Jeppesen 02A - Reciprocating Engine Operation, Maintenance, and Inspection
1/337
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
338 Terms
Type Certificate Data Sheet
Engine instrument range markings are based on limits found in the engine's ________________.
Green, blue, yellow, and red.
Traditionally, instrument markings consist of what color of lines or arcs which include intermediate blank spaces?
Green arcs
They are the most widely used of all the instrument markings and usually indicate a safe, or normal range of operation. Operation within this arc is typically not time restricted.
The maximum limit for continuous operation.
What does the upper end of a green arc indicates?
The minimum limit for continuous operation.
What does the lower end of a green arc indicates?
Left, right
For standardization purposes, the primary engine controls are arranged from ______ to _______ beginning with the throttle, propeller control, and mixture. In addition, each lever is color coded and uniquely shaped.
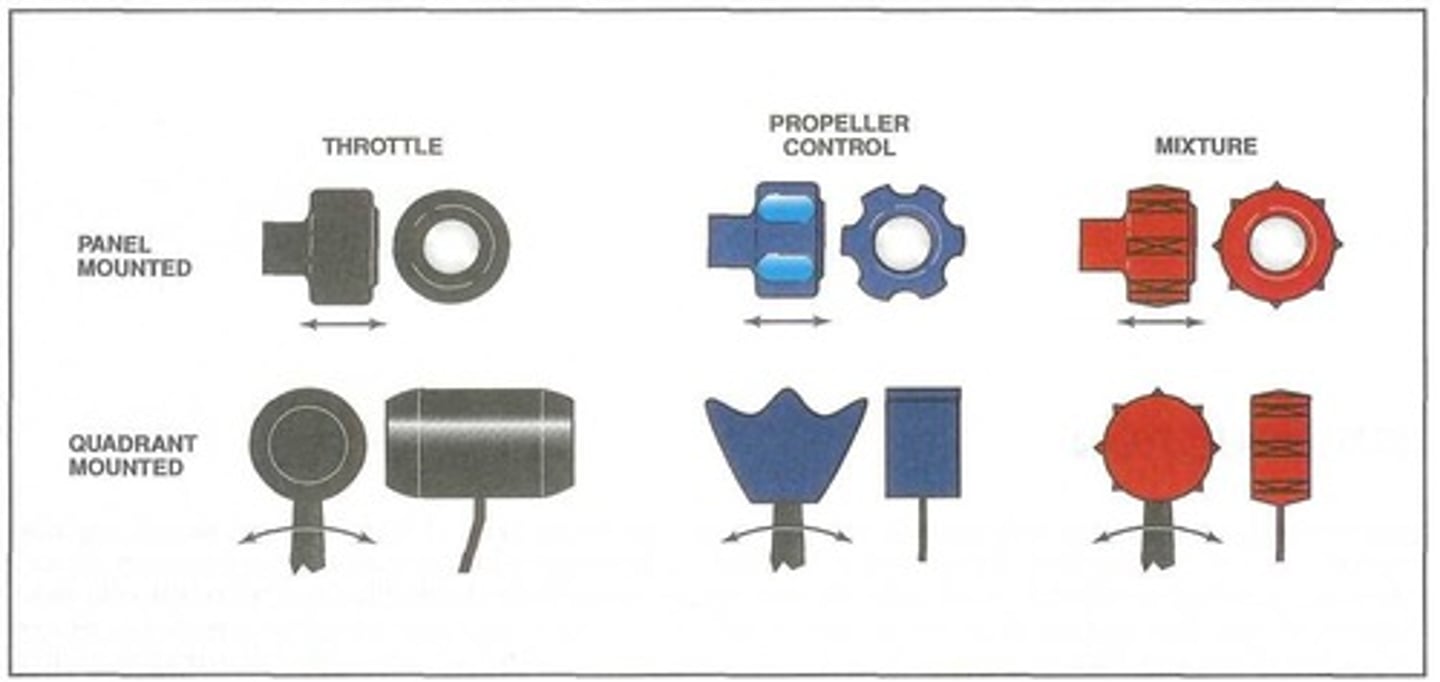
Blue arcs
They are used to indicate an allowable range of operations under a unique set of circumstances.
Blue arcs
This arc may indicate an acceptable fuel flow when flying above a specific altitude.
1. Tachometer
2. Fuel flow
3. Manifold pressure
4. Cylinder head temperature
5. Torque meter
Blue arcs are rarely used and may only be seen on certain engine instruments, such as:
Float-type carburetor
The top fuel pressure gauge is typical for an engine equipped with:

Yellow arcs
It indicates a precautionary range of time limited operation permitted by the manufacturer.
Yellow arcs
Engine operation in this arc is typically an indication of an impending problem or a warning to change an operational setting.
The manufacturer's instructions will specify a caution range.
In some cases, a yellow arc may be omitted on instruments if it is too small to be clearly visible. When this is the case:
Red lines
Indicates a maximum or minimum safe operating limit. Operation beyond this line typically results in a dangerous operating condition.
Red arcs
Indicates a restricted operating range where excessive vibration or other stresses could endanger the engine or airframe.
The instrument glass has moved.
The colored arcs and lines on engine instruments are typically painted directly on the instrument face. However, some older aircraft instrument markings may be painted on the instrument glass. If this is the case, a white line is used as an index mark between the instrument glass and case. Any discontinuity in the white radial line indicates:
The glass must be repositioned and secured.
Any discontinuity in the white radial line indicates the instrument glass has moved. What should be done to solve this problem?
Carburetor air temperature (CAT)
It is measured at the carburetor entrance by a temperature sensing bulb in the ram air intake duct.
Degrees Centrigrade
Carburetor air temperature (CAT) is measured at the carburetor entrance by a temperature sensing bulb in the ram air intake duct. The sensing bulb senses the air temperature in the carburetor and then sends a signal to a cockpit instrument that is calibrated in what measurement?
Inform a pilot when the temperature at the carburetor can support the formation of ice.
The primary purpose of a CAT gauge is:
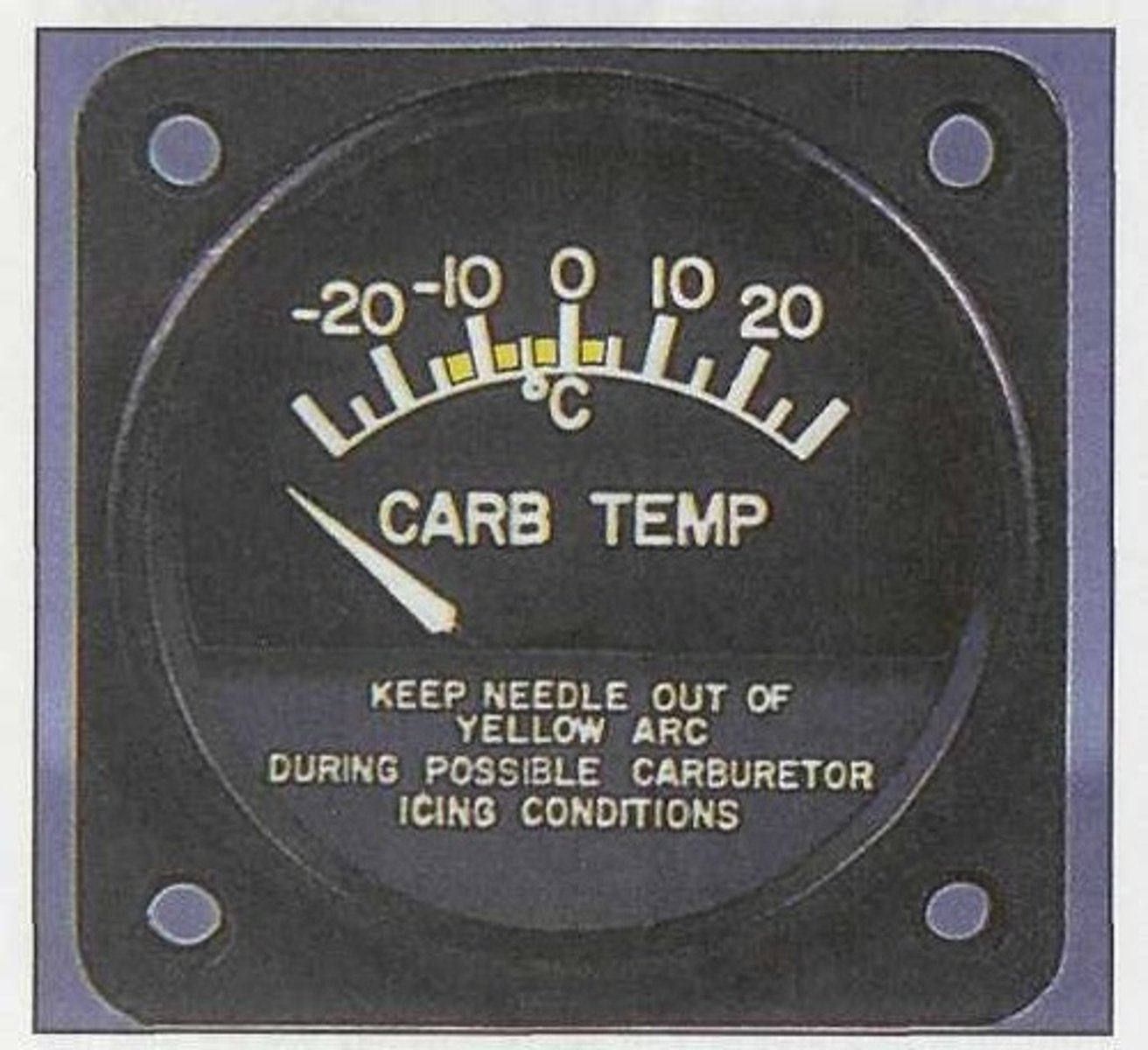
Detonation
Excessively high carburetor air temperatures can indicate the onset of ___________________.
Increases the chance of detonation occurring.
If a CAT gauge has a red line identifying a maximum operating temperature, engine operation above that temperature:
Determine if the fuel is warm enough to support vaporization.
