MKT 351 Final Study
1/54
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Consumer Behavior - final exam study
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
Consumer Behavior
the study of individuals, groups, or organizations and the processes they use to select, secure, use, and dispose of products, services, experiences, or ideas to satisfy needs and the impacts that these processes have on the consumer and society
Norms
Specify ranges of appropriate behavior
Values
widely held beliefs that affirm what is desirable
Sanctions
Penalties for violating norms
Cause-related marketing (CRM)
ties a company and its products to an issue or cause with the goal of improving sales or corporate image while providing benefits to the cause
Social marketing
influence people’s behavior in ways that benefit individuals and society as a whole
Ex: quitting smoking/smoking kills ads
Demographics
describe a population in terms of its size, distribution, and structure
Acculturation
the degree to which an immigrant has adapted to his or her new culture
Household Life Cycle (HLC)
the classification of a household into stages over time based on adult age, marital status, and the presence and age of children
HLC/occupational matrix
Executive/Elite/Professional
Administrative/Professional
Technical/Sales/Clerical
Service/Trade/Craft
Unskilled/Manual
Reference groups
a group whose presumed perspectives or values are being used by an individual as the basis for his/her current behavior
Associative reference group
people who more realistically represent the individuals’ current equals or near-equals—e.g., coworkers, neighbors, or members of churches, clubs, and organizations
Aspiration reference group
others against whom one would like to compare oneself. For example, many firms use athletes as spokespeople, and these represent what many people would ideally like to be.
Dissociative reference groups
social groups that an individual does not want to associate with, due to various reasons such as differing values, social status, or behavioral patterns
Opinion leaders
the “go-to person” for certain types of information
they have enduring involvement for specific product categories
greater knowledge and expertise
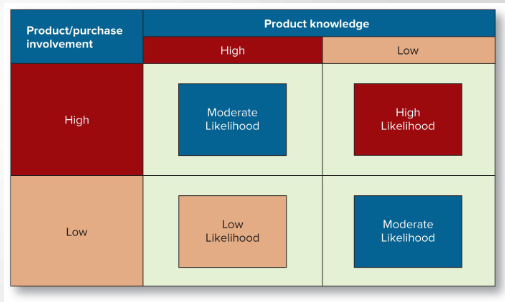
What is the likehood of seeking an opinion leader
Perception
how consumers sense, organize, interpret, and provide meaning to marketing stimuli
Information processing
a series of activities by which stimuli are perceived, transformed into information, and stored
Short term memory (STM)
The portion of total memory that is currently activated or in use – working memory
Long term memory
The portion of total memory dedicated to permanent information storage
Schema
the cognitive framework that helps individuals organize and interpret information based on their prior knowledge and experiences
Personality
reflects the relatively stable behavioral tendencies that individuals display across a variety of situations
Brand personality
the way a brand is personified; the sum of its emotional, psychological and behavioral patterns that remain unique over the course of its lifespan
Attitude
an enduring organization of motivational, emotional, perceptual, and cognitive processes with respect to some aspect of our environment...it is a learned predisposition to respond in a consistently favorable or unfavorable manner with respect to a given object
Attitude components
Cognitive
Affective
Behavioral
Cognitive attitude
Beliefs: “I believe spiders are dangerous”
Affective attitude
Feelings: “I am scared of spiders!”
Behavioral attitude
Response tendencies: “If I see a spider, you better believe I will scream!”
Self-concept
the totality of the individual’s thoughts and feelings having reference to himself or herself as an object
Extended self
Self + Possessions, What product is part of your identity
Psychographics
classifying population groups according to psychological variables such as values, activities/ interests, demographics, media patterns, and usage rates
Situational influence
all those factors particular to a time and place that do not follow from a knowledge of the stable attributes of the consumer and the stimulus and that have an effect on current behavior
What does situational influence NOT include
Characteristics of the consumer
Characteristics of the product
Decision making types
Nominal decision making
Limited decision making
Extended decision making
The process stages
Problem recognition
Information search
Alternative evaluation
Purchase
Post-purchase
Evaluative criteria
the criteria based on which consumers decide what makes it into their consideration and choice sets and what they end up purchasing
Post-purchase dissonance
doubt or anxiety following a difficult, relatively permanent purchase decision
Disposition
physical separation a consumer undergoes with an unwanted or no longed needed product
Evaluation
We start with expectations and compare it to actual performance
Satisfaction
measurement that determines how happy customers are with a company’s products, services, and capabilities
Dissatisfaction
lack of satisfaction
Instrumental performance
The physical functioning of the product
Symbolic performance
Aesthetic or image-enhancement performance of the product
Affective performance
The emotional response that owning or using the product provides
Repeat purchasers
continue to buy the same brand even though they do not have an emotional attachment to it
Committed customers
ability of brands to keep people loyal to their products or services by delivering value
Brand loyalty
involves commitment to the brand– it is a biased behavioral response expressed over time
Switching costs
the costs of finding, evaluating, and adopting another solution
Churn
turnover in a firm’s customer base
CRM
customer relationship management
General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)
EU protection for personal data (Name, IP, Cookies)
Provides consumers with control over their data
Promotes pseudonymization, anonymization and encryption
Third party non-compliances means your org. is not compliant
Native advertising
Ads that are designed to look like organic (unpaid) content
Children’s Online Privacy Protection Act (COPPA)
imposes certain requirements on operators of websites or online services directed to children under the age of 13; online privacy relates to collection and use of information from websites
FTC best practices for native advertising disclosures
An ad is deceptive if there is a material misrepresentation or omission of information that is likely to mislead the consumer
PSA
free ad space on TV and radio