wings, sella turcica, optic canal, foramen ovale)
cribriform plate
(ethmoid bone)
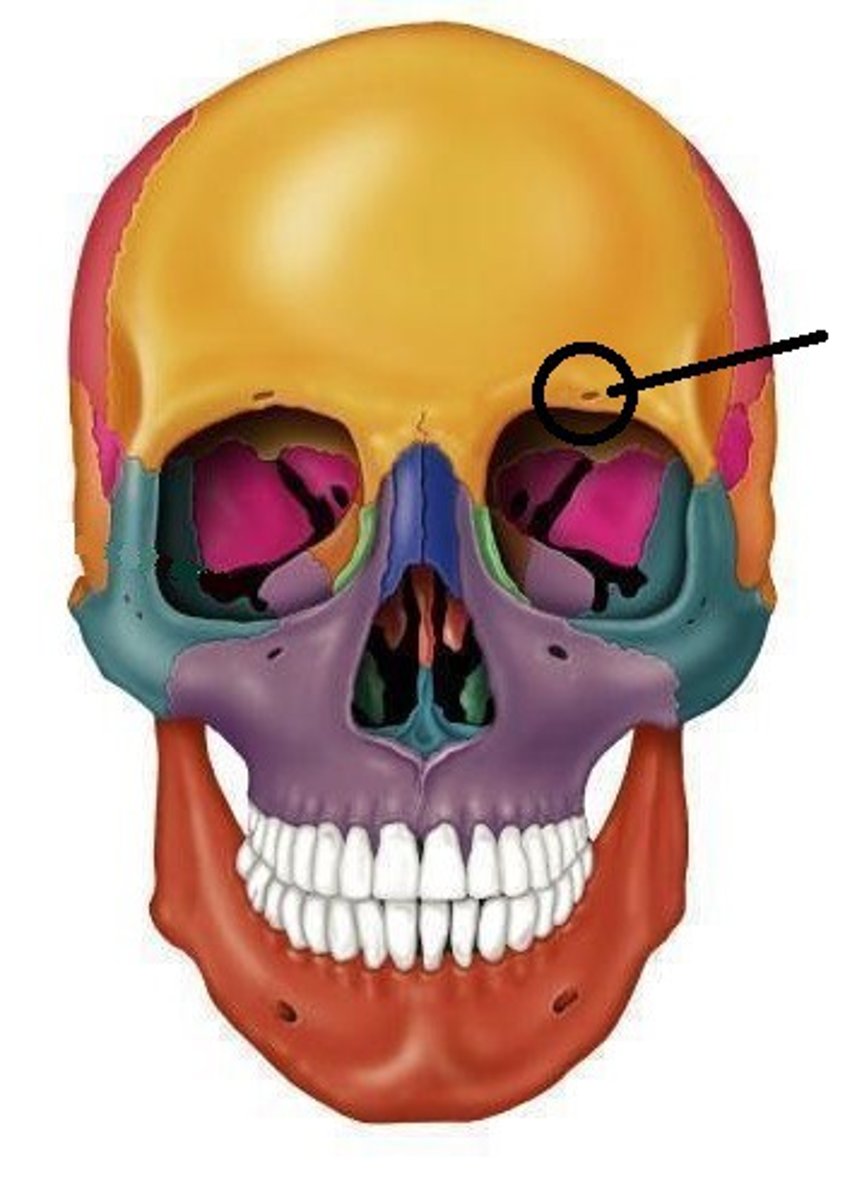
