IB BIOLOGY SL - Midterms (Yr1+Yr2 Sem 1) | Quizlet
1/429
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
430 Terms
Water
A polar molecule, solvent, found inside and outside cells
Buoyancy
Importance of organisms on surfaces (ex. ringed seal) on water
Viscosity
Water's resistance to flowing/overcoming resistance, and energy needed to break
Thermal conductivity
Water conducting heat well
Specific heat
Water having a high heat capacity due to having to break hydrogen and covalent bonds
Monosaccharides (one sugar)
Has high solubility because it is polar, easily transportable, chemically stable, and yields a lot of energy
Fat
Less dense than bone, more buoyant, insulates organisms
Lipids
2x as much energy per gram than carbs, more efficient for long-term energy storage
Steroids
Non-polar, hydrophobic, organic compounds
Monomers (one organic molecule)
Building blocks of organic polymers
Isomers
Molecules with the same molecular formula
Hydrolysis
Breaking down complex molecules by the chemical addition of water
Condensation
Bringing simple molecules into complex molecules with an addition of water in the resultants
Polysaccharides (many sugars)
Made up of many monosaccharides joined by covalent bonds
Cohesion
Attraction between molecules of the same substance (water)
Adhesion
An attraction between molecules of different substances (water v. other)
Catabolic (exergonic reaction)
