Lab 5 (Bromination of Vanillin)
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
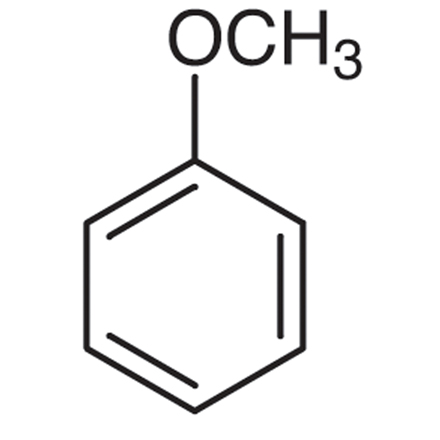
Why does the bromination of anisole prefer the ortho/para position as opposed to the meta position?
Ortho/Para
Has 4 resonance structures
1 resonance structure has positive charge on oxygen (the one with the oxygen is the most stable because all atoms have an octet)
More preferred than ortho
Meta
Reaction creates 3 resonance structures but none of them are super stable (all resonance structures have 1 carbon with only 6 electrons)
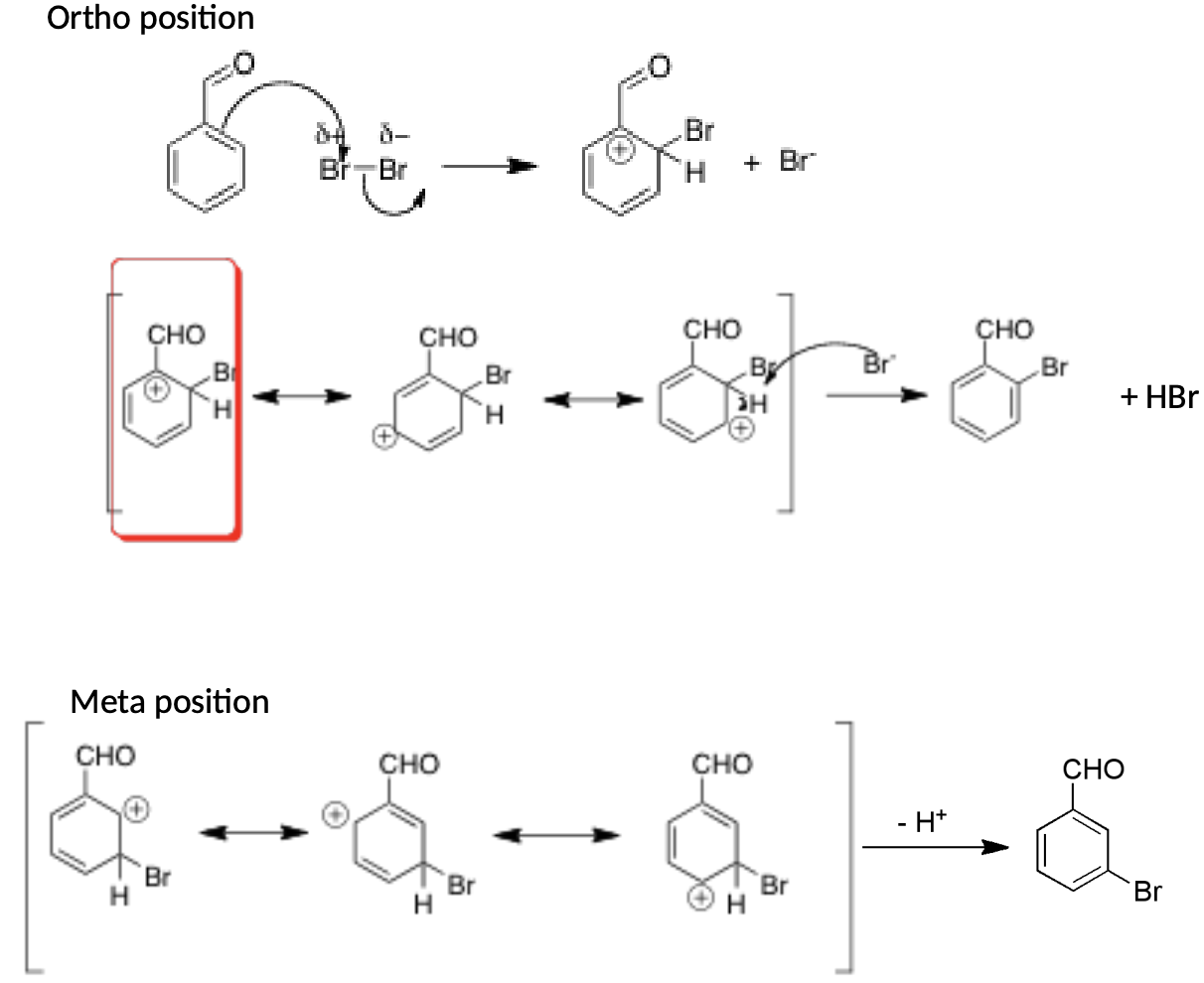
Why does the bromination of benzaldehyde prefer the meta position as opposed to the ortho/para position?
Ortho/Para
All resonance structures have carbon with partial positive charge and no octet so not that stable of a reaction
The carbon next to the aldehyde is already partially positive so the intermediate with that carbon having a partial positive charge is extremely unstable
Meta
In the meta position the resonance structures of the intermediate do not have a partial positive charge on the carbon next to the aldehyde
This makes it more stable than the ortho intermediate so it is faster at reacting
Main product of bromination of benzaldehyde
Classify the following substituents
-Br, -CHO, CH3CH2-, CH3C=O (acetyl), (CH3)2N-, -SO3H
Ortho/Para Directing (Activators)
Br &(deactivating)*
CH3CH2-
(CH3)2N-
Meta Directing (Deactivators)
CHO (aldehyde)
CH3C=O (acetyl)
-SO3H
What are the “green features” of the synthesis which you will perform?