Observation of the CAT before engine startup and just after shutdown provides an indication of fuel temperature in the carburetor body. During startup, this information can be used to:
Fuel trapped in a pressure-type carburetor could expand and produce potentially damaging fuel pressures.
A high CAT after engine shutdown is a warning that:
Vapor lock
High CAT temperatures after shutdown can also indicate the onset of __________, which is the formation of vaporized fuel bubbles in a fuel line that interfere with the flow of fuel to the engine.
A steady increase in CAT readings.
Information provided by CAT gauges can also be useful in troubleshooting. An induction fire would be indicated by:
The fuel selector valve and throttle should be left open until the engine cools. This helps relieve fuel pressure by allowing expanding fuel to return to the tank.
What should be done any time high CAT readings are observed after shutdown?
A momentary rise in CAT.
Information provided by CAT gauges can also be useful in troubleshooting. If severe enough, backfiring may cause:
Pounds per square inch (psi)
Most fuel pressure instruments display fuel pressure in terms of:
Fuel injection system
The bottom fuel pressure is typical for engines equipped with:

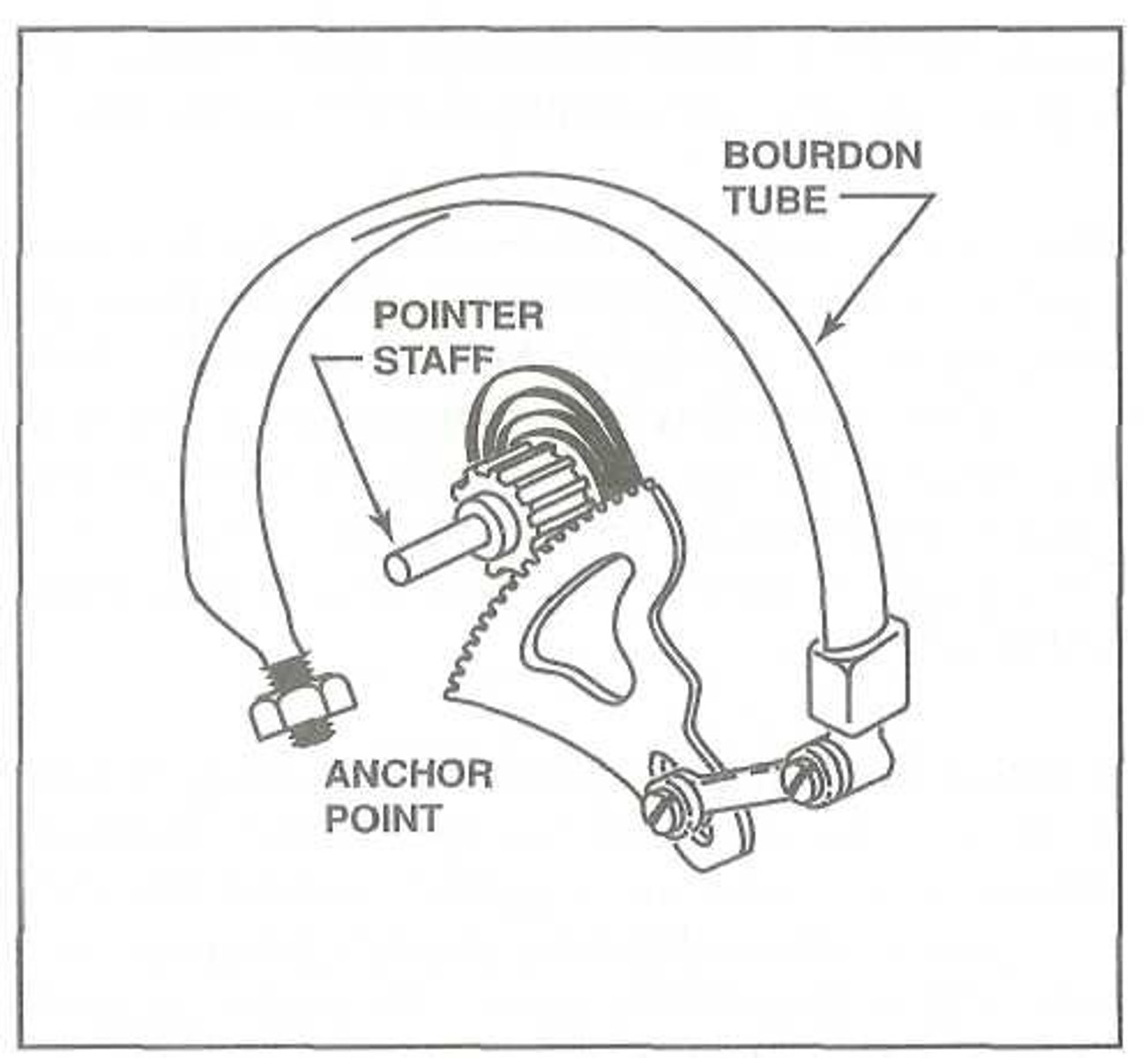
Bourdon tube
One type of fuel pressure gauge uses a __________ which is a metal tube that is formed in a circular shape with a flattened cross section. One end of the tube is open, while the other end is sealed. The open end of this tube is connected to a capillary tube containing pressurized fuel. As the pressurized fuel enters this tube, the tube tends to straighten. Through a series of gears, this movement is used to move an indicating needle on the instrument face.
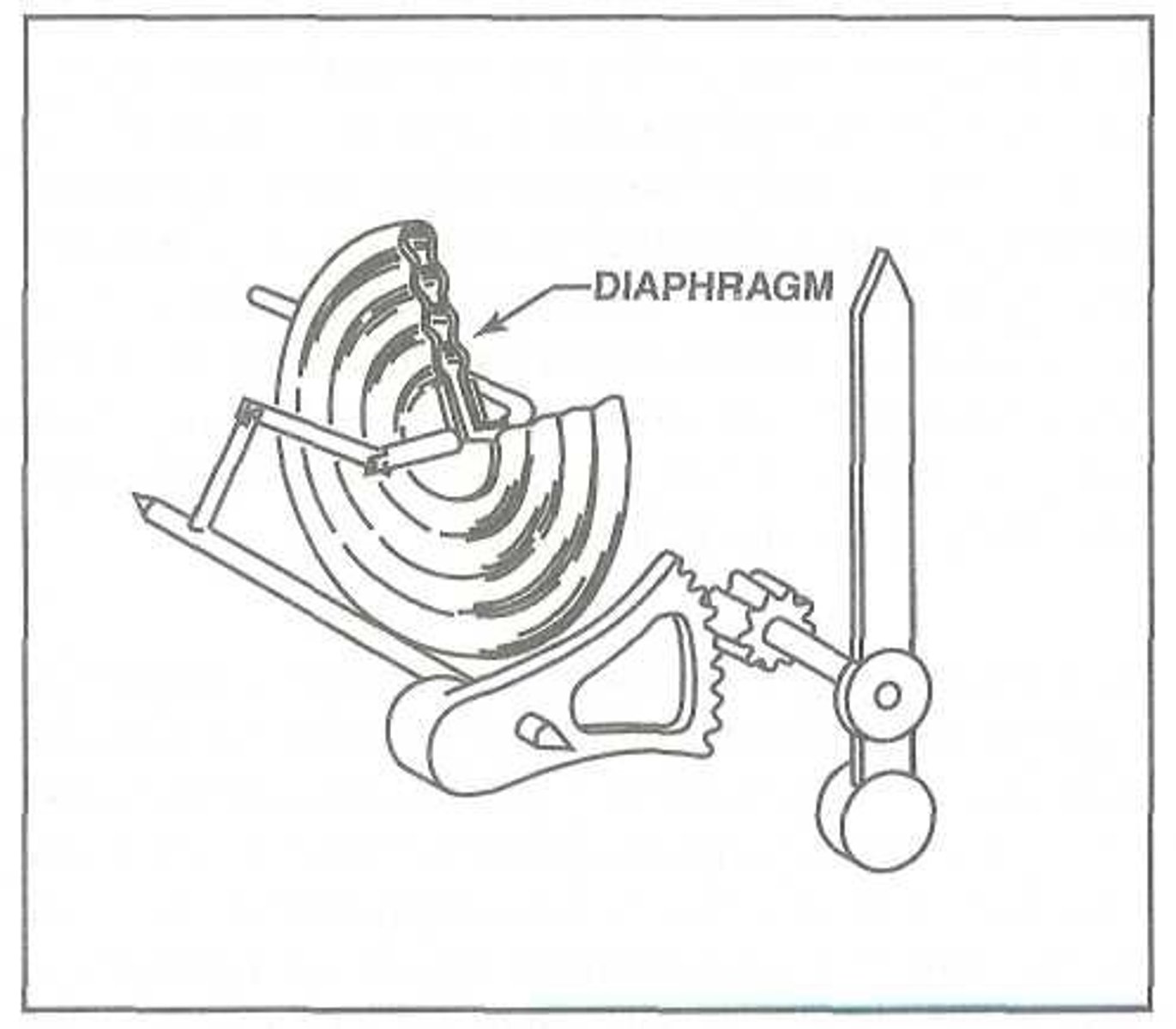
Diaphragm-type
Like the Bourdon tube, this pressure indicator is attached to a capillary tube, which attaches to the fuel system and carries pressurized fuel to the diaphragm. As the diaphragm becomes pressurized, it expands, causing an indicator needle to rotate.
Bellows
A third type of fuel pressure indicator uses a __________ that is attached to a capillary tube. Its advantage over a Bourdon tube or diaphragm is its ability to provide a greater range of motion. The bellows inside the instrument case expands and moves an indicator needle as the fuel pressure increases.