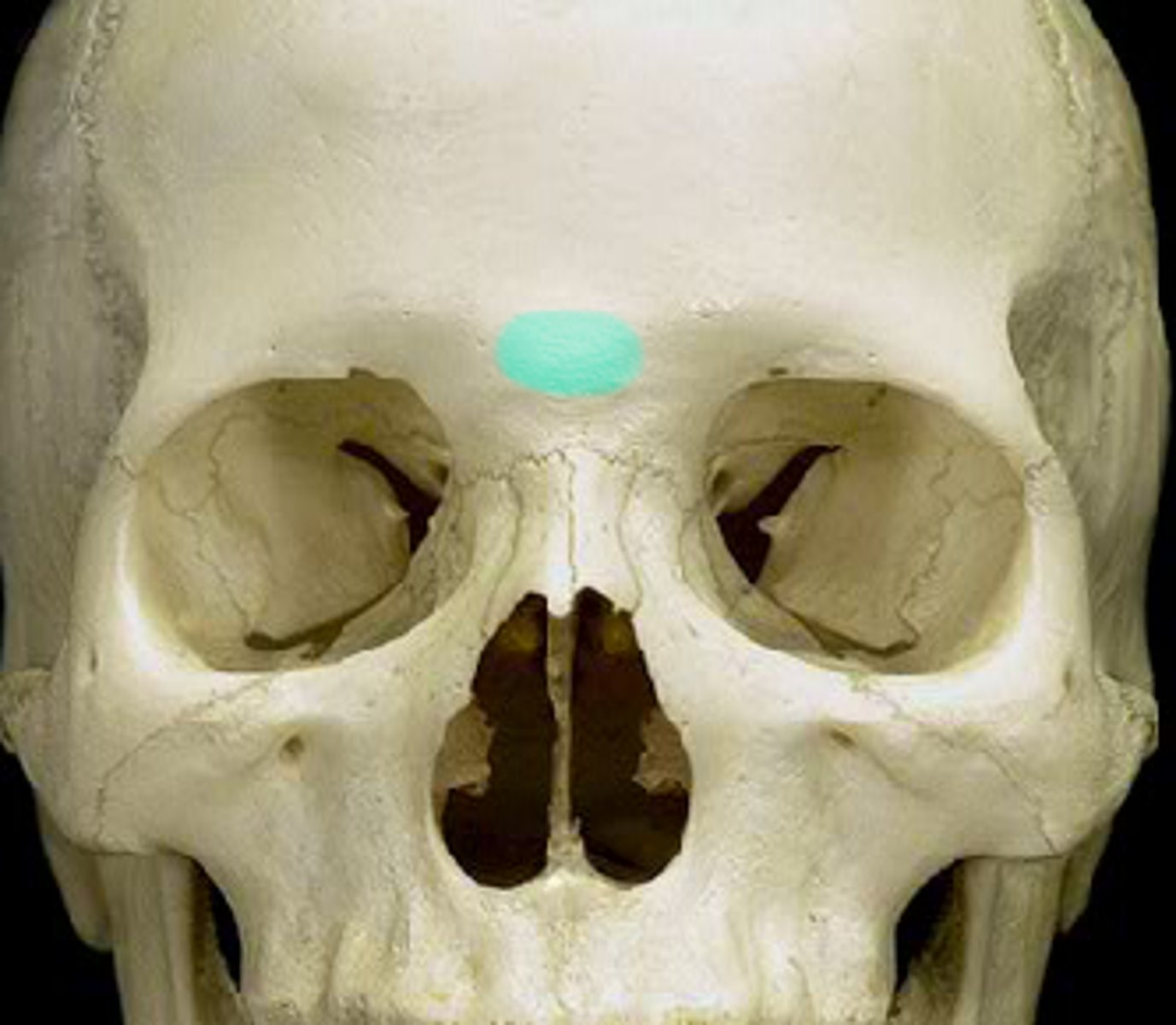
glabella
coronal suture
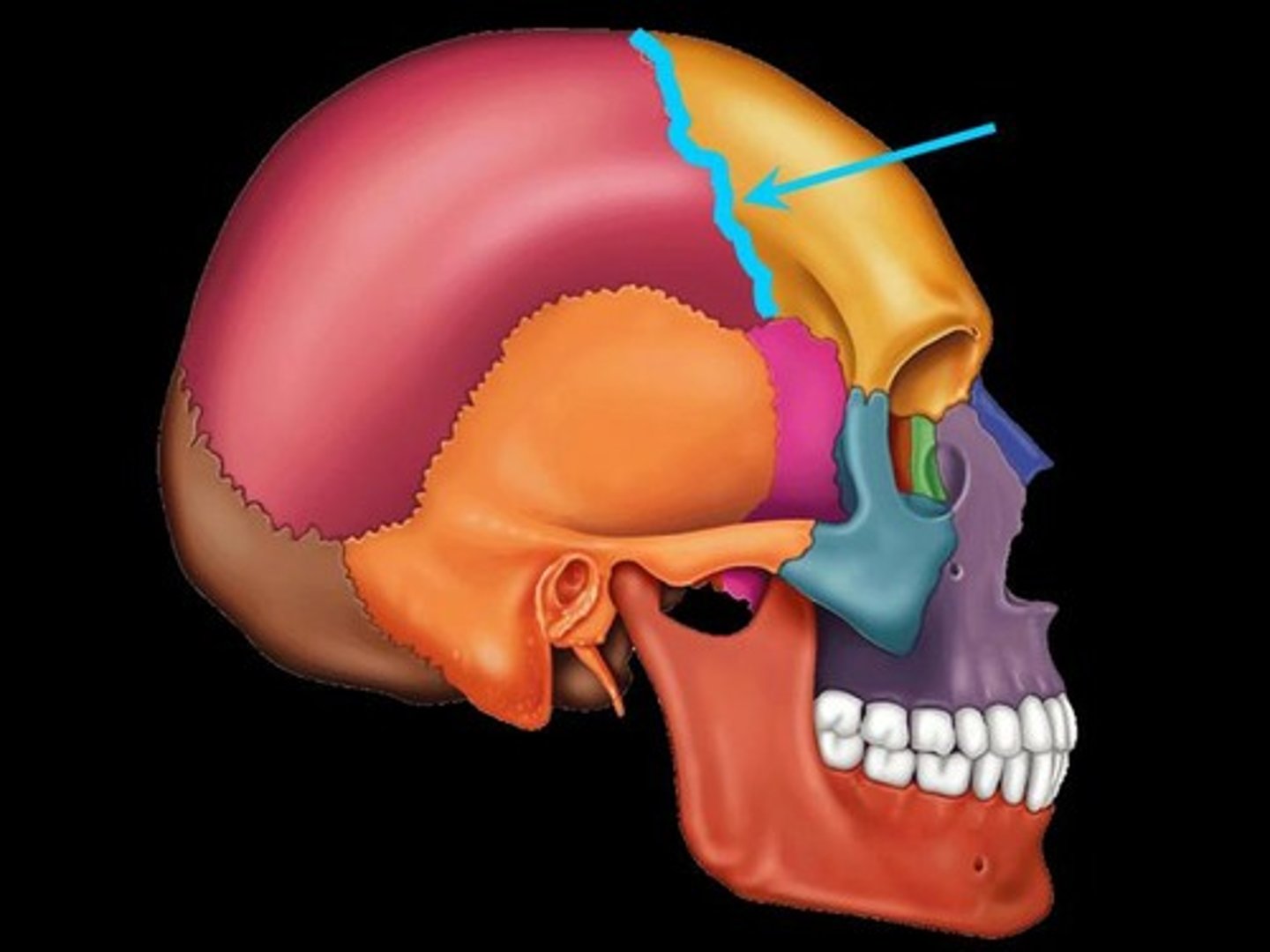
sagittal suture
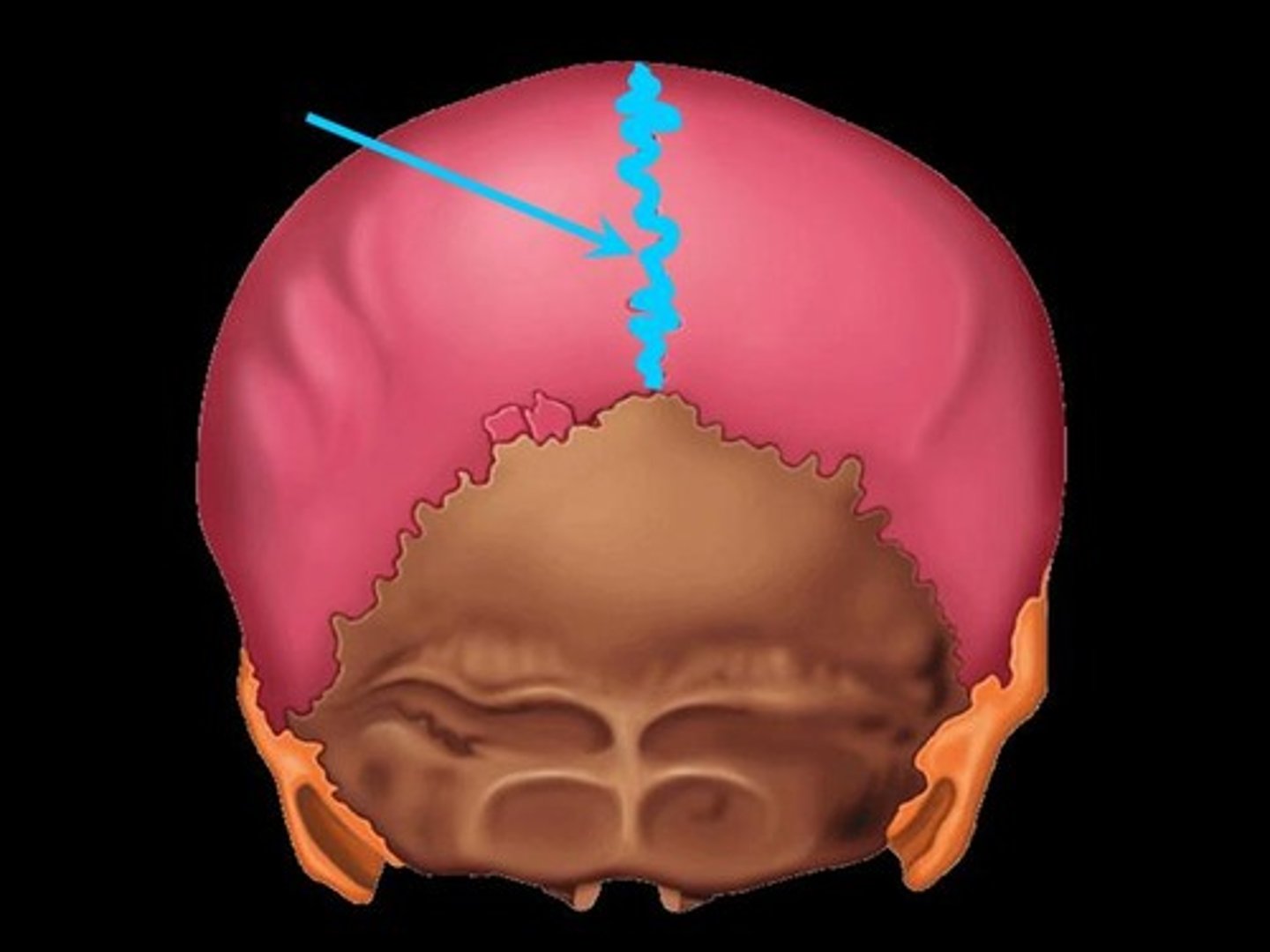
