AP Biology Unit 4 MCQs
1/22
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
Which of the following stages of the cell cycle is NOT part of interphase?
(A) G0
(B) G1
(C) G2
(D) S
(A) G0 is the stage of the cell cycle in which the cell is not actively dividing. Fully differentiated cells are in G0. Interphase consists of G1, S, and G2, so choices (B), (C), and (D) are incorrect.
Deletion of a newly discovered gene in cell cultures results in an increase in the number of mutations during DNA replication in those cells. This newly discovered gene is most likely a(n) __________.
(A) cyclin-dependent kinase gene
(B) oncogene
(C) proto-oncogene
(D) tumor suppressor gene
(D) Tumor suppressor genes detect defects in DNA replication and prevent the replication of cells with those defects. Choice (A) is incorrect because cyclin-dependent kinases are not involved in detecting mutations. Both oncogenes and proto-oncogenes stimulate cell division so choices (B) and (C) are incorrect.
Which of the following is an example of positive feedback?
(A) An increase in body temperature causes sweating, which lowers body temperature.
(B) A decrease in blood glucose levels triggers the release of glucagon, which increases blood glucose levels.
(C) An increase in oxytocin levels increases the strength of uterine muscle contractions.
(D) A decrease in blood calcium levels triggers the release of parathyroid hormone, which increases blood calcium levels.
(C) If positive feedback occurs, a stimulus increases the strength of a response and moves the system further from homeostasis, which is the case with oxytocin and uterine contractions. Choices (A), (B), and (D) are incorrect because they describe negative feedback, which brings a system closer to homeostasis.
Auxin is a plant hormone that triggers cell division. A mutation occurs that deletes the gene for the auxin receptor. Which of the following is the most likely result of this mutation?
(A) The cells will still divide but at a faster rate.
(B) The cells will not be able to divide.
(C) The cells will develop a new receptor for the signaling molecule.
(D) The cells will not be affected by the lack of the auxin receptor.
(B) If the target cell lacks receptors for the signaling molecule, it will not be able to initiate the signal transduction pathway that triggers cell division. Choice (A) is incorrect because the cells will not divide if they lack the appropriate receptor for the ligand; the signaling pathway for cell division will not be triggered. Choice (C) is incorrect because individual cells do not evolve new receptors. If the cell lacks the receptors for the signaling molecule, the cell will not be able to respond to the signal, so choice (D) is incorrect.
Cortisol is a hormone produced in response to stress. Hunger is a stressor that can increase cortisol levels. Which of the following is most likely an effect of increased cortisol levels in response to hunger?
(A) increased activation of the immune response
(B) increased storage of calcium in bones
(C) increased reabsorption of water by the kidneys
(D) increased hydrolysis of glycogen to glucose
(D) Cortisol would stimulate the breakdown of glycogen into glucose. This would provide energy, alleviating one of the symptoms of hunger. Choices (A), (B), and (C) are incorrect because the activation of the immune response, increased storage of calcium in bones, and increased reabsorption of water by the kidneys would not increase the energy available to cells.
How do small ligands move between plant cells?
(A) Receptor proteins on plant cell membranes transport the ligands.
(B) Ligands pass through plasmodesmata that connect plant cells.
(C) Ligands can pass through the plant cell membrane unassisted.
(D) Active transport transfers ligands across the plant cell wall.
(B) Small molecules pass between plant cells through channels called plasmodesmata, an example juxtacrine signaling. Choices (A) and (C) are incorrect because plant cells have a cell wall surrounding the cell membrane. So molecules cannot pass through plant cell membranes unassisted nor can they bind to cell membrane receptors unless they can pass through the cell wall first. Choice (D) is incorrect because not all ligands require active transport.
How do growth factors stimulate cell division?
(A) Growth factors bind to multiple cells, grouping them in multicellular structures.
(B) Growth factors bind to cyclic AMP, removing it from the cytosol.
(C) Growth factors bind to cell membrane receptors, triggering a signal transduction pathway.
(D) Growth factors bind to cell membrane phospholipids, which results in increased cell division.