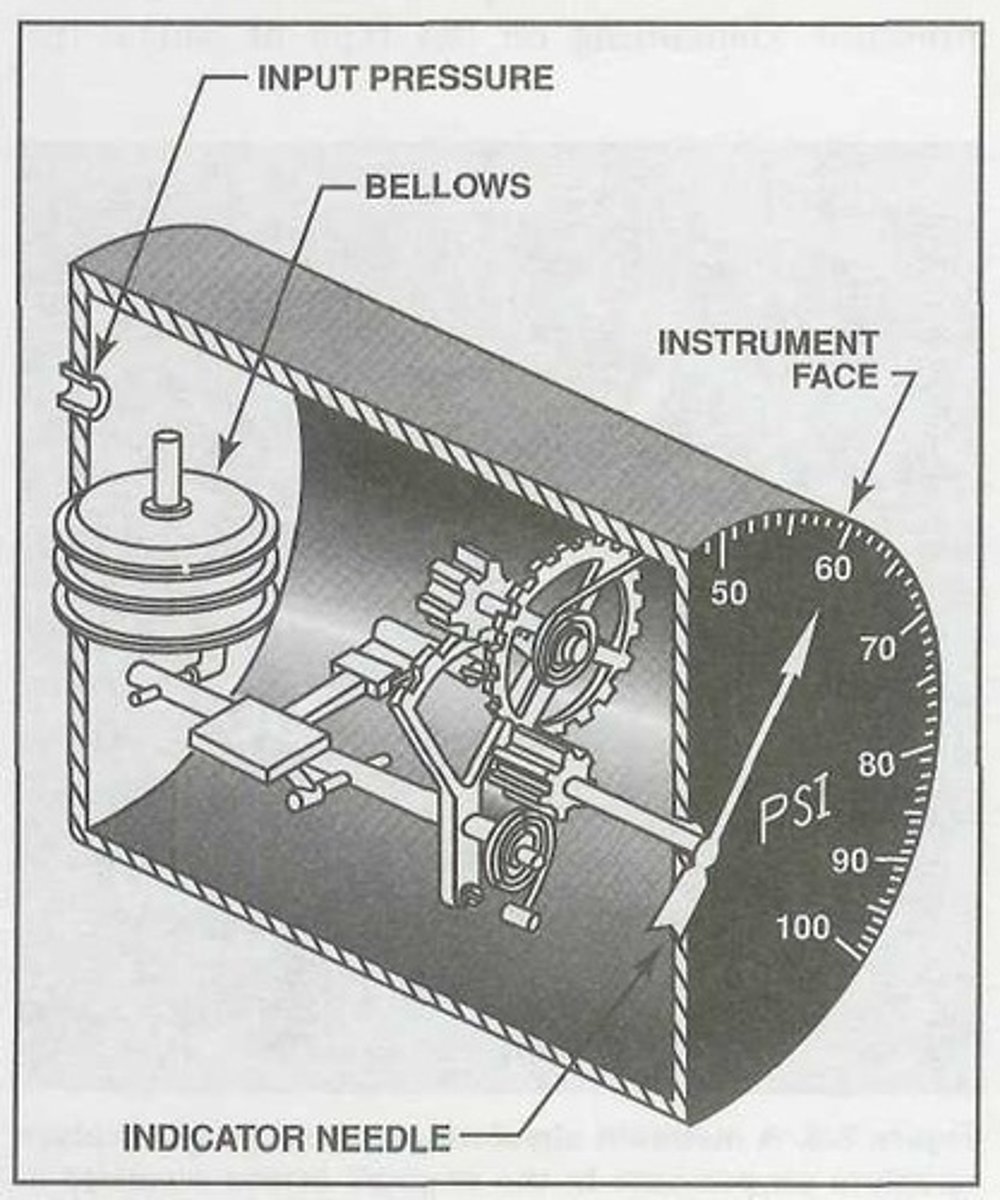
Electric
Fuel pressure indicating systems that are used when the distances between the engine and cockpit become prohibitive for the use of capillary tubing. It is used to avoid bringing fuel into the cockpit.
A pressure drop across the injection nozzles.
On aircraft with direct fuel injection or continuous-flow fuel injection systems, fuel pressure is measured as:
Fuel flow indicator
It measures the rate of fuel an engine burns in gallons per hour or pounds per hour. This provides the most accurate indication of an engine's fuel consumption.
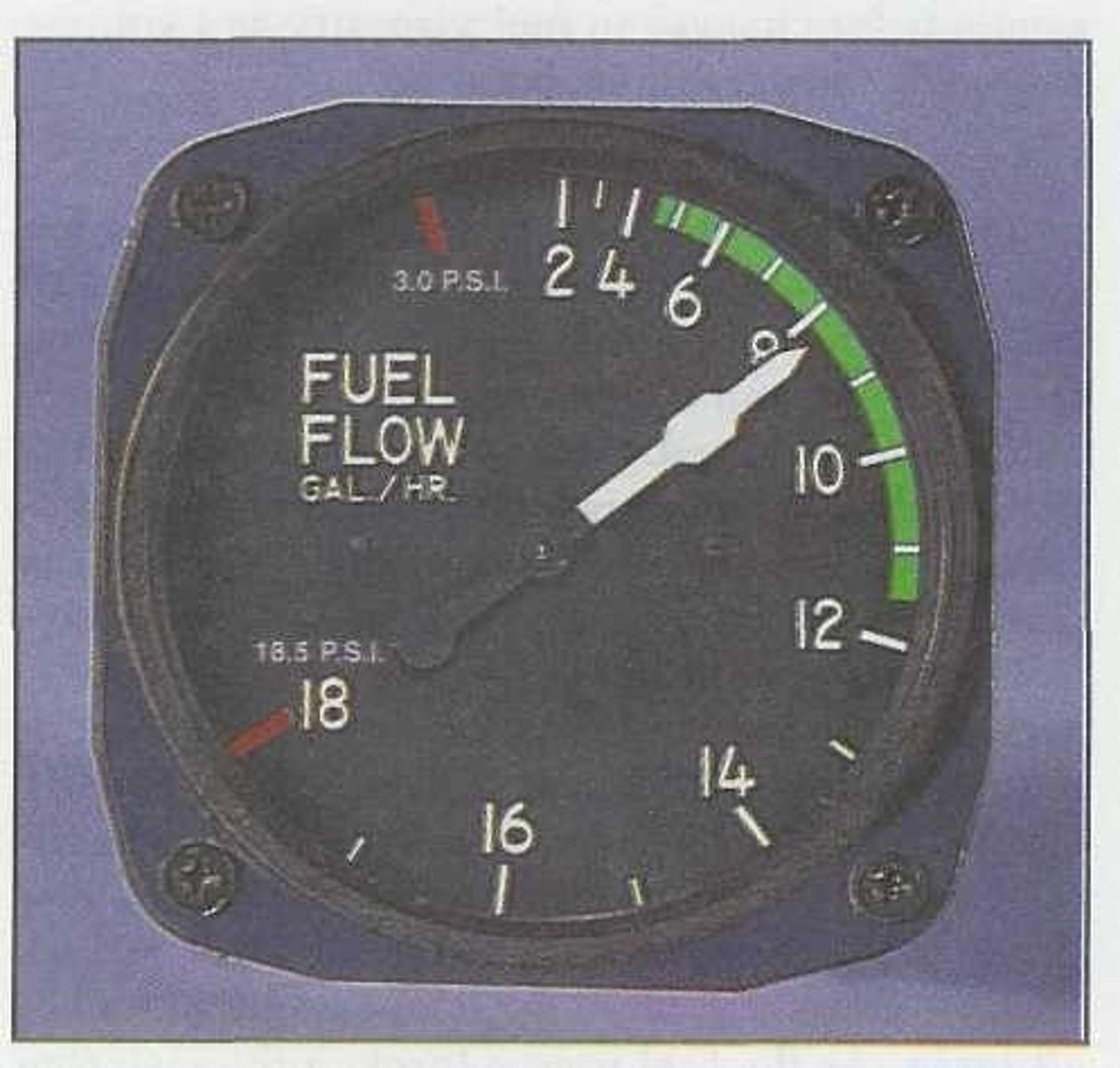

Increases, producing a false, or high fuel flow reading.
If an injector nozzle becomes clogged, the pressure differential across that nozzle:
Autosyn system
Another type of fuel flow measurement system measures the volume of fuel flowing to an engine. This type of system is commonly referred to as a/an ___________ and incorporates a movable vane that is in the fuel line leading to the engine.
The restriction created by the vane must get larger as the vane increases its rotation.
The movement of the vane in an autosyn system must be linear to get an accurate flow measurement. To do this:
Magnesyn system
Because the volume of jet fuel changes dramatically with temperature, the fuel flow on several turbine engines is measured in terms of mass rather than volume. This system consists of two cylinders, an impeller, and a turbine which are mounted in the main fuel line leading to the engine.
Magnesyn system
This system is by far the most accurate means of monitoring fuel flow because it accounts for changes in fuel viscosity and volume caused by changes in temperature.
Fuel totalizer
A computerized fuel system (CFS) with a _____________ is used in both reciprocating and turbine engine aircraft and provides a pilot with a digital readout on the amount of fuel used, fuel remaining, current rate of fuel consumption, and the time remaining for flight at the current power setting.
Totalizer indicators
They are usually mounted on the instrument panel and are electrically connected to a flowmeter installed in the fuel line to the engine.
