Chapter `10
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
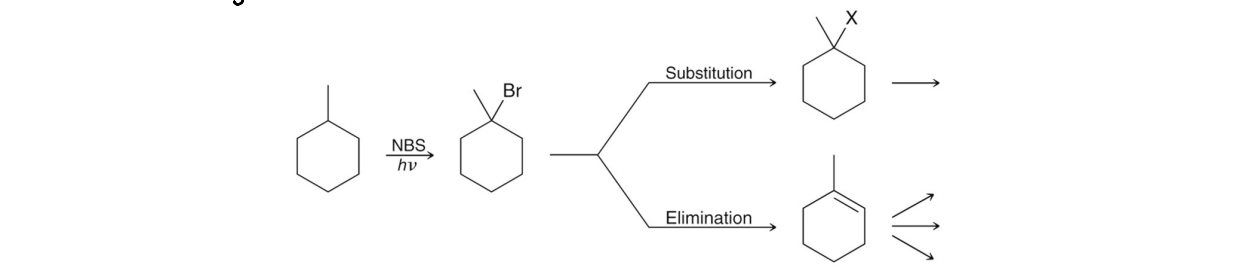
Chlorination of Methane follows three distinct stages what is the first?
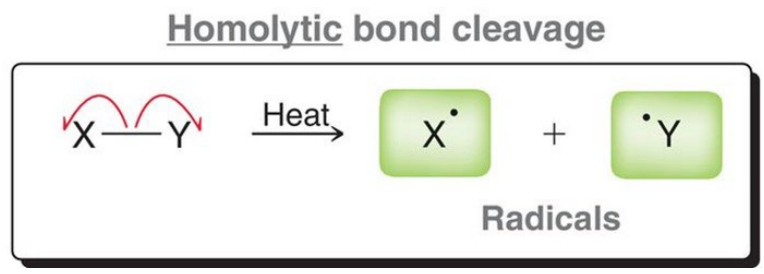
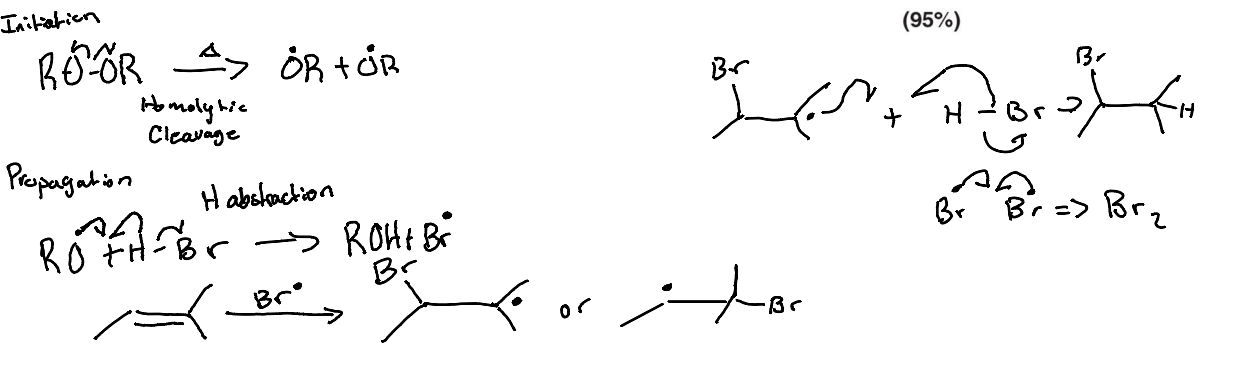
Initiation (Homolytic Bond Cleavage)
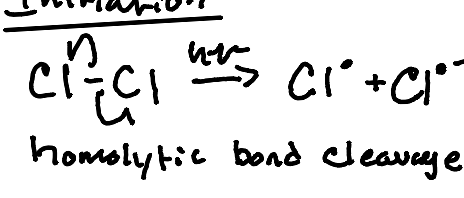
Chlorination of Methane follows three distinct stages what is the second?