A process in which large molecules are broken down and release energy
Anabolic
A process in which large molecules are built from small molecules and require energy
Metabolic
All reactions taken place
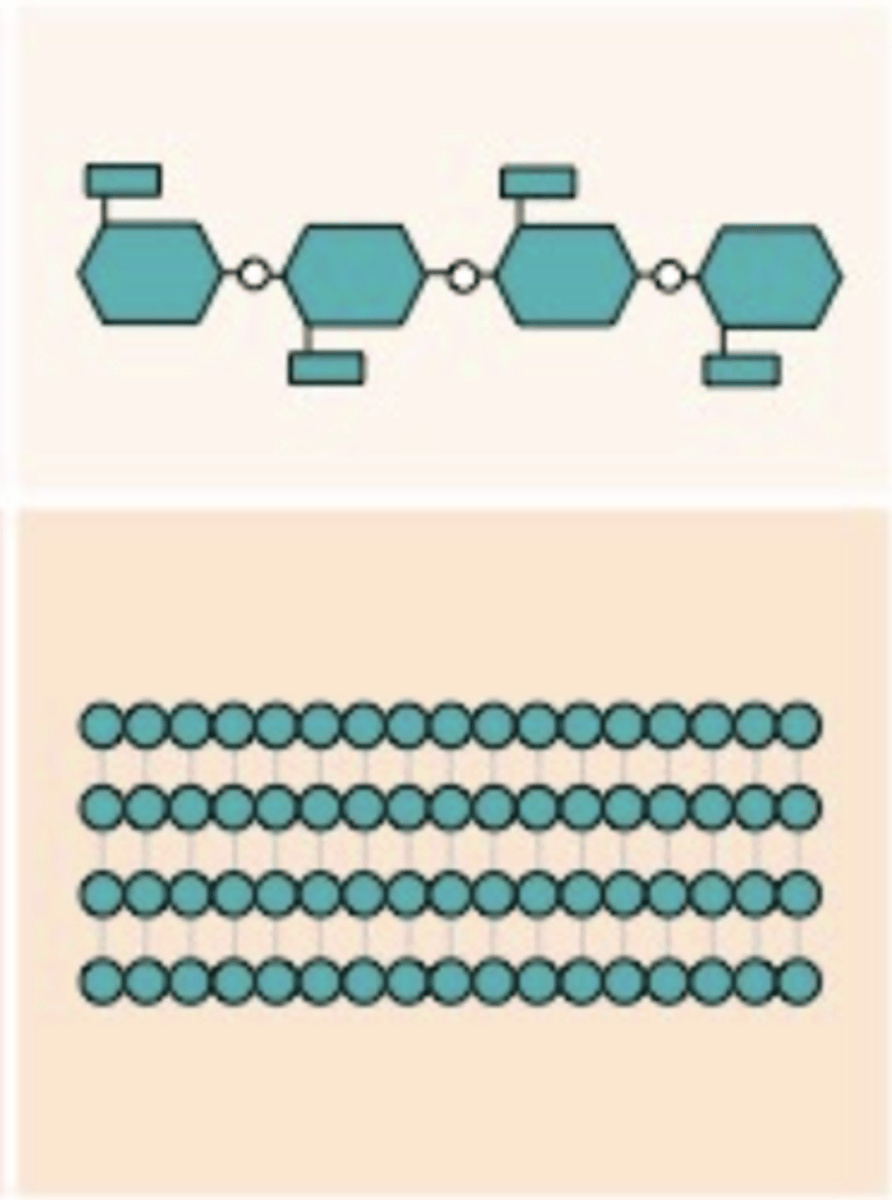
Cellulose
A polysaccharide found in plant walls, with beta glucoses, and are bonded with carbons 1-4
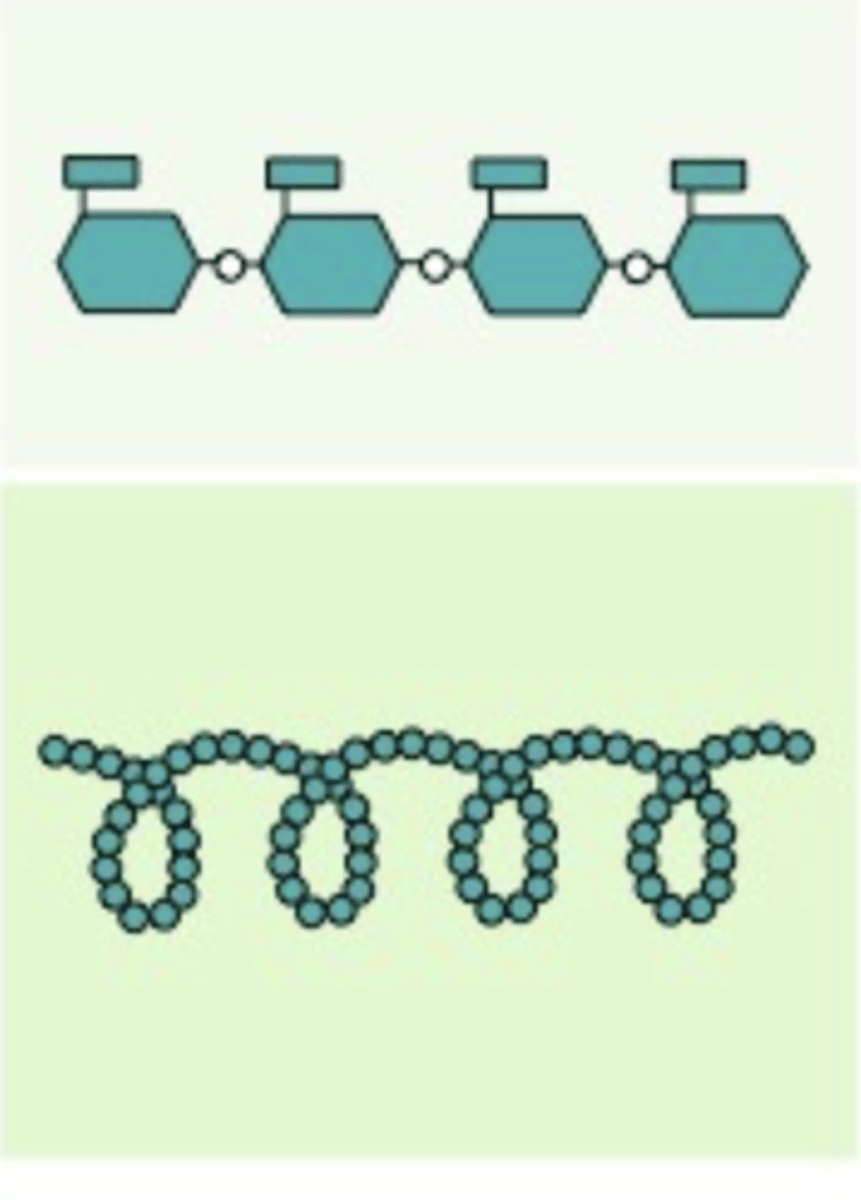
Amylose
A polysaccharide found in plants, with alpha glucoses, and are bonded with carbons 1-4, and is a starch
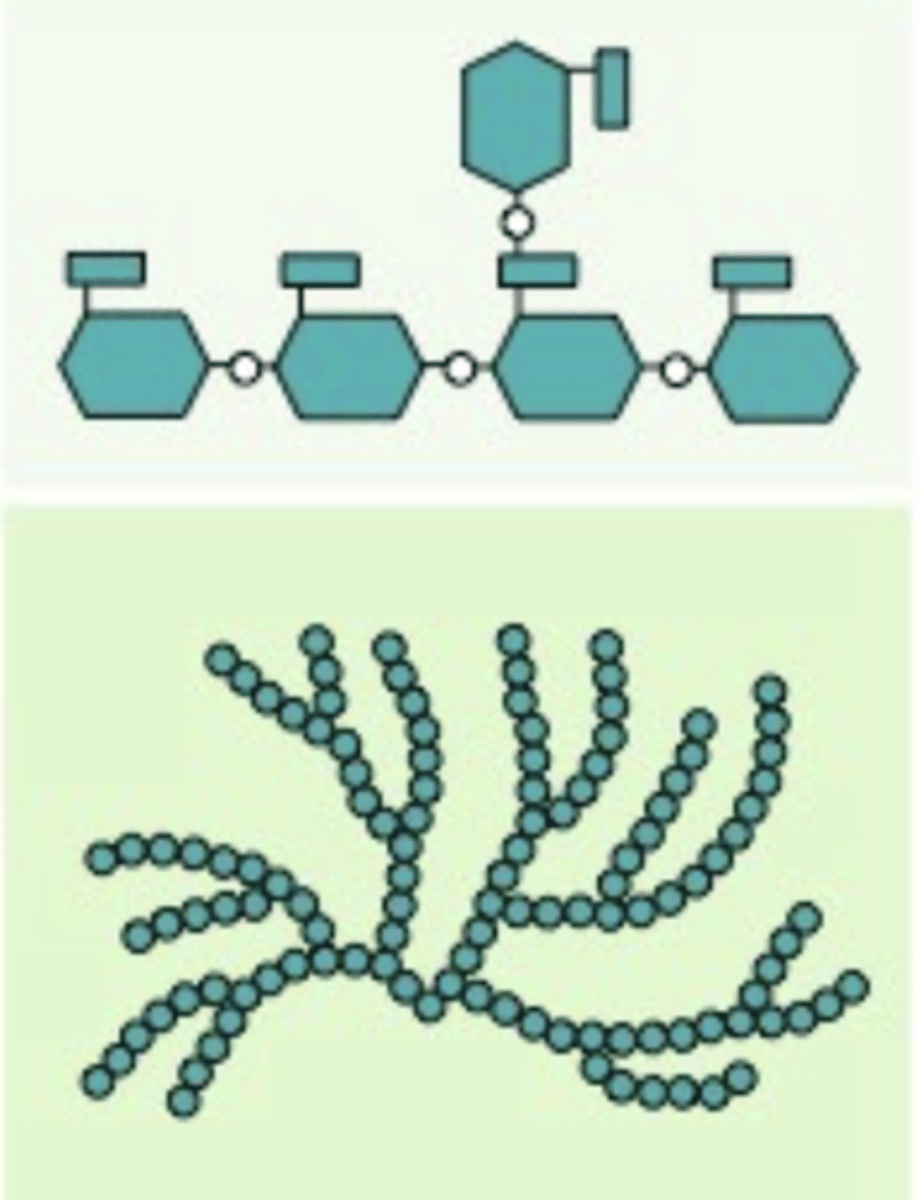
Amylopectin
A polysaccharide found in plants, with alpha glucoses, and are bonded with carbons 1-4, and 6, and is a starch
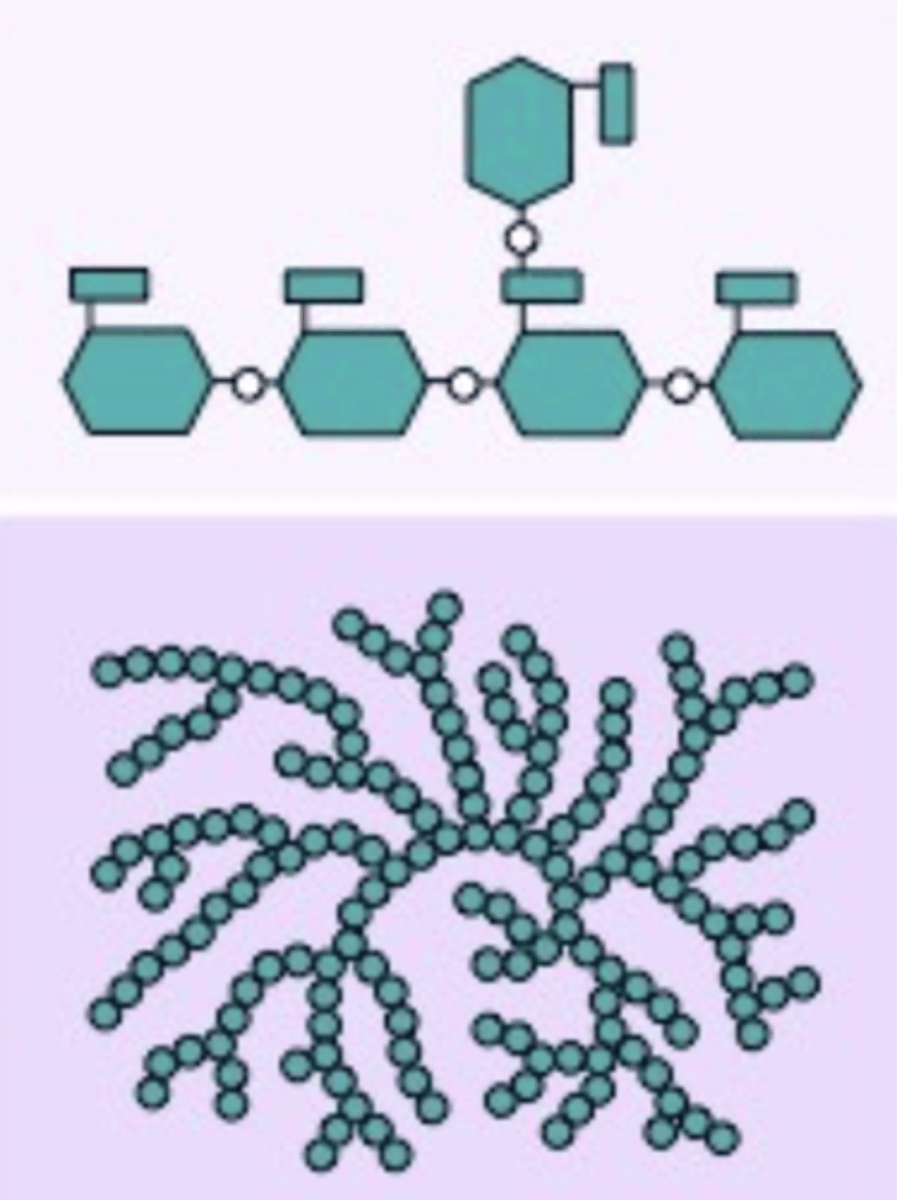
Glycogen
A polysaccharide found in animals, with alpha glucoses, and are bonded with carbons 1-4, and 6, and serves in energy storage
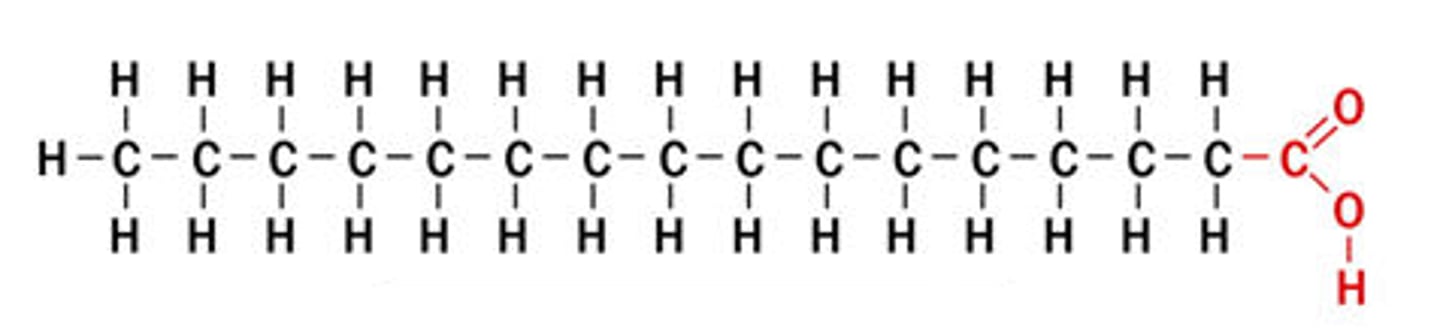
Saturated fatty acid
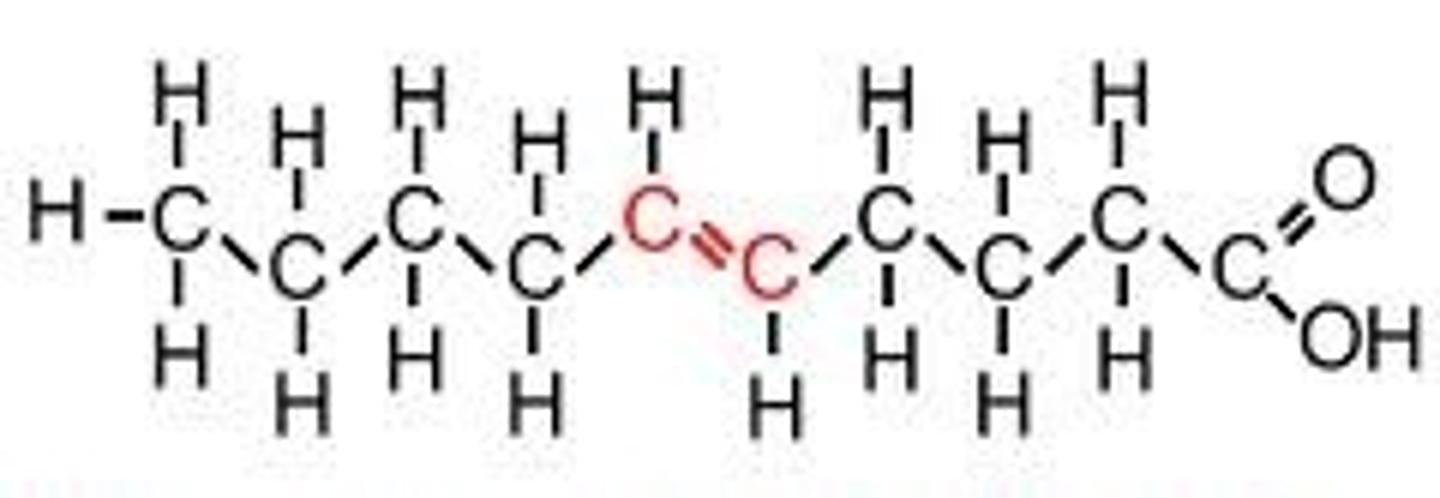
Trans unsaturated fatty acid
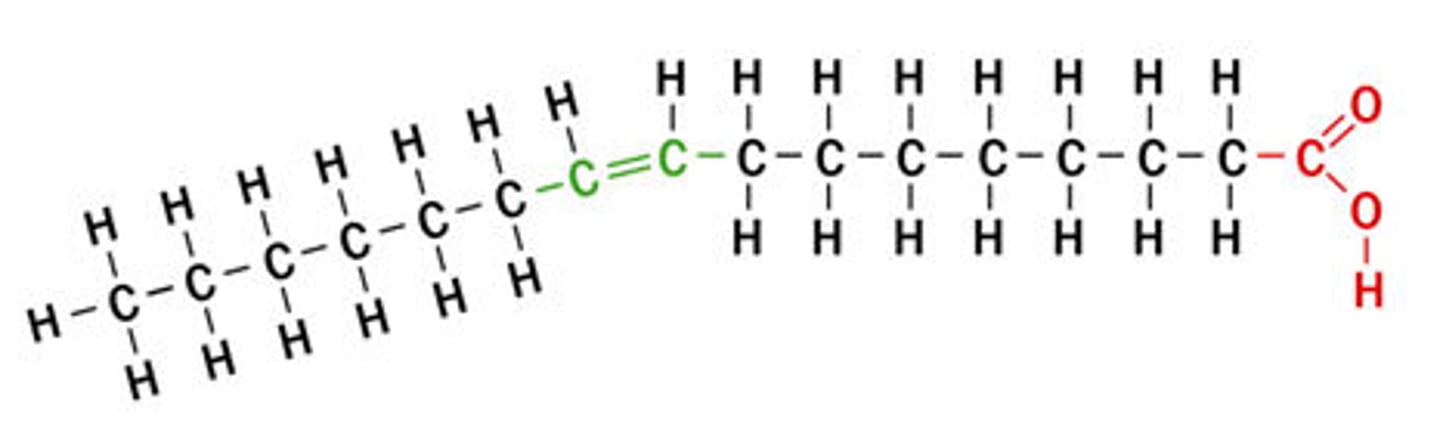
Cis unsaturated fatty acid
Triglycerides
An energy-rich compound made up of a single molecule of glycerol and 3 molecules of fatty acid, resulting in 3 condensation reactions and 3 water molecules as by-products (results in a glycosidic bond)
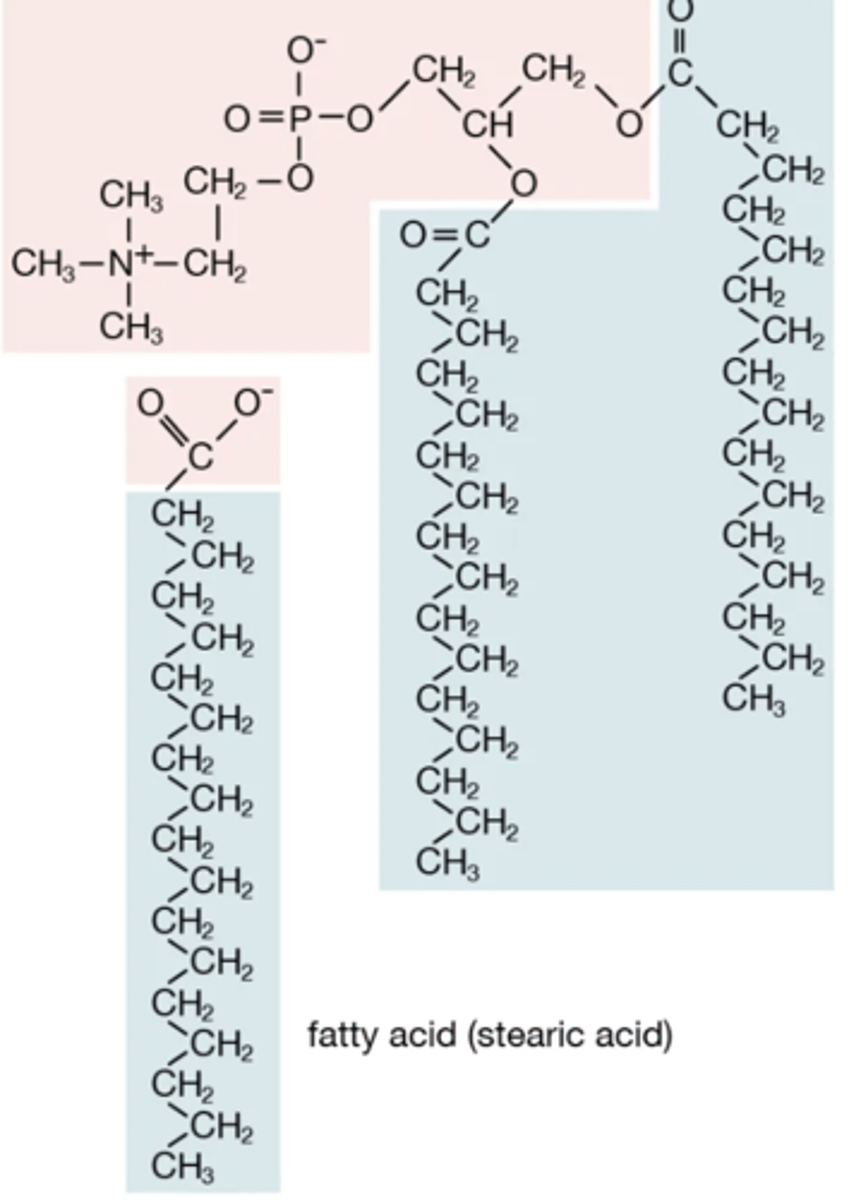
Phospholipids
A lipid consisting of a glycerol bound to two fatty acids and a phosphate group, that have amphipathic components.
