Lab 5- Muscles
1/131
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
132 Terms
What is an agonist?
Most responsible for producing a particular movement; Prime mover
What is an example of an agonistic action?
Flexion at the elbow by Biceps Brachii
What is an antagonist?
A muscle that opposes or reverses a movement
What is an example of a antagonist?
Biceps muscle is antagonized by the triceps
What is a synergist?
Either assists agonist with the same movement or by reducing undesirable or unnecessary movement
What is an example of a synergist?
Muscles that flex the fingers
What is a fixator?
Specialized synergists; immobilize the origin of a prime mover so that all the tension is exerted at the insertion
What is an example of a fixator?
Muscles that help maintain posture
What are the 7 ways to name muscles?
Direction of fibers
Muscle size
Muscle location
Muscle shape
Number of origins
Location of attachments
Muscle action
What is the origin of a muscle?
The larger/less movable attachment, anchor
What is the insertion of a muscle?
The movable attachment
What is the action of a muscle?
Contraction and relaxation
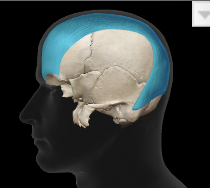
What muscle is this?
Epicranius
What is the origin(s) of the epicranius?
Frontal belly- epicranial aponeurosis
Occipital belly- Occipital and temporal bones
What is the insertion(s) of the epicranius?
Frontal belly- skin of the eyebrows and root of nose
Occipital belly- epicranial aponeurosis
What is the action of the epicranius?
With aponeurosis fixed= frontal belly raises eyebrows
Occipital belly fixes aponeurosis and pulls scalp posteriorly
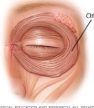
What muscle is this? (eye in image)
Obicularis oculi
What is the origin of the obicularis oculi?
Frontal and maxillary bones and ligaments around orbit
What is the insertion of the obicularis oculi?
Tissue of eyelid
What is the action of the orbicularis oculi?
Closes eye, produces blinking, squinting, and draws down eyebrows
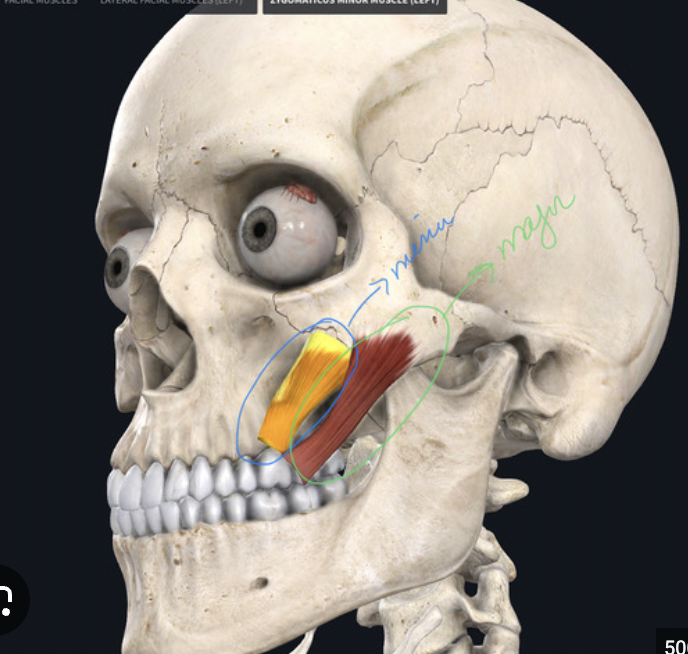
What muscle is this?
Zygomaticus (major and minor)
What is the origin of the zygomaticus?
zygomatic bone
What is the insertion of the zygomaticus?
Skin and muscle of the upper lip
What is the action of the zygomaticus
Raises lateral corners of mouth upward (smiling muscles)
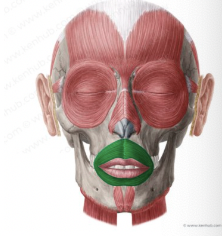
What muscle is this?
Orbicularis oris
What is the origin of the orbicularis oris?
