CD3: Endo Final
1/279
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
280 Terms
212
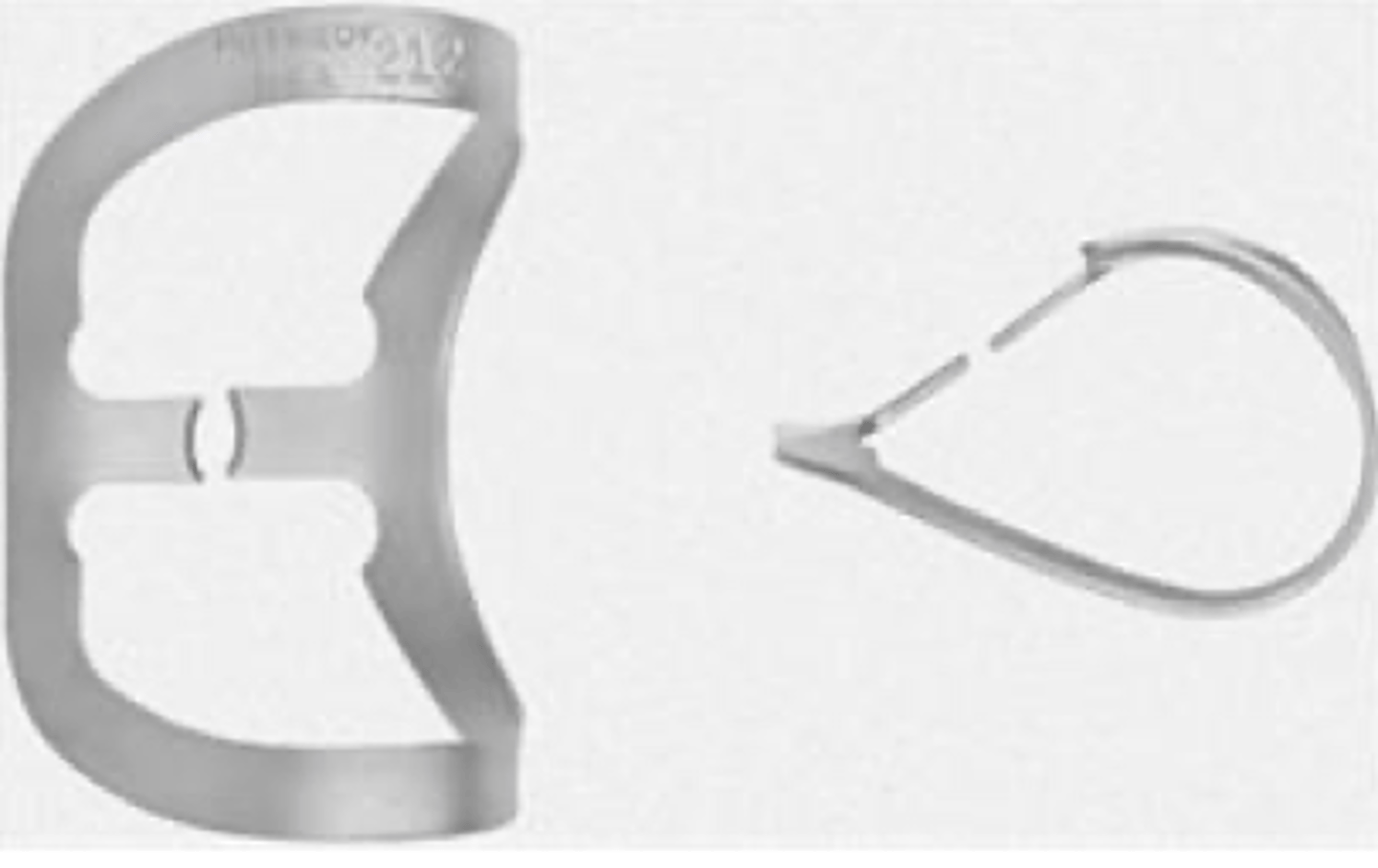
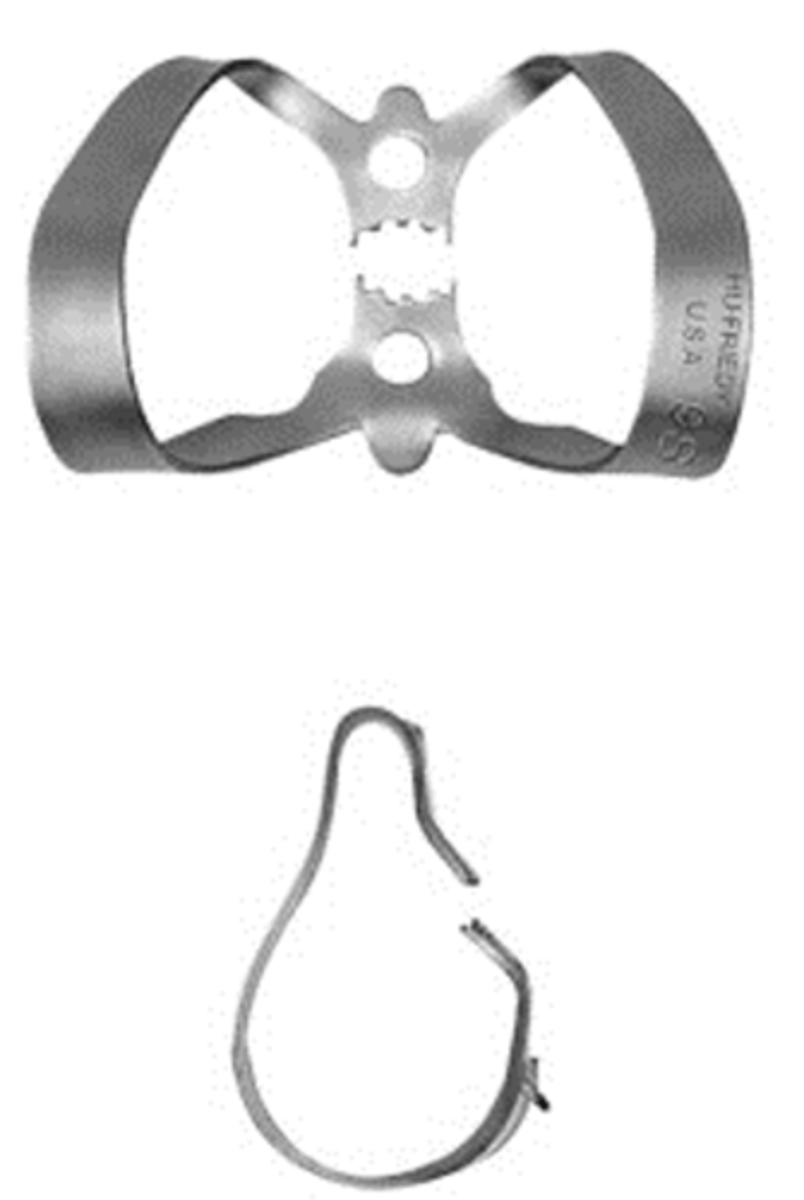
which retainer do we use for isolated endo treatment on anterior teeth?
what does EDTA stand for?
ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid
TU-17/23 DE Explorer
(EXTU17/236)
Combination of #TU17 end for subgingival calculus detection and #23 end for caries detection. #TU17 end features a balanced tip design for ease and comfort

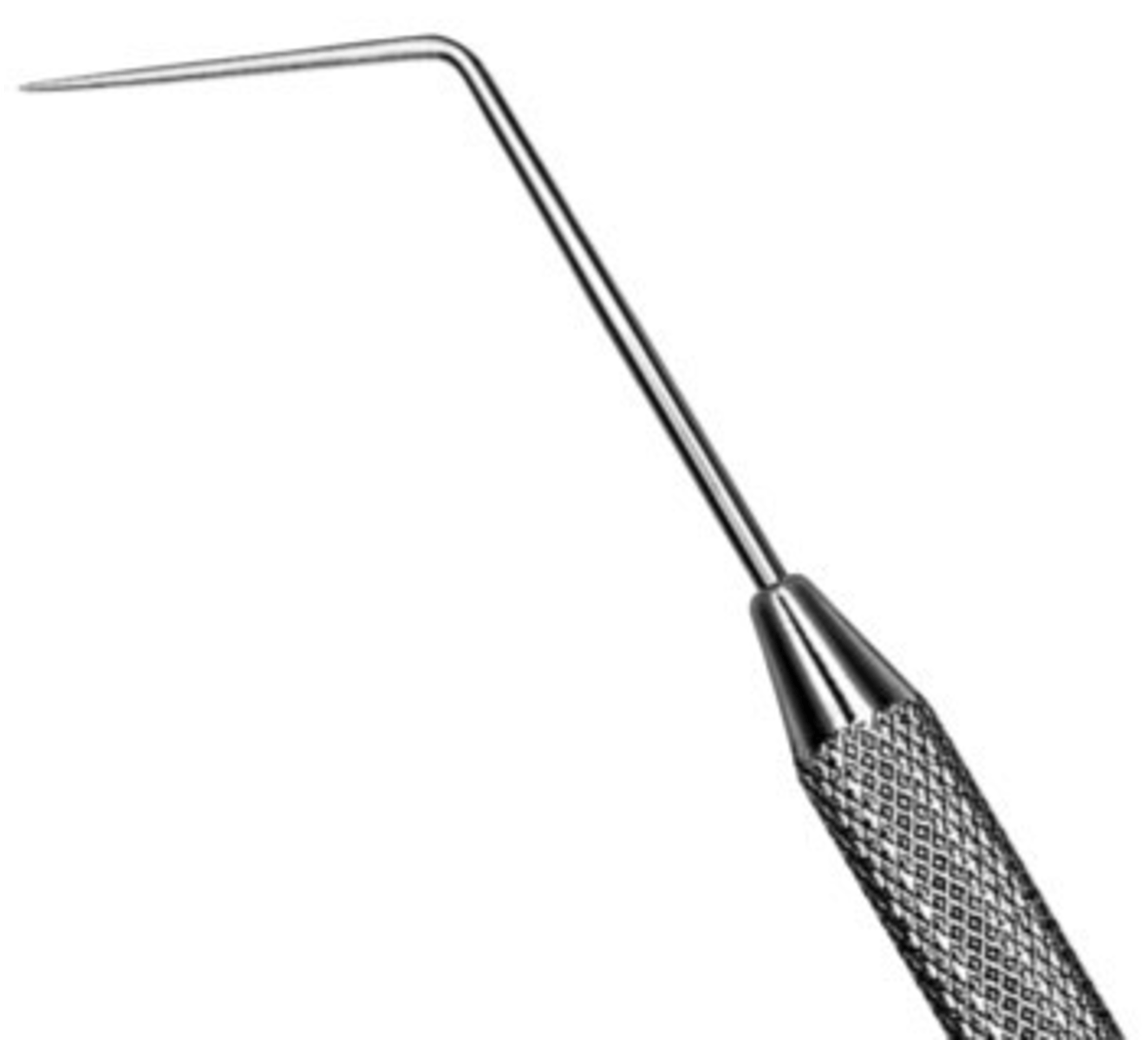
DG16 DE Endodontic Explorer
(EXDG16)
•Double ended instrument with fine, delicate tips.
•Used to locate orifices of canals.
•Very sharp (place cotton rolls on both ends in Simulation clinic when not in use).

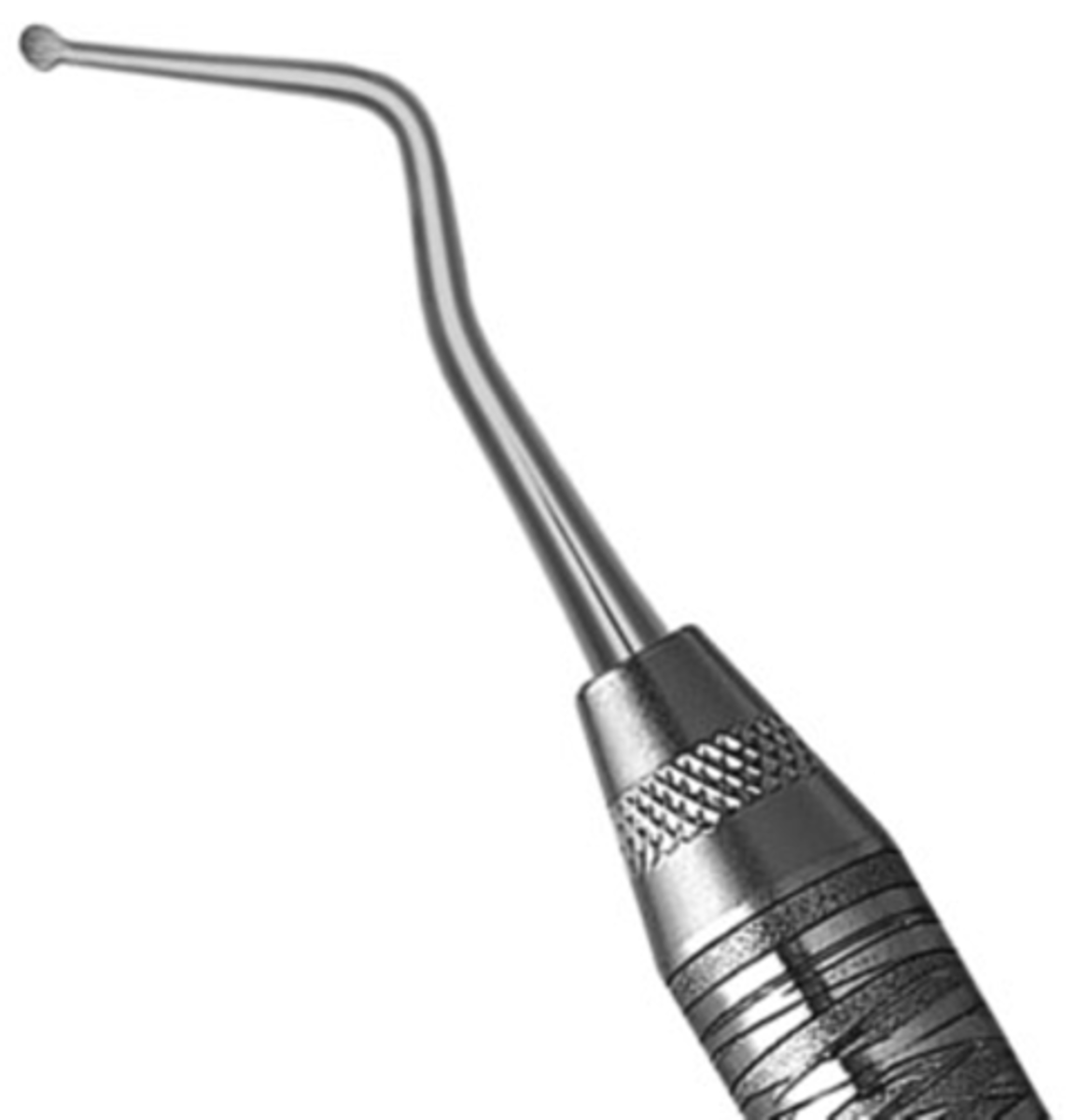
#32L DE Endodontic Excavator
(EXC32L6)
•Double ended instrument.
•The 32L Endo Excavator features an extended length shank for easy access and removal of dentin
•The long shank allows you to reach deeper into the coronal pulp space.
•This spoon may also be helpful in deeper interproximal lesions.

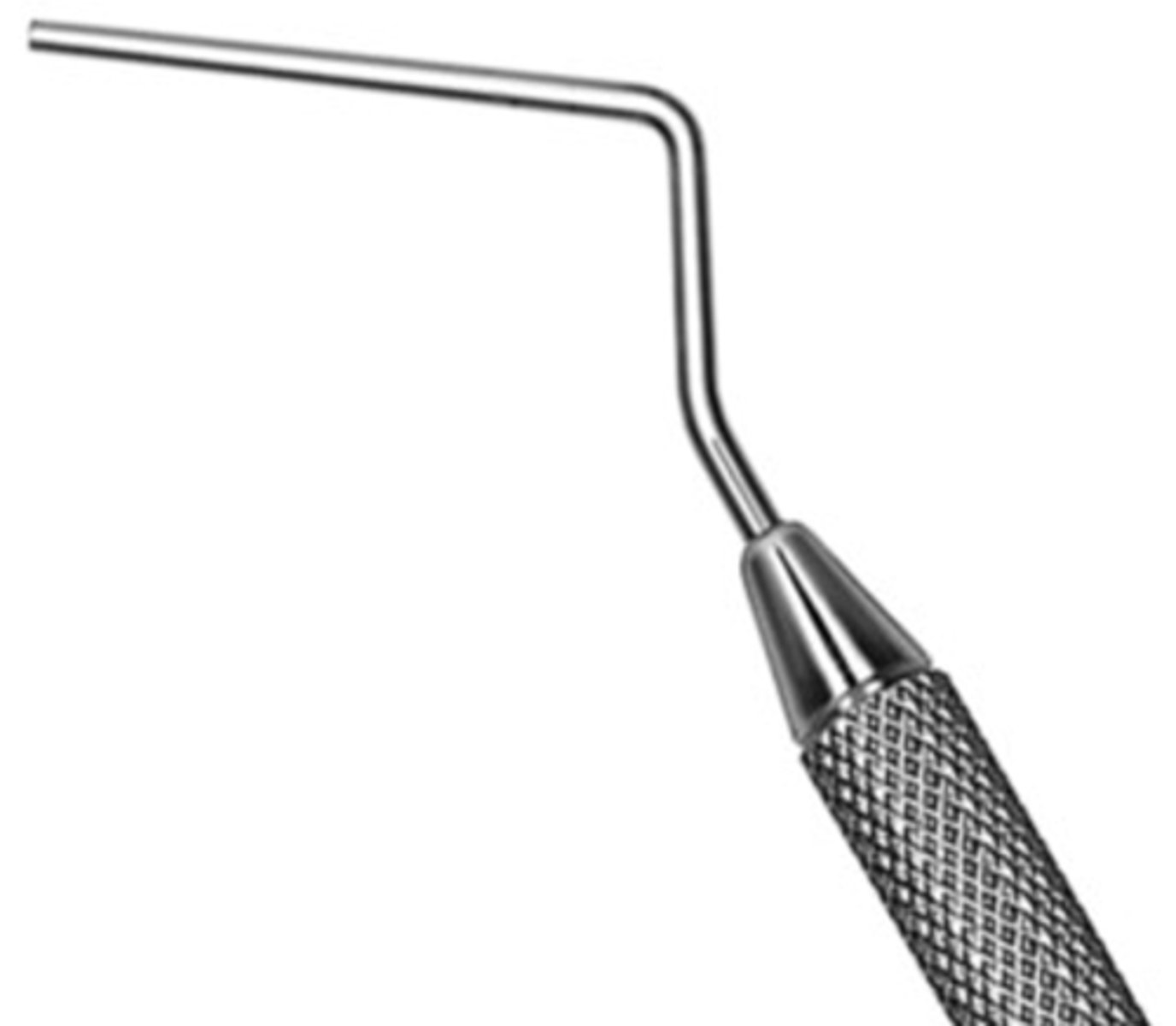
#9/11 DE Root Canal Plugger
•Double ended instrument
•May be heated
•Used to compact filling material during vertical condensation.
•Marked at 5 mm intervals to assess penetration depth.

