Chapter 12 - Touch/Nociceptors
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
Somatic sensation
Enables perception of touch, pain, and temperature. Receptors are broadly distributed across entire body (some are present in internal organs as well)
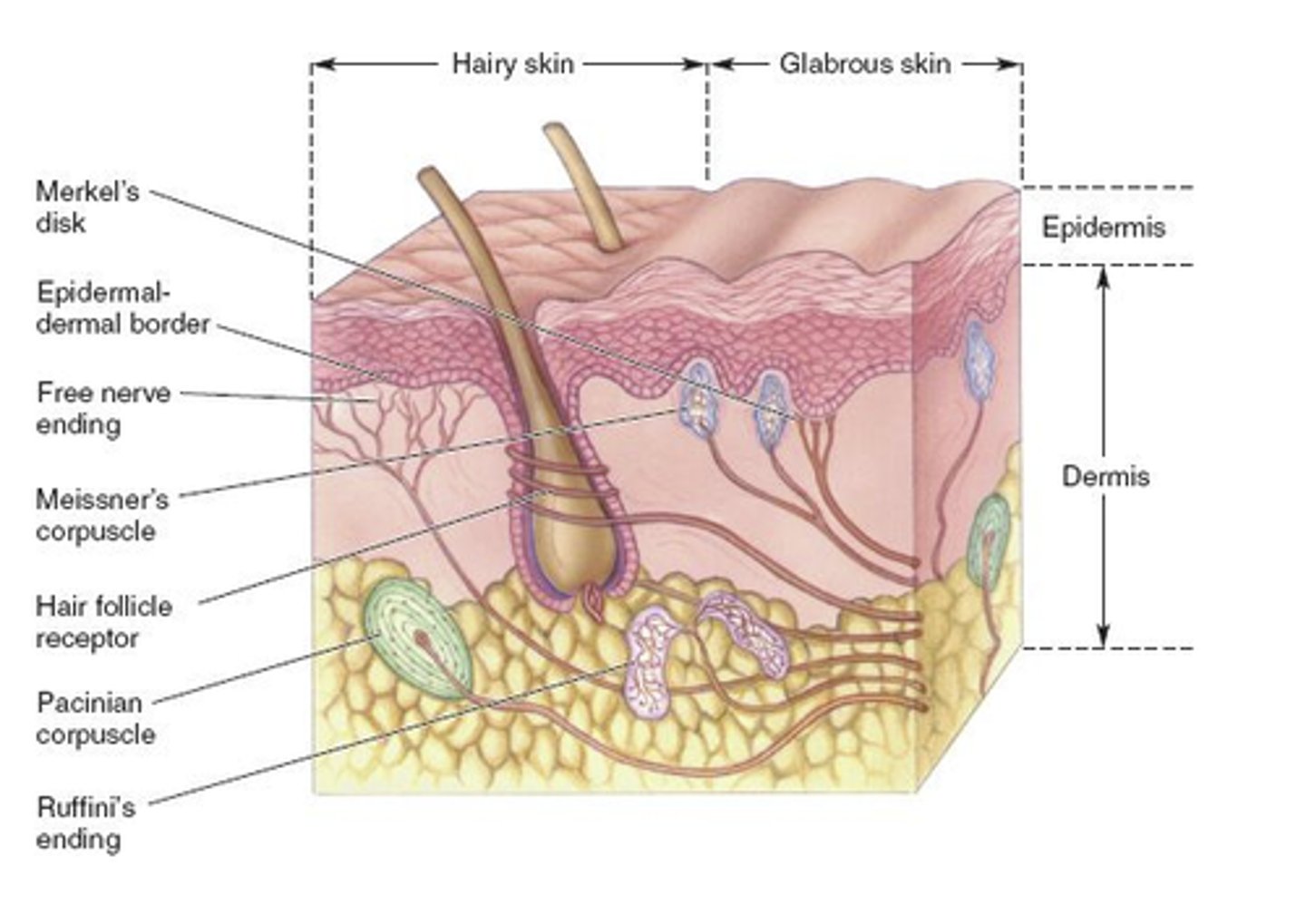
Glabrous skin
Skin that does not have hair, tends to have higher densities of sensitive, high-resolution mechanoreceptors
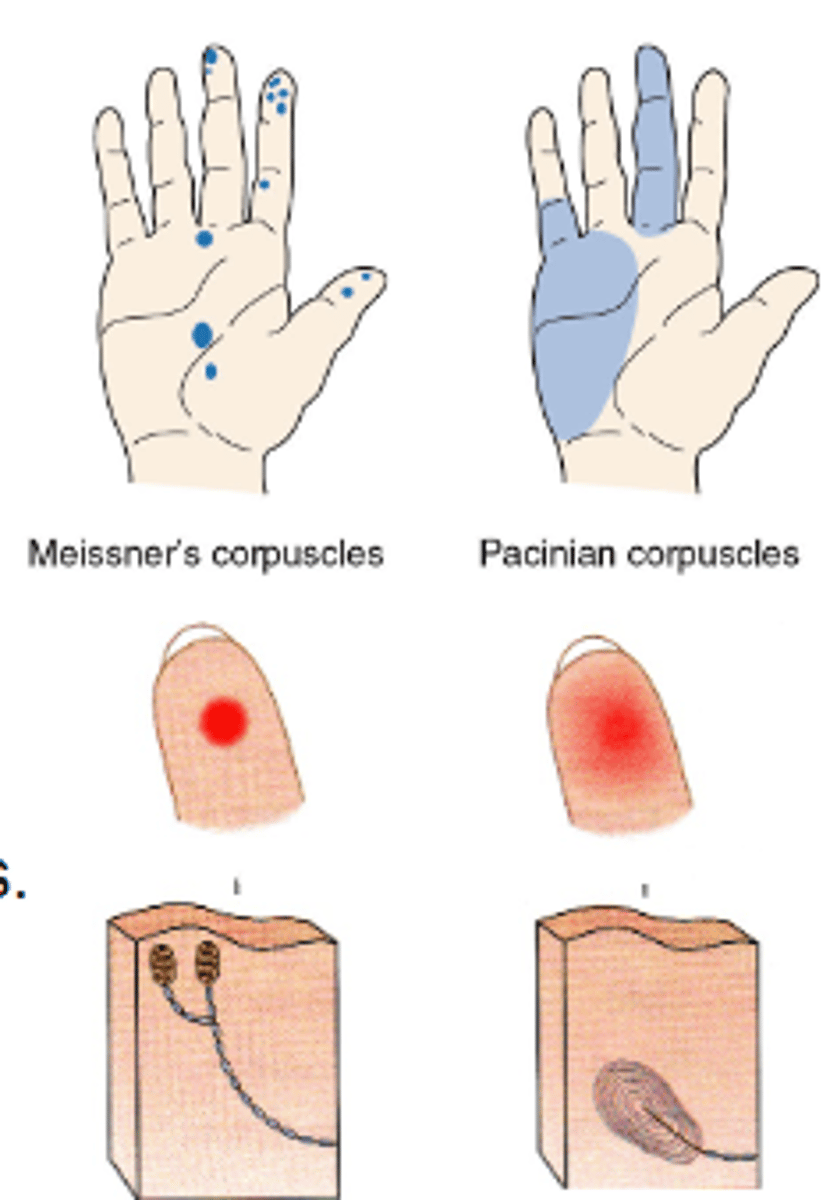
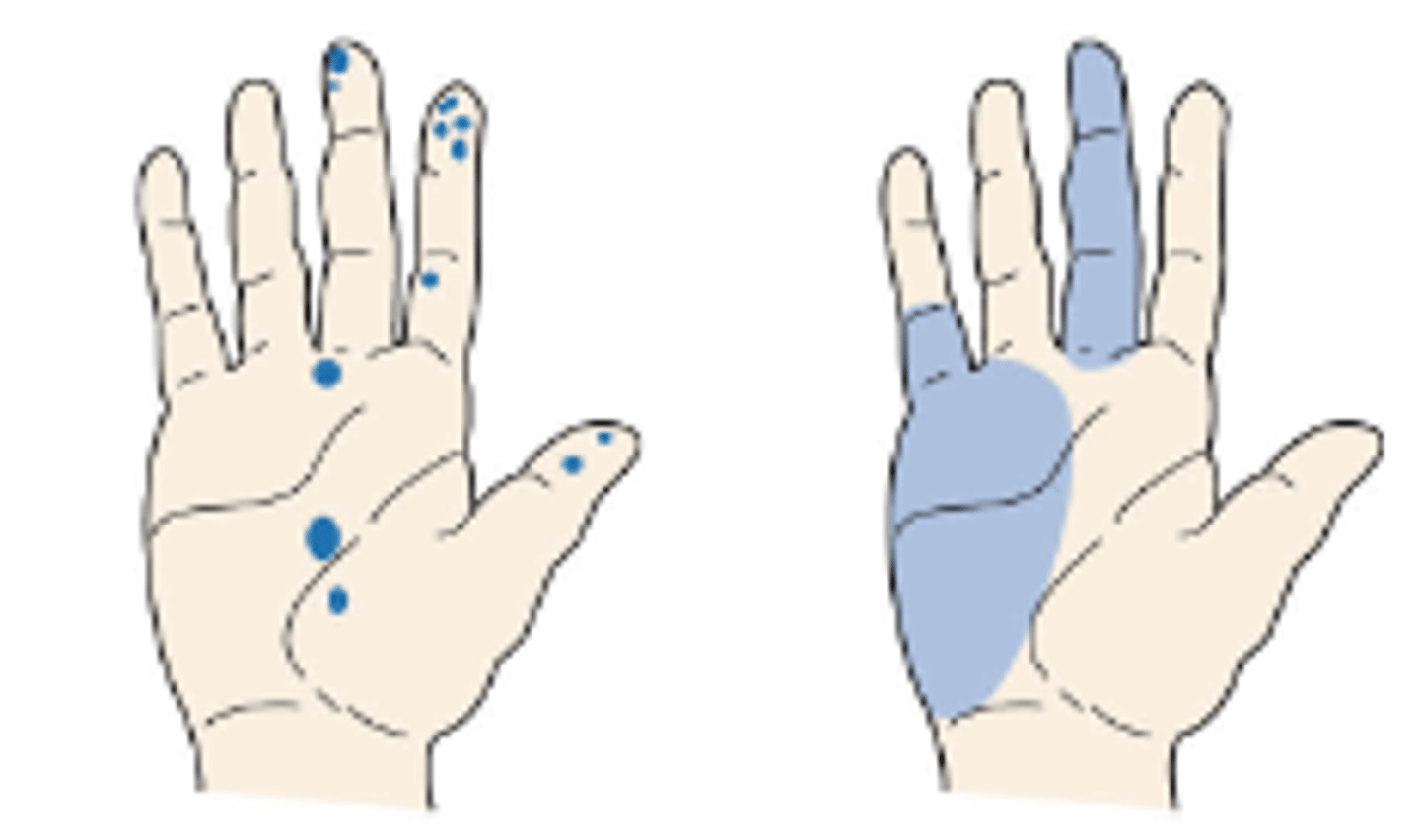
Receptive fields
Varies by shapes and size, related to anatomy and branching characteristics of underlying receptor cells.
Different receptor types provide different degrees of precision w/ regards to touch location.
Slowly adapting afferents
Exhibit more sustained responses to continuous pressure.
May be important for shape vs. size perception
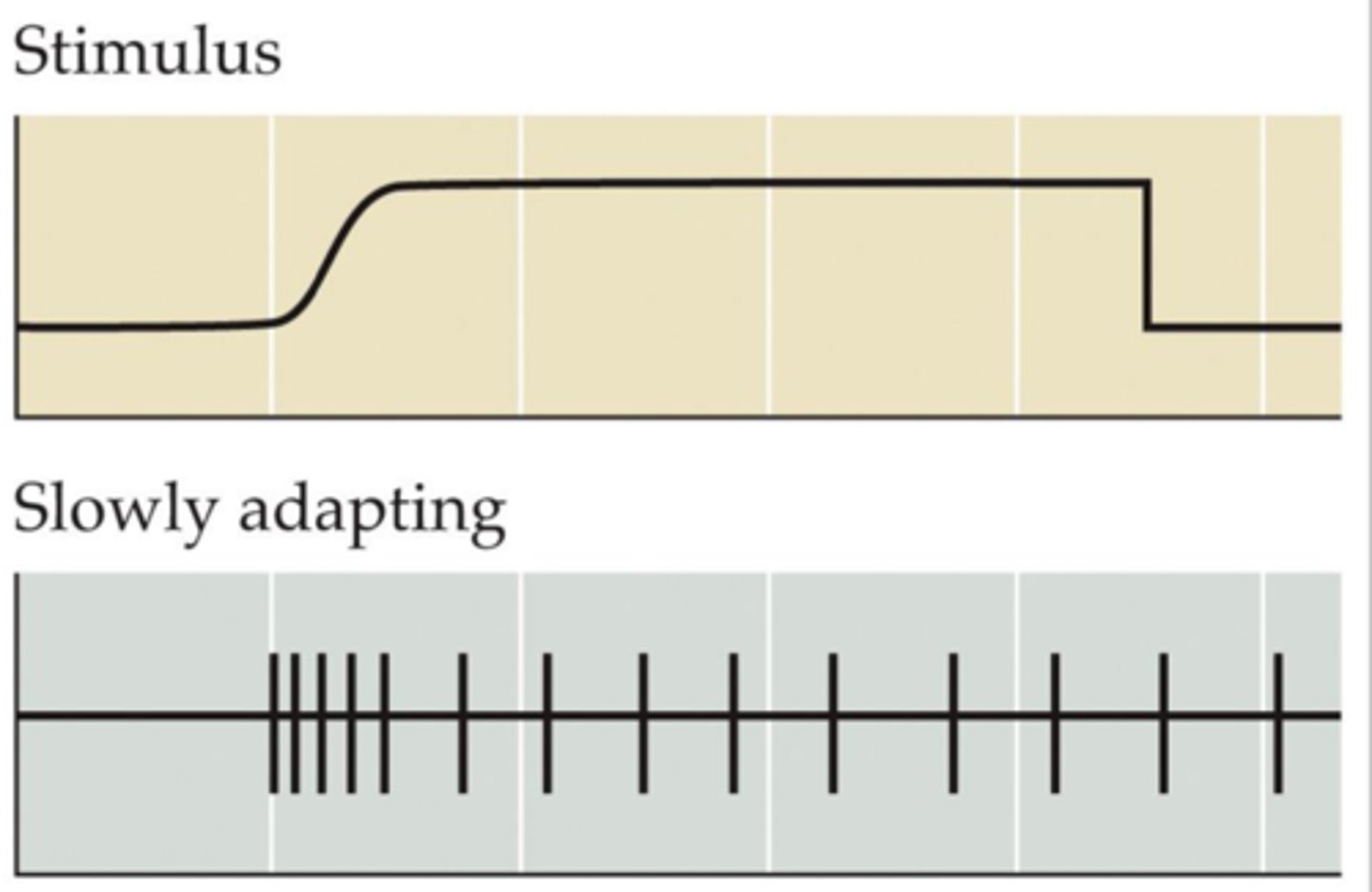
Rapidly adapting afferents
Become more silent in response to continuous pressure.
May be important for rapid changes to ongoing stimulation
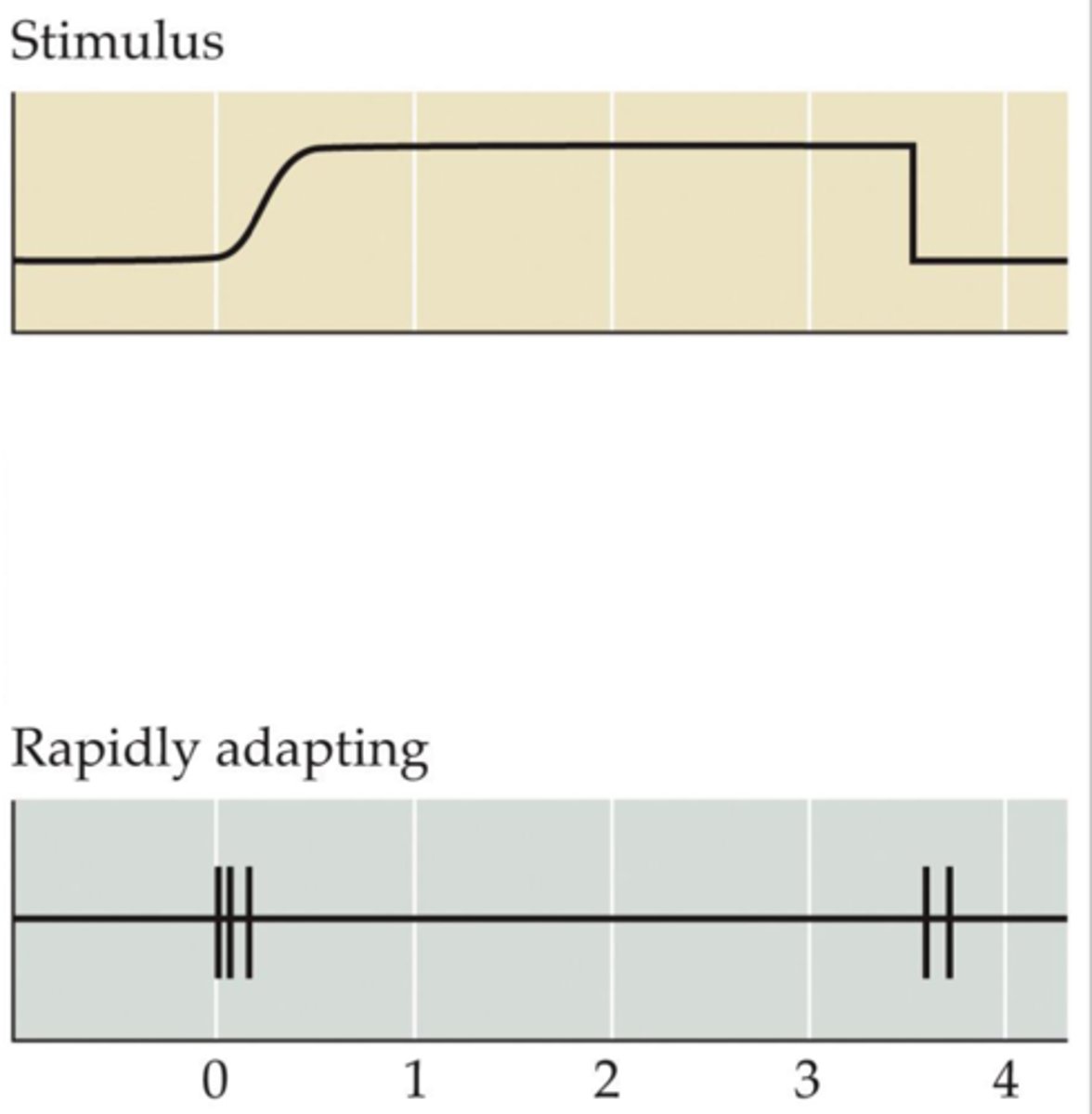
Stimulus frequency
Analogous to "texture", the function by which each receptor type exhibits thresholds.
