Topic 6 - waves
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
wavelength
distance between the same points on 2 consecutive waves
amplitude
distance from the equilibrium line to the maximum displacmnet
freuqnecy
the number of waves that pass a single point per second
period
the time taken for a whole wave to completely pass a single point
velocity =
frequency x wavelength
period =
1 / frequency
relationships (p and f)
period is inversely proportional to frequency
smaller period = higher frequency = greater velocity
what are the 2 types of waves?
transverse and longitudinal
transverse waves
vibrate perpendicular to the direction of travel
have peaks and troughs
e.i light or waves on the electromagnetic spectrum
longitudinal waves
vibrate parallel to the direction of travel
have compressions and rarefactions
e.g. sound waves
RP -- measuring velocity in a ripple tank
place a pencil at any point on the tank.
Then you time for a minute and you count how many waves pass the point in a minute, then divide by 60 to get the number of waves per second.
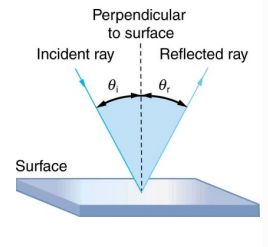
reflections of waves
light will reflect if the object is opaque and is not absorbed by the material because the electrons will absorb the light energy and then re emit is as a reflected wave
the smoother the surface the stronger the reflected wave
roughs surfaces scatter the light in all directions
angle of incidence = angle of reflection
transmissions
the process of passing through the material and emerging
occur when waves pass through a transparent material
absorption
if the frequency of light matches the energy levels of the electrons the light will be absorbed
if a material appears green, only green light has been reflected and the rest of the frequencies in visible light have been absorbed
sound waves:
sound waves travel through solids causing vibrations
our outer ear collects the sound and channels it down the earl canal
the sound wave hits the eardrum (a tightly stretched membrane which vibrate as the pressure air waves reach it)
the eardrum vibrates at the same frequency of the sound wave, converting the sound energy into mechanical vibrations, which are then transmitted to the inner ear for processing.
compression and rarefaction on eardrum
Compression forces the eardrum inward
Rarefaction forces the eardrum outward, due to pressure
what range can humans hear
20Hz to 20 000Hz as it gives us the greatest survival advantages
what happens when we listen to loud sounds
in the cochlea the hair can die or get damaged
so we cant listen to higher frequency sounds
what happens to ultrasound when it reaches a boundary between 2 medias
they are partially reflected back
the rest pass through
a receiver next to the emitter can record the reflected waves:
the speed of the waves are constant, so measuring the time between emission and detection can show distance from the source
what are the 2 sesmic waves
primary waves
secondary waves
P waves
longtidunal
can pass through solids and liquids
faster
S waves
transverse
only pass through solids
how do we know the earths centre is liquid
on the other side of the earth only P waves are detected because S waves cant penetrate liquid
how to find the depth in the ocean
a pulse of ultrasound can be sent below the ship, time taken to reflect can be used to calculate depth
used to find how far the seabed is below the ship
are EM waves logitudinal or transvers
transverse
trend from radio wave to gamma ray
decreasing wavlength causes increasing frequency
as frequency increases, energy of the wave increases
The EM spectrum
radio
microwave
infrared
visible
ultraviolet
X-ray
Gamma ray
in space all waves …
have the same velocity
if entering a denser material the light will …
bend towards the normal because it slows down
(shorter wavelengths slow down more than longer wavelengths, blue light shows more than read)
why do materials interact differently with different parts of the EM spectrum
because the wavelengths and frequency are different
what has a longer wavelength red or blue
red
Why does dispersion of white light happen in a prism?