squamous suture
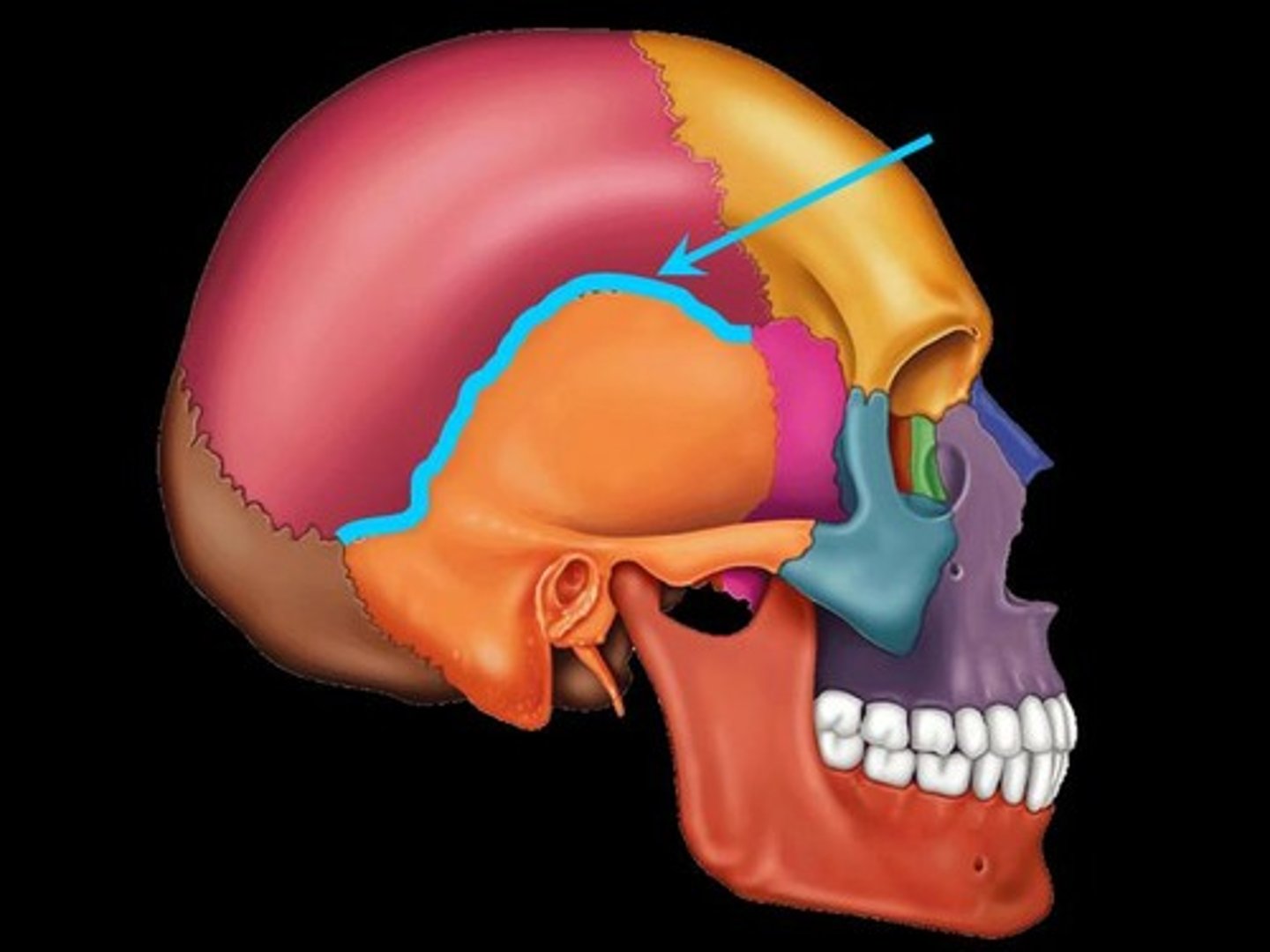
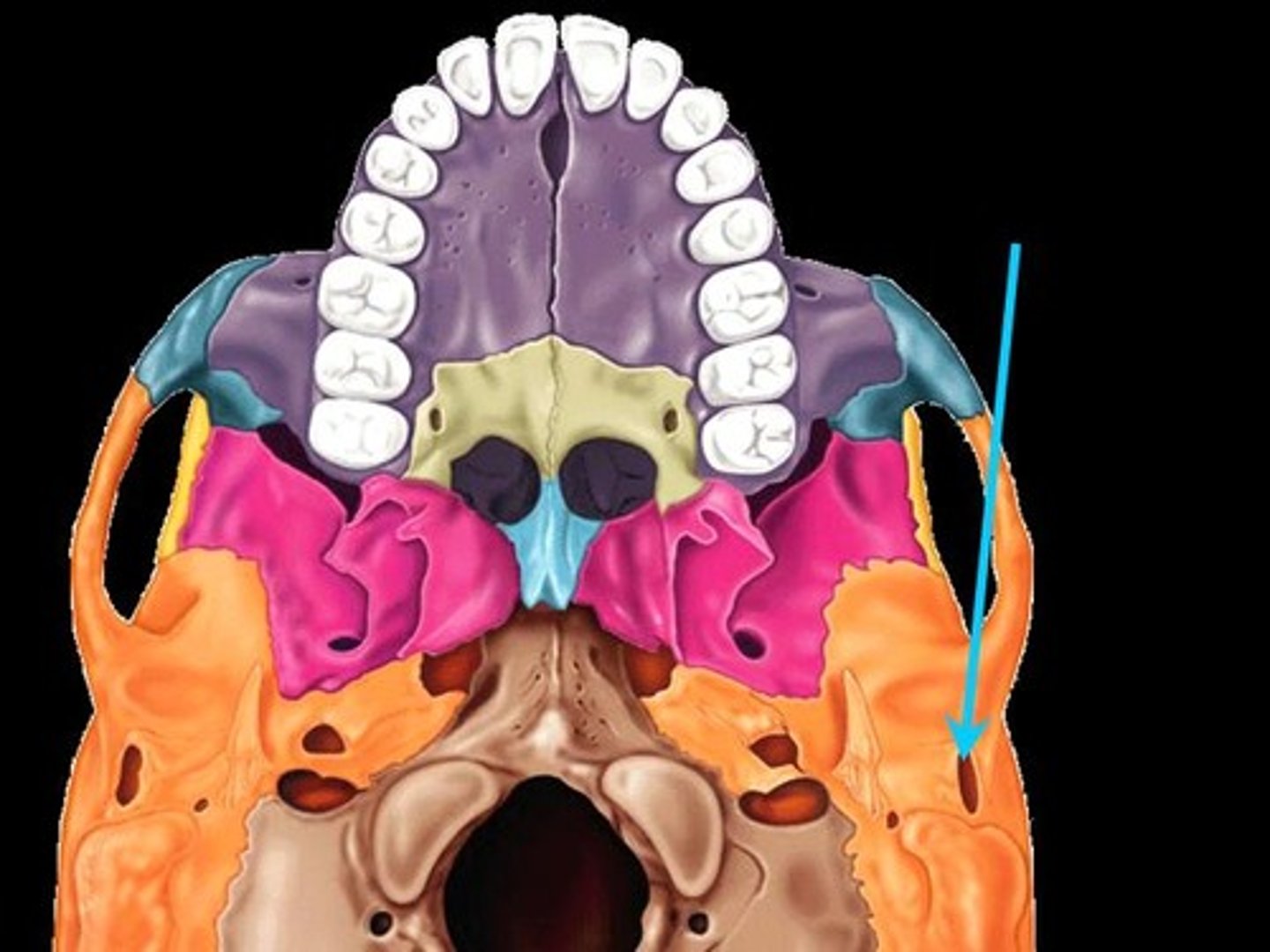
zygomatic process
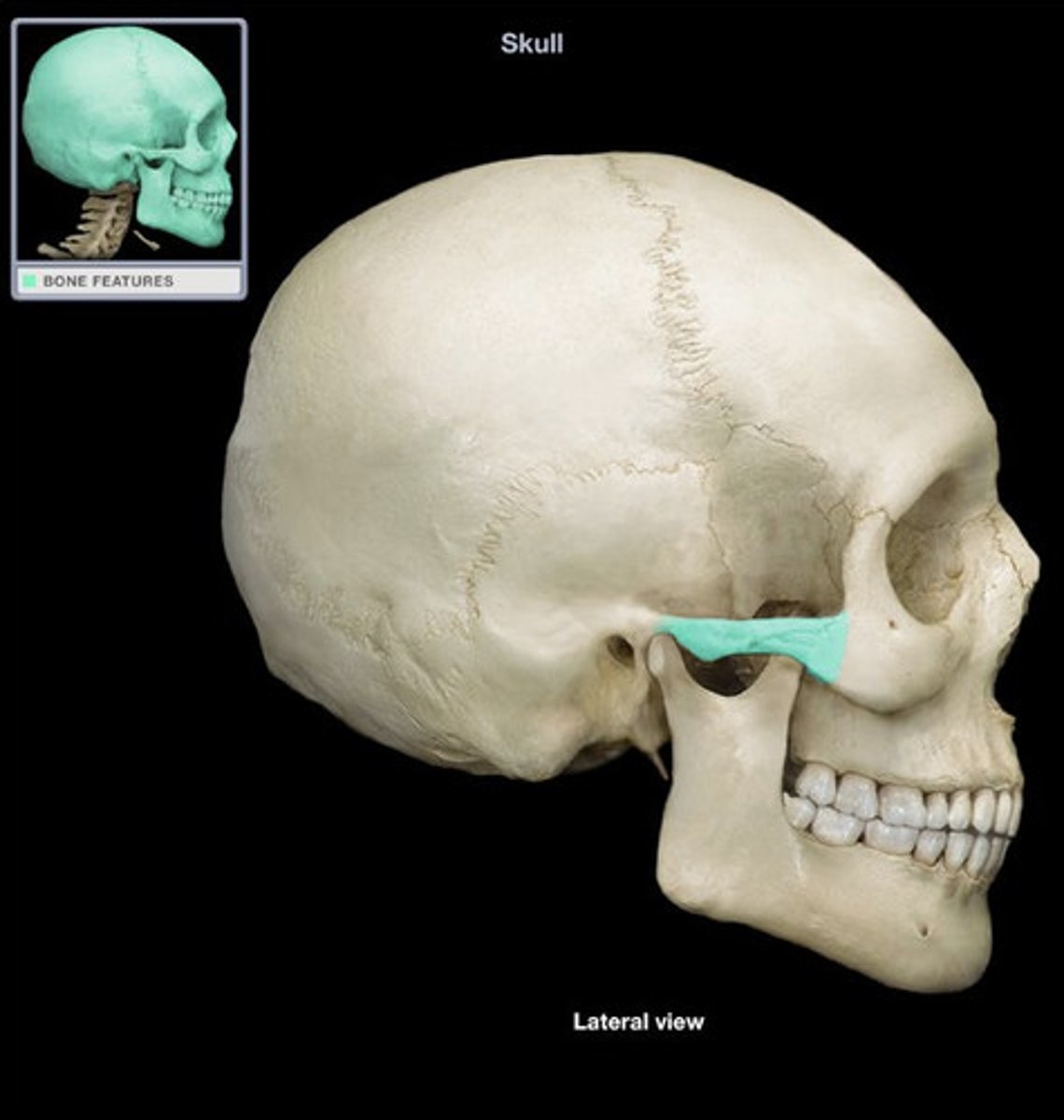