#5/7 DE Root Canal Plugger
•Double ended instrument
•May be heated
•Used to compact filling material during vertical condensation.
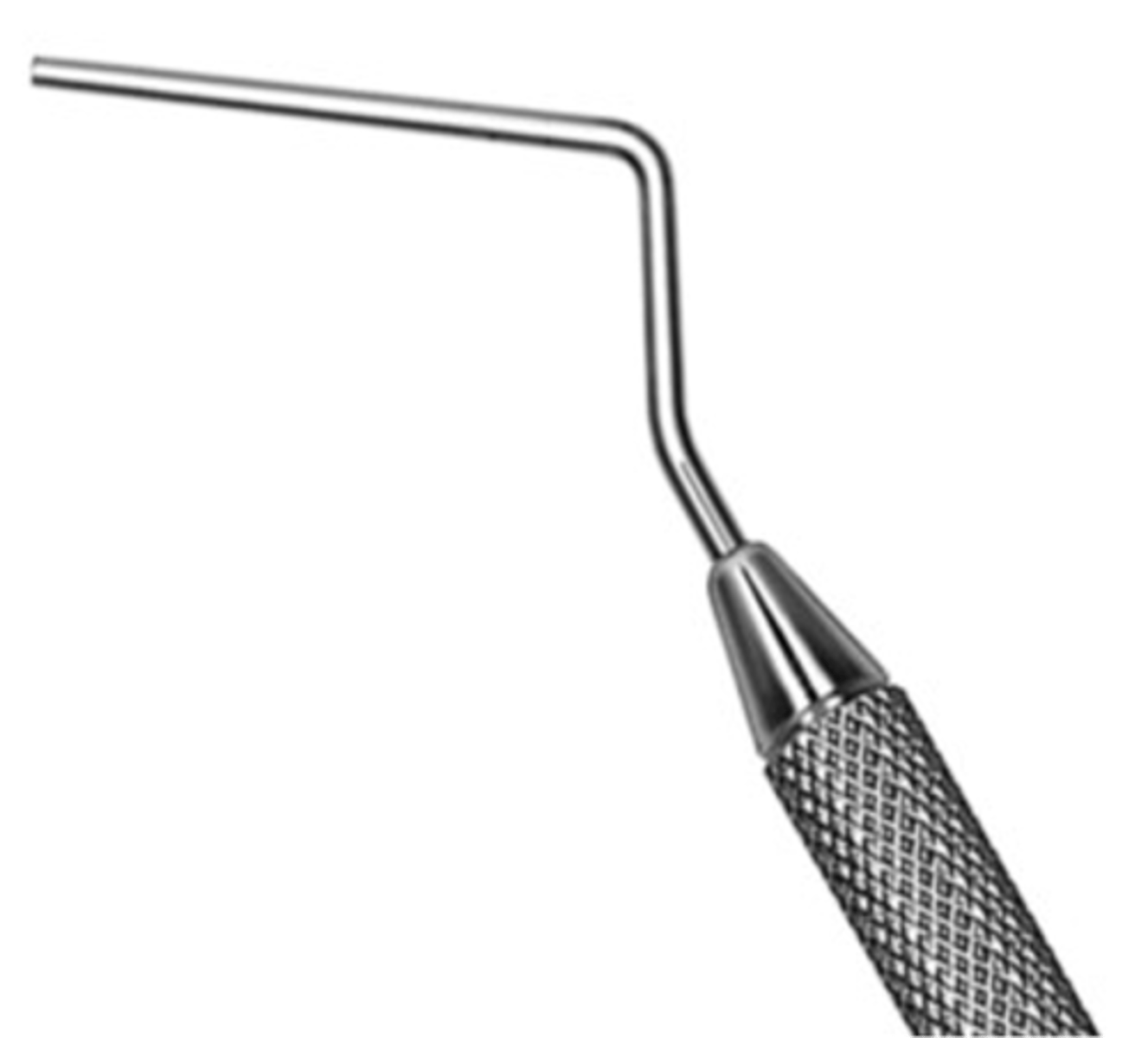

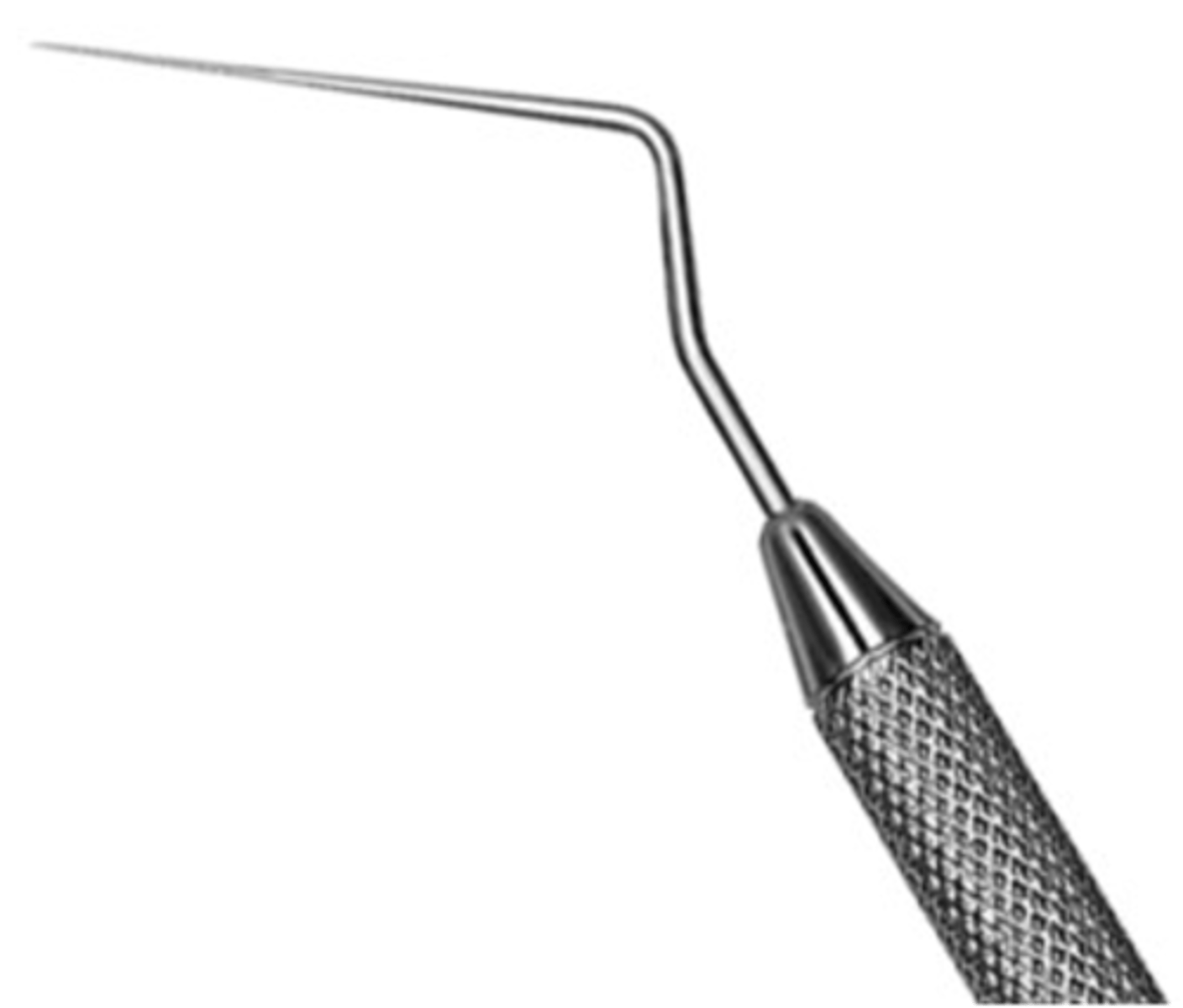
D11 SE Root Canal Spreader
•Used to compact filling material during lateral condensation
•Not used for finding canals
•Not to be heated
D11T SE Root Canal Spreader
•Titanium provides greater flexibility
•Used to compact filling material during lateral condensation
•Not used for finding canals
•Not to be heated

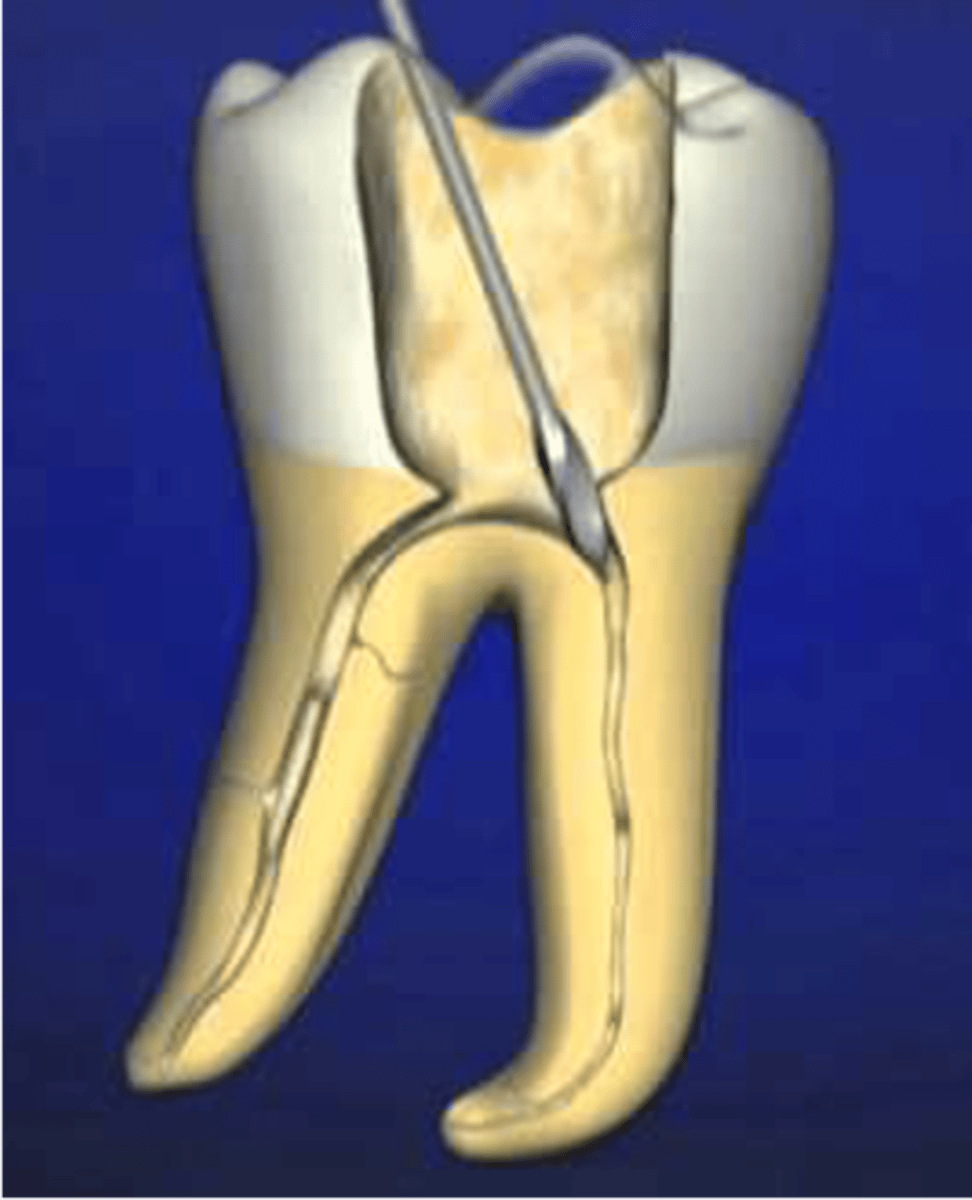
exploring and finding canals
Spreaders are not for ...
#1 DE Glick Plastic Plugger
•Used to compact gutta percha during vertical condensation
•Combination blade and 11 marked plugger
•May be heated if using as a condenser/plugger

#14A
•Deeply festooned jaws for partially erupted or irregularly shaped molars
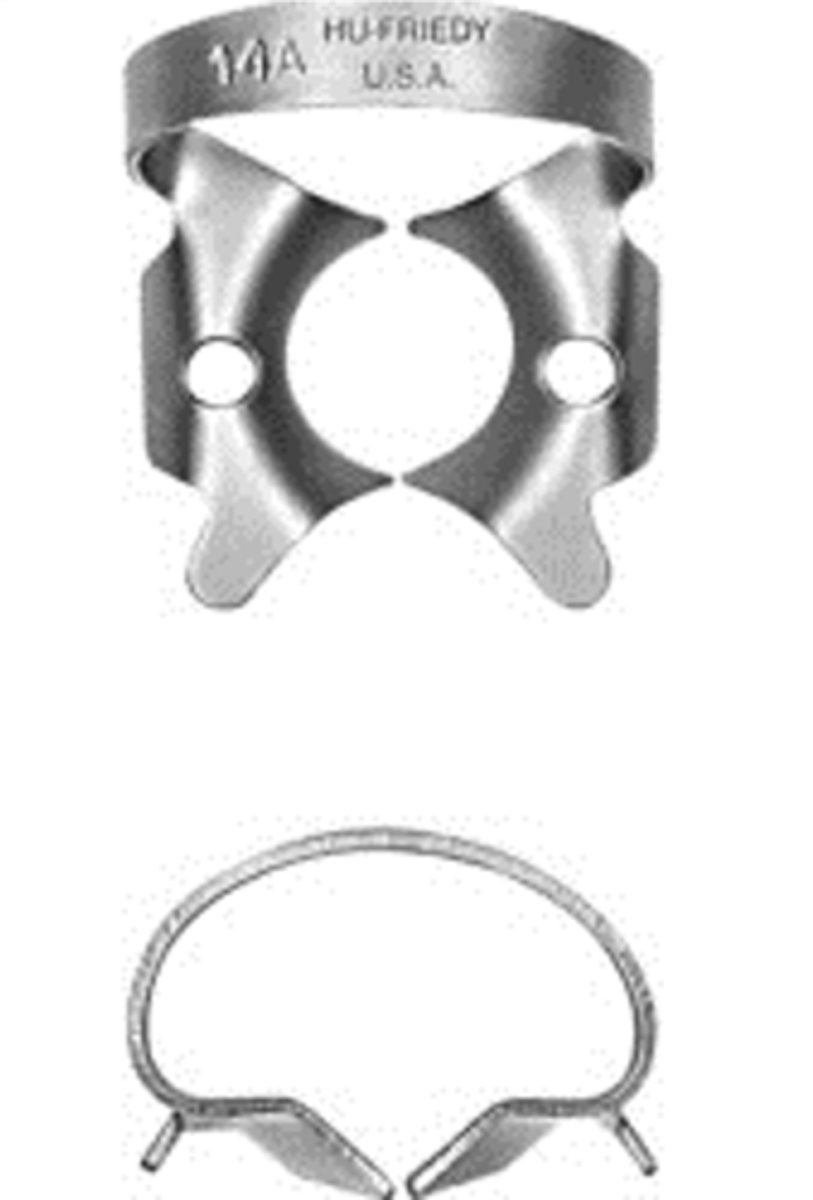

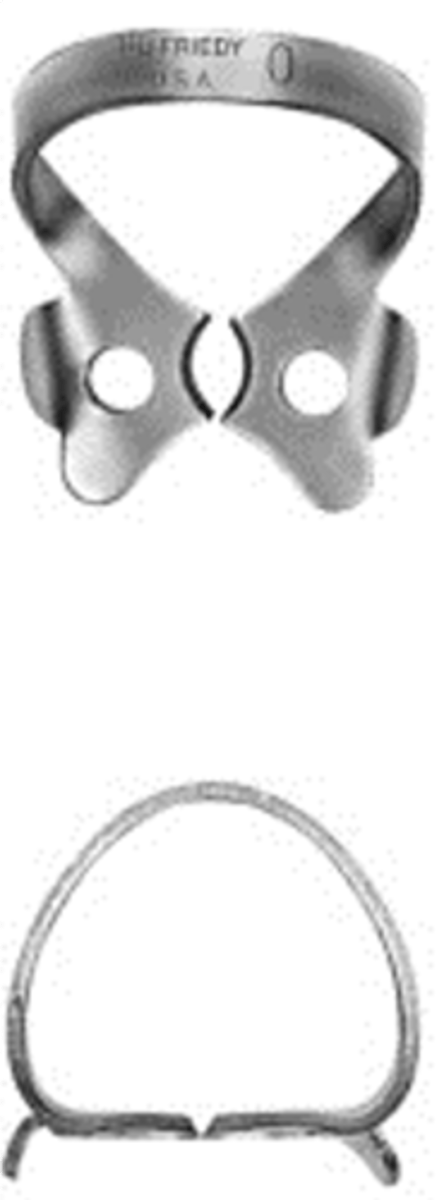
#0
•Flat jaws and high bow for longer premolars
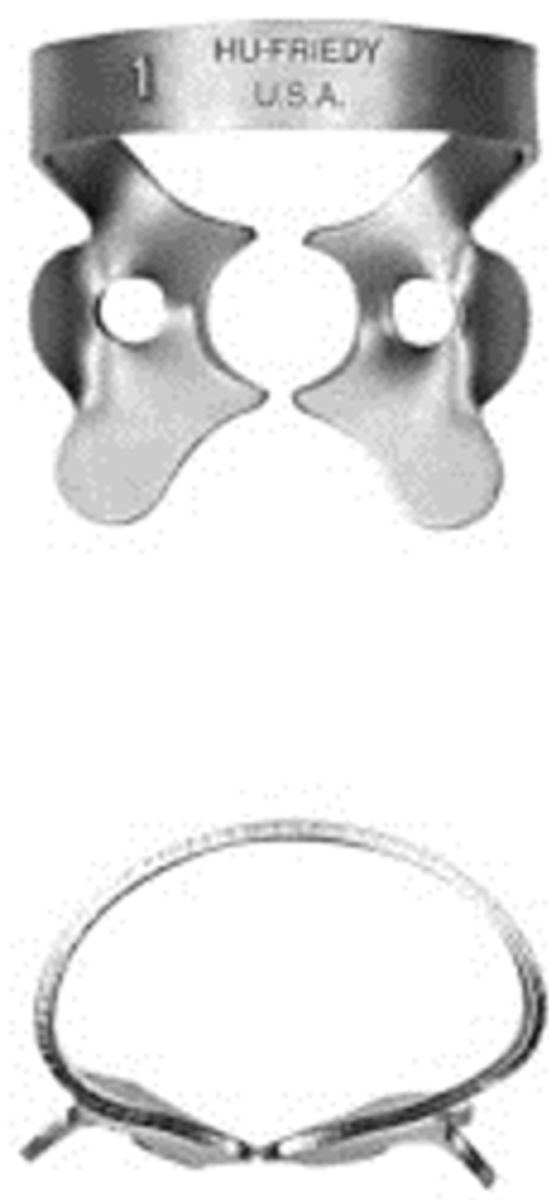
#1
•Slightly festooned jaws for upper premolars
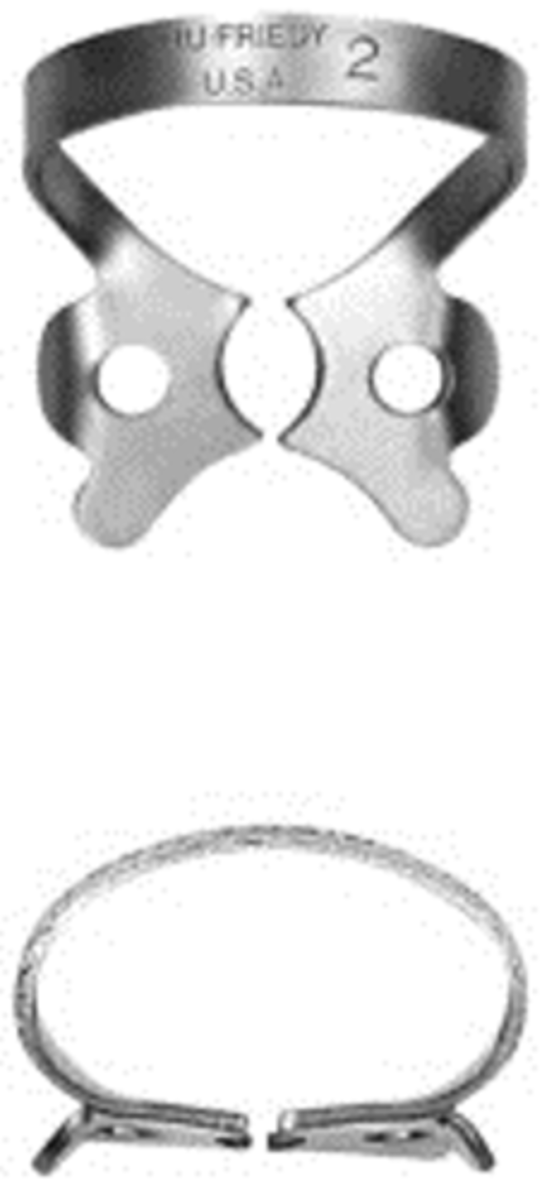
#2
•Flat jaws for premolars