Arises indirectly from maxilla and mandible; fibers blended with other fibers associates with the lips
What is the insertion of the orbicularis oris?
Inserts into muscle and skin at angles of mouth
What is the action of the orbicularis oculi?
Closes lips; purses and protrudes lips (kissing and whistling muscle)
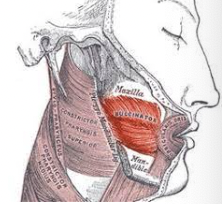
What muscle is this?
Buccinator
What is the origin of the buccinator?
Molar region of maxilla and mandible
What is the insertion of the buccinator?
Orbicularis oris
What is the action of the buccinator?
Draws corner of mouth laterally; compresses cheek; holds food between teeth during chewing
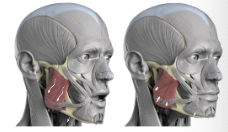
What muscle is this?
Masseter
What is the origin of the masseter?
Zygomatic arch and bone
What is the insertion of the masseter?
Angle and ramus of mandible
What is the action of the masseter?
Prime mover of jaw closure; elevates mandible
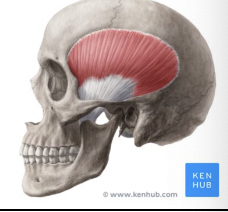
What muscle is this?
Temporalis
What is the origin of the temporalis?
Temporal fossa
What is the insertion of the temporalis?
Coronoid process of mandible
What is the action of the temporalis?
Closes jaw; elevates and retracts mandible
What muscle is this?
Platysma
What is the origin of the platysma?
Fascia of chest (over pectoral muscles and deltoid)
What is the insertion of the platysma?
Low margin of mandible, skin, and muscle at corner of mouth
What is the action of the platysma?
Tenses skin of neck; depresses mandible; pulls lower lip back and down
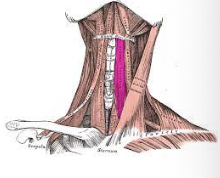
What muscle is this?
Sternohyoid
What is the origin of the sternohyoid?
Manubrium and medial end of clavicle
What is the insertion of the sternohyoid
Lower margin of hyoid bone
What is the action of the sternohyoid?
Depresses larynx and hyoid bone; if mandible fixed can also flex skull
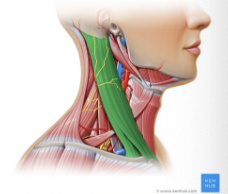
What muscle is this?
Sternocleidomastoid
What is the origin of the sternocleidomatoid?
Manubrium of the sternum and medial portion of the clavicle
What is the insertion of the sternocleidomastoid?
Mastoid process of temporal bone and superior nuchal line of occipital bone
What is the action of the sternocleidomastoid?
Simultaneous contraction of both muscles causes flexion of neck, acting independently, rotates head toward shoulder on opposite side
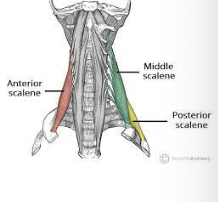
What muscle is this?
Scalenes
What is the origin of the scalenes?
Transverse process of cervical vertebrae
What is the insertion of the scalenes?
Anterolaterally on ribs 1 and 2
What is the action of the scalenes?
Flex and slightly rotate the neck; elevate ribs 1 and 2
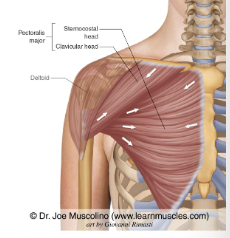
What muscle is this?
Pectoralis major
What is the origin of the pectoralis major?
Clavicle, sternum, cartilage of ribs 1-6 (or 7), and aponeurosis of external oblique muscle
What is the insertion of the pectoralis major?
Fibers converge to insert by tendon into inter-tubercular suculus of humerus
What is the action of the pectoralis major?
Prime mover of arm flexion; adducts medially rotates arm; with arm fixed, pulls chest up (forced inspiration)
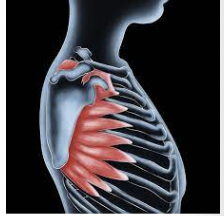
What muscle is this?