Propogation (Hydrogen Abstraction, Halogen Abstraction)
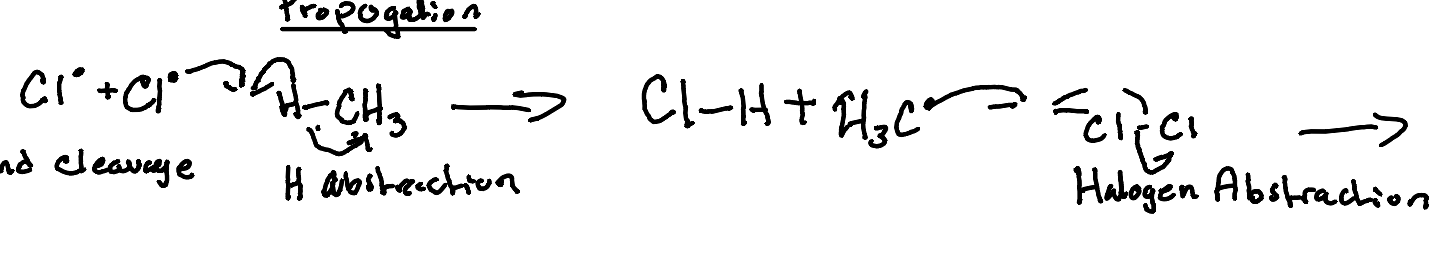
Chlorination of Methane follows three distinct stages what is the third?
Termination (Coupling)
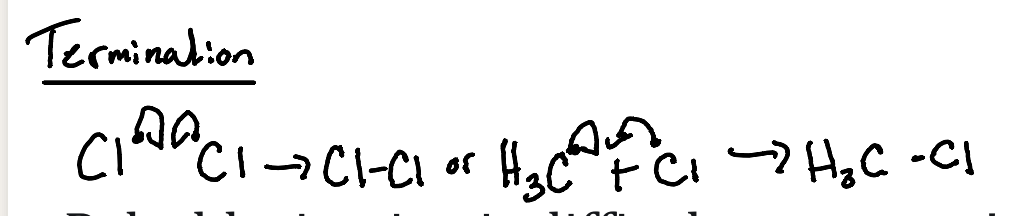
What are the only two halogens that are useful?
Chlorine and Bromine
What is the purpose of a radical inhibitor?
To react with radicals, preventing a chain process from occurring. Stabilized radicals and compounds that easily form stabilized radicals are good inhibitors.
What are the two examples of radicals mentioned?
Oxygen and Hydroquinone
What is a radical initiator?
A substance that possesses a weak bond that cleaves homiletically with heat or light.
What are the most common radical initiators?
Dihalides
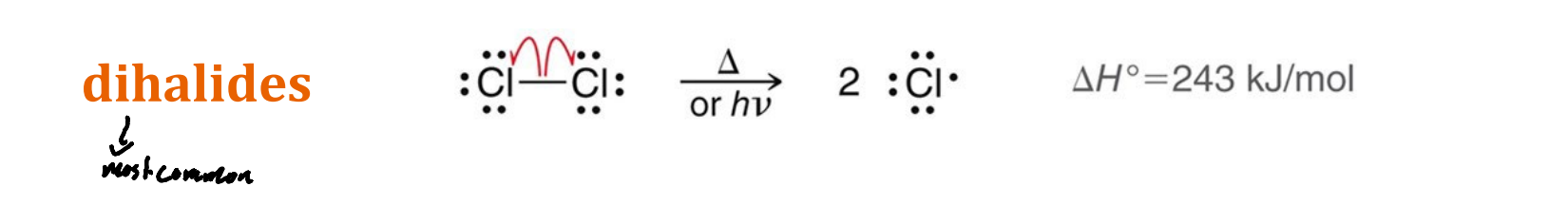
What are the other two radical initiators, other than dihalides, mentioned in class?
