AP Psych Unit 4: Social Psychology and Personality
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
78 Terms
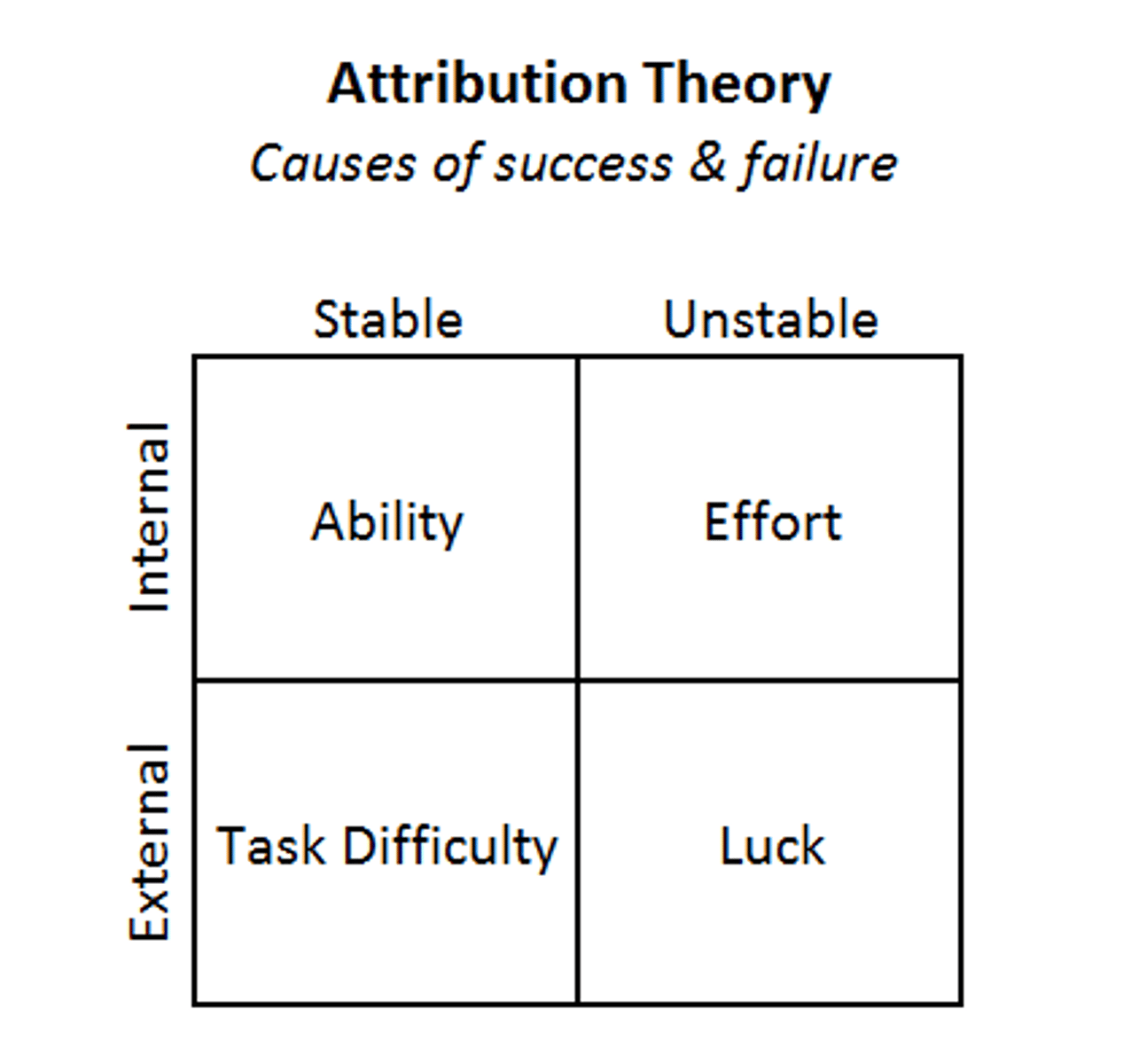
attribution theory
the theory that we explain someone's behavior by crediting either the situation or the person's disposition
fundamental attribution error
the tendency for observers, when analyzing another's behavior, to underestimate the impact of the situation and to overestimate the impact of personal disposition

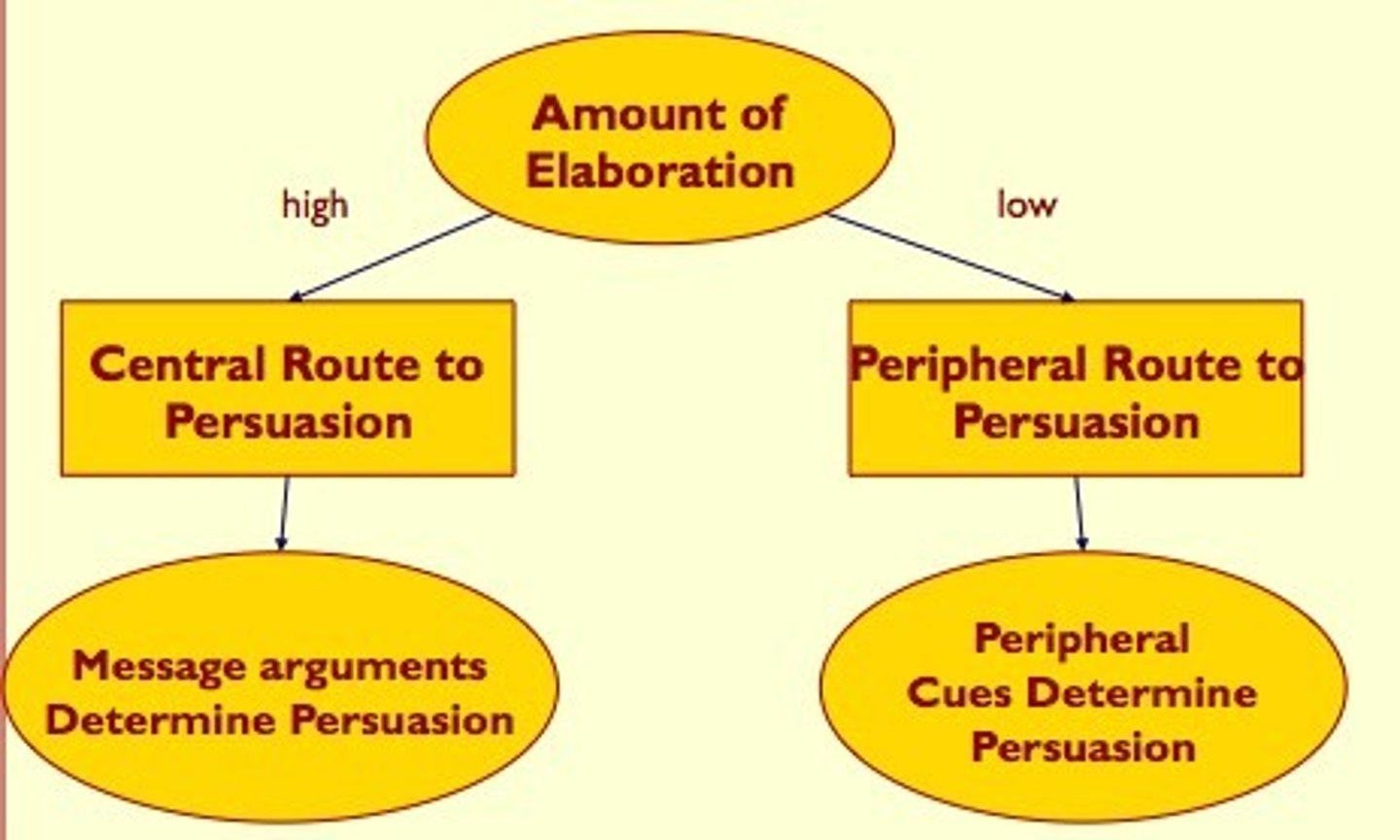
peripheral route persuasion
occurs when people are influenced by incidental cues, such as a speaker's attractiveness

central route persuasion
occurs when interested people focus on the arguments and respond with favorable thoughts

foot-in-the-door
the tendency for people who have first agreed to a small request to comply later with a larger request

door-in-the-face
asking for a large commitment and being refused and then asking for a smaller commitment
social facilitation
imitative behavior involving the spread of behavior, emotions, and ideas; laughing when someone else laughs

