General Terminology (Cram 1/2)
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
Abnormalities that can be seen with the naked eye
Gross pathology
Changes that require the aid of a microscope to be observed
Microscopic pathology
An individual trained to study disease processes
Pathologist
A series or combination of signs resulting from a single cause
Syndrome
Description of abnormal functions, animals cannot have these
Symptoms
Manifestation of disease that can be determined by physical exam or observation
Clinical signs
Abnormality of the affected tissue
Lesion
Expected outcome of the disease
Prognosis
What are the five levels of prognosis?
Excellent
Good
Fair
Guarded
Grave
The study of the causes of disease
Etiology
Factors that are capable of causing disease or tissue damage
Etiological agents
What are the two categories of etiological agents?
Internal factors
External factors
What are the three internal factors?
Genetic
Immune system
Aging
What are the four external factors?
Physical
Infectious
Chemical
Environmental
Most disease are ______ (involving many factors/causative agents)
multifactorial
What are the three classifications of disease?
Congenital disease
Idiopathic disease
Acquired disease
Pneumonia, flea bite dermatitis, and corneal ulcers are all examples of which classification of disease?
Acquired disease
Cancer eye in white faced cattle is an example of which classification of disease?
Congenital disease
The cause of disease is not known, what classification of disease is this?
Idiopathic disease
What are the eight categories used to describe lesions?
Colour
Consistency
Distribution
Margins
Morphological diagnosis
Size
Shape
Surface
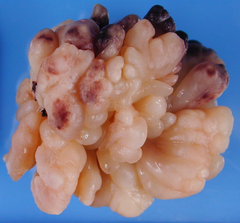
What shape is this lesion?
Botryoid
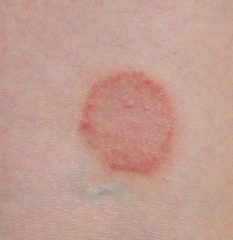
What shape is this lesion?
Circular

What shape is this lesion?
Irregular

What shape is this foreign body?
Oblong
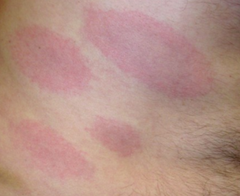
What shape is this lesion?
Ovoid
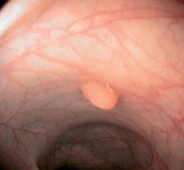
What shape is this lesion?
Polypoid

What shape is this lesion?
Cyst (fluid filled polyp)
Lesion that is shaped like a kidney
Reniform
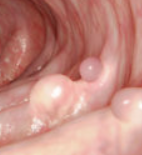
What shape is this lesion?
Spheroid
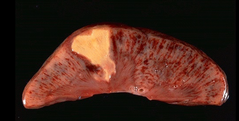
What shape is this lesion?
Wedge–shaped

What is the surface of this lesion?
Bulging
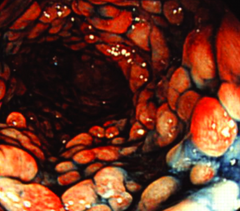
What is the surface of this lesion?
Cobblestoned

What is the surface of this lesion?
Crusting
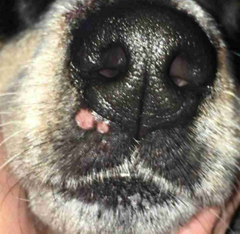
What is the surface of this lesion? (Does not go through dermal layer like ulcer)
Erosion
Lesion that has a grainy surface
Granular
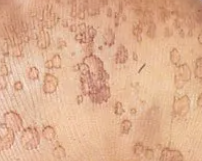
What is the surface of this lesion?
Pitted

What is the surface of this lesion?
Corrugated
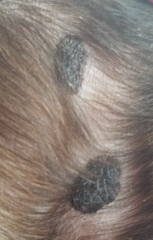
What is the surface of this lesion?
Rough
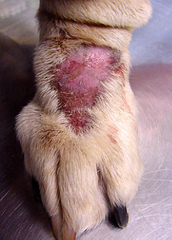
What is the surface of this lesion?
Smooth
Lesion that has lines going in the same direction
Striated
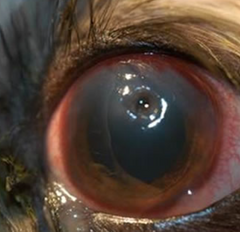
What is the surface of this lesion?
Ulcerated
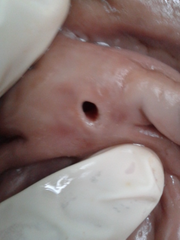
What is the surface of this lesion?
Umbilicated
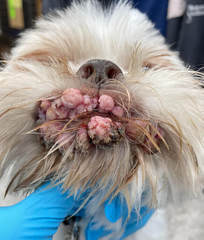
What is the surface of this lesion?
Verrucous
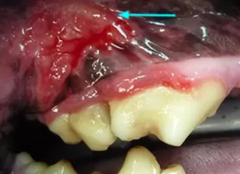
What are the margins of this lesion?
Indistinct
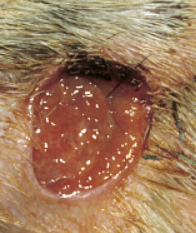
What are the margins of this lesion?
Well–demarcated/distinct
Lesion with margins that go deep into tissue
Infiltrative
Lesion with nipple–like projection
Papillary
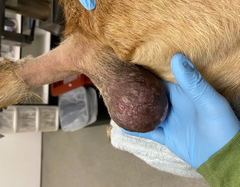
What are the margins of this lesion?
Pedunculated
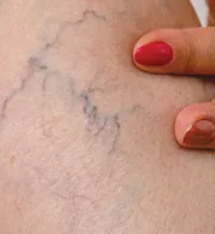
What are the margins of this lesion?
Serpiginous
Lesion with margins that resemble the teeth of a knife
Serrated
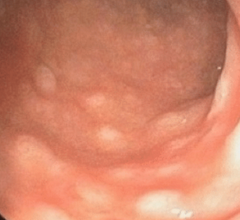
What are the margins of this lesion?
Sessile
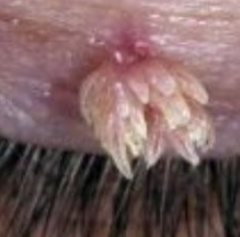
What are the margins of this lesion?
Villous