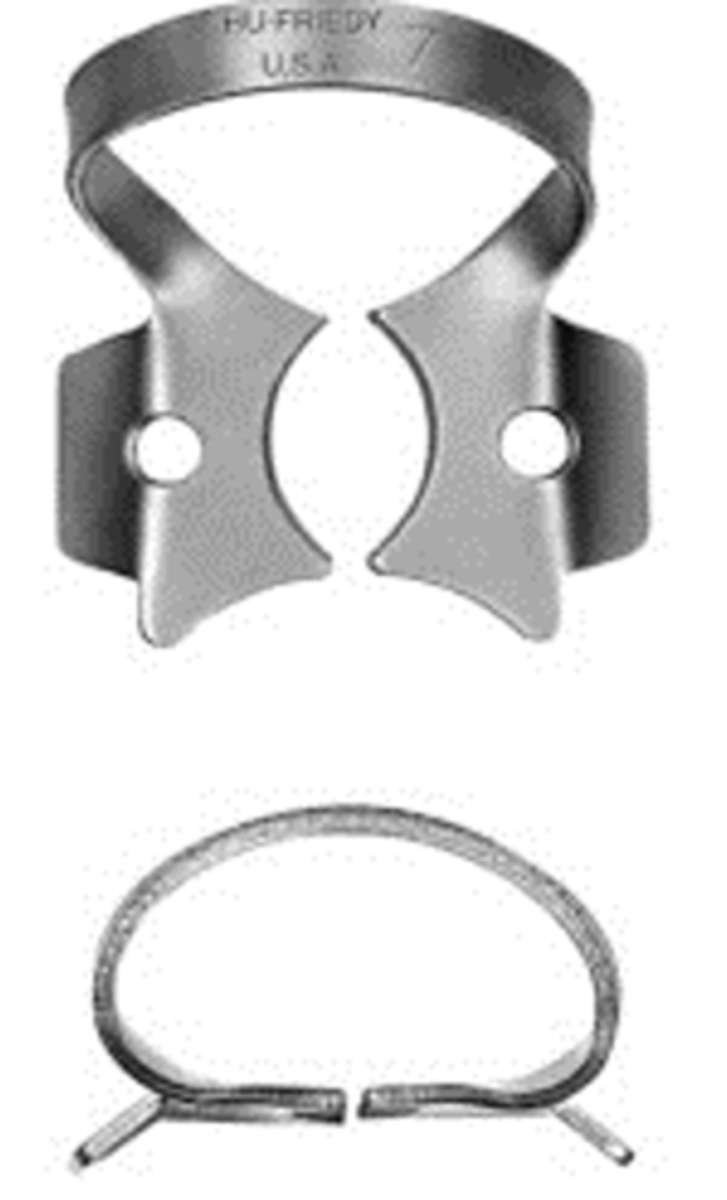
#7
•Flat jaws for lower molars

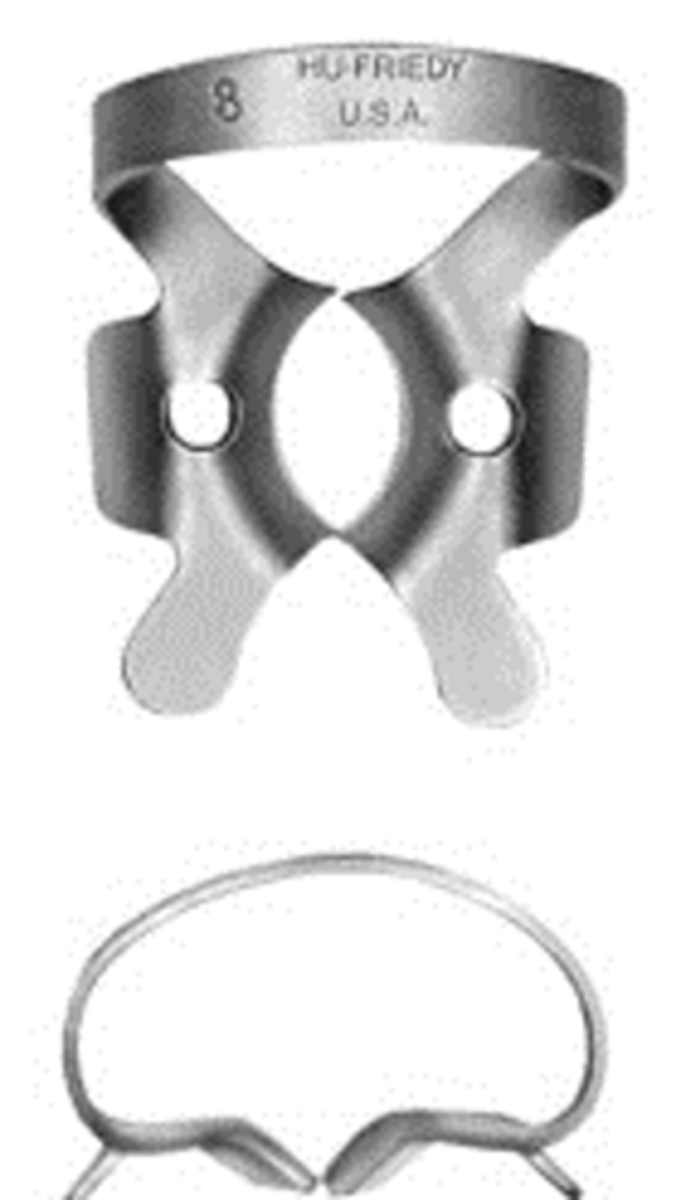
#8
•Deeply festooned jaws for upper molars

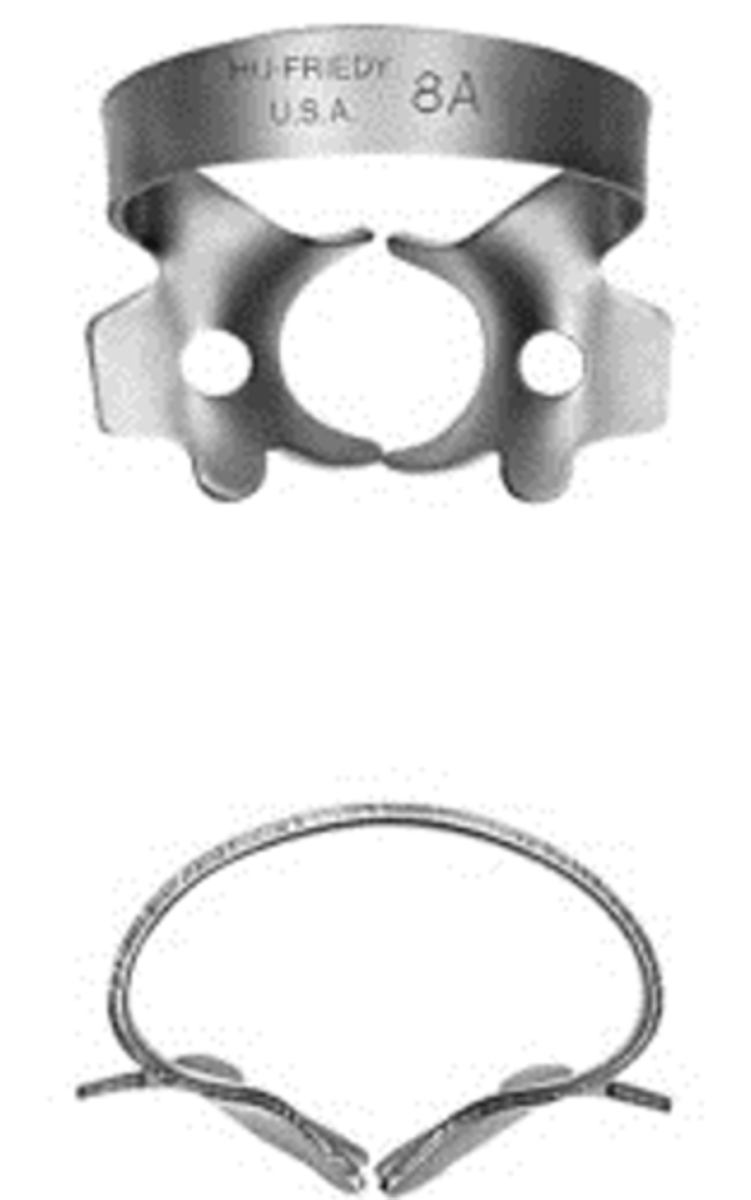
#8A
•Deeply festooned four-point jaws for molars

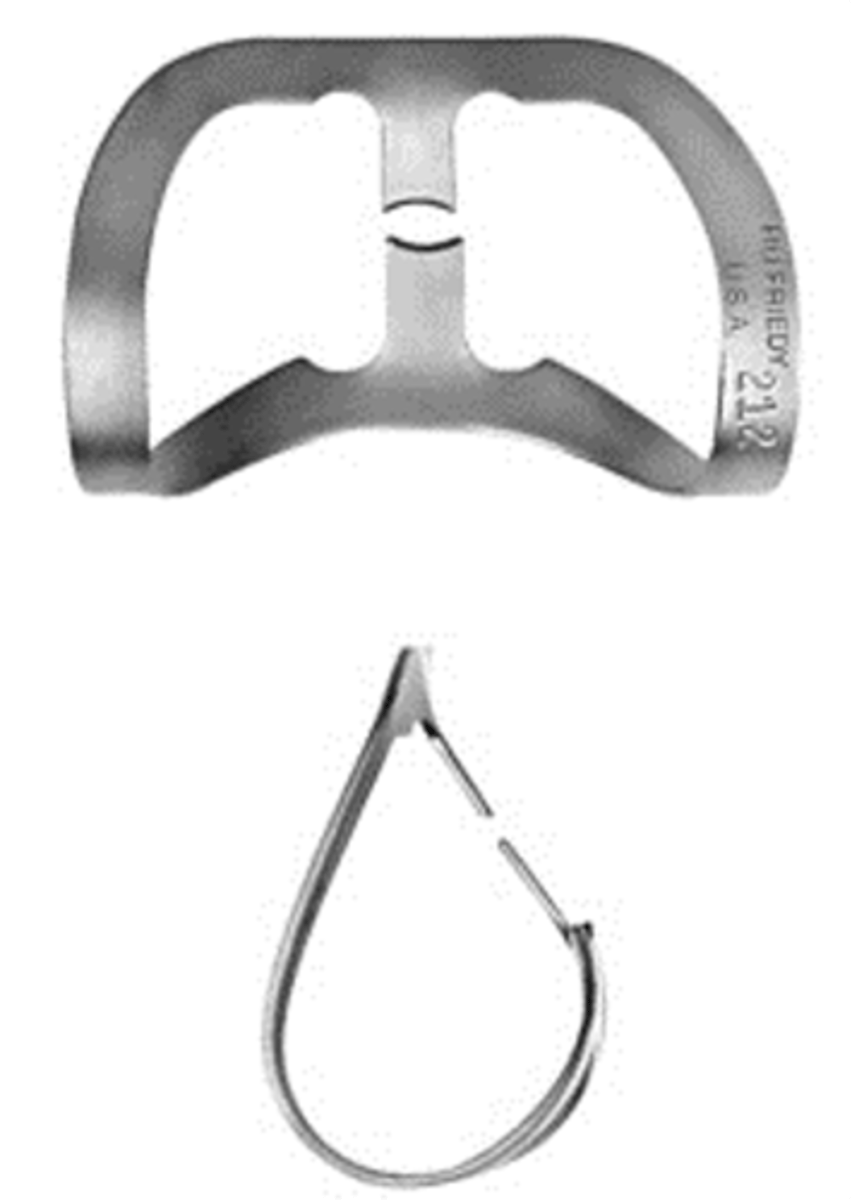
#212
•Flat jaws for labial caries on anterior teeth