Conformity
Adjusting one's behavior or thinking to coincide with a group standard.

normative social influence
influence resulting from a person's desire to gain approval or avoid disapproval

informational social influence
the influence other people have on us because we want to be right

social loafing
the tendency for people in a group to exert less effort when pooling their efforts toward attaining a common goal than when individually accountable

Deindividuation
the loss of self-awareness and self-restraint occurring in group situations that foster arousal and anonymity

group polarization
the enhancement of a group's prevailing inclinations through discussion within the group

Groupthink
the mode of thinking that occurs when the desire for harmony in a decision-making group overrides a realistic appraisal of alternatives
actor-observer bias
the tendency to blame our actions on the situation and blame the actions of others on their personalities

Discrimination
unjustifiable negative behavior toward a group and its members

Ethnocentrism
evaluation of other cultures according to preconceptions originating in the standards and customs of one's own culture.

in-group bias
tendency to favor individuals within our group over those from outside our group
outgroup
a group that one does not belong to or identify with
scapegoat theory
the theory that prejudice offers an outlet for anger by providing someone to blame

just-world phenomenon
the tendency for people to believe that people get what they deserve and deserve what they get

implicit attitude
unfounded negative belief of which we're unaware regarding the characteristics of an out-group
mere-exposure effect
the tendency of liking what we are familiar with

altruism
unselfish concern for the welfare of others

bystander effect
the finding that a person is less likely to provide help when there are others around

reciprocity norm
an expectation that people will help, not hurt, those who have helped them

social-responsibility norm
an expectation that people will help those needing their help

social trap
a situation in which the conflicting parties, by each rationally pursuing their self-interest, become caught in mutually destructive behavior
Motivation
a need or desire that energizes and directs behavior

drive-reduction theory
the idea that a physiological need creates an aroused tension state that motivates an organism to satisfy the need

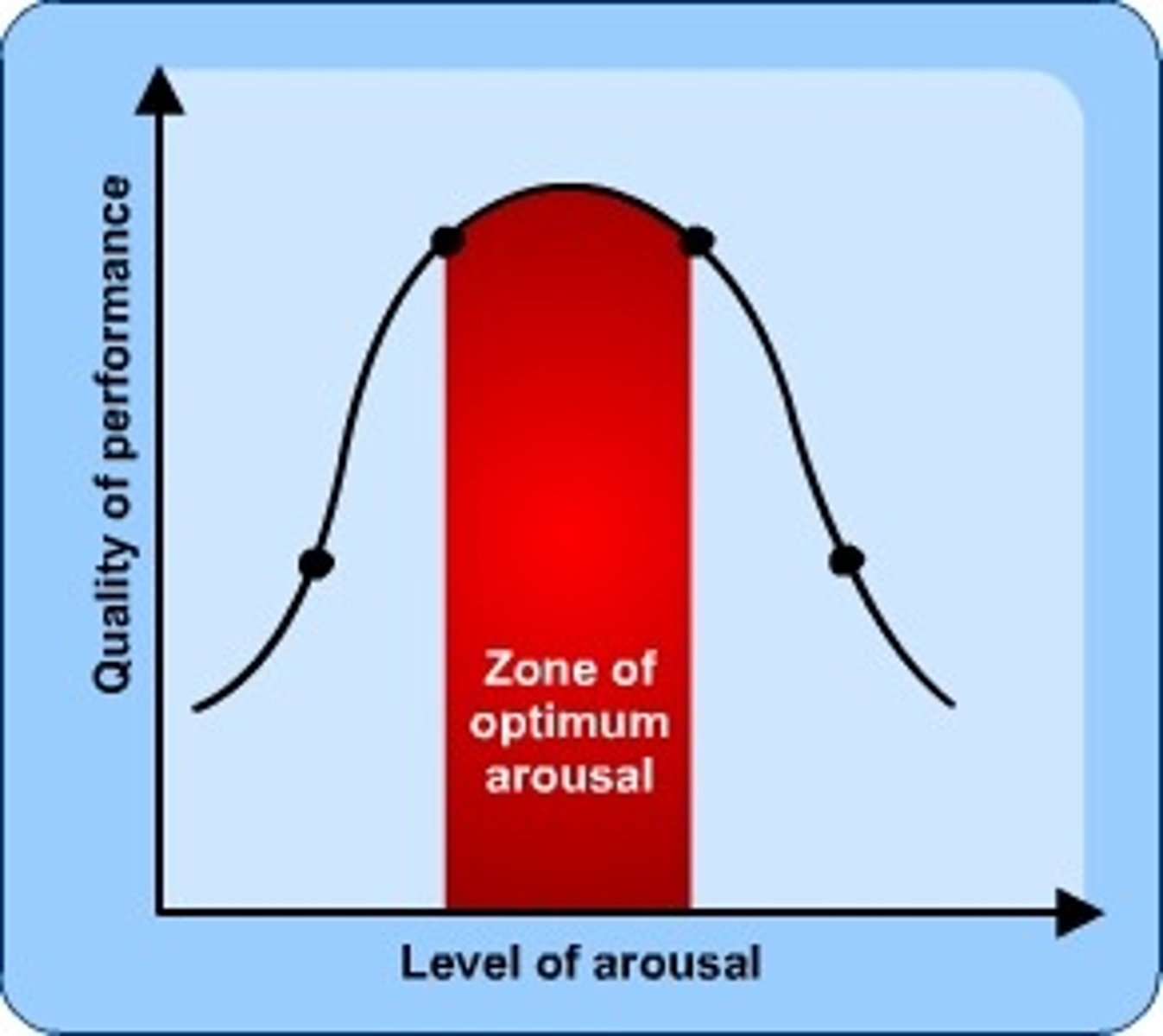
arousal theory
A theory of motivation suggesting that people are motivated to maintain an optimal level of alertness and physical and mental activation.
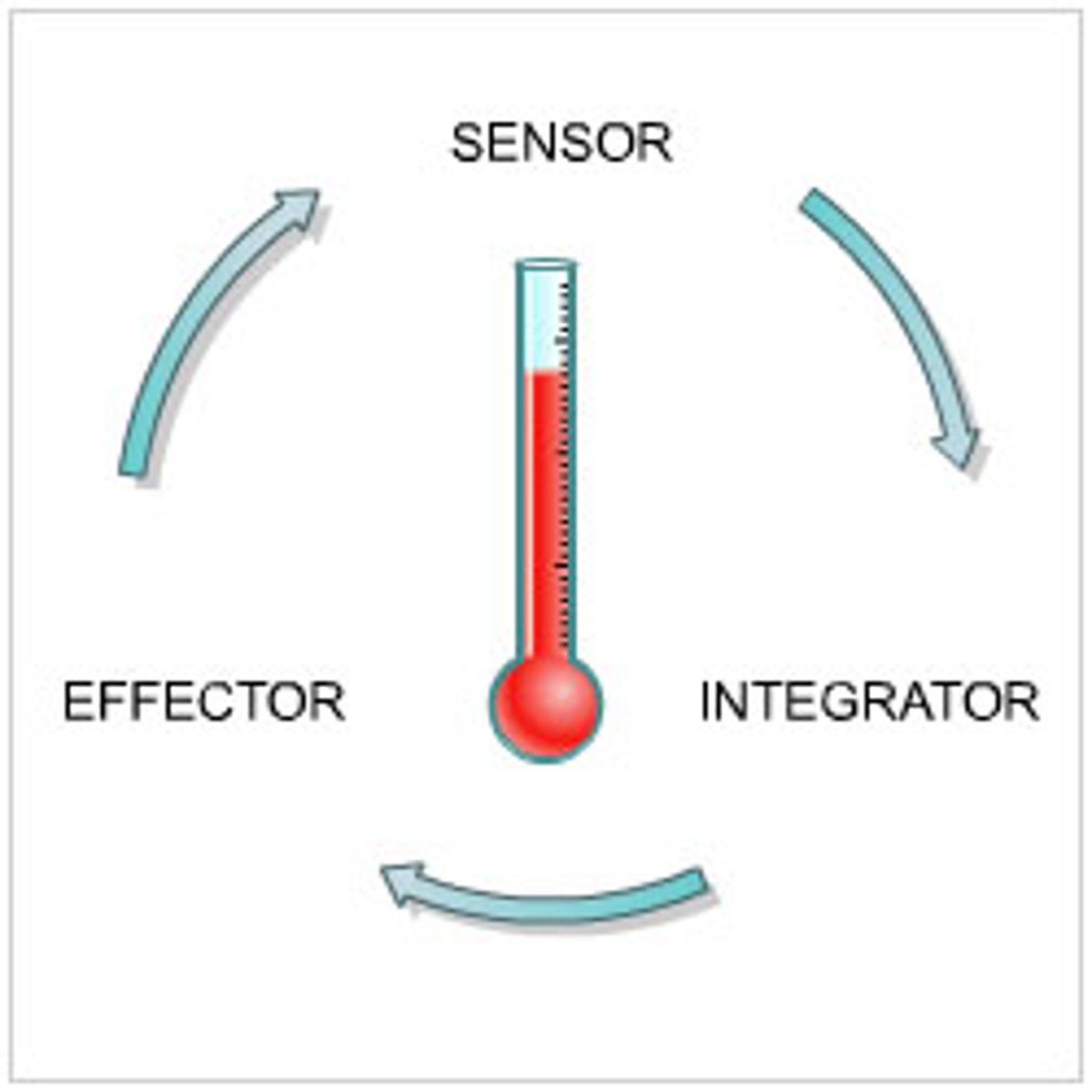
Homeostasis
A tendency to maintain a balanced or constant internal state; the regulation of any aspect of body chemistry, such as blood glucose, around a particular level
lateral hypothalamus
stimulates hunger in the brain