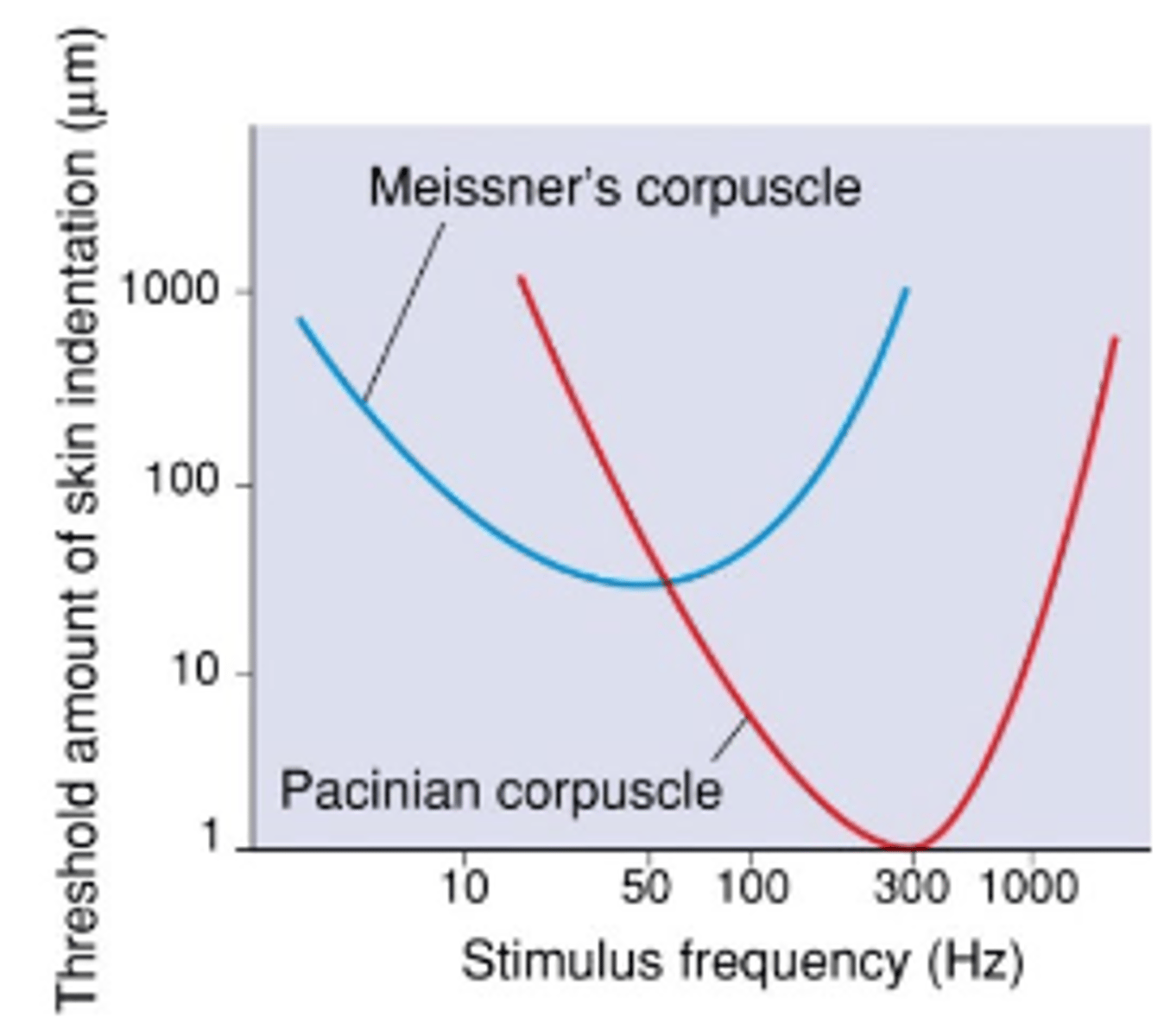
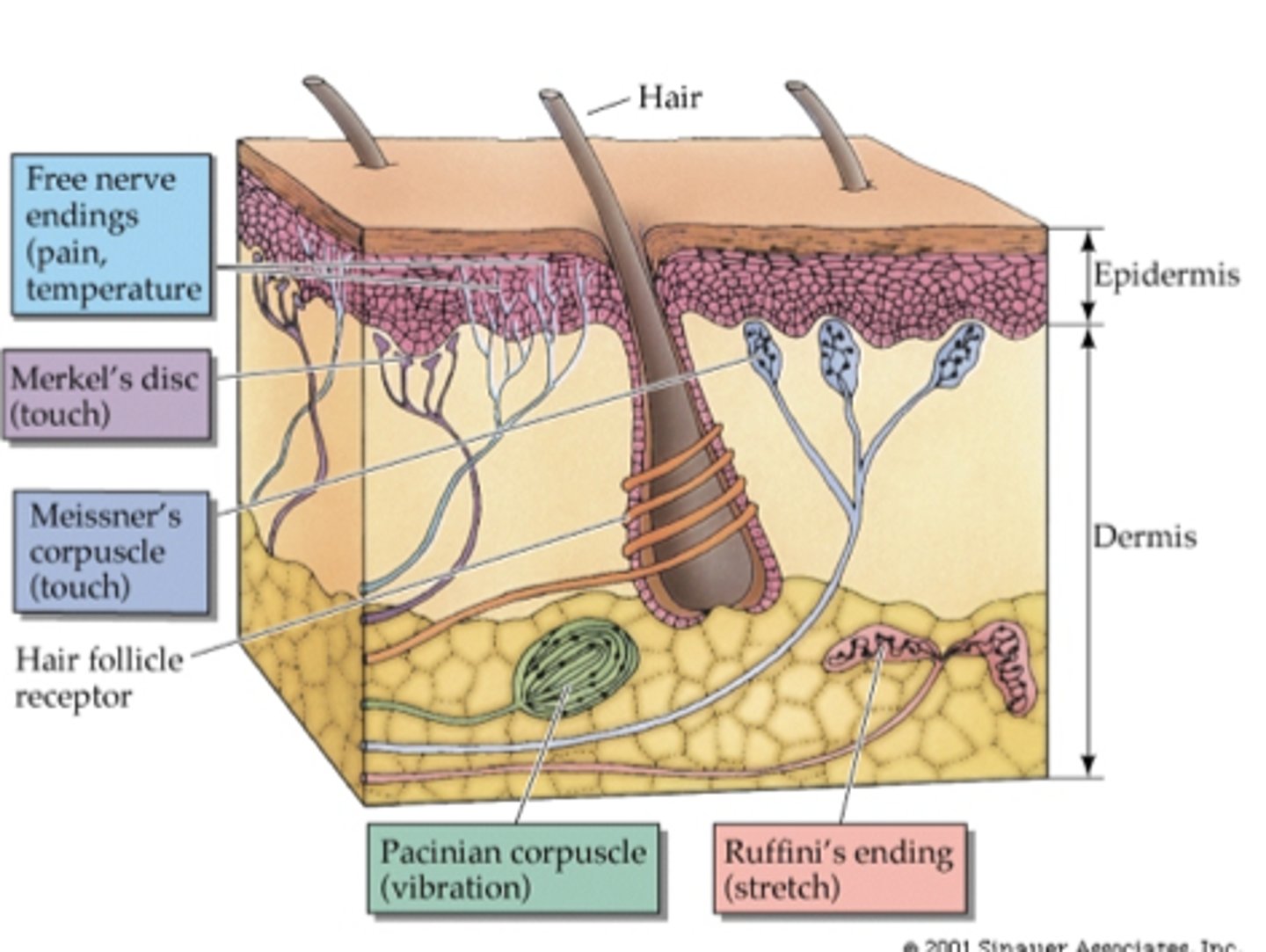
Pacinian corpuscles
Deep pressure, fast vibrations.
Respond to light pressure at higher frequencies
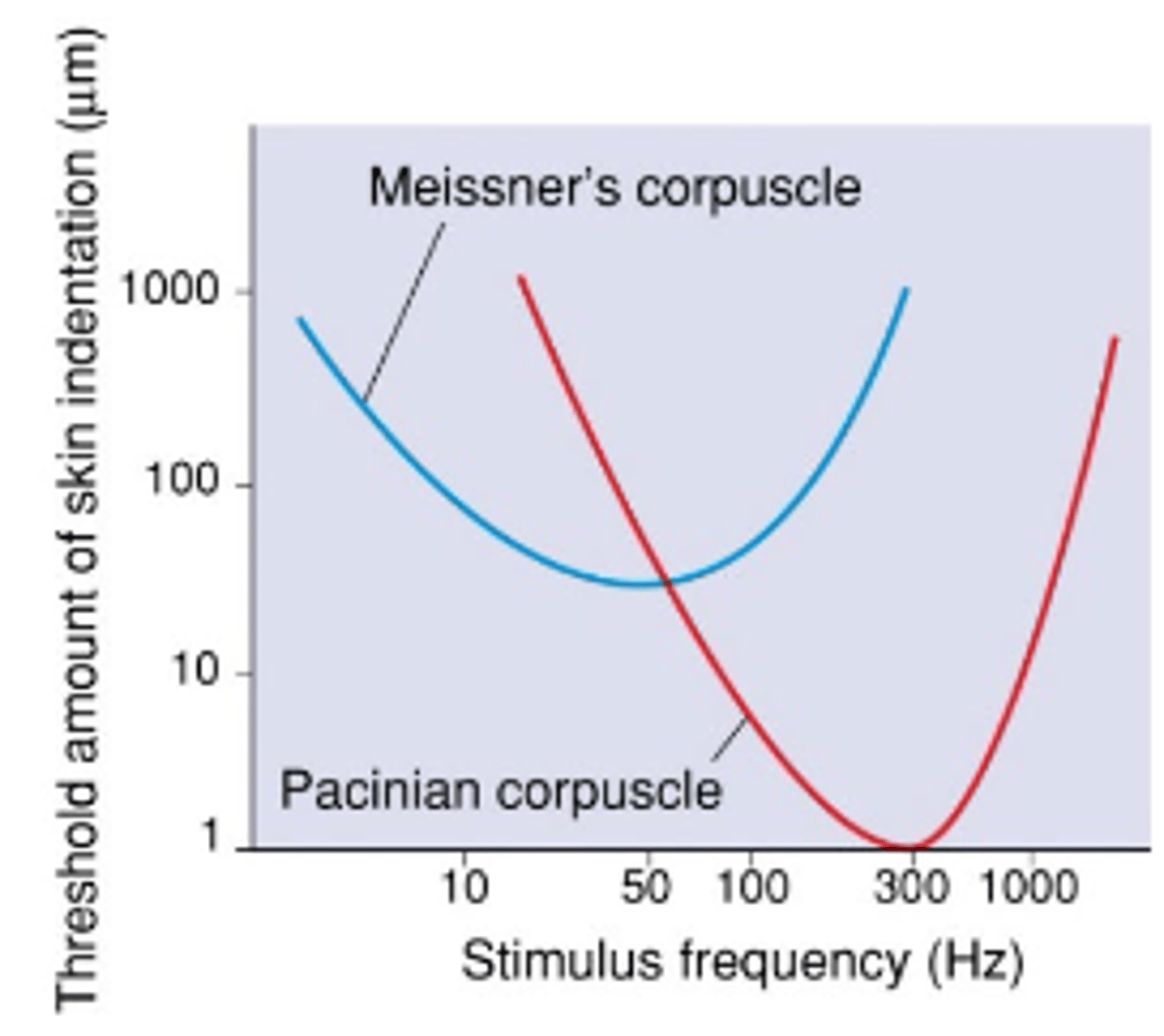
Meissner's corpuscles
Changes in texture, slow vibrations.
Respond to lower frequency stimulation but requires more force
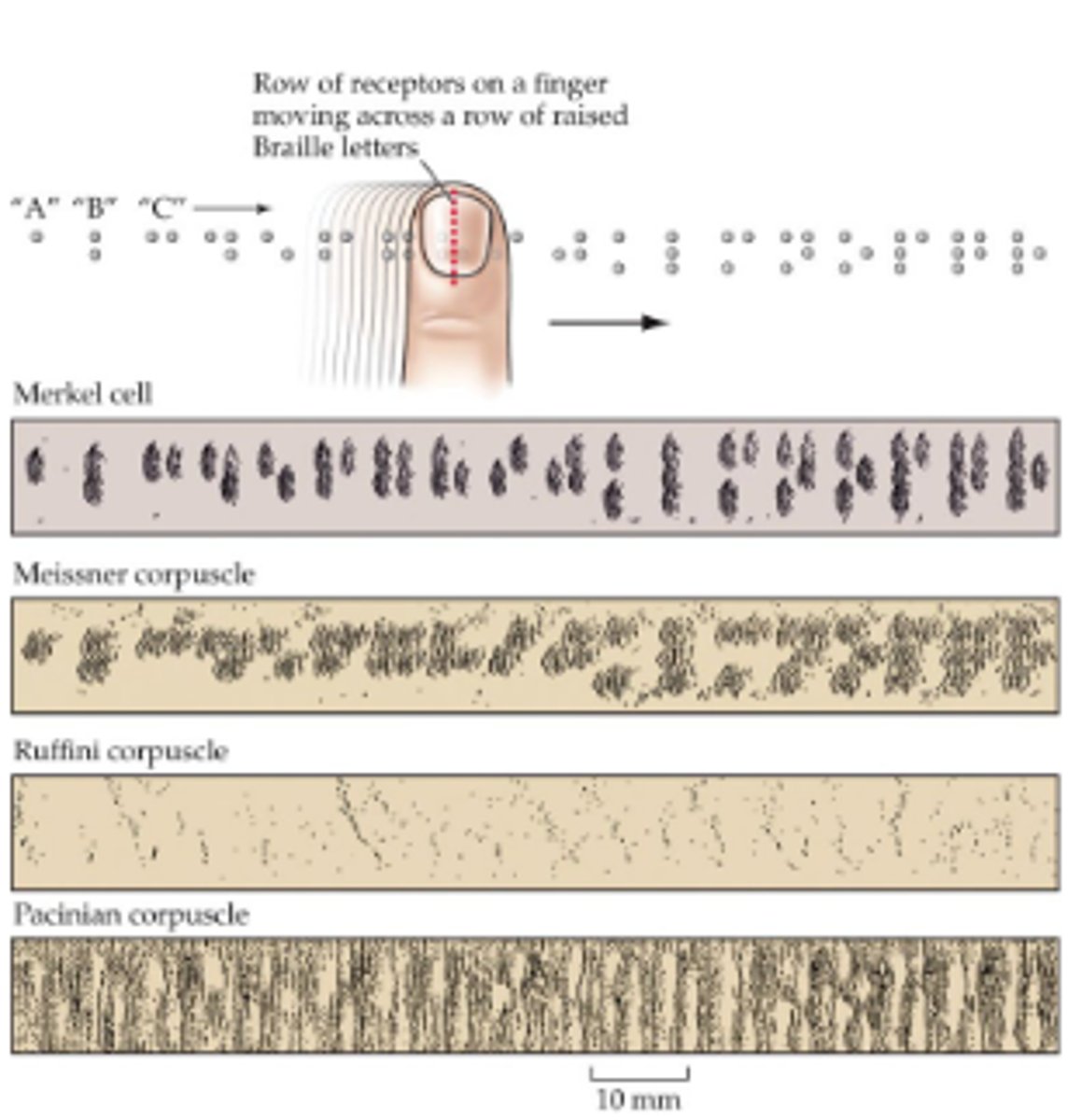
Merkel cells
Touch receptors in fingertips, have small endings w/ high spatial resolution.