#9S
•Offset flat serrated jaws for anterior teeth
tip size!
Endo Files: Color indicates...
White, Yellow, Red, Blue, Green, Black
#15 -
#20 -
#25 -
#30 -
#35 -
#40 -
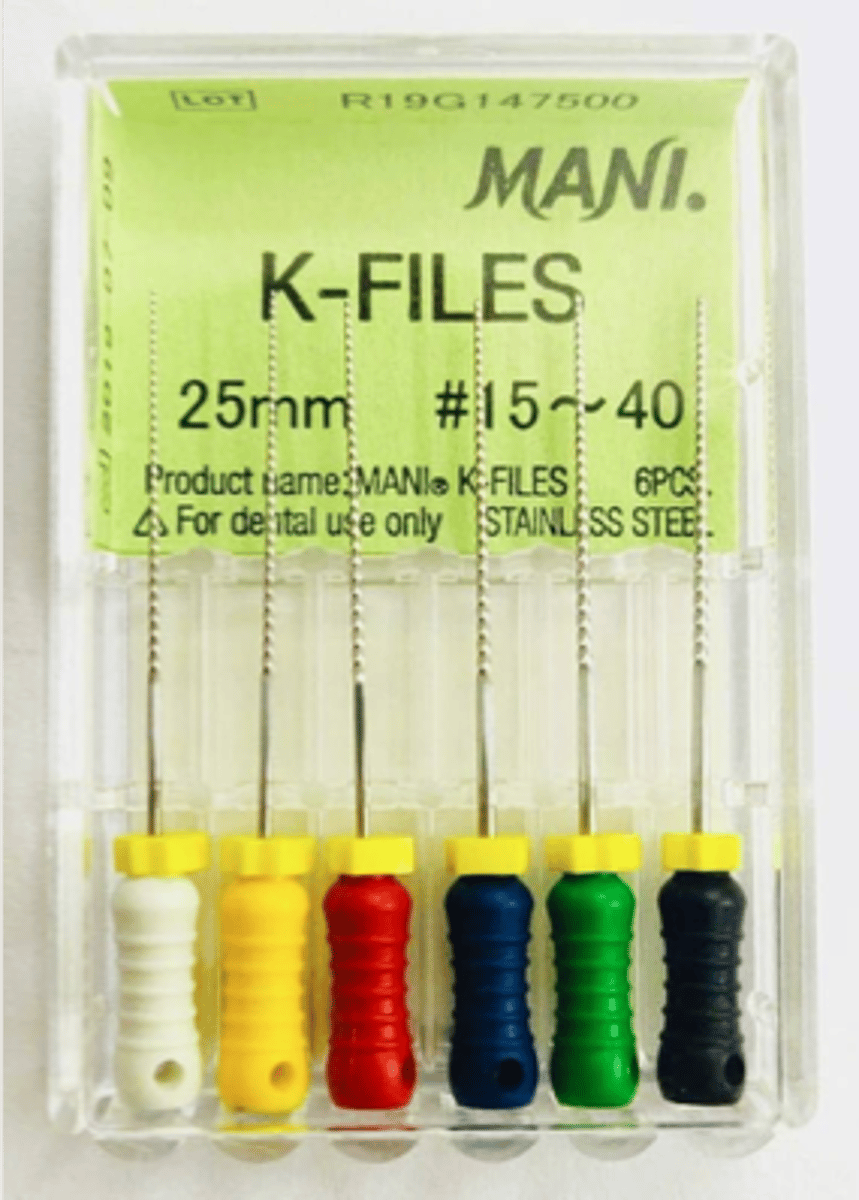
Stainless Steel K-Files
•Penetration and enlargement
•Square or triangular cross section
•"Quarter-turn, Pull."
•Standard Lengths - 21 mm, 25 mm, 31 mm
•Cutting Length - 16 mm
•ISO Color-Coded 006-140
Stainless Steel
which file types are sterilized and come with blister packs recommended for single use?
Single use
Endodontic files exhibit signs of wear during normal use, which increases dramatically with multiple use. _______ therefore reduces the risk of file breakage and thus increases patient safety.
cutting efficiency
Research has shown that using files for multiple cases reduces their __________ and therefore leads to a poorer performance. ___________ is therefore achieved when a new instrument is used for each patient.
bacteria and tissue remnants
Research shows that certain __________may remain on the instrument, post-sterilization. Single patient use will therefore eliminate such risk.
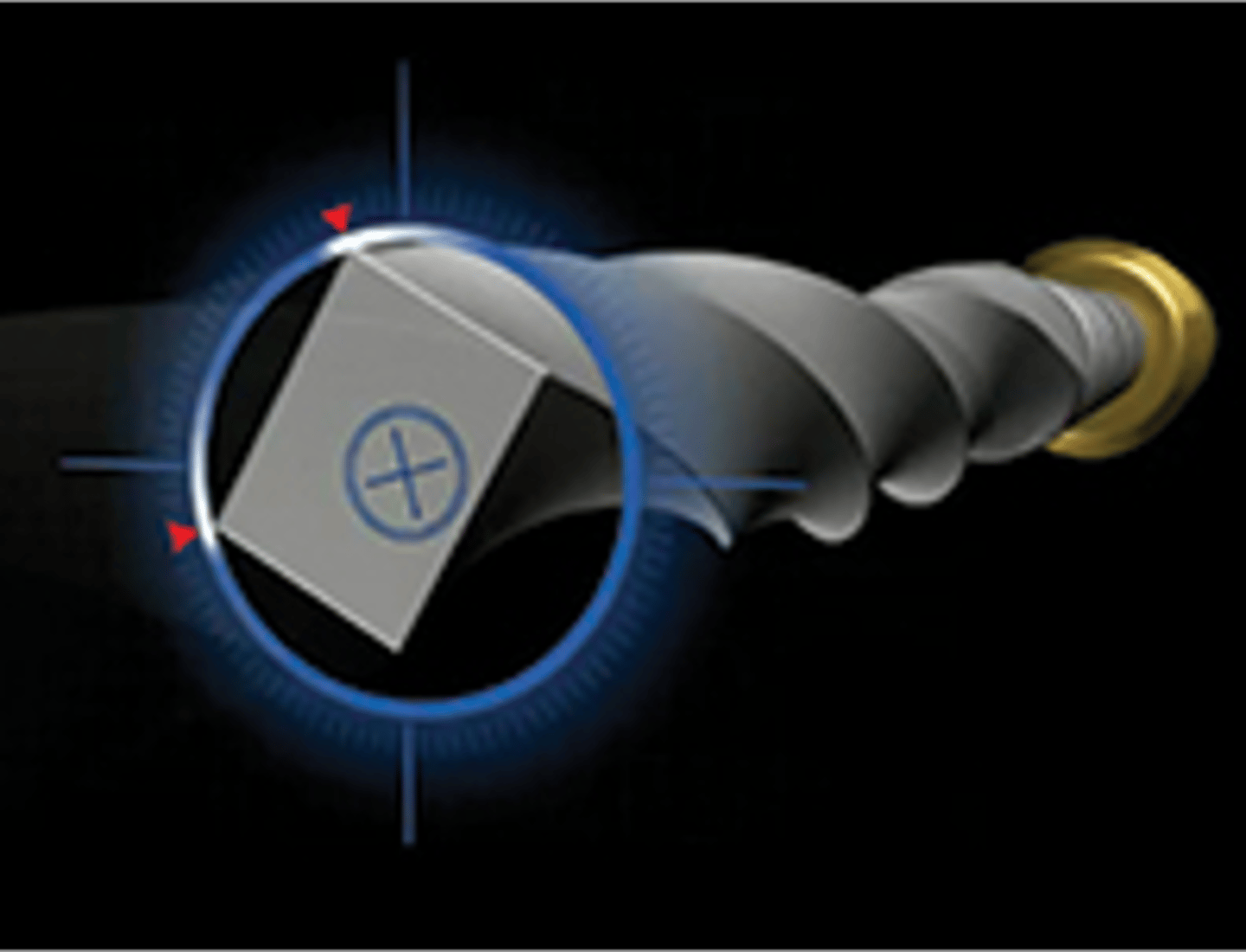
PROTAPER NEXT
features a patented off-center, rectangular core that adds greater strength as the file tracks down the canal
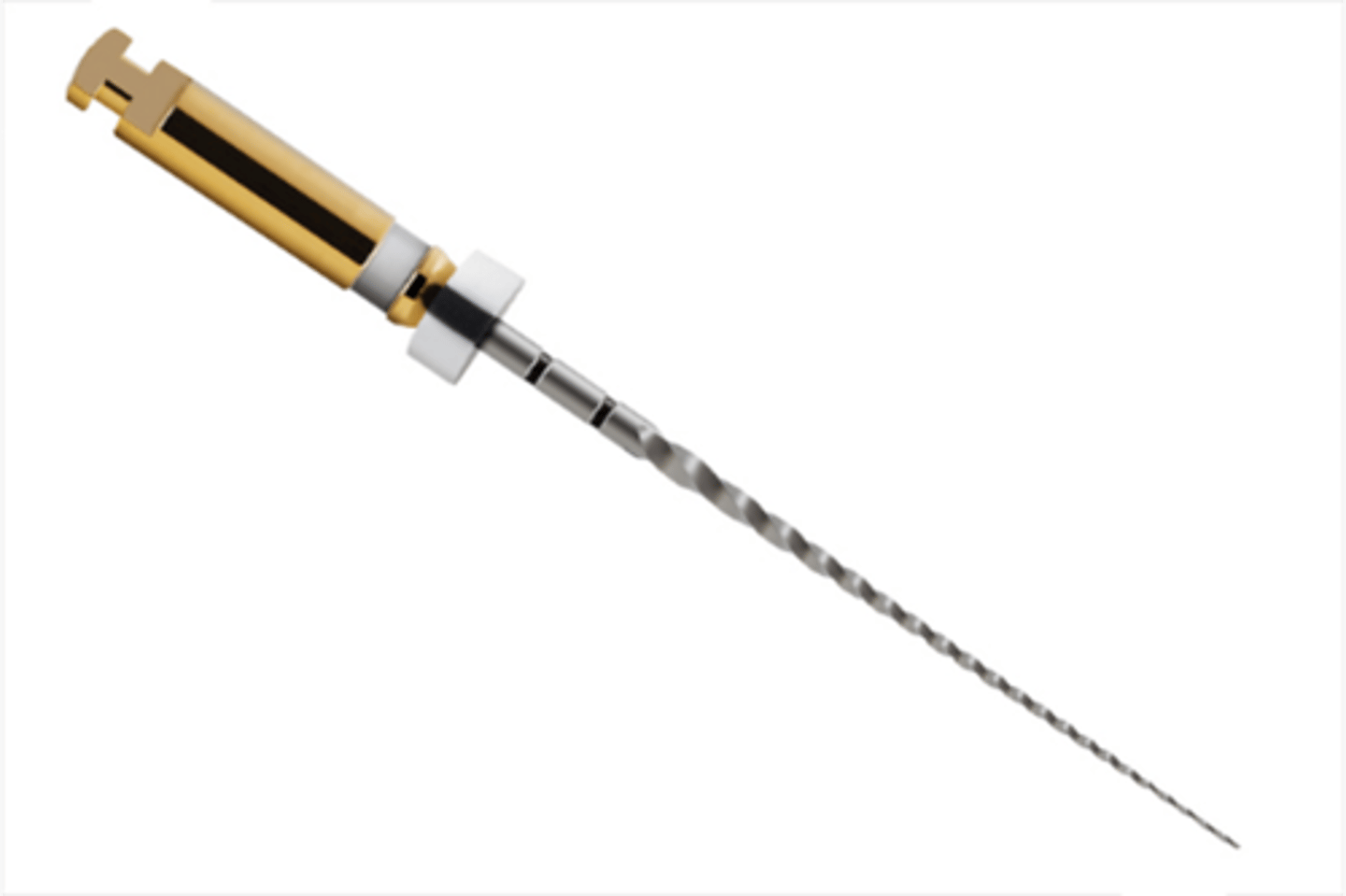
ProTaper Universal SX
•recommended for radicular access prior to canal shaping.
•Single length - 19 mm
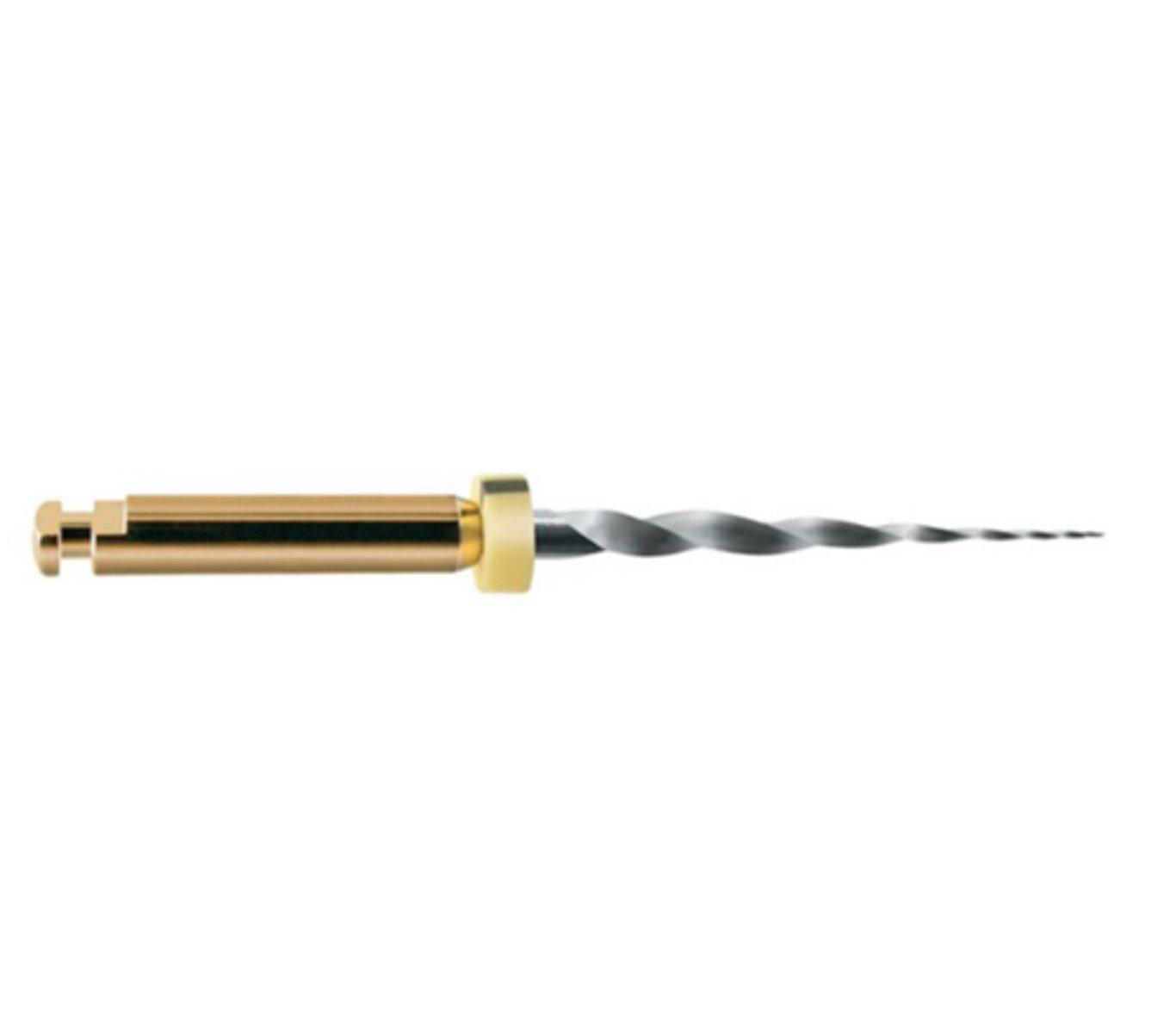

ProGlider Rotary Glide Path File
•The root canal path is lined with twists & curves that require flexibility in a file to create a predictable glide path. This file cuts this path with precision, creating a free fall to the apex for shaping file systems
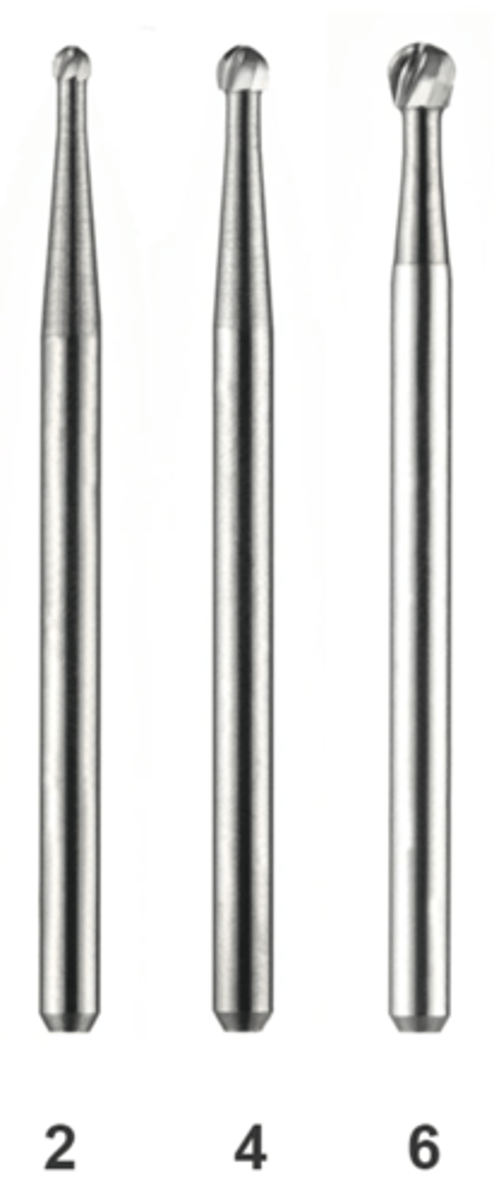
Friction Grip Round
•#2, 4, and 6
•Come in Standard Length and Surgical Length
•Used in high speed handpiece for initial access preparation

Endo-Z
•Used for finishing internal walls of access preparation
•Long, tapered bur creates a funnel shape for easier access in the pulp chamber
•9 mm cutting surface length with a non-cutting tip

Gates Glidden
•You will use #2 and 3
•Comes in sizes 1-6
•Enlarges the coronal portion of the canal for bulk removal of tooth structure
•Used for orifice shaping prior to instrumentation
Friction Grip Round #2, #4, #6
High-speed handpiece: Initial access
Endo-Z (Endo "Safety" Bur)
High-speed handpiece: Finishing internal walls of access prep
Latch Round #2, #4 - Surgical Length
Slow-speed handpiece: Extending access
ProTaper SX File
Endo Handpiece: Orifice shaping prior to Instrumentation
2.5% NaOCl in clinic
Irrigating solution
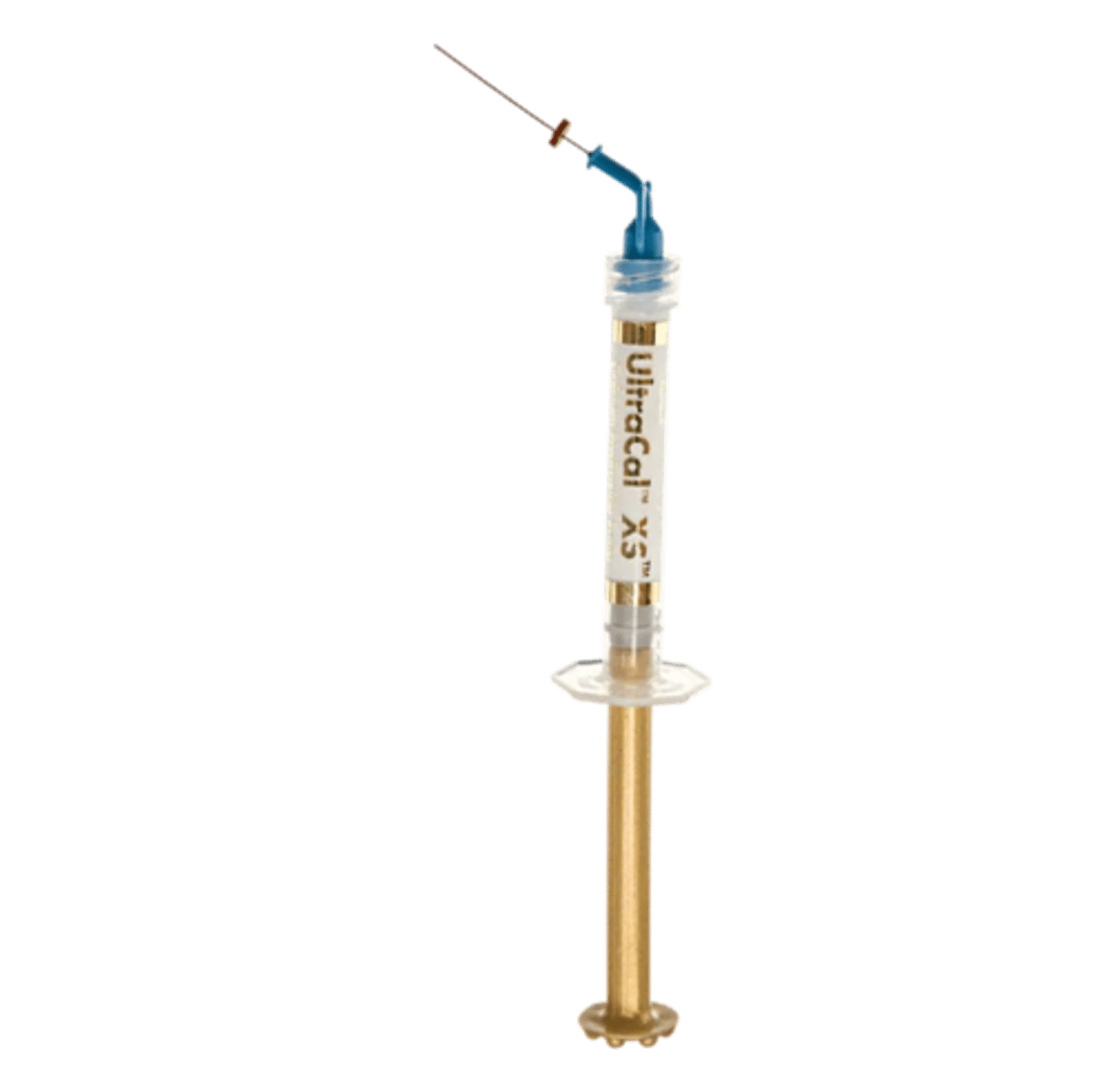
UltraCal XS30%-35% (Calcium Hydroxide Paste)
•Intracanal, inter-appointment medicament
•Aqueous and radiopaque
•High pH - 12.5
•Superior at delivery control
Jordco EndoGel
•Lubricant
•Aids in the negotiation of root canals by endodontic instruments
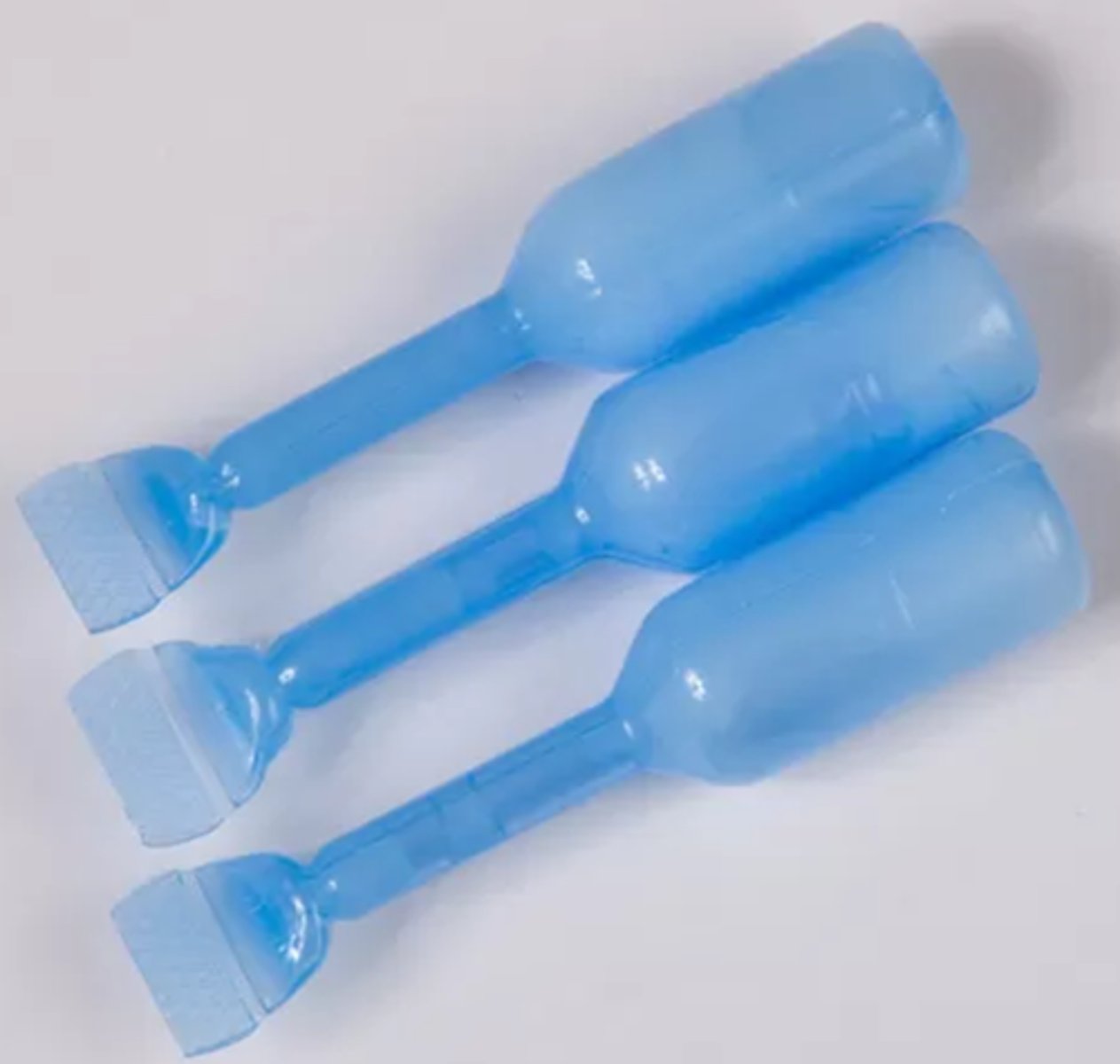

