c1.2 cell respiration
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
what is ATP?
adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is a nucleotide consisting of
ribose
3 phosphate groups
adenine
it is known as the energy currency of cells and more specifically used for storing and transferring energy.
what are 5 important properties of ATP?
water-soluble but unable to diffuse easily across membranes
very reactive but also easily reversible
energy produced through hydrolysis is sufficient
what are some cellular processes requiring ATP?
active transport (pumping substances against their conc. gradient requires energy and the energy from hydrolysis causes a change to the protein pump)
anabolism (endergonic reaction so each condensation reaction requires energy; the linkage of a monomer to polymer requires the conversion of ATP to ADP)
movement of cell components + cell
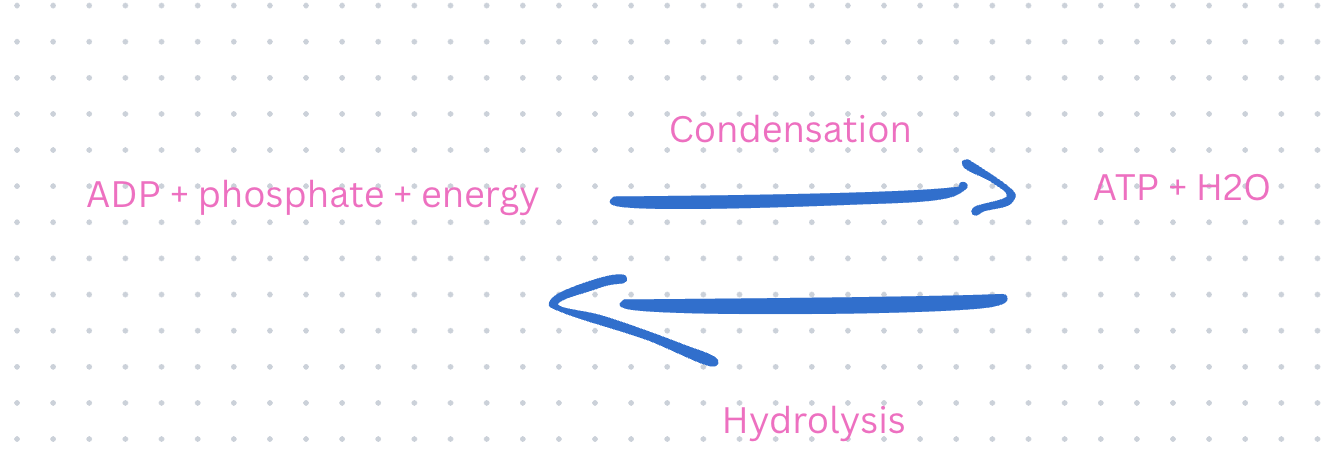
describe converting between ATP and ADP
When a cell breaks ATP into ADP (adenosine diphosphate) and a phosphate, it releases energy that the cell can use.
But to make ATP again from ADP and phosphate, the cell needs to use energy. It is a phosphorylation reaction.
define cell respiration.
the oxidation of carbon compounds to release energy in the form of ATP.
what are the main substrates of cell respiration?
glucose and fatty acids
what is the first step of cell respiration for both anaerobic and aerobic?
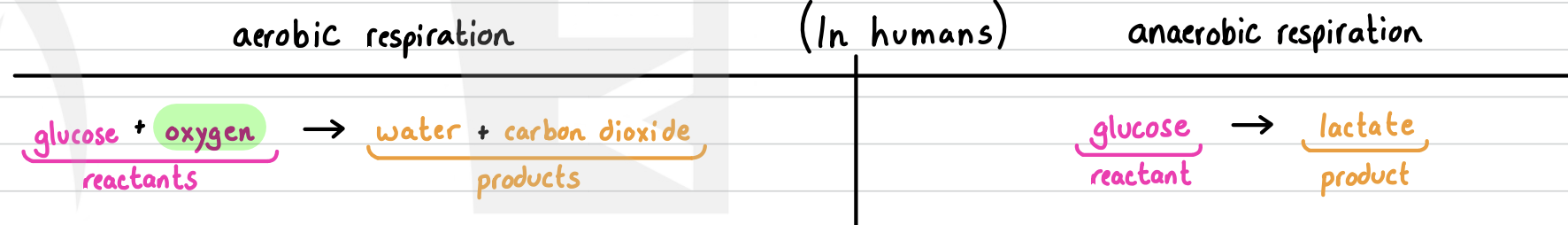
glycolysis: breakdown of glucose into 2 pyruvate molecules producing a net 2 ATP (FYI: anaerobic is cell respiration in the absence of oxygen, aerobic requires oxygen)
explain anaerobic respiration.
lactic acid fermentation produces lactate: this happens when there is a high demand of energy and not enough oxygen to perform aerobic respiration. however, there is a limit to the amount of lactate that can be stored due to increasing acidic conditions.
alcoholic fermentation produces ethanol and carbon dioxide: occurs in yeast. used commercially to produce alcoholic beverages and bake bread.
explain aerobic respiration.
after glycolysis, the Krebs cycle process happens along with the electron transport chain—yielding a greater amount of ATP.
compare anaerobic and aerobic respiration

what are the word equations for anaerobic and aerobic respiration?