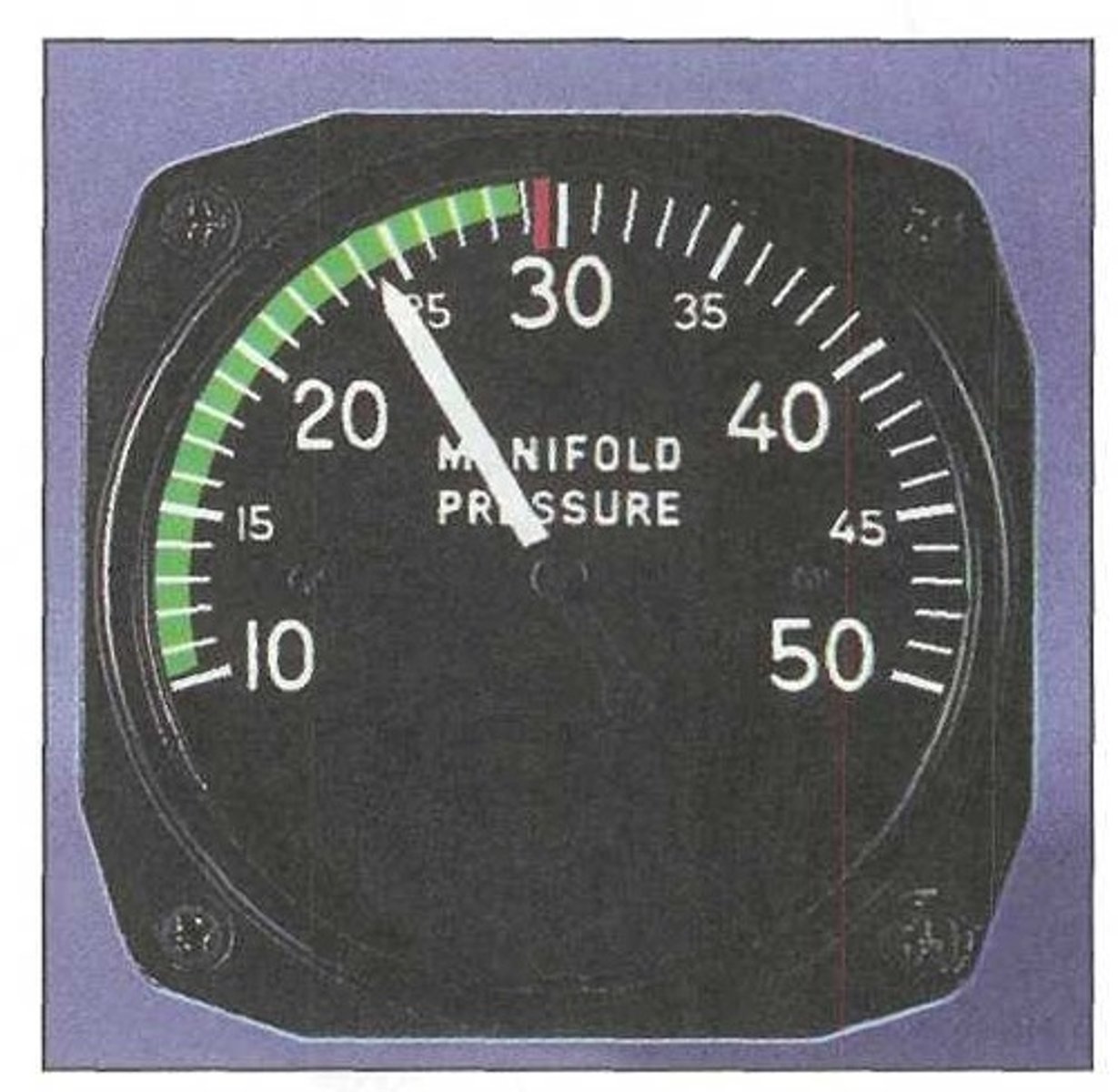
Manifold absolute pressure (MAP) gauge
It measures the absolute pressure of the fuel/air mixture within the intake manifold. It is used on all aircraft that have a constant-speed propeller to indicate engine power output.
A pressure level that will not damage the engine.
Since MAP directly affects a cylinder's mean effective pressure (mep), a pilot uses MAP gauge indications to set the engine power at:
It helps the pilot to avoid excessive manifold pressure.
Since MAP directly affects a cylinder's mean effective pressure (mep), a pilot uses MAP gauge indications to set the engine power at a pressure level that will not damage the engine. This is especially true for aircraft with turbocharged engines because:
Normal operating range.
A manifold absolute pressure gauge displays absolute air pressure in the engine's intake manifold in inches of mercury. The green arc indicates:
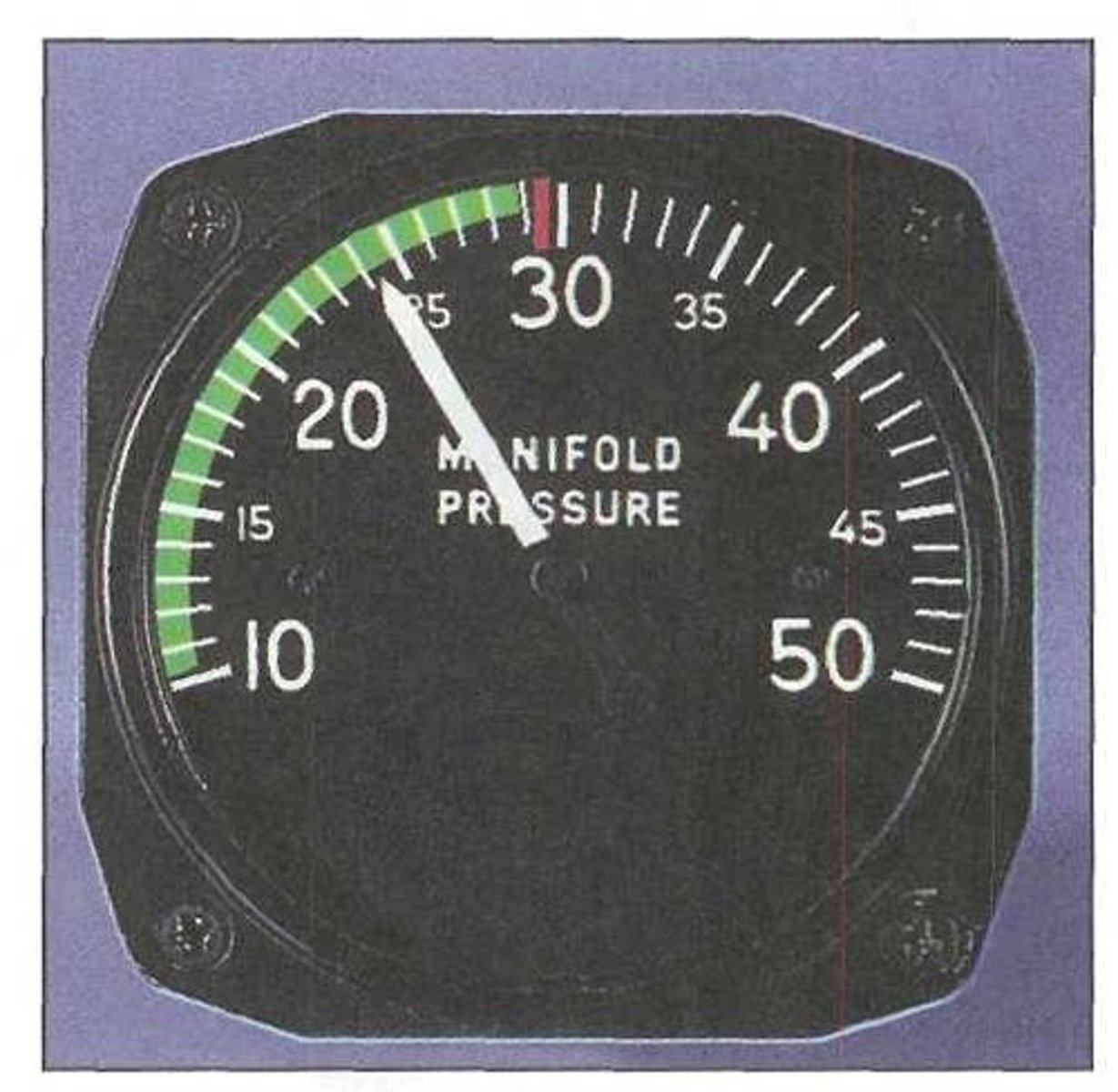

Maximum allowable manifold pressure.
A manifold absolute pressure gauge displays absolute air pressure in the engine's intake manifold in inches of mercury. The red line indicates:

The manifold pressure drops significantly, sometimes to half the existing ambient air pressure.
Before an engine is started, the manifold pressure gauge displays the local ambient, or atmosphere pressure. However, once the engine is started:
Will not exceed ambient pressure.
At full power, the manifold pressure in normally aspirated engines:
Can exceed ambient pressure.
At full power, the manifold pressure in turbocharged engines:
Manifold absolute pressure (MAP) gauge
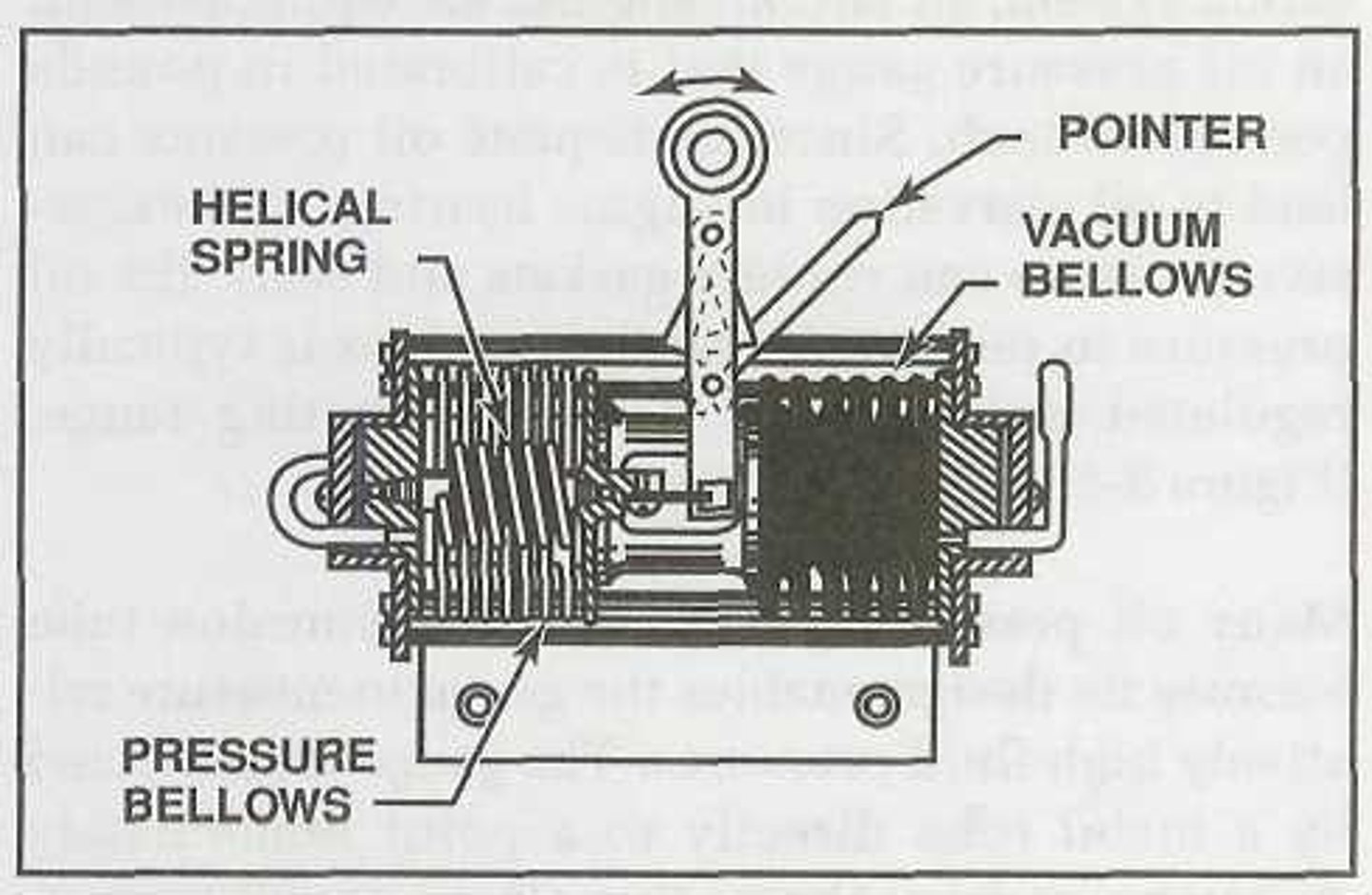
It consists of a sealed diaphragm constructed from two discs of concentrically corrugated thin metal which are soldered together at the edges to form a chamber. The chamber is evacuated, creating a partial vacuum which can be used as a reference point to measure absolute pressure.