Emotions
signals that tell your mind and body how to react. The basic emotions are fear, contempt, disgust, sadness, anger, happiness, and surprise

facial feedback
the tendency of facial muscle states to trigger corresponding feelings such as fear, anger, or happiness

approach-approach conflict
Conflict that results from having to choose between two attractive alternatives

avoidance-avoidance conflict
Conflict that results from having to choose between two distasteful alternatives

Type A personality
personality type that describes people who are competitive, driven, hostile, and ambitious

Type B personality
Personality characterized by relatively relaxed, patient, easygoing, amicable behavior.

relative deprivation
the perception that we are worse off than those with whom we compare ourselves
Personality
an individual's characteristic pattern of thinking, feeling, and acting

Psychodynamic theory (Psychoanalysis)
Freud's theory of personality that attributes thoughts and actions to unconscious motives and conflicts; the techniques used in treating psychological disorders by seeking to expose and interpret unconscious tensions
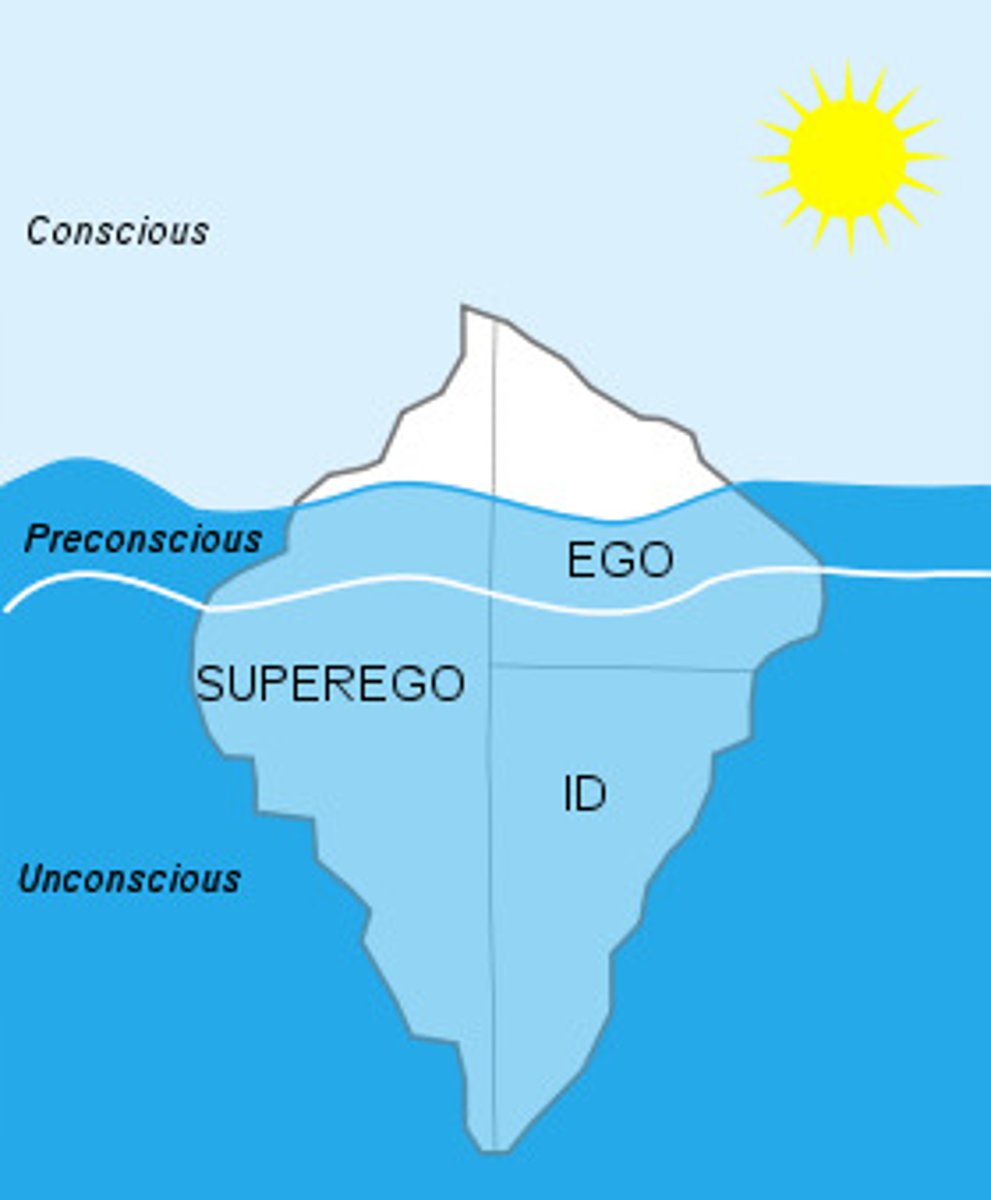
Id
a reservoir of unconscious psychic energy that, according to Freud, strives to satisfy basic sexual and aggressive drives; operates on the pleasure principle, demanding immediate gratification.
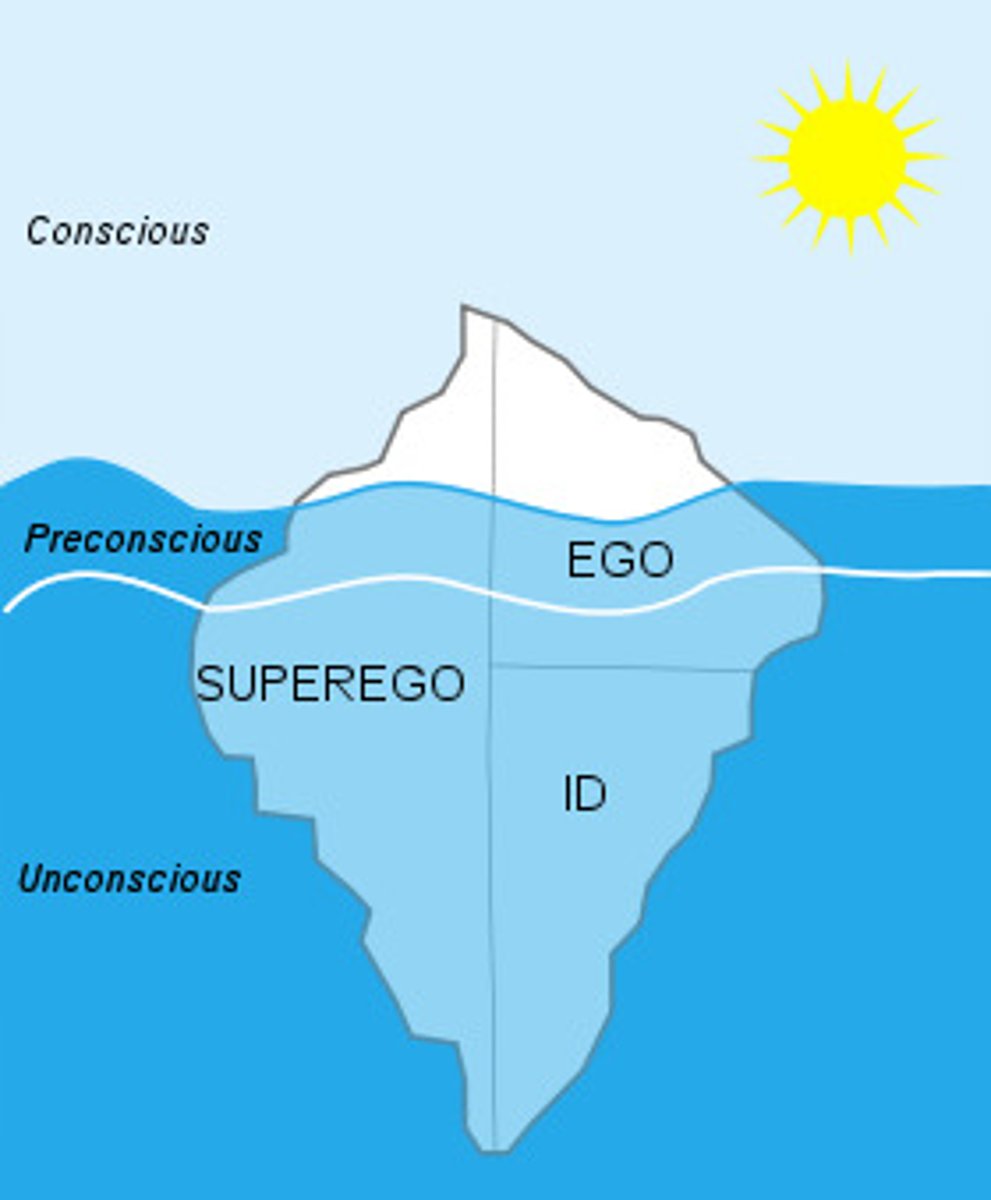
ego
the largely conscious, "executive" part of personality that, according to Freud, mediates among the demands of other parts of the mind; operates on the reality principle
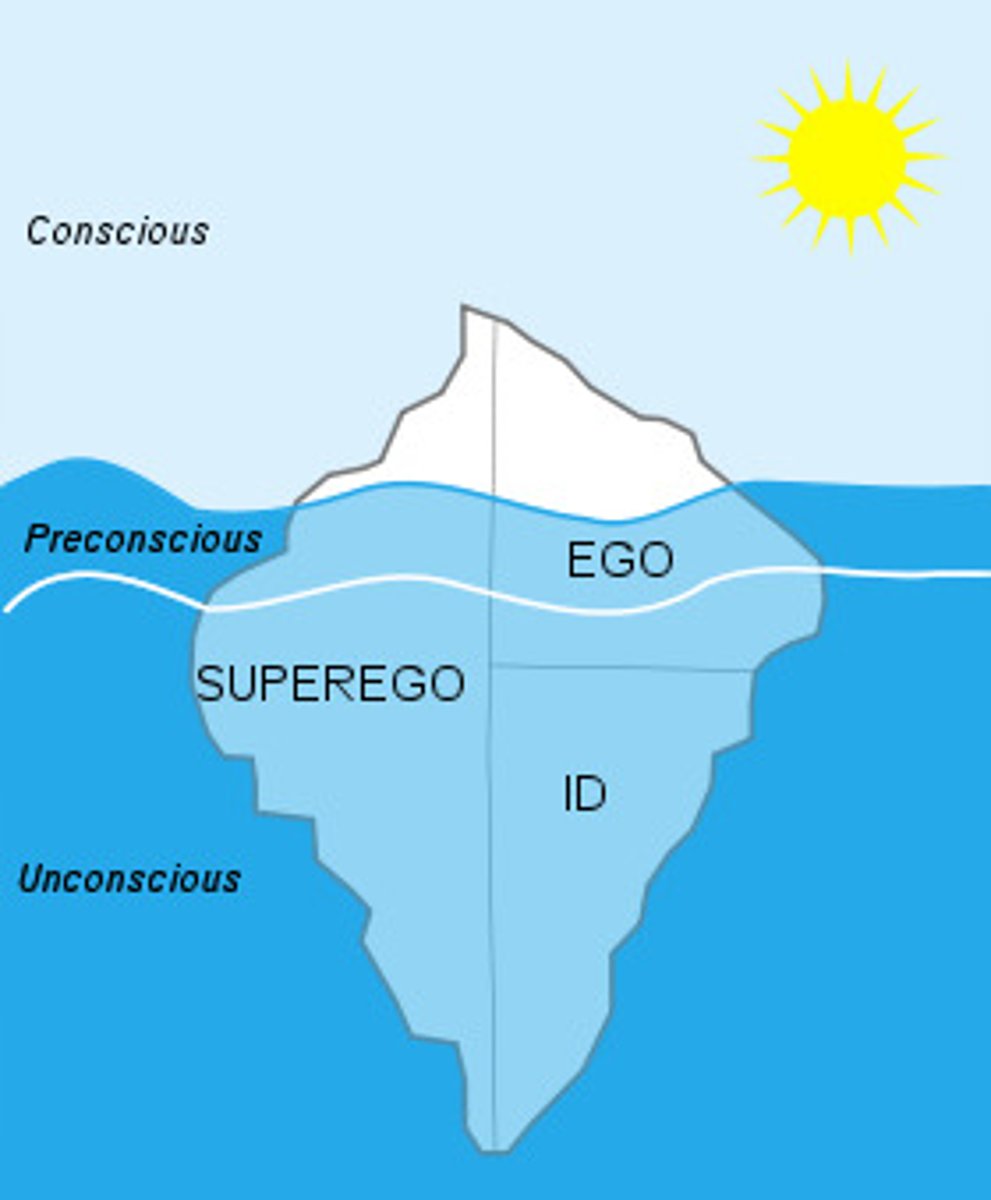
Superego
the part of personality that, according to Freud, represents internalized ideals and provides standards for judgment (the conscience) and for future aspirations
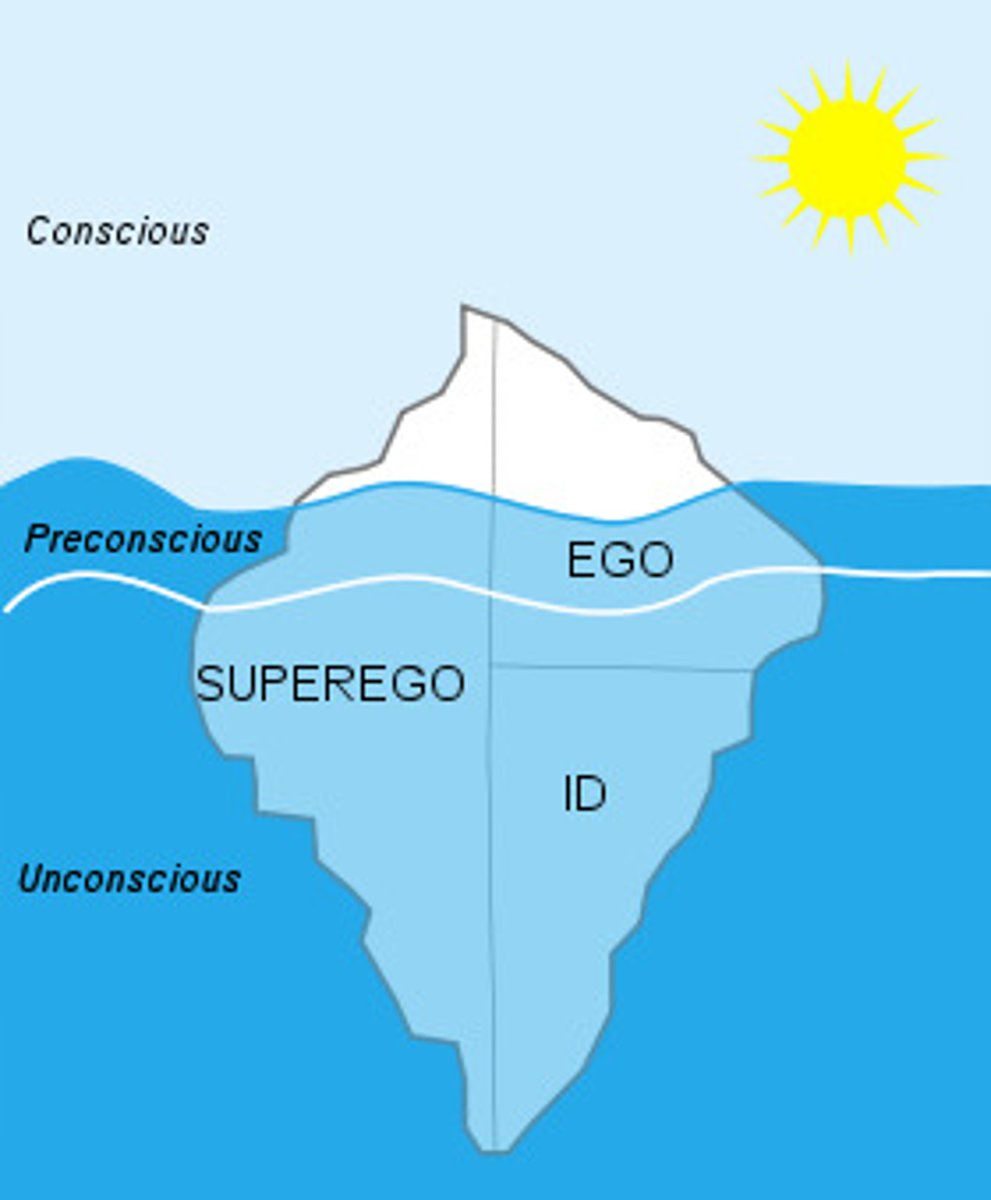
defense mechanisms
the ego's protective methods of reducing anxiety by unconsciously distorting reality. they are Denial, Displacement, Projection, Rationalization, Reaction Formation, Regression, Repression, and Sublimation.