Peptide bond
The chemical bond that forms between the carboxyl group of one amino acid and the amino group of another amino acid
Glycosidic bond
Bond formed by a dehydration reaction between two monosaccharides
Ester bond
The bond formed when fatty acid molecules are joined to glycerol molecules in condensation reactions
Primary structure
The first level of protein structure; the specific sequence of amino acids making up a polypeptide chain
Essential foods
A molecule that must be taken in, in the diet and cannot be created by the body itself
Non-essential amino acids
Amino acids that the body can synthesize on its own; does not need to get from dietary sources
Denaturation
A process in which a protein unravels, losing its specific structure and hence function; can be caused by environmental factors
Active site
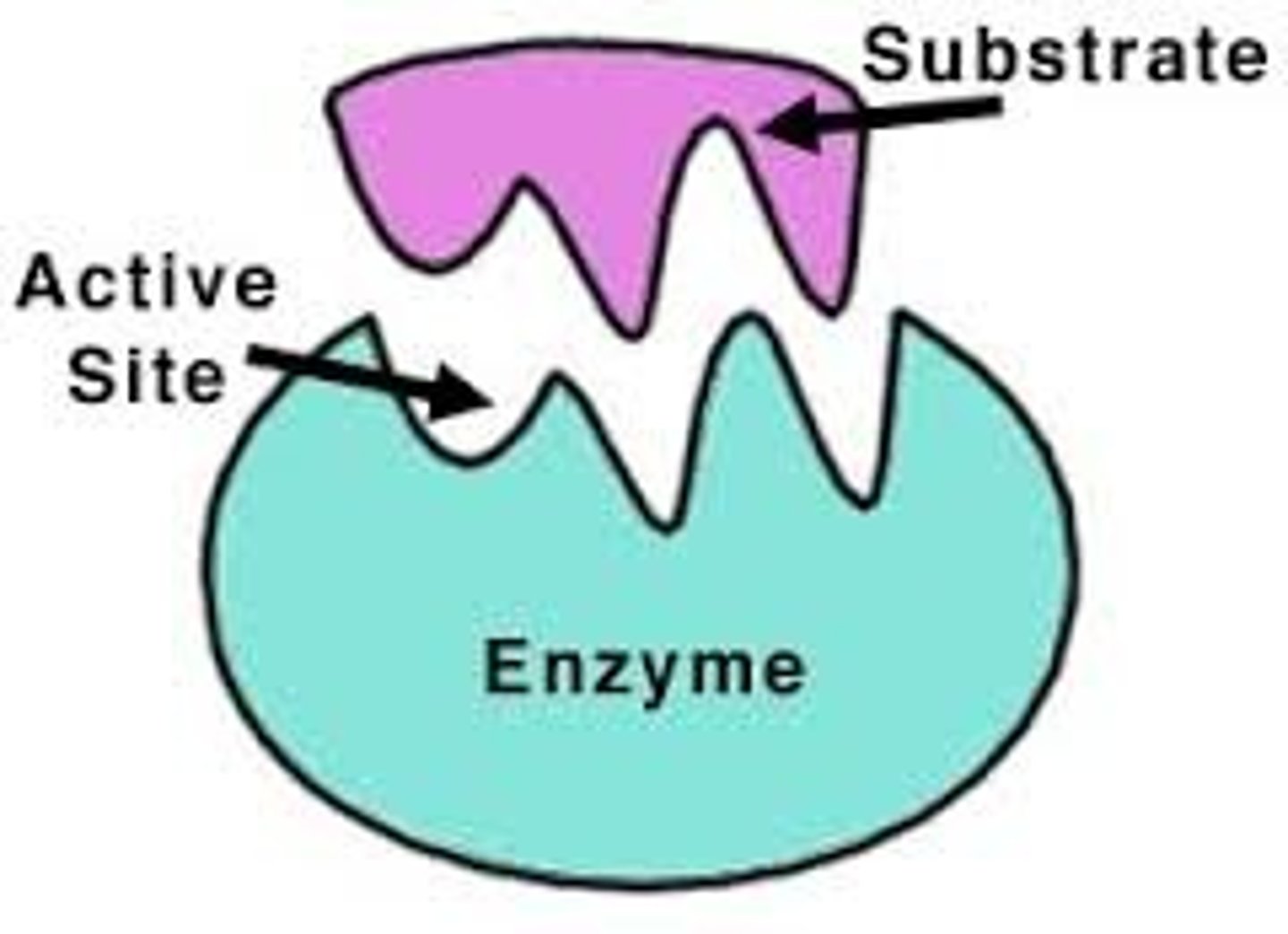
Enzyme-substrate complex
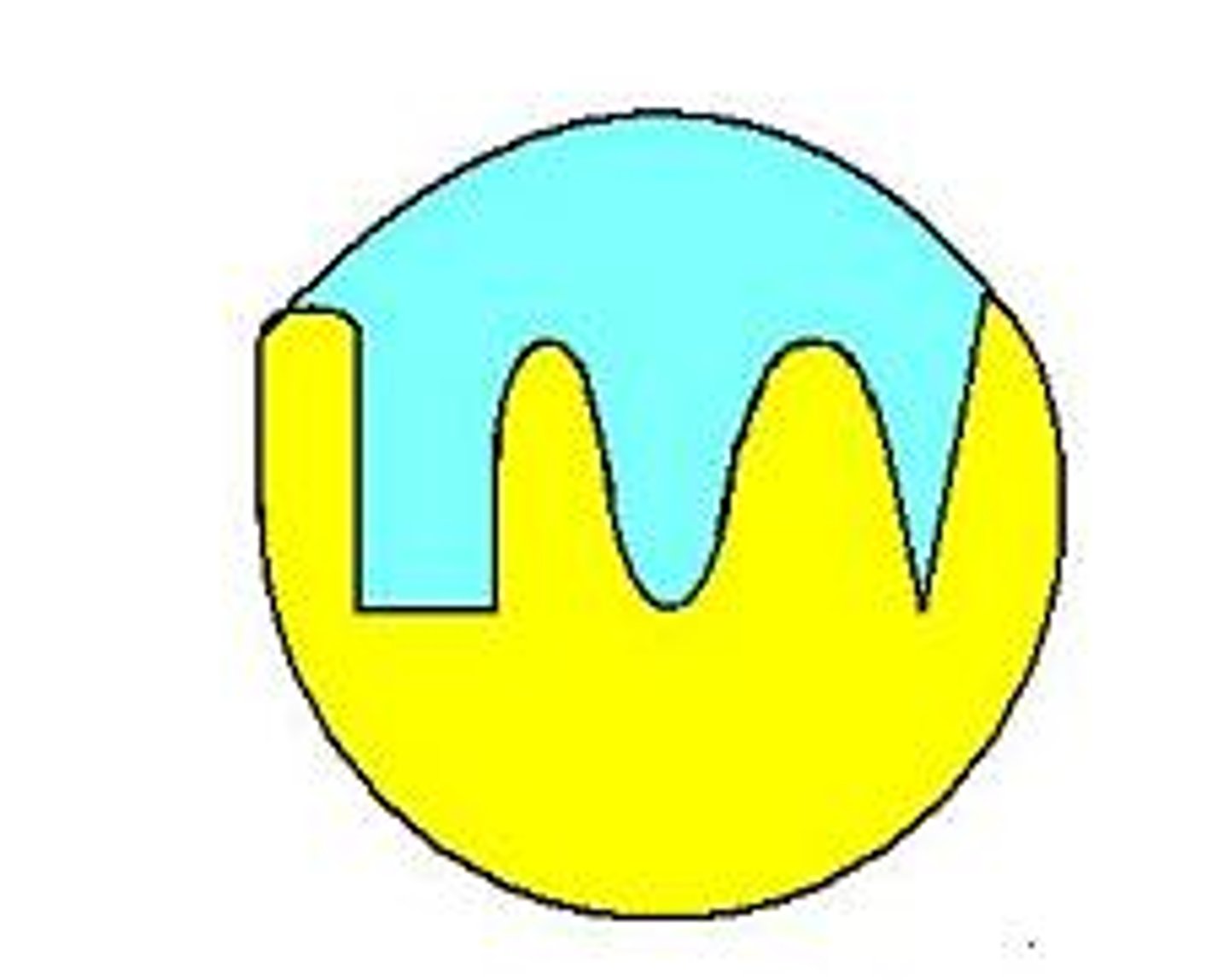

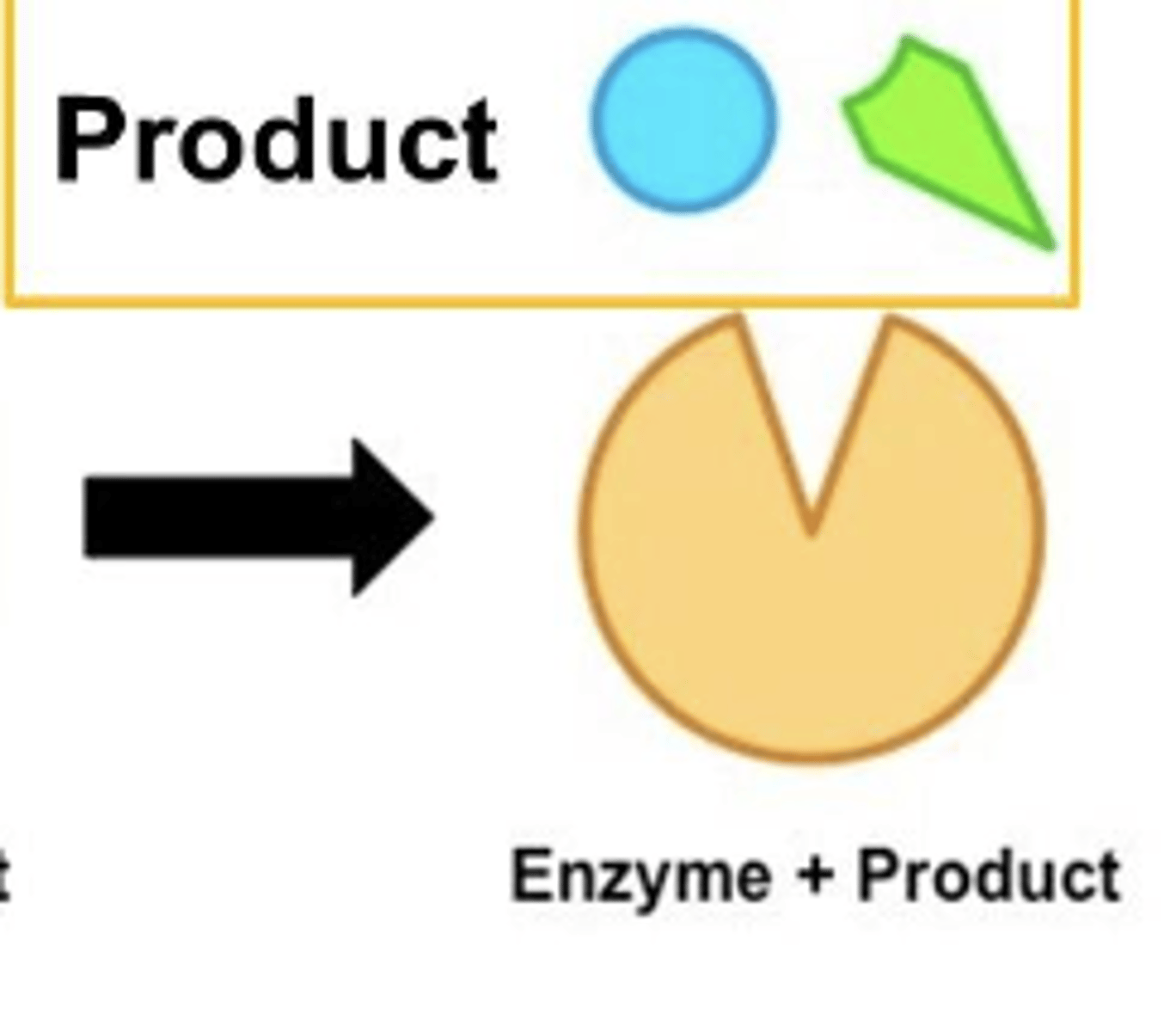
Catalysis reaction
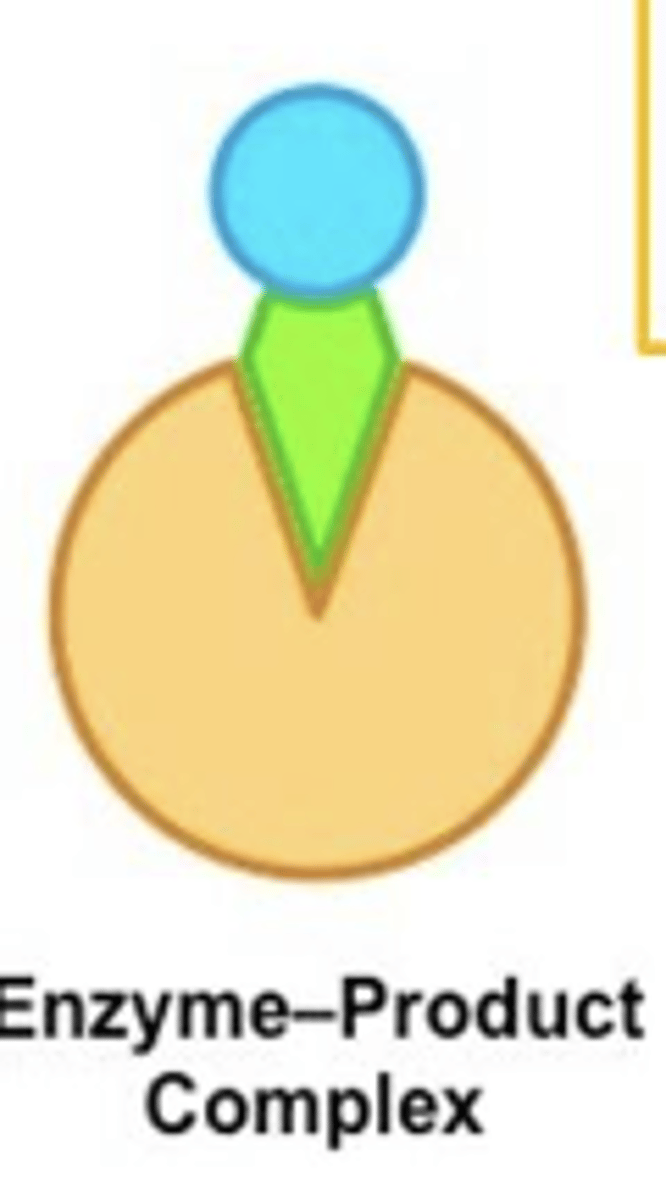

Release of enzyme products (catabolic)
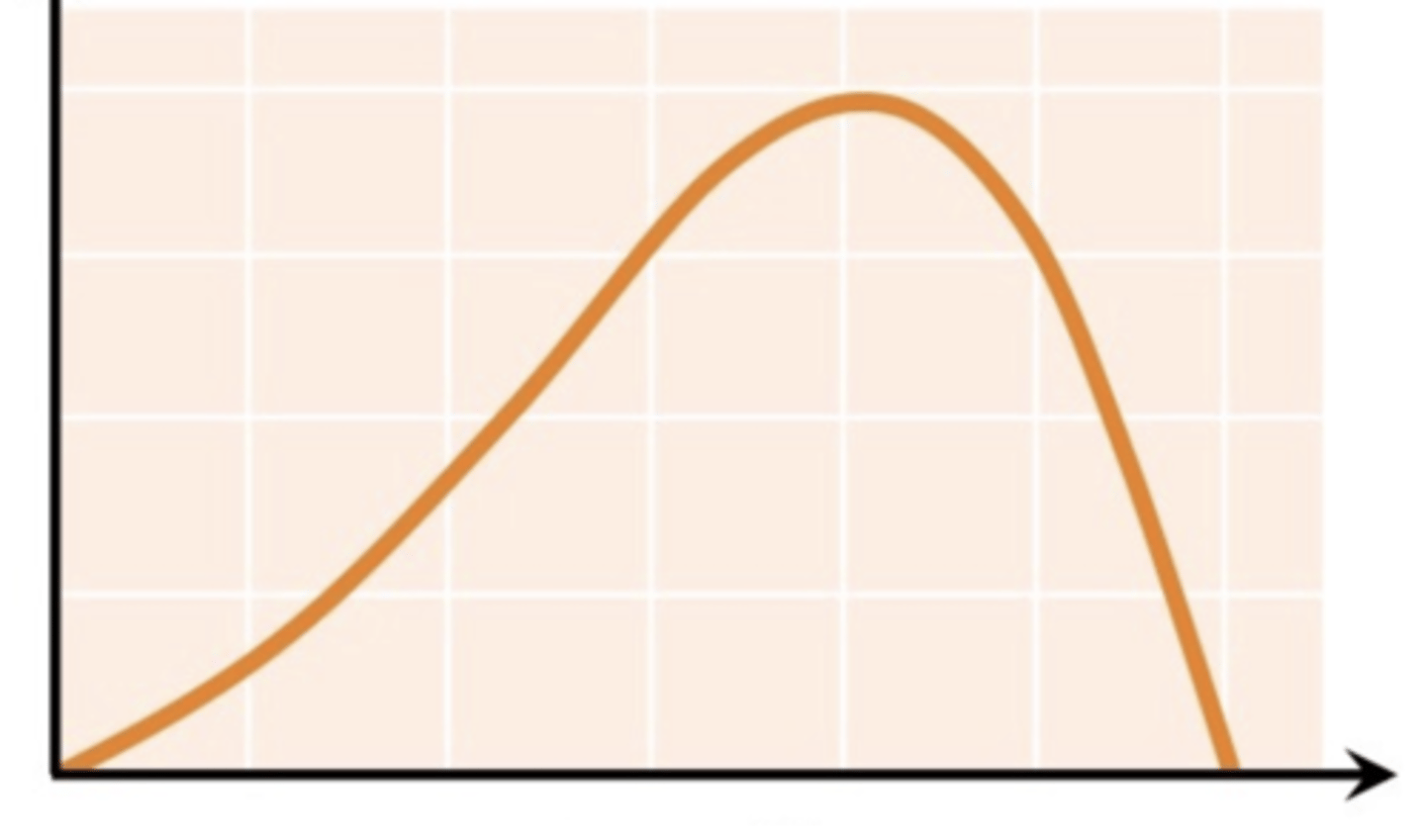
Effect of temperature on enzyme activity