Alkyl peroxides an Acyl peroxides
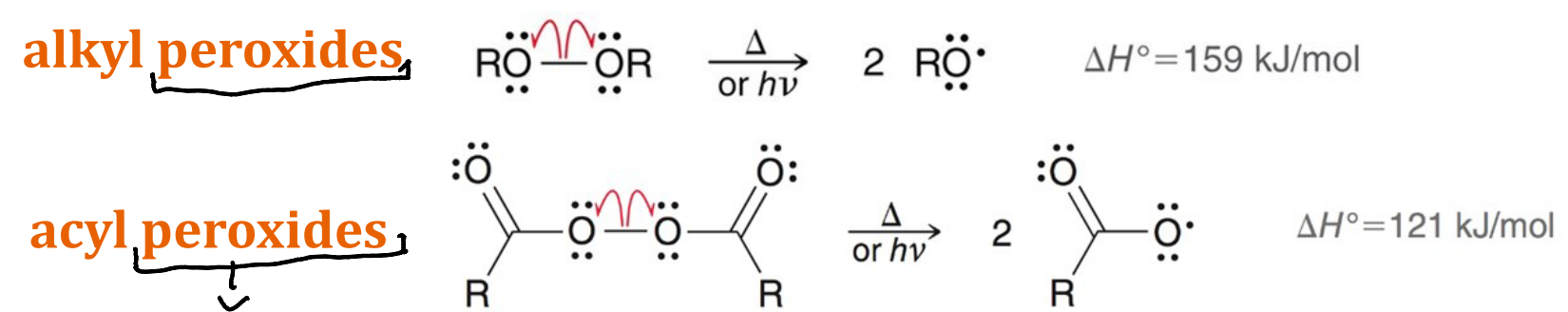
Of the radical initiators mentioned in class what are the most reactive?
Acyl peroxides
Whaat is the name of the first step in radical mechanisms where a radical species is formed from a non-radical species?
Initiation step
What is the name of the second step of the radical mechanism where radicals react with a non-radical to make new radicals and new non-radicals?
Propagation step
What is the name of the third step of the radical mechanism where two radicals react to make a non radical.
Termination step
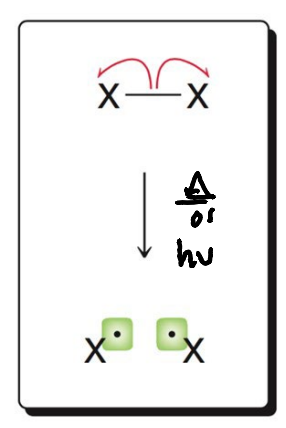
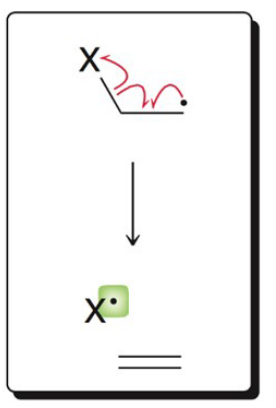
What image shows the initiation mechanism of homolytic cleavage?
.
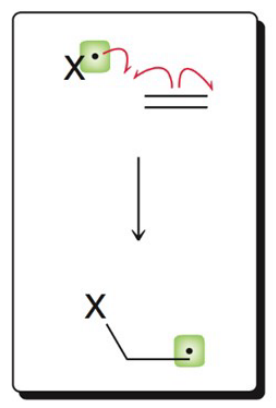
What image shows the propagation mechanism of addition to a π bond?
.
What image shows the propagation mechanism of hydrogen abstraction?
.
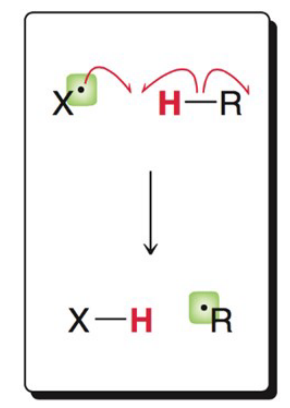
What image shows the propagation mechanism of halogen abstraction?
.
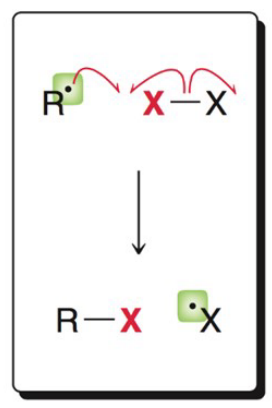
What image shows the propagation mechanism of elimination?
.
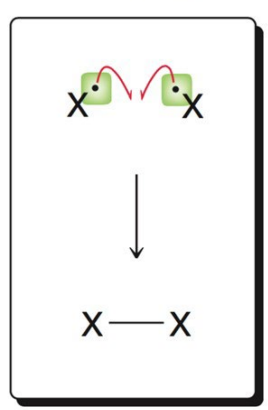
What image shows the termination mechanism of coupling?