inferiority complex
a pattern of avoiding feelings of inadequacy rather than trying to overcome their source

projective test
a personality test that provides ambiguous stimuli designed to trigger projection of one's inner dynamics such as the Thematic Apperception test or Rorschach

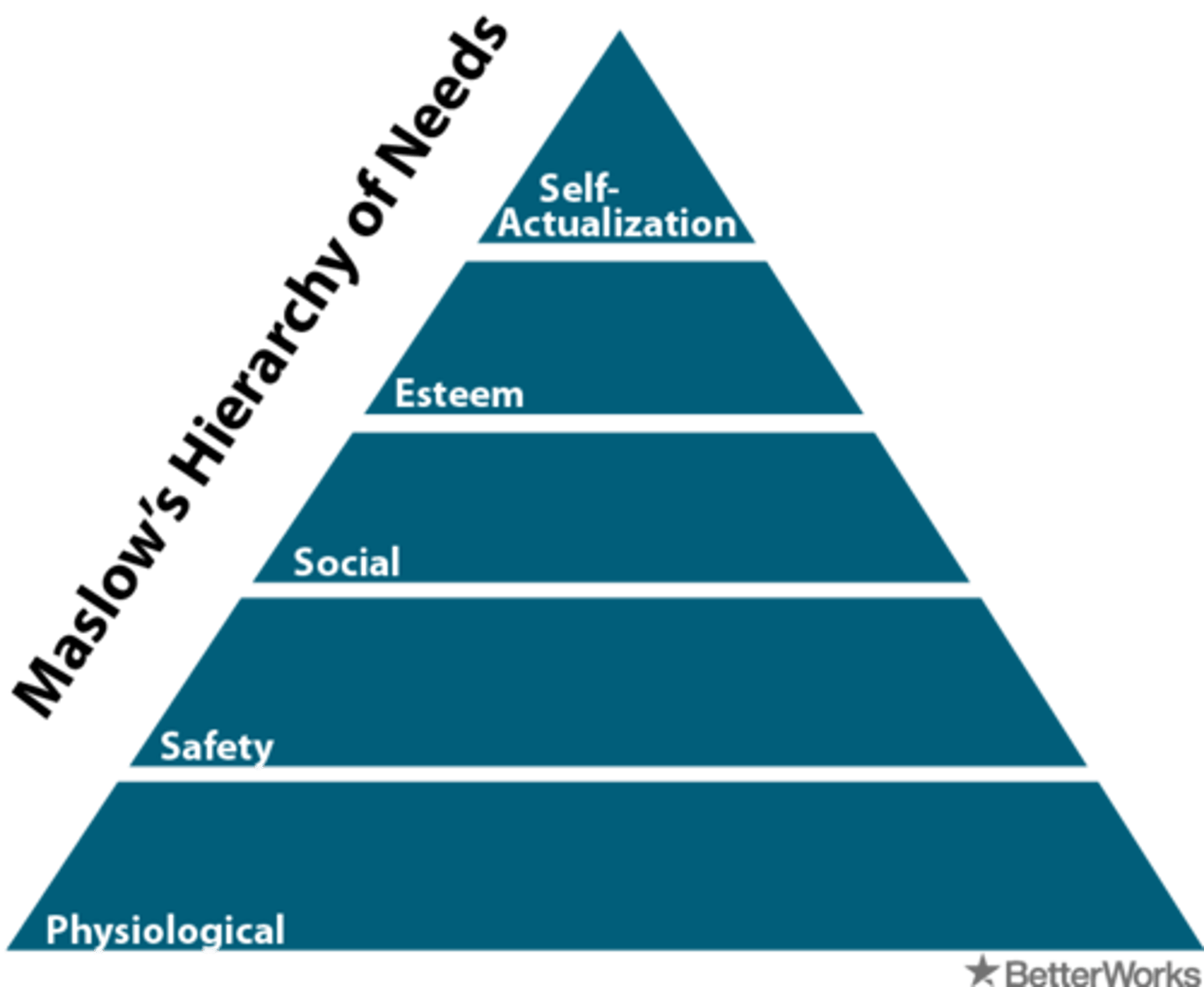
self-actualization
according to Maslow, the ultimate psychological need that arises after basic physical and psychological needs are met and self-esteem is achieved; the motivation to fulfill one's potential
unconditional positive regard
a caring, accepting, nonjudgmental attitude, which Carl Rogers believed would help clients to develop self-awareness and self-acceptance