High density of mechanoreceptors, brain dedicates more tissue to processing these signals.
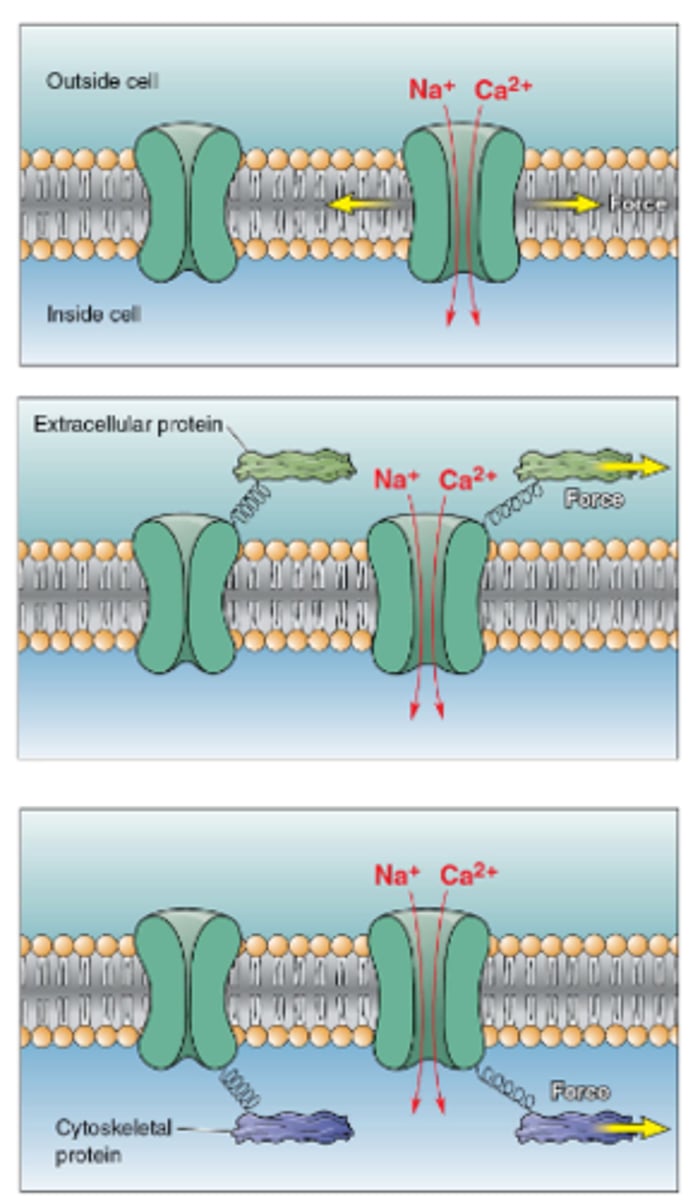
Mechanisms by which mechanical force is converted to a neural code
Ion channels sensitive to stretching of lipid membrane.
Ion channels that open with force applied to extracellular structures
Ion channels that open w/ deformation and stress on cell's cytoskeleton
Piezo1 and Piezo2
Recently discovered mechanosensors
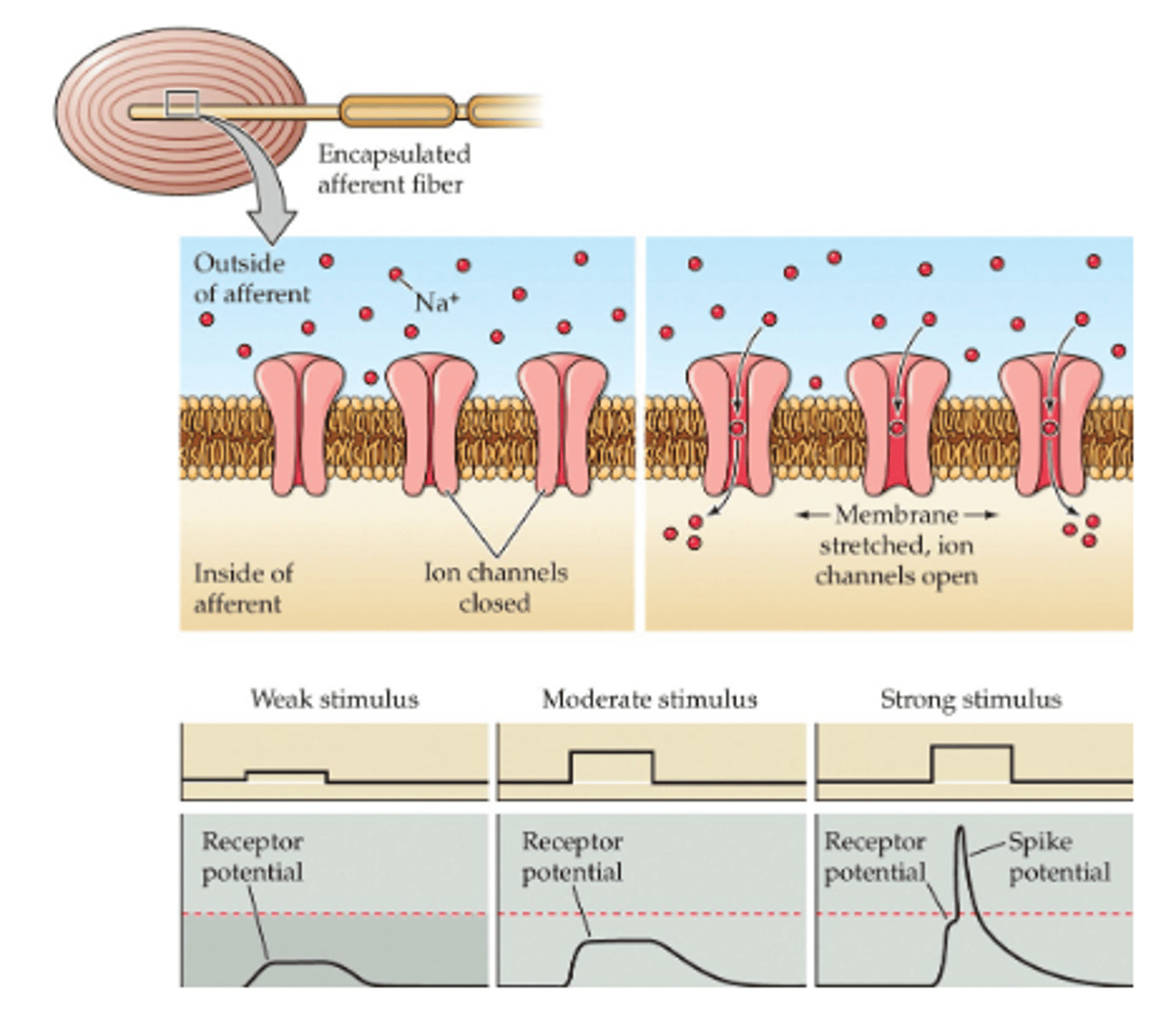
Action potentials
Caused by physical pressure on mechanoreceptors which opens ion channels in order to cause depolarization.
# is typically proportional to magnitude of the stretch/pressure
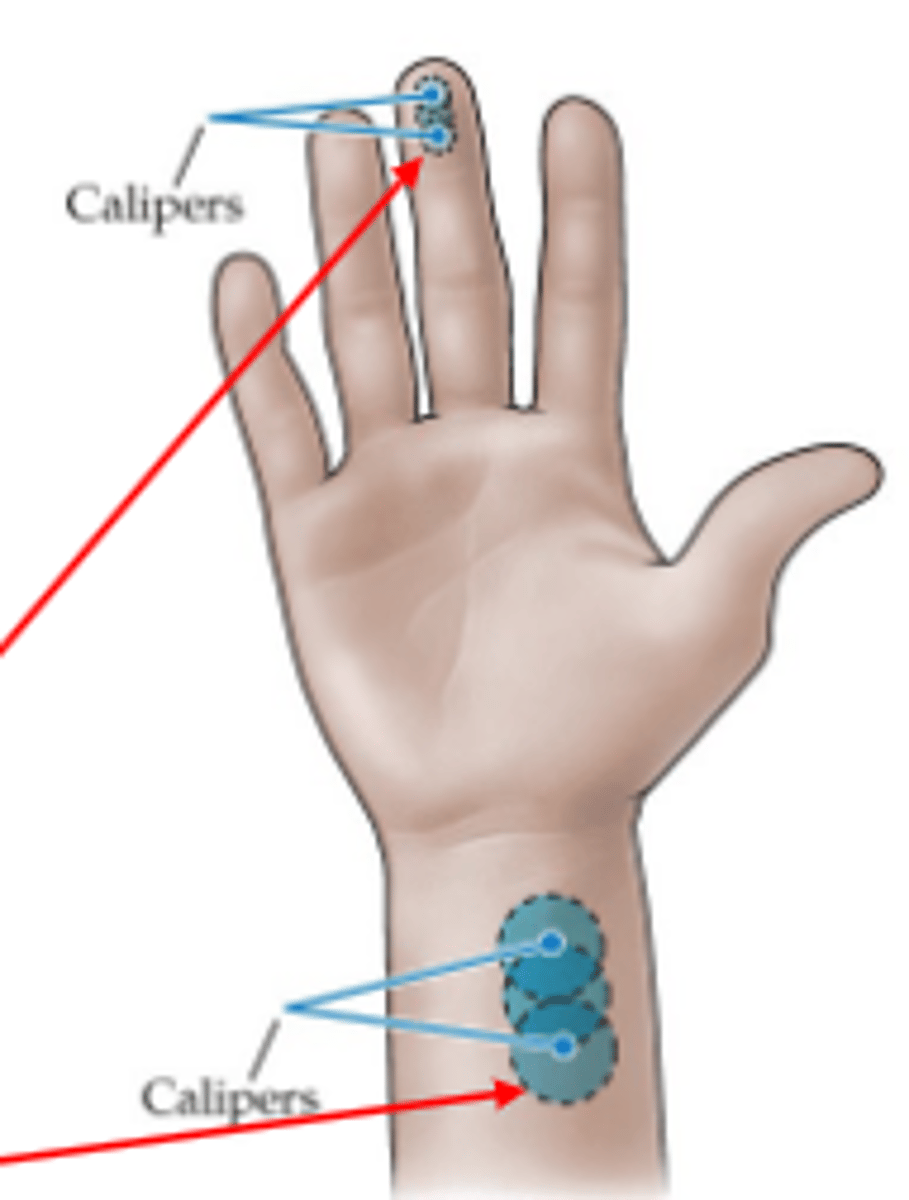
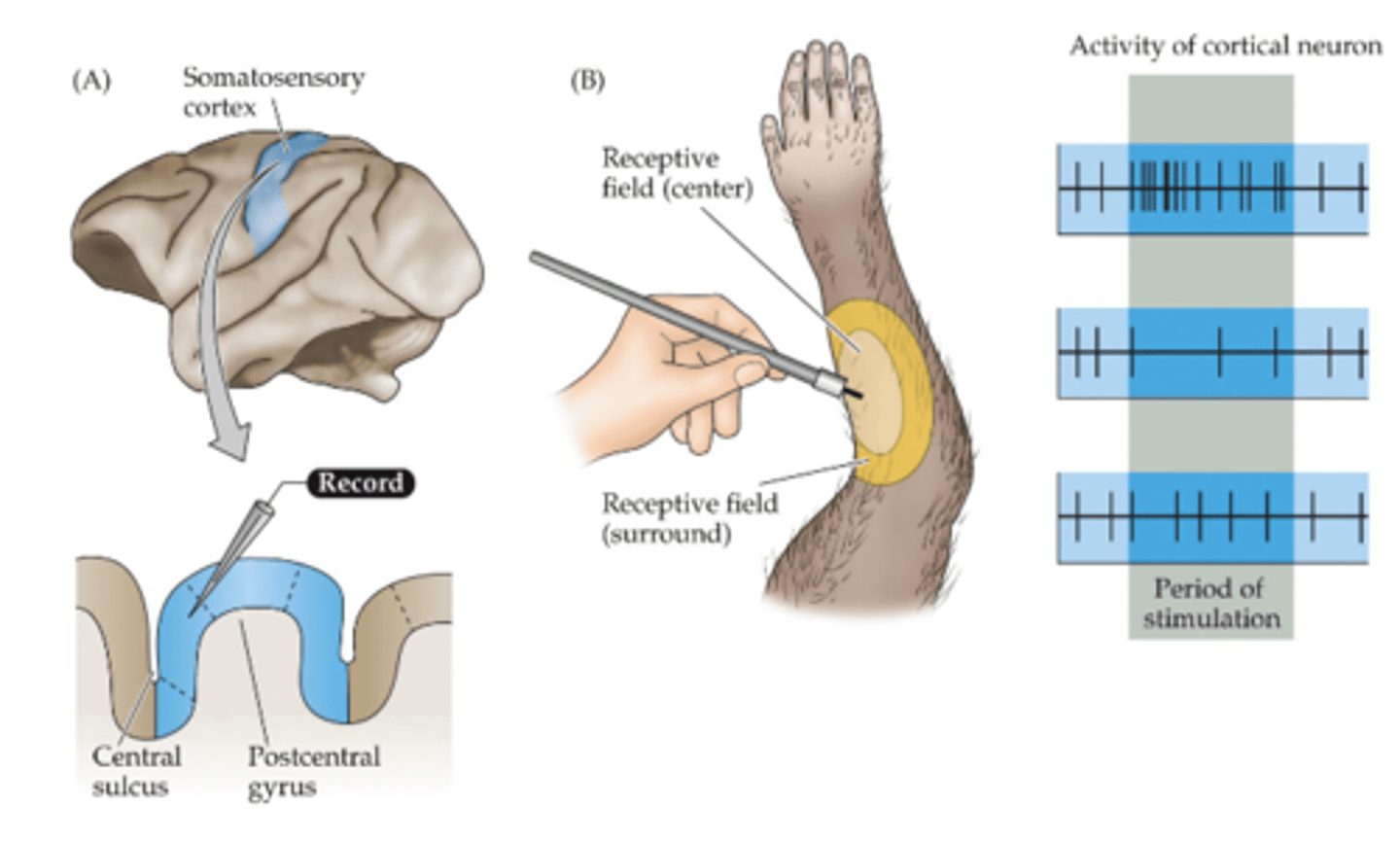
Two-point discrimination
The ability to discriminate detailed stimulus. Only a single point of contact is perceived if within the receptive field of a single sensory neuron, two are perceived if extended across the fields of two different sensory neurons.
Receptive fields map to areas of the body and their density varies greatly.
Which of the following has receptive fields that may cover an entire finger or half of the palm?
