Midterm Refresher: Coagulation Cascade
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
types of arterial thrombosis
Myocardial infarction, stroke
what plays a major role in arterial thrombosis
platelets play a major role
examples of venous thromboembolism
deep vein thrombosis, pulmonary embolism, portal/hepatic vein thrombosis
what plays a major role in venous thromboembolism?
clotting factors and clotting cascade play a major role
function of platelets
regulate hemostasis
Removed by spleen, liver and bone marrow
platelet reference range
150,000 - 450,000
thrombocytopenia
low platelets
what value is risk for bleeding with trauma
platelet count <50,000
what lab value is risk for spontaneous bleeding
<20,000
what is thrombocythemia/thrombocytosis
high platelets c
clinical consequence of thrombocythemia/thrombocytosis
Arterial or venous thrombosis
Hemorrhage
what drugs can cause thrombocytopenia
antineoplastics
HEPARIN
Anti-infectives
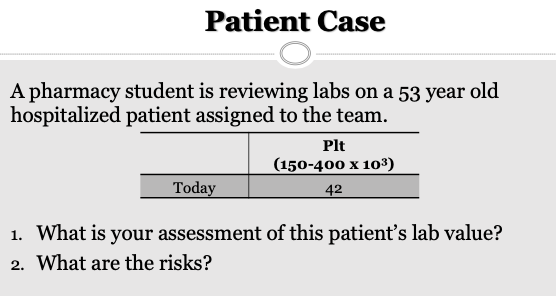
Patient has LOW platelets
Patient is at risk for bleeding with trauma (<50,000)
What is MPV
Mean platelet volume 7-11 fl
Useful to distinguish hypoproductive and hyper destructive causes (part of CBC)
Platelet tests monitor:
anticoagulant therapy to assess efficacy or confirm presence or absence of drug
(dose is usually proportional to effect)
Can also be used to identify deficiencies of coagulation factors
PT/INR
Warfarin monitoring, hepatic function
aPTT
Heparin!!!!!!A
ACT
High dose heparin or DTIs
Anti-Xa
LMWH, factor Xa inhibitors
how does heparin work
inhibits the activation of clotting factors
how does warfarin work
blocks synthesis of clotting factors
Blocks vit K synthesis → this is why you avoid vitamin K diets with warfarin
what is PT
