Biloggical psychology - brain areas,
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
What are the three main functions of the nervous system?
1. Receive information via the CNS (Central Nervous System). 2. Process information via the CNS. 3. Coordinate a response with the PNS (Peripheral Nervous System).
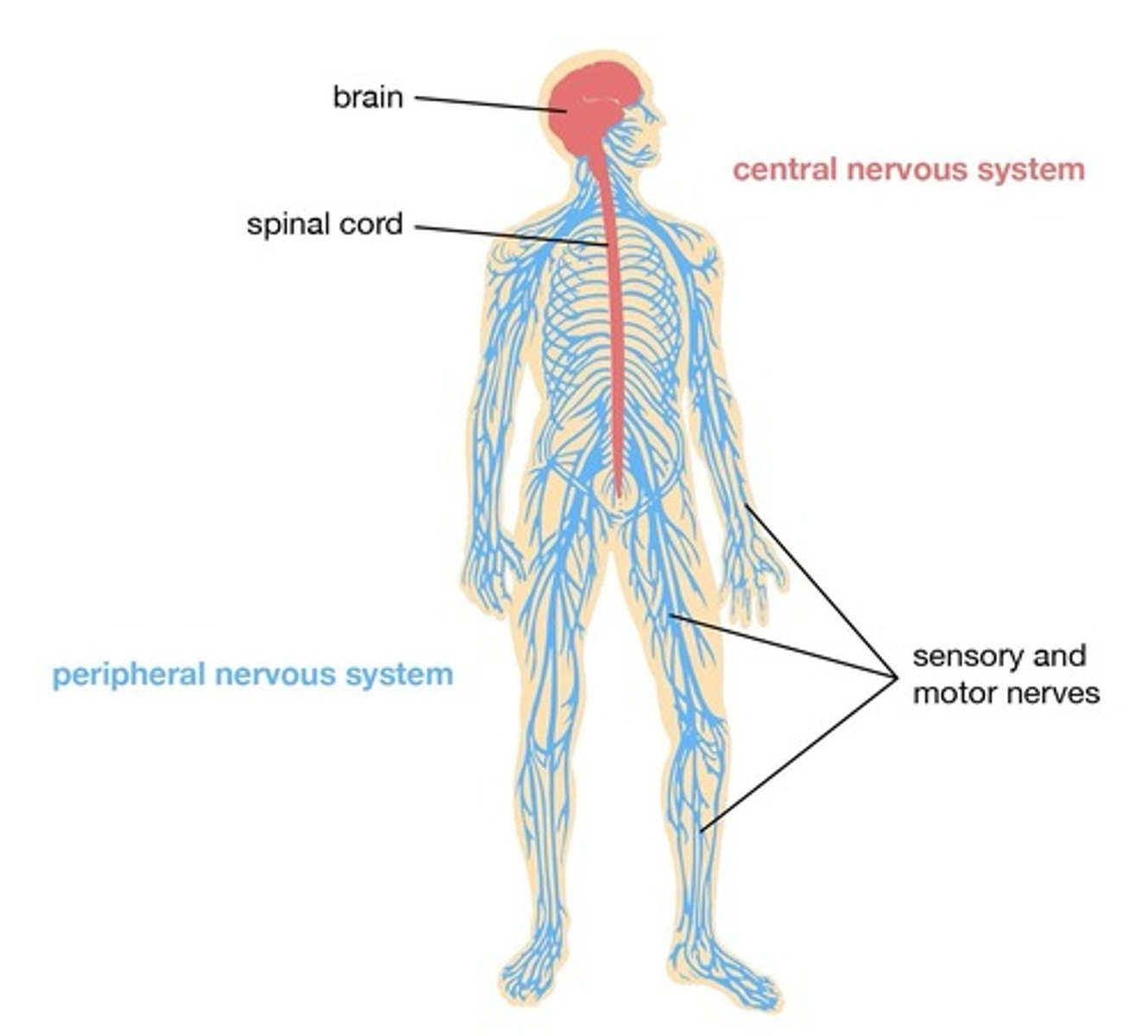
What does the Central Nervous System consist of?
The brain and spinal cord.
What is the role of the Peripheral Nervous System?
It carries sensory information to the CNS and motor information away from the CNS.
What are the two divisions of the Peripheral Nervous System?
Somatic and Autonomic.