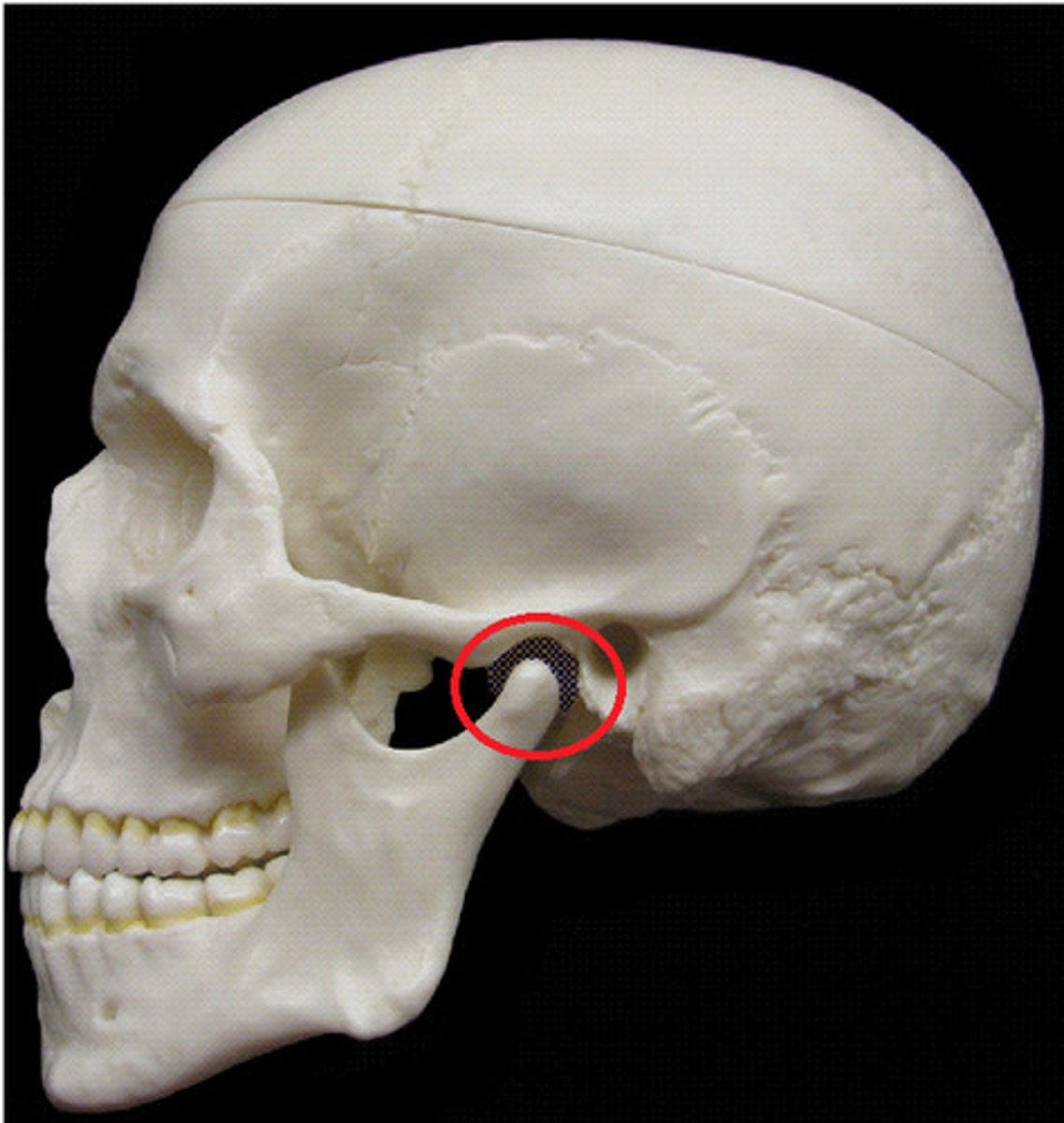
mandibular fossa (side)
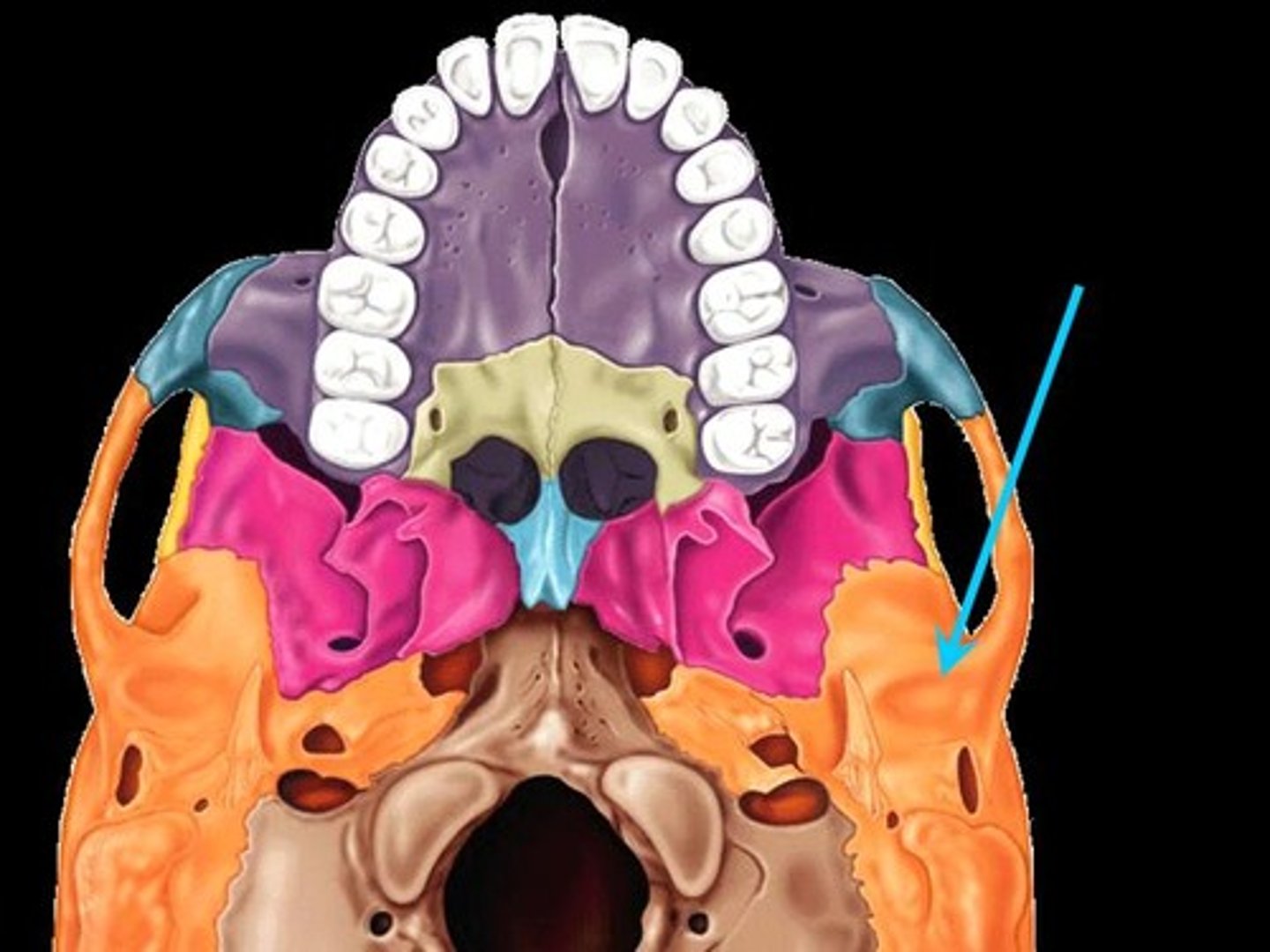
mandibular fossa (inferior view)