Pacinian corpuscles
Afferent axons
Axons that carry information to CNS - enter the spinal cord through dorsal roots
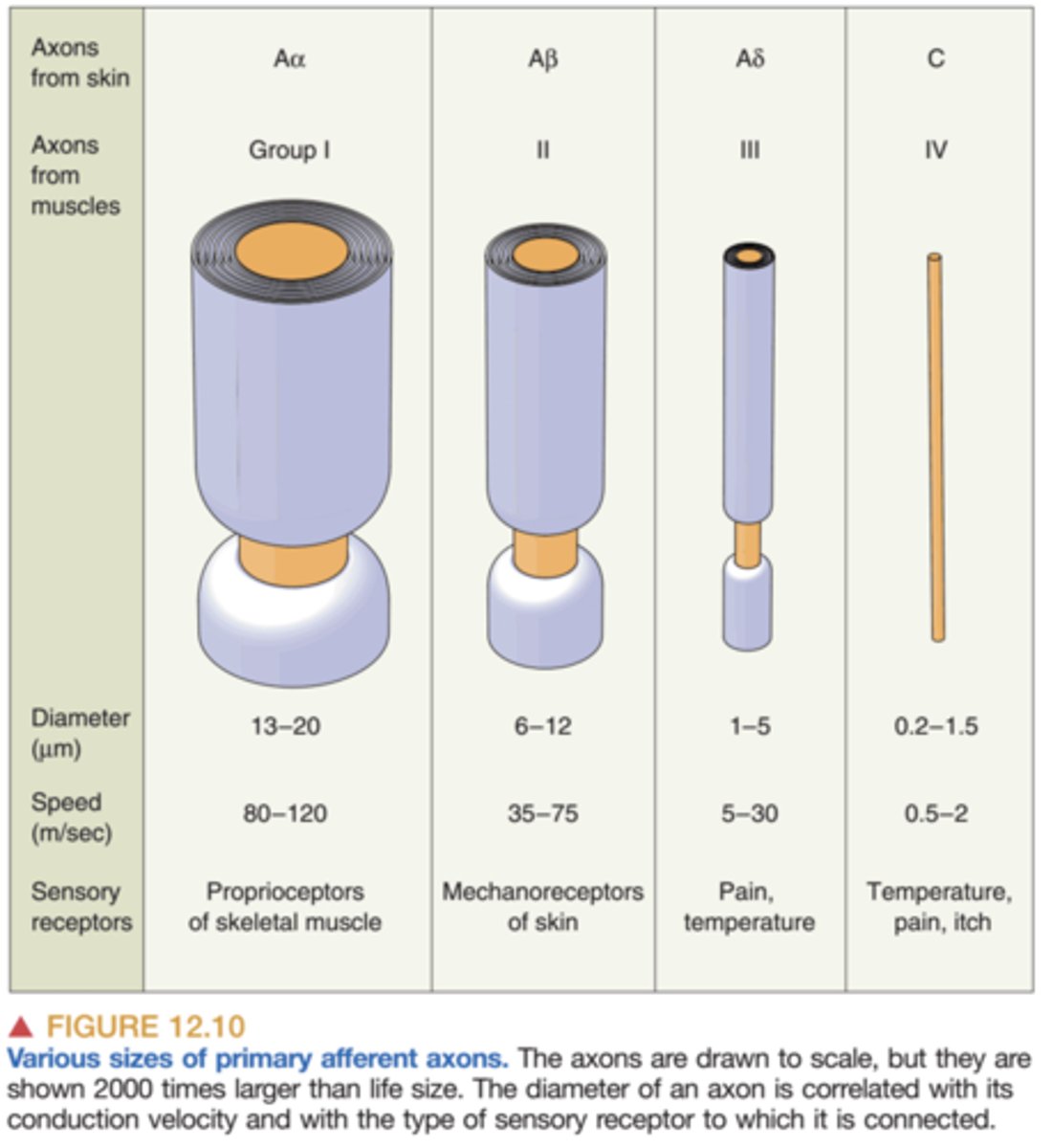
Aα fibers
Mediate proprioception
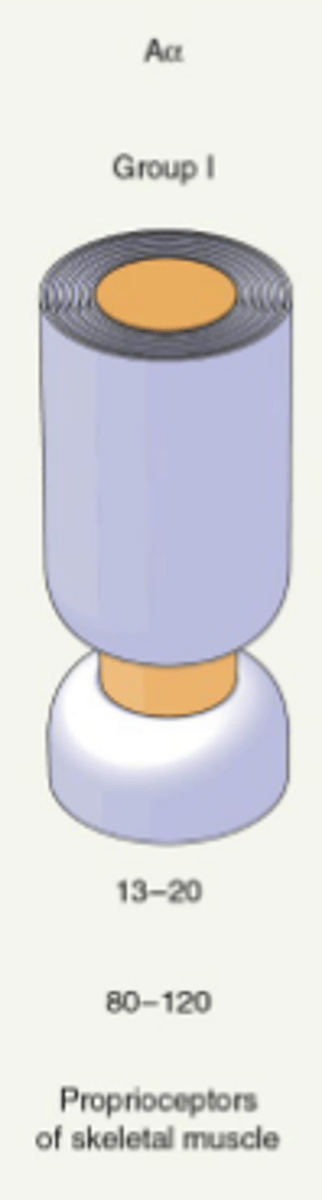
Aβ fibers
Mediate touch perception
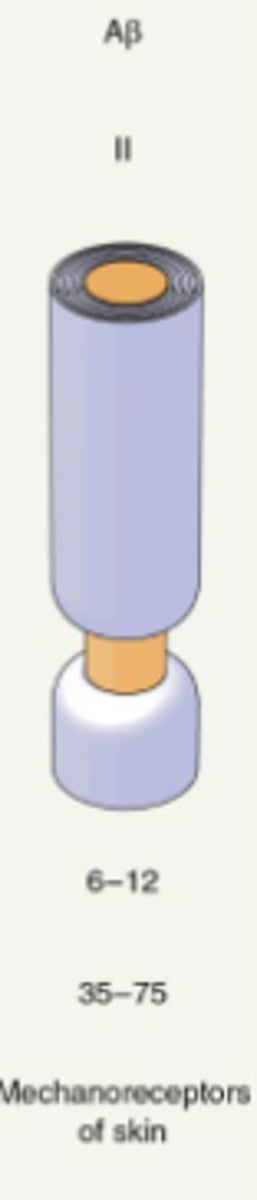
C fibers
Mediate pain, temperature, and itch

Dorsal root ganglia
Cell bodies of sensory neurons gather here and primary afferents enter to spinal cord through them
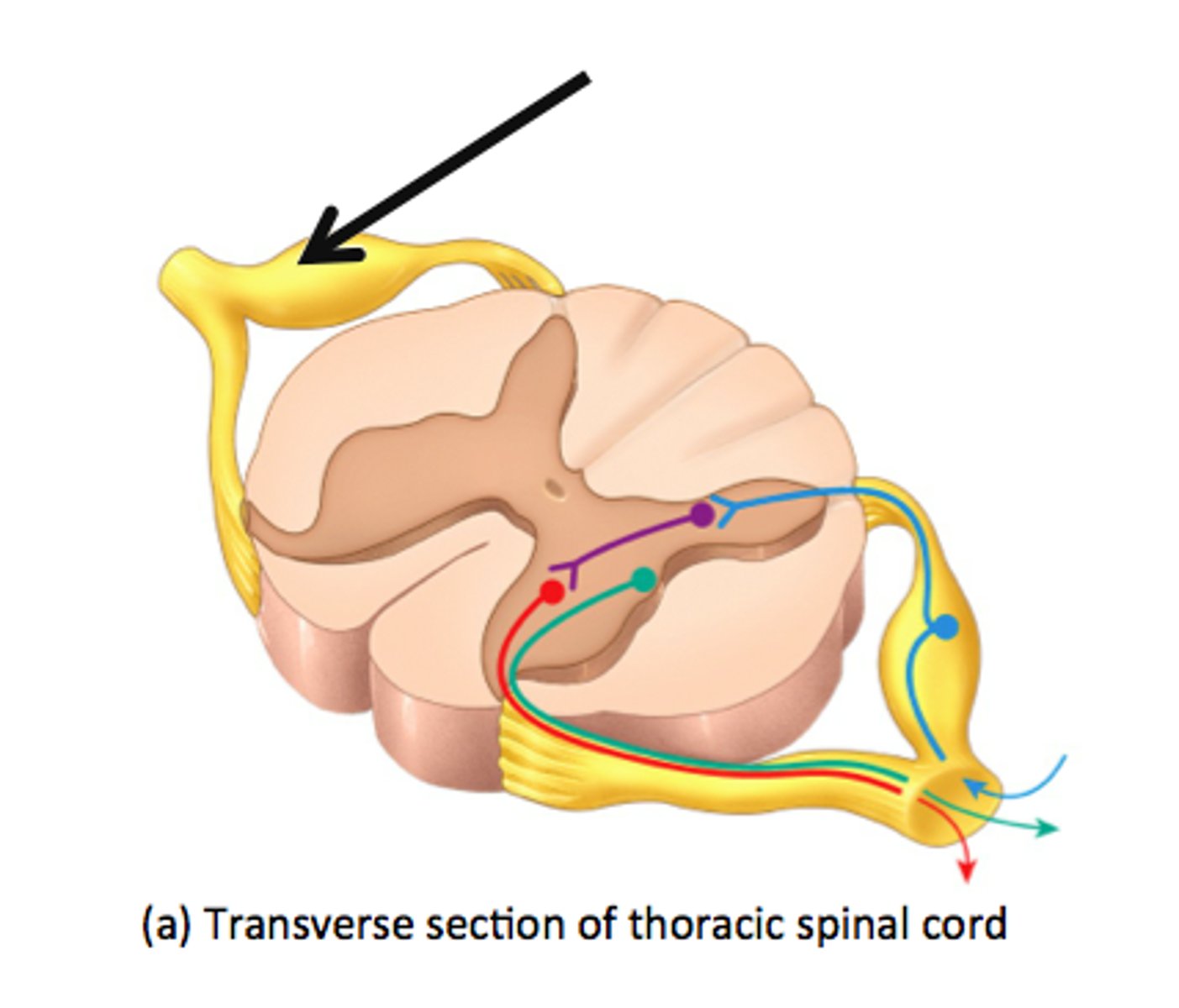
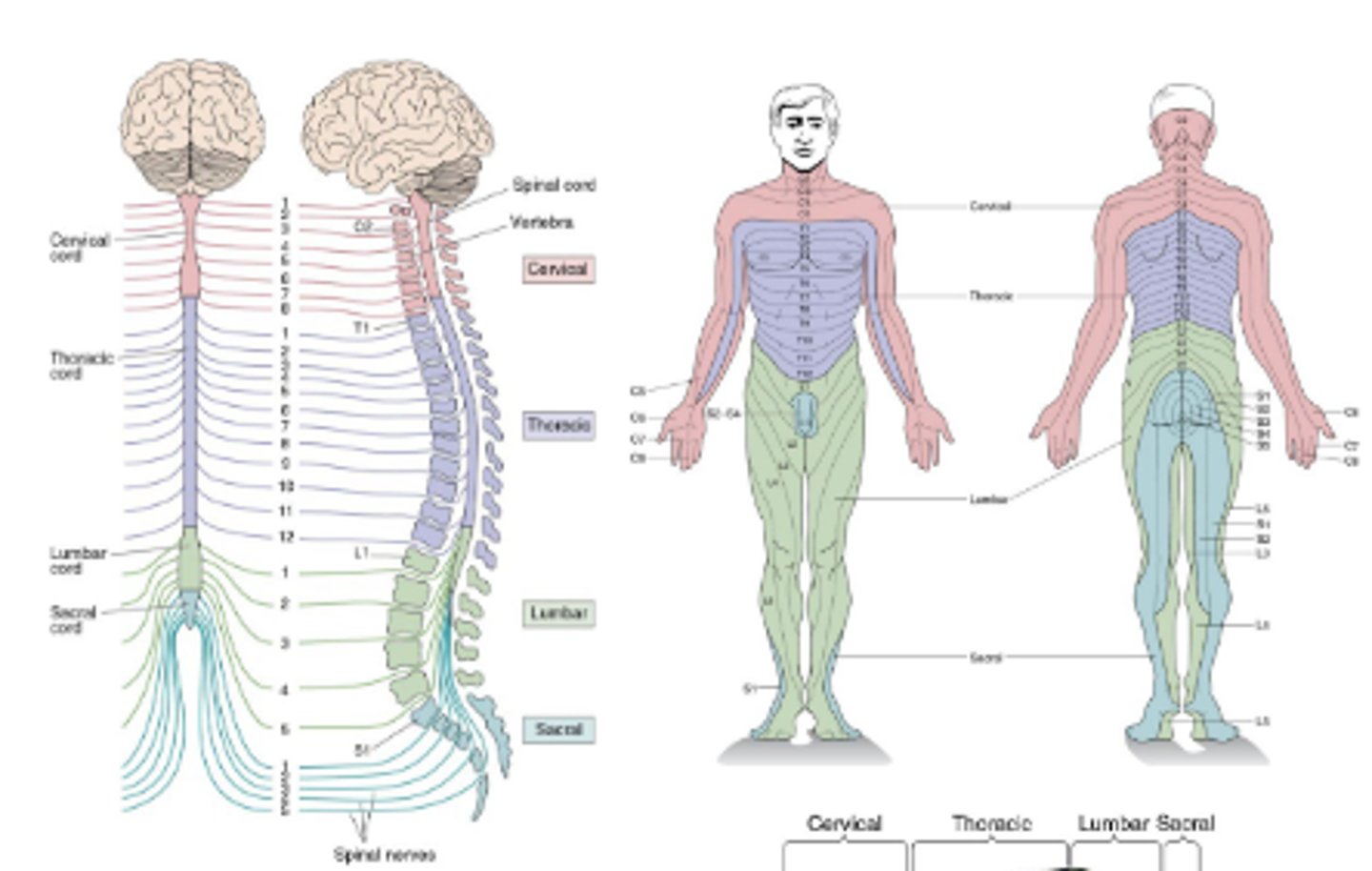
Spinal nerves
Innervate segments of the body. Dermatomes are innervated by the dorsal root in single spinal segments
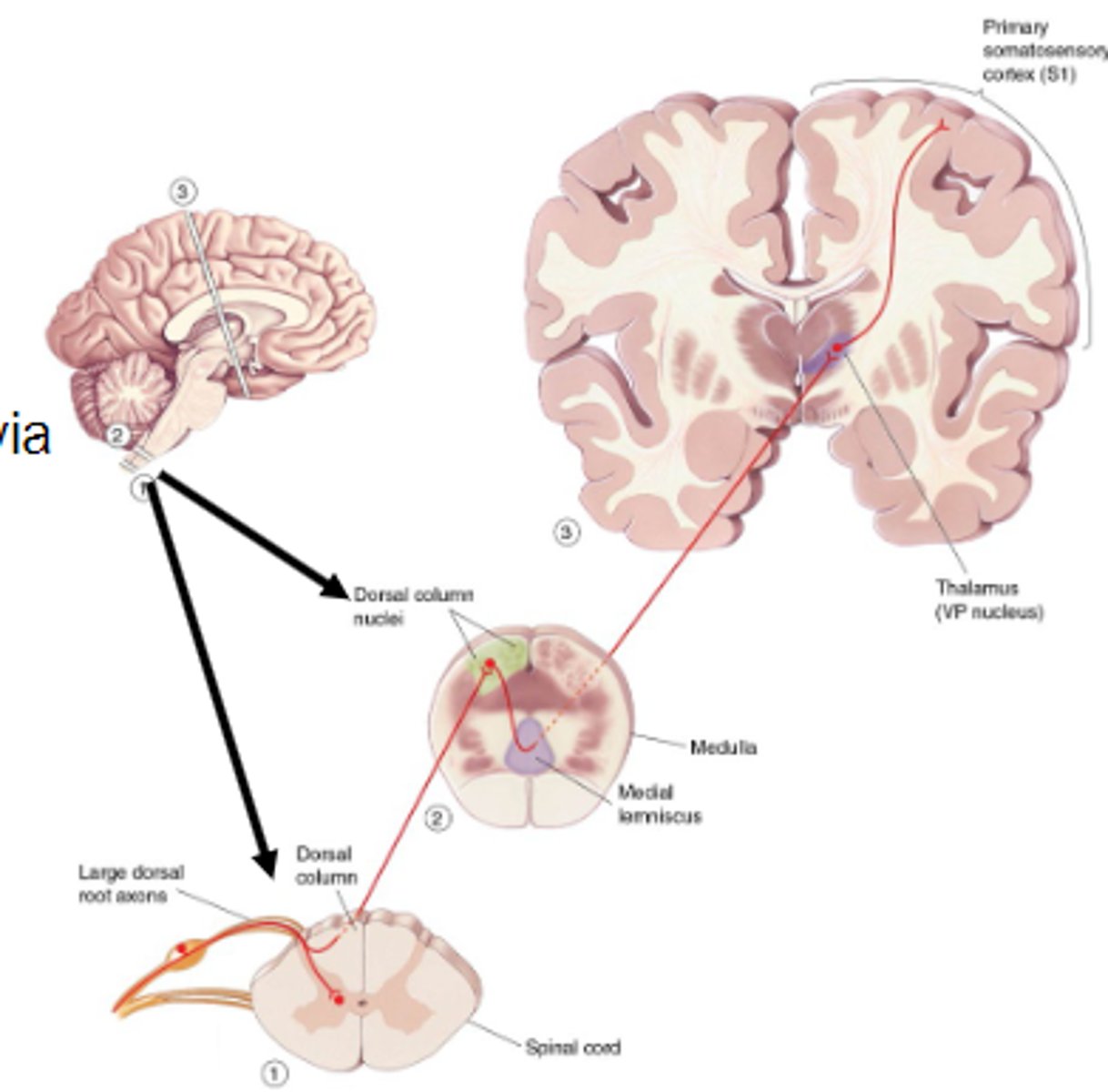
Dorsal column-medial lemniscal pathway
Mediates signals about touch and proprioception, Alpha/beta axons enter the ipsilateral side and terminate in dorsal column nuclei.