No organic (halogenated) solvents (only water, acetic acid, and ethanol)
No toxic reagents (no heavy metals, chlorinated reagents, etc.)
Purification by crystallization from water/ethanol, no wastes (like in case of chromatography)
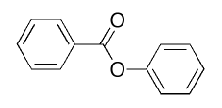
What will be the main product in bromination of phenyl benzoate?
Ortho/para relative to activator (OH) activators always take priority over deactivators
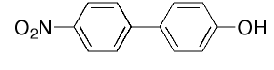
What is the main product of bromination of the following compound:
Ortho relative to OH again activators always take priority over deactivators
What reagents will you use to generate bromine in your experiment? Write the balanced equation for formation of bromine from reagents which you will use.
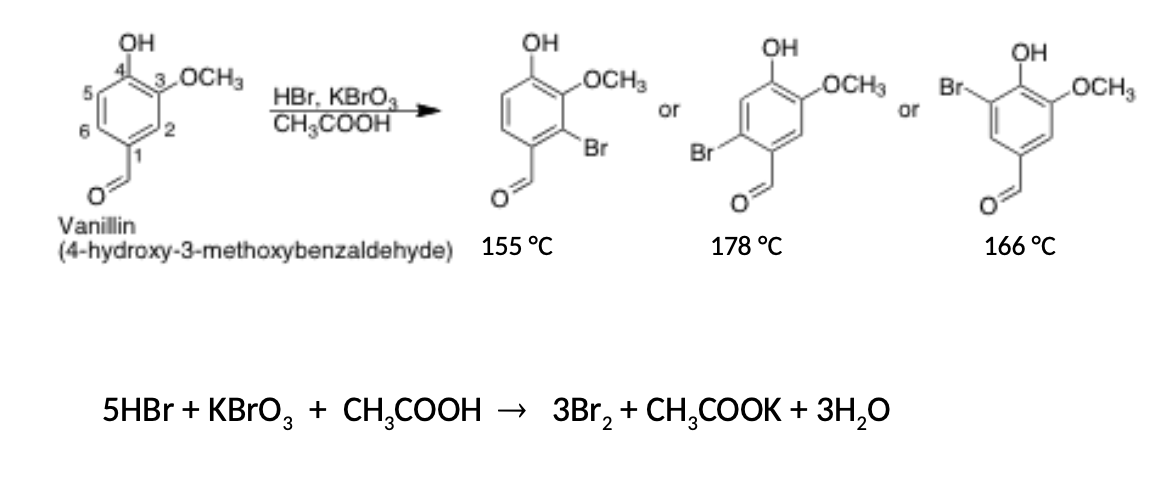
Suppose you brominated 3.4 g of vanillin (m.w. = 152 g/mol), and you got the monobrominated vanillin (m.w. = 231.0 g/mol) in 75% yield. How many grams of mono bromovanillin did you get? Show your calculations, assume that vanillin is the limiting reagent
3.88g of mono bromovanillin
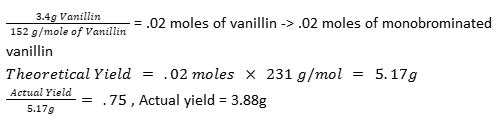
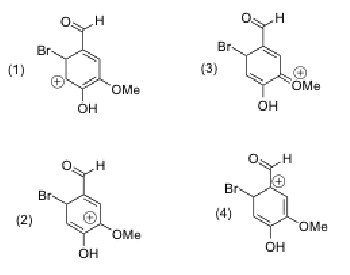
Which resonance form, for the intermediate in bromination of vanillin at the 6 position, is the least stable?
4, because the aldehyde is already partially positive so a positive charge on the carbon attached to it would be even less stable
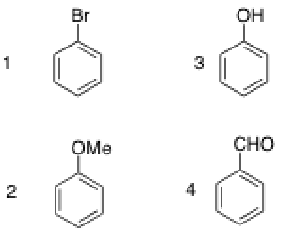
Which of the following compounds should be the least reactive in electrophilic bromination?
4, since the carbonyl in the aldehyde is a deactivating group
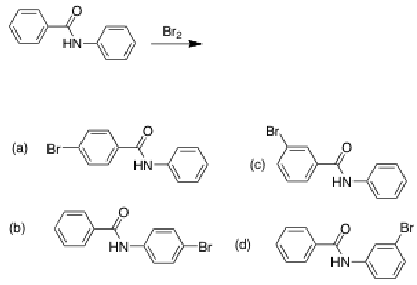
What should be the main product in the following reaction?
B, because the amine substituent is activating so the bromination is more likely to occur on that benzene
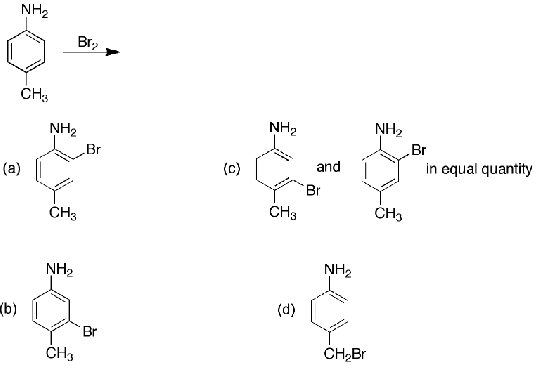
What is the main product of bromination of p-methylaniline?
A, both substituents are activators (ortho/para) but amine is a stronger activator than an alkyl group so it takes priority