(C) Growth factors bind to receptors, which triggers a signal transduction process that stimulates cell division. Grouping cells together would not trigger cell division, so choice (A) is incorrect. Removing cyclic AMP from the cytosol would most likely disrupt the signaling process that is required to trigger cell division, so choice (B) is incorrect. Choice (D) is incorrect because growth factors bind to receptor proteins, not to membrane phospholipids.
In some autoimmune disorders, the body produces antibodies that bind to cell surface receptors on target cells, blocking them from interacting with other molecules Which of the following is the most likely effect of the binding of the antibodies to the receptors?
(A) increased stimulation of the target cell
(B) the target cell’s inability to respond to ligands
(C) no effect on the target cell
(D) stimulation of gene expression in the target cell
(B) If an antibody binds to the receptor, the ligand will be prevented from binding to the receptor, and the signaling process will not occur. Choice (A) is incorrect because the result will be decreased, not increased, stimulation of the target cell. The effect of the antibody will be decreased stimulation of the target cell, so choice (C) is also incorrect. Since the antibody is preventing the ligand from binding to the receptor, no stimulation of gene expression could be triggered, making choice (D) incorrect as well.
Which of the following best describes the roles of calcium ions and cyclic AMP in the signal transduction process?
(A) They act as ligands.
(B) They act as receptor proteins.
(C) They act as secondary messengers
(D) They act as protein kinases.
(C) Both calcium ions and cyclic AMP function as secondary messengers during cell signaling. Ligands bind to the receptor to start the cell signaling process; neither calcium ions not cAMP do this, so choice (A) is incorrect. Receptor proteins and protein kinases are proteins, but neither calcium ions nor cAMP are proteins. So choices (B) and (D) are incorrect.
Which of the following removes phosphate groups from other molecules?
(A) cyclic AMP
(B) protein kinase
(C) protein phosphatase
(D) adenylyl cyclase
(C) Protein phosphatases remove phosphate groups from other molecules. Choice (A) is incorrect because cyclic AMP functions as a secondary messenger. Protein kinases add phosphate groups to molecules, so choice (B) is incorrect. Choice (D) is incorrect because adenylyl cyclase is the enzyme that catalyzes the formation of cAMP.
The hormone insulin travels through the circulatory system to reach target cells. Insulin is involved in which type of cell signaling?
(A) autocrine signaling
(B) juxtacrine signaling
(C) paracrine signaling
(D) endocrine signaling
(D) Insulin travels long distances through the circulatory system, so this is an example of endocrine signaling. Choice (A) is incorrect because autocrine signaling involves a cell that produces a ligand, and the ligand then binds to a receptor on the same cell that produced the ligand. Juxtacrine signaling is between cell that are in direct contact, so choice (B) is incorrect. Choice (C) is incorrect because paracrine signaling occurs over short distances.
Neurotransmitters travel short distances across synapses. This is an example of which type of signaling?
(A) autocrine signaling
(B) juxtacrine signaling
(C) paracrine signaling
(D) endocrine signaling
(C) Signaling over short distances is paracrine signaling. Choice (A) is incorrect because autocrine signaling involves a cell that produces a ligand and the ligand then binds to a receptor on the same cell that produced the ligand. Juxtacrine signaling is between cells that are in direct contact, so choice (B) is incorrect. Endocrine signaling occurs over long distances, so choice (D) is incorrect.
Which of the following is the most likely reason why some cells do not respond to certain ligands?
(A) Nonresponsive cells lack cyclic AMP.
(B) Nonresponsive cells lack receptors for the ligand.
(C) Nonresponsive cells lack the gene for the ligand.
(D) Nonresponsive cells cannot metabolize the ligand.
(B) If a cell acks the receptor for ligand, the signal transduction process cannot start. Choice (A) is incorrect because is cAMP was lacking, the cell might still be able to mount an incomplete response if the ligand could bind to a receptor and trigger steps in the signal transduction process that do not depend on the presence of cAMP. Ligands are usually not produced in their target cells, so lacking a gene for the ligand would likely have no effect on the target cell, making choice (C) incorrect. Choice (D) is incorrect because the inability to metabolize a ligand would likely not affect the target cell’s ability to respond to the ligand.