Endodontic Irrigating Syringe
•Features side-vented needle
•Mostly used for irrigation with sodium hypochlorite
96%, 86%
"The rate of success for cases with vital or non-vital pulps but having no periapical radiolucency exceed ______, whereas only _____ of the cases with pup necrosis and periapical radiolucency showed apical healing
pulp necrosis
When a tooth pulp has radiolucency, the diagnosis is most likely...
apical constriction
what does the apex locator pick up on?
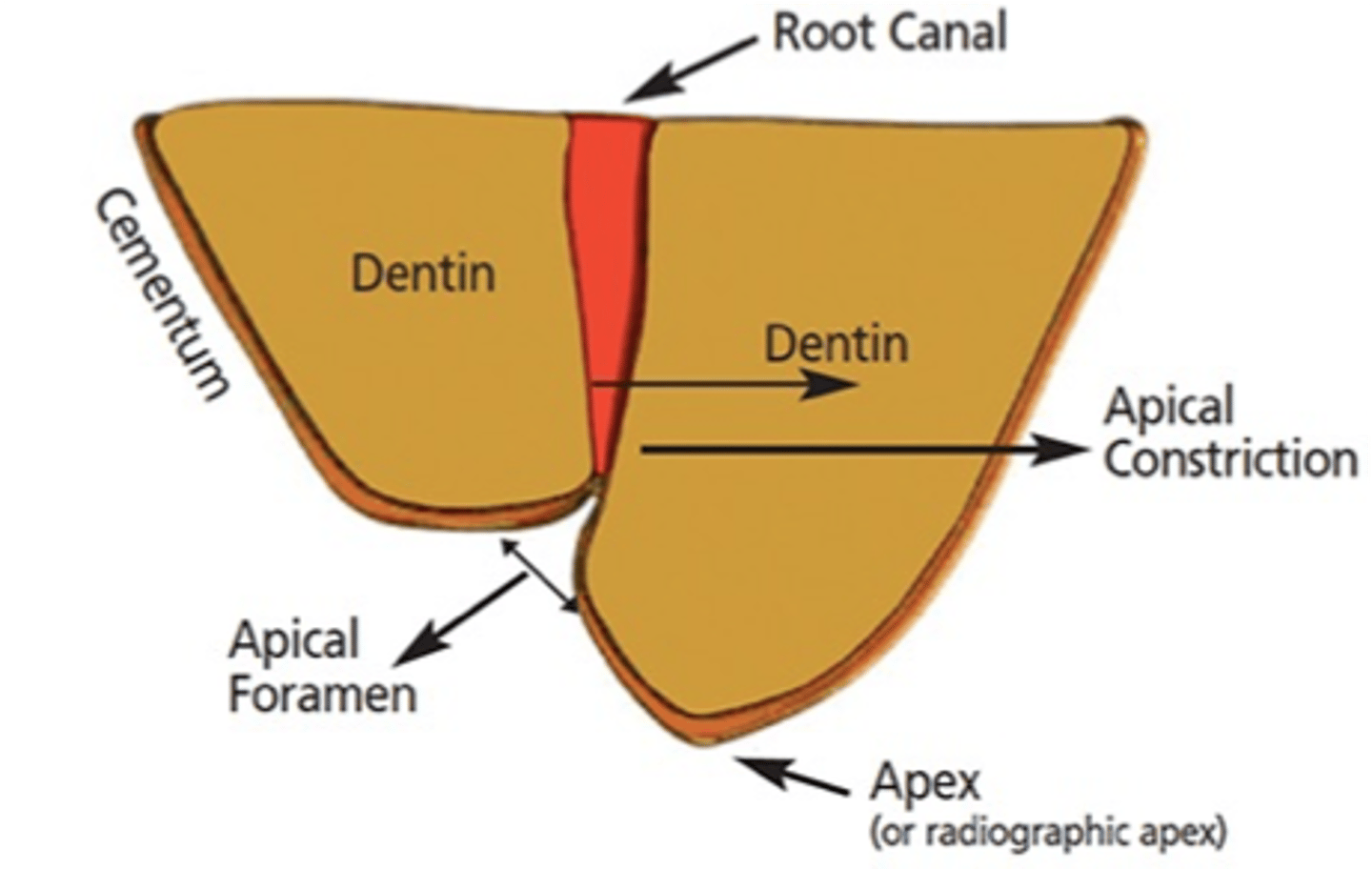
0.5mm
what is the distance measured from the apical constriction to the apical foramen
90%
When it was possible to instrument the canal to the apical constriction, how many percent of the periapical lesions healed?
69%
Only how many percentage of the cases healed when it was not possible to instrument the canal to its total length
within 2mm, >2mm from apex, long
These results are for teeth with Pulp Necrosis + Apical Lesion: within how many mms of the radiographic apex leads to 94%, 68%, and 76% success rate?
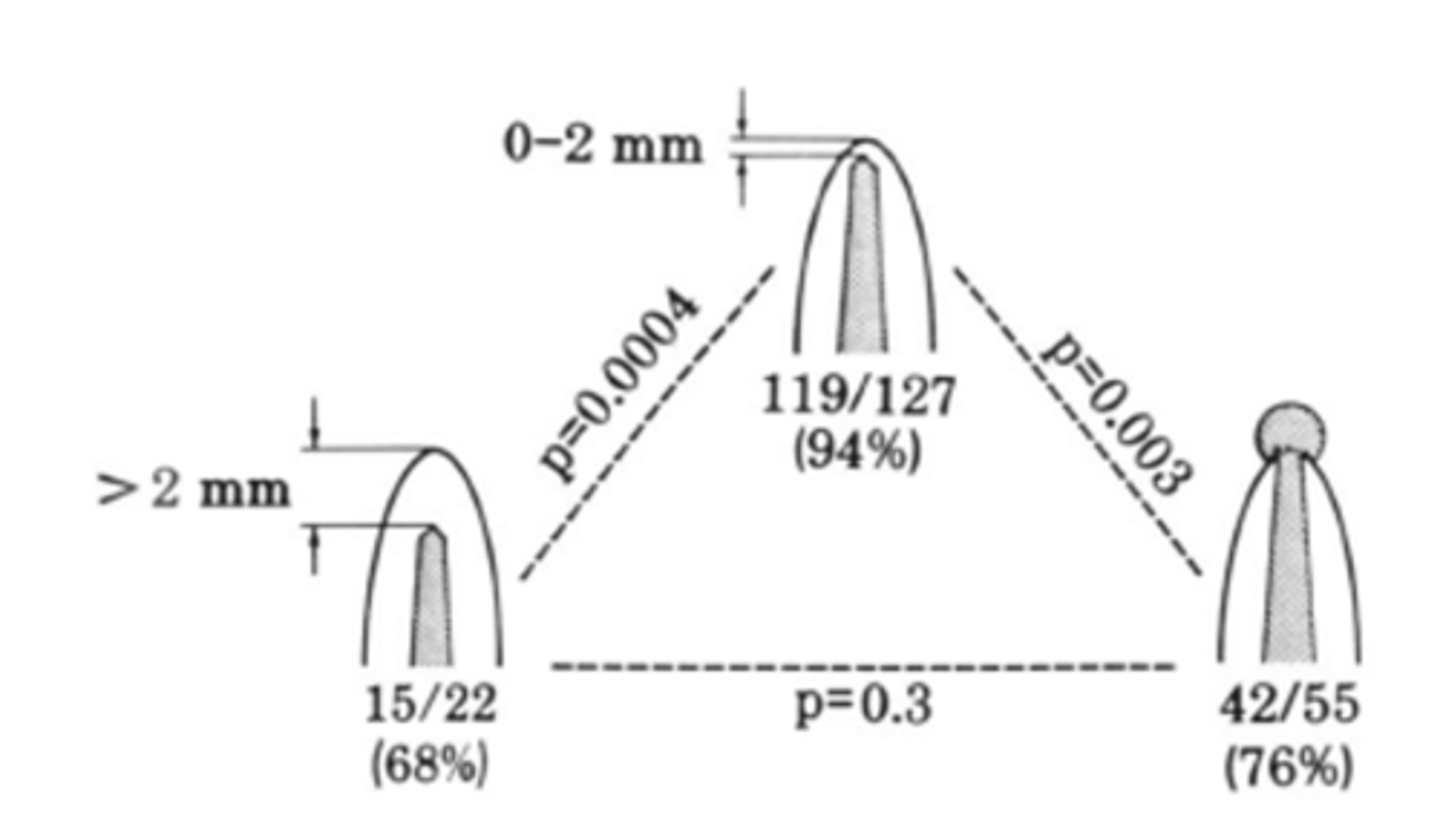
as good as
The prognosis for treatment of non-vital (Necrotic) teeth with periapical lesions was _______ that for vital teeth when the instrumentation and filling of the root canal could be carried out to an optimal level
periapical lesion.
Does Pulpal Diagnosis and/or PA Status Affect Prognosis?
-The most significant prognostic factor was presence of a ...
~0.5 mm
The apical constriction is typically located ______from the radiographic apex
LENGTH (~0.5 mm from the radiographic apex)
Aim to obturate teeth AT ...
estimated working length
Purpose of measurement calibration: To know the ________of the tooth before starting the treatment
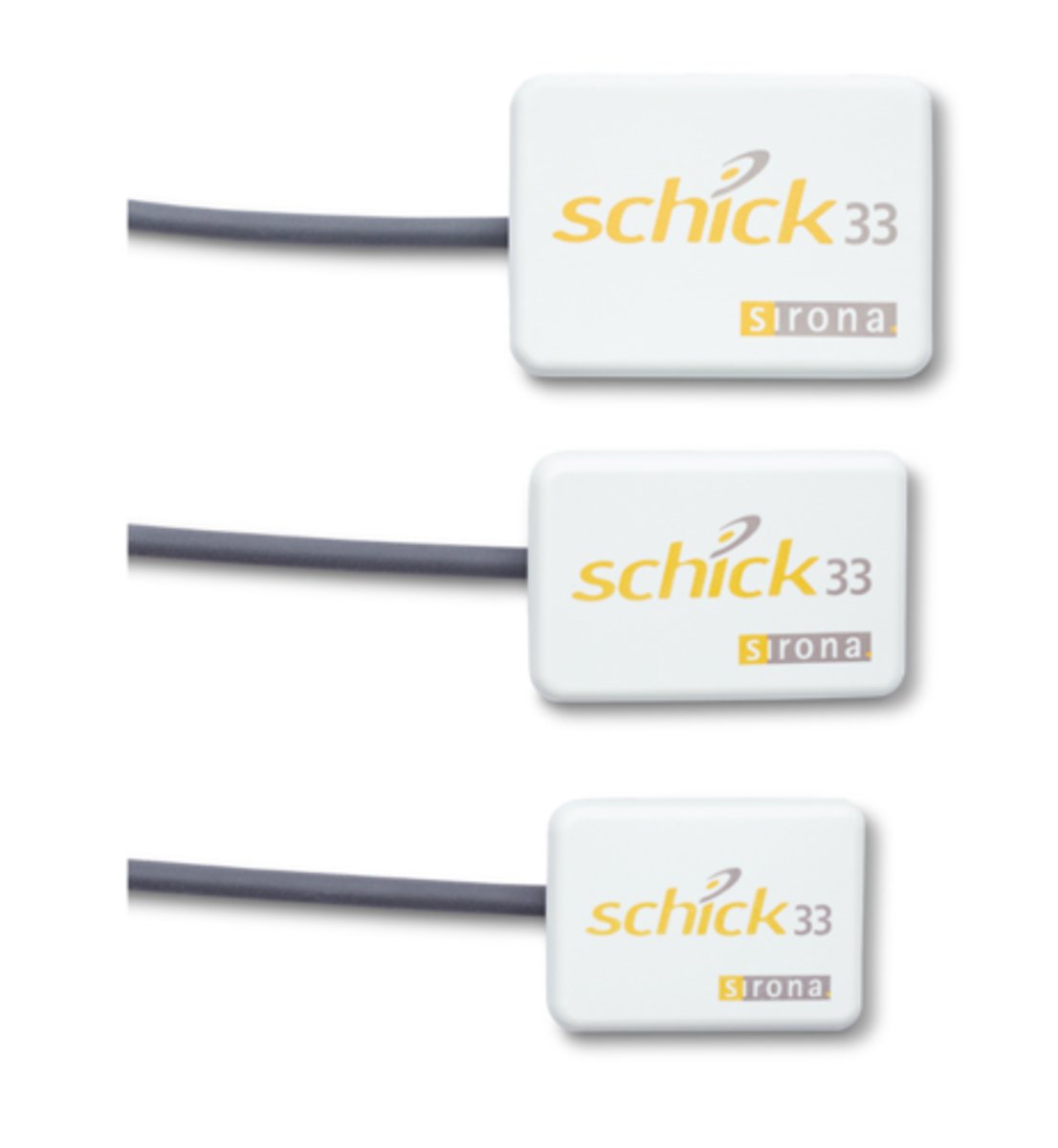
Size 2
Which SCHICK 33 sensor size for Adult bitewings and single tooth images
Active area: 25.6 x 36 mm

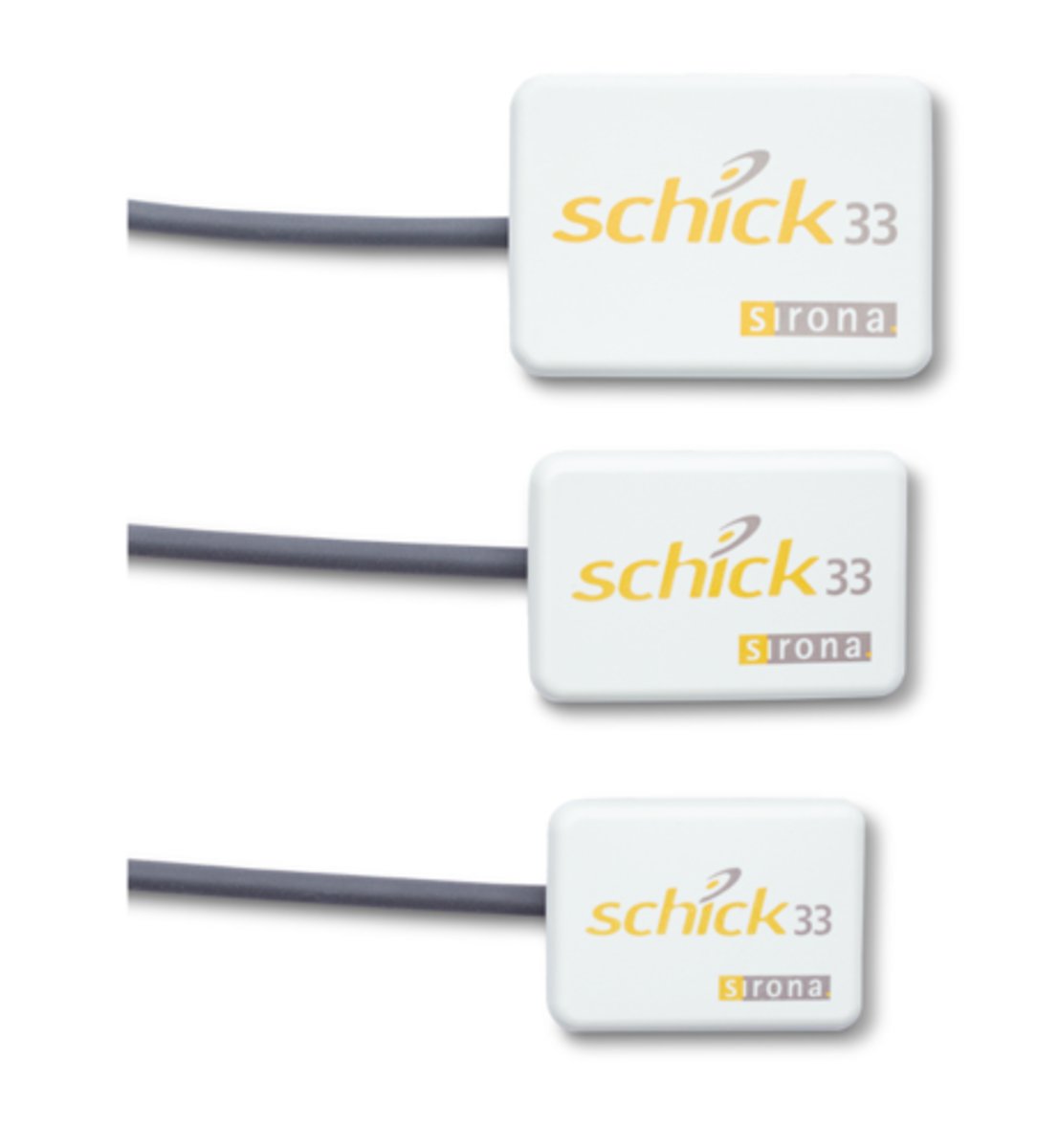
Size 1
Which SCHICK 33 sensor size for Single tooth images for smaller adults, patients with a shallow palate and bitewings for larger children
Active area: 20 x 30 mm