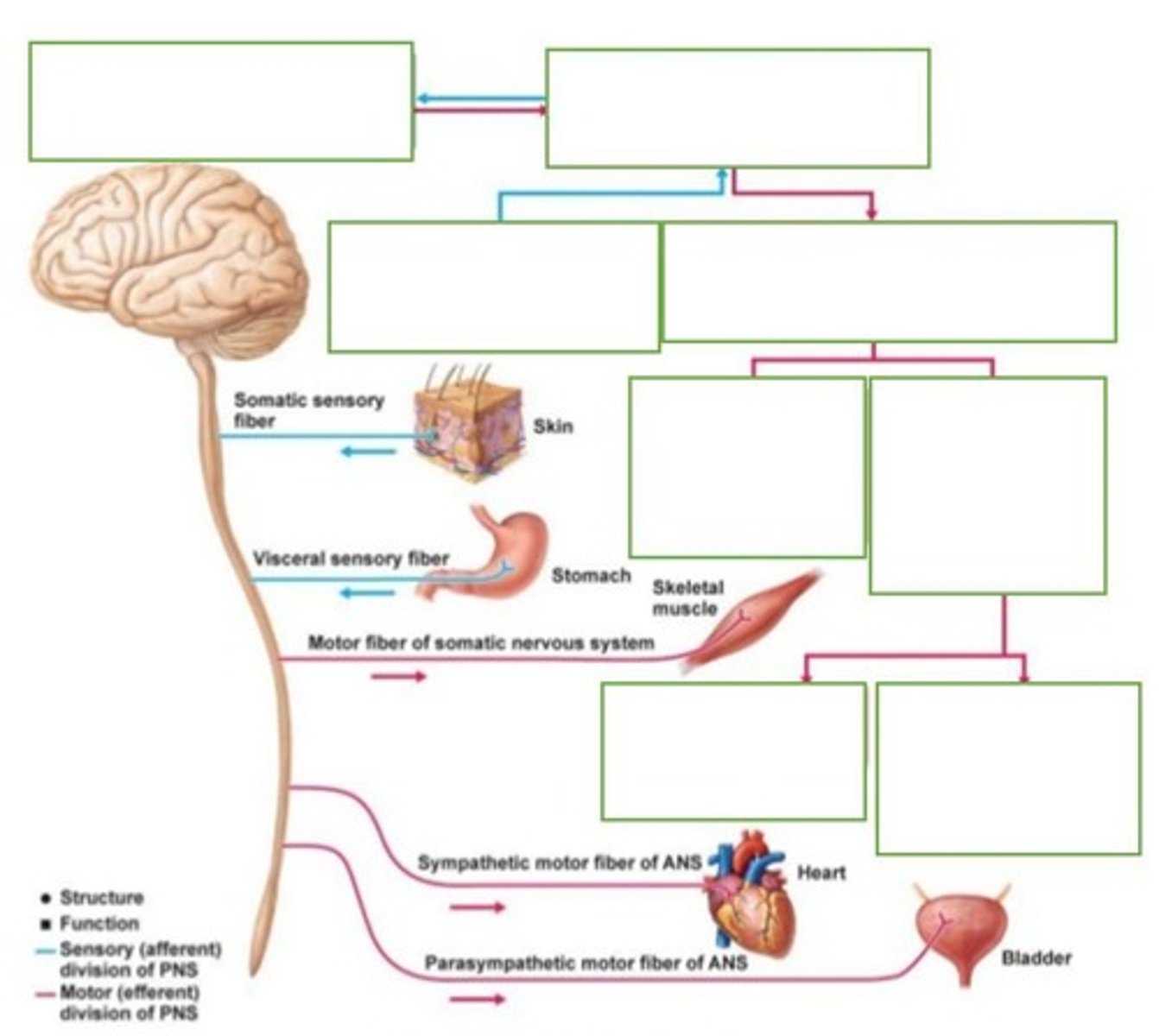
What is the function of the Somatic Nervous System?
It controls voluntary movements and carries sensory and motor pathways.
What are the two types of pathways in the nervous system?
Afferent pathways (sensory, carrying information to the CNS) and Efferent pathways (motor, carrying information away from the CNS).
What are the two branches of the Autonomic Nervous System?
Sympathetic and Parasympathetic.
What is the function of the Sympathetic Nervous System?
Prepares the body for a 'fight or flight' response.
What is the function of the Parasympathetic Nervous System?
Returns the body to a resting state and maintains homeostasis.
What is an Action Potential?
A low charge that travels along the axon of a neuron.
What is the role of synapses in neural communication?
Synapses moderate communication between neurons by converting electrical signals into chemical signals.
What are neurotransmitters?
Chemical messengers that carry signals from one neuron to another across the synaptic gap.
What are the three sections of the brain?
Forebrain, Midbrain, and Hindbrain.
What is the function of the Hypothalamus?
Regulates hormones for temperature, thirst, hunger, and other basic processes.
What is the function of the Thalamus?
Filters sensory information (except for smell) to the relevant brain centers.
What is the role of the Cerebral Cortex?
Involves perception, language, learning, memory, problem-solving, and control of body movement.
What does the Medulla control?
Heart rate, breathing, digestion, swallowing, and reflexes.
What is the function of the Cerebellum?
Regulates posture, balance, and fine muscle movement.
What is the function of the Frontal Lobe?
Involves movement (motor cortex), speech (Broca's area), emotion, personality, initiative, and decision-making.
What is the function of the Temporal Lobe?
Involves hearing, visual perception, memory, and emotional responses.
What does the Occipital Lobe process?
Visual signals.
What is the role of Broca's area?
Responsible for speech production.
What is the role of Wernicke's area?
Responsible for language comprehension.
What is the difference between sensory neurons, motor neurons, and interneurons?
Sensory neurons transmit information from the environment to the CNS, motor neurons send signals from the CNS to muscles, and interneurons connect sensory and motor pathways within the CNS.
How does neural transmission occur?
Through Action Potentials (electrical signals) and neurotransmitters (chemical signals) across synapses.
What happens during the resting state of a neuron?
The neuron is negatively charged until it receives sufficient stimulation to trigger an Action Potential.
What is homeostasis in the context of the nervous system?
The process of returning the body to a resting state after a sympathetic response.
What physiological changes occur during the sympathetic response?