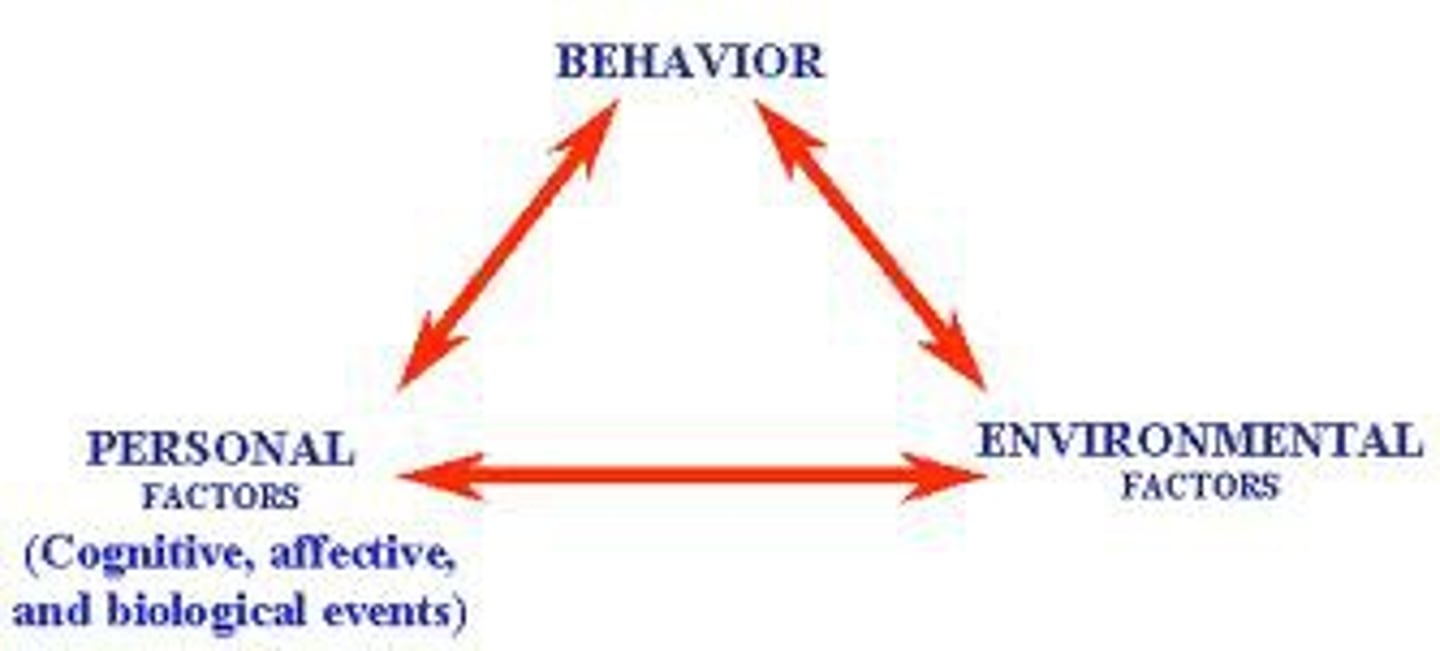
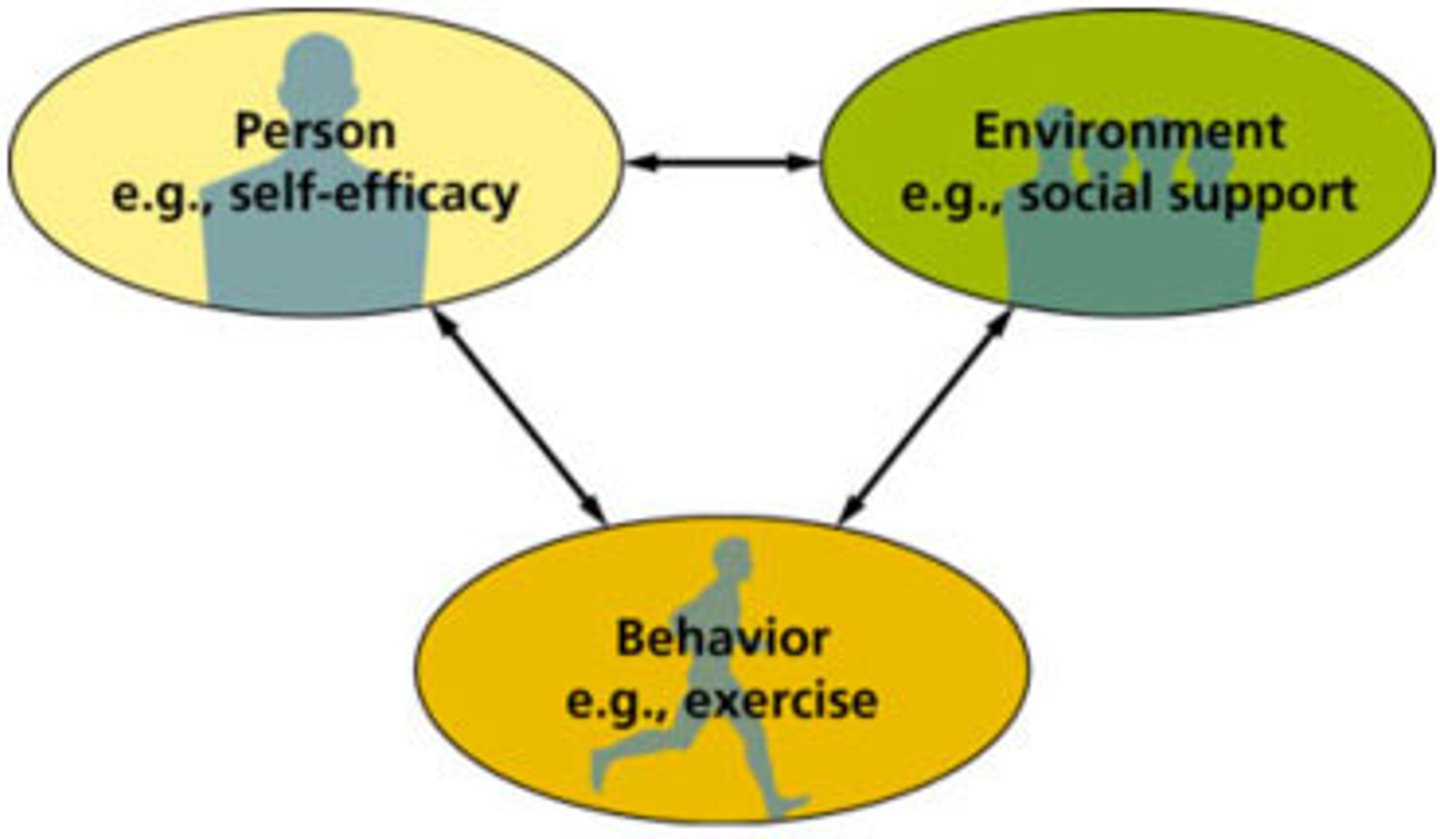
reciprocal determinism
Bandura's idea that though our environment affects us, we also affect our environment
self-efficacy
An individual's belief that he or she is capable of performing a task.