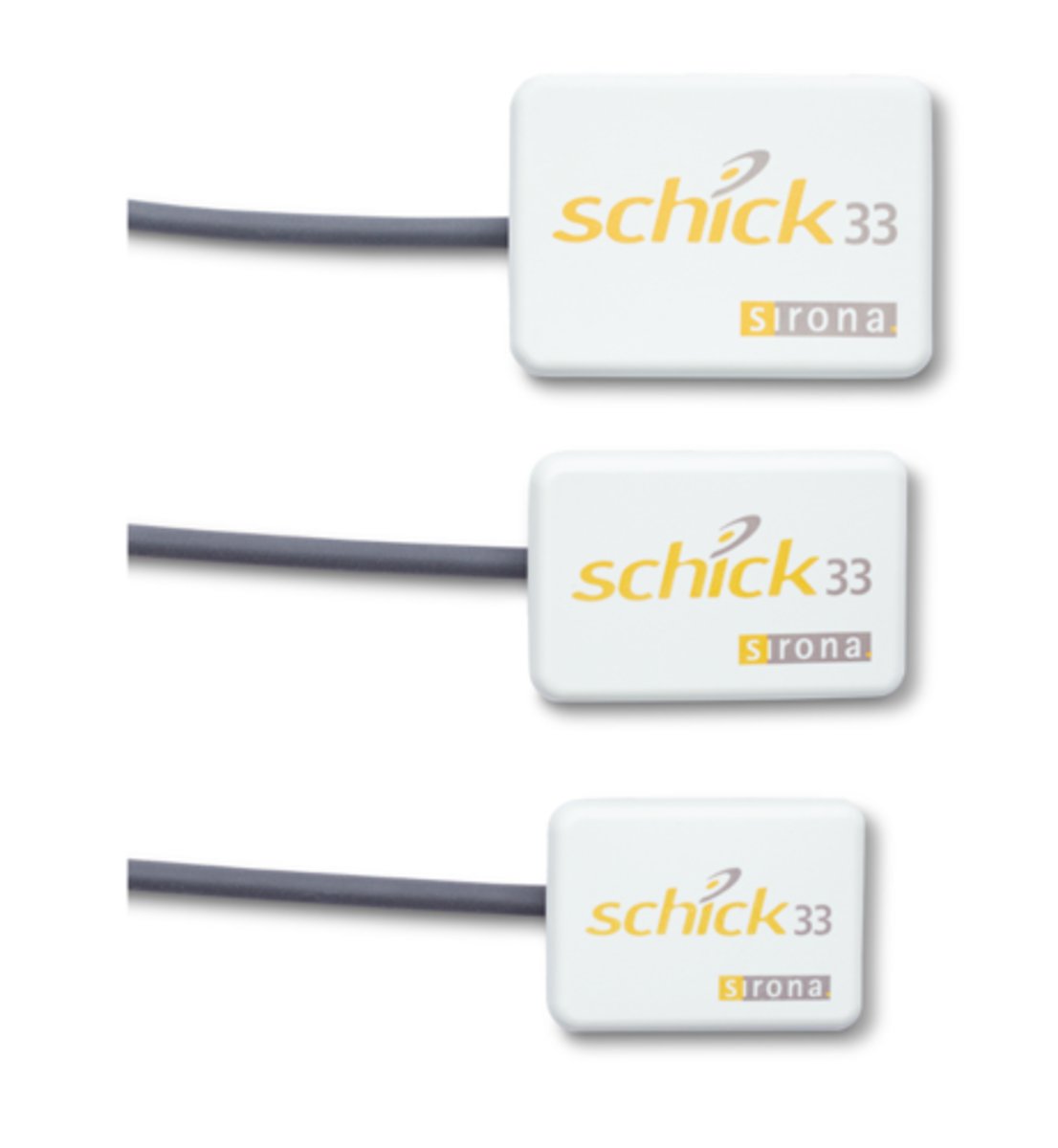
Size 0
Which SCHICK 33 sensor size for For pedo
Active area: 18 x 24 mm