external acoustic meatus
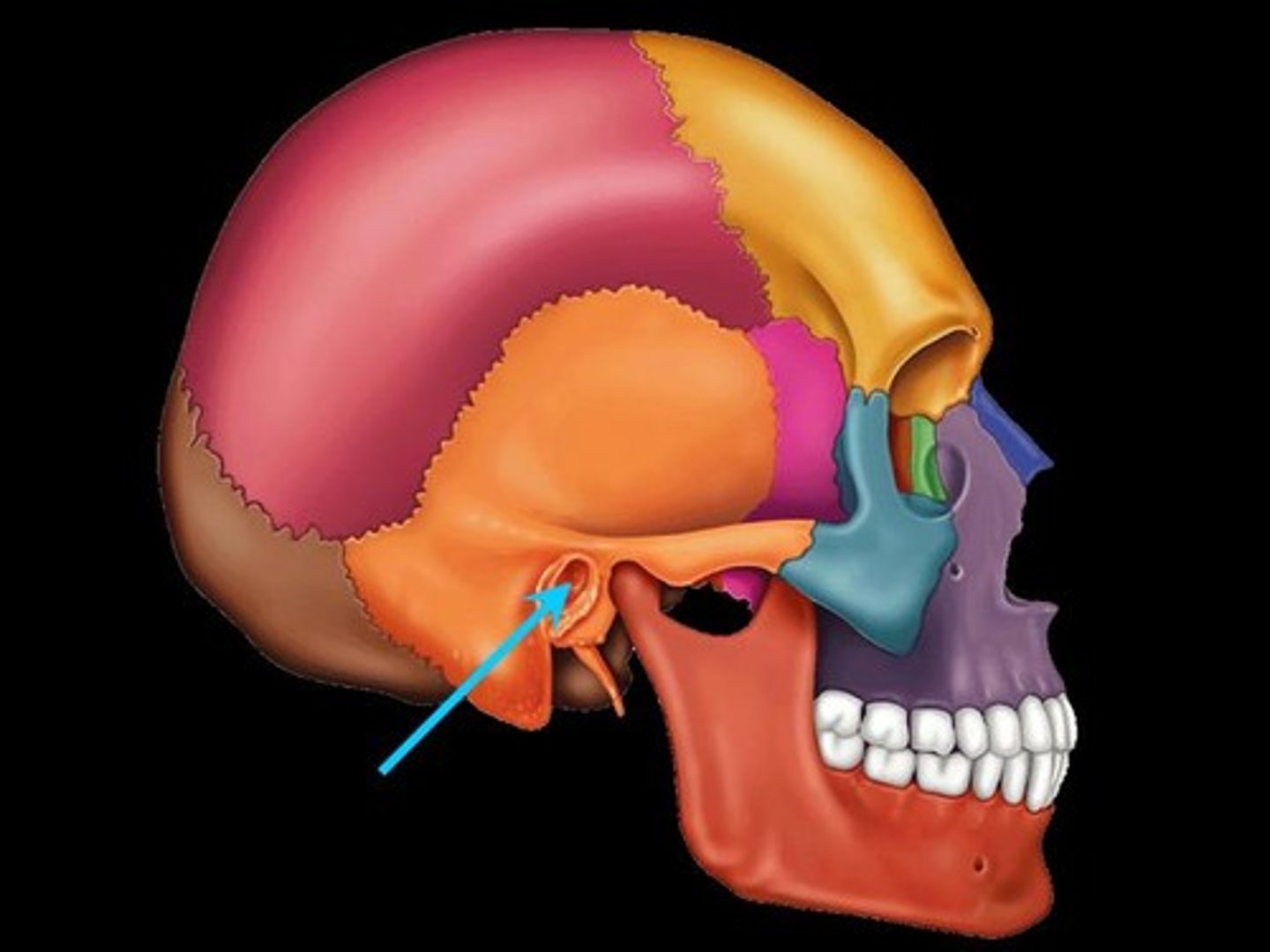
styloid process
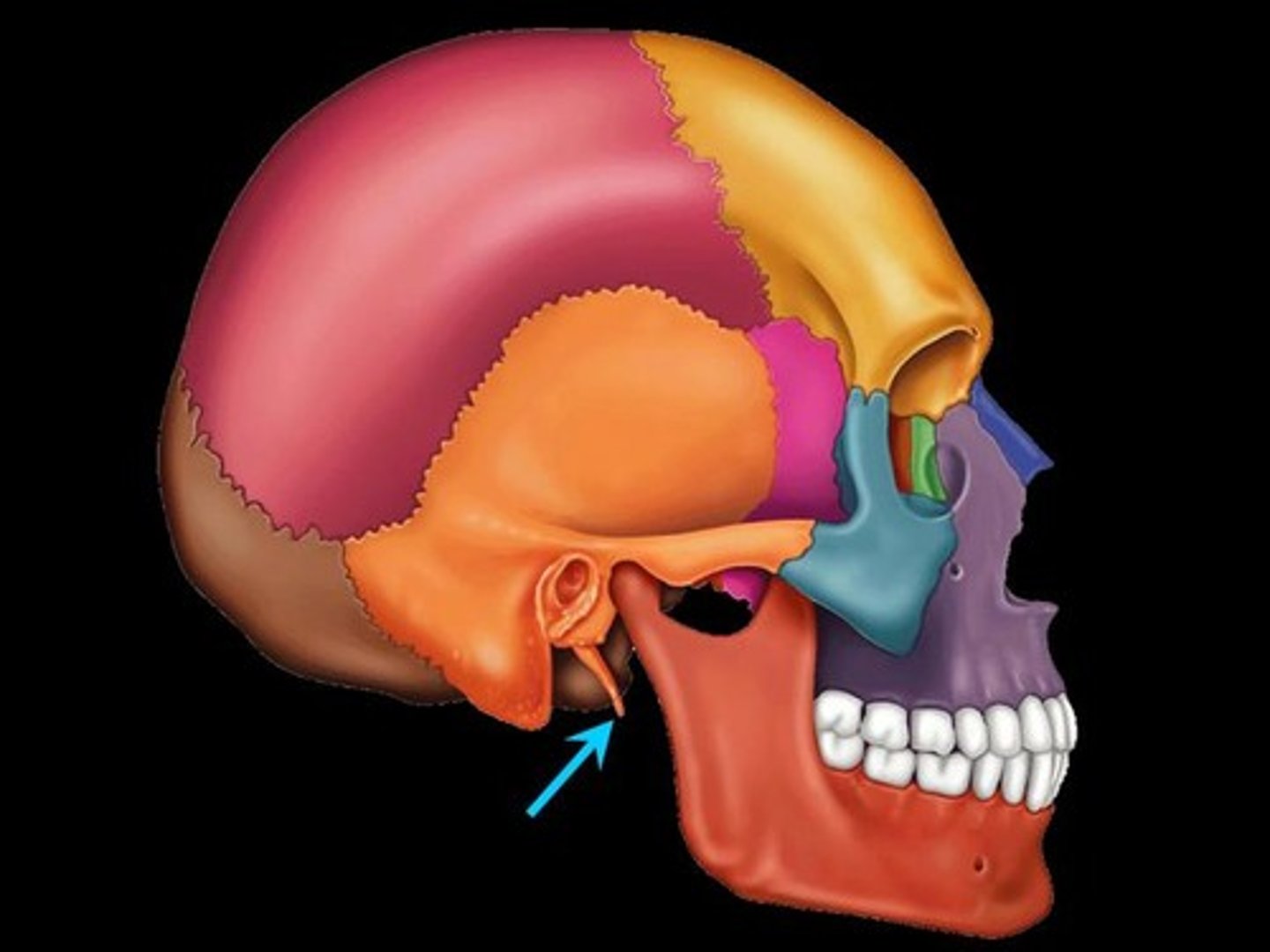