The different wavelengths refract a different amount,
depending on their wavelength
red refracts the least
how are radio wave produced
oscillation in electrical circuits
when radio waves are absorbed they create an alternating current the same frequency as the radio waves
when electrons move to a higher orbit …
the atoms has absorbed EM radiation
when the electrons falls to a lower orbit
the atoms has emitted EM radiation
if an electron gains enough energy …
It can leave the atom to form an ion
where are gamma rays originate from?
the decay of an atomic nuclei
what rays are hazardous for human
UV light
x rays
gamma rays
what is radiation dose
how much exposure leads to harm for a person
X-ray risks
ionisation radiation that can cause the mutation of genes - causing cancer
Uses of EM waves
Radio - TV and radio
Long wavelength, can travel far without losing quality
Microwaves - Satellite communication, cooking food
Can penetrate atmosphere to reach satellites
Infrared - Cooking food, infrared cameras
Transfers thermal energy
Visible - Fibre optics
Best reflection/scattering in glass (others have too short/long wavelengths)
UV - Sun tanning, energy efficient lamps
Radiates the least heat but more energy
X-ray - Medical imaging and treatment (and gamma)
Very high in energy, and can penetrate material easily
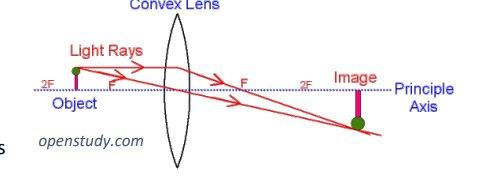
convex lenses (virtual or real)
both
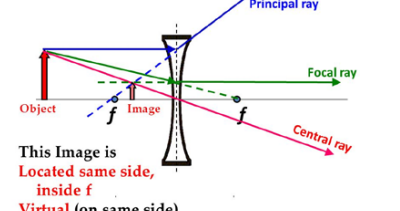
concave virtual or real
only virtual image

concave lens
spreads light outwards
used in glasses to correct short sightedness
convex lenses
focus light inwards
used for magnifications
used to correct long - sightedness as it focuses the rays closer
magnification =
image height/ object height
specular is
a single reflection of a smooth surface
diffuse
reflections off a rough surface causes scattering
how do colour filters work
they only let one wavelength (colour) through and absorb every other colour
if all wavelengths are reflected its
white!
id all wavelengths are absorbed its
black
the wavelength which is absorbed =
the colour it appears
do all objects emit and absorb infrared radiation
yes
the hotter the body:
the greater amount of radiation released per second
the greater amount of short wavelength radiation releases
what is a black body
an object that absorbs all the radiation it recieves,
it emits all radiation
if a body is increasing tempreature
it is absorbing more energy that it emitts
if a body is cooling down
energy is released at a greater rate than it absorbs
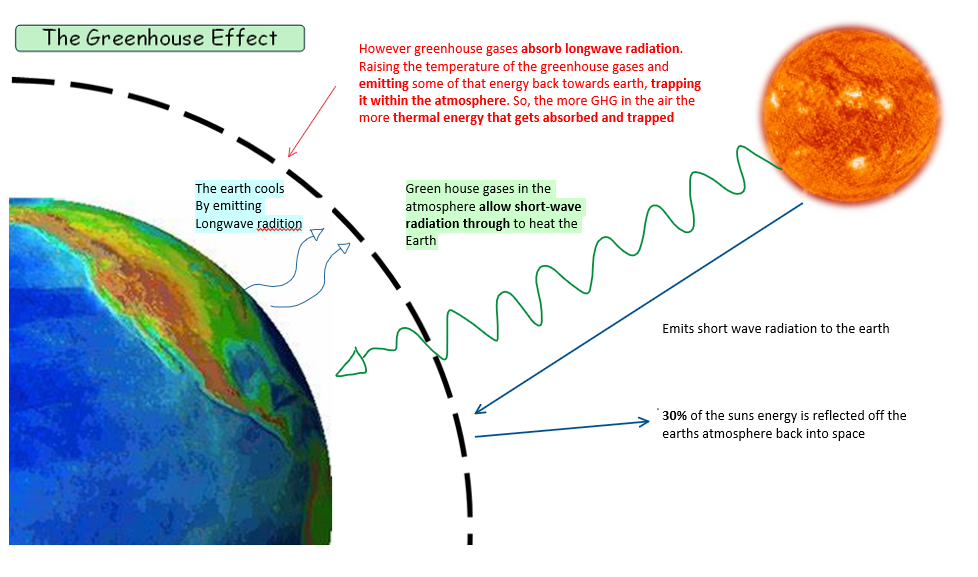
green house gas effect
YAYAYAYAY
similarty of tranverse and longitutidinal
both transfer energy without transfering matter