.
True or False
Methyl Shifts can occur in a Radical Rearrangement.
False; two electrons would need to be moved making it not a radical reaction
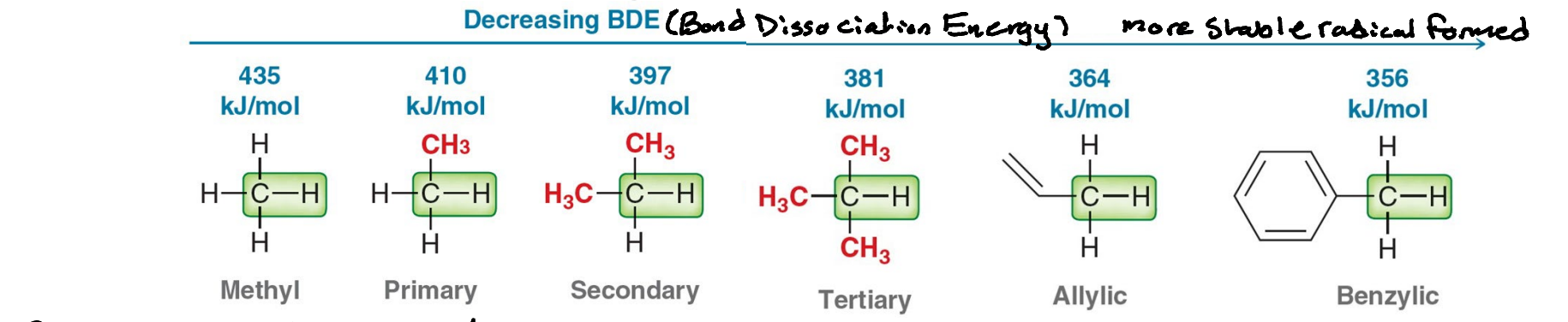
How is bond strength proportional to carbon radical stability?
As the stability of carbon radicals increases, the bond strength of the corresponding C-H bond decreases, making it easier to break. Making the relation inversely proportion.
Is a vinylic radical stable or unstable?
Highly unstable
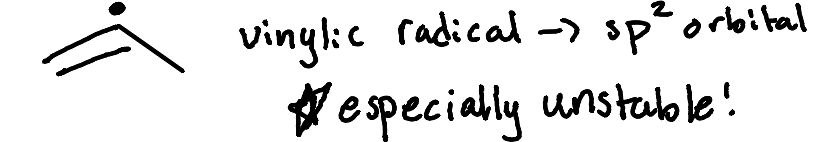
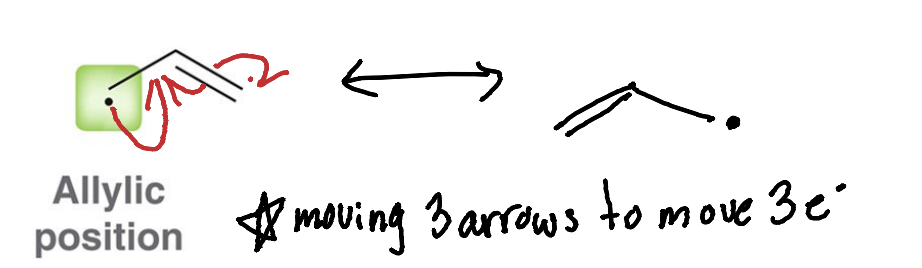
how many arrows are needed to move a radical in resonance?
Three
What is a radical?
A free electron from homolytic bond cleavage.
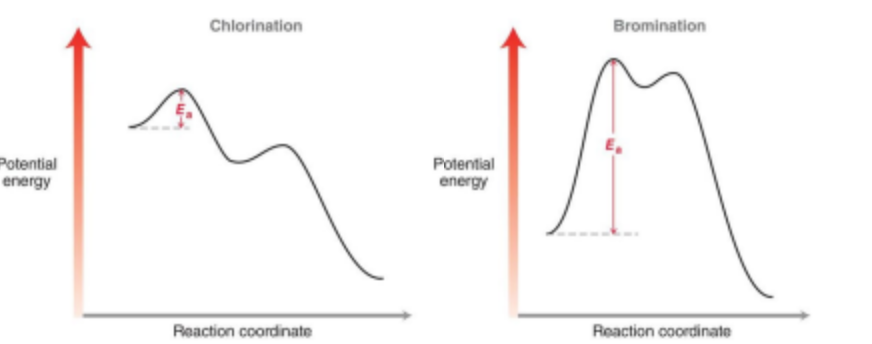
Bromination is a mush slower process than chlorination. What does this mean?