mastoid process
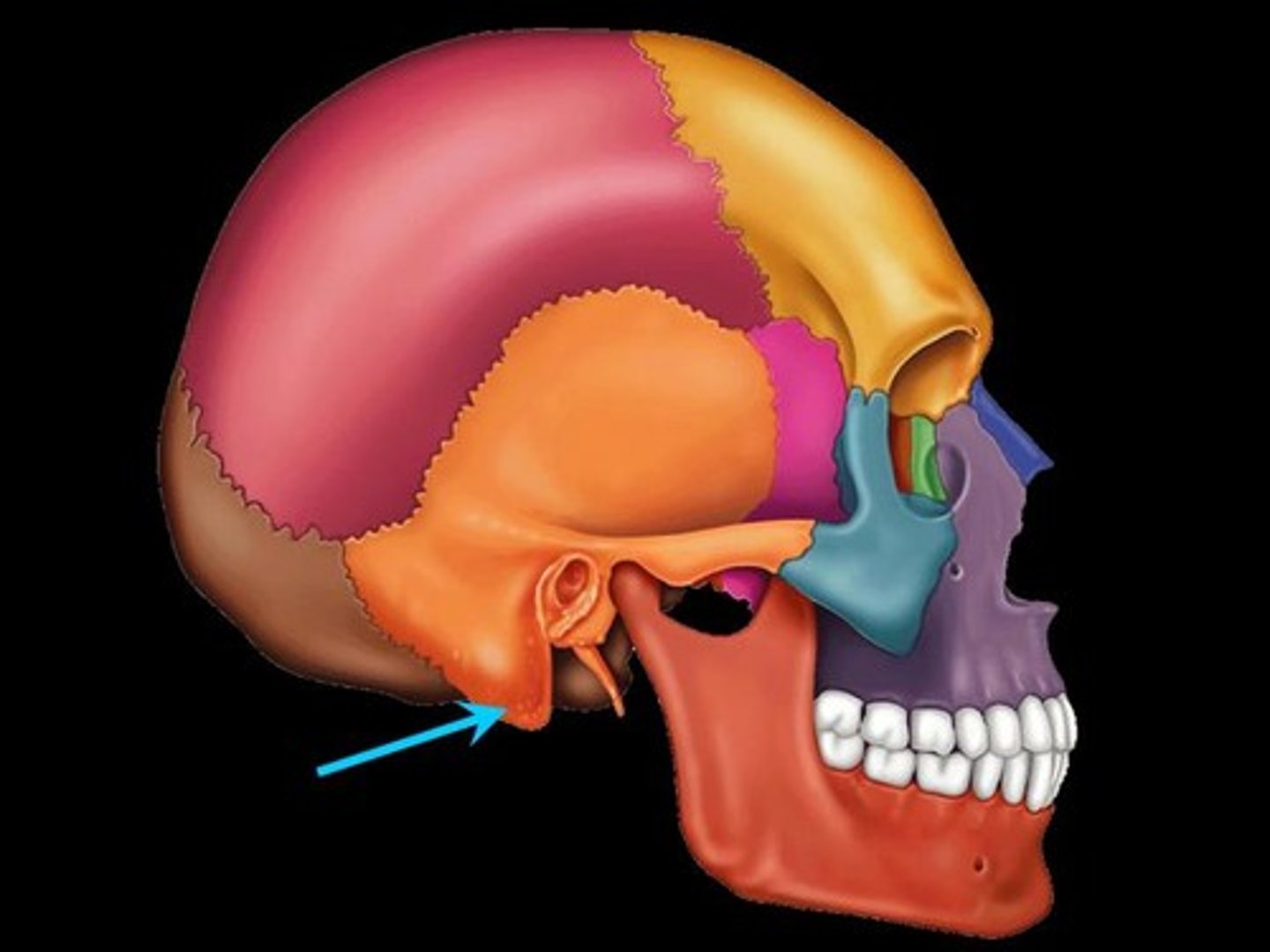
jugular foramen
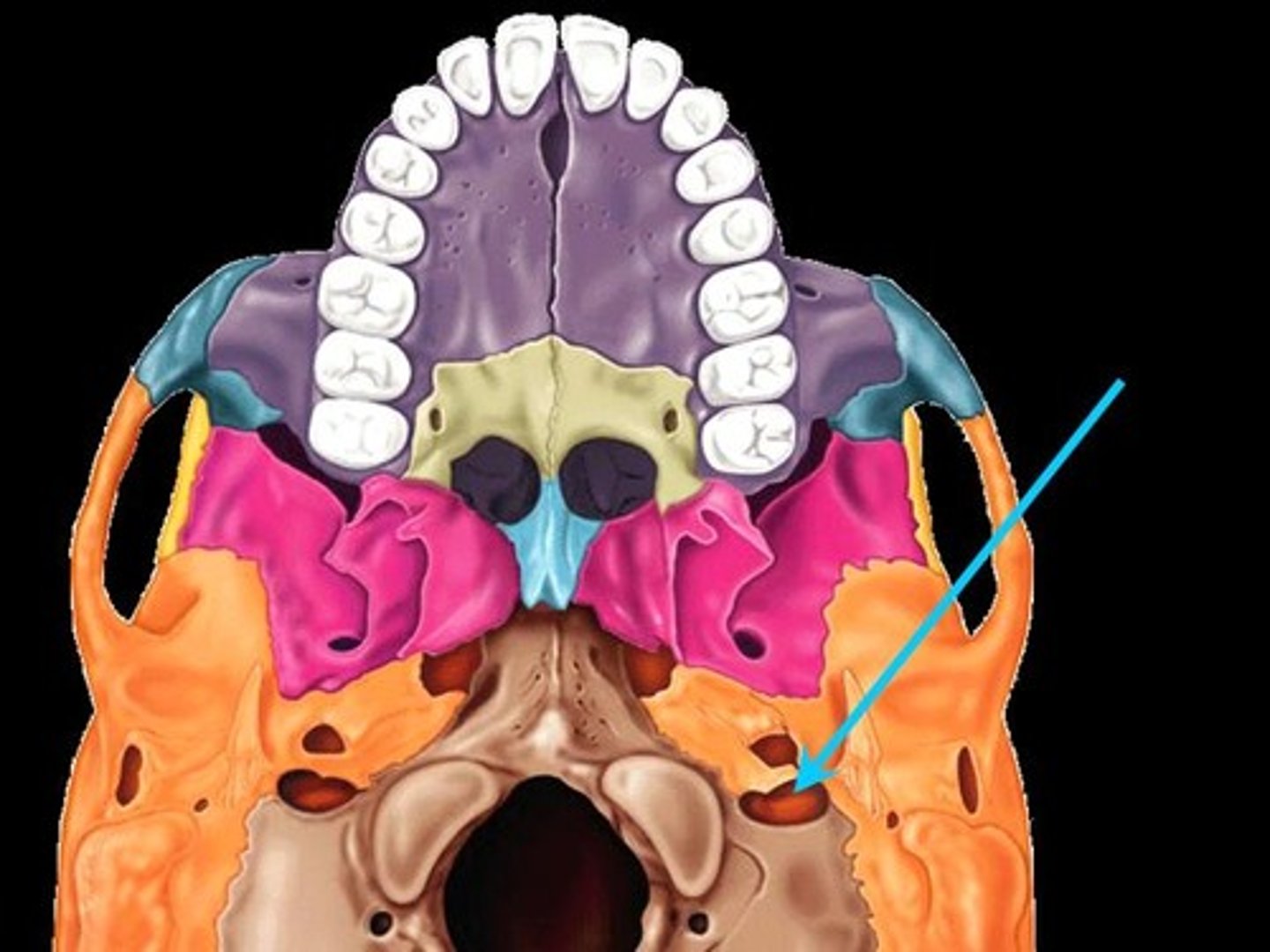
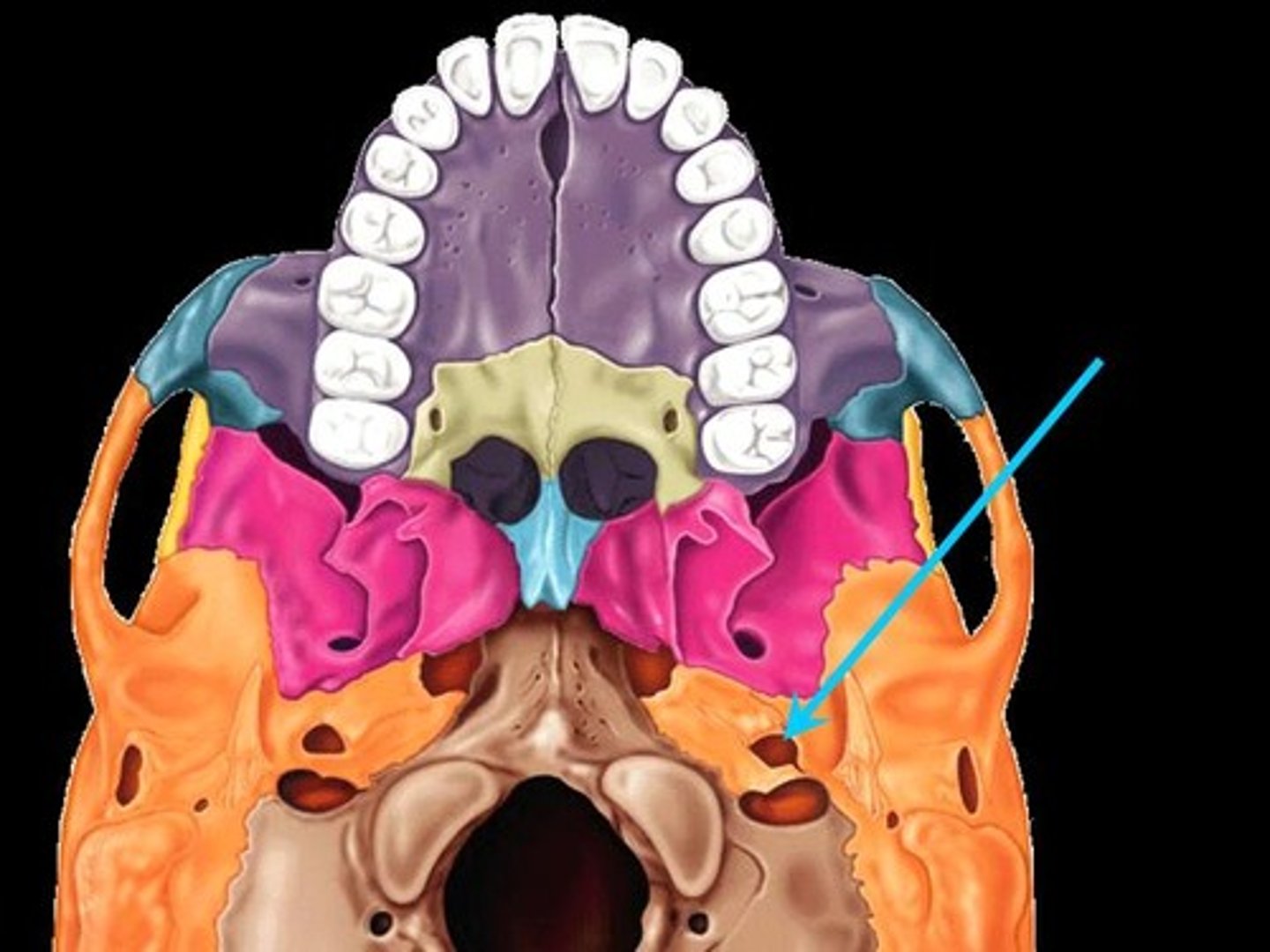