Gradual increasing collisions, than denaturation as an enzyme cannot survive at high temperatures
Effect of pH on enzyme activity
Enzymes must work at optimal pH
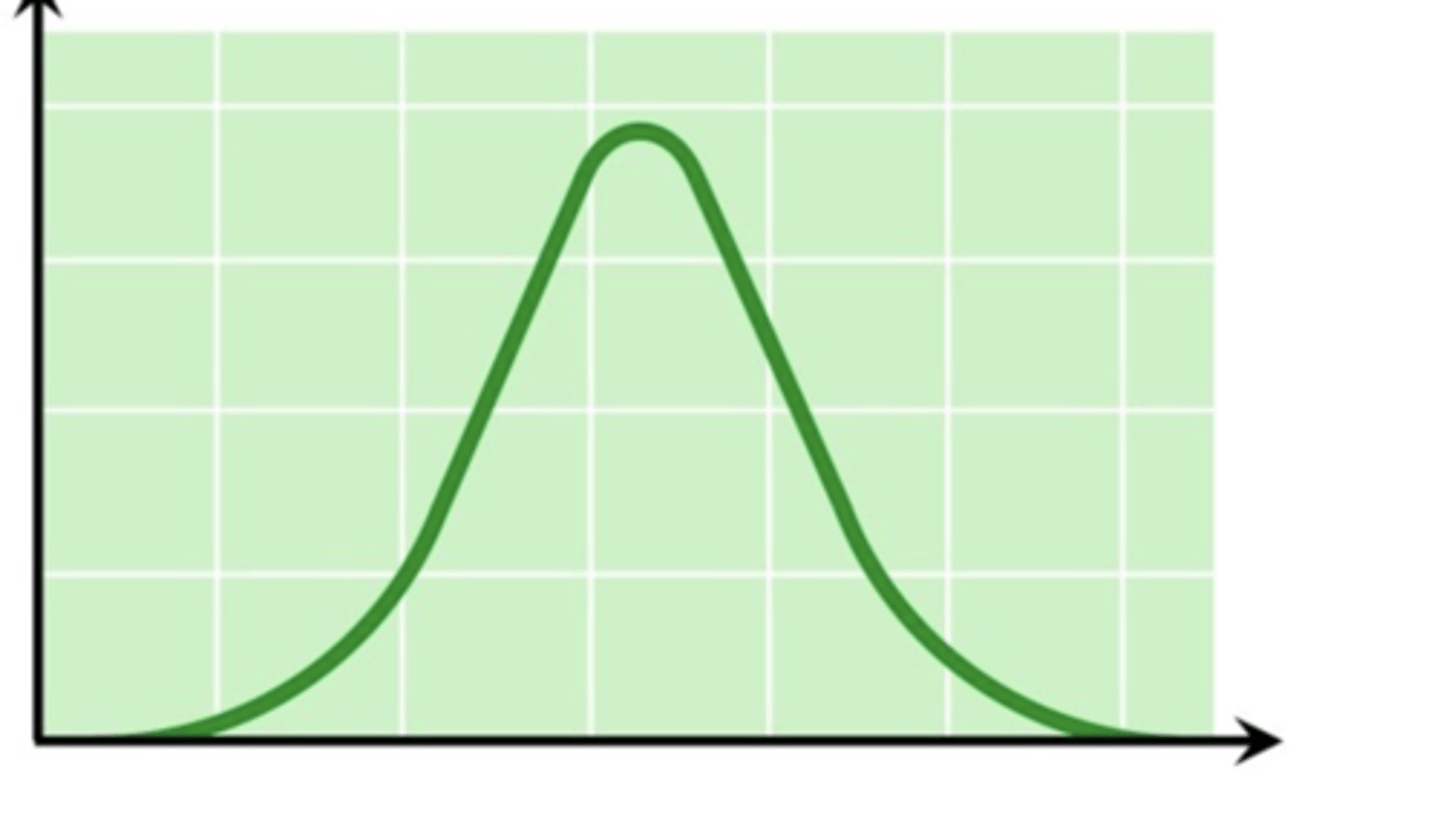
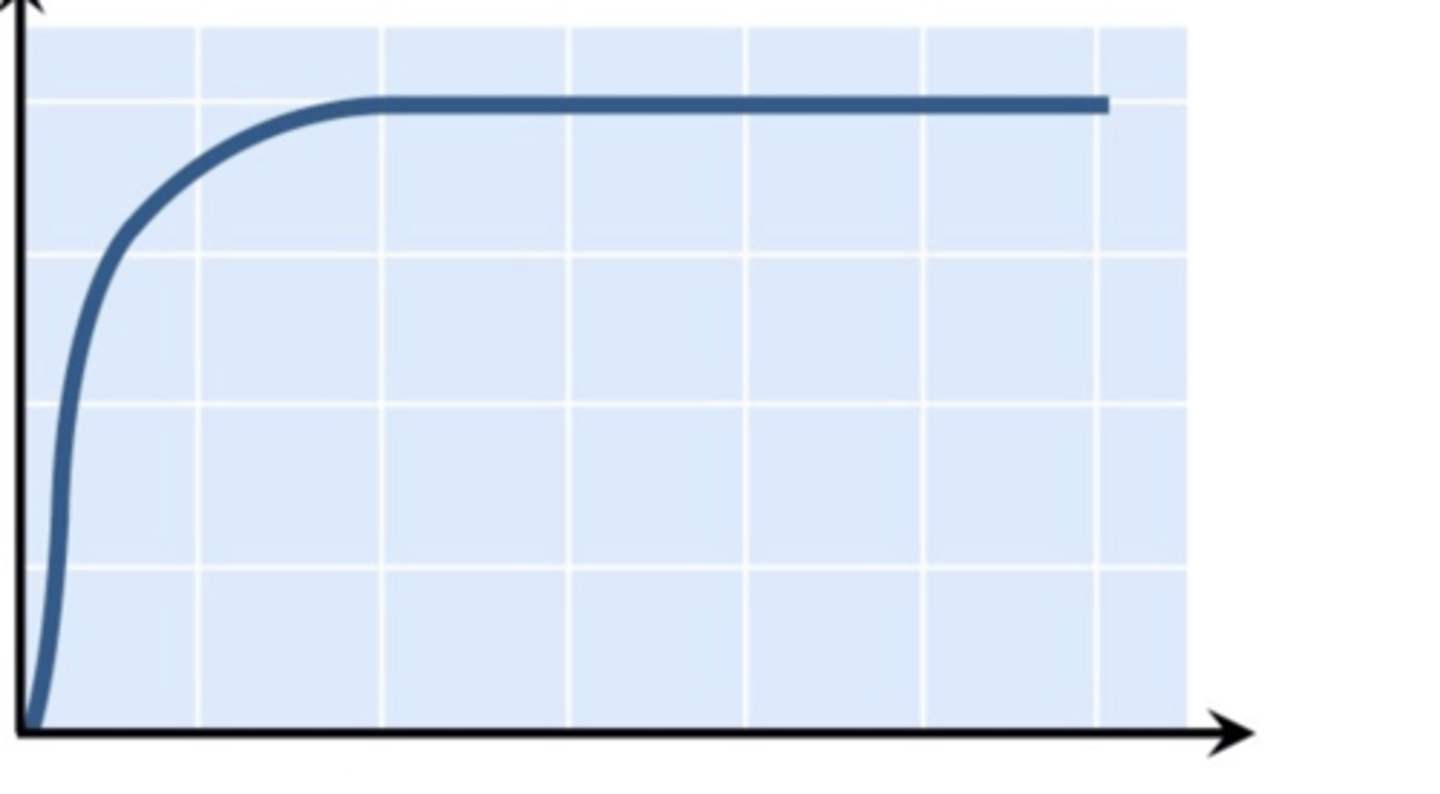
Effect of substrate concentration on enzyme activity
It increases, than plateaus, as all enzymes are occupied and working at maximum capacity
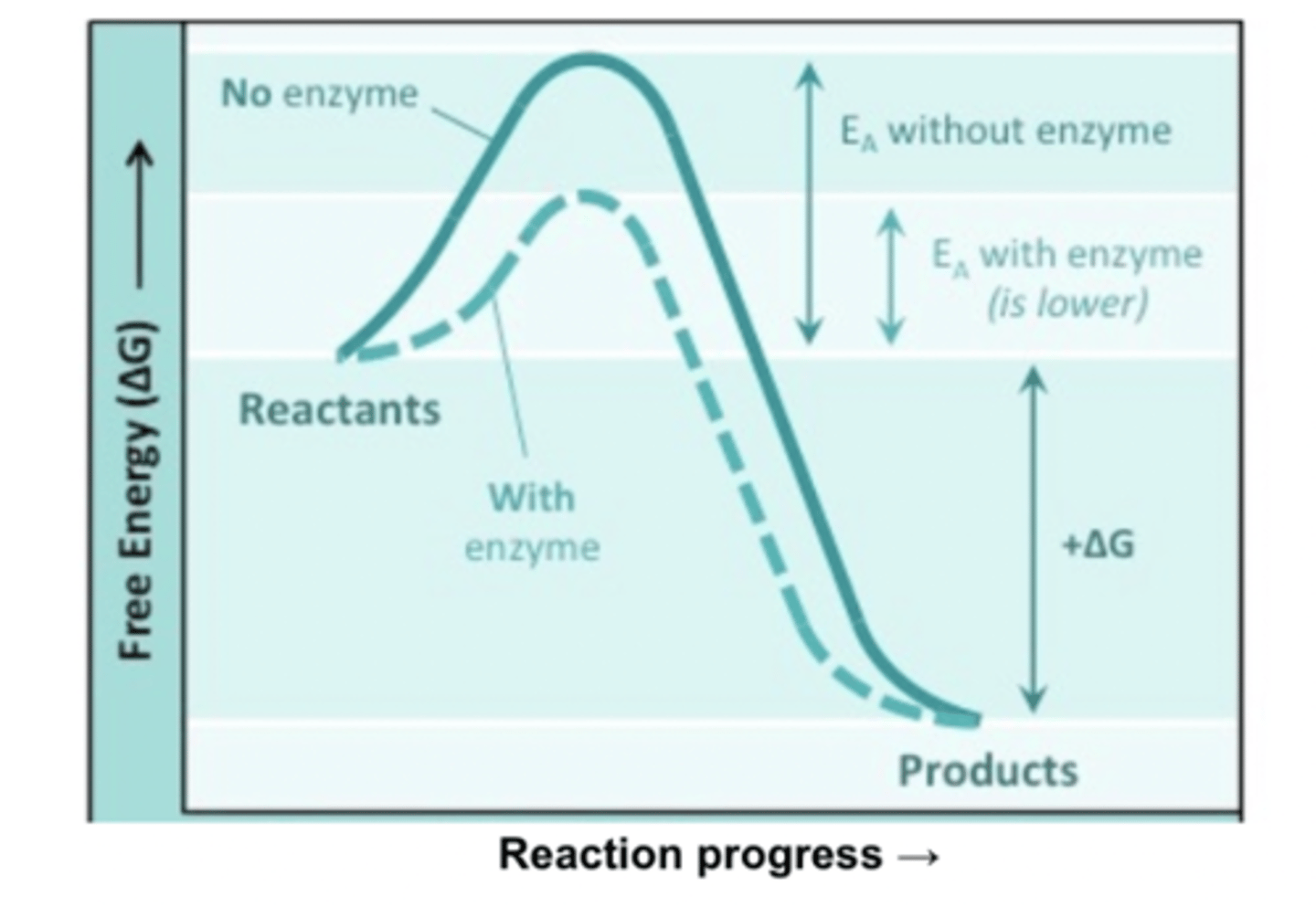
Catabolic reaction
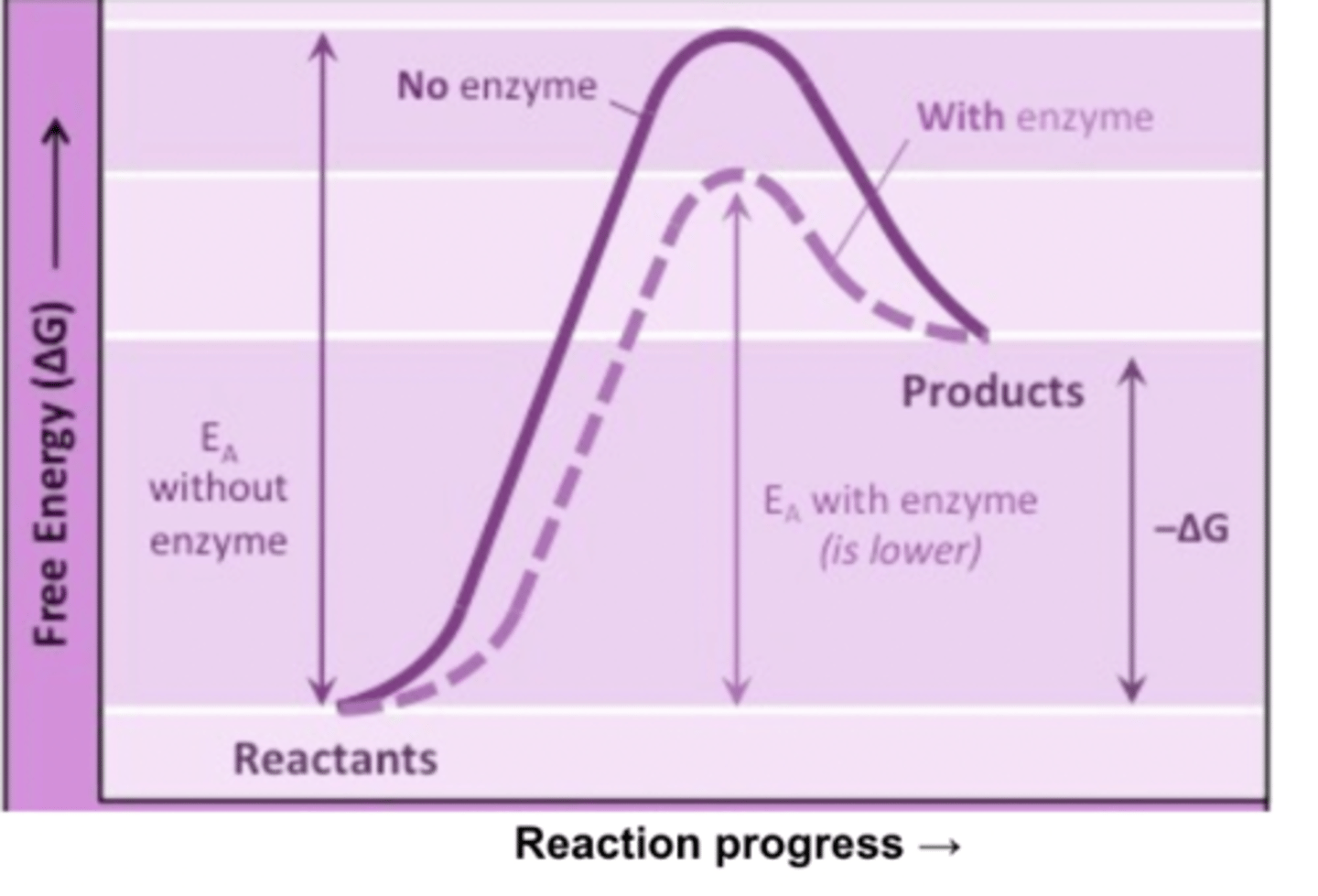
Anabolic reaction
Solvent properties of water
Attraction due to polar covalent bonds, ions, polar, or charged molecules dissolve, molecules are separated and surrounded by water
Collision theory
As concentration of substrate concentration increases, rate of reaction increases (high temp--> more movement--> more frequent collisions)
Photosynthesis formula
Carbon dioxide + water -(light energy)-> glucose + oxygen gas
Rf value formula (chromatography)

Absorption spectra
The specific frequency of light a substance absorbs and keeps
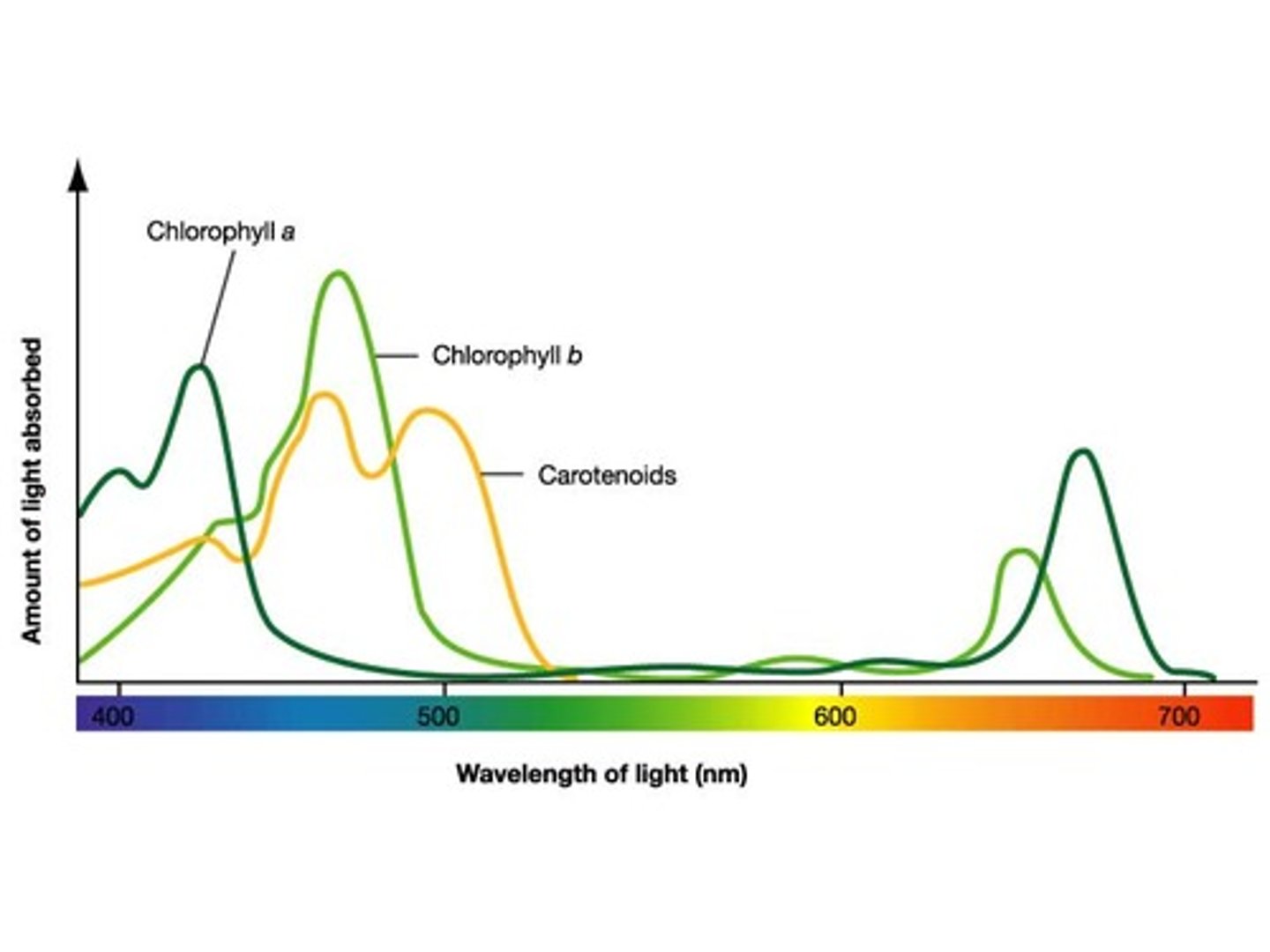
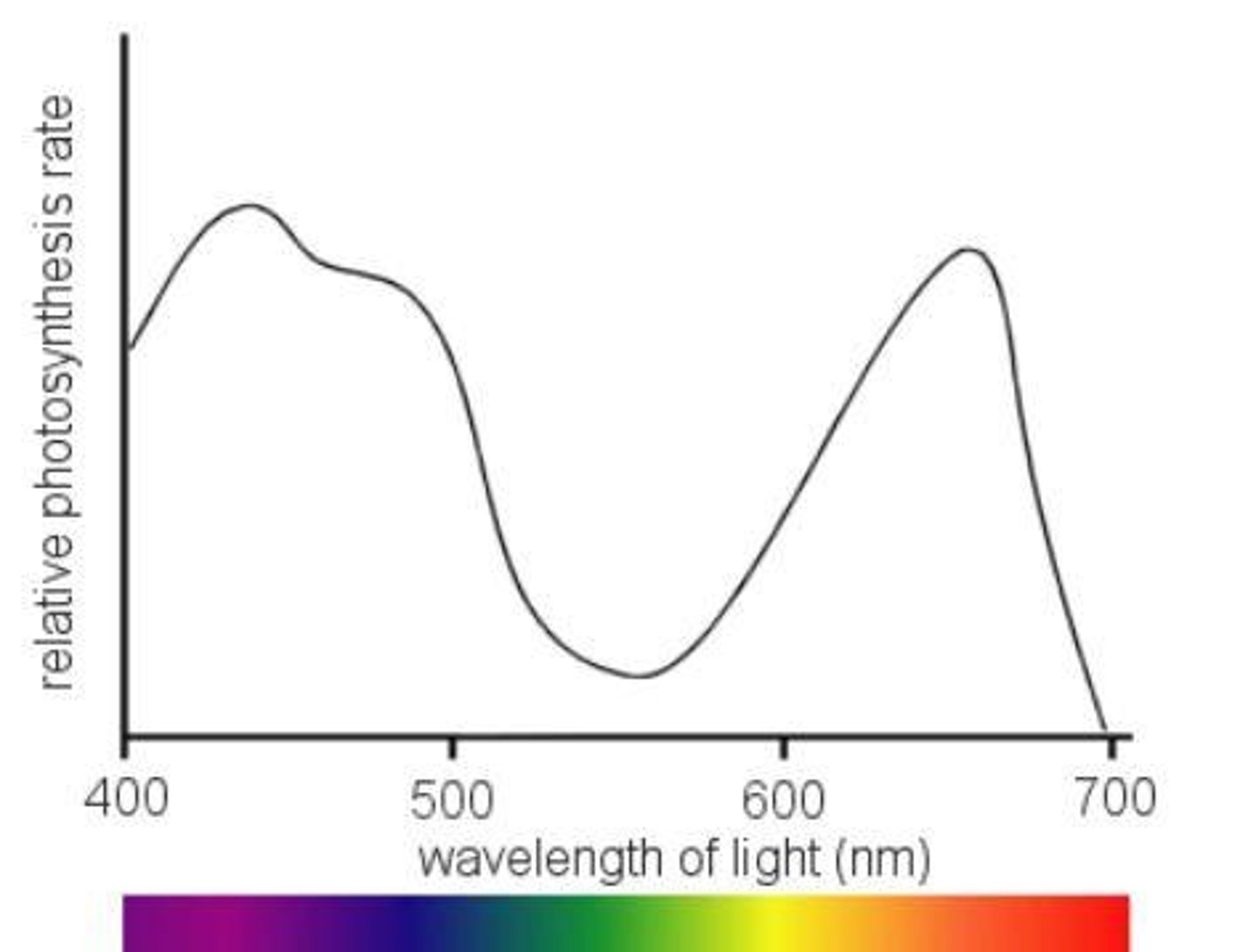
Action spectra
Rate of photosynthesis of whole plant at different wavelengths
ATP