One of the bellows measures ambient atmospheric pressure while the other measures pressure in the intake manifold.
Another manifold pressure gauge uses a series of stacked diaphragms or bellows which are particularly useful for measuring low or negative pressures. Differential pressure between the two bellows causes motion, which is transmitted to the gauge pointer through a mechanical linkage. In a MAP gauge:
Purge valve
This valve purges moisture that collects in the pressure line near the MAP gauge. With the engine running at idle, this valve is opened for 30 seconds or more, then closed. When this is done, it creates a strong suction which effectively removes the moisture from the pressure line.
Indicate the local atmospheric pressure.
Whenever you run an engine with a manifold pressure gauge, you should check the gauge for proper operation. Before the engine is started, the MAP gauge should:
Drop.
Whenever you run an engine with a manifold pressure gauge, you should check the gauge for proper operation. Once the engine is started, the MAP gauge should:
The sense line between the instrument and induction manifold may be disconnected, broken, or collapsed.
If the MAP gauge does not drop and continues to indicate atmospheric pressure once the engine is started:
The restriction in the sense line is probably too large.
A way to solve the problem if the MAP gauge does not drop once the engine is started is to increase engine power. The manifold pressure should increase evenly and in proportion to the engine power output. If this does not occur:
Oil temperature gauge
Allows a pilot to monitor the temperature of the oil entering the engine.
Oil circulation cools the engine as it lubricates the moving parts.
The oil temperature gauge allows a pilot to monitor the temperature of the oil entering the engine. This is important because:
Degrees Fahrenheit
Oil temperature gauges sense oil temperature at the engine's oil inlet and mostly are calibrated in terms of:
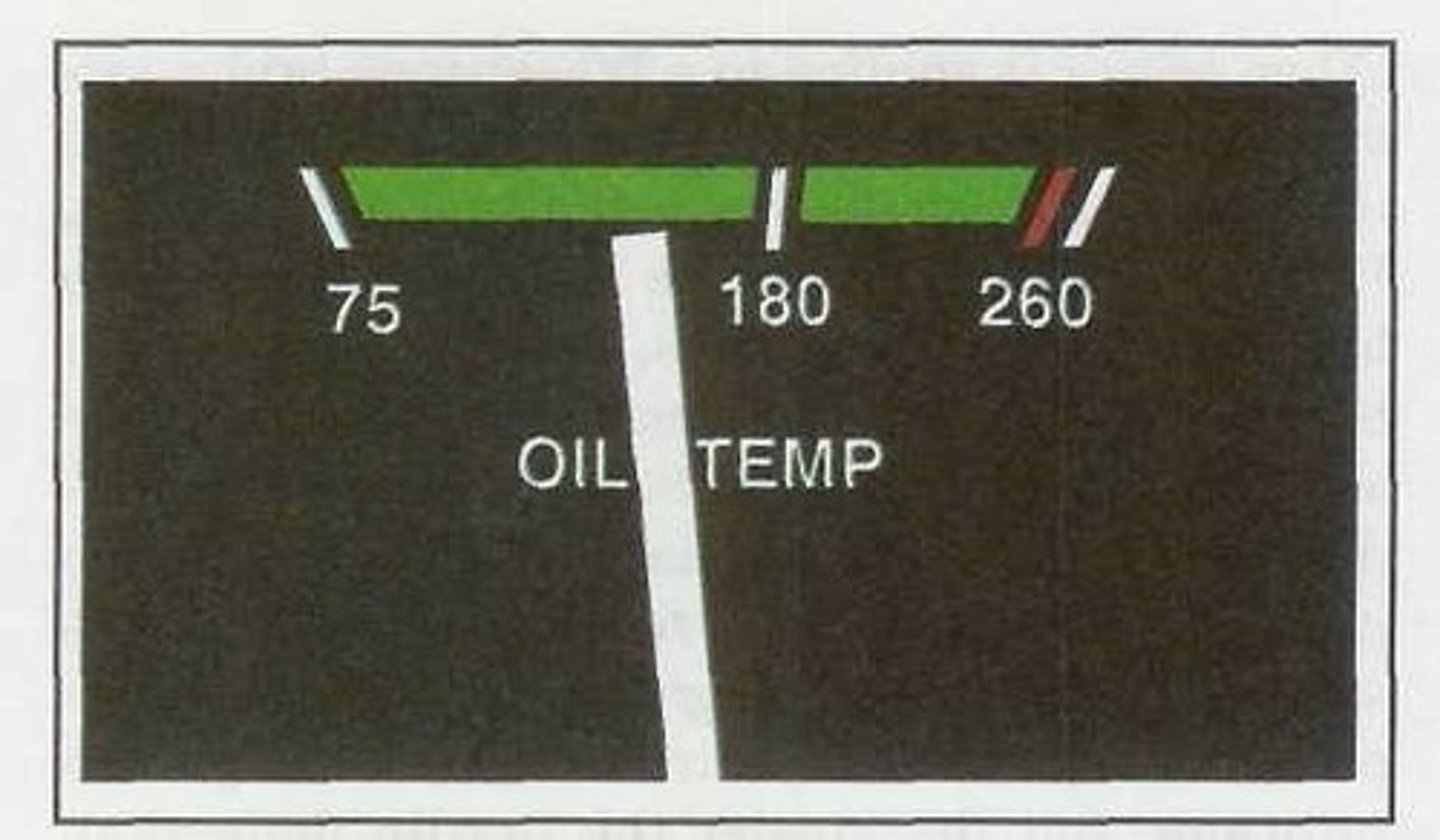
Desired oil temperature range for continuous operation.
The green arc between 75°F and 245°F on this oil temperature instrument shows:
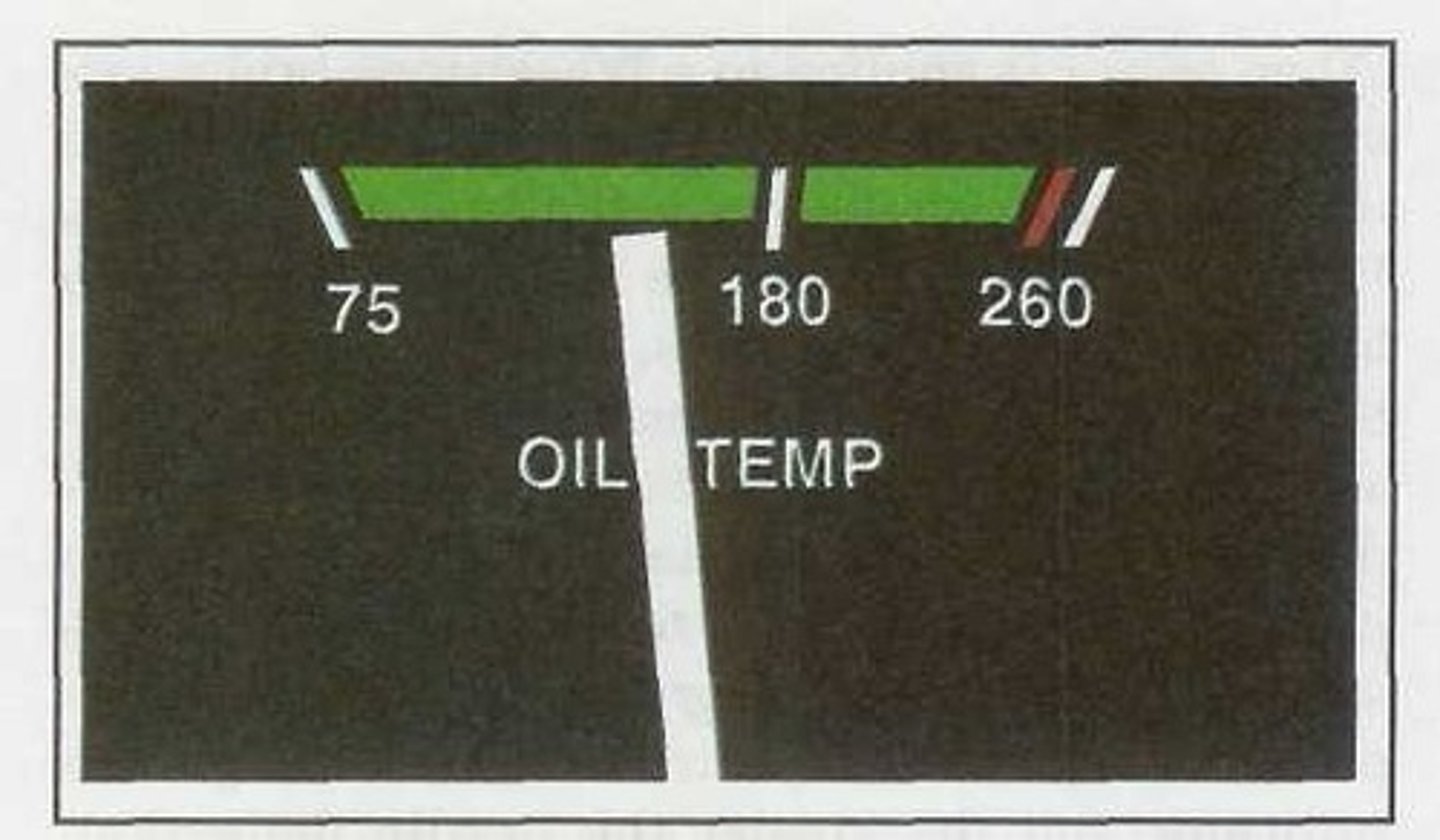
The maximum permissible oil temperature.
