The Cytoskeleton + Cell Surfaces (2A)
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
Cell Wall Composition
in eukaryotes - made of cellulose
molecules bind into microfibrils which provide the cell wall’s rigidity & function
in prokaryotes - made of peptidoglycan
polymer consisting of sugars & amino acids forms mesh-like layer
Cell Wall Location
found on the outermost part of the cell
Cell Wall, Cell Types
can be seen in prokaryotes and plant cells (not animal cells)
Cell Wall Function
provides the cell with structural support, shape, and serves as a barrier, which controls what comes in and out of the cell
primary - provide protection and structure to the cell
Cell Wall Shape
a rigid structure surrounding the cell membrane (outermost layer of the cell)
Is the Cell Wall Membrane-Bound?
NO! it is outside of the cell membrane
Extracellular Matrix Structure
boundary cell, has strong interwoven fibers
EM Composition
glycoproteins + polysaccharides
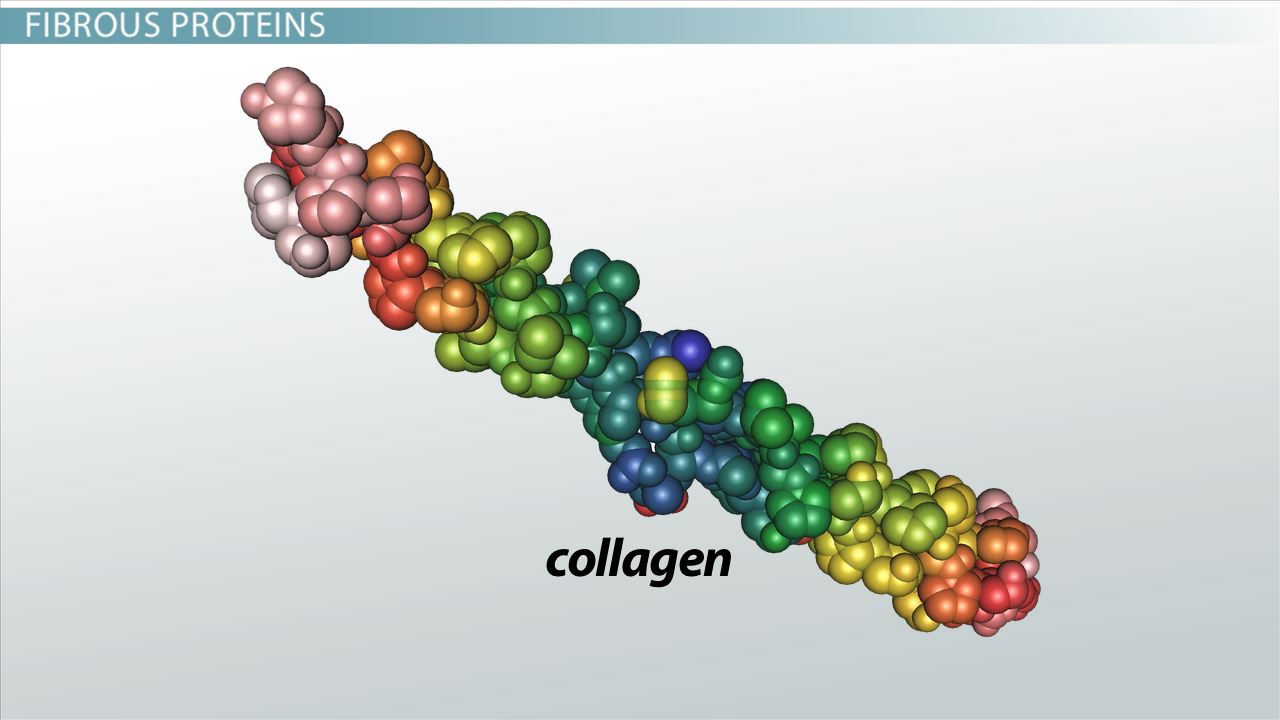
EM Shape
resembling a mesh or a lattice
Is the EM Membrane-Bound?