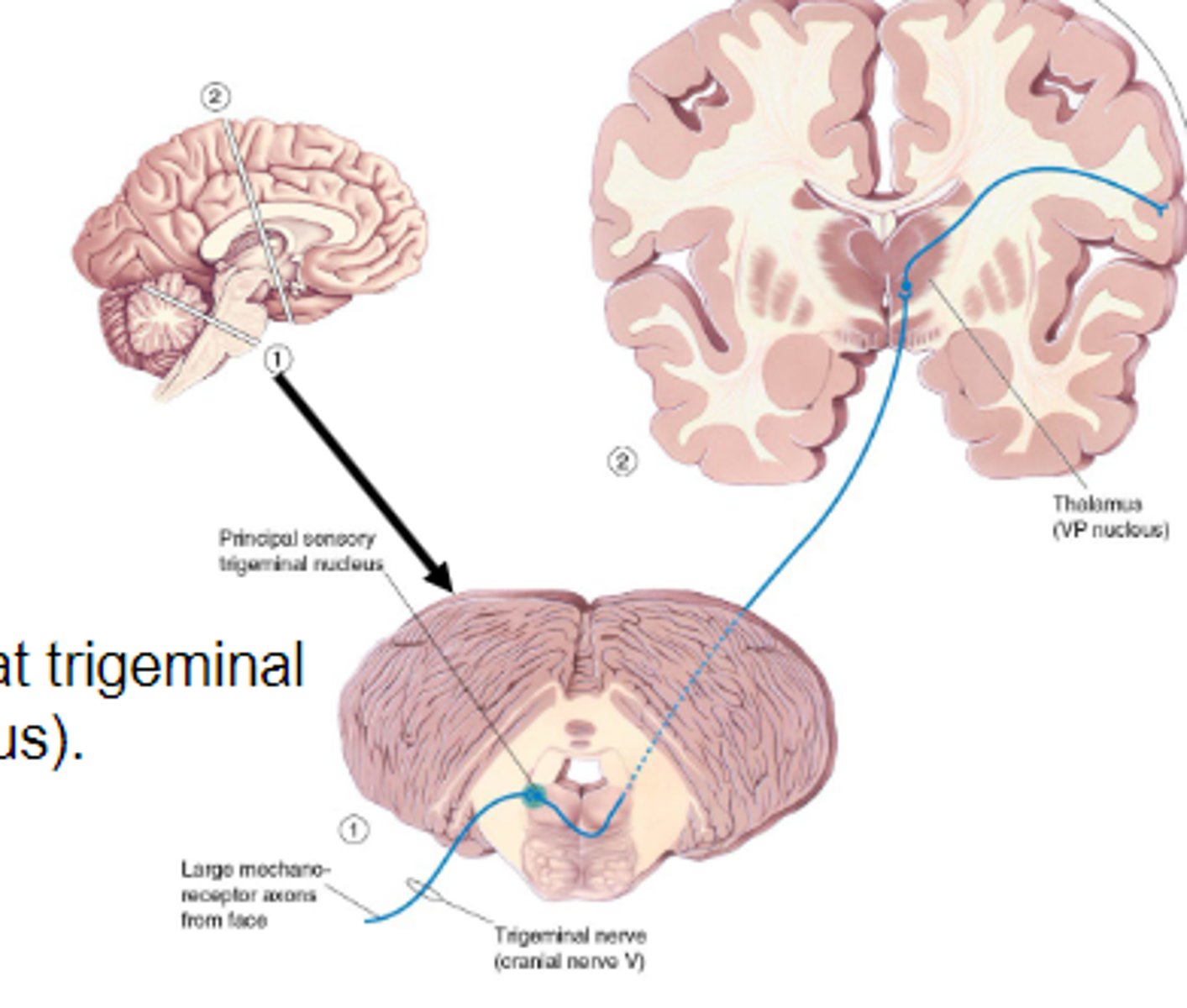
Trigeminal nerve pathway
Carries somatic signals that aren't carried by spinal cord (face, head).
Somatosensory information from face comes primarily through this pathway. Has similar sensory connections as dorsal root ganglia BUT crosses at trigeminal nucleus
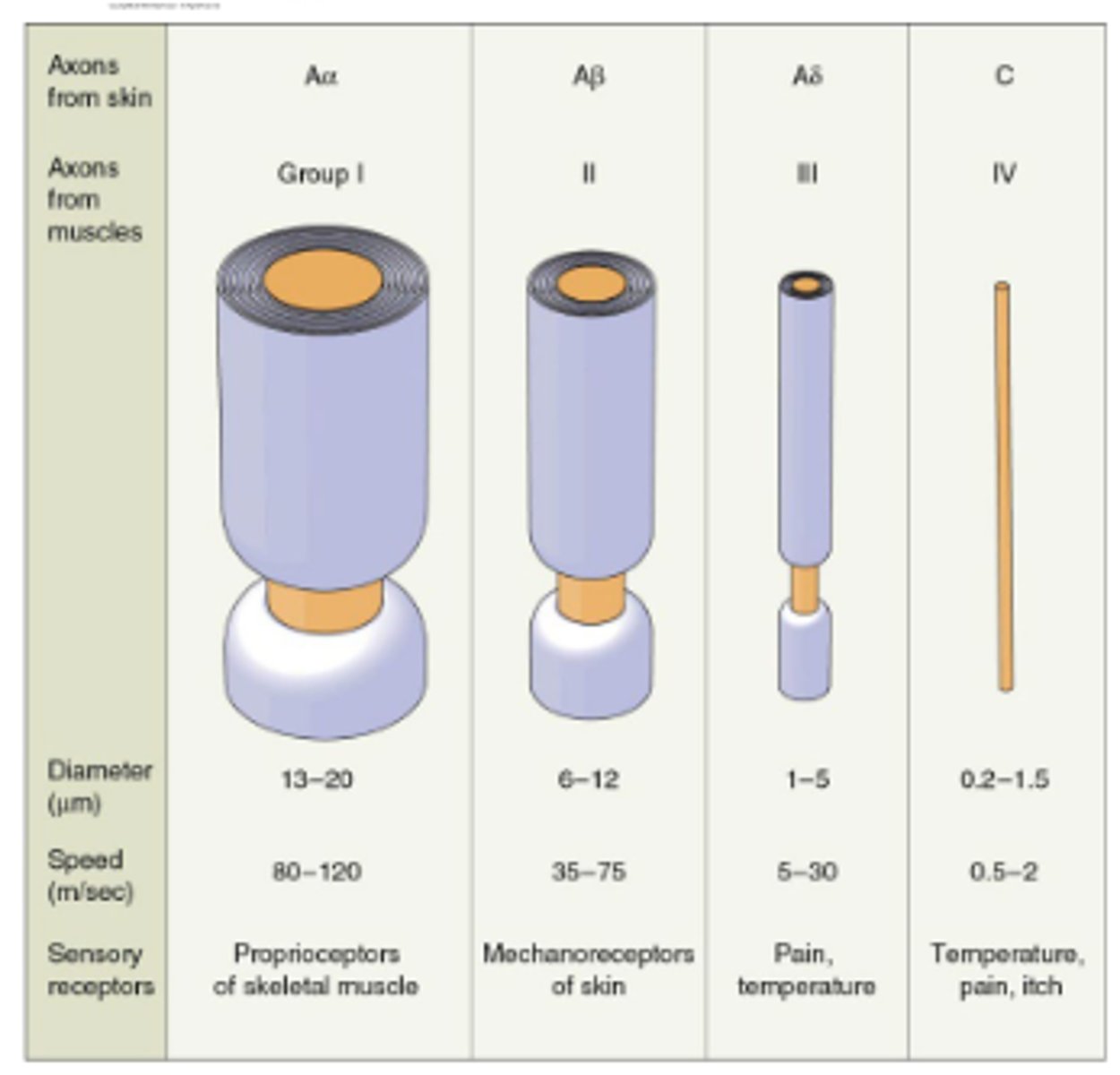
Primary sensory afferent axons have widely varying diameters, and their size correlates with the type of receptor to which they are attached. Which of these axons are the smallest and slowest?
Temperature, pain and itch
A dermatome is an area innervated by:
Fibers of the cells from a single nucleus in the brain stem
Primary somatosensory cortex
Responsive to somatosensory stimuli
Lesions impair somatic sensation
Electrical stimulation evokes somatic sensation
Layered like visual cortex
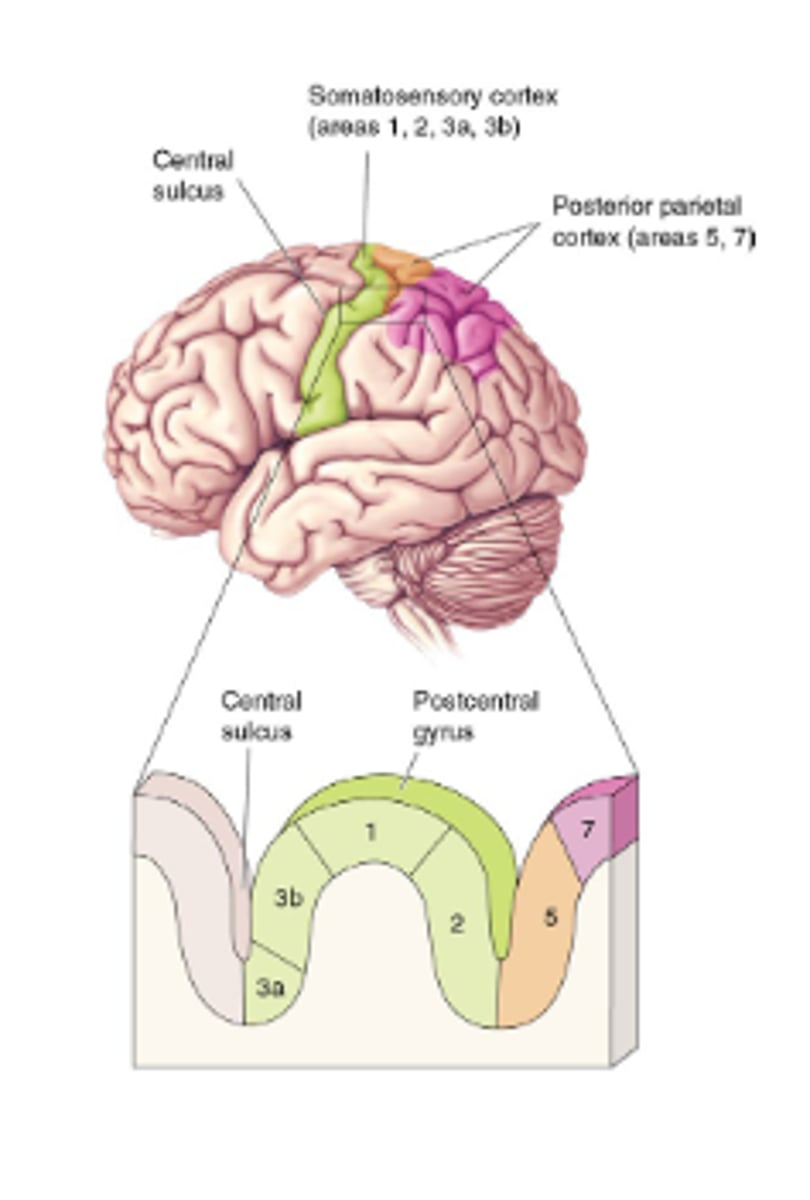
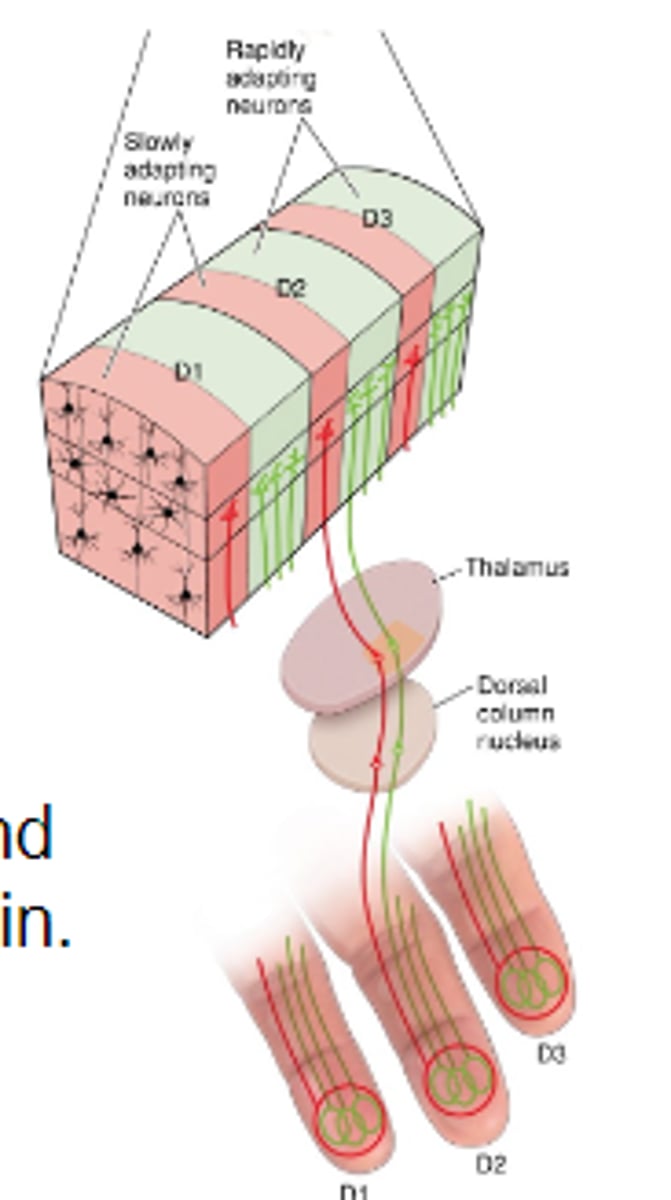
S1 neurons
Neurons w/ similar inputs and responses are stacked vertically into columns
Contains neurons innervated by both rapid/slow adapting mechanoreceptors.
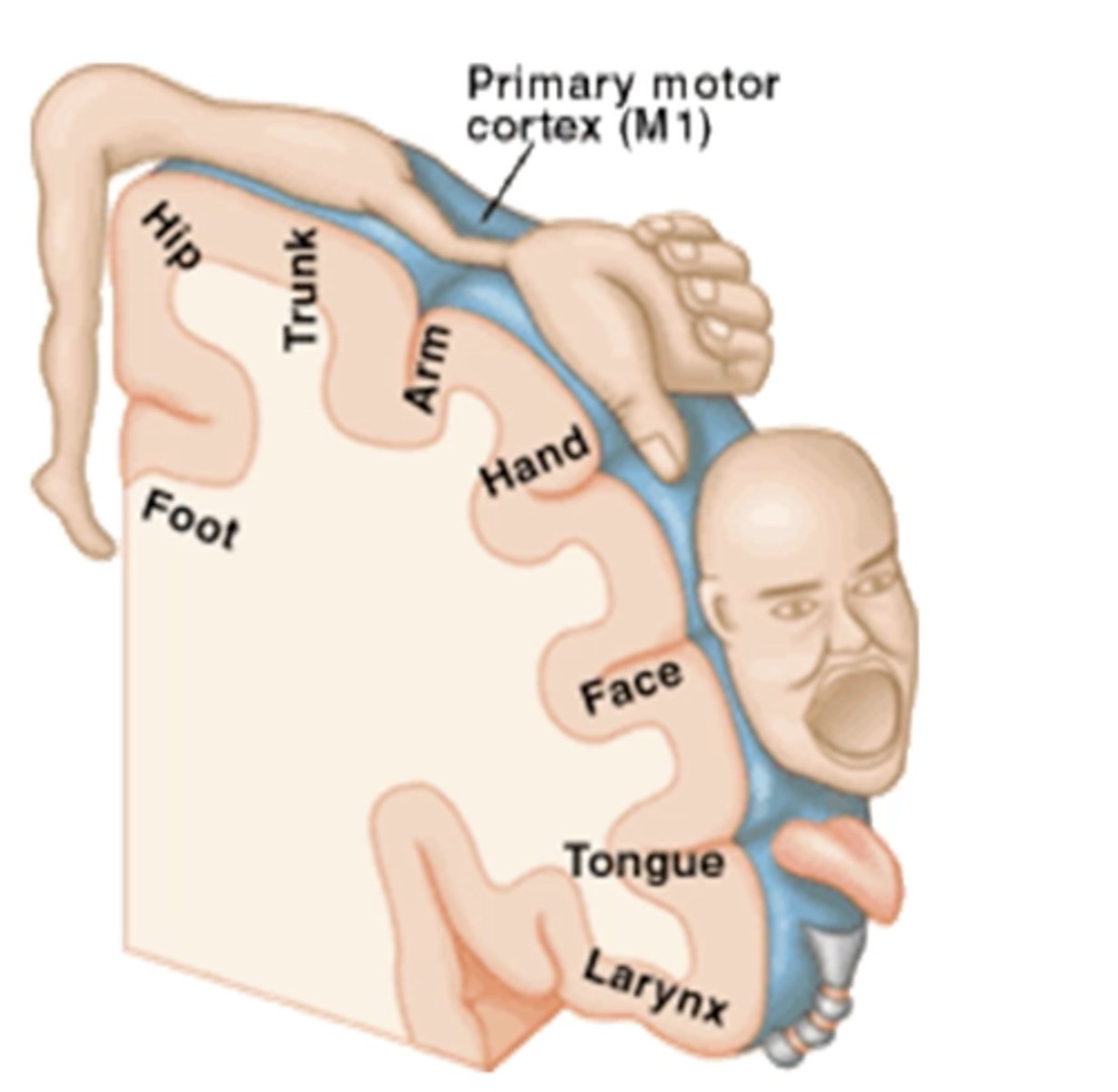
Somatotopy
Receptive fields of s1 neurons create a map of the body on the cortex.