The red line is located at 245°F on this oil temperature instrument and indicates:
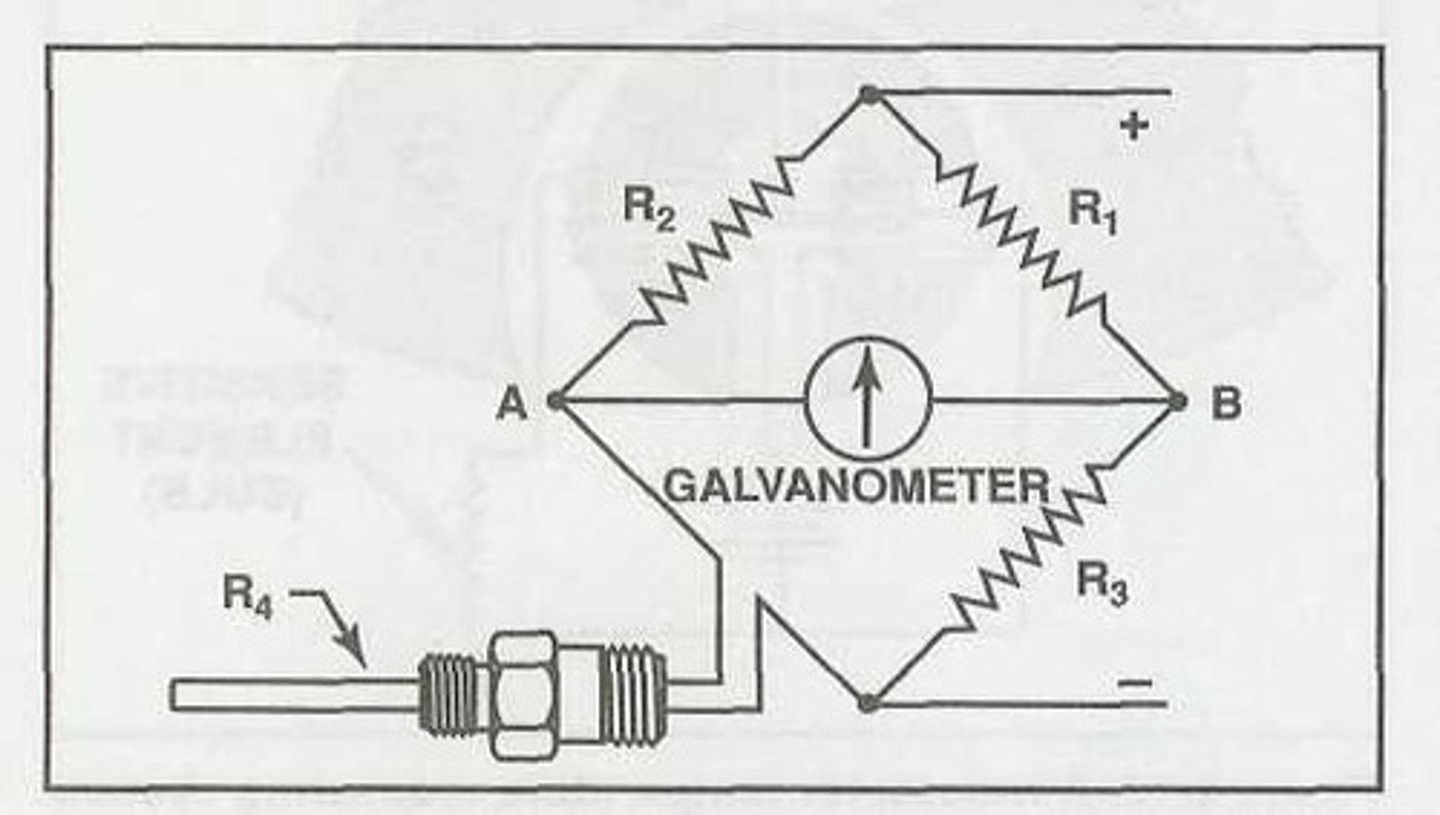
Wheatstone bridge
Most modern oil temperature systems are electrically operated. This circuit consists of three fixed resistors and one variable resistor whose resistance varies with temperature of the oil flowing past the probe.
Degrees
A typical Wheatstone bridge has three fixed resistors and one variable resistor. The temperature probe contains the variable resistor, whose resistance varies with the temperature of the oil flowing past the probe. The bridge in the circuit consists of a galvanometer that is calibrated in _______ to indicate temperature.
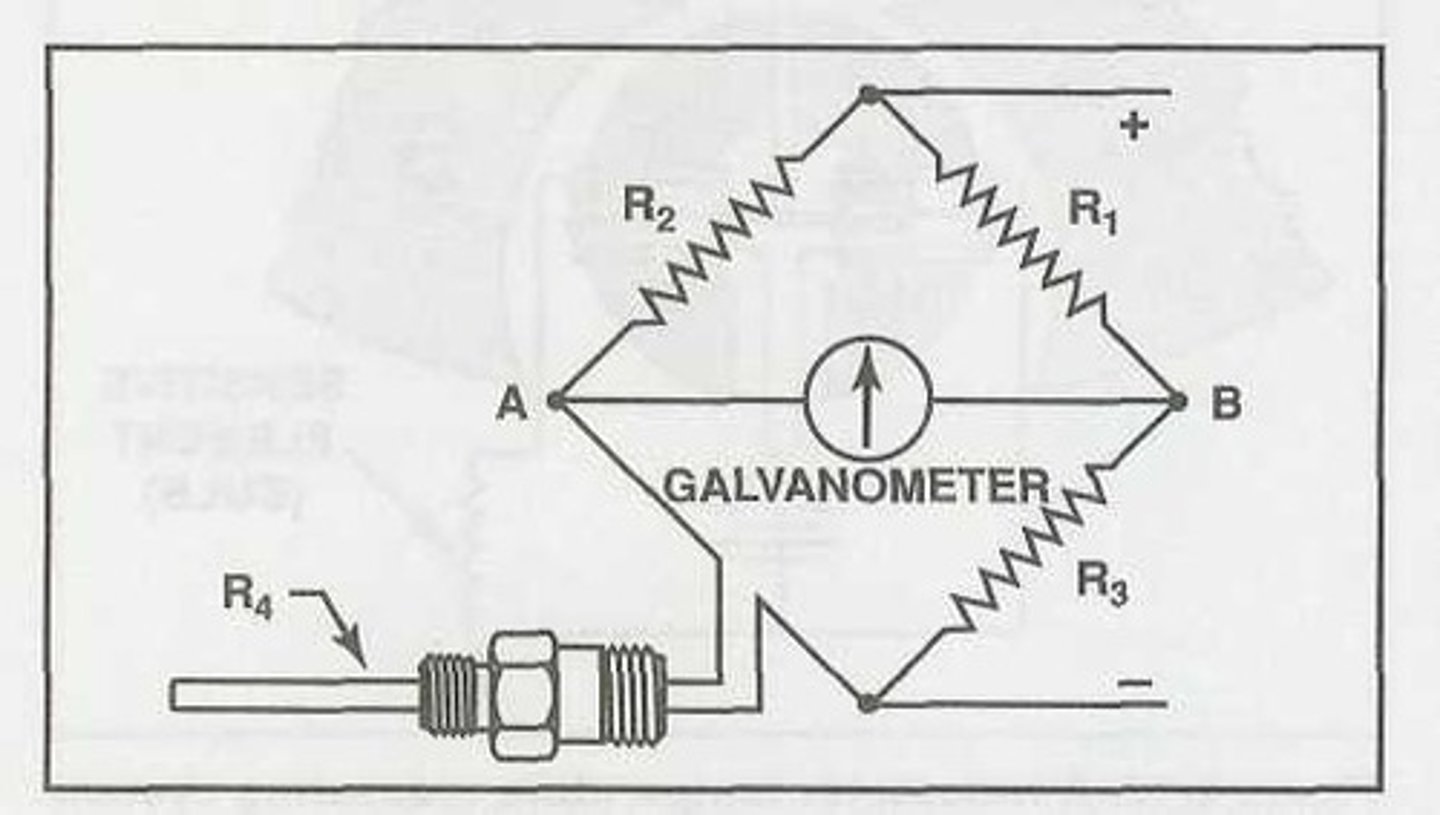
A voltage differential between the bridge junctions, causing current to flow through the galvanometer indicator. The greater the voltage differential, the greater the current flow through the indicator and the greater the needle deflection.