Serratus anterior
What is the origin of serratus anterior?
Lateral aspects of ribs 1-8 (boxers muscle)
What is the insertion of serratus anterior?
Vertebral border of anterior surface of scapula
What is the action of serratus anterior?
Prime mover of forcibly protracting and holding the scapula against chest wall; rotates scapula; essential in raising arm, fixes scapula for abduction
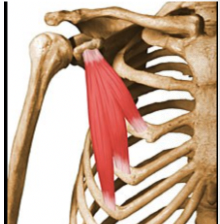
What muscle is this?
Pectoralis minor
What is the origin of pectoralis minor?
Anterior surface of ribs 3-5; near their costal cartilage
What is the insertion of pectoralis minor?
Coracoid process of scapula
What is the action of pectoralis minor?
When ribs fixed, draws scapula forward and inferiorly; with scapula fixed, draws ribcage up; 3 movements= flexion of whole arm, inversion of humerus, and adduction of whole arm
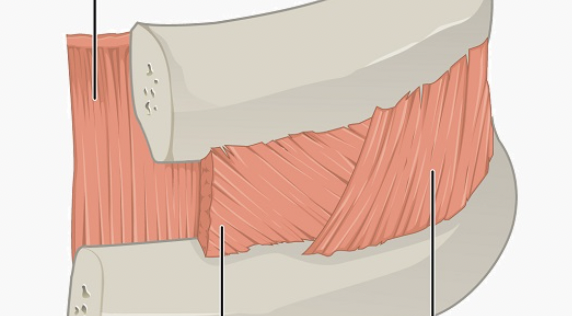
What muscle is this? (on the outside)
External intercostal
What is the origin of the external intercostals?
inferior border of rib above (hand in pocket)
What is the insertion of the external intercostals?
Superior border of rib below
What is the action of the external intercostals?
Pulls ribs towards one another to elevate the rib cage; aid in inspiration
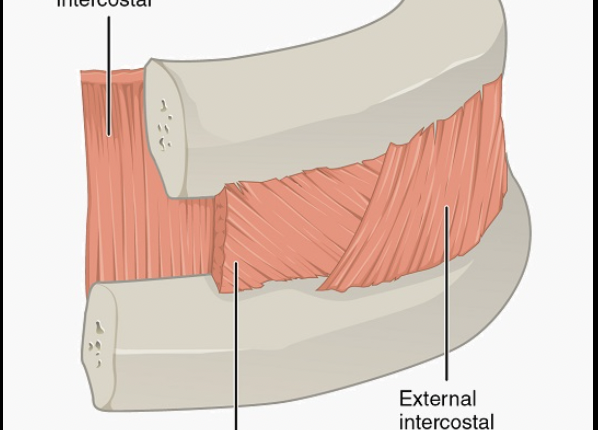
What muscle is this (second layer)
Internal intercostals
What is the origin of the internal intercostals?
Superior border of rib below (hands crossed against chest)
What is the insertion of the internal intercostals?
Inferior border of rib above
What is the action of the internal intercostals?
Draws ribs together to depress rib cage; aid in forced expiration; antagonistic to external intercostals
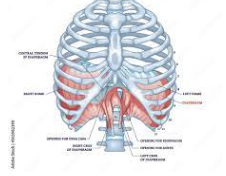
What muscle is this?
Diaphragm
What is the origin of the diaphragm?
Inferior border of rib and sternum, costal cartilages of last six ribs and lumbar vertebrae
What is the insertion of the diaphragm?
Central tendon
What is the action of the diaphragm?