Pupil dilation, increased heart rate, decreased saliva production, and relaxed bladder.
What is the role of the corpus callosum?
Allows communication between the left and right hemispheres of the brain.
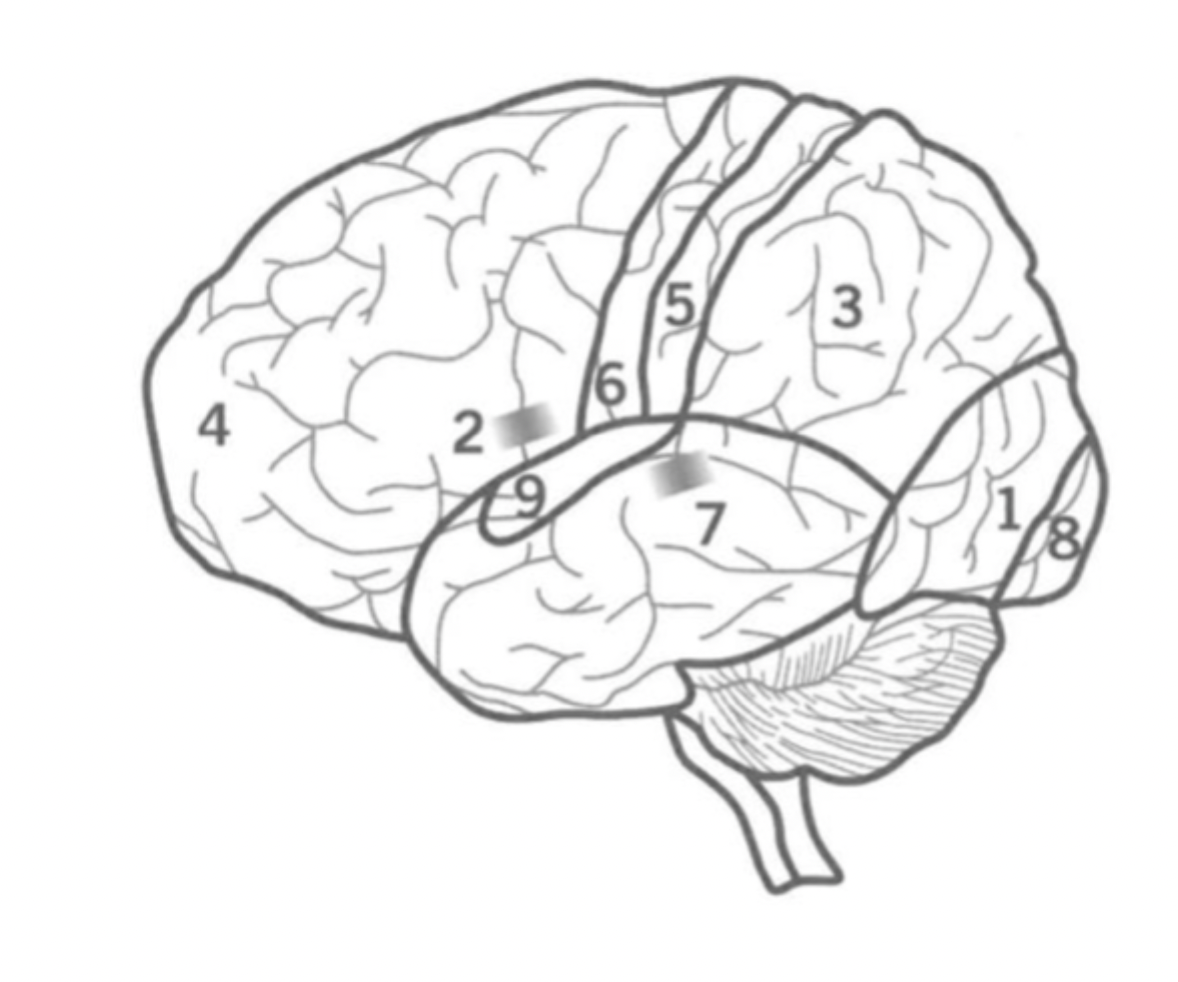
what is the function of the Occipital lobe
Where is it
processes visual information
recgonises objects
identifying colours
perceiving depth
1
back of cerebral cortex.