Bromination is much more selective.
With substrates more complex than ethane, multiple monohalogenation products are possible. Which product is the major one?
The More Substituted Halogenation
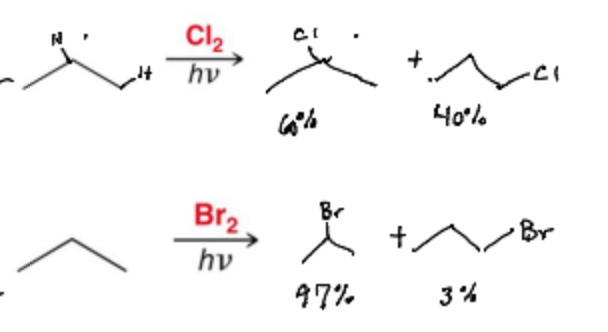
When determining the selectivity of a halogen radical reaction what should you focus on?
The H-abstraction step (The rate determining step)
Where does the selectivity in the Halogenation Radical Reaction come from?
Hammonds Postulates
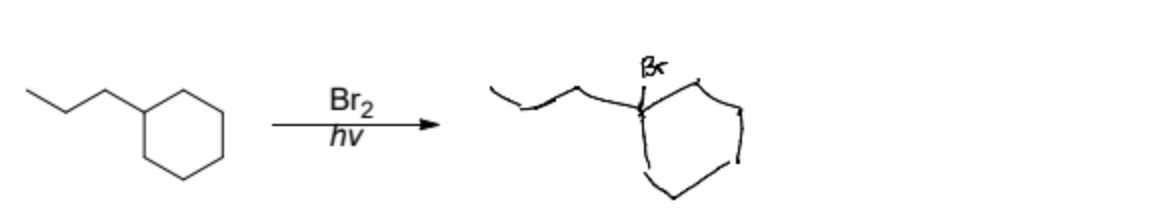
In a Bromine Halogenation using radicals where does the bromine normally attach?
The most substituted point of the reaction
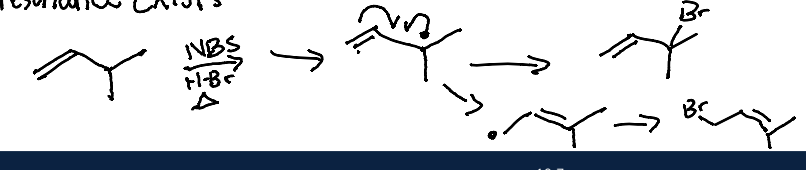
When an alkene is present in a molecule. What is used in order to add BR with a radical instead of alkene addition?
NBS is used or the concentration of HBr and Br2, are low. This method allows for selective bromination at the allylic position rather than the alkene.
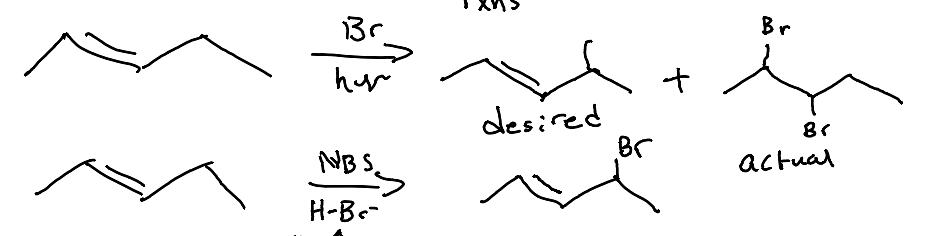
In an NBS Allylic Halogenation with NBS initiation. what is always the major product?
The more stable alkene in Allyic Radical Halogenation
How does a Peroxide add in an anti-markovnikov arrangement?
Radical chemistry
What is the real advantage of halogenation?
Functionalizing an otherwise unreactive alkane, which can then be converted into other useful functional groups.