There are more cortical spaces dedicated to certain areas
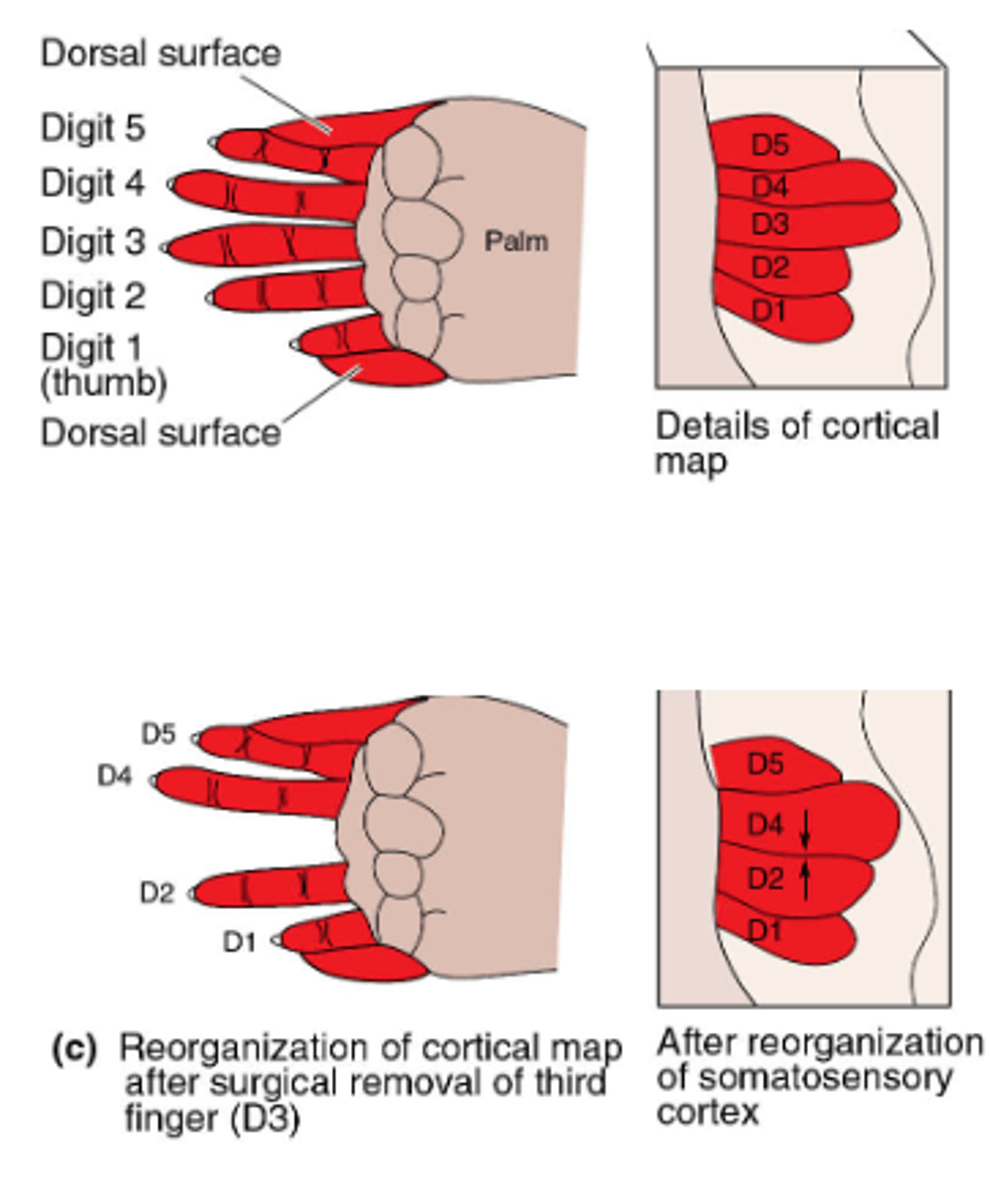
Somatotopic plasticity
Removing a digit in a reptile hand causes the cortical space to reorganize to fit the change.
Overstimulating causes the OPPOSITE effect
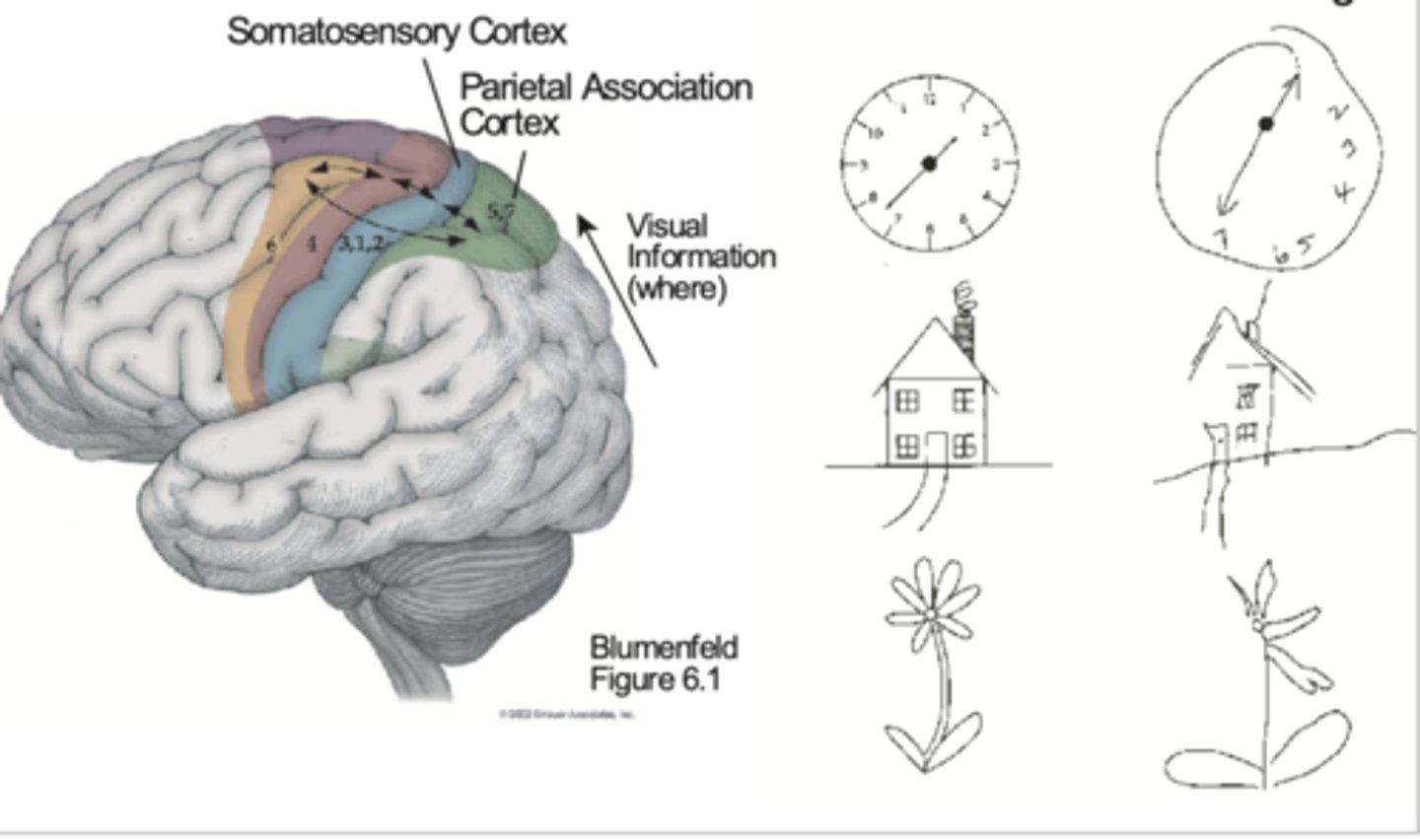
Posterior parietal cortical areas
Higher order somatic cortical areas. Involved in extracting perception of objects
Lateral inhibition
Provides contrast enhancement for somatic receptive fields. Mechanism by which contrast between neighboring points is enhanced
Allows brain to differentiate between the responses of two nearby sets of neurons.
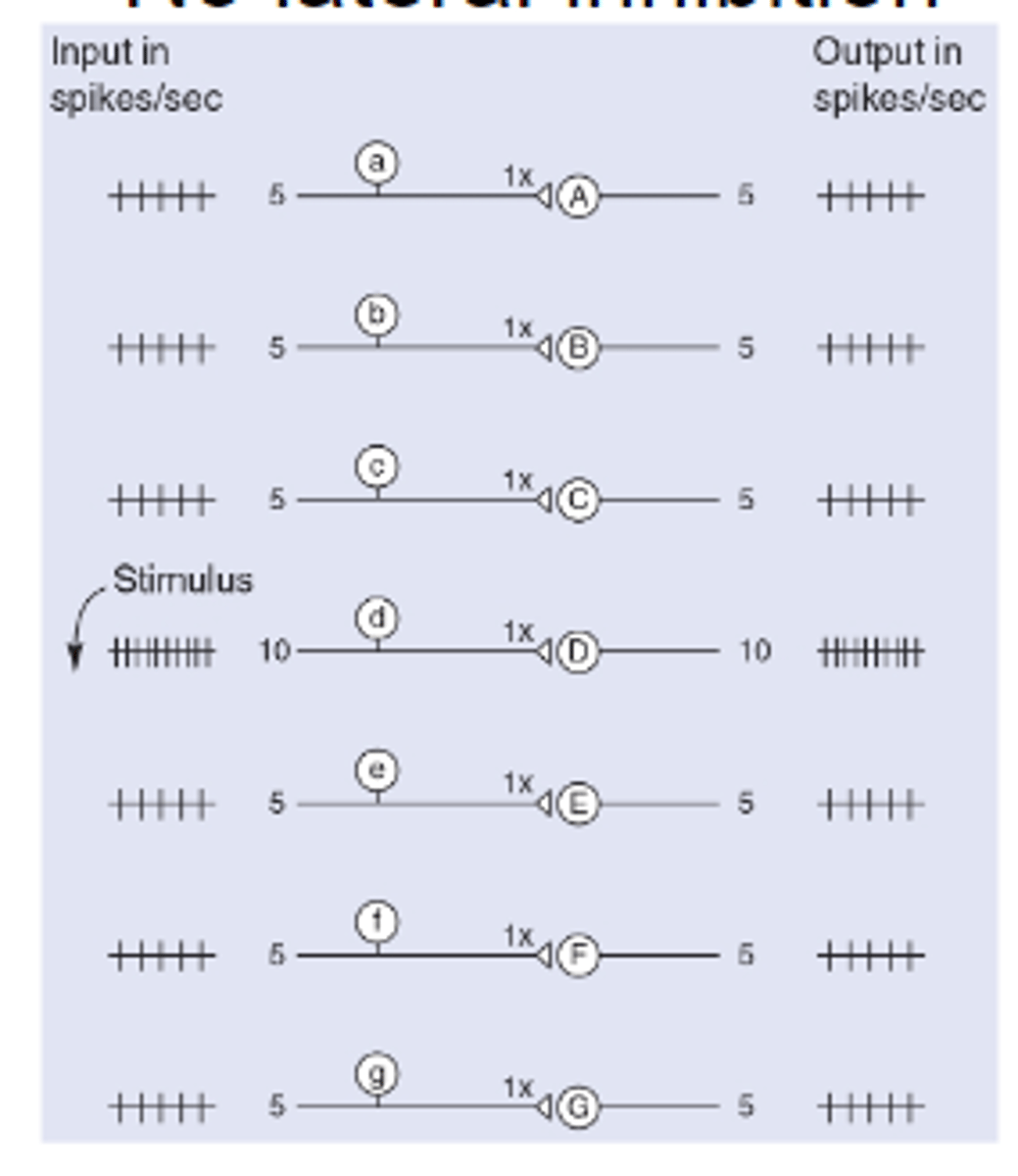
No lateral inhibition
Difference between center and surround is small
Somatotopy
Cortical neurons are arranged in same topology as peripheral receptive fields on the skin.
Areas w/ denser receptive fields have bigger cortical representation, more neurons dedicated to processing!
Feature extraction
Cortical somatosensory neurons have more complex receptive fields than just location.
Orientation of pressures and direction of movement of touch across multiple receptive fields also cause a neuronal response.
What type of information does the dorsal-column-medial-lemniscal pathway carry?
Touch and vibration
Nociceptors
Expressed in branching unmyelinated nerve endings.
Activated by strong mechanical stimulation, temperature extremes, oxygen deprivation, chemicals, etc. Pain perception!
Transduction of painful stimuli
-Protease can breakdown kininogen to form bradykinin, which binds and activates nociceptors.
-ATP release activates ATP-gated ion channels located on nociceptors, causing an increase in extracellular K+ which then causes depolarization
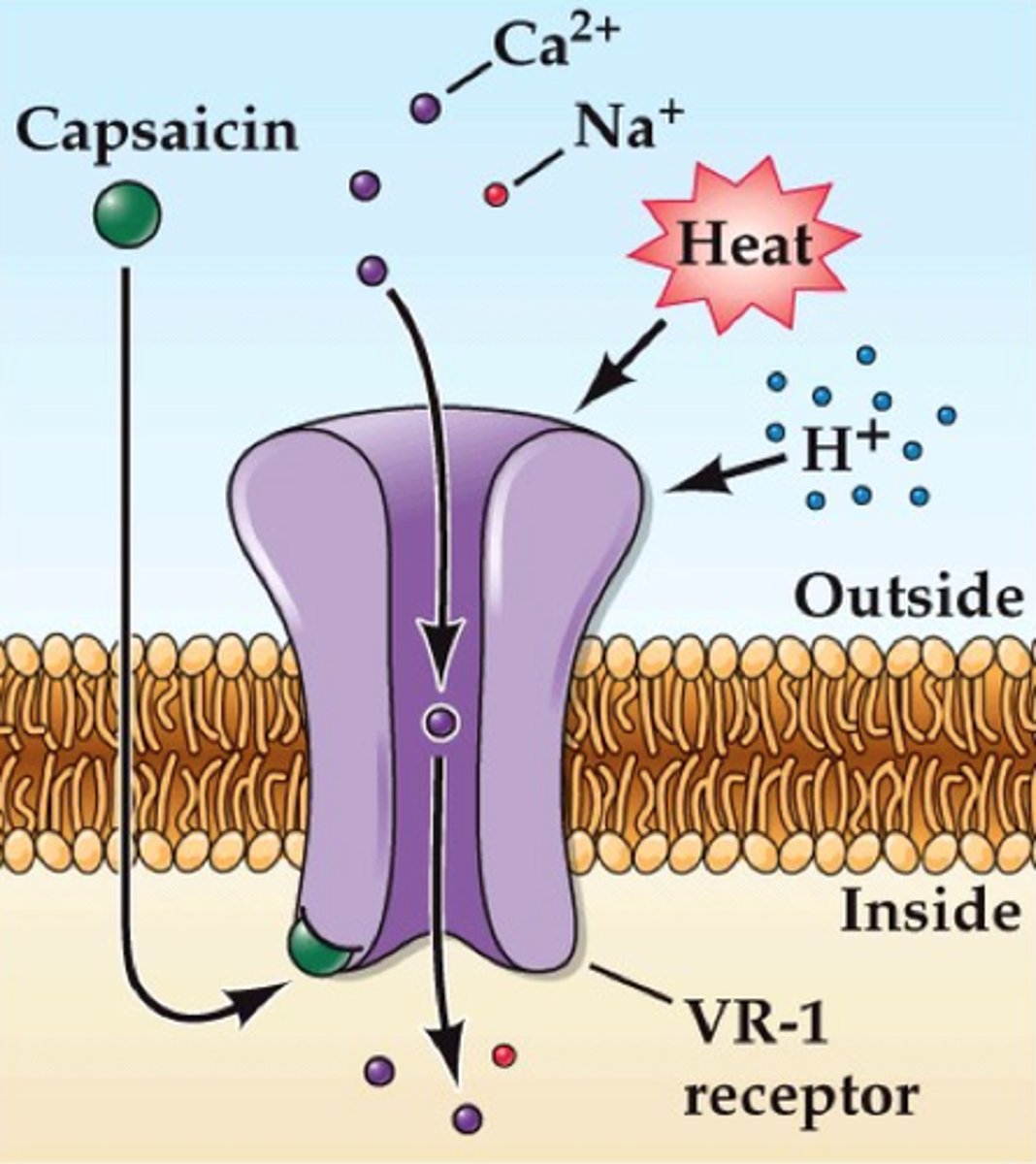
TRPV1
Mediates heat nociception, activated at temperatures greater than 43C. Tissue damage may release chemicals that open this channels
Also activated by capsaicin, which may mimic chemicals released from damaged tissue. Capsaicin cannot be detected w/o TRPV1
Itch
Pain can modulate or suppress itch (imagine scratching a bug bite!)
Histamine binds to TRPV1 which causes itchiness.