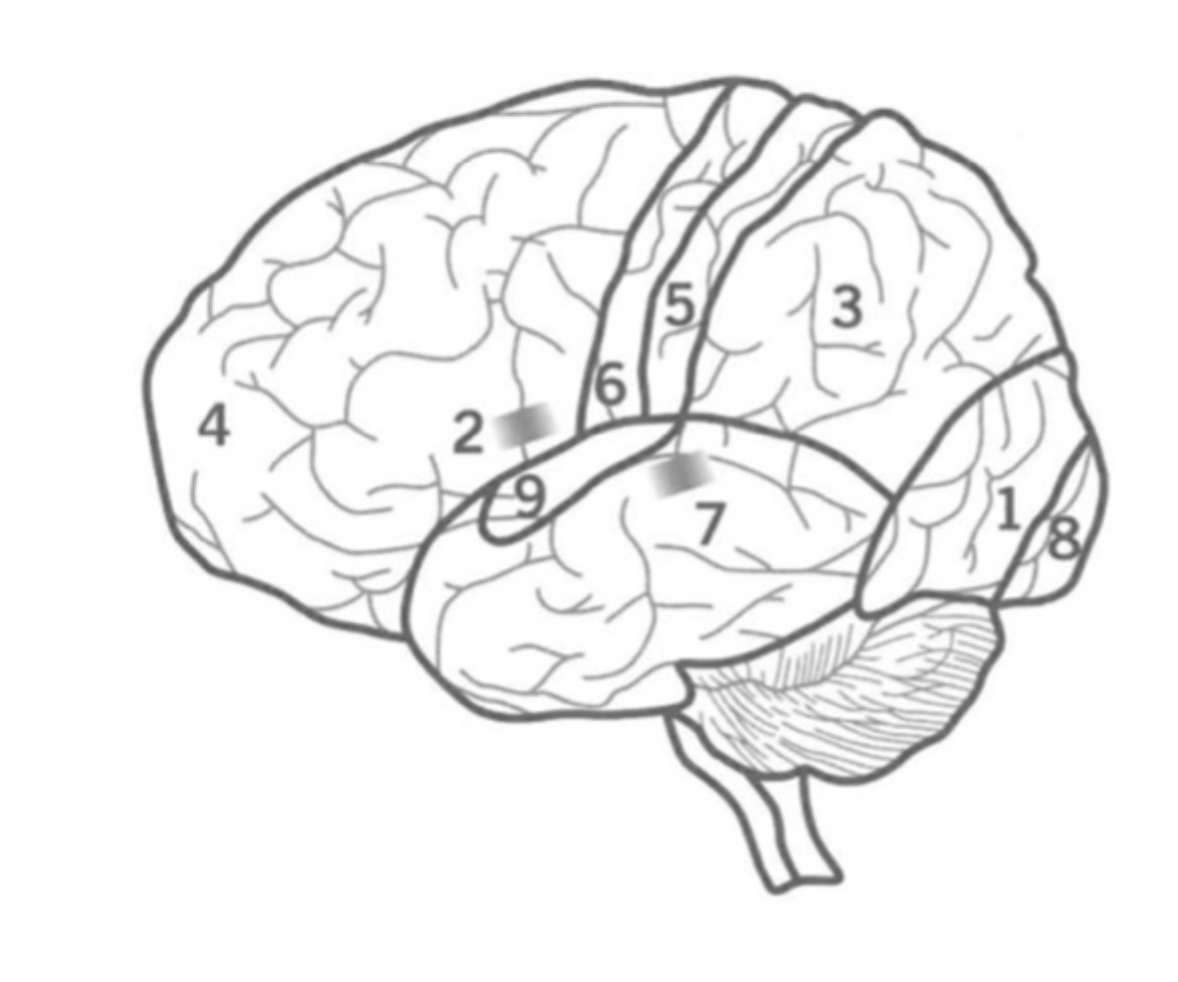
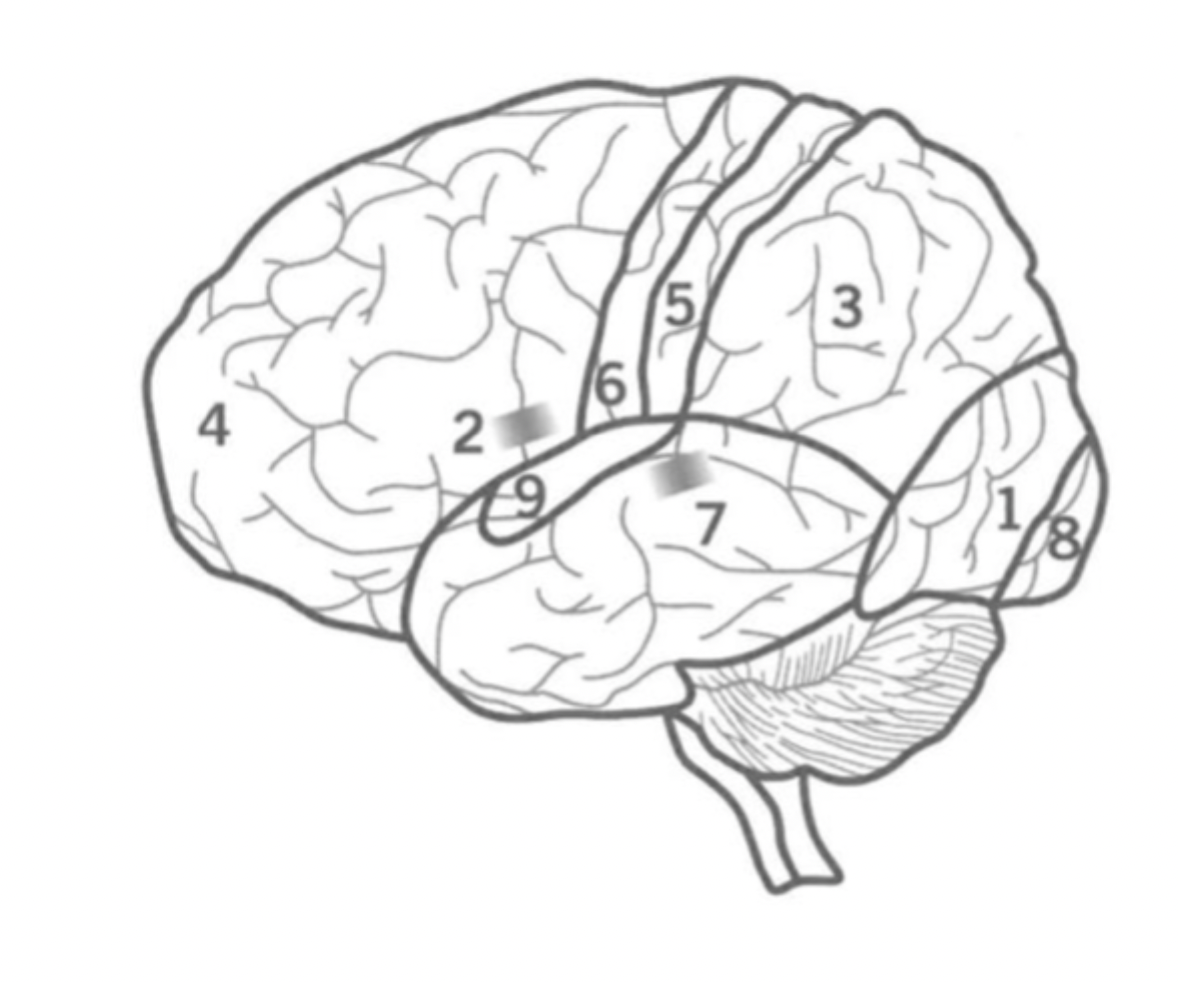
what is the function of Bronca’s area?