No! located outside of the cell membrane
EM location
attached to the cell membrane through glycoproteins binding to membrane proteins called integrins
EM, Cell Types
eukaryotic animal cells
EM Function
holds one cell to another cell (like glue) + protects and supports cell membrane
primary - provide structural support for cells within a tissue
EM Interactions
helps cell membrane (+ connects to it)
communicates changes occurring inside and outside of the cell through the cytoskeleton
Cilia Shape
short, numerous appendages that propel Paramecium (hairs)
animal cells
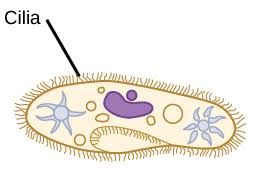
Flagella Shape
tail-like shape, long, identified by looking for a long tail attached to the main body of bacteria + archaea cells
Cilia + Flagella Composition
composed of microtubules unwrapped in an extension of the plasma membrane
“9+2” pattern
nine pairs of doublet microtubules surround a central pair of singlet microtubules
Cilia Function
signal receiving “antenna” for the cell but are nonmotile with this function.
all cells have a primary cilium that is important in embryonic development, sensory reception, and cell function
Cilia + Flagella Function
help with cell mobility and movement
dynein proteins are key mechanism in motion of cilia and flagella
Are Cilia + Flagella Membrane-Bound?
Yes! they are both wrapped in an extension of the plasma membrane
Tight Junctions
made of mainly proteins called “claudins”
looks like a branch network w/ lots of strands
attached to the plasma membrane
located on the edge because it has to bind to other cells to create a seal
found in animal cells
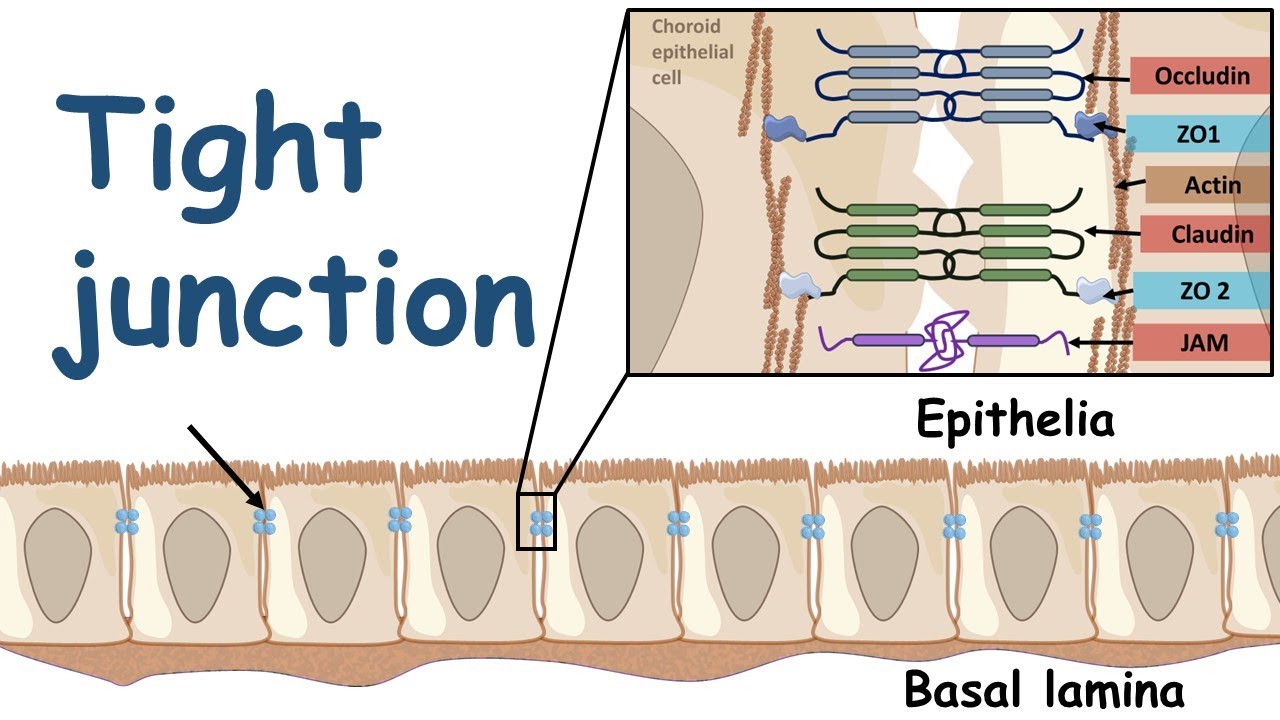
Tight Junctions Function
creates a seal that prevents fluid from moving across a layer of cells
prevents contents of digestive track from leaking to other tissue
Are Junctions Membrane-Bound?