When power is applied to a Wheatstone bridge circuit and all four resistances are equal, no difference in potential exists between the bridge junctions. However, when the variable resistor is exposed to heat, its resistance increases, causing more current to flow through the fixed resistor R3 than the variable resistor. The disproportionate current flow produces:
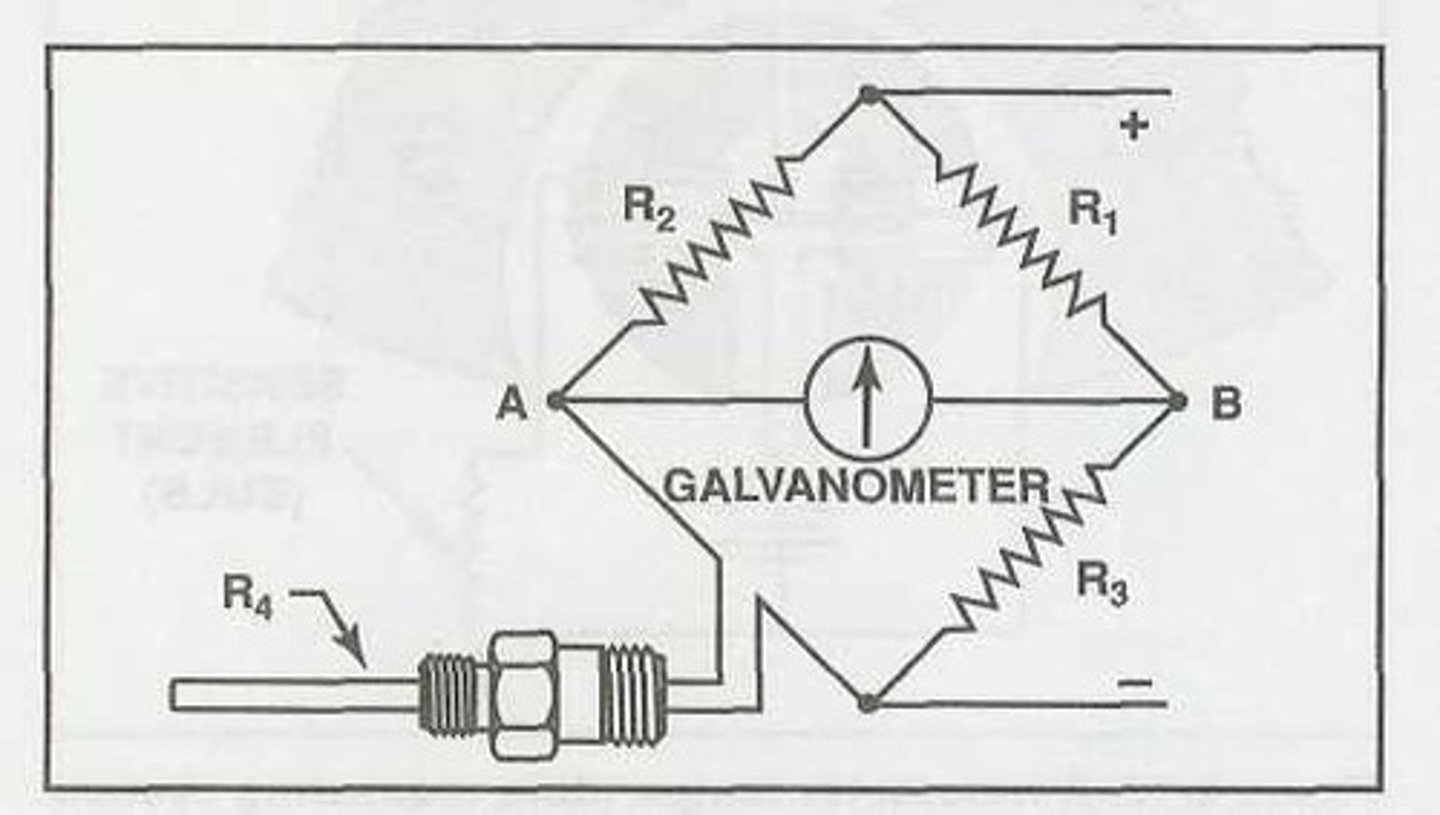
Ratiometer
This circuit measures current ratios and is more reliable than a Wheatstone bridge, especially when the supply voltage varies.
Ratiometer
Typically, this circuit consists of two parallel branches powered by the aircraft electrical system. One branch consists of a fixed resistor and coil, and the other branch consists of a variable resistor and coil. The two coils are wound on a rotor that pivots between the poles of a permanent magnet, forming a meter movement in the gauge.
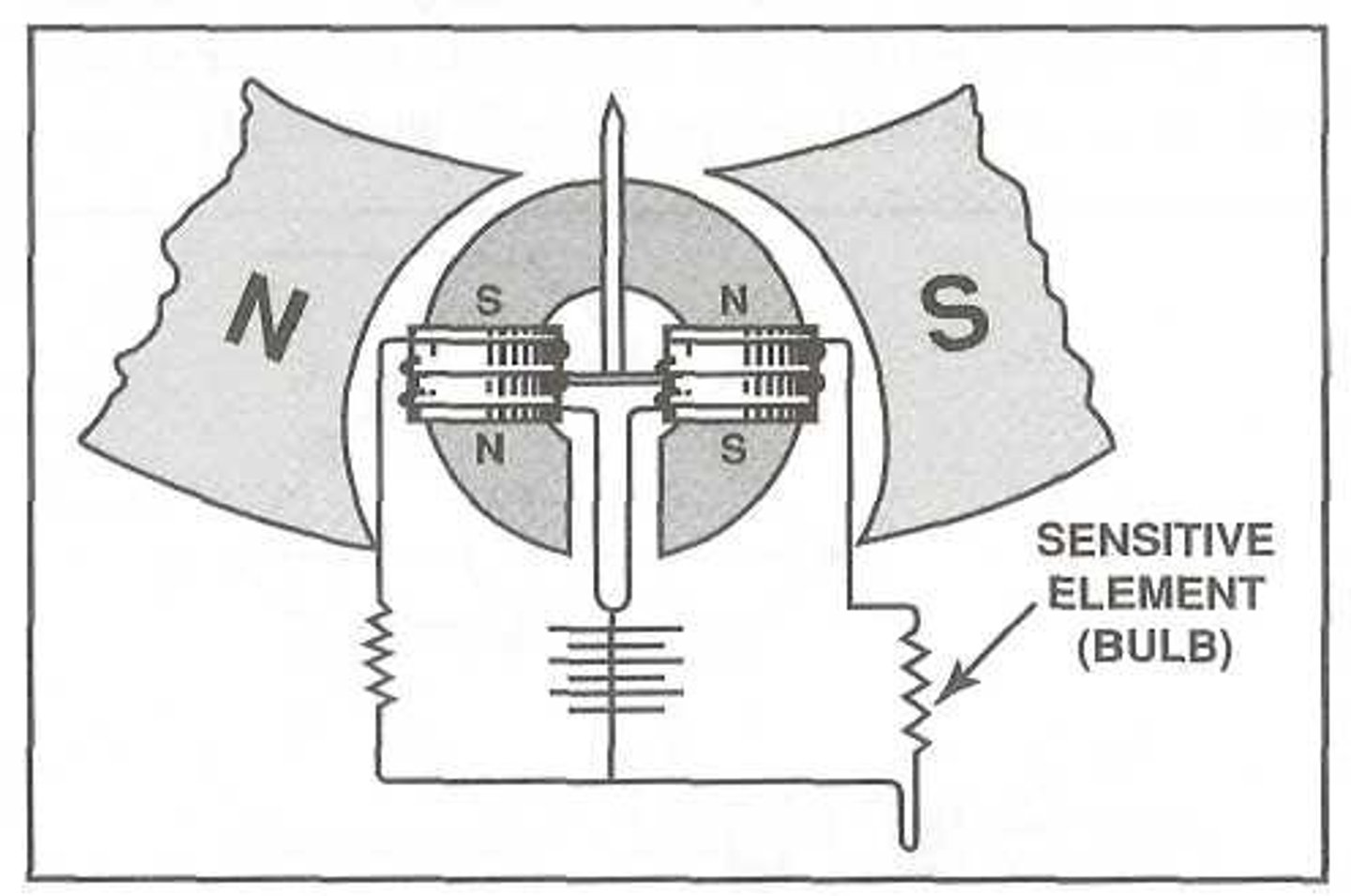
Ratiometer
Temperature measuring systems that are especially useful in applications where accuracy is critical or large variations of supply voltages are encountered.
Vapor pressure or Bourdon tube type
With this type of instrument, a Bourdon tube is connected by a capillary tube to a liquid filled temperature sensing bulb which is used by some older oil temperature gauges.
Pounds per square inch (psi)
Oil pressure gauges are calibrated in terms of:
Oil pressure gauge
To allow a pilot to monitor the effectiveness of a given lubrication system, all aircraft engines are equipped with a/an:
Oil starvation in engine bearings.
Inadequate oil pressure can lead to:
Rupture of gaskets and seals.
Excessive oil pressure can lead to:
Over a fairly narrow operating range.
Since inadequate oil pressure can lead to oil starvation in engine bearings and excessive pressure can rupture gaskets and seals, the oil pressure in most reciprocating engines is typically regulated:

Ensures enough oil pressure to protect bearing surfaces without rupturing engine seals and gaskets.
The oil pressure limits of 25 psi minimum and 90 psi maximum on this gauge are representative of a typical small aircraft engine. The normal operating range of 60 to 90 psi:

Bourdon tube
Many oil pressure gauges utilize a/an _________ because its design enables the gauge to measure relatively high fluid pressures.
Filling the oil line with a very light oil.
One disadvantage of the Bourdon tube type of oil pressure indicating system is that it does not work well in cold weather because the oil in the line between the engine and cockpit gauge tends to congeal. The congealed oil then causes false readings of either low or no oil pressure. This error can be minimized by:
Prevent possible damage to an engine until the reason for lack of oil pressure can be determined.
Some aircraft manuals caution you to shut down an engine after 30 seconds in warm weather or one minute in extremely cold weather if no sign of oil pressure is present. Engine shutdown in this case is a precaution taken to:
Air is trapped in the oil line leading to the instrument or that some unit in the oil system is functioning improperly.
Excessive pointer oscillation of an oil pressure gauge typically indicates that:
Low oil quantity.
Low oil pressure or fluctuations from zero to normal are often signs of:
Normal operating range.