where is it?
Co-ordinates muscles to formulate fluent speech.
2
left hemisphere Frontal lobe
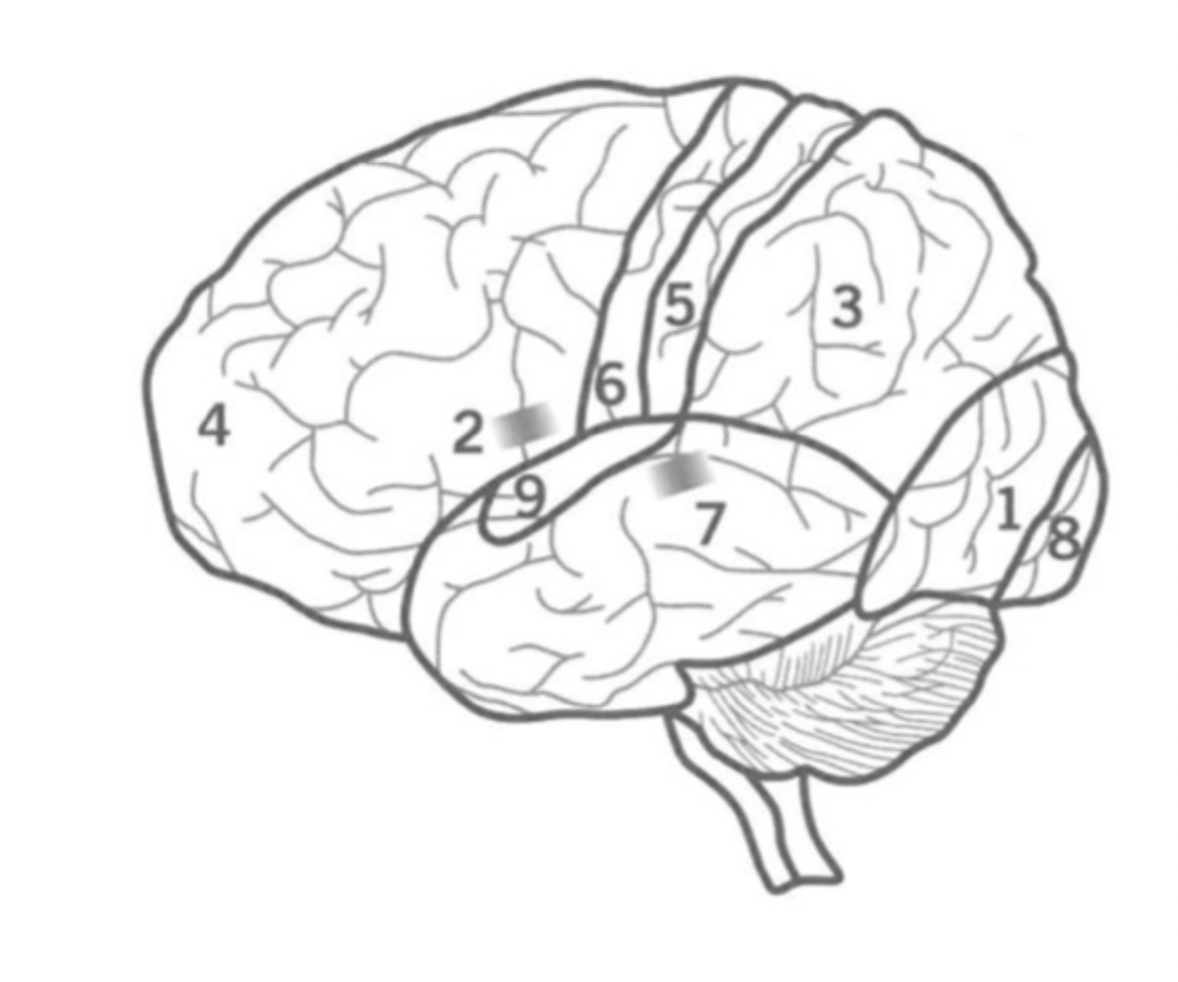
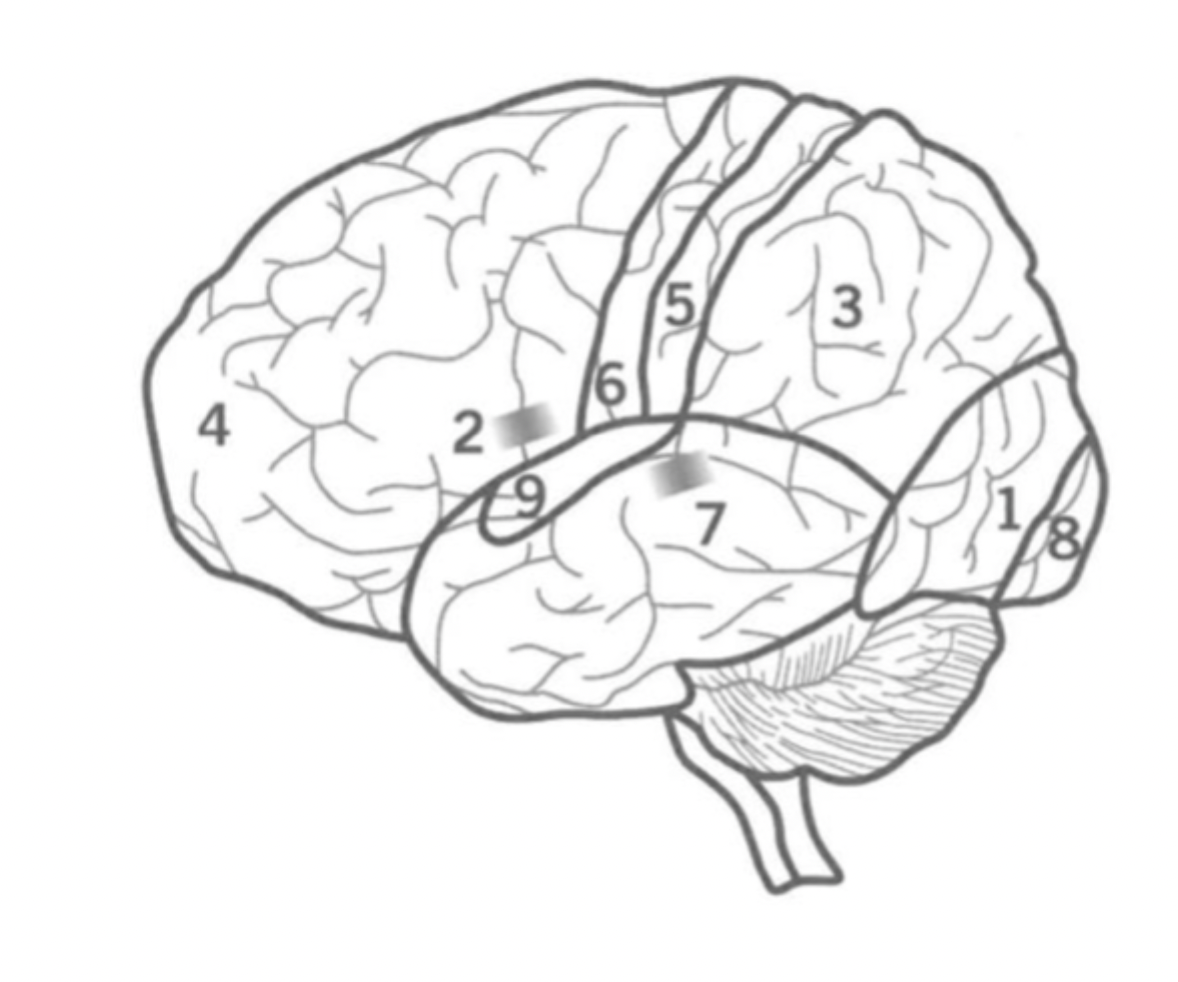
What is the Parietal lobe’s function?
where is it?
3
Sensory integration and Spatial awareness.
between occipital and Frontal lobes.
contains Primary sensory cortex.