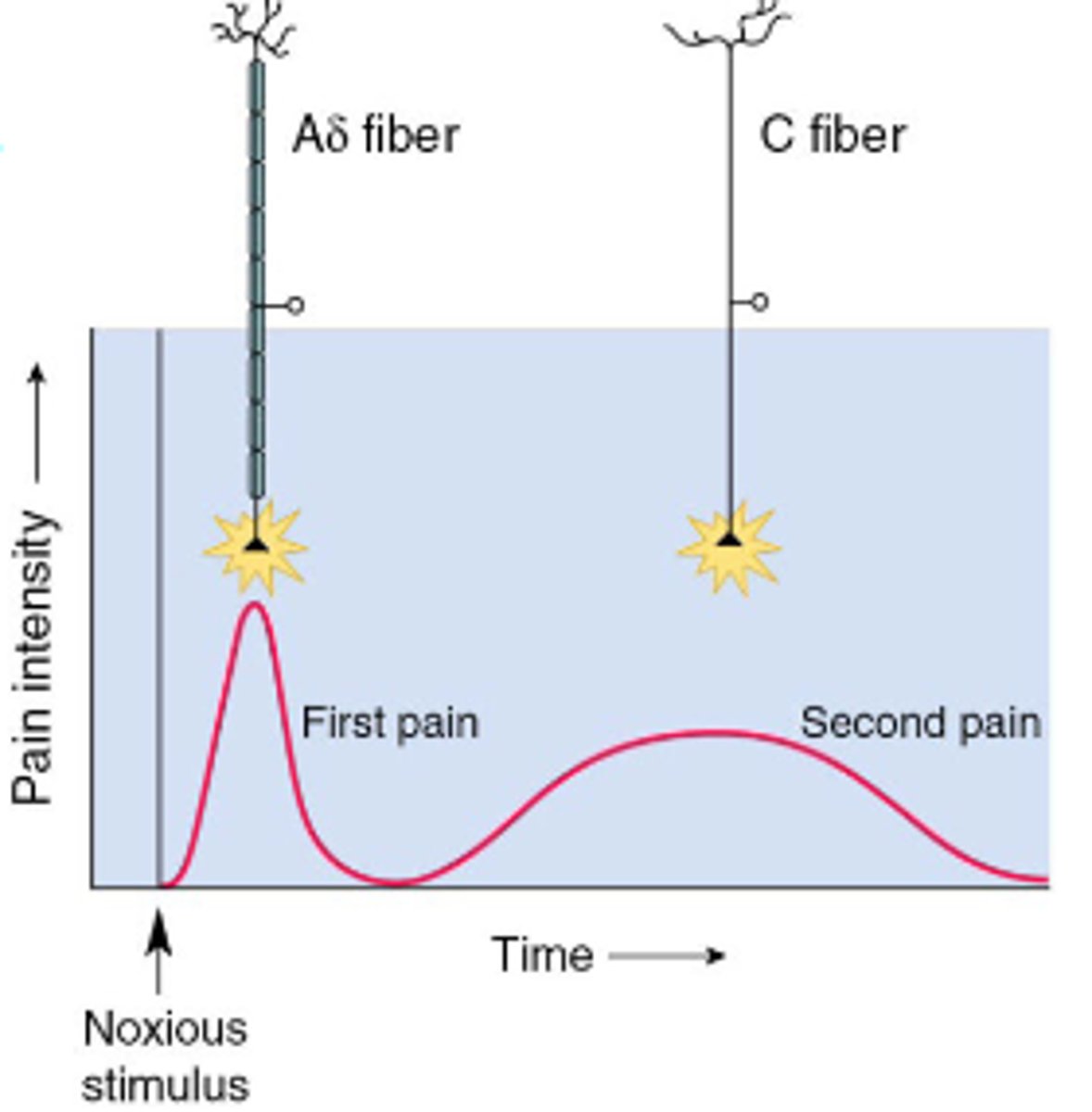
Dual axon pathways
Nociception is transmitted via Aδ and C axons, nociception is much slower than somatic touch.
Two distinct pain perceptions - first pain (fast, sharp) and second pain (slow, dull)
Pain pathway
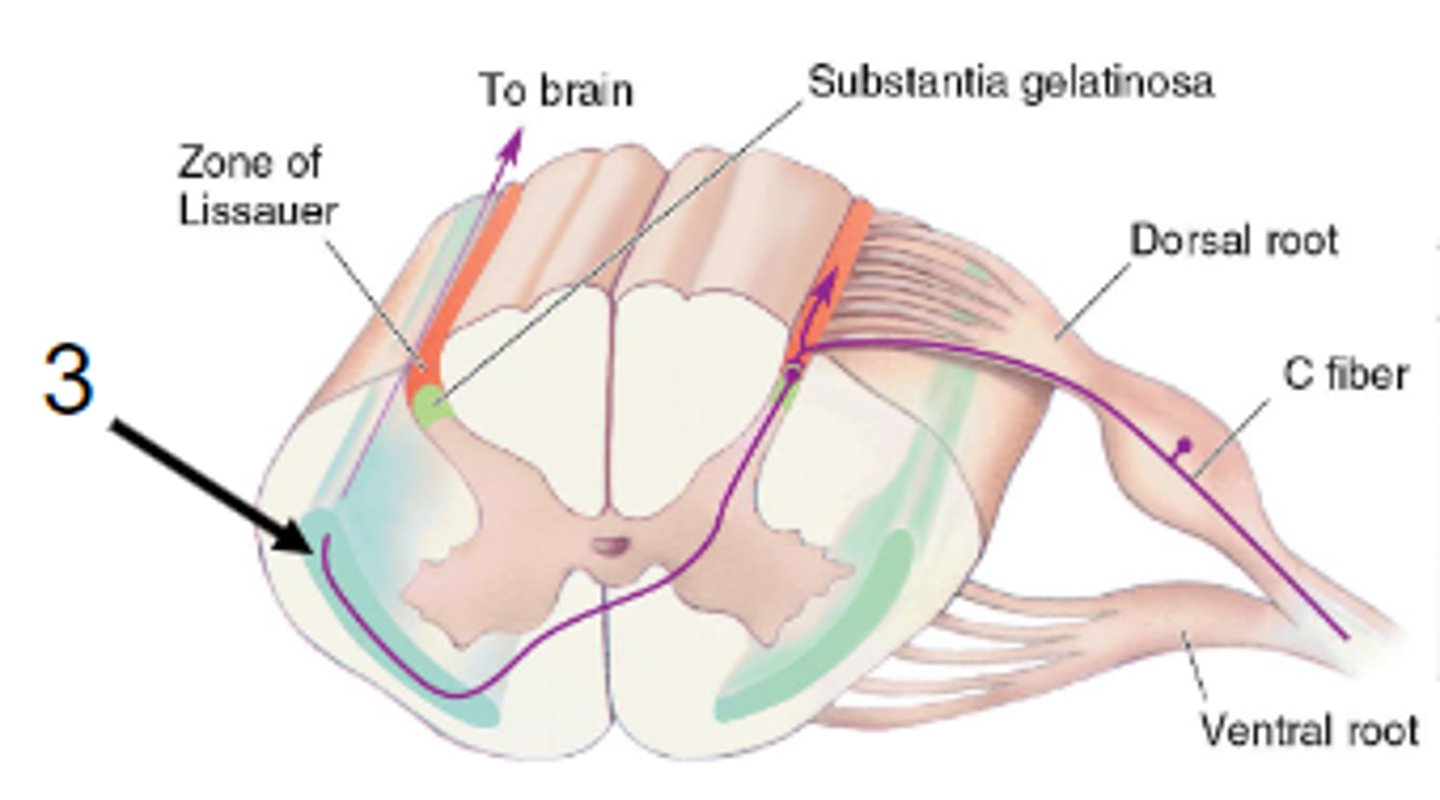
Nociceptive primary afferents have cell bodies in dorsal root ganglia.
Primary afferents branch on ipsilateral side at a short distance on spinal cord
Projections from neurons in substantial gelatinosa cross and ascend
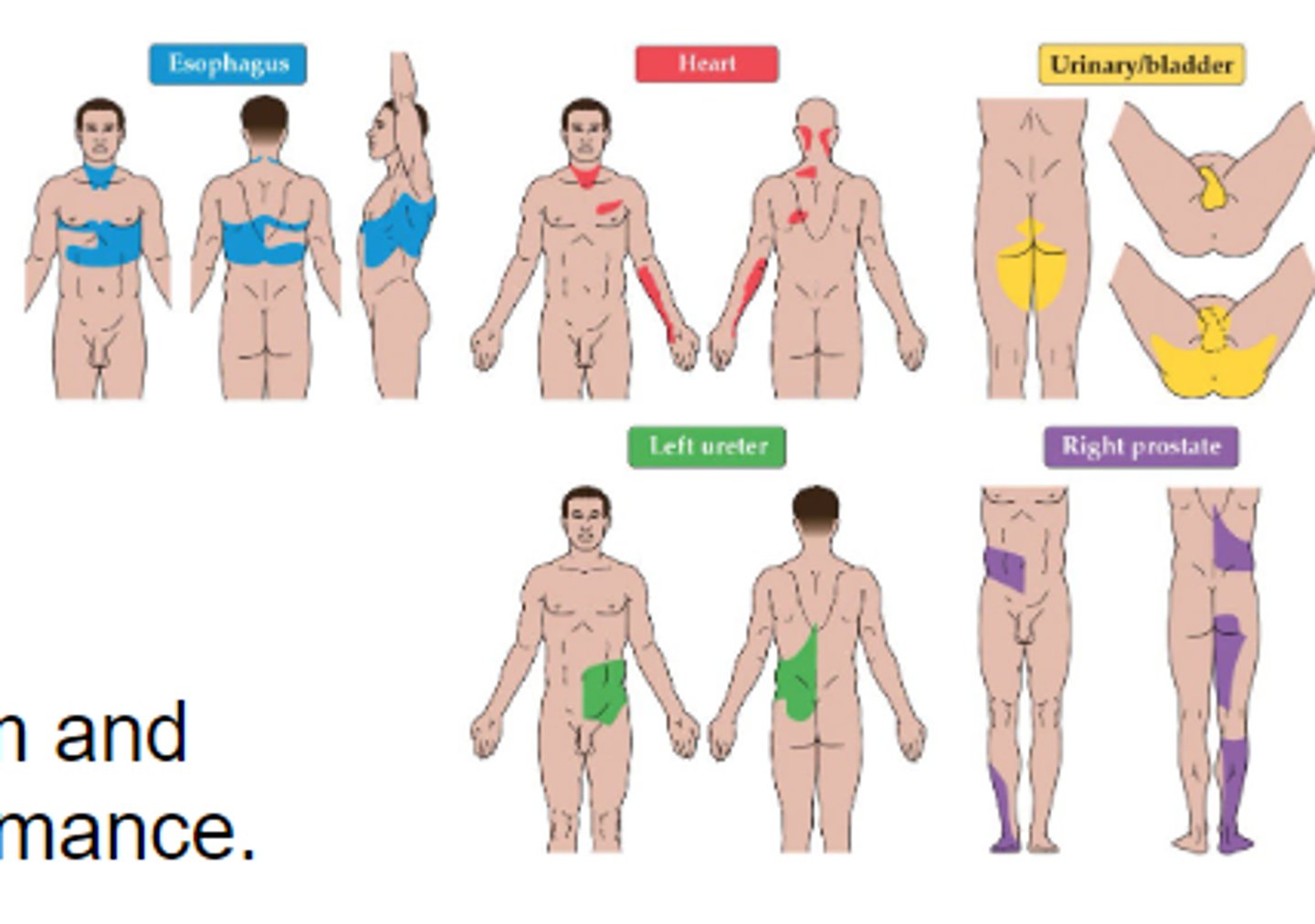
Referred pain
Damage/issue w/ an internal organ results in specific sensations of pain across the body. Caused by visceral nociception (from organs) mixing w/ cutaneous nociception
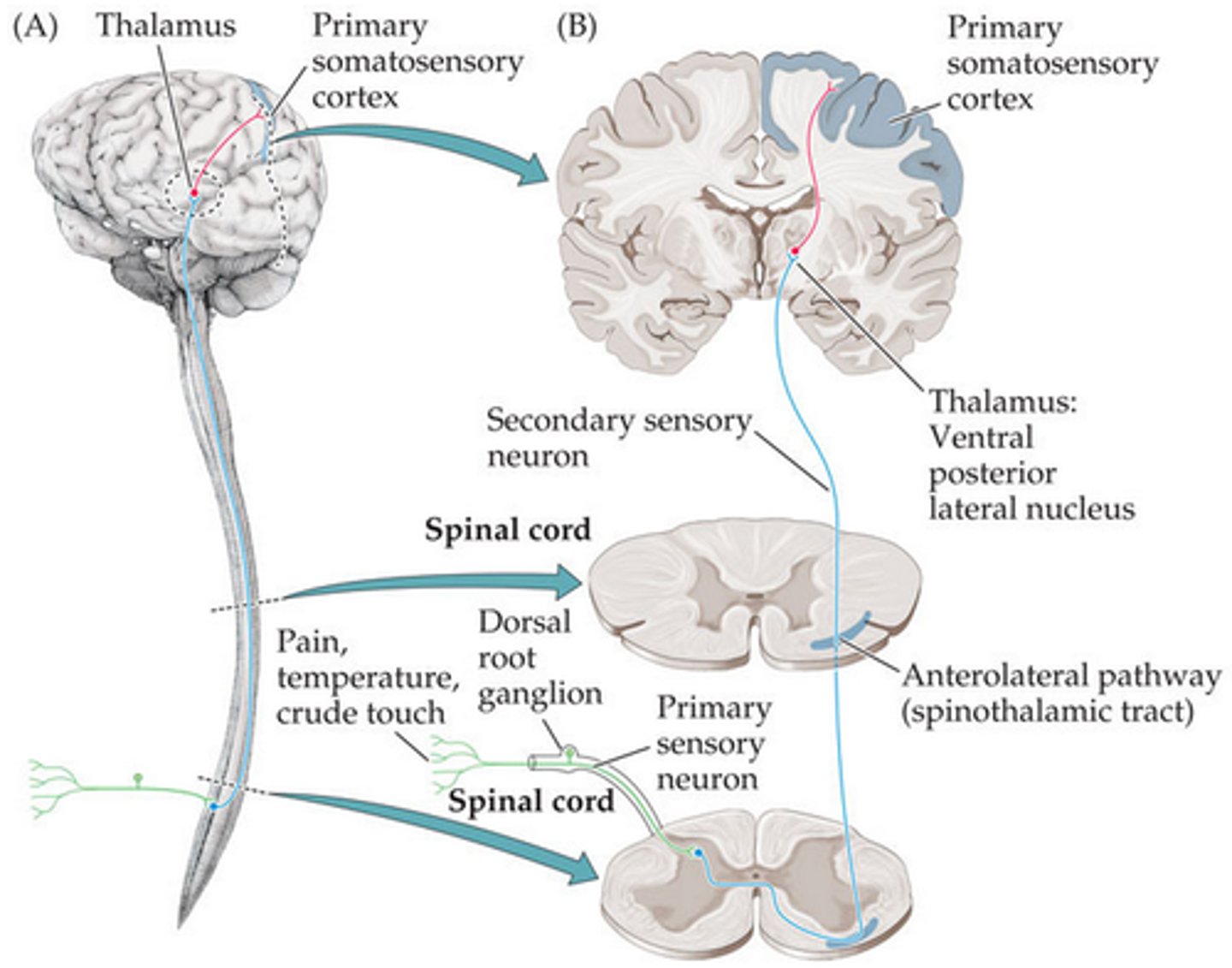
Spinothalamic pathway
The route from the spinal cord to the brain that carries most of the information about skin temperature and pain.
1. Synapses on 2nd order neurons in substantia gelatinosa
2. Decussates
3. Ascends to thalamus
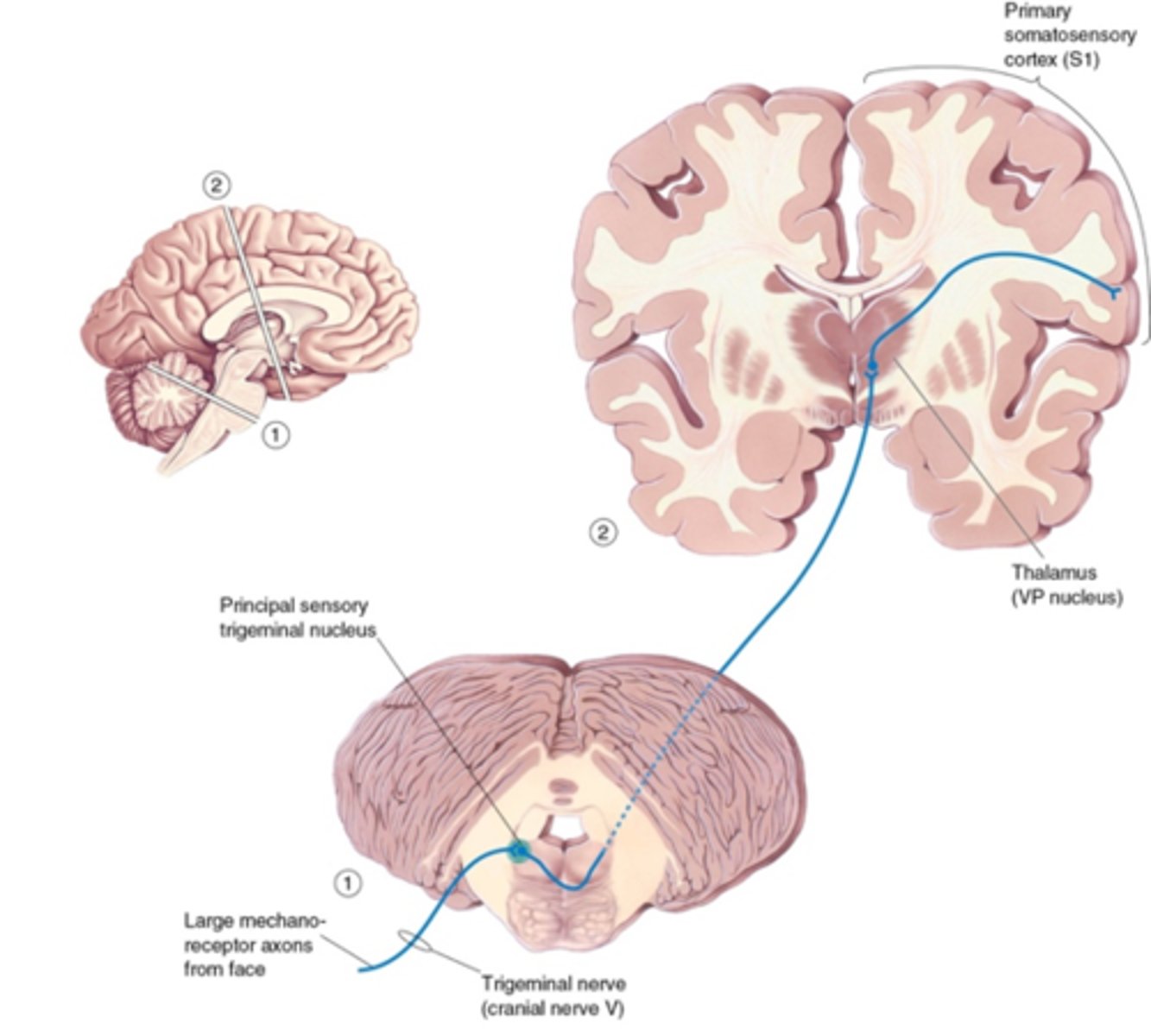
Trigeminal pathway
Carries pain and temperature information from the face and head.