cognitive dissonance
Inner tension that a consumer experiences after recognizing an inconsistency between behavior and values or opinions

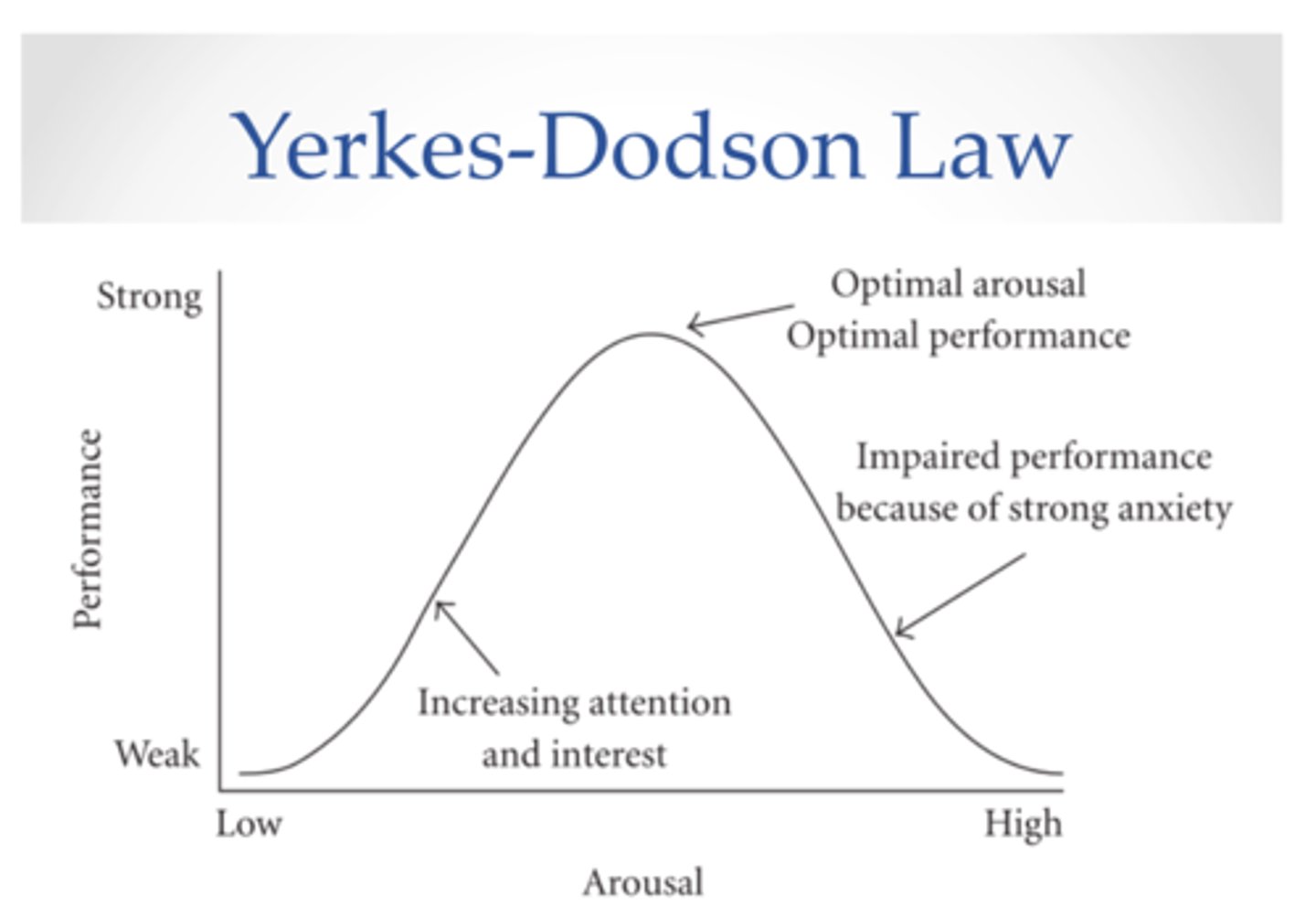
Yerkes-Dodson Law
the principle that performance increases with arousal only up to a point, beyond which performance decreases
False consensus effect
the tendency to overestimate the extent to which others share our beliefs and behaviors

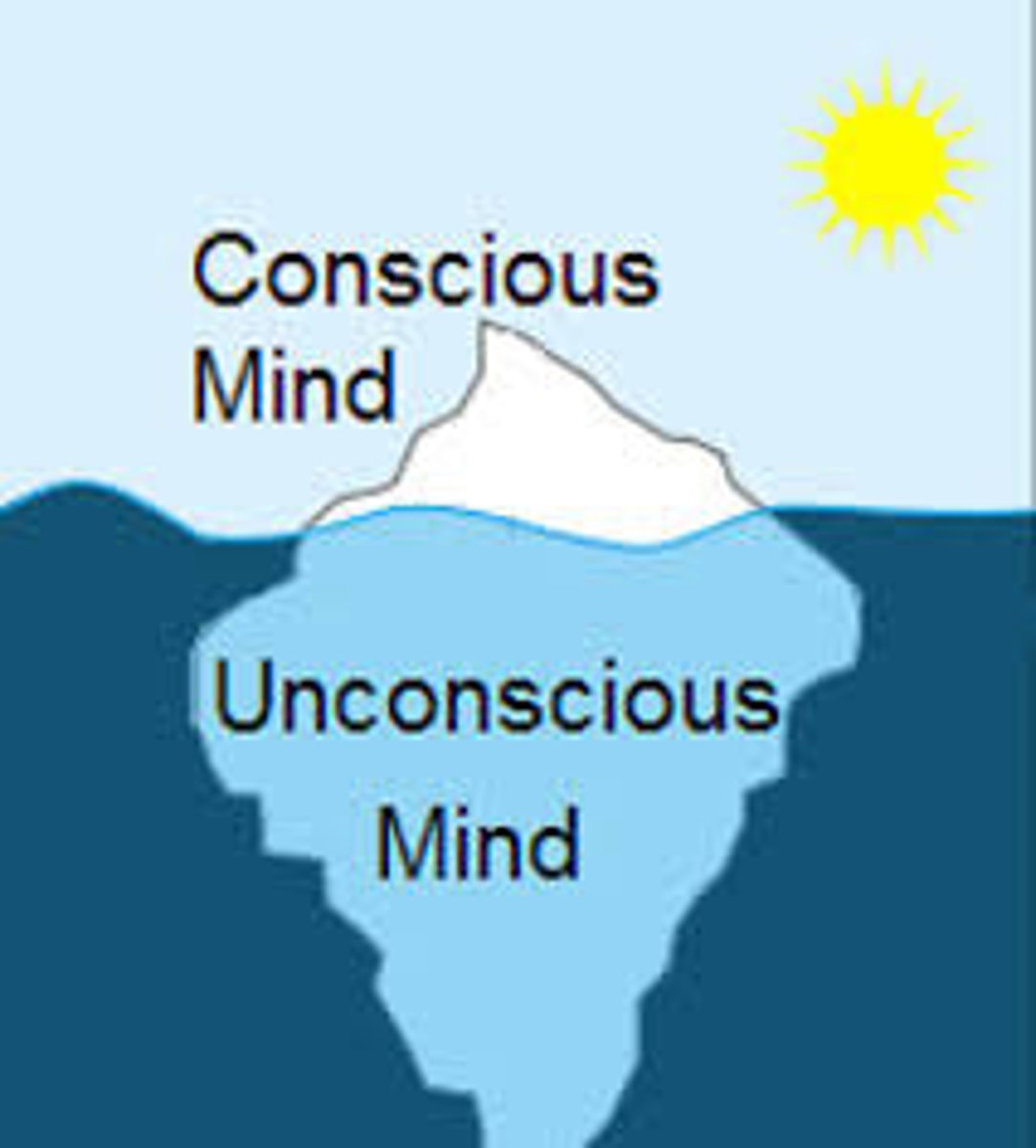
Unconscious processes
thoughts and feelings outside of our awareness
Humanistic perspective
the psychological view that assumes the existence of the self and emphasizes the importance of self-awareness and the freedom to make choices