Main energy source that cells use for most of their work
ATP to ADP
Energy released, broken down through hydrolysis
ADP to ATP
Energy required, H2O released from condensation reaction
Anaerobic respiration
glucose --> lactate + ATP
Aerobic respiration
glucose + oxygen --> carbon dioxide + water + ATP
Cellular respiration equation
glucose --> carbon dioxide + water + ATP
Nucleotide
Monomer of a nucleic acid, which has covalent bonds within
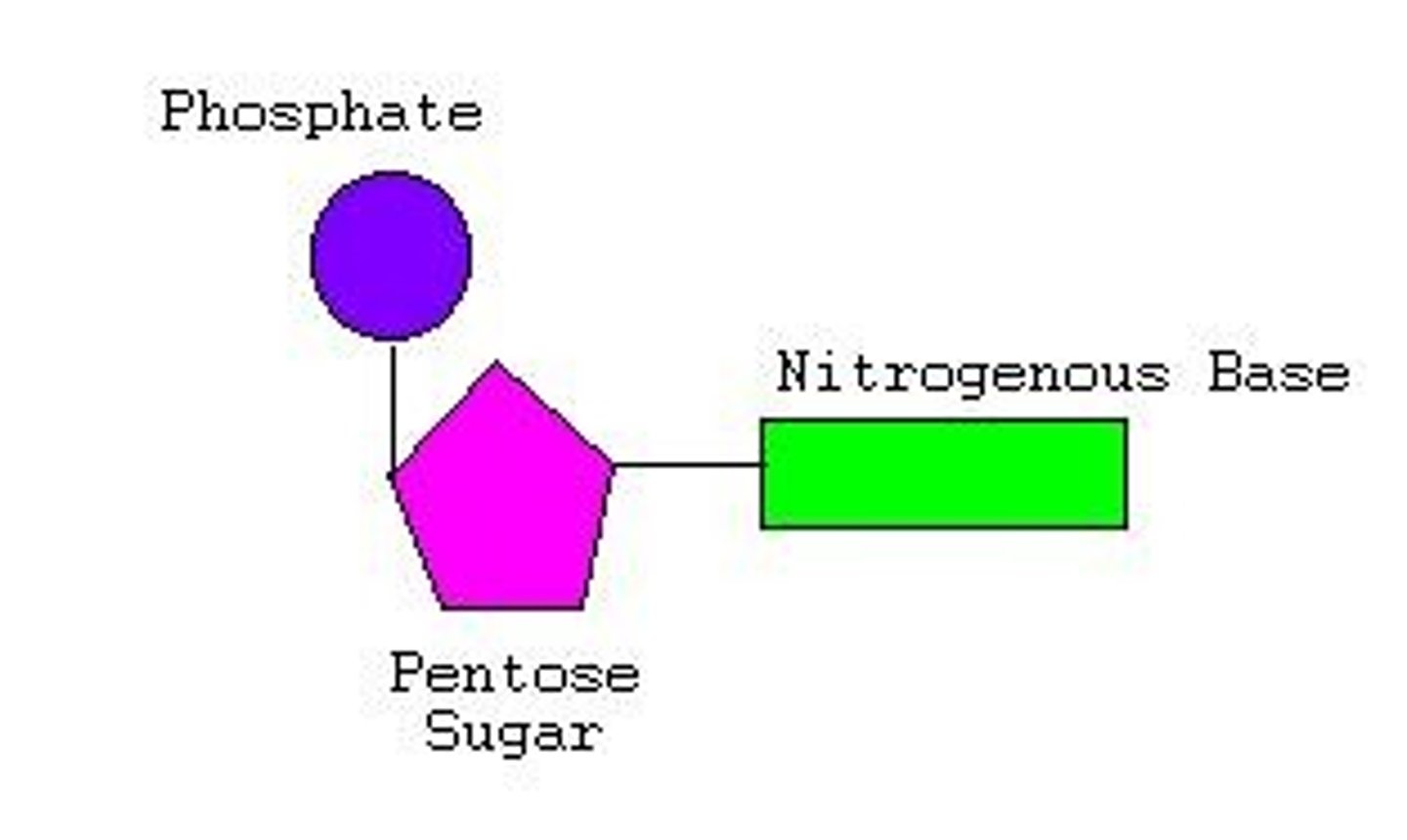
Condensation reaction
Chemical reaction between RNA molecules to form a polymer, forming covalent bonds, with OH group and H removed (forming water)
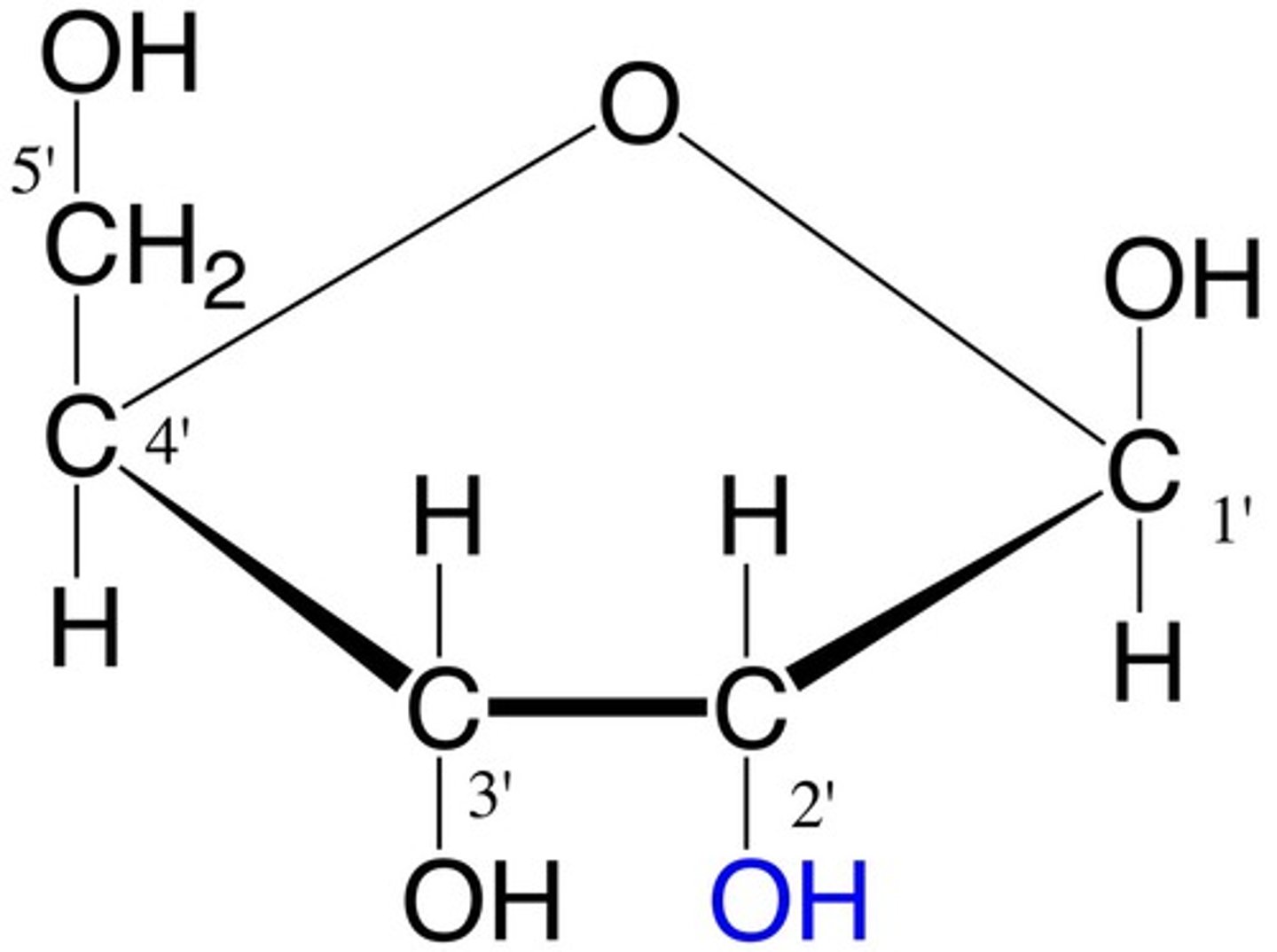
Ribose
Pentose sugar in RNA (bonded w/ OH in carbon 2
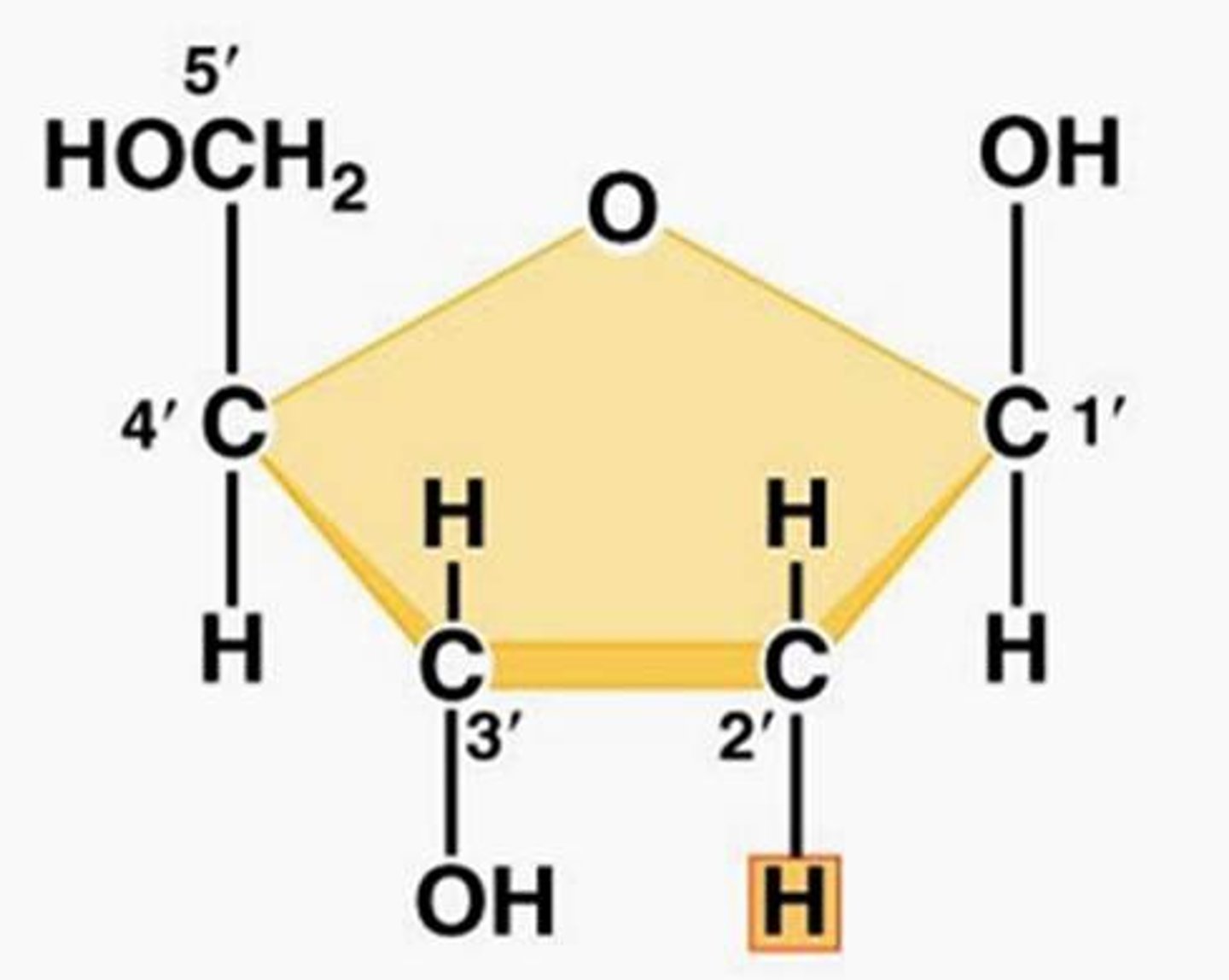
Deoxyribose
Pentose sugar in DNA (bonded w/ H in carbon 2)
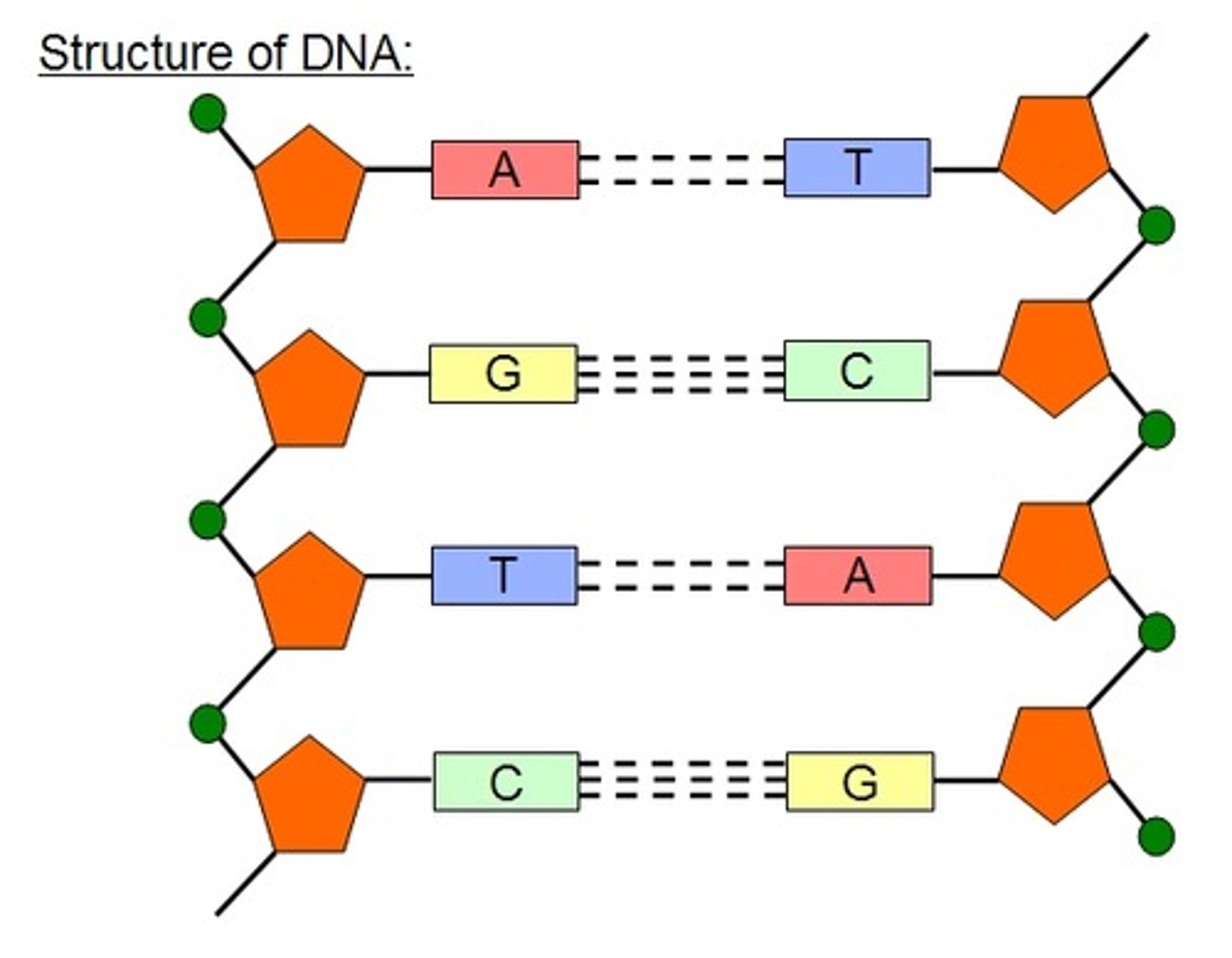
Bond between complementary base pairs in DNA
Hydrogen bonds
DNA with multiple nucleotides
DNA Replication
Process in which DNA is copied
Parent strands
Original strands before DNA replication
Daughter strands
New strands after DNA replication
Helicase
Enzyme that unwinds the parent DNA strands, and breaks hydrogen bonds