0.5 mm
Estimated Working Length (EWL) : Determined by subtracting _____from the radiographic length of the tooth.
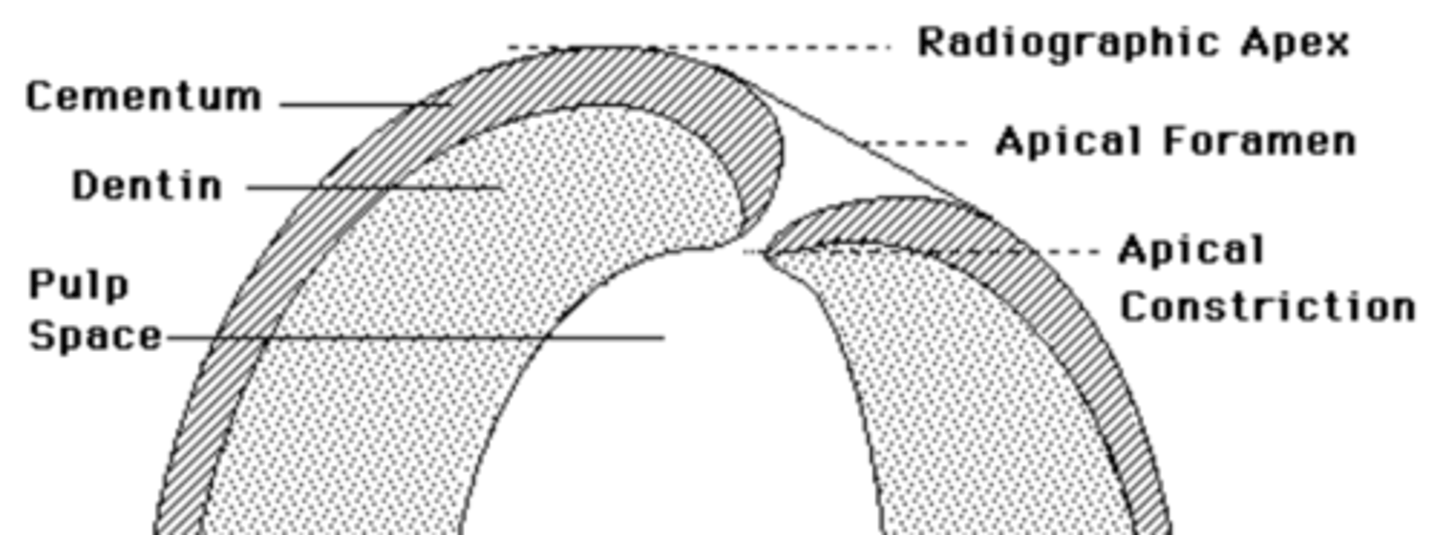
major diameter
The apical foramen is also frequently called the _________ to distinguish it from the minor diameter commonly known as the apical constriction
triangular
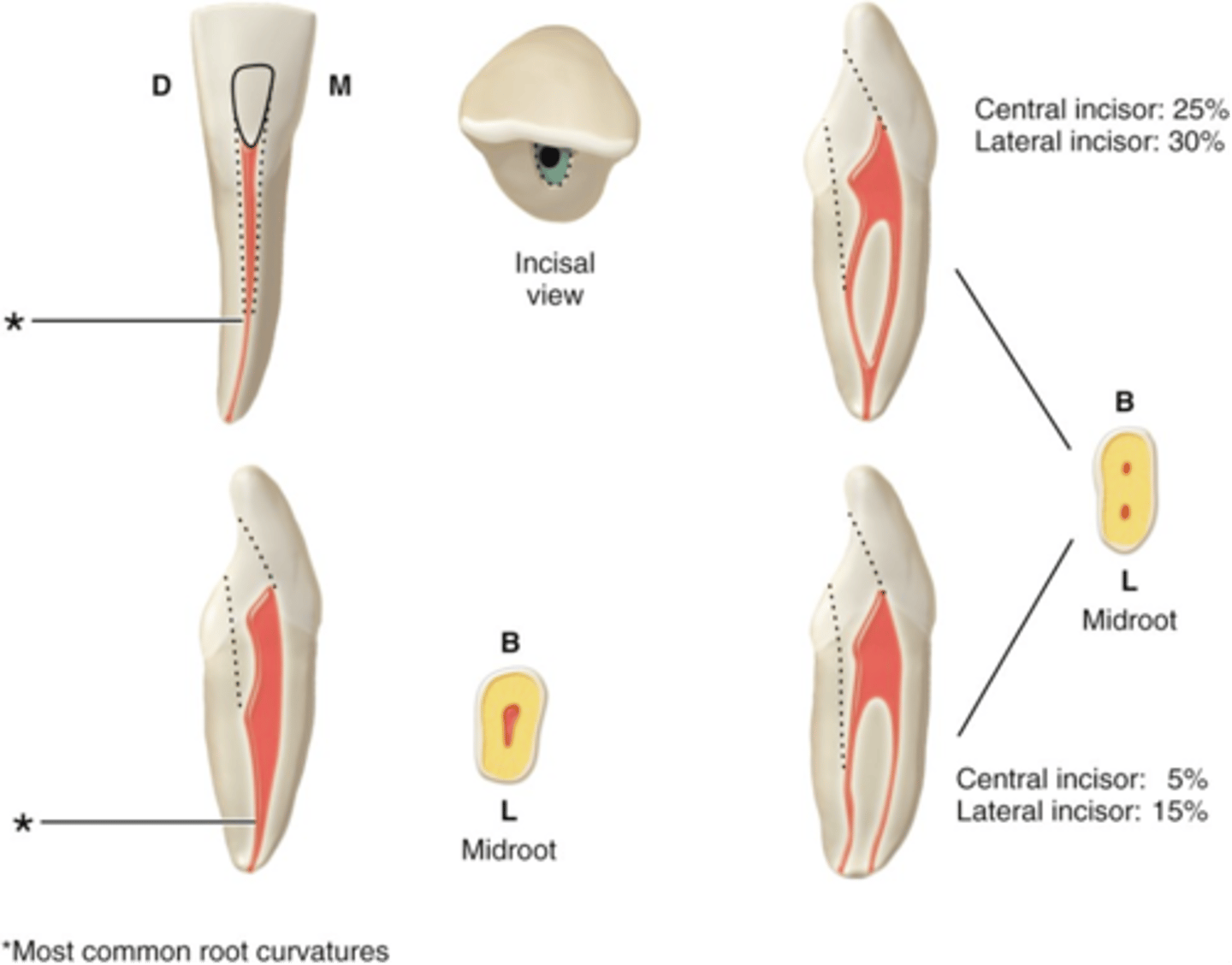
maxillary central incisors access shape
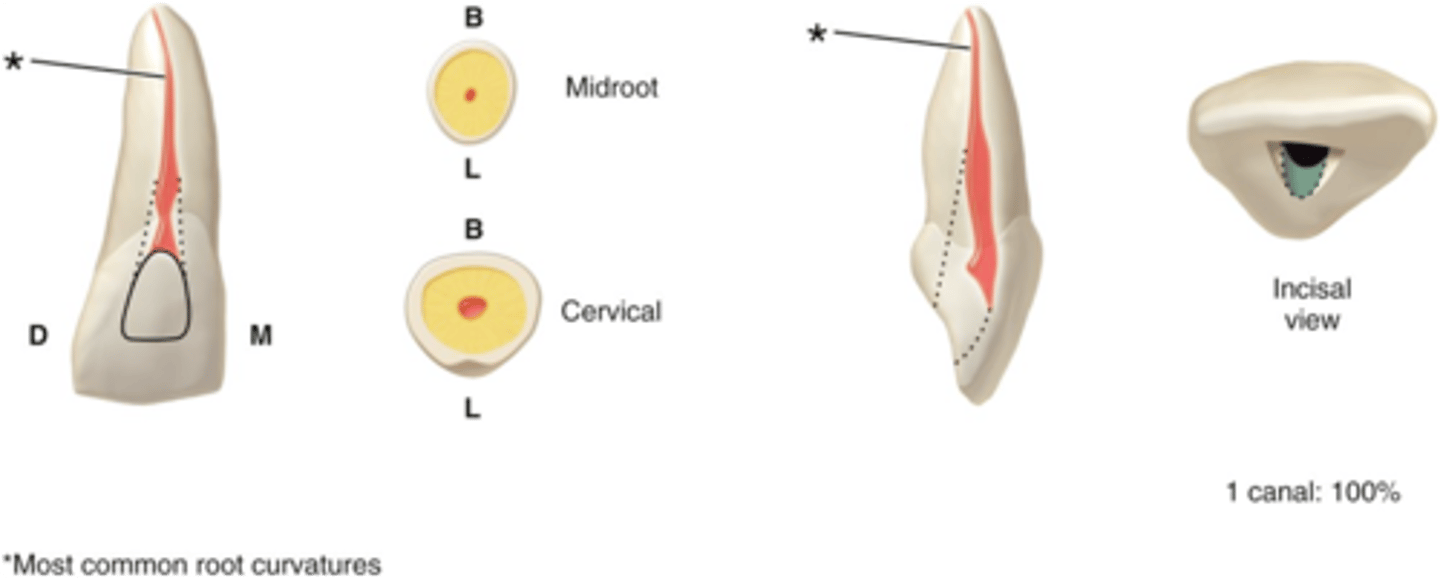
cervical 1/3
the Lingual ledge of maxillary central incisors dentin is in the ______of the crown and root.
1
maxillary central incisors number of canals
S
maxillary central incisors configuration of canals
rounded, triangular/ovoid
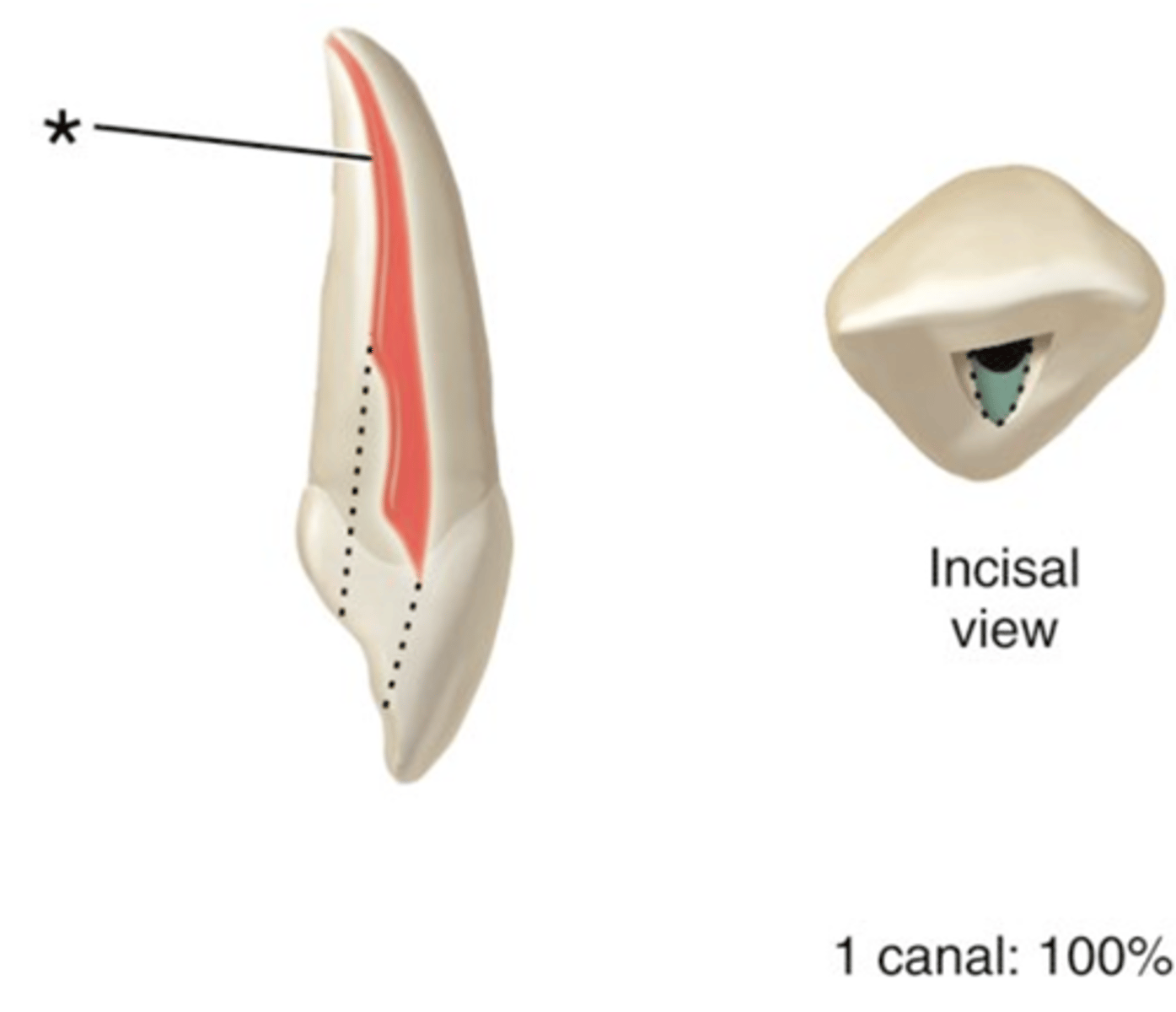
Maxillary lateral incisors access shape
1
Maxillary lateral incisors number of canals
S
Maxillary lateral incisors configuration of canals
ovoid
maxillary canine access shape
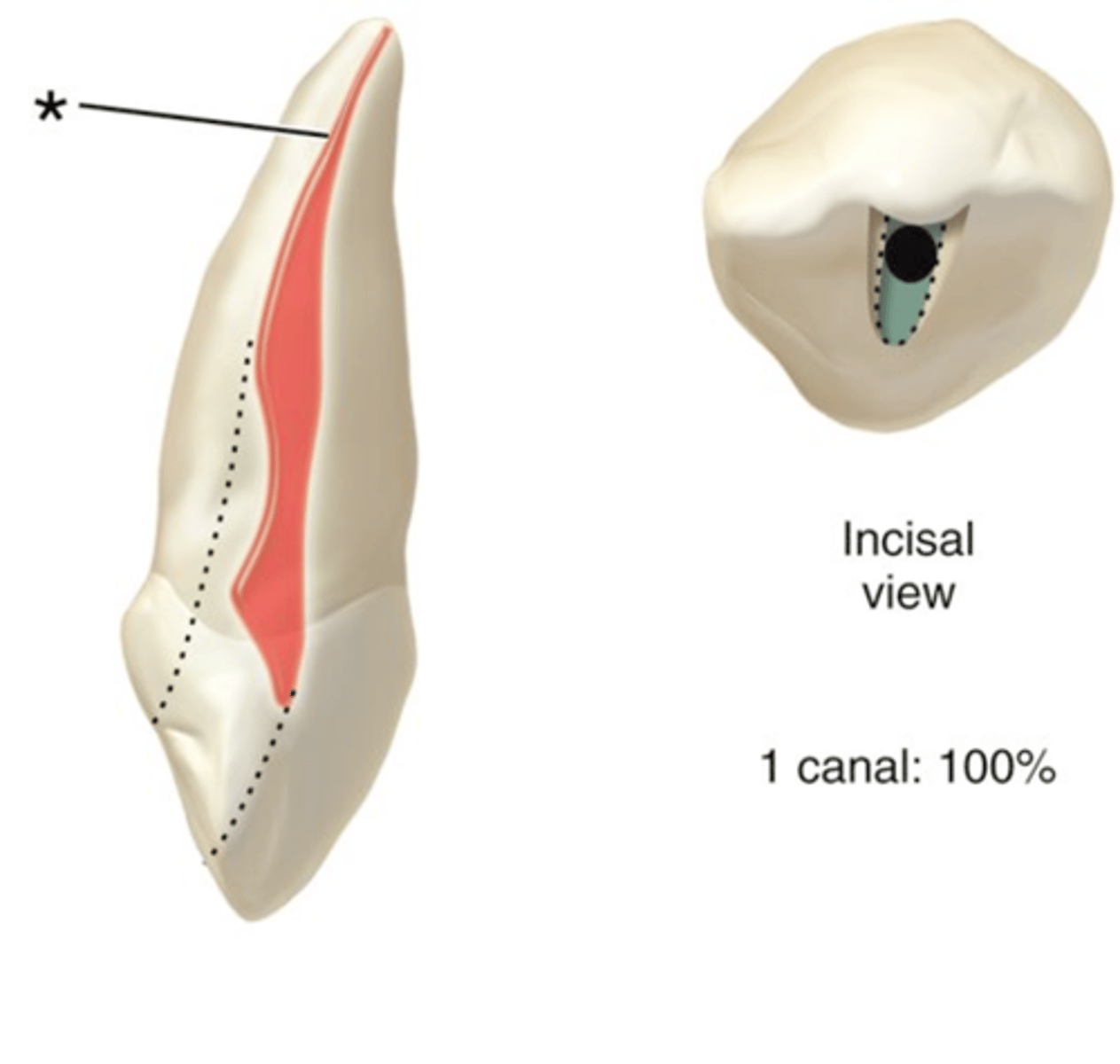
1
maxillary canine number of canals
S
maxillary canine configuration of canals
ovoid
maxillary first premolars access shape
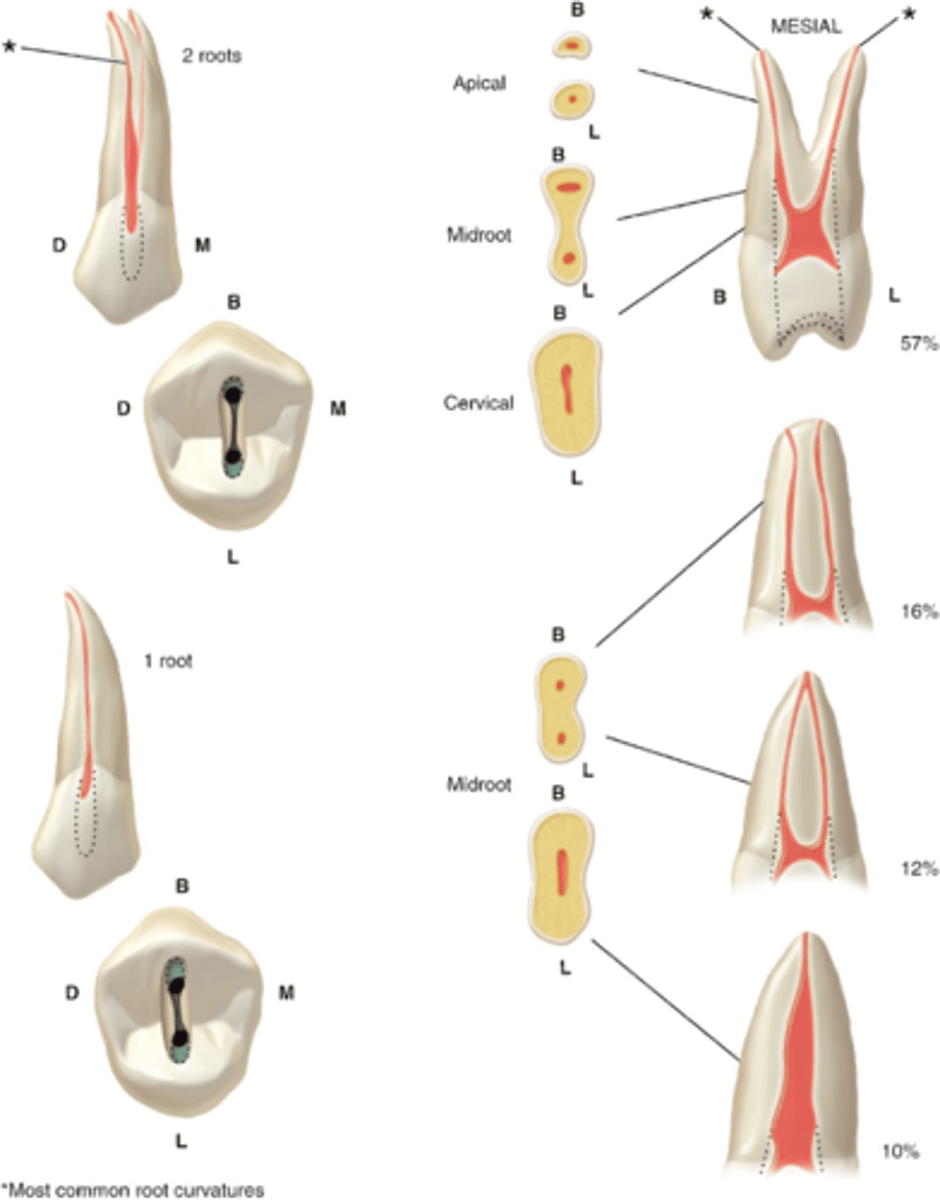
2
maxillary first premolars number of canals
B,P
maxillary first premolars configuration of canals
ovoid
maxillary second premolar access shape
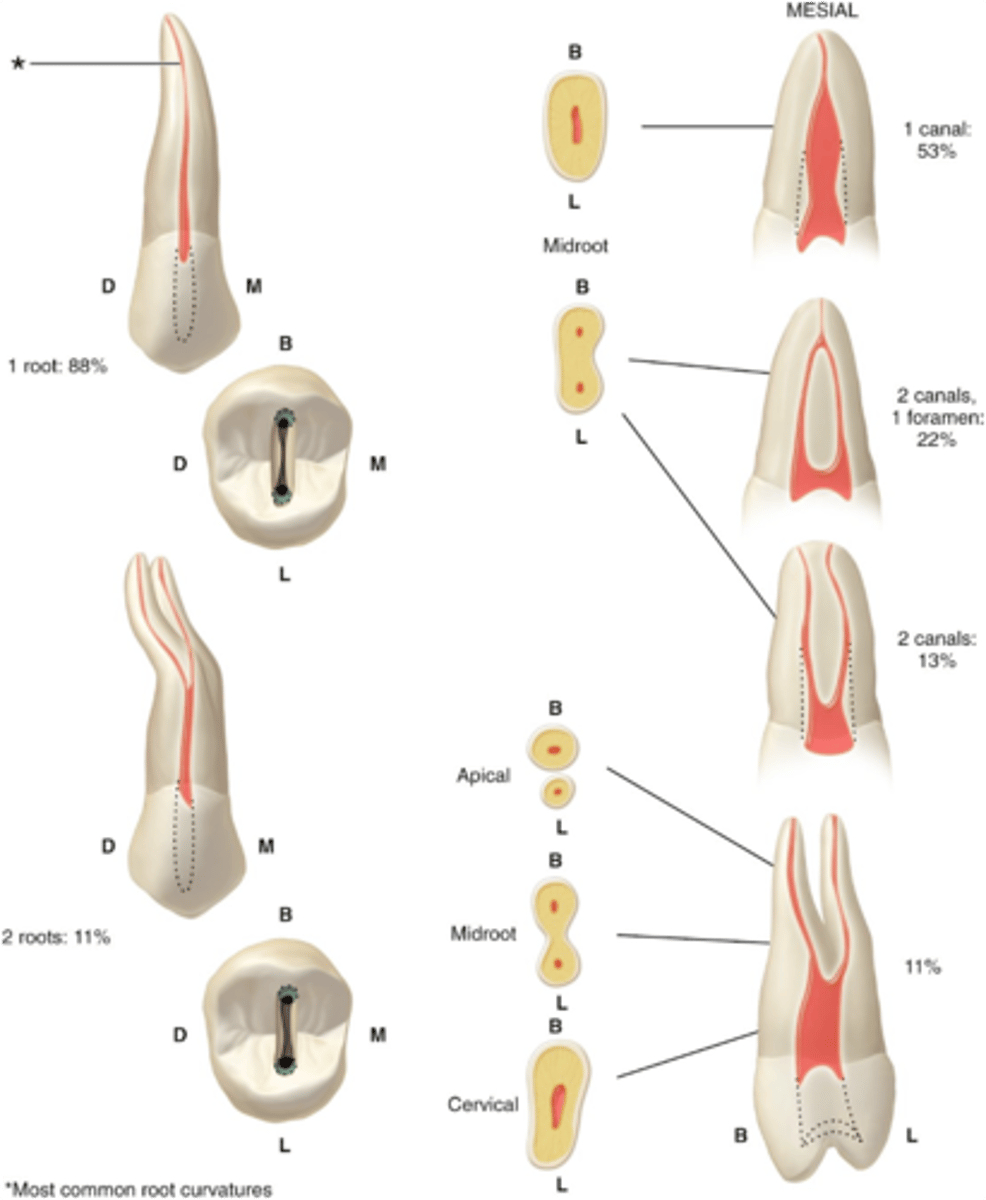
1-2
maxillary second premolars number of canals
S or B+P
maxillary second premolars configuration of canals
oblong triangular
maxillary first molar access shape
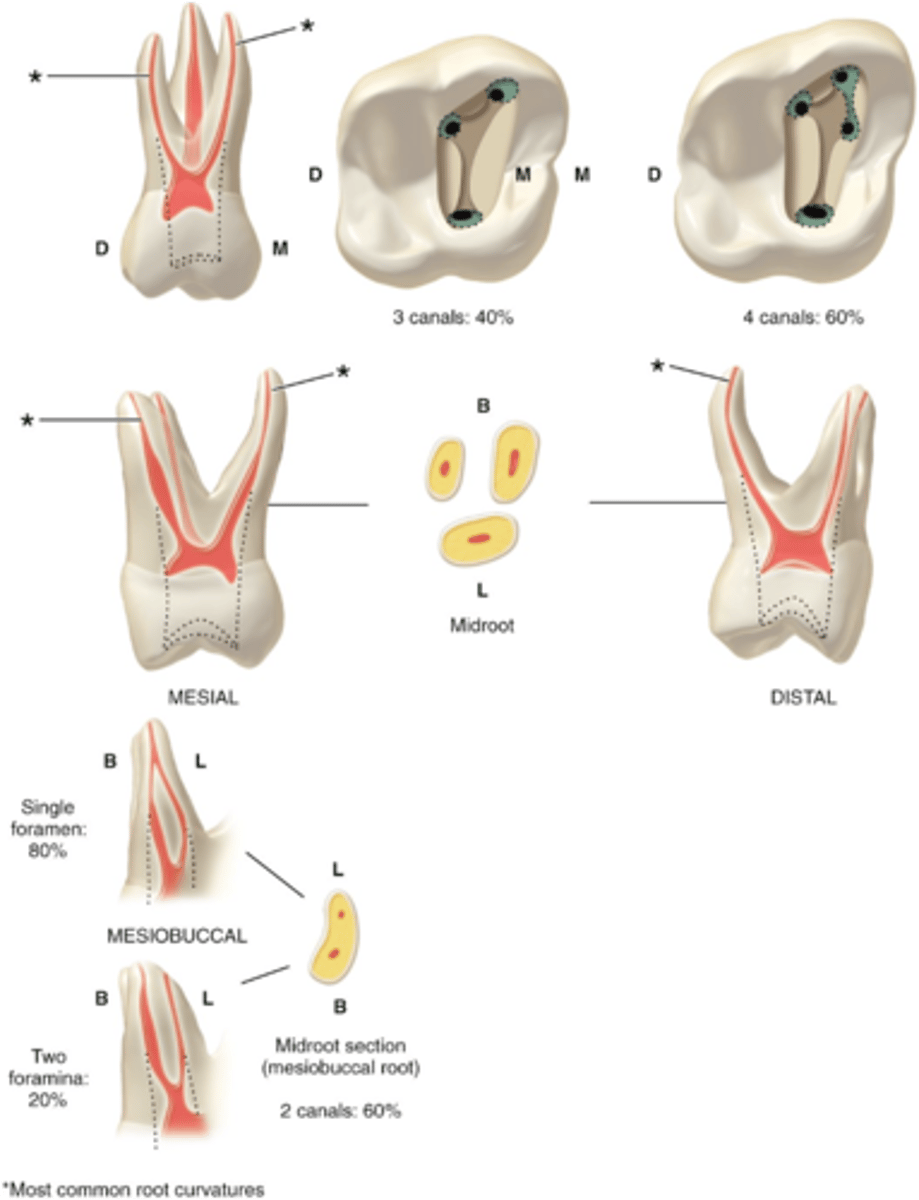
3-4
maxillary first molar number of canals
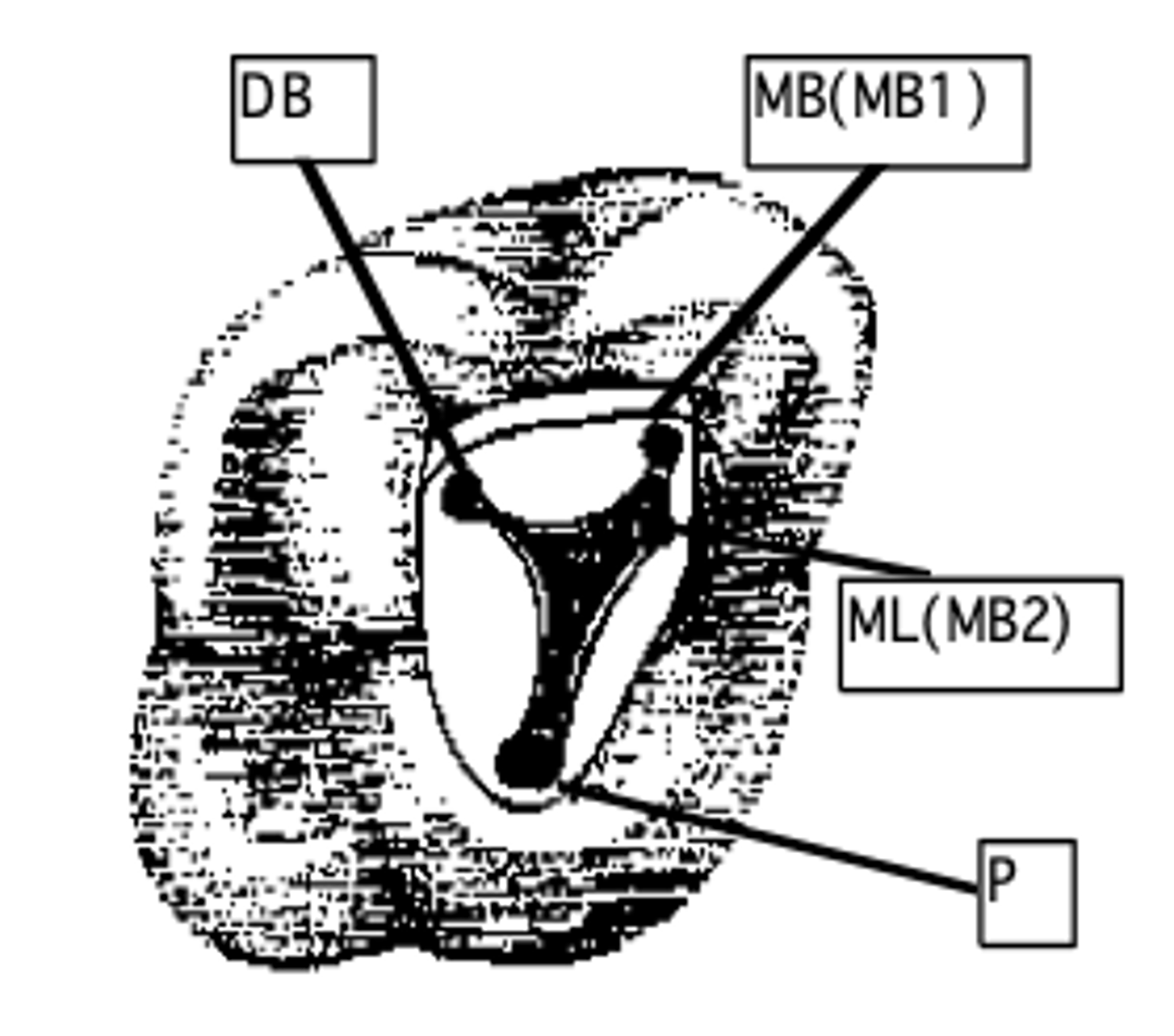
MB, (MB2), DB, P
maxillary first molar configuration of canals
1 or 2
MB root of maxillary first molar can have how many canals?