Social cognitive theory
Bandura's theory of personality that emphasizes both cognition and learning as sources of individual differences in personality
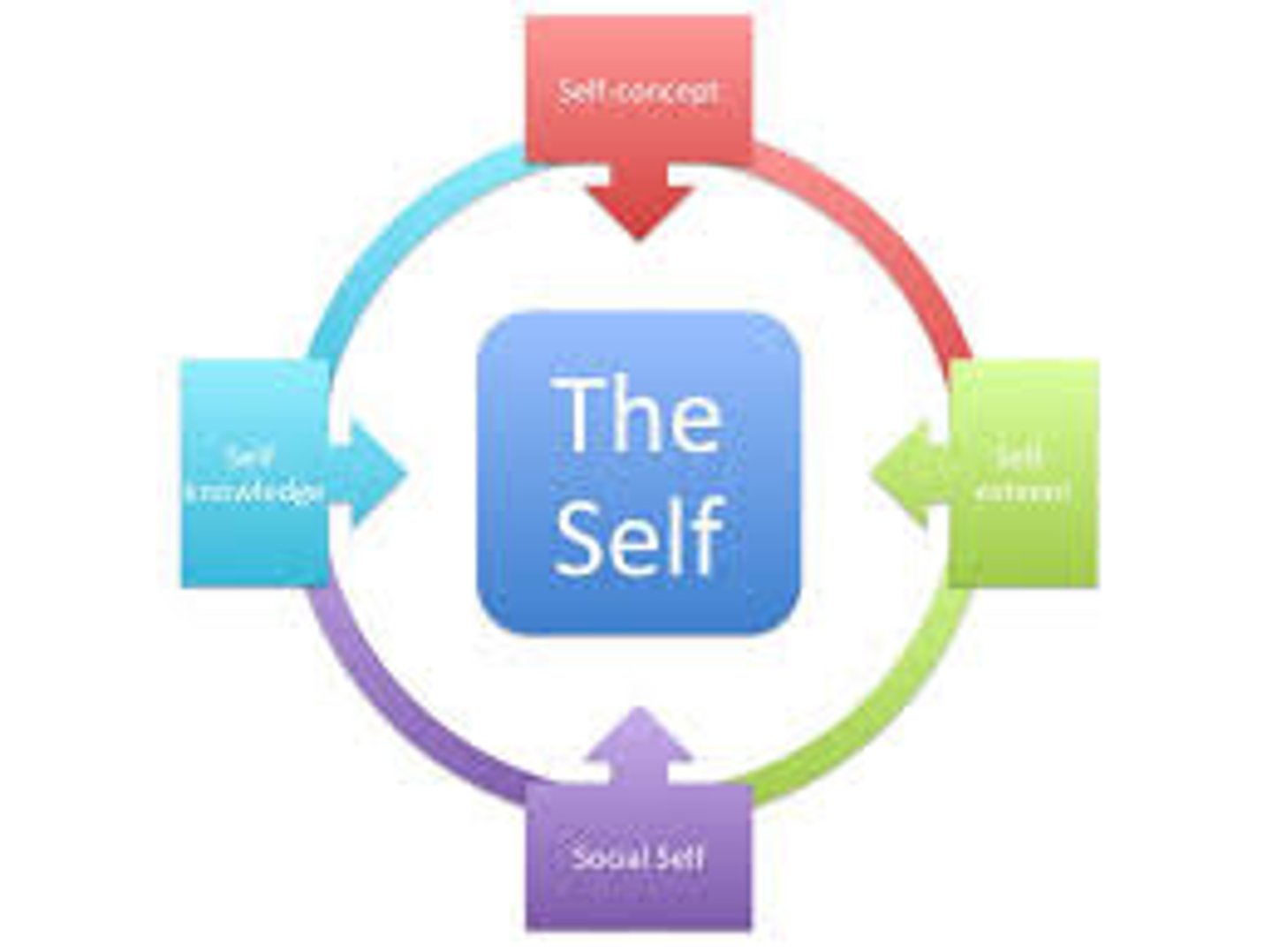
Self esteem
one's feelings of high or low self-worth

Self concept
our understanding and evaluation of who we are
Trait theory
A theory of personality that focuses on identifying, describing, and measuring individual differences in behavioral predispositions such as the Big 5 Personality or Myers Briggs Personality tests
Factor analysis
a statistical procedure that identifies clusters of related items (called factors) on a test; used to identify different dimensions of performance that underlie a person's total score.
Individualism
giving priority to one's own goals over group goals and defining one's identity in terms of personal attributes rather than group identifications

Collectivism
giving priority to the goals of one's group (often one's extended family or work group) and defining one's identity accordingly

Self serving bias
the tendency for people to take personal credit for success but blame failure on external factors
Stereotype
A generalized belief about a group of people

Dispositional attribution
assuming that another's behavior is due to personality factors, not situational ones

Halo effect
tendency of an interviewer to allow positive characteristics of a client to influence the assessments of the client's behavior and statements

Superordinate goals
shared goals that override differences among people and require their cooperation

Diffusion of Responsibility
the tendency for individuals to feel diminished responsibility for their actions when they are surrounded by others who are acting the same way

Obedience
A form of compliance that occurs when people follow direct commands, usually from someone in a position of authority

Self Fulfilling prophecy
an expectation that causes you to act in ways that make that expectation come true.

Elaboration likelihood model
theory identifying two ways to persuade: a central route and a peripheral route
Ghrelin
A hunger-arousing hormone secreted by an empty stomach

Leptin
A hormone produced by adipose (fat) cells that acts as a satiety factor in regulating appetite.

Incentive theory
A theory of motivation stating that behavior is directed toward attaining desirable stimuli and avoiding unwanted stimuli.

Instincts
innate tendencies that determine behavior

Motivational conflicts theory
According to Lewin when an organism is in conflict between two opposite motives (approach-approach, avoidance-avoidance, approach-avoidance)