DNA Polymerase
Enzyme that builds the daughter DNA strands, through complementary base pairings, with condensation (anabolic) reactions
Covalent bonds (replication)
Bond formed between nucleotides on the growing daughter strand
Hydrogen bonds (replication)
Bond formed between parent strand and daughter strand
Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
Way of amplifying (making many copies of) a specific region in DNA in the lab, mimicking DNA replication, within a machine (thermal cycler)
Denaturation (PCR)
1st step: separation of DNA strands using heat, using the Helicase enzyme to break hydrogen bonds
Annealing (PCR)
2nd step: Forming hydrogen bonds by primers attaching to original strand, through complementary base pairing
Elongation (PCR)
3rd step: Taq polymerase extends strand by adding nucleotides to primers
Restriction enzyme (endonuclease)
Protein that digests DNA existing in bacteria, cutting in the restriction site
EcoR1
Enzyme that produces a jagged cut which results in sticky ends to easily attach other DNA molecules
EcoRV
Enzyme that produces a blunt cut
Gel electrophoresis
Separation of DNA fragments and proteins for comparison
Transcription
Takes place within the nucleus, DNA instructions for making a polypeptide are copied to mRNA with the RNA polymerase enzyme
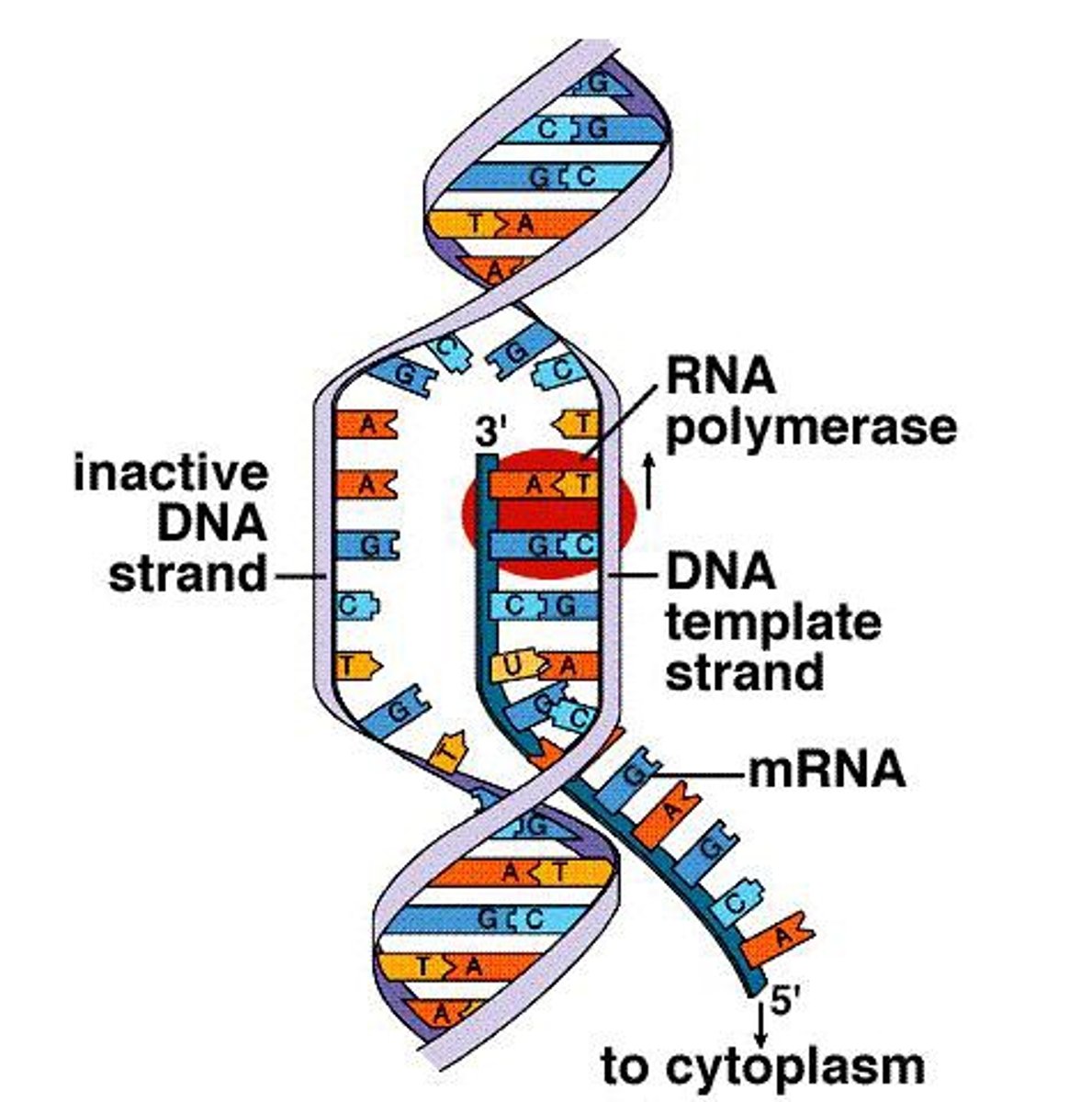
RNA Polymerase
Enzyme that unwinds the DNA and also builds complementary RNA strand during transcription
Initiation (Transcription)
RNA polymerase attaches to the promoter section of the gene, and unwinds the DNA
Elongation (Transcription)
DNA is read and a complementary RNA strand is created, growing to its 3 primer ends, with condensation reactions creating covalent bonds
Termination (Transcription)
The RNA transcript is released from the template at the termination site and the polymerase detaches from the DNA
Translation
Takes place within the cytoplasm, and ribosome is attached to mRNA in order to build a polypeptide (protein)
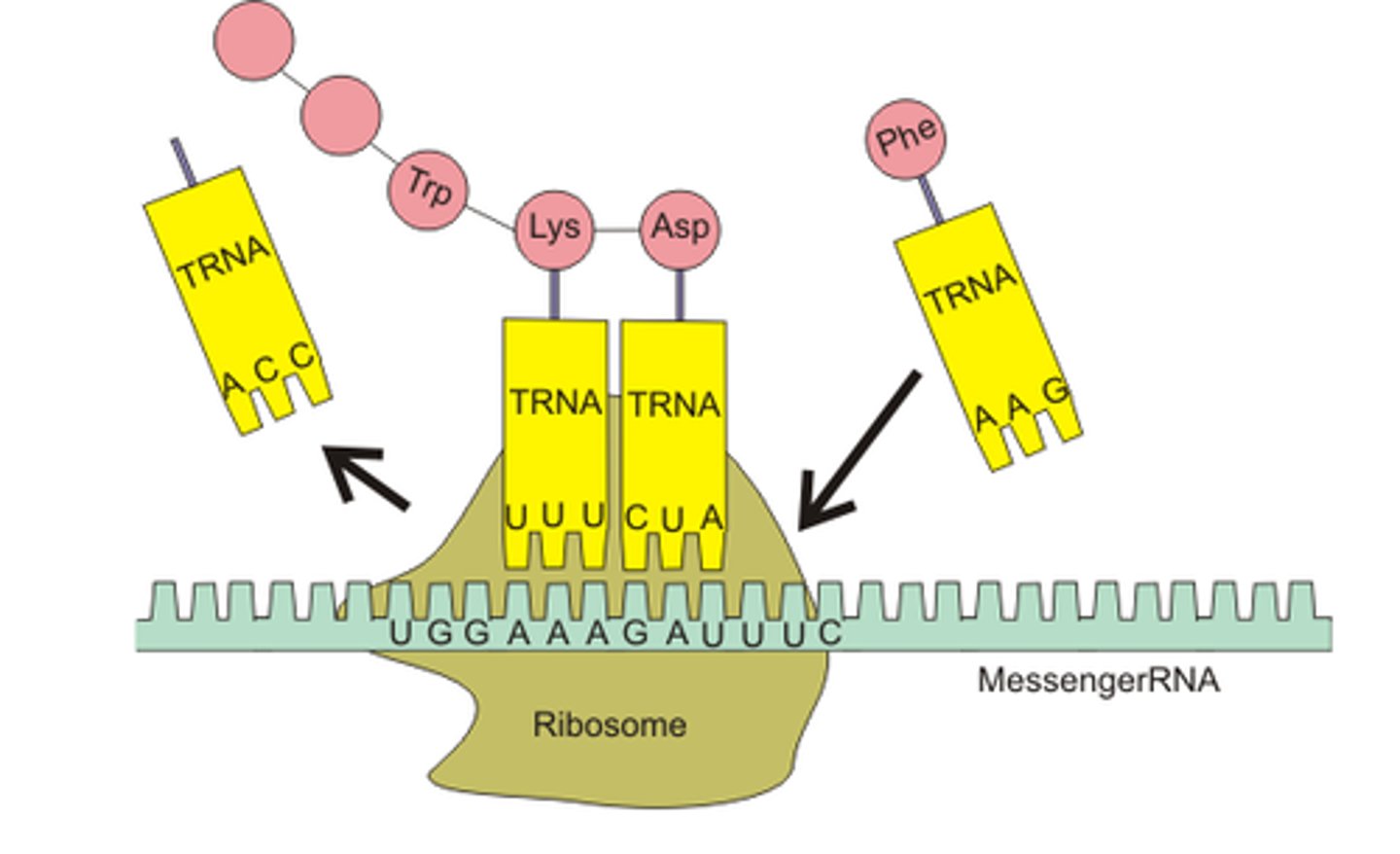
RNA's involved in translation
rRNA, mRNA, tRNA
Anticodon
Complementary set of 3 nucleotides on a tRNA molecule, with hydrogen bonds formed between them, attached to amino acid
Initiation (Translation)
Small subunits of ribosome come together around mRNA strand, and bind, large subunit binds to the trNA
Elongation (Translation)
Addition tRNAs bind to ribosome, with peptide bonds on adjacent tRNAS, and the left tRNA leaves a large subunit, and two can be fully bonded at once
Termination
When mRNA stop codon enters, the ribosome complex falls apart, and the protein is released into the cell
mRNA nucleotides for 1 amino acid
3
mRNA codons for 1 amino acid
1
Degenerate
For each amino acid, there may be more than 1 codon
Mutation
Permanent change in the DNA sequence
Substitution
A mutation in which a nucleotide or a codon in DNA is replaced with a different nucleotide
Insertion
A mutation involving the addition of one or more nucleotide pairs to a gene
Deletion
A mutation which is the deletion of one or more bases
Single Nucleotide Polymorphism (SNP)
Variations in DNA between different individuals resulting from single base substitutions, possible by degeneracy
Frameshift error
Error caused by the misreading of the mRNA, results in a completely different sequence due to insertion
Germ cells
Reproductive cells that give rise to sperm and ovum, and can inherit mutated genes
Somatic cells
Bodily cells, that can get cancer
Three domains of life
Bacteria, Archaea, Eukarya