A chemotherapy drug stops the replication of DNA. During which stage of the cell cycle would this drug have the greatest effect?
(A) G0
(B) G1
(C) G2
(D) S
(D) DNA is replicated during the S stage of the cell cycle, so a drug that blocks the replication of DNA would have the greatest effect during the S stage. DNA does not replicate during G0, G1, or G2, so choices (A), (B), and (C) are incorrect.
A cell has reached full maturity, is fully differentiated, and no longer divides. Which of the following describes this stage of the cell cycle?
(A) G0
(B) G1
(C) G2
(D) S
(A) During G0, the cell is not dividing and has exited the cell cycle, G1, G2, and S are all stages that prepares the cell to divide, so choices (B), (C), and (D) are incorrect.
Which stage of mitosis has twice as many chromosomes at is end as it had at its beginning?
(A) prophase
(B) metaphase
(C) anaphase
(D) telophase
(C) At the beginning of anaphase, each chromosome consists of two sister chromatids. During anaphase, these chromatids sperate, and at the end of anaphase, each of the chromatids is considered a separate chromosome. Thus, anaphase ands with twice as many chromosomes as it had at its beginning. During prophase, chromosomes condense and become visible, but the number of chromosomes does not change. So choice (A) is incorrect. Choice (B) is incorrect because in metaphase, chromosomes line up along the center of the cell but the number of chromosomes does not change. In telophase, two new nuclei are formed and the number of chromosomes per cell at the end of telophase is less than it was at the beginning of telophase. Thus, choice (D) is also incorrect.
During which stage of mitosis do the centromeres of chromosomes attach to spindle fibers and line up in a single column in the center of the cell?
(A) prophase
(B) metaphase
(C) anaphase
(D) telophase
(B) During metaphase, chromosomes line up in the center of the cell on the metaphase plate. Prophase is when chromosomes condense and become visible, so choice (A) is incorrect. Anaphase is when sister chromatids separate and begin to move to opposite ends of the cell, so choice (C) is incorrect. Telophase is when two new nuclei are formed, so choice (D) is also incorrect.
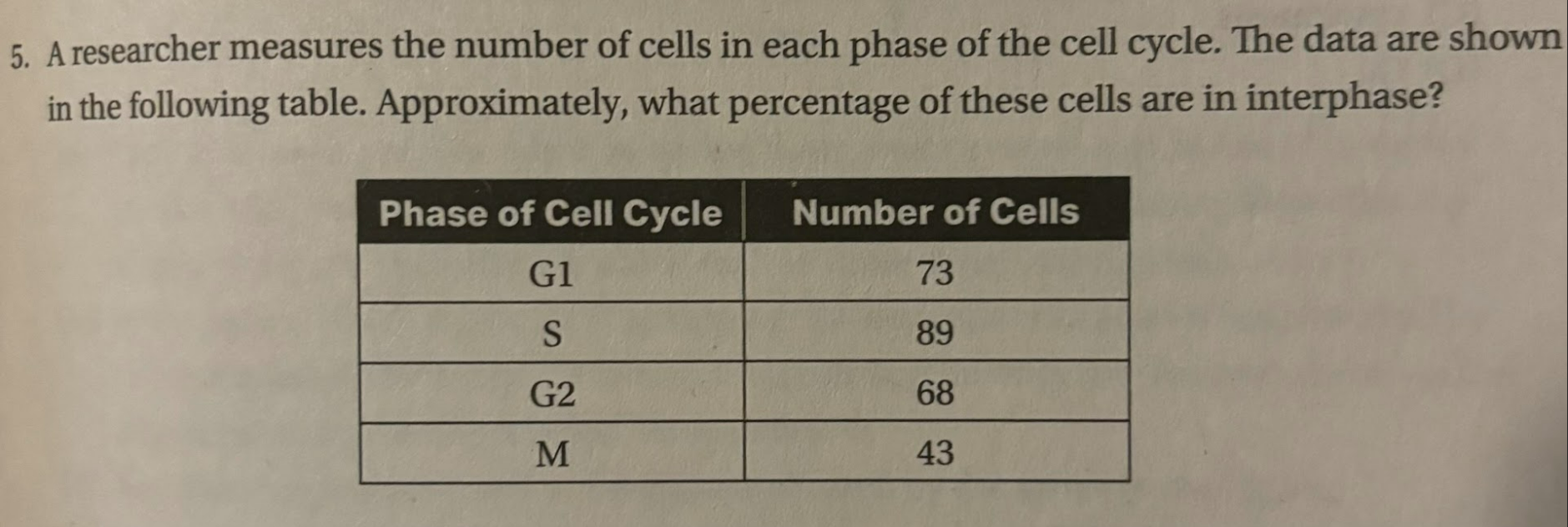
(A) 16%
(B) 33%
(C) 52%
(D) 84%
(D) Interphase consists of G1, S, and G2. Therefore, the number of cells in interphase is 73 + 89 + 68 = 230 cells. The total number of cells is 73 + 89 + 68 + 43 = 273. So the percentage of cells in interphase is ²³⁰⁄₂₇₃ ≈ 84%. Choice (A) is incorrect because 16% is the approximate percentage of cells that are in mitosis. Choice (B) is incorrect because 33% is the approximate percentage of cells that are in the S stage. Choice (C) is incorrect because 52% is the approximate percentage of cells in G1 and G2.
