Vital Pulp Therapies - Indirect and Direct Pulp Cap
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
What is minimally invasive dentistry?
emphasises prev & least possible intervention
What is the preferred methods to manage deep carious lesions?
- selective caries removal: 1 stage
- stepwise caries removal: 2 stage
What is the 'restorative cycle'?
Once a rest has failed it enters this cycle
1) Initial Lesion
2) Restoration Placement
3) Structural Degradation
4) Restoration Failure...
How far is deep dentine from the occlusal surface approximately?
4-5mm
What is the proximity of the pulp from the occlusal surface and the DEJ approximately?
- 5mm from occl surface
- >3mm from DEJ
Where are most pulpal exposures from?
lateral pulp horn not the floor of the cavity
What materials are available for pulp capping?
- CSCs: biodentine, MTA > provide a better pulpal response compared to CaOH2
- CaOH2 > generally more avail
What does calcium hydroxide require sealing with, before a definitive restoration is placed?
GIC/RMGIC
When can a definitive restoration be placed, after CSC was placed as a lining?
r/v at 3 months & cut back to place definitive restoration
What equipment is required for VPT?
• Rubber dam, clamps, wedjets & frame (essential as VPTs should be carried out w/ aseptic conditions)
• Tweezers
• Cons kit
• Calcium hydroxide applicator or BPE probe
• Mixing spatulas
• Sodium hypochlorite (0.5 -5%)
• Cw wool pellets
• Biodentine
• Dycal (setting calcium hydroxide)
• GI & applicator
When is DPC indicated?
- Dentine is lost due to caries, trauma or a prev iatrogenic intervention & a cavity exists
- However, in this case the soft tissue of the pulp is exposed & in most cases is bleeding
- If symptoms exist they should be relatively mild & not considered to be indicative of IP