Yes! they have proteins that directly embed themselves within the plasma membrane of adjacent cells
Anchor Junctions
intermediate filaments made of sturdy proteins
anchored in the plasma membrane (membrane-bound)
found in animal cells
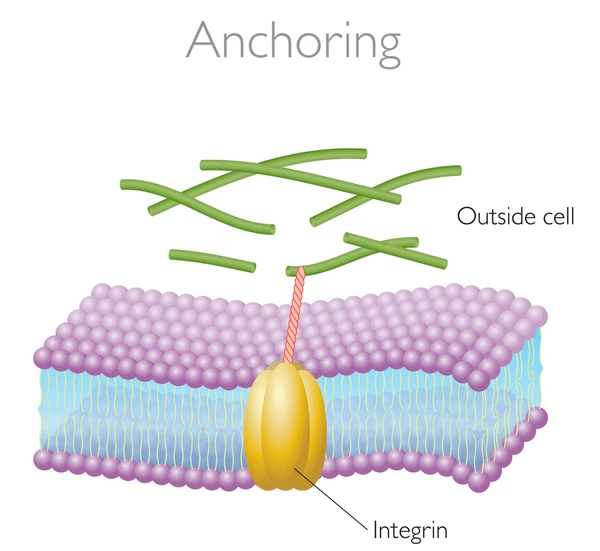
Anchor Junctions Function
function like “rivets”
fasten cells together into strong sheets
Gap Junctions
set of 6 proteins in the plasma membrane
small gaps in cell tissue
attached to plasma membrane
found in animal cells
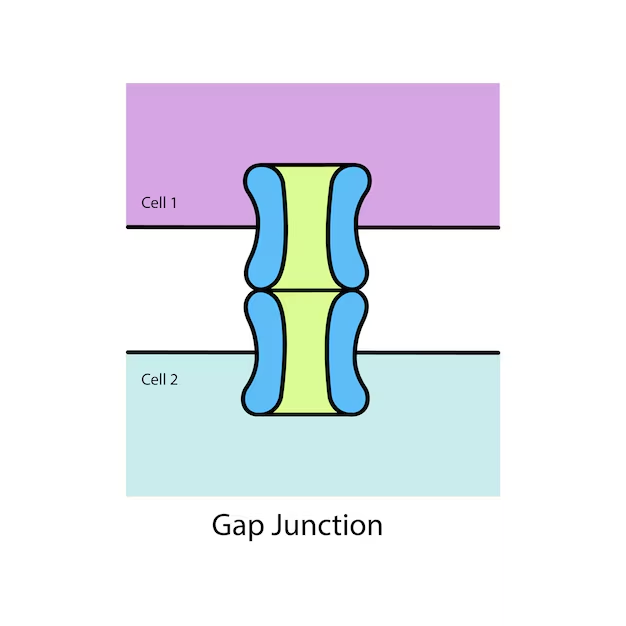
Gap Junctions Function
their main function is to transport ions, nutrients, and other substances that allow cells to communicate
Gap Junction Interaction
the gap junctions interact with the plasma membrane of their own cells and the gap junctions of other cells to communicate with each other
Cytoskeleton Composition
made from microfilaments (10nm) which are made of actin, intermediate filaments (6-7nm)
which are made from various proteins (keratin)
the final type of molecule that makes up the cytoskeleton are microtubules (25nm) (made from tubulin proteins)
Cytoskeleton
looks like a group of hair
found in the cytoplasm of both eukaryotic cells (a+p)
Cytoskeleton Function
primary
shapes + supports the cell
helps things move around the cell
Cytoskeleton Interactions
supports the plasma membrane
helping give the cell its overall shape
correct positioning of organelles
provides tracks for the transport of vesicles
in some cells, allows the cell to move
Is the Cytoskeleton Membrane-Bound?
No! it is not enclosed by a membrane