carotid canal
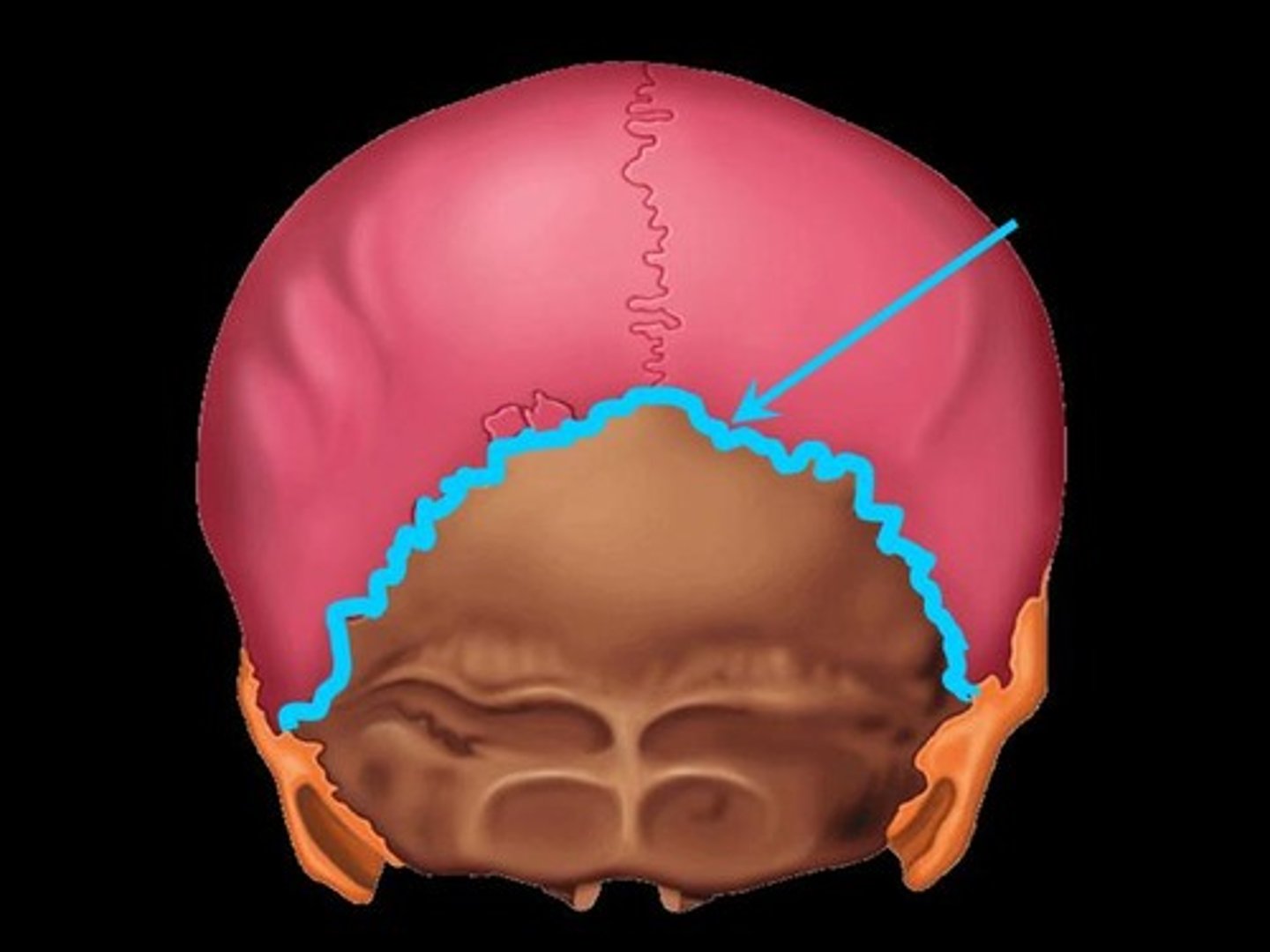
lambdoid suture
foramen magnum
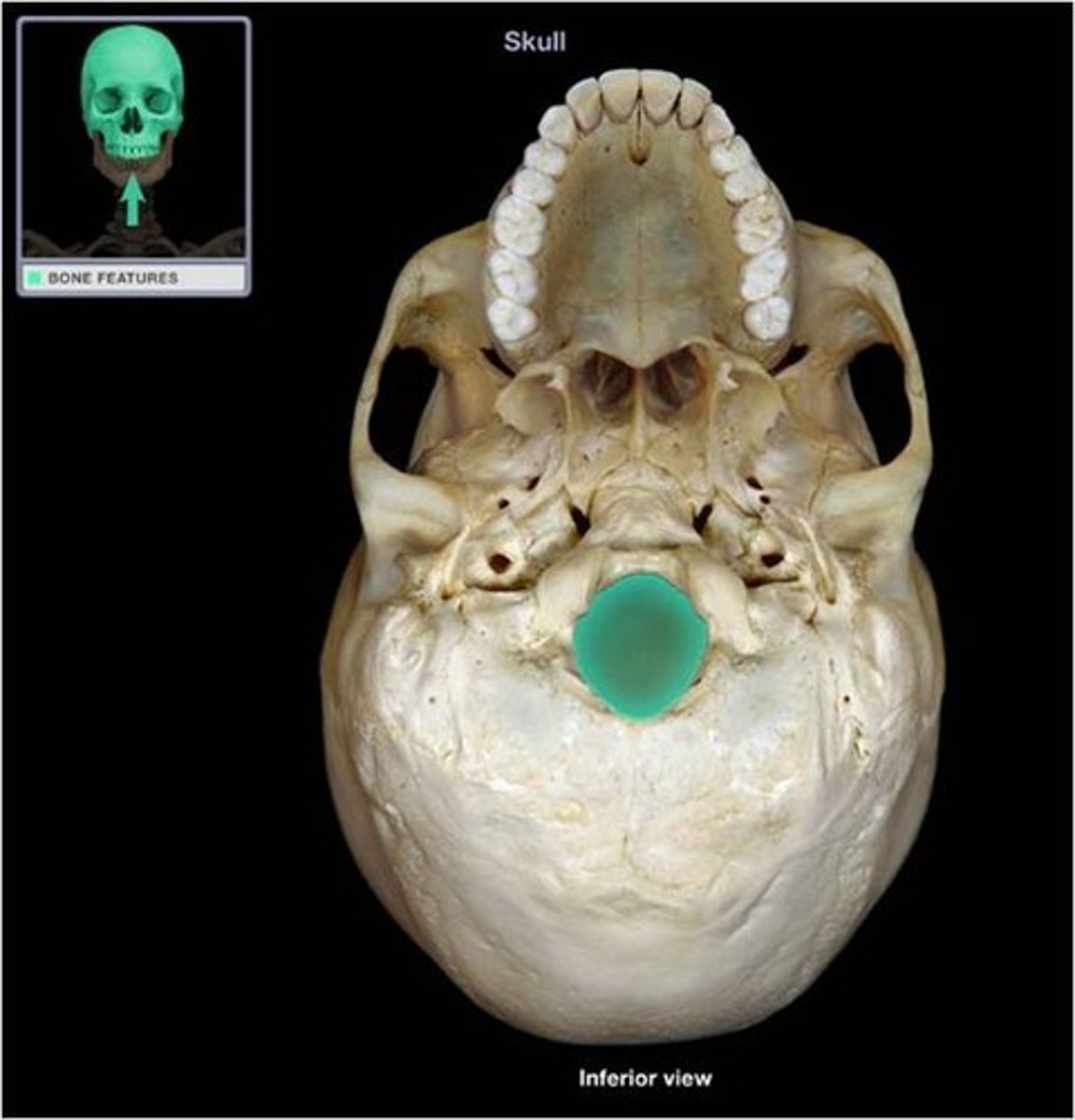