measures the time for clot formation in seconds
what is a NORMAL range for INR?
0.9-1.1
what is the THERAPEUTIC range for INR?
2-3
or
2.5-3.5
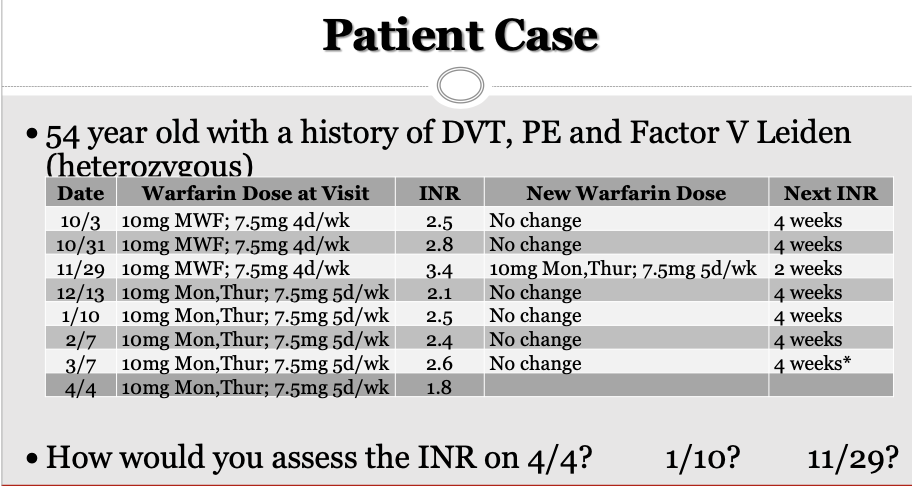
11/29: INR 3.4 → Supratherapeutic (high)
01/10: INR is therapeutic
04.04: INR is subtherapeutic (low)
Therapeutic range is 2-3 or 2.5-3.5

Patient is at risk for heparin induced thrombocytopenia (due to low platelets)
LMWH
enoxaparin, dalteparinf
factor xa inhibitors
Apixaban
Rivaroxaban
Edoxaban
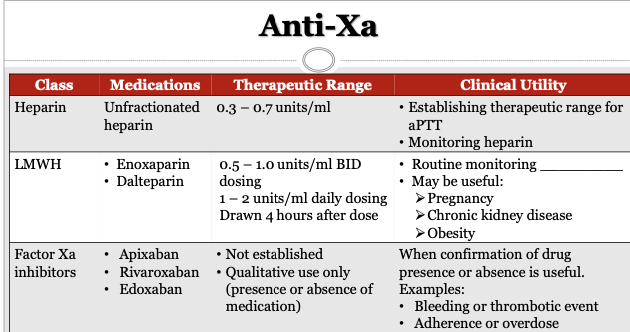
Anti-Xa is used to confirm the presence of a drug as efficacy is generally achieved via weight based dosing
T/F Routine monitoring of LMWH is done via anti-xa
Not routinely done due to weight based dosing
maybe good for pregnancy, chronic kidney disease, obesity (due to changes in weight)
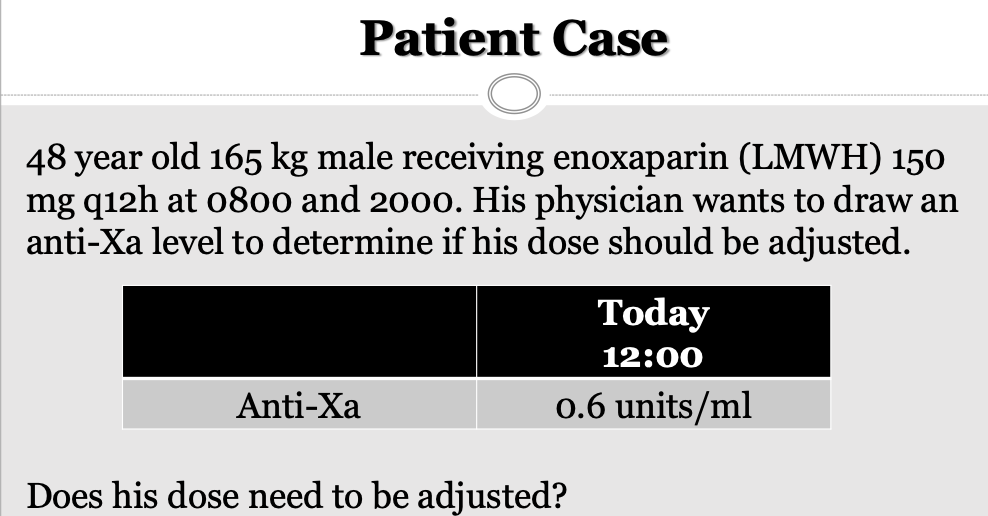
We are looking to 0.5-1
This is therapeutic
Draw again 4 hours from now (for LMWH)

Factor Xa inhibitor; taking for a fib; presents with slurred speech and left-sided weakness
Factor Xa test is good for adherence to see levels of apixaban; this is not a routine monitoring
T/F An advantage of POC devices is their slow turn around time
FALSE
POC devices are convenient and cost effective
causes of thrombophillia
antithrombin III deficiency
Protein C or S deficiency
Protrombin G20210A mutation
Activated protein C resistance
Factor V leiden
what is the clinical usefulness of a D-Dimer?
A negative test can RULE out a venous thromboembolism (DVT, PE)
If it is positive maybe investigate PE further
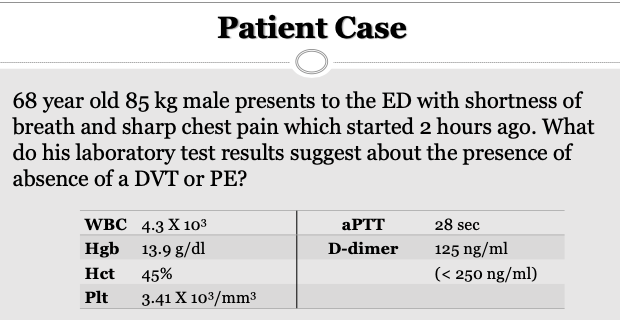
D-Dimer: Not elevated so PE can be ruled out (Normal range: variable; < 0.5 mcg/ml or < 200ng/ml)
aPTT is normal (Normal range: 22 – 38 sec (variable)
D-dimer range
<200 ng/mL