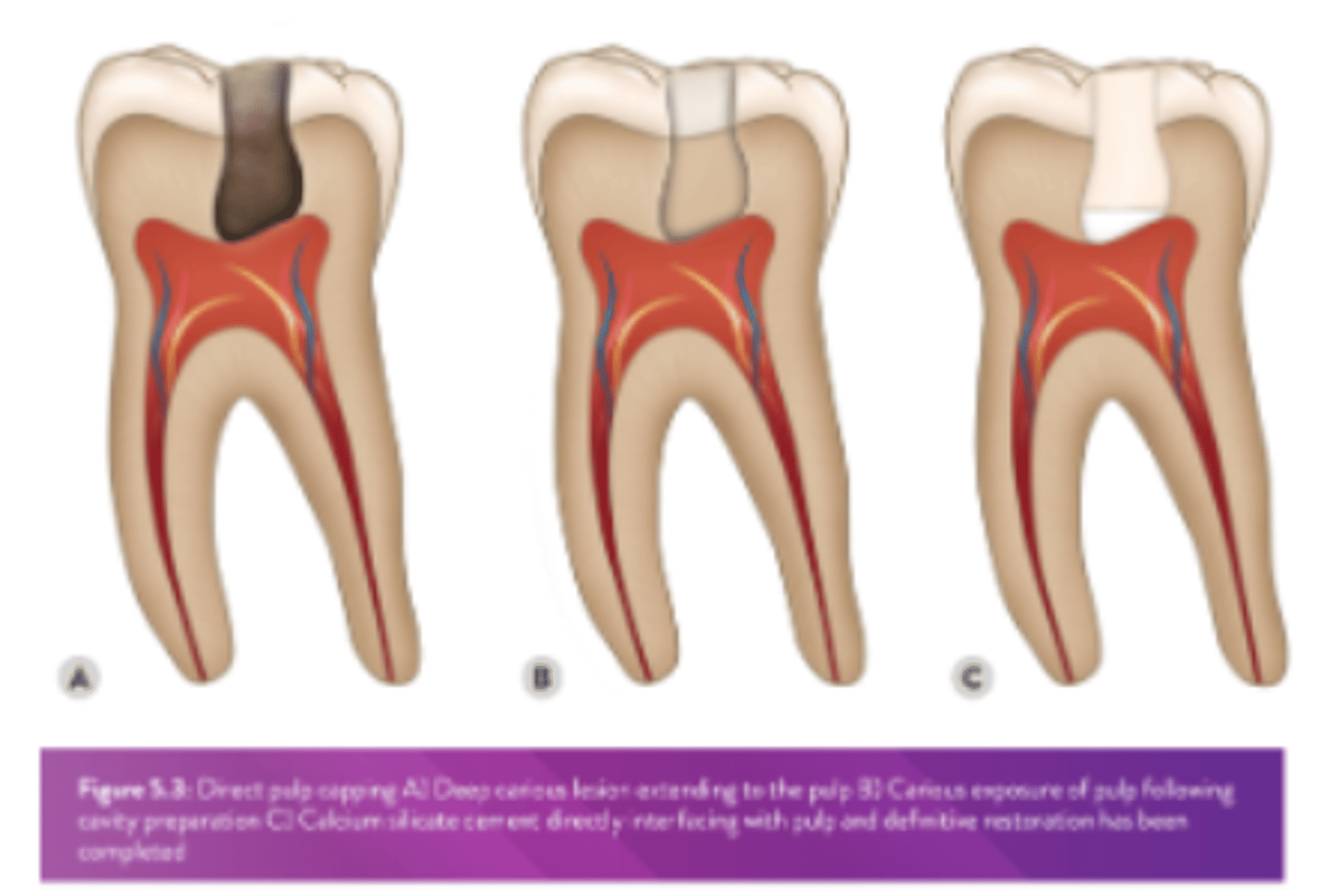
OSS: Tooth preparation for DPC
• Isolate w/ a rubber dam & prepare LR6d cavity as indicated (small <1mm pulpal exposure)
• Carefully approach the floor & axial wall where a pulpal exposure might be anticipated
• Pin prick exposure only, consider pulpal position, 5 mm from the occlusal surface or >3 mm from DEJ: 'pulpal blush', stop
How should the cavity be disinfected?
- cavity should be disinfected using cotton pellets soaked (removing gross excess) w/ sodium hypochlorite (0.5-5%) (water on OSS to replicate) for 30-60s
> dry well
• If bleeding is not controlled within 5m - a partial pulpotomy is indicated
-Seek advice from dentist
How should be biodentine be mixed?
• Open Capsule
• 5 drops of liquid (contains Ca chloride & hydrosoluble polymer)
• Use exact amount as can be temperamental in terms of consistency
• Reseal & triturate for 30s
> 9-12m to reach initial set
> approx 48hrs for full set
How should biodentine be cut back to place a final restoration after 3 months review?
- cut back BD to leave clear EDJ
- BD left in situ as dentine replacement
- restore w/ comp
What is the indications for an IPC?
dentine is lost due to caries, trauma or a prev iatrogenic intervention & a cavity exists which is close to the pulp but dentine still remains over the pulp tissue
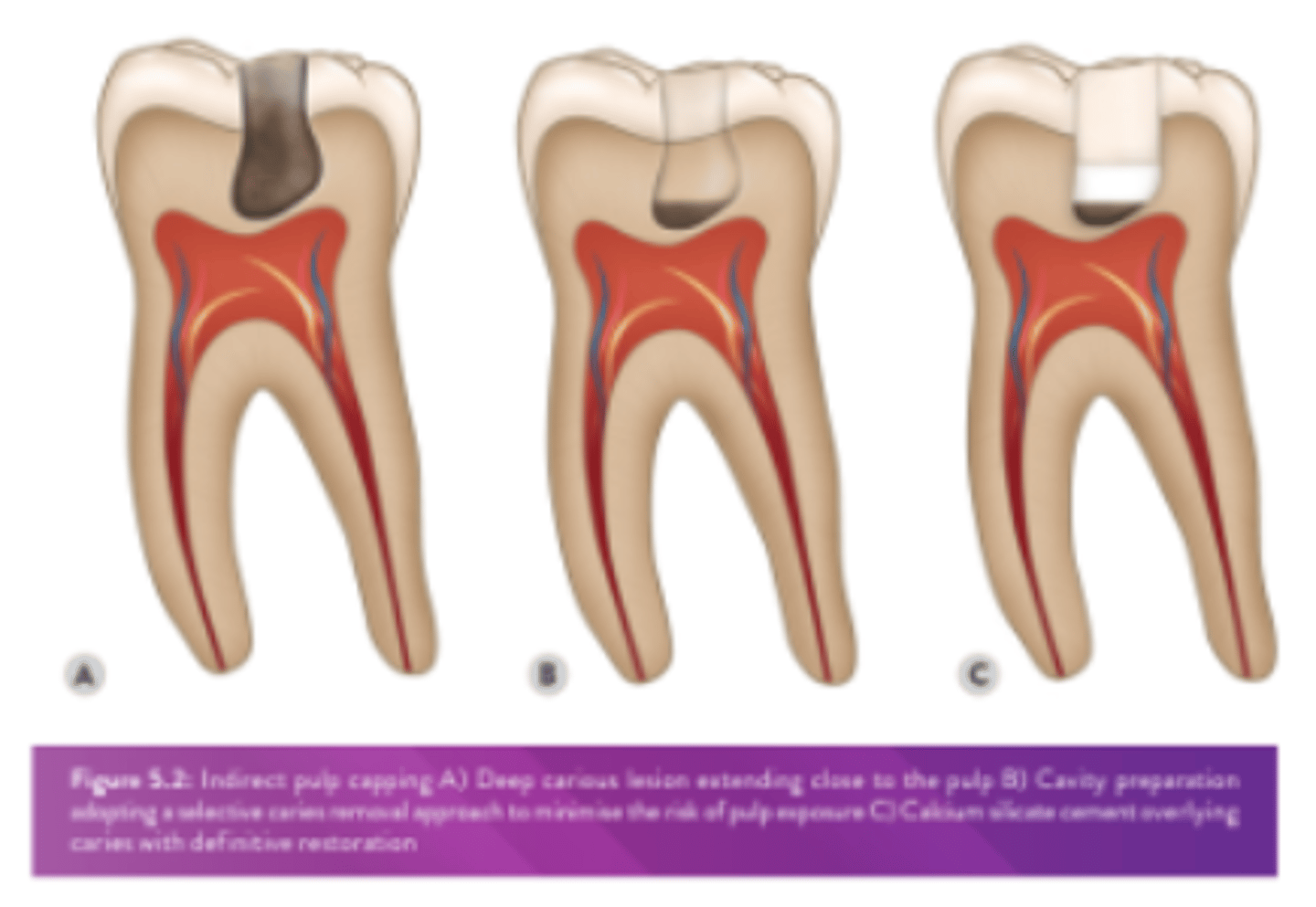
How should calcium hydroxide be mixed?
- base & catalyst to mix
- stimulates formation of secondary dentine
- setting time 2-3m
How should dycal be placed for an IPC? What should then be placed?
- place small amount of dycal (setting CaOH2) via BPE probe on deepest part of the cavity
- place layer GIC over Ca(OH)2 to seal
- keep enamel margins clear
What are the recalls for review following pulp capping?
- r/v at 6m, hx & clinical examination