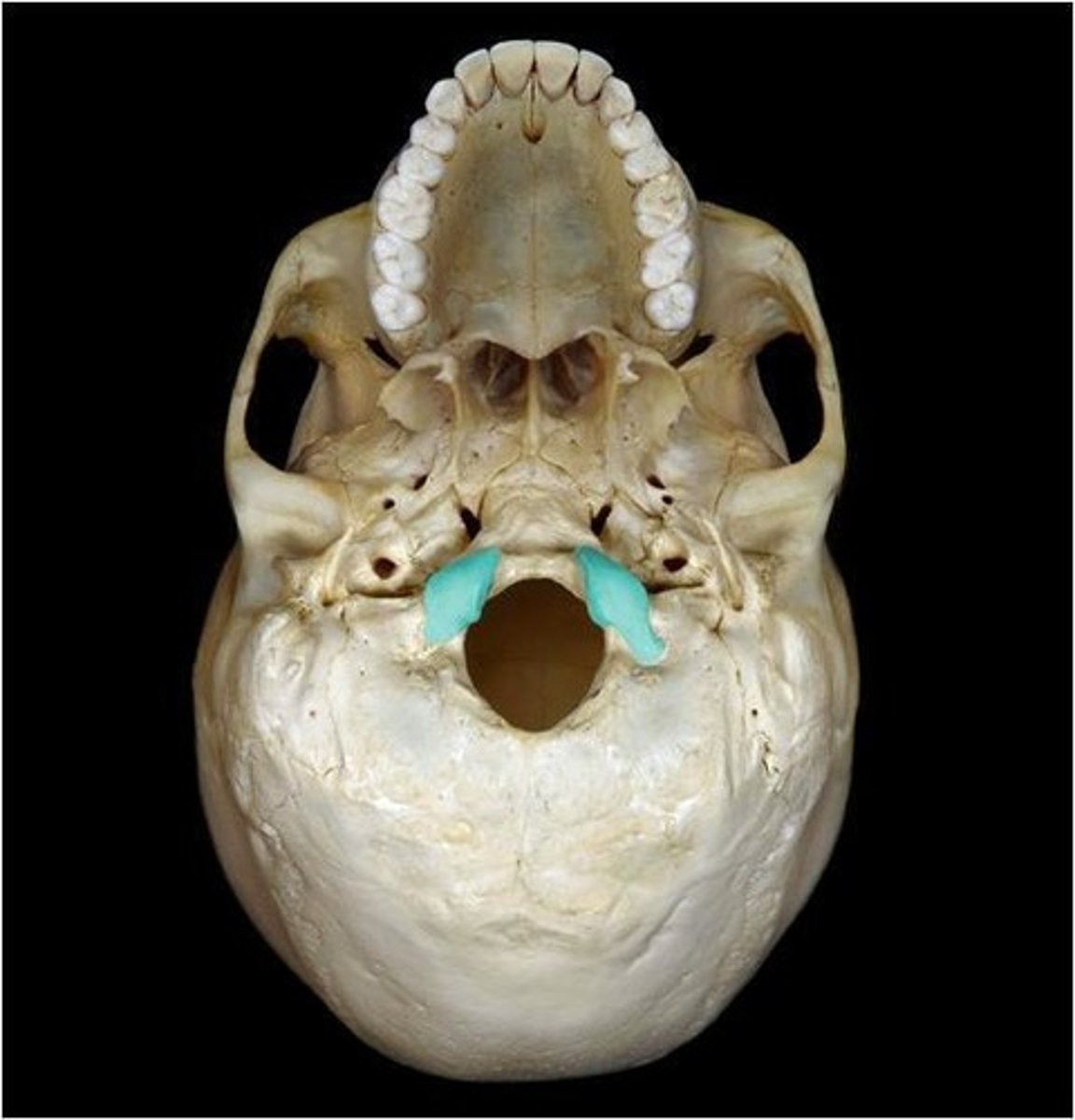
occipital condyle
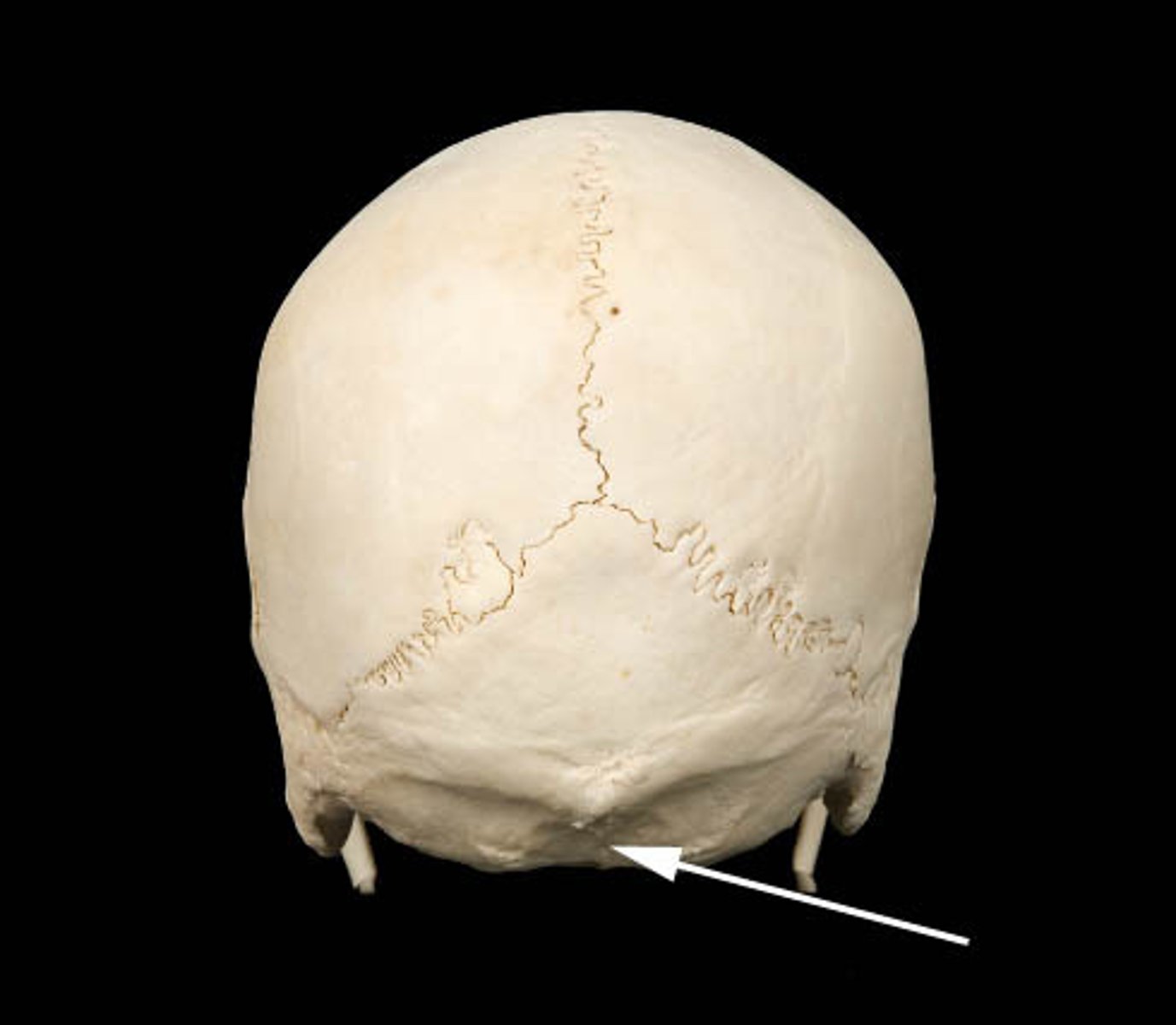
external occipital crest
greater wing
(sphenoid bone)