Prime mover of inspiration flattens on contraction, increasing vertical dimensions of thorax; increases intra-abdominal pressure
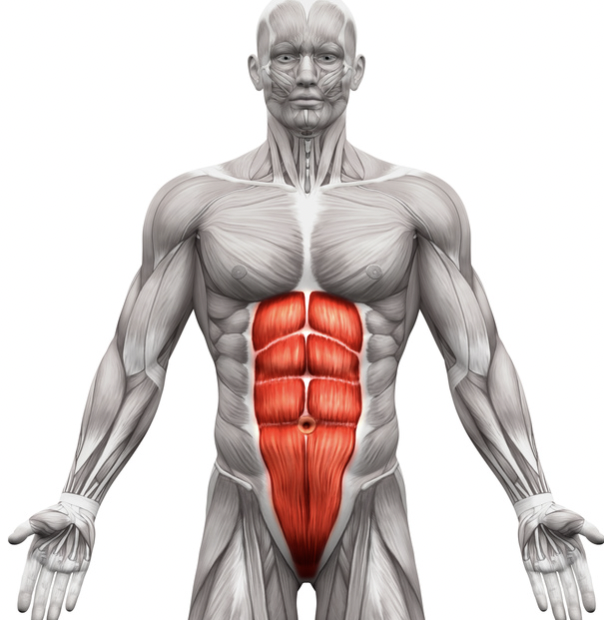
What is this muscle?
Rectus abdominis
What is the origin of the rectus abdominis?
Pubis crest and symphysis
What is the insertion of the rectus abdominis?
Xiphoid procces and costal cartilages of ribs 5-7
What is the action of the rectus abdominis?
Flexes and rotates vertebral column; increases abdominal pressure; fixes and depresses ribs; stabilizes pelvis during walking'; used in sitting up and curl ups
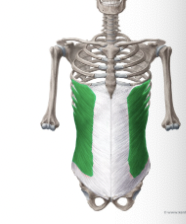
What muscle is this?
External oblique
What is the origin of the external obliques?
Anterior surface of the lower eight ribs
What is the insertion of the external obliques?
Linea alba, pubic crest, and tubercles and iliac crest
What is the action of the external oblique?
Same ad rectus abdominis; compresses abdominal wall, aids in muscles of back in trunk rotation and lateral flexion; used in oblique curl ups
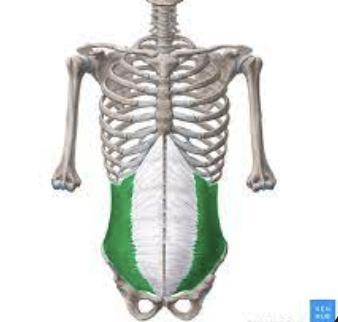
What muscle is this?
Internal oblique
What is the origin of the internal oblique?
Lumbar fascia, iliac crest, and inguinal ligament
What is the insertion of the internal oblique?
linea albe, pubic crest, and costal cartilages of the last three ribs
What is the action of the internal oblique?
Compress abdominal wall, aids muscles of the back in trunk rotation and lateral flexion, used in oblique curls
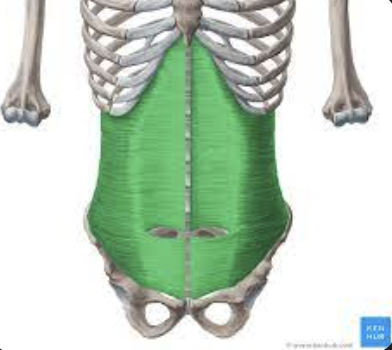
What muscle is this?
Transervse abdominis
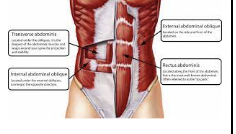
What is the origin of the transverse abdominis?
Ingiunal ligament, iliac crest, cartilages of last 5 or 6 ribs, and lumbar fascia
What is the insertion of the transverse abdominis?
Linea alba and pubic crest
What is the action of the the transverse abdominis?
Compresses abdominal contents
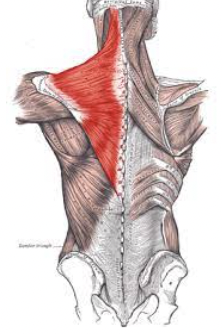
What muscle is this?
Trapezius
What is the origin of the trapezius?
Occipital bone; ligamentum nuchae; Spine of C7 and all thoracic vertebrae
What is the insertion of the trapezius?
Acromion and spinous process of scapula; lateral third of clavicle
What is the action of the trapezius
Extends head; raises, rotates, and retracts (adducts) scapula and stabilizes it; superior fibers elevate (shrugging) ; inferior fibers depress scapula