- 1y r/v w/ radiograph
- pt should be warned of possibility of further tx should symptoms occur
How to use dycal as a DPC:
1. Rinse cavity w/ (NaOCl)
2. Heavy bleeding may be controlled w/ a cotton pellet moistened w/ sterile saline; gently dry
3. Dispense equal volumes of base & catalyst pastes
4. Using a Ca(OH)2 applicator, stir imm to mix thoroughly until a uniform colour is achieved; do not over-spatulate; complete mixing within 10s. Using BPE, place directly on the exposed pulp & dentine at 0.8-1.0mm thickness; avoid placing on enamel/margins of the cavity
6. Allow to completely set ~ 2-3m
7. Remove any set excess from retention areas, enamel, &/or margins w/ a sharp spoon excavator or a bur
How to use Dycal as an IPC:
1. Wash cavity thoroughly w/ water spray & air dry
2. Dispense & mix Dycal Liner components
3. Apply mixed material to desired dentine surfaces; if subsequent use of a dentine bonding agent is desired, place Dycal® Liner only on the deepest (<1mm remaining) dentine, leaving the rest of the cavity surface free for bonding
4. Remove any set excess from retention areas, enamel, &/or margins w/ a sharp spoon excavator or a bur
What is a Class I pulp exposure?
- No preoperative presence of a deep carious lesion
- Pulp exposure judged clinically to be through sound dentine w/ an expectation that the underlying pulp tissue is healthy
- Exposure due to a traumatic injury or iatrogenic exposure
What is a Class II pulp exposure?
- Preop presence of a deep or extremely deep carious lesion
- Pulp exposure judged clinically to be through a zone of bacterial contamination w/ an expectation that the underlying pulp tissue is inflamed
- Enhanced operative protocol rec
The pulp is under threat from which three main sources?
- Trauma
- Iatrogenic damage
- Caries