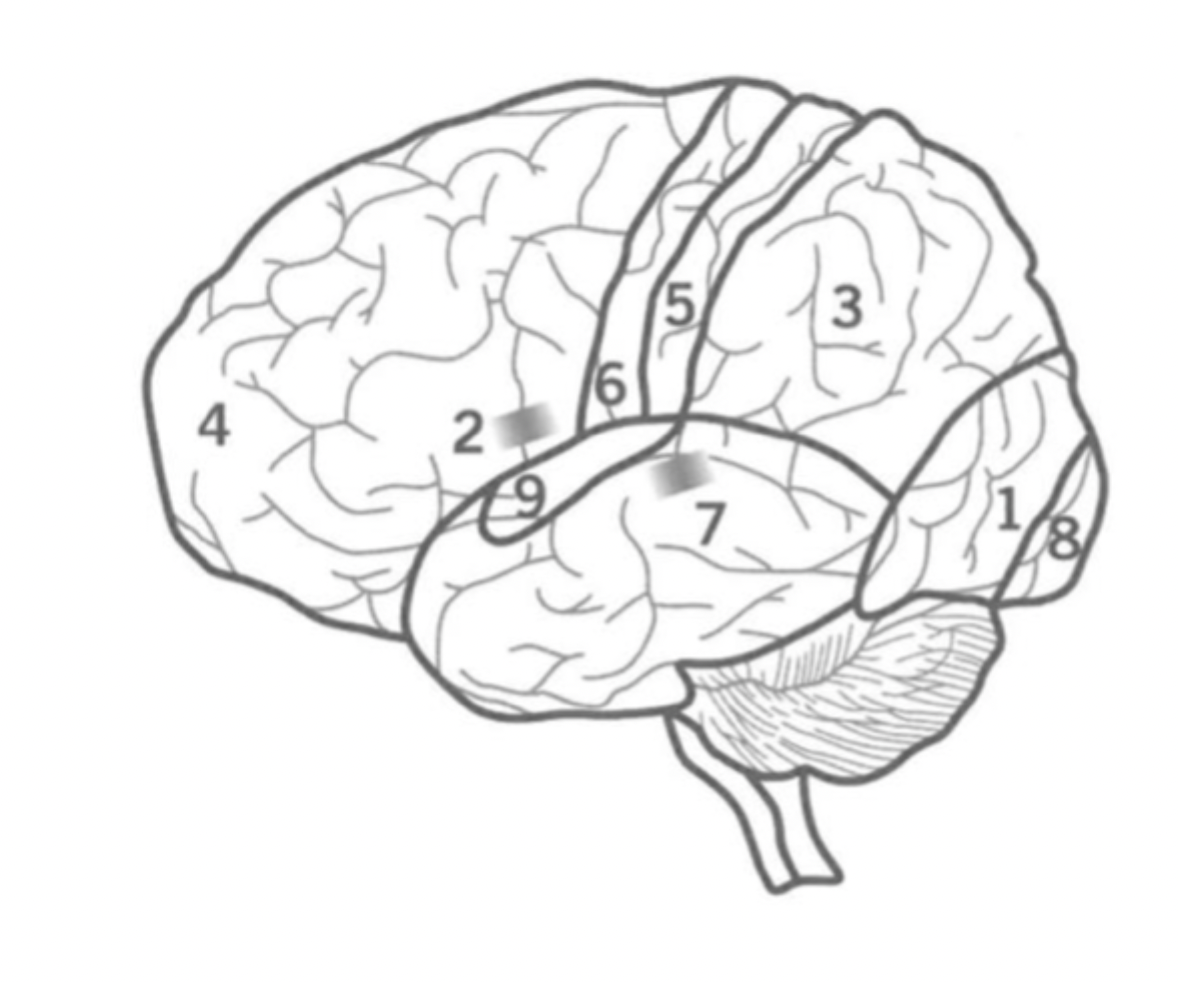
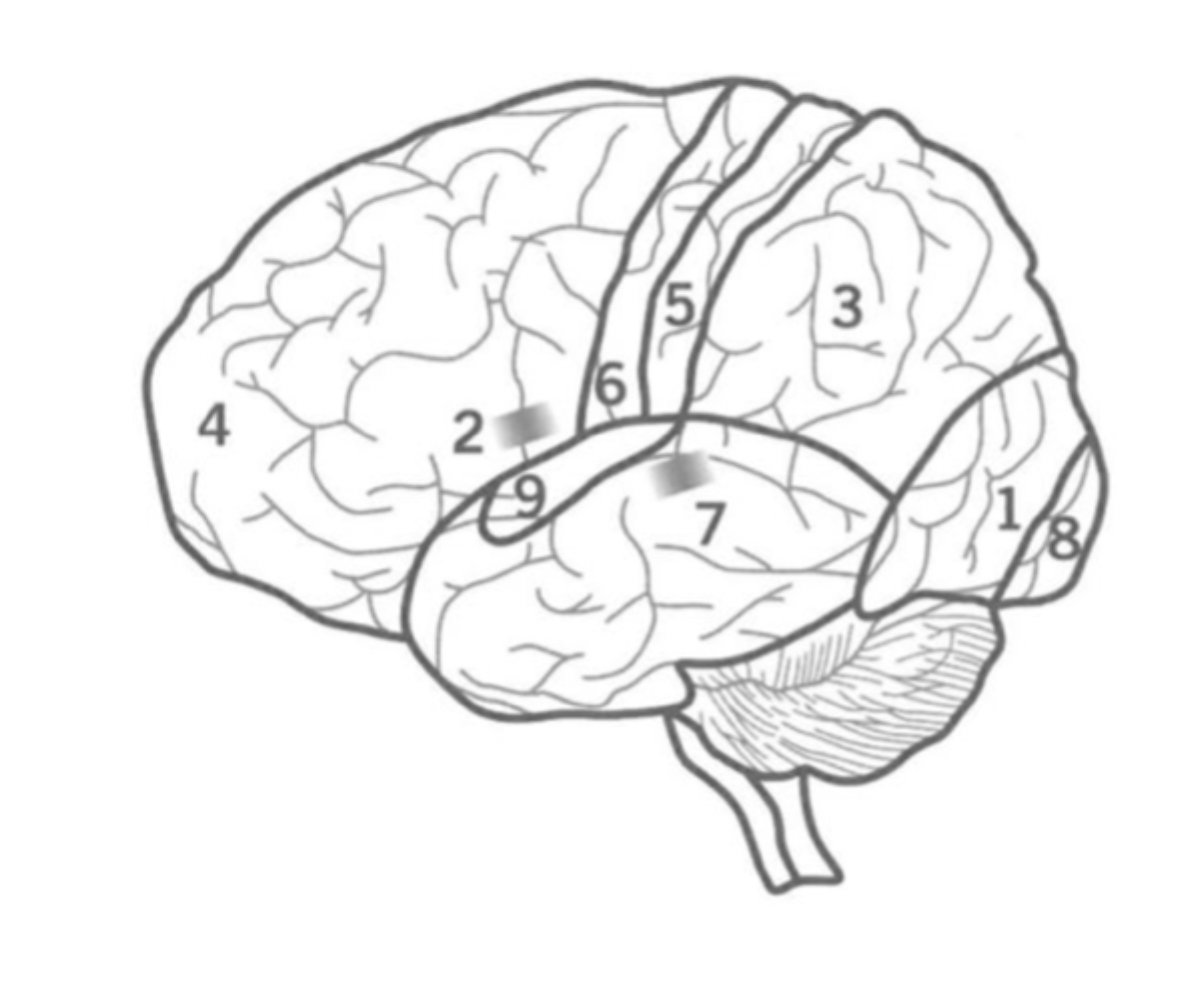
What is the Pre-Frontal cortex?
