Chapter 8 Central Nervous System (copy)
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
71 Terms
what can be found in white matter? what are the special localized areas called?
myelinated axons, specifically called tracts; funiculus/funiculi
what can be found in gray matter? what are the different regions called?
cell body and dendrites; horns (be specific like dorsal horn or ventral horn)
all incoming sensory information coming from spinal cord will enter from which side? (dorsal/ventral)
dorsal (afferent)
all information leaving the spinal cord going to the effectors will leave through which side? (dorsal/ventral)
ventral (efferent)
what are the two types of tracts in the white matter of the spinal cord? and what kind of information do they carry?
ascending tract carries SENSORY information TO the brain; descending tract carries COMMANDS to MOTOR neurons
spinal cord is a reflex center, does it need to go to the brain to process when a reflex happens? are reflexes voluntary or involuntary?
no, the spinal cord is also an integrating center so it doesn’t need to go to the brain in order to produce a reflex; involuntary
what is the function of the somatosensory tract? ascending or descending?
carries incoming GENERAL sensory information from body to the brain; ascending tract
what is the pathway of the somatosensory tract?
spinal cord → medulla oblongata → pons → midbrain → thalamus → primary somatosensory cortex of the parietal lobe of the cerebrum
what is the function of the thalamus?
sensory relay station; sorts the types of sensory information and relays it to the corresponding lobe/cortex, it can also get ignore certain sensory information that isn’t important like clothes on your skin
ex: hearing → auditory cortex
do all senses need to be relayed by the thalamus?
everything except for smell/olfactory will need to be relayed by the thalamus
what happens at the medulla?
decussation or crossing over
what is the function of the corticospinal tract? is it ascending or descending?
carries motor information from motor cortex to spinal cord; descending tract
what is the pathway of the corticospinal tract?
primary motor cortex of frontal lobe → midbrain → pons → medulla (decussation happens here) → spinal cord
which side of the body does the right cerebrum control?
the left side of the body
which side of the body does the left cerebrum control?
the right side of the body
what are the three structures that make up the brain stem?
medulla, pons, and midbrain
what are the pyramids of the medulla?
they are the two medial bumps of the medulla that contains the corticospinal tract (white matter)
which type of the nervous system is the medulla essential to?
it is essential to the autonomic nervous system
what are the two centers that are inside the medulla? what do they control?
cardiovascular center - heart rate
respiratory center - breathing rate
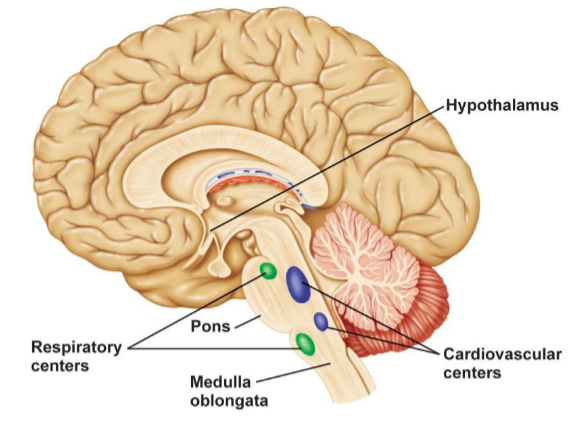
where are the pons located?
sitting between cerebrum and cerebellum
what are the three functions of the pons?
relay station between the cerebrum and cerebellum (important because cerebrum has to communicate with cerebellum in order to produce a motor movement)
passage for sensory and motor tracts (the tracts has to pass through here to get to their destination)
respiratory center INSIDE the pons (works together with medullary respiratory center)
which two structures have respiratory centers?
pons (pons respiratory centers) and medulla (medullary respiratory centers)
where is the midbrain located?
right above the pons (the little bumps)
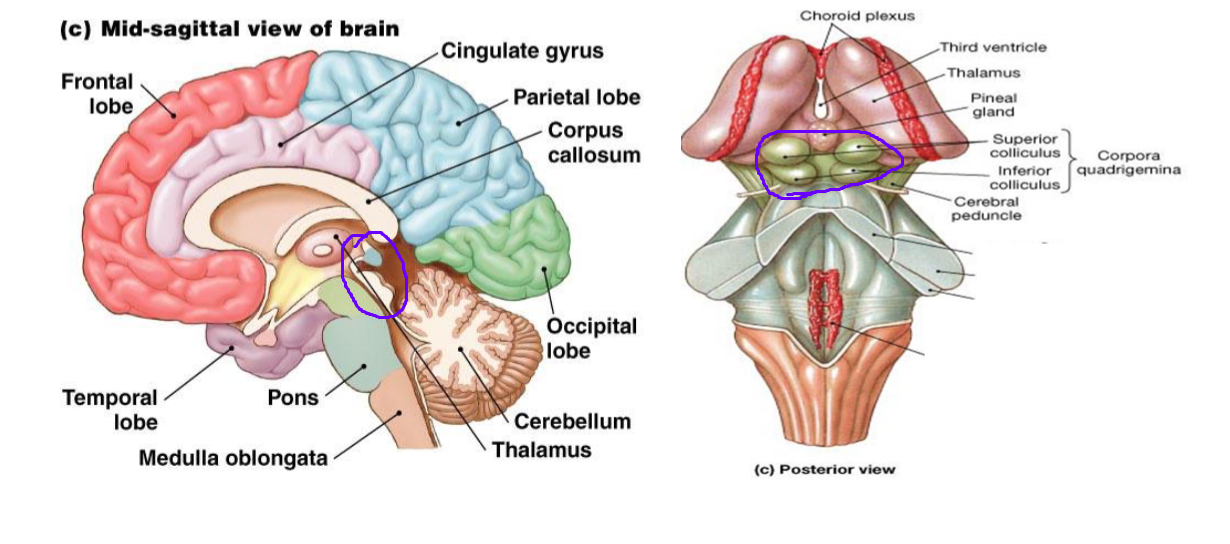
what are the upper two bumps of the midbrain for?
upper two bumps (superior colliculus) is for involuntary eye movement
what are the lower two bumps of the midbrain for?
lower two bumps (inferior colliculus) is to get auditory information to auditory cortex for hearing
what are the three functions of the midbrain?
passageway of sensory and motor tracts (ascending and descending tracts)
controls eye movement - involuntary eye movement (eyes moving with head)
routes auditory information to auditory cortex in the temporal lobe
what structures does the diencephalon include?
epithalamus, thalamus, and hypothalamus
(the “eyes, the face and the beak” of the bird)
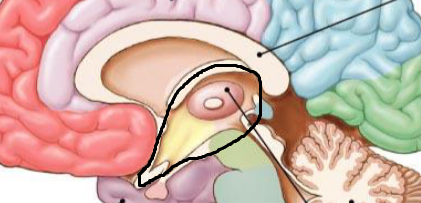
what are the three functions of the thalamus?
composed of nuclei (neuron cell bodies)
processes and relays sensory info to their appropriate cortex; it can also terminate senses that aren’t important such as clothing on skin
regulates sleep, awareness, learning and memory
does the thalamus have a left and right?
yes, it has a left side and a right side and it is connected and can communicate with each other
how does the hypothalamus activate the sympathetic nervous system?
“master control of ANS”, activates sympathetic nervous system (fight or flight), releases epinephrine (tells adrenal medulla to release adrenaline)
helps maintain blood glucose concentrations through effects on endocrine pancreas
stimulates shivering and sweating
how does the hypothalamus maintain body temperature?
through shivering and sweating
how does the hypothalamus control body osmolarity?
body osmolarity = blood concentration
motivates thirst and drinking behavior (dehydration/hydration)
stimulates secretion of vasopressin (hormone kind of like ADH) (we don’t really need to know until endocrine chapter)
how does the hypothalamus control reproductive functions?
directs secretion of oxytocin for uterine contractions and milk release (it does release oxytocin for men too)
directs trophic hormone control of anterior pituitary hormones FSH and LF (controls pituitary gland)
how does the hypothalamus control food intake?
stimulates satiety center
stimulates feeding center
(basically hungry or feeling full)
how does the hypothalamus influence cardiovascular control center in medulla oblongata?
the hypothalamus oversees the medulla oblongata
how does the hypothalamus control the circadian rhythm?
the optic nerve goes through the optic chiasm (OC) and right above it is the suprachiasmatic nucleus (SC)
visual input gets also sent to the suprachiasmatic nucleus to know the amount of daylight you see per day
it will work with pineal gland to release appropriate amounts of melatonin to sleep
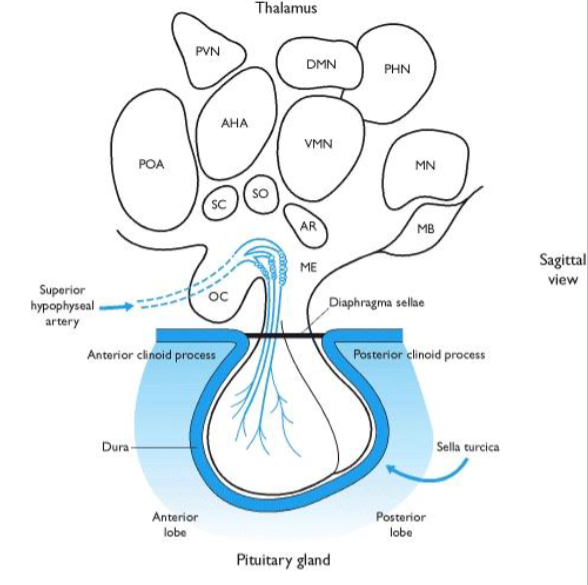
what are the 9 functions of the hypothalamus?
activates sympathetic nervous system (master control of ANS)
maintains body temperature
controls body osmolarity
controls reproductive functions
controls food intake
interacts with limbic system to influence behavior and emotions
influences cardiovascular control center in medulla oblongata
secretes trophic hormones that control release of hormones from anterior pituitary gland
controls circadian rhythm
what is the purpose of the cerebellum?
receives sensory input and contributes to coordination, timing and precision of motor movement
basically refining the motor output that the primary motor cortex sends out
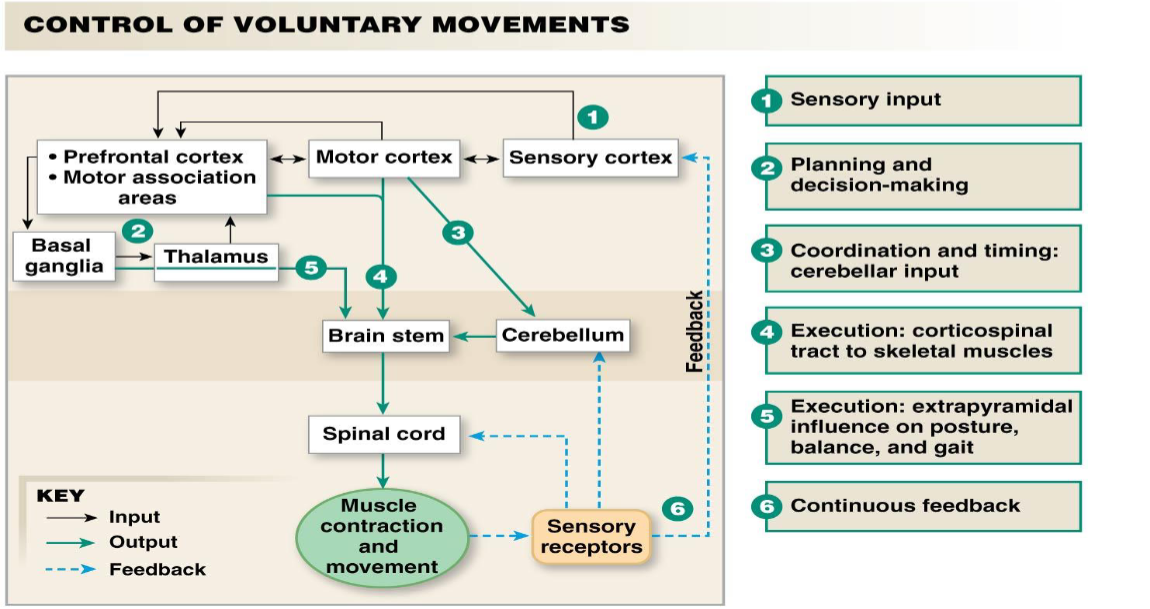
what are the steps for control of voluntary movements? (where does it go in the brain)
sensory input
motor cortex will “think” the movement needed
prefrontal cortex, motor association areas, basal ganglia, thalamus will plan the movement
cerebellum will refine and make the movement precise
all gets sent to brain stem → spinal cord → muscle contraction and movement
what is cerebellar hypoplasia?
its a condition when someone has an underdeveloped cerebellum
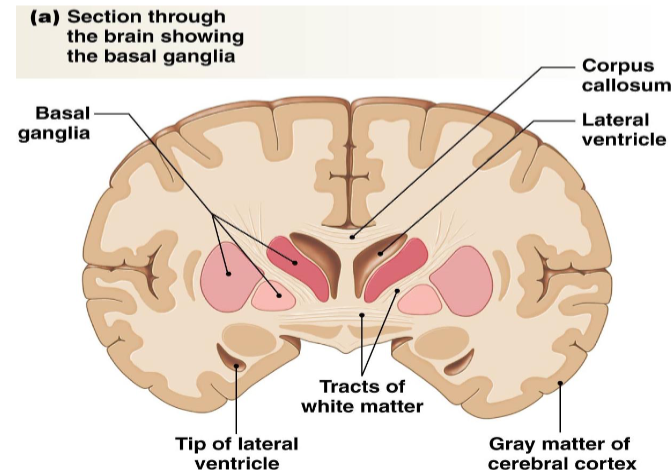
what is grey matter made up of?
neuron cell bodies and dendrites
which two parts of the brain are gray matter?
cerebral cortex and basal nuclei (referred to as basal ganglia but the more correct term is nuclei)
what is the basal nuclei (basal ganglia) function?
controls voluntary movement, procedural learning, cognition and emotion
also part of the planning process of producing a movement
what is white matter made up of?
myelinated axons
what is the name of the structure that connects the two cerebrum hemispheres? what does it do?
corpus collosum; it connects the two hemispheres of the cerebrum and allows it to communicate
what are the five lobes of the brain?
frontal, parietal, occipital, temporal, insula/insular
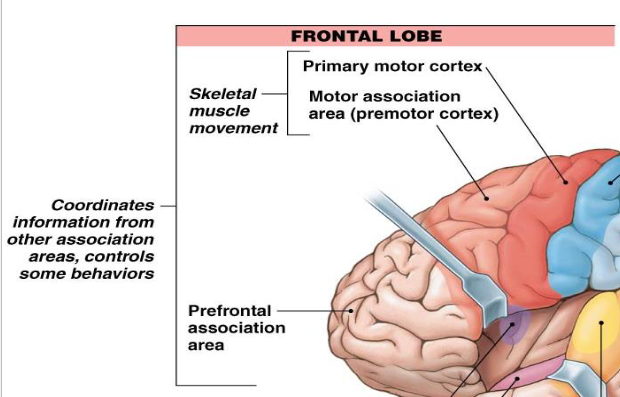
what does the frontal lobe contain/function?
has primary motor cortex, motor association area (premotor cortex) for skeletal muscle movement
prefrontal association area
your personality is in this area of the brain
what does the parietal lobe contain/function?
primary somatic sensory cortex, sensory association area
only deals with sensory!!
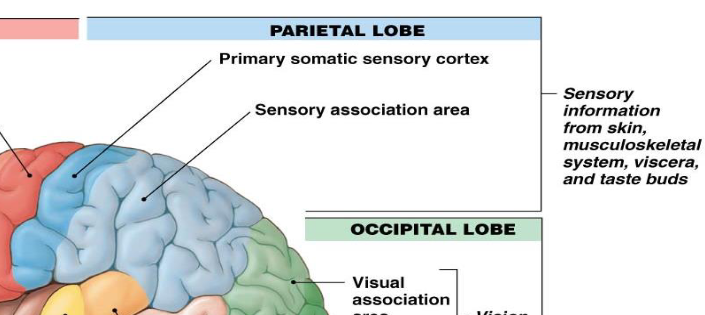
what does the occipital lobe contain/function?
visual association area, visual cortex
function is for vision
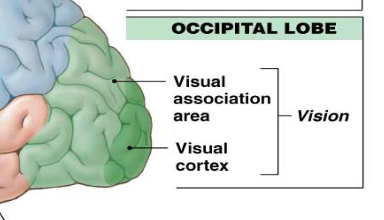
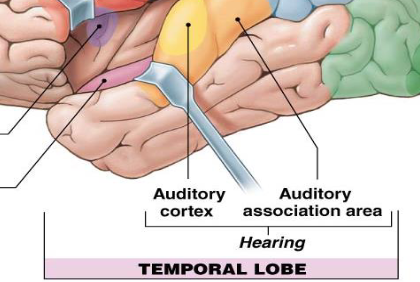
what does the temporal lobe contain/function?
auditory cortex, auditory association area
for hearing and balance/equilibrium
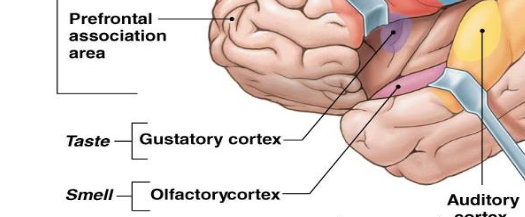
what does the insula/insular lobe contain/function?
gustatory cortex for taste
olfactory cortex for smell
what is cerebral laterization?
the distribution of functional areas in the two cerebral hemispheres is not symmetrical
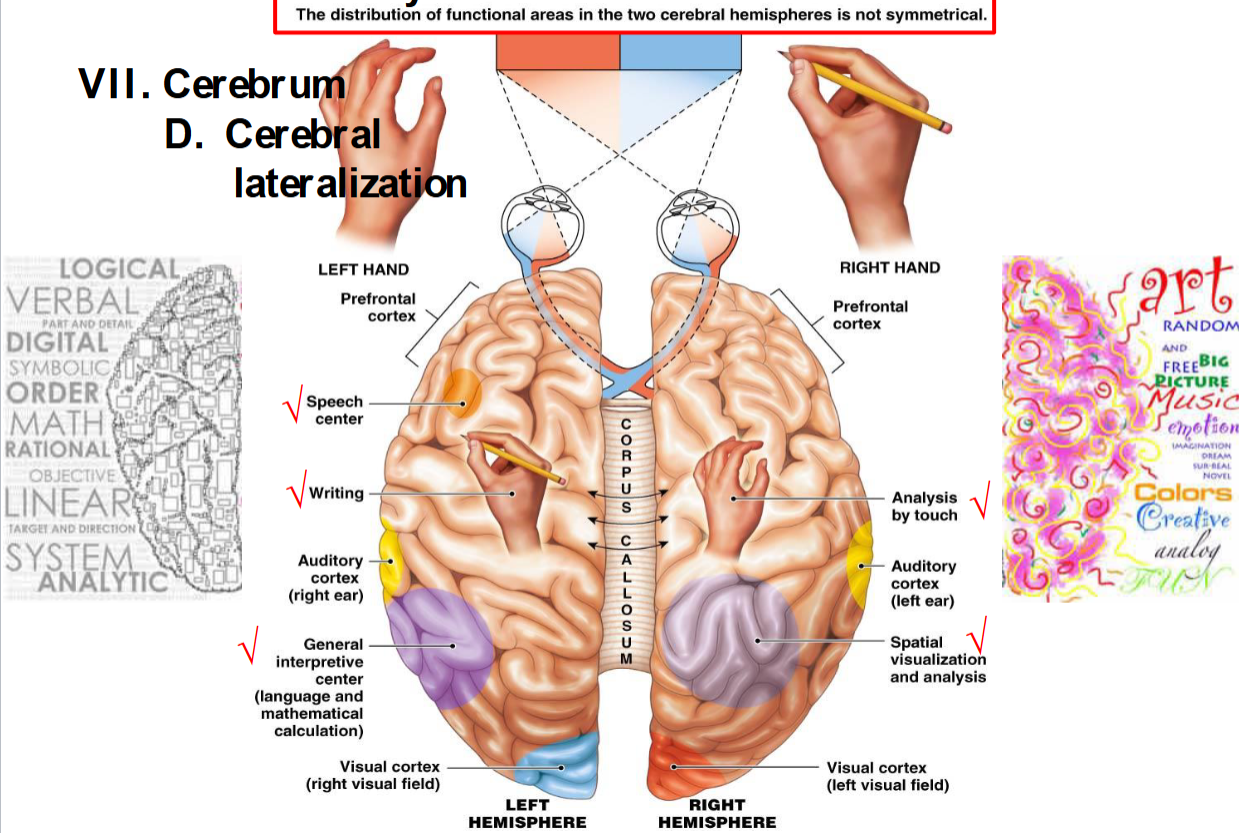
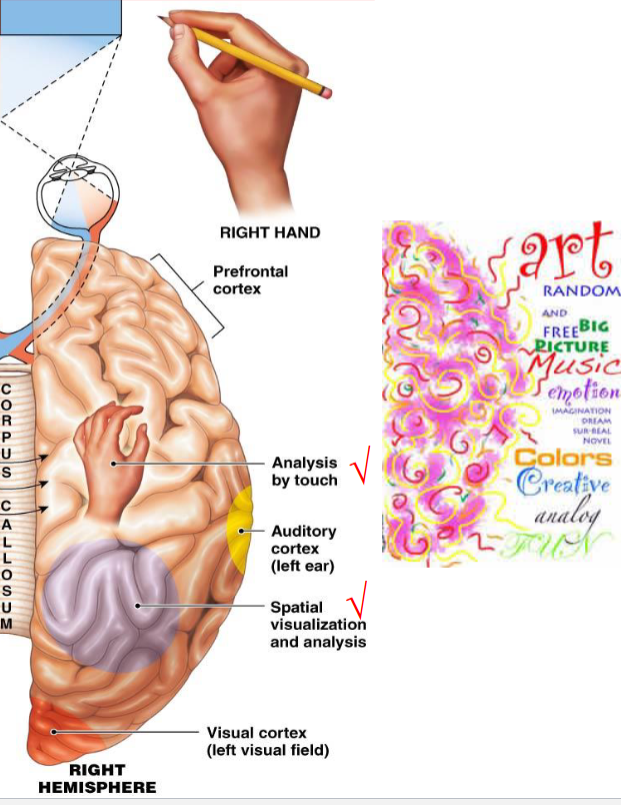
what does the right hemisphere usually deal with?
analysis by touch (textures), spatial visualization and analysis (reading a map)
associated with art, music, creativity, etc.
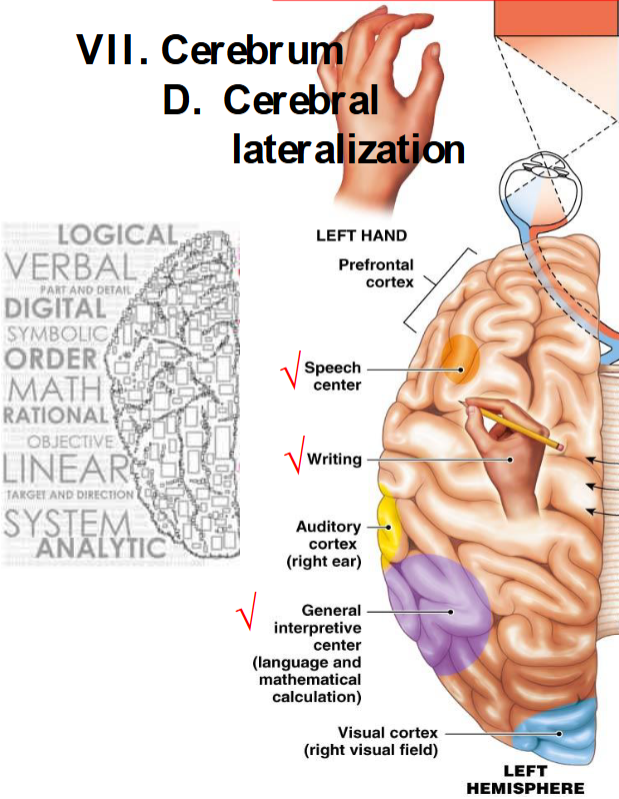
what does the left hemisphere usually deal with?
speech center, writing, general interpretive center (language and mathematical calculation)
associated with logic, math, rationality, etc.
what is the definition of sleep?
a state of reduced mental and physical activities and altered consciousness
when does your brain produce gamma waves? + awake or asleep?
during concentration, info processing, learning, problem solving
awake
> 30Hz (frequency; meaning 30 or more spikes per second)
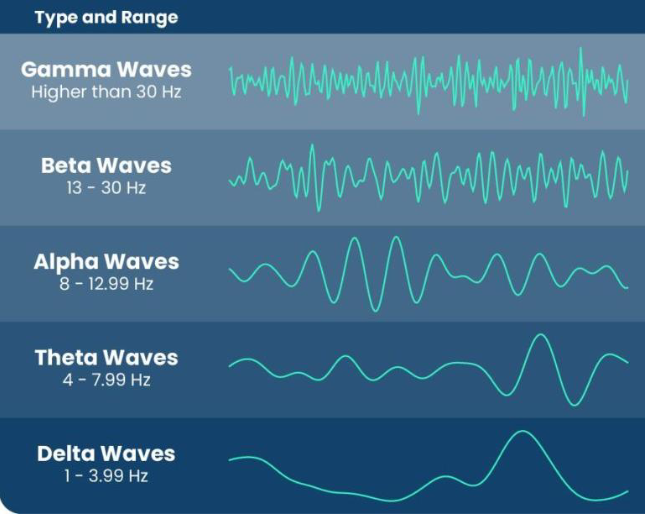
when does your brain produce beta waves? + awake or asleep?
during normal waking consciousness; doing normal awake conscious things
awake
13 - 30 Hz
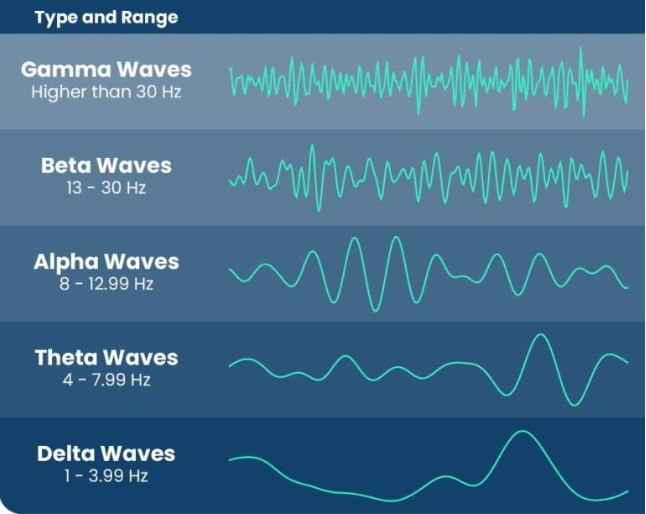
when does your brain produce alpha waves? + awake or asleep?
during unfocused/relaxed, light meditation
awake
8 - 12.99 Hz
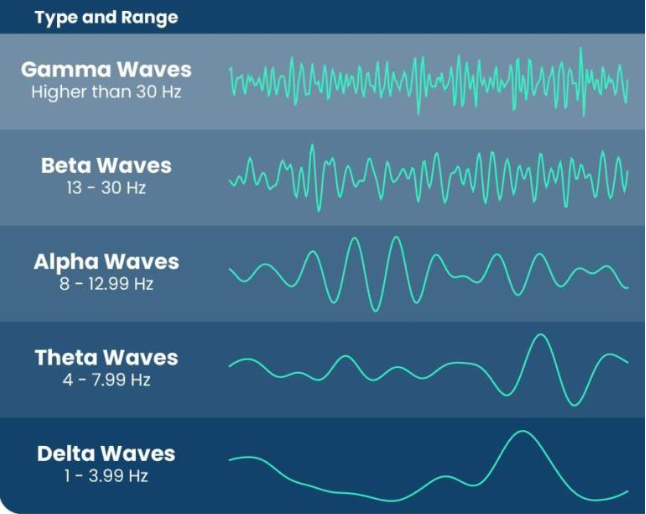
when does your brain produce theta waves? + awake or asleep?
during light sleep, deep meditation
asleep but can easily wake up
4 - 7.99 Hz
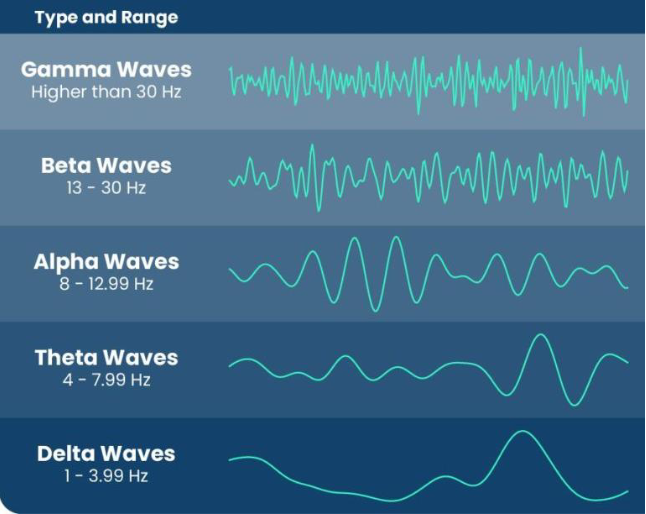
when does your brain produce delta waves? + awake or asleep?
during deep sleep, healing, restorative sleep
asleep/deep sleep
1 - 3.99 Hz
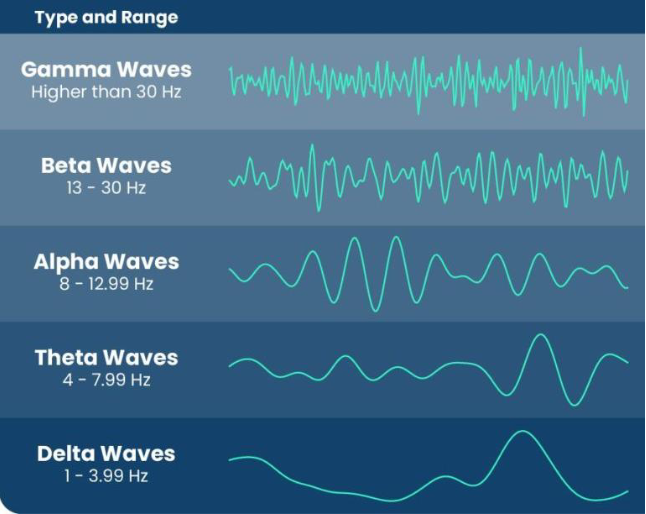
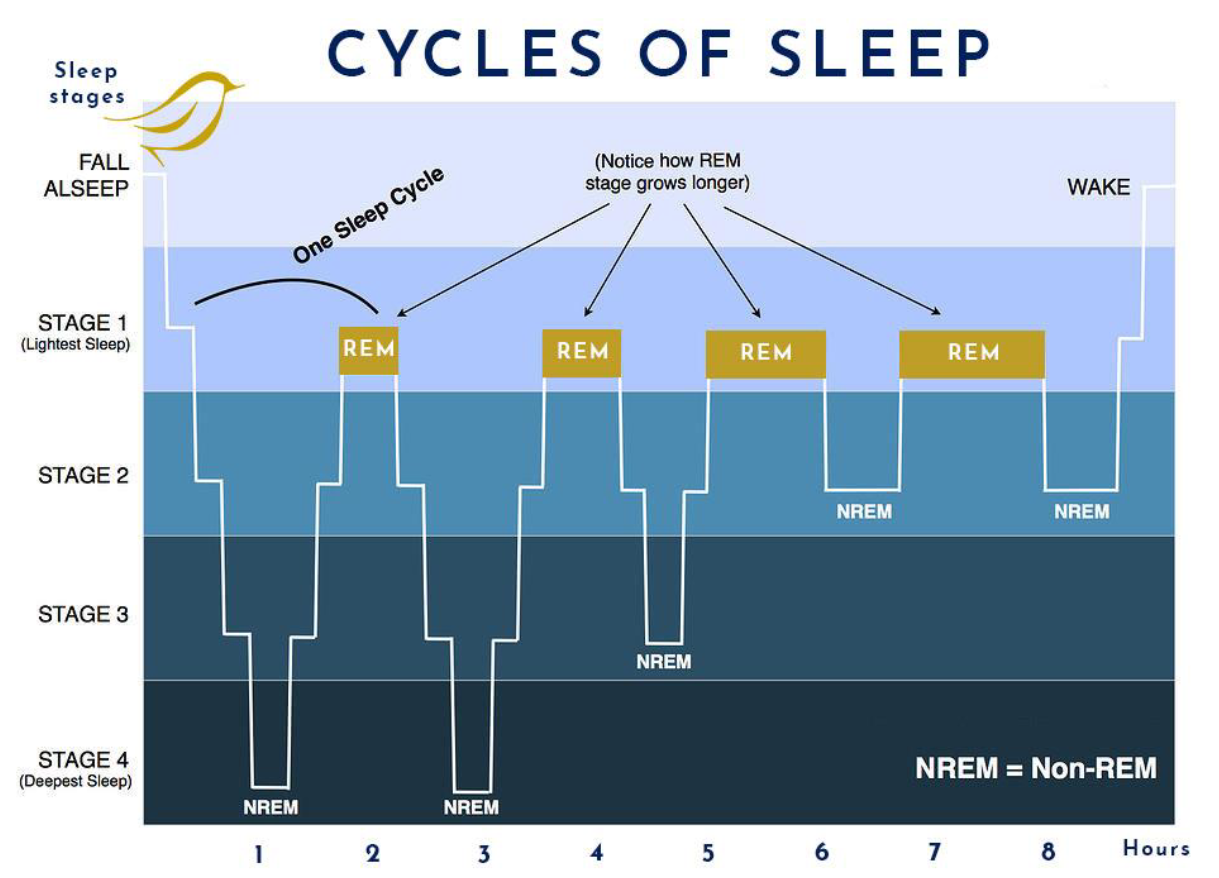
what are the two categories that a sleep cycle can be broken up into?
REM (rapid eye movement) and Non-REM or NREM (no rapid eye movement)
what happens in NREM sleep?
no rapid eye movement
parasympathetic (rest and digest!) activities increase
muscles not paralyzed (major muscles)
what happens in REM sleep?
rapid eye movement
sympathetic activities increase (heart rate increase, etc.)
vivid dream stage
increased metabolism
major muscle groups paralyzed (atonia)
which stages of sleep are for NREM?
stages 1 - 3/4
what kind of waves are seen at stage 1 and 2 of sleep?
theta waves
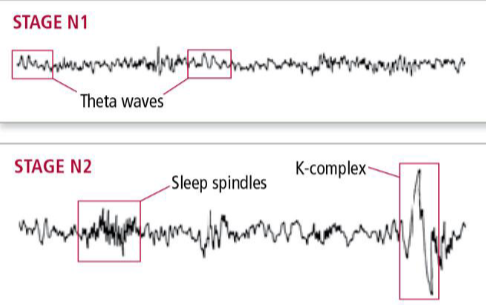
what kind of waves are seen at stage 3 and 4 of sleep?
delta waves

how long does it take to go from stage 1 to stage 3 of NREM sleep?
usually around an hour average
how long does REM sleep last?
usually around 30 minutes
how long does one sleep cycle last?
usually lasts around 90 minutes
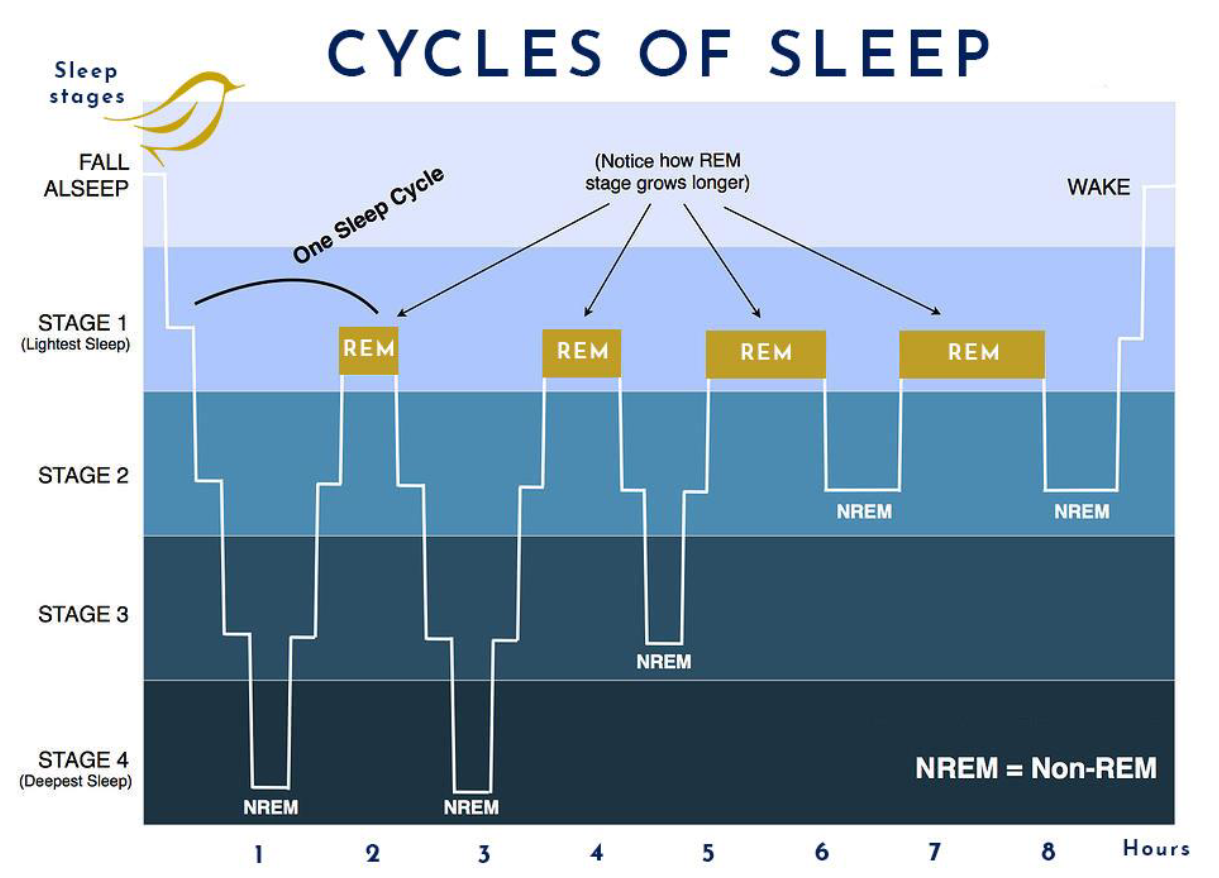
which stage of sleep is the most important? and why?
stage 4 because that is when healing and restoration happens
the ____ stage grows longer the closer you are to waking up. (NREM / REM)
REM