1. Primary afferent innervates 2nd order neurons in spinal trigeminal nucleus
2. Decussates
3. Ascends to thalamus
Touch vs. pain
Touch ascends ipsilaterally (same side) and is mediated by the dorsal column-medial lemniscus pathway
Pain ascends contralaterally (opposite side) and is mediated by the spinothalamic/trigeminal pathway.
Nociceptive vs. mechanosensory pathways
Nociceptive information decussates at the level of spinal cord innervation, while mechanosensory information doesn't cross until reaching the dorsal column nucleus
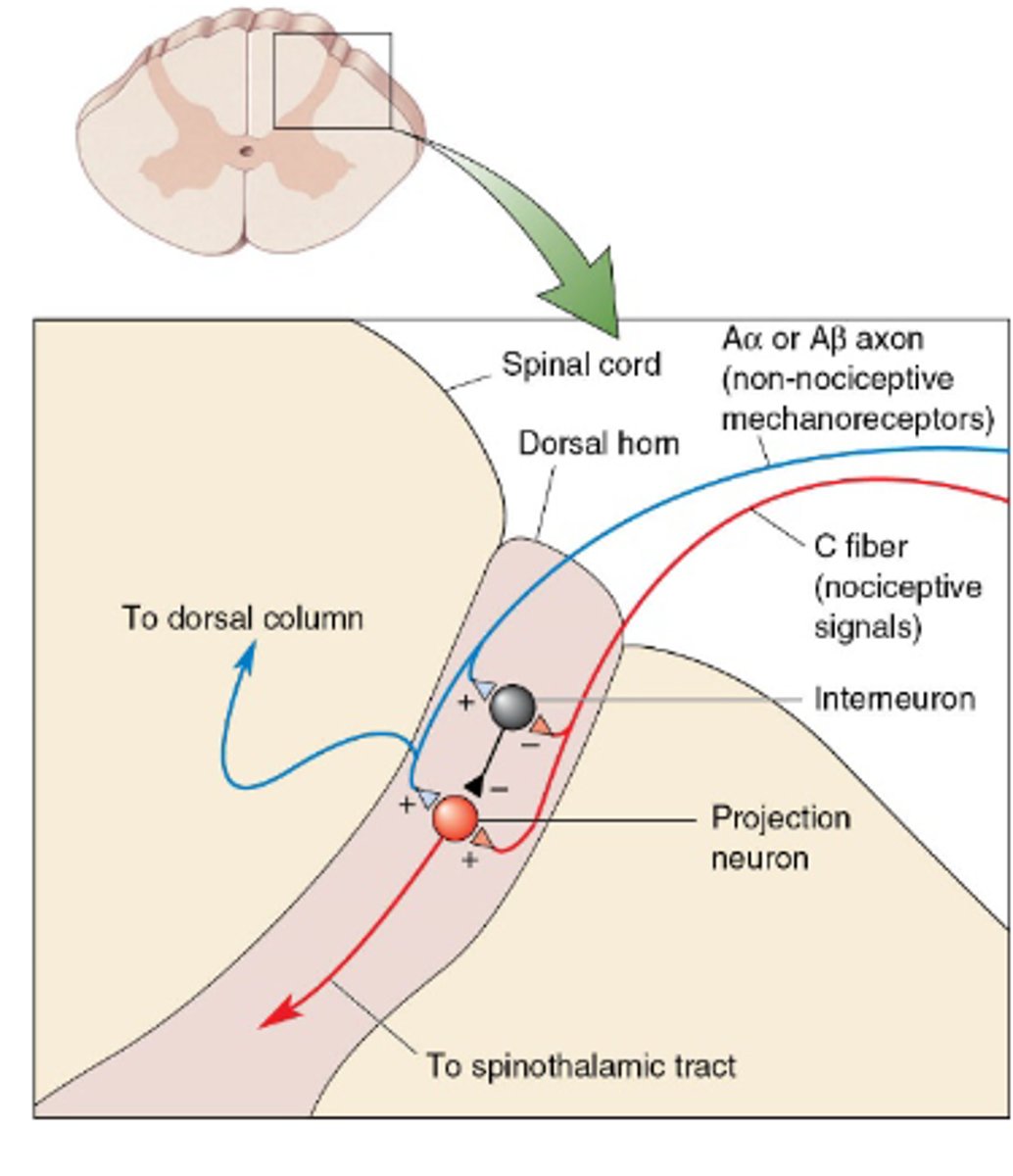
Gate theory of pain
Mechanical stimulation could activate an interneuron that inhibits spinothalamic tract. Concurrent activation of somatic and nociceptive neuron leads to a reduced nociceptor response
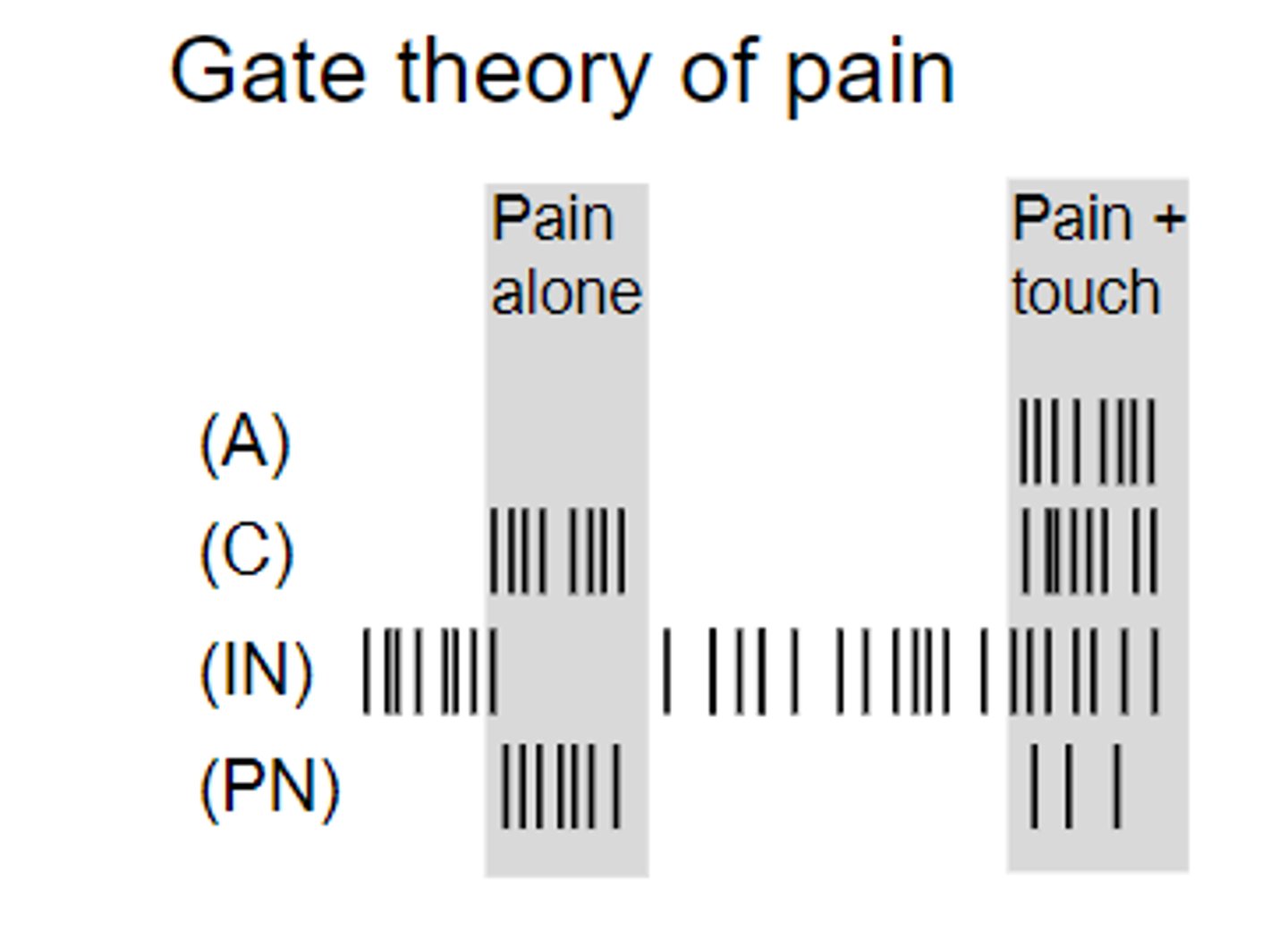
Gate theory of pain
IN normally inhibits PN - decreasing pain.
During pain - (C) inhibits IN, increasing PN
Pain + touch - partially activates IN, inhibiting PN
Endogenous opioids
Endorphins, enkephalins, and dynorphins. Directly modulates nociceptive fibers by binding to receptors in the CNS.
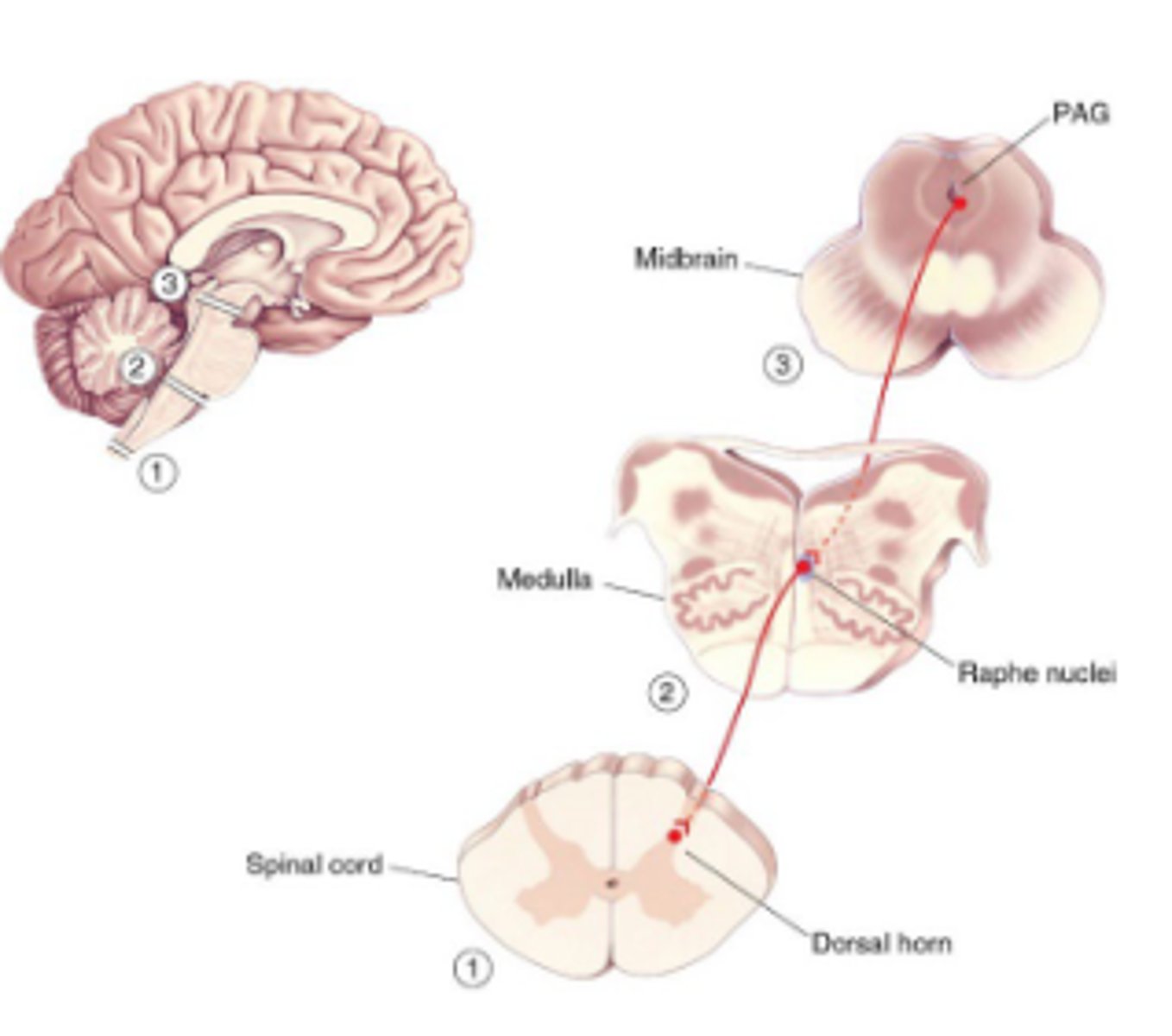
Descending feedback
Electrical stimulation of periaqueductal gray matter (PAG) results in analgesia (being pain-free while conscious)
PAG receives input from parts of brain involved w/ emotional state, which descend to spinal cord.
TRP channels
Mediate temperature sensing, an array of different receptors which allow for perception of very small differences in temperature
Adaptation
Thermoreceptors exhibit this - are usually most sensitive to initial temperature changes which then eventually falls off.
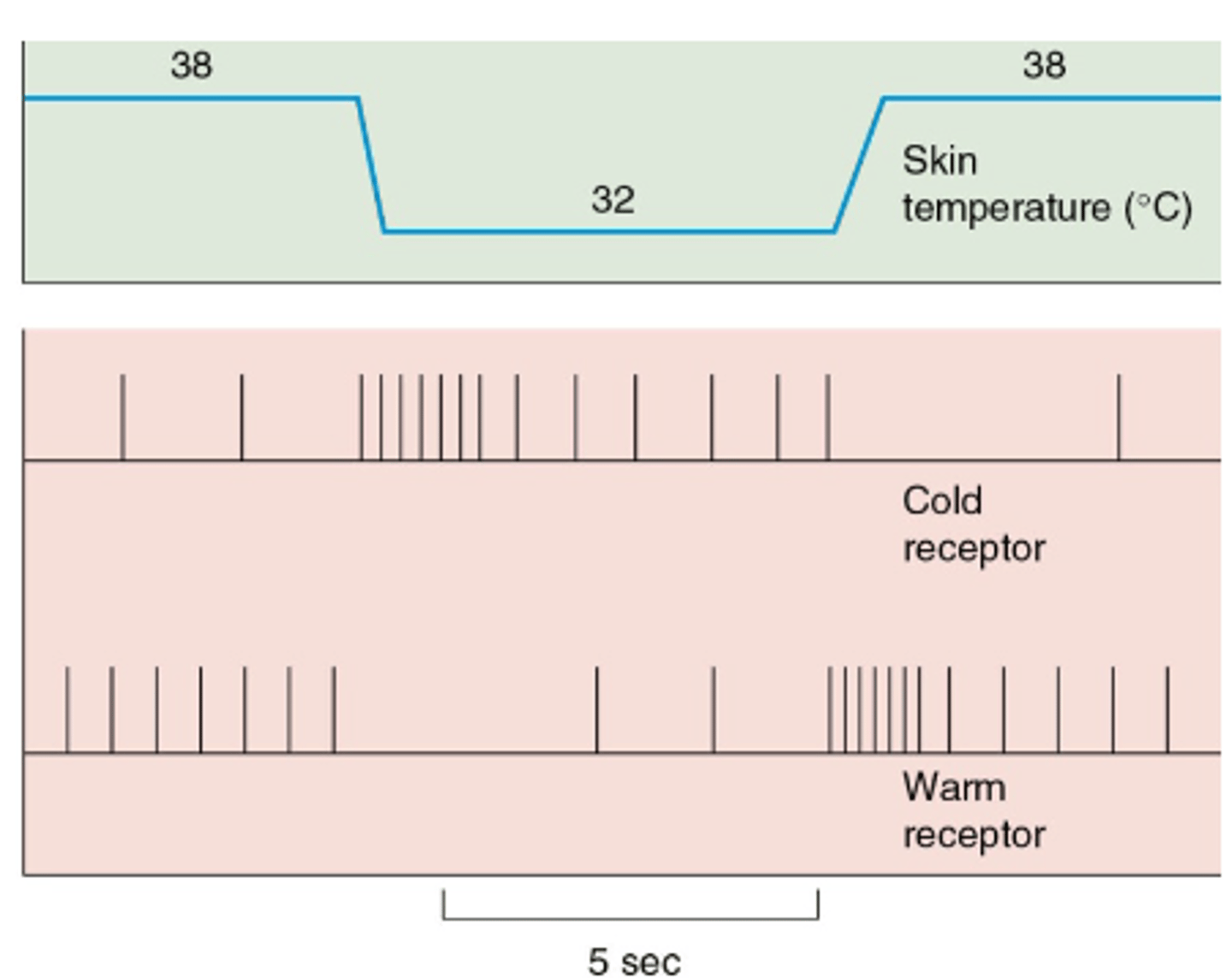
Hot receptors
Coupled to C fibers
Cold receptors
Coupled to Aδ and C fibers