A typical cylinder head temperature gauge consists of a relatively large green arc and a single red line. The range between 200°F and 475°F indicates:
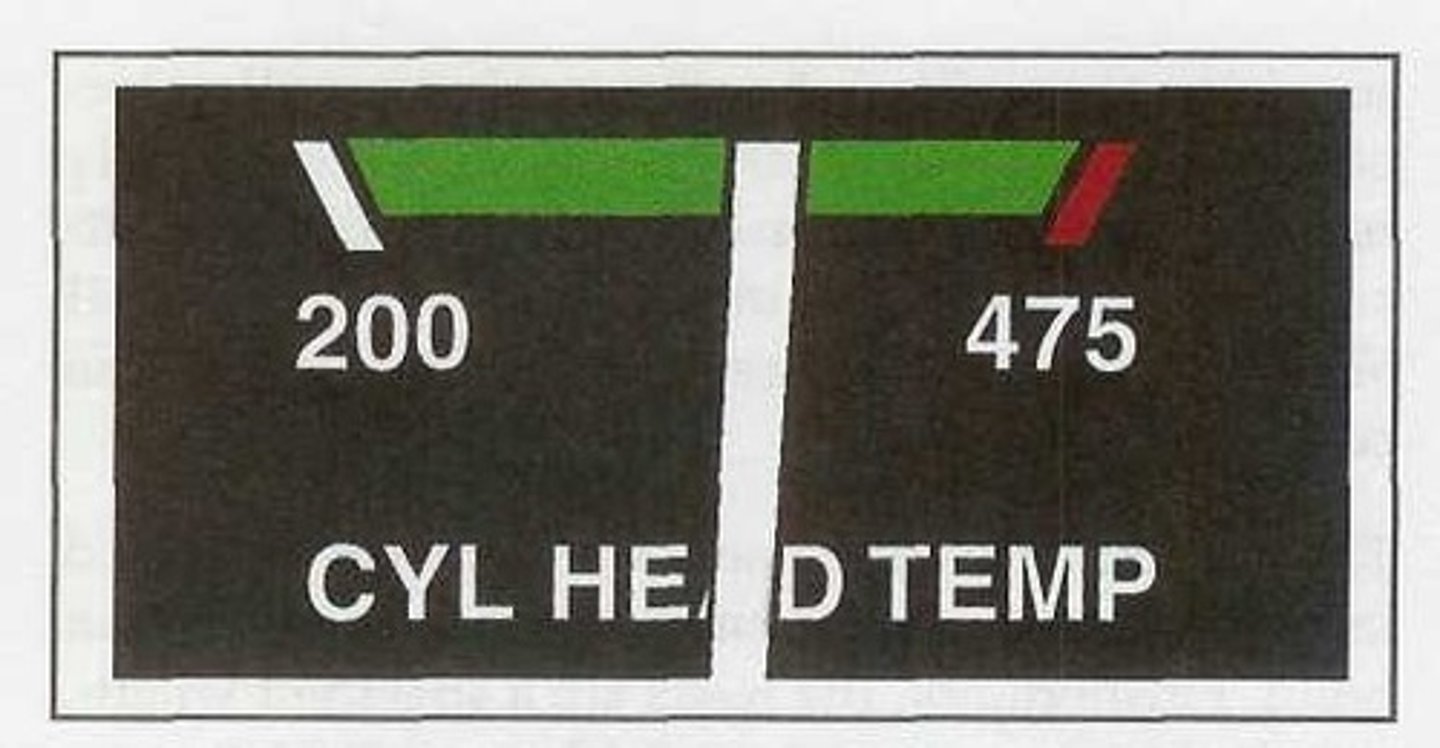
Cylinder head temperature (CHT) gauge
The engine temperature can have a dramatic impact on engine performance. Therefore, most reciprocating engine powered aircraft are equipped with a _________________ that allows a pilot to monitor engine temperatures.
Galvanometer
Most cylinder head temperature gauges have _____________ meters that display temperatures in degrees Fahrenheit.
Galvanometer
It measures the amount of electrical current produced by a thermocouple.
Thermocouple
It is a circuit consisting of two dissimilar metal wires connected together at two junctions to form a loop. Anytime a temperature difference exists between the two junctions, a small electrical current is generated that is proportional to the temperature difference and measurable by the galvanometer.
Iron and constantan, or chromel and alumel.
Typical dissimilar metal combinations used for thermocouples are:
Operating independent of aircraft power.
Since a thermocouple generates its own electrical current, it is capable of:
Hot junction
The two junctions of a thermocouple circuit are commonly referred to as a hot junction and a cold junction. This junction is installed in the cylinder head in one of two ways; the two dissimilar wires may be joined inside a bayonet probe which is then inserted into a special well in the top or rear of the hottest cylinder, or the wires may be imbedded in a special copper spark plug gasket.
Cold junction
The two junctions of a thermocouple circuit are commonly referred to as a hot junction and a cold junction. This junction, or reference junction, is typically located in the instrument case.
First, be sure to observe all color-coding and polarity markings because accidentally reversing the wires causes the meter to move off-scale on the zero side. In addition, ensure that all electrical connections are clean and torqued to the correct value.
Thermocouple instrument systems are polarized and extremely sensitive to resistance changes within their electrical circuits. Therefore, several precautions must be observed when replacing or repairing them:
Wiring leads
Thermocouple ____________ are typically supplied in matched pairs and secured together by a common braid in which their lengths cannot be altered because doing so changes their resistance.
The hottest cylinder.
Simple CHT systems use a single indicator that monitors:
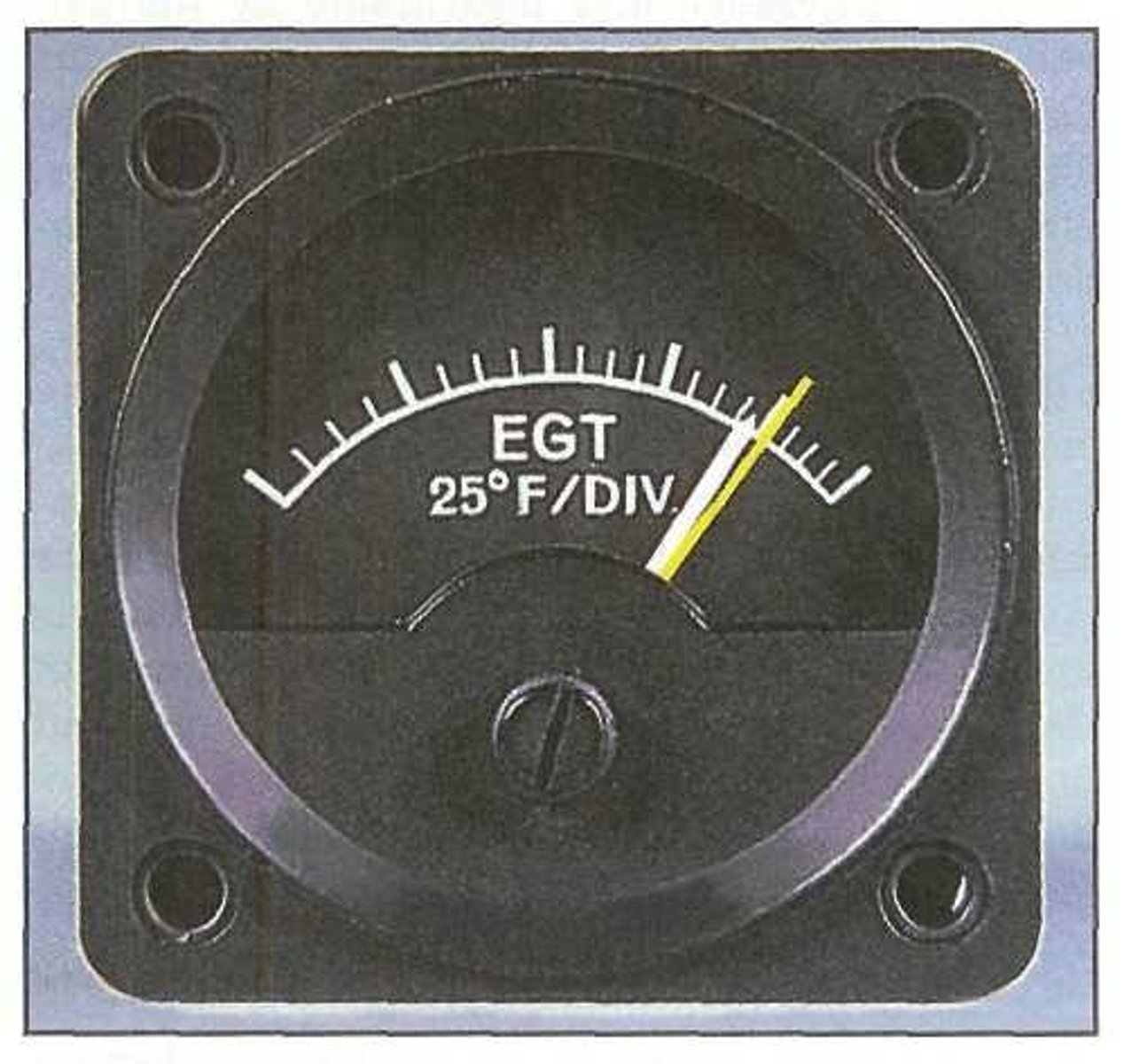
Exhaust gas temperature (EGT) gauge
It measures the temperature of the exhaust at some point past the exhaust port.
Exhaust gas temperature (EGT) gauge
The fuel/air mixture can be set for best fuel efficiency by using a/an ___________ and following the aircraft checklist instructions. This gauge is calibrated in degrees Fahrenheit with 25°F per divisions.

Alumel and chromel
Like the cylinder head temperature gauge, EGT gauges also use thermocouples to sense temperature. However, the thermocouple wiring for an EGT is usually made from:
Alumel
The thermocouple wiring for an EGT is usually made from alumel and chromel. It is typically used as the negative lead, and is enclosed in green insulation.
Chromel
The thermocouple wiring for an EGT is usually made from alumel and chromel. It is the positive lead and is normally enclosed in white insulation.
Somewhere on the exhaust manifold and is directly exposed to the exhaust gas stream.
The hot junction of an EGT thermocouple is usually mounted:
In the instrument case.
The cold junction of an EGT thermocouple is located: