Untitled
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/105
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 9:07 PM on 9/7/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
106 Terms
1
New cards
What is the relationship between humans and their environment?
Humans and animals depend on plants to survive
2
New cards
Botany
Plant biology/plant science
3
New cards
Plant Anatomy
Study of internal structure of plants
4
New cards
Plant Physiology
Study of plant function
5
New cards
Plant Taxonomy
Study of describing, naming, classifying organisms
6
New cards
Plant Systemics
-Related field to Plant Taxonomy - but broader
-Study of developing methods for grouping organisms
-Study of developing methods for grouping organisms
7
New cards
Plant Geography
Study of how and why plants are distributed where they are
8
New cards
Plant Ecology
Study of the interaction of plants with one another and their environment
9
New cards
Plant Morphology
Study of form and structure of plants
10
New cards
Genetics
-Science of hereditary
-Branches: Plant breeding and Genetic Engineering
-Gregor Mendel
-Branches: Plant breeding and Genetic Engineering
-Gregor Mendel
11
New cards
Cell Biology
Science of cell structure and function
12
New cards
Economic Botany and Ethnobotany
Focus on practical uses of plants and plant products
13
New cards
Effects humans have on the environment
-Drained wetlands
-Cleared natural vegetation
-Dumped wastes and pollution
-Used pesticides and herbicides
-Cleared natural vegetation
-Dumped wastes and pollution
-Used pesticides and herbicides
14
New cards
Ways for humans to reduce environmental impact
-Change agricultural practices
-Render pollutants harmless
-Recycle
-Replace pesticides with biological pest controls
-Conserve water and energy
-Preserve habitats and species
-Render pollutants harmless
-Recycle
-Replace pesticides with biological pest controls
-Conserve water and energy
-Preserve habitats and species
15
New cards
Prokaryotic Cells
-Lack nucleus
-Free floating DNA in nucleoid region mixed with cytoplasm
-No organelles
-No nuclear membrane surrounding DNA
-Examples: Bacteria and Archaea
-Free floating DNA in nucleoid region mixed with cytoplasm
-No organelles
-No nuclear membrane surrounding DNA
-Examples: Bacteria and Archaea
16
New cards
Eukaryotic Cells
-Contains nucleus bounded by Nuclear membrane
-Cell walls
-Membrane-bound organelles
-Examples: Plants and animals
-Cell walls
-Membrane-bound organelles
-Examples: Plants and animals
17
New cards
Protoplasm
-Surrounds cell wall
-Consists of all living components of a cell
-Consists of all living components of a cell
18
New cards
Cell Wall
-Supports and protects the cell
-Contains Cellulose: main structural component of cell walls
-Contain matrix of:
-Hemicellulose: holds cellulose fibrils
together
-Pectin: gives stiffness
-Glycoproteins: proteins with associated
sugars; keep cells tight
-Primary wall, Secondary wall, Middle lamella
-Contains Cellulose: main structural component of cell walls
-Contain matrix of:
-Hemicellulose: holds cellulose fibrils
together
-Pectin: gives stiffness
-Glycoproteins: proteins with associated
sugars; keep cells tight
-Primary wall, Secondary wall, Middle lamella
19
New cards
Primary Cell Wall
-Thin and flexible
-Laid down on either side of middle lamella
-Made of cellulose: main structural component
-Laid down on either side of middle lamella
-Made of cellulose: main structural component
20
New cards
Secondary Cell Wall
-Produced between the primary cell wall and plasma membrane
-Cellulose microfibrils embedded in lignin for strength
-Derived from primary wall by thickening and inclusion of lignin
-Lignin makes wall less flexible
-Used to reinforce plant walls
-Cellulose microfibrils embedded in lignin for strength
-Derived from primary wall by thickening and inclusion of lignin
-Lignin makes wall less flexible
-Used to reinforce plant walls
21
New cards
Middle Lamella
-First produced when new cell wall are formed
-Forms in middle of two cells
-Made of Pectin
-Shared by two adjacent cells
-Forms in middle of two cells
-Made of Pectin
-Shared by two adjacent cells
22
New cards
Plamsa Membrane
-Bounds all living components of a cell
-Phospholipid bilayer: semipermeable outer boundary of cell
-Regulates movement of
substances into and out of cell
-Composed of phospholipids arranged in two layers with proteins interspersed throughout
-Hydrophilic heads, Hydrophobic tails
-Fluid mosaic model
-Phospholipid bilayer: semipermeable outer boundary of cell
-Regulates movement of
substances into and out of cell
-Composed of phospholipids arranged in two layers with proteins interspersed throughout
-Hydrophilic heads, Hydrophobic tails
-Fluid mosaic model
23
New cards
Cytoplasm
Consists of all cellular components between plasma membrane and nucleus
24
New cards
Cytosol
Fluid within cytoplasm containing organelles
25
New cards
Organelles
-Perform specialized functions in cell
-Various shapes and sizes
-Most are membrane-bound
-Various shapes and sizes
-Most are membrane-bound
26
New cards
Nucleus
-Control center of cell
-Contains DNA
-Sends coded messages from DNA to be used in other parts of the cell
-Bounded by Nuclear envelope
-Contains DNA
-Sends coded messages from DNA to be used in other parts of the cell
-Bounded by Nuclear envelope
27
New cards
Nuclear Envelope
-Surrounds Nucleus
-Composed of two membranes
-Complex pores occupy up to 1/3 of total surface area
-Permit only certain kinds of molecules to pass between nucleus and cytoplasm
-Composed of two membranes
-Complex pores occupy up to 1/3 of total surface area
-Permit only certain kinds of molecules to pass between nucleus and cytoplasm
28
New cards
Nucleolus (Nucleoli)
-Organelle within nucleus
-Contains RNA and proteins
-Contains RNA and proteins
29
New cards
Chromatin Strands
-Located in nucleus
-Composed of DNA and proteins
-Coil to become chromosomes
-Composed of DNA and proteins
-Coil to become chromosomes
30
New cards
Chromosomes
-Located in nucleus
-Condensed DNA
-Condensed DNA
31
New cards
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
-Enclosed space
-Network of flattened sacs and tubes forming channels throughout cytoplasm
-Facilitates cellular communication and channeling of materials
-Synthesizes membranes for other organelles and modifies proteins
-Composed of Rough ER and Smooth ER
-Network of flattened sacs and tubes forming channels throughout cytoplasm
-Facilitates cellular communication and channeling of materials
-Synthesizes membranes for other organelles and modifies proteins
-Composed of Rough ER and Smooth ER
32
New cards
Rough ER
-Synthesis, secretion, and storage of proteins
-Ribosomes distributed on outer surface
-Ribosomes distributed on outer surface
33
New cards
Smooth ER
-Lipid secretion
-Few, if any, ribosomes
-Few, if any, ribosomes
34
New cards
Ribosomes
-Consist of two subunits composed of RNA and proteins
-Link amino acids to construct complex proteins
-Subunits assembled in nucleolus
-No bounding membranes
-May occur on outside of Rough ER, in cytoplasm, chloroplasts, and other organelles
-Link amino acids to construct complex proteins
-Subunits assembled in nucleolus
-No bounding membranes
-May occur on outside of Rough ER, in cytoplasm, chloroplasts, and other organelles
35
New cards
Dictyosomes
-Golgi bodies in animals
-Stacks of flattened discs or vesicles
-Scattered throughout cytoplasm
-Modify carbohydrates attached to proteins that are synthesized and packaged in the ER
-Assemble polysaccharides and collect them in small vesicles
-Vesicles pinched off from margins of dictyosomes
-Vesicles migrate to plasma membrane, fuse with it, and secrete contents to outside of cell
-Contents may include cell wall polysaccharides, floral nectars, and essential oils in herbs
-Collecting, packaging, and delivery centers of cell; "Post office" of cell
-Stacks of flattened discs or vesicles
-Scattered throughout cytoplasm
-Modify carbohydrates attached to proteins that are synthesized and packaged in the ER
-Assemble polysaccharides and collect them in small vesicles
-Vesicles pinched off from margins of dictyosomes
-Vesicles migrate to plasma membrane, fuse with it, and secrete contents to outside of cell
-Contents may include cell wall polysaccharides, floral nectars, and essential oils in herbs
-Collecting, packaging, and delivery centers of cell; "Post office" of cell
36
New cards
Plastids
-Storage and manufacture of carbohydrates
-Chloroplasts are most common
-Bounded by double membrane
-Grana (granum): contain thylakoids
-Thylakoid membranes contain
chlorophyll
- First steps of photosynthesis
occur in thylakoid membranes
-Stroma: matrix of enzymes involved in photosynthesis
-Small circular DNA molecule
-Encodes for production of
certain proteins for
photosynthesis
-Other types: Chromoplasts and Leucoplasts
-Chloroplasts are most common
-Bounded by double membrane
-Grana (granum): contain thylakoids
-Thylakoid membranes contain
chlorophyll
- First steps of photosynthesis
occur in thylakoid membranes
-Stroma: matrix of enzymes involved in photosynthesis
-Small circular DNA molecule
-Encodes for production of
certain proteins for
photosynthesis
-Other types: Chromoplasts and Leucoplasts
37
New cards
Chromoplasts
-Type of plastid
-"Chromo" = color
-Synthesize and accumulate carotenoids (yellow, orange, red)
-"Chromo" = color
-Synthesize and accumulate carotenoids (yellow, orange, red)
38
New cards
Leucoplasts
-Type of plastid
-Colorless
-Amyloplasts (synthesize starches) and Elaioplasts (synthesize oils)
-Colorless
-Amyloplasts (synthesize starches) and Elaioplasts (synthesize oils)
39
New cards
Mitochondria
-Releases energy produced from cellular respiration
-Bounded by two membranes
-Inward membrane: forms
numerous cristae (folds),
increases surface area
available to enzymes in matrix
-Matrix fluid also contains DNA, RNA, ribosomes, proteins, and dissolved substances
-Bounded by two membranes
-Inward membrane: forms
numerous cristae (folds),
increases surface area
available to enzymes in matrix
-Matrix fluid also contains DNA, RNA, ribosomes, proteins, and dissolved substances
40
New cards
Microbodies
-Small, spherical bodies
-Distributed throughout the cytoplasm
-Contain specialized enzymes
-Bounded by a single membrane
-Peroxisomes: serve in photorespiration and help in detoxification
-Glyoxisomes: aid in conversion of fat to carbohydrates
-Distributed throughout the cytoplasm
-Contain specialized enzymes
-Bounded by a single membrane
-Peroxisomes: serve in photorespiration and help in detoxification
-Glyoxisomes: aid in conversion of fat to carbohydrates
41
New cards
Cytoskeleton
-Involved in movement within cell and in cell's architecture
-Network of microtubules and microfilaments
-Network of microtubules and microfilaments
42
New cards
Microtubules
-Thin, hollow, tubelike
-Composed of tubulins (proteins)
-Control addition of cellulose to cell wall
-Involved in movement of flagella and cilia
-Found in fibers of spindles and phragmoplasts in dividing cells
-Composed of tubulins (proteins)
-Control addition of cellulose to cell wall
-Involved in movement of flagella and cilia
-Found in fibers of spindles and phragmoplasts in dividing cells
43
New cards
Microfilaments
-Role in cytoplasmic streaming
-Cytoplasmic streaming:
movement of cytoplasm in a
circular motion within the cell
for transportation of certain
materials
-Thinner than microtubules
-Cytoplasmic streaming:
movement of cytoplasm in a
circular motion within the cell
for transportation of certain
materials
-Thinner than microtubules
44
New cards
Vacuole
-In mature cells, 90% of volume may be taken up by central vacuoles
-Bounded by vacuolar membranes (tonoplasts)
-Filled with cell-sap (water fluid, slightly to moderately acidic)
-Contains dissolved substances (salts, sugars, organic acids, small proteins)
-Frequently contains anthocyanins (red, blue, purple water-soluble pigments)
-Functions: maintenance of cell pressure and pH, storage of numerous cell metabolites and waste products
-Bounded by vacuolar membranes (tonoplasts)
-Filled with cell-sap (water fluid, slightly to moderately acidic)
-Contains dissolved substances (salts, sugars, organic acids, small proteins)
-Frequently contains anthocyanins (red, blue, purple water-soluble pigments)
-Functions: maintenance of cell pressure and pH, storage of numerous cell metabolites and waste products
45
New cards
Plasmodesmata
-Allows fluids and dissolved substances to pass through primary walls of adjacent cells
-Cytoplasmic strands that extend between cells through minute openings
-Cytoplasmic strands that extend between cells through minute openings
46
New cards
Differences between plant and animal cells
Plants:
-Cell walls
-Cell plate and plasmodesmata
-Plastids and (Central) vacuoles
Animals:
-Internal or external skeletons
-No cell walls
-Plasma membrane = cell membrane
-Divide by pinching in two
-No cell plate or plasmodesmata
-Centrioles present during cell division
-No plastids of vacuoles
-Cell walls
-Cell plate and plasmodesmata
-Plastids and (Central) vacuoles
Animals:
-Internal or external skeletons
-No cell walls
-Plasma membrane = cell membrane
-Divide by pinching in two
-No cell plate or plasmodesmata
-Centrioles present during cell division
-No plastids of vacuoles
47
New cards
Major Plant Organs
-Roots
-Stems
-Leaves
-Flowers
-Stems
-Leaves
-Flowers
48
New cards
What are tissues?
-Groups of cells that are similar in structure and function
49
New cards
What is the function of meristems and where are they located?
-Function: growth
-Location: at or near the tips of roots and shoots
-Location: at or near the tips of roots and shoots
50
New cards
Apical Meristem
-Found at tips of roots and shoots
-Roots and shoots increase in length as apical meristem produces new cells
-Primary growth
-Protoderm: outer layer, becomes epidermis
-Ground meristem: cortex and pith
-Procambium: inside layer, divides into vascular tissues (xylem and phloem)
-Roots and shoots increase in length as apical meristem produces new cells
-Primary growth
-Protoderm: outer layer, becomes epidermis
-Ground meristem: cortex and pith
-Procambium: inside layer, divides into vascular tissues (xylem and phloem)
51
New cards
Lateral Meristem
-Produce secondary tissues
-Increase girth of roots and stems
-Secondary growth
-Vascular Cambium: secondary xylem and secondary phloem, function in support and conduction
-Cork Cambium: bark, cork and phelloderm
-Increase girth of roots and stems
-Secondary growth
-Vascular Cambium: secondary xylem and secondary phloem, function in support and conduction
-Cork Cambium: bark, cork and phelloderm
52
New cards
Intercalary Meristem
-Growth region at base of grass leaves
-Elongation of stem length
-Occur in plants that do NOT have vascular cambium or cork cambium
-Located at nodal region (leaf attachment area)
-Elongation of stem length
-Occur in plants that do NOT have vascular cambium or cork cambium
-Located at nodal region (leaf attachment area)
53
New cards
Simple Tissues
-Composed of one type of cell
-Examples: Parenchyma, Collenchyma, Sclerenchyma
-Examples: Parenchyma, Collenchyma, Sclerenchyma
54
New cards
Parenchyma Tissue
-Most abundant tissue in plants
-Contains of parenchyma cells
-Living cytoplasm
-Various shapes
-Loosely packed
-Intercellular space between them
-Thin, pliable walls
-Function in photosynthesis and storage
-Repair of tissues (retain ability to divide after produced)
-Apples and starch vegetables
-Aerenchyma, Chlorenchyma, Transfer cells
-Contains of parenchyma cells
-Living cytoplasm
-Various shapes
-Loosely packed
-Intercellular space between them
-Thin, pliable walls
-Function in photosynthesis and storage
-Repair of tissues (retain ability to divide after produced)
-Apples and starch vegetables
-Aerenchyma, Chlorenchyma, Transfer cells
55
New cards
Aerenchyma
-Parenchyma tissue
-Extensive connected air spaces
-Usually in aquatic plants- help plants float
-Extensive connected air spaces
-Usually in aquatic plants- help plants float
56
New cards
Chlorenchyma
-Parenchyma tissue
-Contains chloroplasts that function in photosynthesis
-Contains chloroplasts that function in photosynthesis
57
New cards
Transfer Cells
-Parenchyma tissue
-Develop irregular extensions of inner wall
-Increase surface area of plasma membrane
-Nectaries of flowers
-Develop irregular extensions of inner wall
-Increase surface area of plasma membrane
-Nectaries of flowers
58
New cards
Collenchyma Tissue
-Contains of collenchyma cells
-Collen = elastic
-Living cytoplasm
-Thick cell walls, uneven thickness
-Pliable and strong
-Suberin in-between cells; gives flexibility
-Function = support
-Present in petiole (stalk) of plant
-Collen = elastic
-Living cytoplasm
-Thick cell walls, uneven thickness
-Pliable and strong
-Suberin in-between cells; gives flexibility
-Function = support
-Present in petiole (stalk) of plant
59
New cards
Sclerenchyma Tissue
-Contains sclerenchyma cells
-Scleren = hard
-Dead at maturity
-Function in mechanical support (standing upright)
-Thick, tough secondary walls
-Normally impregnated with lignin
-Two types
-Sclereids (stone cells):
scattered in tissue, as long as
wide
-Fibers: much longer than wide,
contain lumen (tiny cavities
within fibers), secondary cell
walls
-Scleren = hard
-Dead at maturity
-Function in mechanical support (standing upright)
-Thick, tough secondary walls
-Normally impregnated with lignin
-Two types
-Sclereids (stone cells):
scattered in tissue, as long as
wide
-Fibers: much longer than wide,
contain lumen (tiny cavities
within fibers), secondary cell
walls
60
New cards
How are parenchyma, collenchyma, and sclerenchyma tissues distinguished from one another?
-Parenchyma and Collenchyma cells are LIVING (no secondary wall)
-Sclerenchyma cells are DEAD (contains secondary wall)
-Sclerenchyma cells are DEAD (contains secondary wall)
61
New cards
Complex Tissues
-Composed of two or more kinds of cells
-Examples: Vascular tissues (Xylem and Phloem), Epidermis, Periderm
-Examples: Vascular tissues (Xylem and Phloem), Epidermis, Periderm
62
New cards
Vascular tissue
-Xylem and Phloem
-Phloem is larger than Xylem
-Phloem is larger than Xylem
63
New cards
Xylem
-Conduction of water
-Composed primary of dead cells
-Located closer to center
-Types: Vessels, Tracheids, Fibers, Rays
-Composed primary of dead cells
-Located closer to center
-Types: Vessels, Tracheids, Fibers, Rays
64
New cards
Types of Xylem
-Vessels: long tubes made of vessel elements
-Thick secondary cell walls
-Open at both ends
-Perforation plate between end
walls
-Dead at maturity
-Tracheids: tapered at ends with pairs of pits that allow water pass from cell to cell
-Dead at maturity
-Thick Secondary cell walls
-May have spiral thickenings on
cell walls
-Pits: areas WITHOUT
secondary cell wall
-Fibers: much longer than wide
-Pits are normally absent
-Rays: function in lateral conduction and food storage
-Elongated
-Living
-Composed of long-lived Parenchyma cells
-Thick secondary cell walls
-Open at both ends
-Perforation plate between end
walls
-Dead at maturity
-Tracheids: tapered at ends with pairs of pits that allow water pass from cell to cell
-Dead at maturity
-Thick Secondary cell walls
-May have spiral thickenings on
cell walls
-Pits: areas WITHOUT
secondary cell wall
-Fibers: much longer than wide
-Pits are normally absent
-Rays: function in lateral conduction and food storage
-Elongated
-Living
-Composed of long-lived Parenchyma cells
65
New cards
Phloem
-Conduct dissolved food materials produced by photosynthesis throughout plant
-Types: Sieve Tube Members and Companion Cells
-Types: Sieve Tube Members and Companion Cells
66
New cards
Phloem Cell Types
-Sieve Tube Members
-Lack secondary cell walls and
nuclei
-Lay end to end to form sieve
tubes
-Walls have sieve plates with
small pores
-Callose forms callus plug
(prevents leaking of sieve tube
contencts when cell injured)
-Companion Cells
-Aid in conduction of food
-Lack secondary cell walls and
nuclei
-Lay end to end to form sieve
tubes
-Walls have sieve plates with
small pores
-Callose forms callus plug
(prevents leaking of sieve tube
contencts when cell injured)
-Companion Cells
-Aid in conduction of food
67
New cards
Epidermis
-Protective layer one cell-layer thick covering all plant organs
-Composed of parenchyma cells, guard cells of stomata, secretory glands and hairs
-Doesn't contain chloroplasts
-Trichomes: hair-like extensions; extends from epidermis
-Cutin: fatty substance on surface of outer walls that forms cuticle
-Cuticle: prevents water loss by
evaporation
-Resistant to bacteria and other disease organisms
-Composed of parenchyma cells, guard cells of stomata, secretory glands and hairs
-Doesn't contain chloroplasts
-Trichomes: hair-like extensions; extends from epidermis
-Cutin: fatty substance on surface of outer walls that forms cuticle
-Cuticle: prevents water loss by
evaporation
-Resistant to bacteria and other disease organisms
68
New cards
Stomata
-Rigid, living cells
-Open and close to preserve or absorb gasses, water, etc.
-Open and close to preserve or absorb gasses, water, etc.
69
New cards
Periderm
-Constitutes outer bark
-Form of epidermis
-Found in woody plants
-Form of epidermis
-Found in woody plants
70
New cards
Epidermis vs. Periderm
-In woody plants, the epidermis is sloughed off and replaced by periderm
-Periderm has cork cells that secret suberin
-Suberin makes cork cells waterproof, prevent them from drying out, and protects them from mechanical injury and freezing temps
-Periderm has cork cells that secret suberin
-Suberin makes cork cells waterproof, prevent them from drying out, and protects them from mechanical injury and freezing temps
71
New cards
Simple vs. Compex Tissues
-Simple = one cell type
-Parenchyma, Collenchyma,
Sclerenchyma
-Complex = at least two cell types
-Vascular (xylem and phloem),
epidermis, periderm
-Parenchyma, Collenchyma,
Sclerenchyma
-Complex = at least two cell types
-Vascular (xylem and phloem),
epidermis, periderm
72
New cards
Conifers have...
-No vessels
-No companion cells
-No companion cells
73
New cards
What types of substances do secretory cells secrete?
-May function individually or as part of a secretory tissue
-Secrete
-Flower nectar
-Citrus oils
-Glandular hair mucilage
-Latex (poison ivy)
-Resins (sticky substance in
Christmas trees
-Secrete
-Flower nectar
-Citrus oils
-Glandular hair mucilage
-Latex (poison ivy)
-Resins (sticky substance in
Christmas trees
74
New cards
How do roots develop?
-Upon germination, embryo's radicle grows out and develops into primary root
-Radicle may develop into thick taproot with thinner branch roots
OR
-Radicle may be replaced by Fibrous roots
-Adventitious Roots develop from stem or leaf, NOT another root
-Radicle may develop into thick taproot with thinner branch roots
OR
-Radicle may be replaced by Fibrous roots
-Adventitious Roots develop from stem or leaf, NOT another root
75
New cards
Tap Roots
-Straight tapering root growing vertically downward and forming the center from which subsidiary rootlets spring
-Dicots
-Examples: carrot, beetroot, parsley
-Dicots
-Examples: carrot, beetroot, parsley
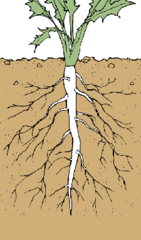
76
New cards
Fibrous Roots
-Large number of fine roos of similar diameter
-Monocots and some dicots
-Examples: wheat, rice, banana, onion
-Monocots and some dicots
-Examples: wheat, rice, banana, onion
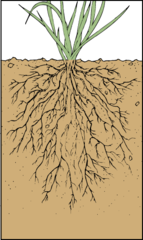
77
New cards
Adventitious Roots
-"not belonging to"
-Develop from stem or leaf, NOT another root (radicle)
-Both dicots and monocots
-Examples: prop roots of corn, rhizomes in ferns, club mosses
-Develop from stem or leaf, NOT another root (radicle)
-Both dicots and monocots
-Examples: prop roots of corn, rhizomes in ferns, club mosses

78
New cards
Root Cap
-Thimble-shapped mass of parenchyma cells covering each root tip
-Protects tissues from damage as root grows
-Protects tissues from damage as root grows
79
New cards
3 Sub Apical Regions of Root Tip
-Region of Cell Division
-Composed of apical meristem
in center of root tip
-Cells are actively dividing
-3 Primary meristems:
protoderm, ground meristem,
procambium
-Primary growth
-Region of Cell Elongation
-Cells become several times
their original length
-Region of Maturation
-Cells differentiate into various
distinctive cell types
-Root hairs form
-Composed of apical meristem
in center of root tip
-Cells are actively dividing
-3 Primary meristems:
protoderm, ground meristem,
procambium
-Primary growth
-Region of Cell Elongation
-Cells become several times
their original length
-Region of Maturation
-Cells differentiate into various
distinctive cell types
-Root hairs form
80
New cards
Root Hairs
-Epidermal cell extensions with thin cuticle
-Absorb water and minerals
-Adhere tightly to soil particles
-Increase total absorptive surface of root
-Absorb water and minerals
-Adhere tightly to soil particles
-Increase total absorptive surface of root
81
New cards
Root Tip Diagram
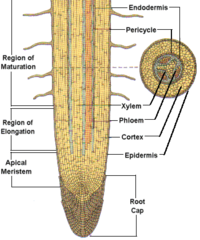
82
New cards
3 Primary Meristems
-Protoderm: gives rise to epidermis
-Outer most meristem
-Ground Meristem: gives rise to cortex and pith
-Bulk of plant tissue
-in between protoderm and
procambium
-Procambium: gives rise to primary xylem and primary phloem
-inner most meristem
-Outer most meristem
-Ground Meristem: gives rise to cortex and pith
-Bulk of plant tissue
-in between protoderm and
procambium
-Procambium: gives rise to primary xylem and primary phloem
-inner most meristem
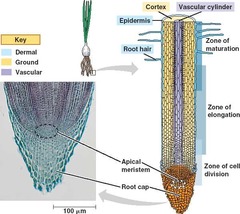
83
New cards
Epidermis
-Protective layer one cell-layer thick covering all plant organs
-Composed of parenchyma cells, guard cells of stomata, secretory glands and hairs
-Doesn't contain chloroplasts
-Trichomes: hair-like extensions; extends from epidermis
-Cutin: fatty substance on surface of outer walls that forms cuticle
-Cuticle: prevents water loss by
evaporation
-Prevents water loss, regulates gas exchange, absorbs water and mineral nutrients
-Composed of parenchyma cells, guard cells of stomata, secretory glands and hairs
-Doesn't contain chloroplasts
-Trichomes: hair-like extensions; extends from epidermis
-Cutin: fatty substance on surface of outer walls that forms cuticle
-Cuticle: prevents water loss by
evaporation
-Prevents water loss, regulates gas exchange, absorbs water and mineral nutrients
84
New cards
Cortex
-In between the epidermis (outside) and endodermis (inside)
-Transportation of materials into the central cylinder of root
-May be used for food storage in form of starch
-Transportation of materials into the central cylinder of root
-May be used for food storage in form of starch
85
New cards
Endodermis
-Inner boundary of cortex
-Consists of a single-layered cylinder of compact cells
-Cell walls impregnated suberin
-Suberin: substance that gives
elasticity, in collenchyma cells
-Except for passage cells
-Normal living cells
-Red bands
-Thickness allows endodermis to push water into xylem
-Consists of a single-layered cylinder of compact cells
-Cell walls impregnated suberin
-Suberin: substance that gives
elasticity, in collenchyma cells
-Except for passage cells
-Normal living cells
-Red bands
-Thickness allows endodermis to push water into xylem
86
New cards
Pericycle
-Outer boundary of vascular cylinder
-Forms lateral (branch) roots and part of vascular cambium
-Regulates the formation of lateral roots by rapidly dividing
-Forms lateral (branch) roots and part of vascular cambium
-Regulates the formation of lateral roots by rapidly dividing
87
New cards
Stele (Vascular cylinder)
-Core of tissue inside endodermis
-Xylem and Phloem
-Xylem and Phloem
88
New cards
Food Storage Root
-Starch and other carbohydrates
-Portion that connects the stem to the root
-Combination of stem and root
-Ex: Sweet Potatoes, Carrots, Beets, Turnips, Radishes
-Portion that connects the stem to the root
-Combination of stem and root
-Ex: Sweet Potatoes, Carrots, Beets, Turnips, Radishes
89
New cards
Water Storage Roots
-Pumpkin family, especially in arid regions
-Manroot
-Manroot
90
New cards
Propagative Roots
-Adventitious bud of roots, develop into suckers (aerial suckers)
-Sweet Potatoes, Bunyan tree
-Sweet Potatoes, Bunyan tree
91
New cards
Pneumatophores
-In plants with roots growing in water
-Spongy roots that extend above the water's surface and enhance gas exchange between atmosphere and subsurface roots
-Ex: Mangroves
-Spongy roots that extend above the water's surface and enhance gas exchange between atmosphere and subsurface roots
-Ex: Mangroves
92
New cards
Aerial Roots
-Orchids: Velamen roots, with epidermis several layers thick to
reduce water loss
-Ivies (English ivy, Virginia creeper)
-Aerial roots aid plants in
climbing
reduce water loss
-Ivies (English ivy, Virginia creeper)
-Aerial roots aid plants in
climbing
93
New cards
Contractile Roots
-Pull plant deeper into the soil
-Ex: Lily bulbs, dandelions
-Ex: Lily bulbs, dandelions
94
New cards
Buttress Roots
-Stability in shallow soil
-Ex: Tropical Trees
-Ex: Tropical Trees
95
New cards
Parasitic Roots
-Most have no chlorophyll and dependent on chlorophyll-bearing plants for nutrition
96
New cards
Where do branch roots originate?
-Arise in the pericycle (a cylinder of parenchyma cells lying just inside the endodermis)
97
New cards
How do endodermal cells differ from other types of cells?
-Lack a symplast region
-Are nonselective with regard to solute uptake
-Have a high rate of water transport
-Are completely surrounded by a waxy layer
-Prevent the apoplastic movement of water and ions
-Water must pass through the selectively permeable plasma membrane of the endodermal cells before it reaches the vascular system.
-Are nonselective with regard to solute uptake
-Have a high rate of water transport
-Are completely surrounded by a waxy layer
-Prevent the apoplastic movement of water and ions
-Water must pass through the selectively permeable plasma membrane of the endodermal cells before it reaches the vascular system.
98
New cards
What is the function of the root cap, and from which meristem does it originate?
-Protective cap of live parenchyma cells
-Produced by the apical meristem
-Produces mucilage or mucigel (slimy lubricant)
-Produced by the apical meristem
-Produces mucilage or mucigel (slimy lubricant)
99
New cards
If you were given cross sections of young roots of a monocot and dicot plants, how could you tell them apart?
100
New cards
Distinguish between a tiny root and a root hair. What is the function of a root hair?
-A root or tiny root is a multicellular organism with multiple tissue layers and other types of roots
-Root hairs absorb water and minerals and adhere tightly to soil particles and are not separate cells
-Root hairs absorb water and minerals and adhere tightly to soil particles and are not separate cells