Which process best describes what occurs when soft tissues between the fingers dies during embryonic development?
(A) apoptosis
(B) DNA replication
(C) mitosis
(D) cytokinesis
(A) Apoptosis is programmed cell death, and it can occur during embryonic development when the soft tissue between the fingers to separate. While choices (B), (C), and (D) also occur during embryonic development, choice (A) is the best answer because it is the most specific to the formation of the fingers during embryonic development.
During which process are the cytoplasm (and its cellular contents) divided between daughter cells?
(A) apoptosis
(B) DNA replication
(C) mitosis
(D) cytokinesis
(D) Cytokinesis is the division of the cytoplasm. Choice (A) is incorrect because apoptosis is programmed cell death. DNA replication occurs during the S stage of the cell cycle, so choice (B) is incorrect. Choice (C) is also incorrect because mitosis is the process of evenly distributing replicated chromosomes between the daughter nuclei.
Which of the following is a correct statement?
(A) Cancer cells exhibit anchorage dependence.
(B) Somatic cells exhibit density-dependent inhibition.
(C) Somatic cells spend most of their time in mitosis.
(D) Cancer cells exhibit density-dependent inhibition.
(B) Many somatic cells in organs and tissues exhibit density-dependent inhibition. Cancer cells do not exhibit anchorage dependence not do they exhibit density-dependent inhibition, so choices (A) and (D) are incorrect. Choice (C) is incorrect because noncancerous cells spend most of their time in interphase, not mitosis.
Which of the following best describes a role of mitosis?
(A) Mitosis distributes cytosol between the daughter cells.
(B) Replication of DNA occurs during mitosis.
(C) Replication of cell organelles occurs during mitosis.
(D) Mitosis distributes genetic material between the daughter cells.
(D) Mitosis is the distribution of genetic material between the daughter cells. Cytokinesis, not mitosis, is the distribution of cytosol between the daughter cells, so choice (A) is incorrect. Choice (B) is incorrect because the replication of DNA occurs during the S stage, not mitosis. Replication of cell organelles occurs during G1 and G2, not mitosis, so choice (C) is incorrect.
During which phase of the cell cycle is a cleavage furrow or cell plate formed?
(A) interphase
(B) mitosis
(C) cytokinesis
(D) G0
(C) Cytokinesis is the division of the cytoplasm. In animal cytokinesis, a cleavage furrow is formed. In plant cytokinesis, a cell plate is formed. DNA and cellular organelles are replicated during interphase, but the cytoplasm is not yet divided. So choice (A) is incorrect. Choice (B) is incorrect because mitosis is the distribution of genetic material between the daughter cells. G0 is the nondividing phase of the cell cycle, so choice (D) is incorrect.