oblong triangular
Maxillary second molar access shape
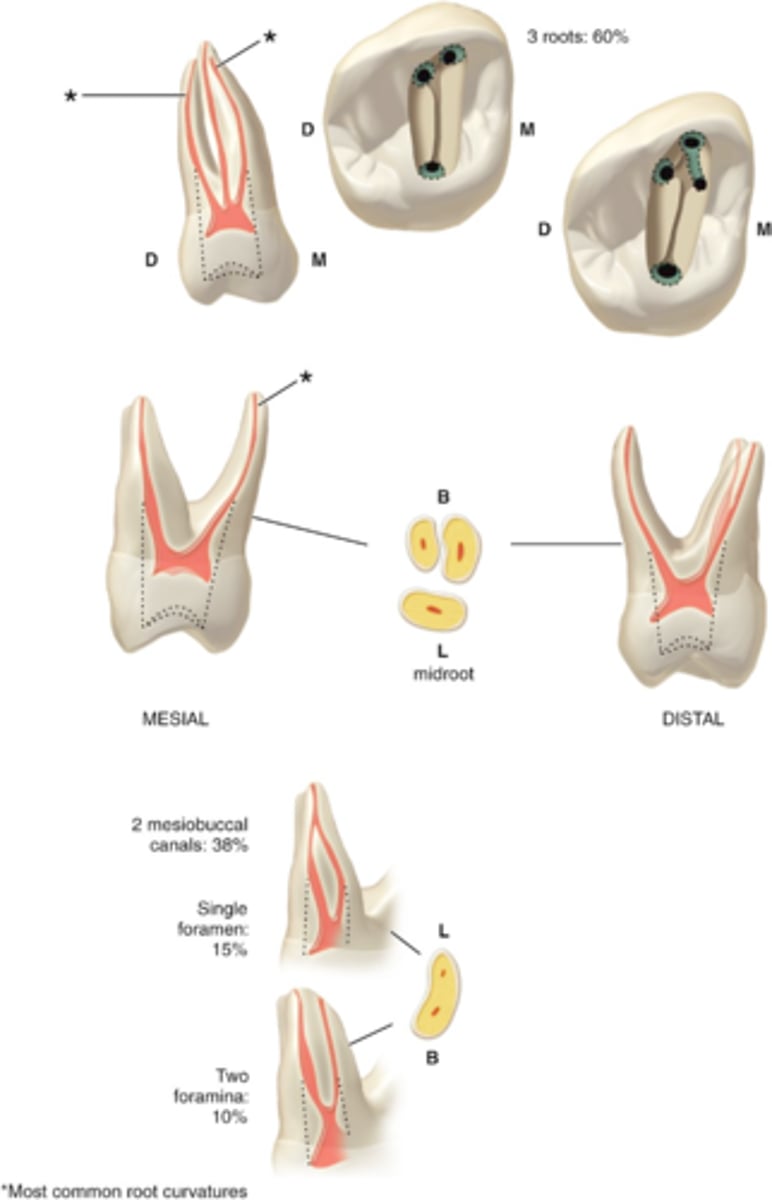
3-4
maxillary second molar number of canals
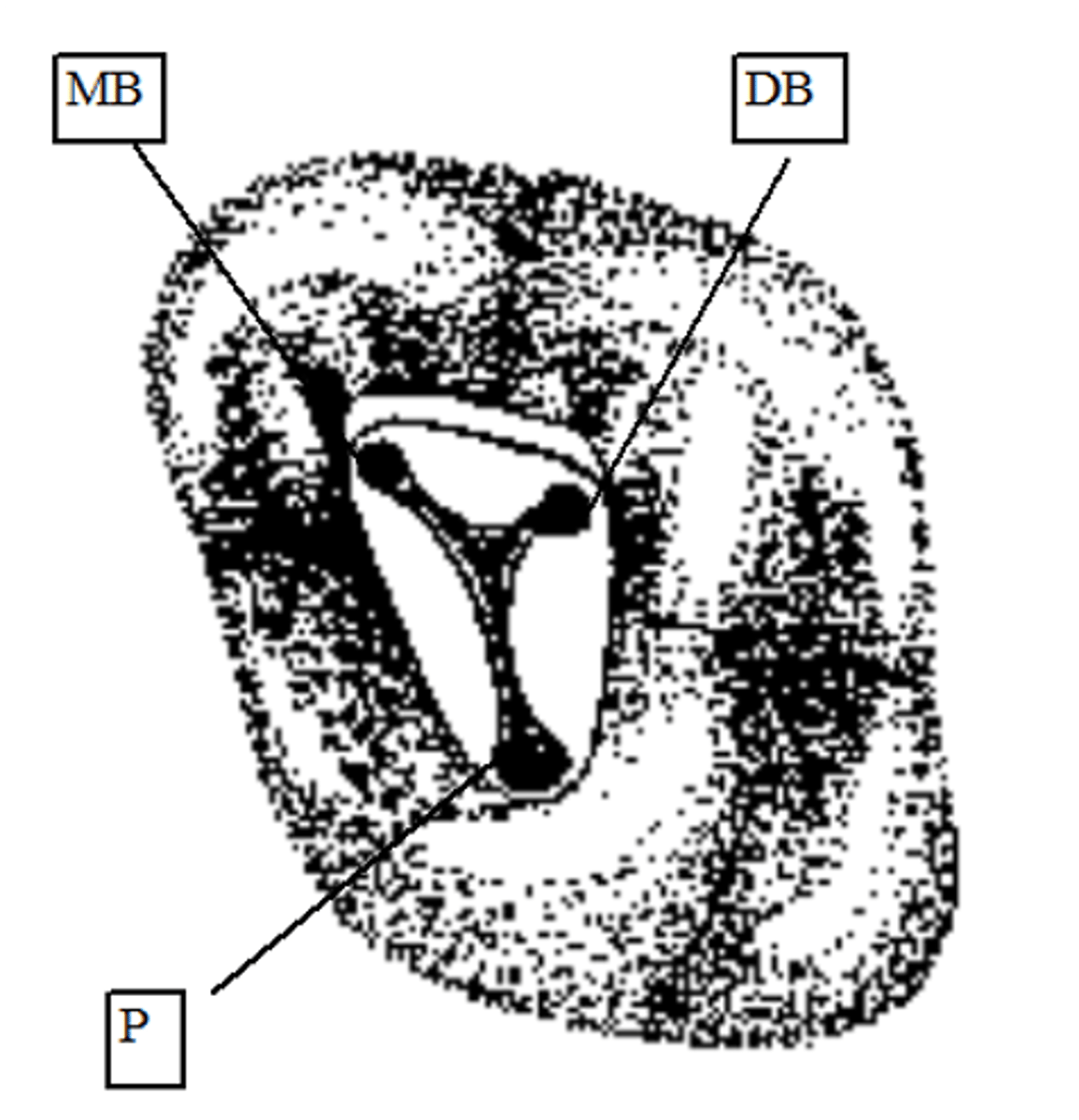
MB, (MB2), DB, P
maxillary second molars configuration of canals
1 or 2
MB root of maxillary second molar can have how many canals
Maxillary Right First Molar (Tooth #3)
Maxillary Left Second Molar (Tooth #15)
rounded, triangular, or ovoid
Mandibular incisors access shape
1-2
mandibular incisors number of canals
S or B+L
mandibular incisors configuration of canals
ovoid
mandibular canine access shape
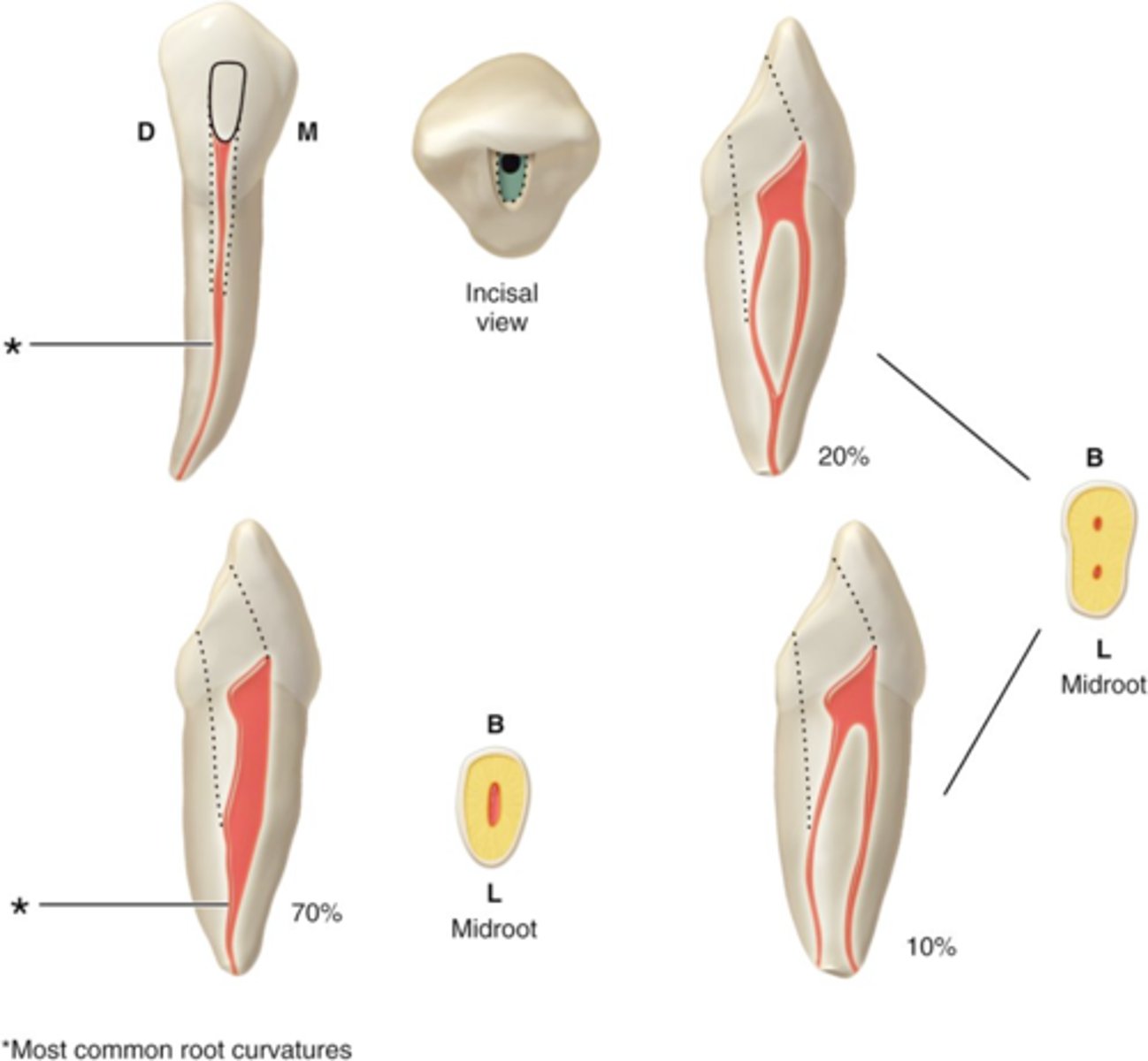
usually 1
mandibular canine number of canals
S or B+L
mandibular canine configuration of canals
ovoid or round
mandibular first premolar access shape
*The apical portion of the roots of these teeth may vary greatly in form. This is not often seen on radiograph and requires thorough evaluation of the canal system.
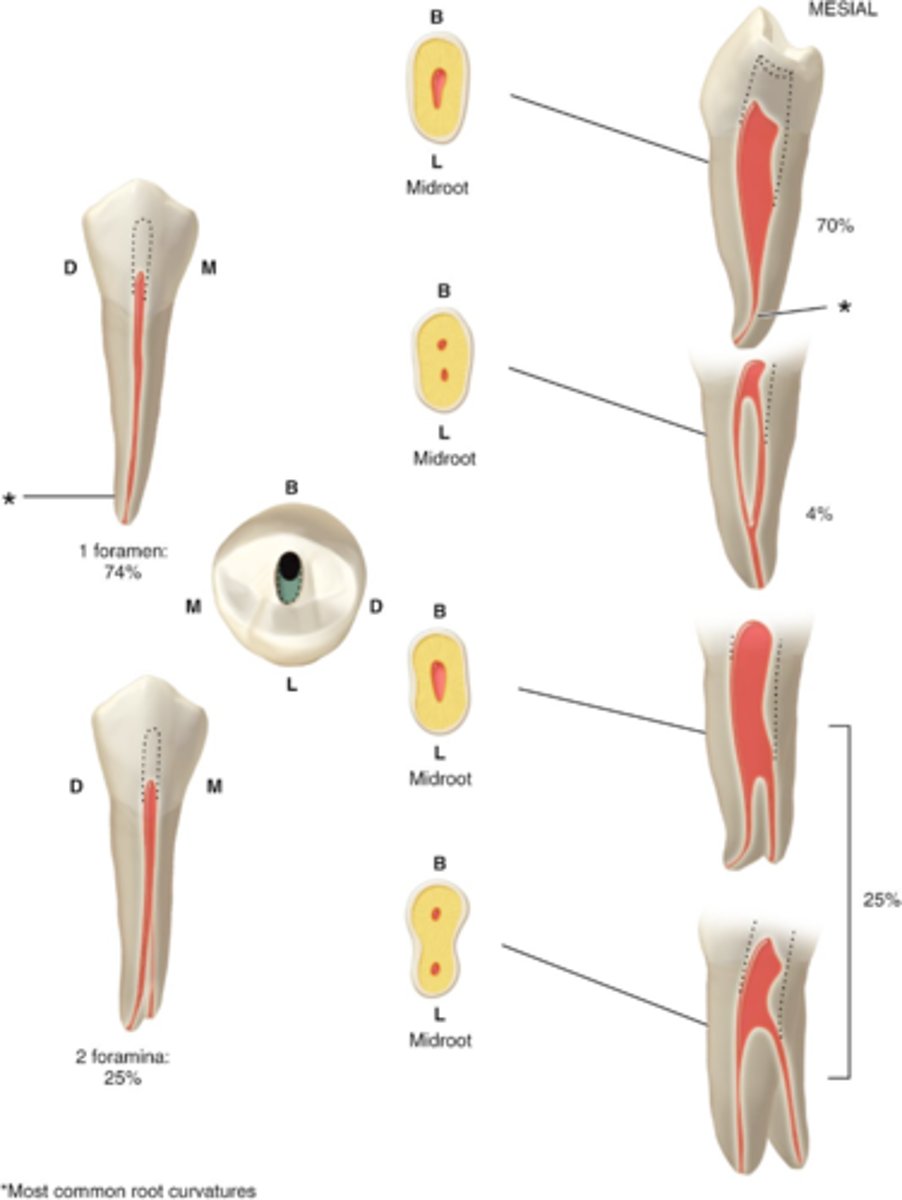
usually 1
mandibular first premolar number of canals
S or B+L
mandibular first premolar configuration of canals
ovoid or round
mandibular second premolar access shape
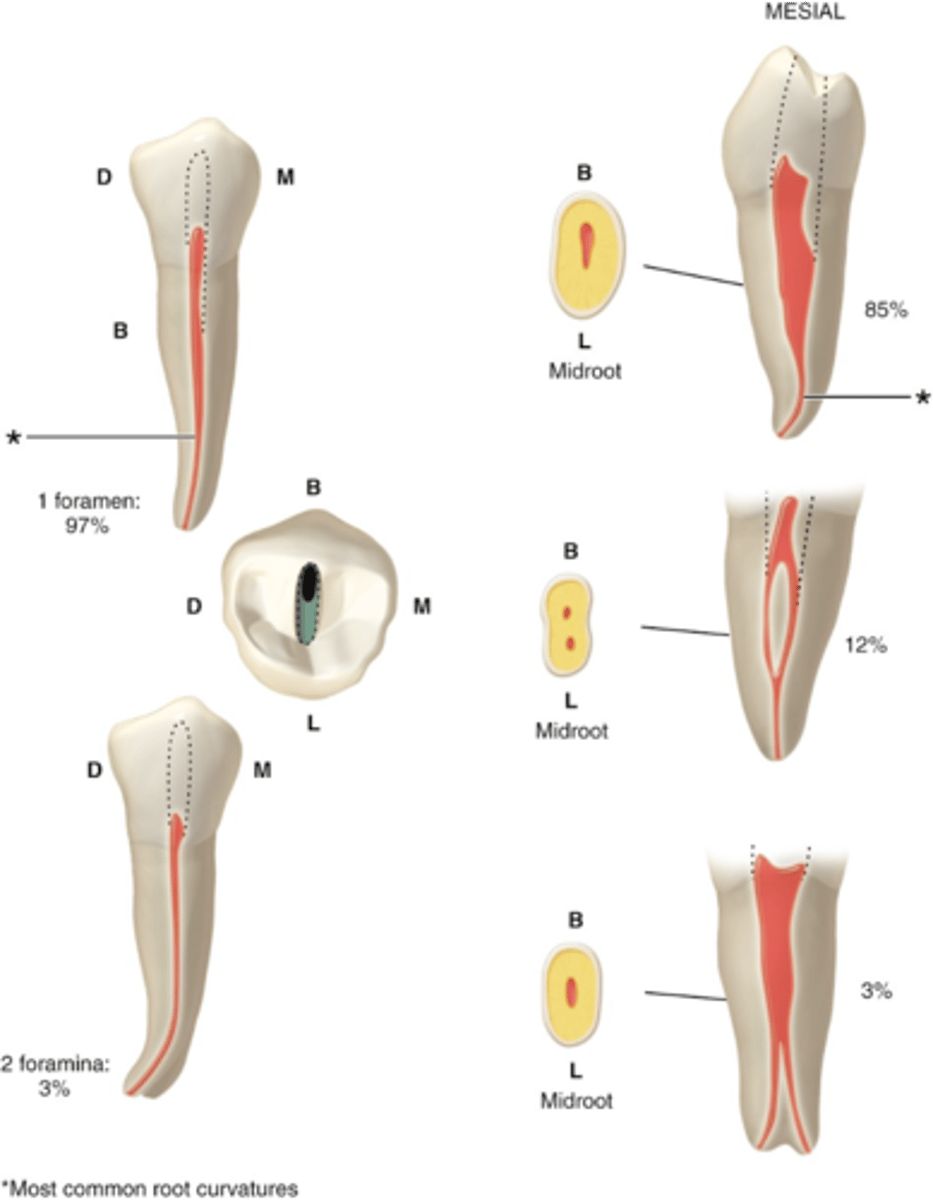
usually 1
mandibular second premolar number of canals
S or B+L
mandibular second premolar configuration of canals
triangular or rectangular
mandibular first molar access shape
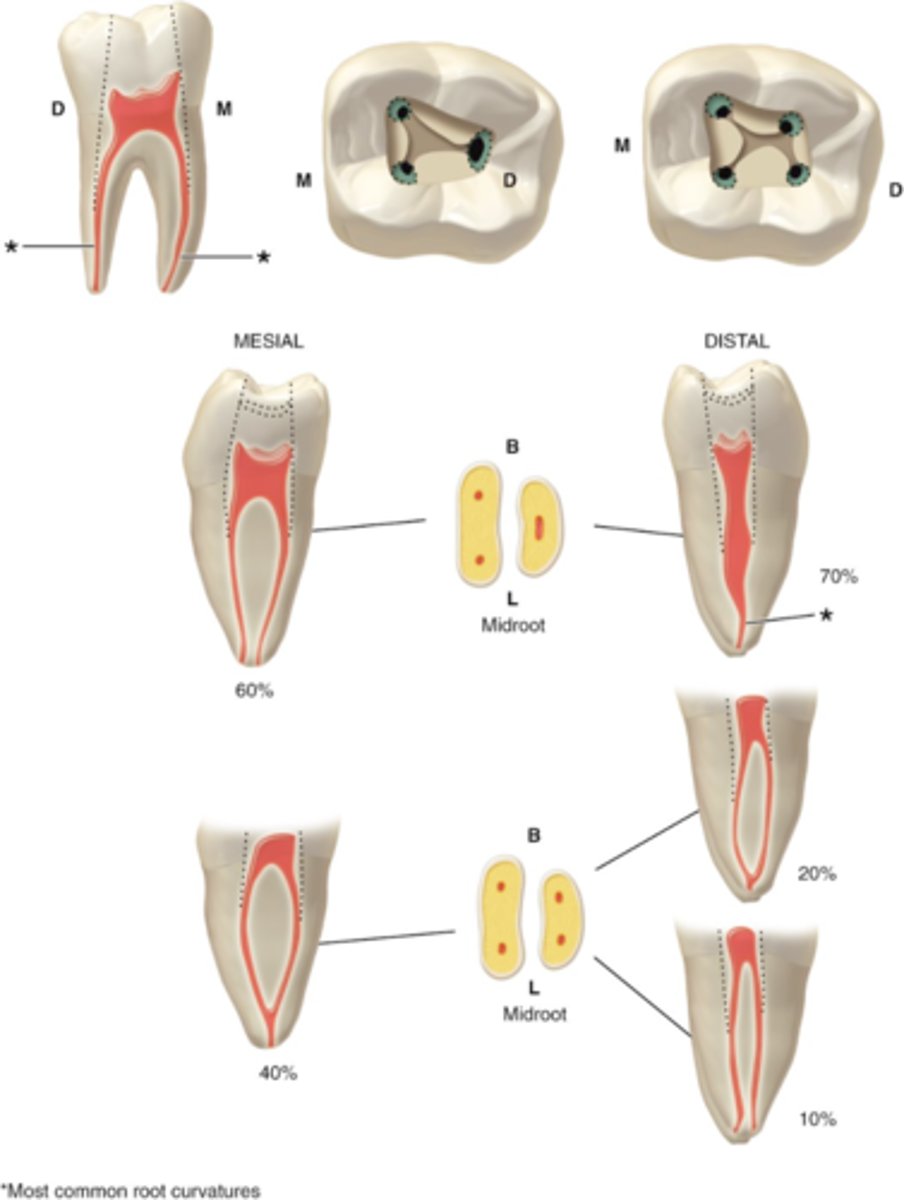
3-4
mandibular first molar number of canals
MB, ML, D, (DB+DL)
mandibular first molar configuration of canals
MB + ML canals (and occasionally Mid-M), Usually curves toward the distal in the apical 1/3
Mesial root of first mandibular molar contains