Where is it?
4
Executive functions including attention, inhibition and decision making.
Contains bronca’s area and Primary motor cortex.
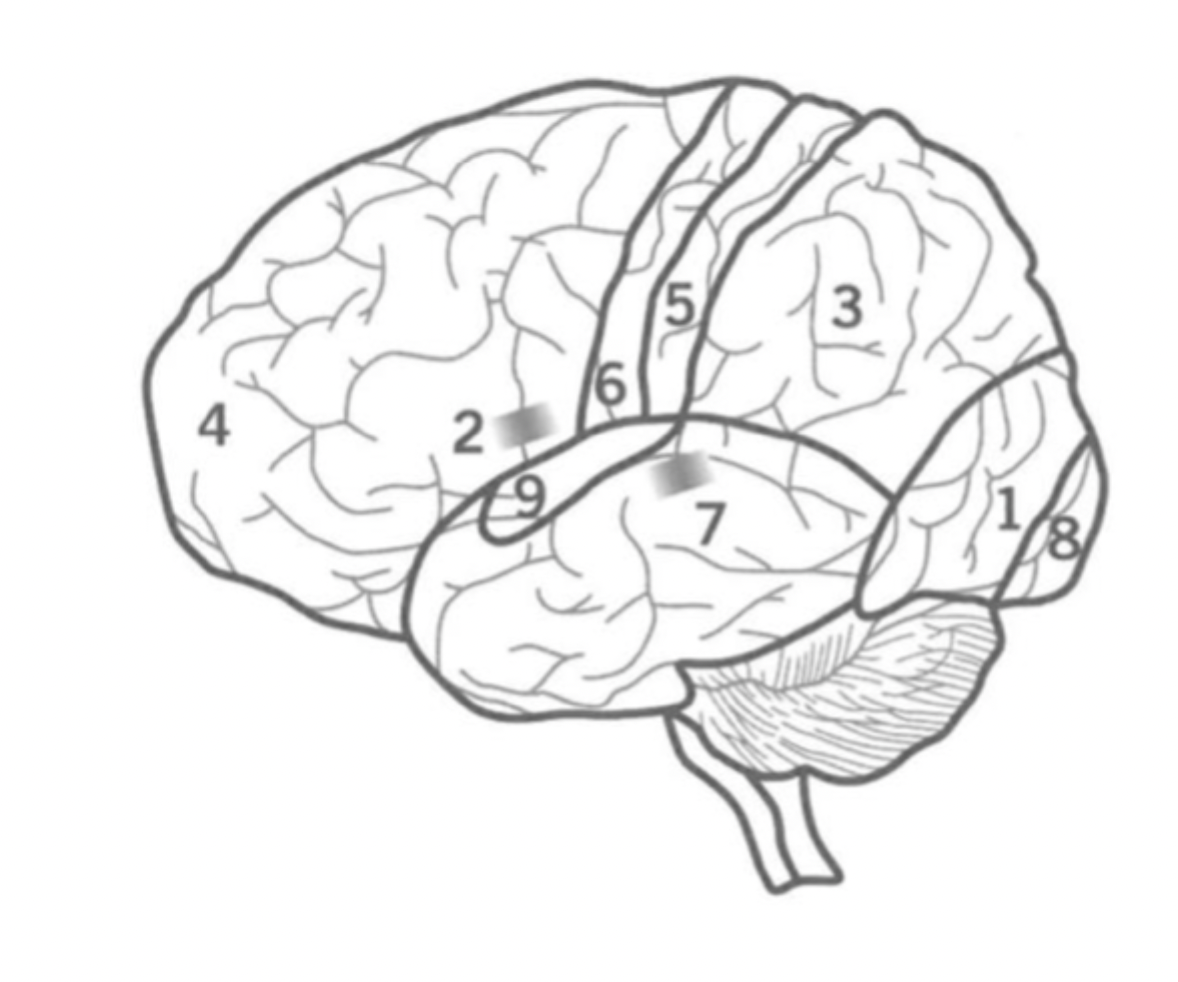
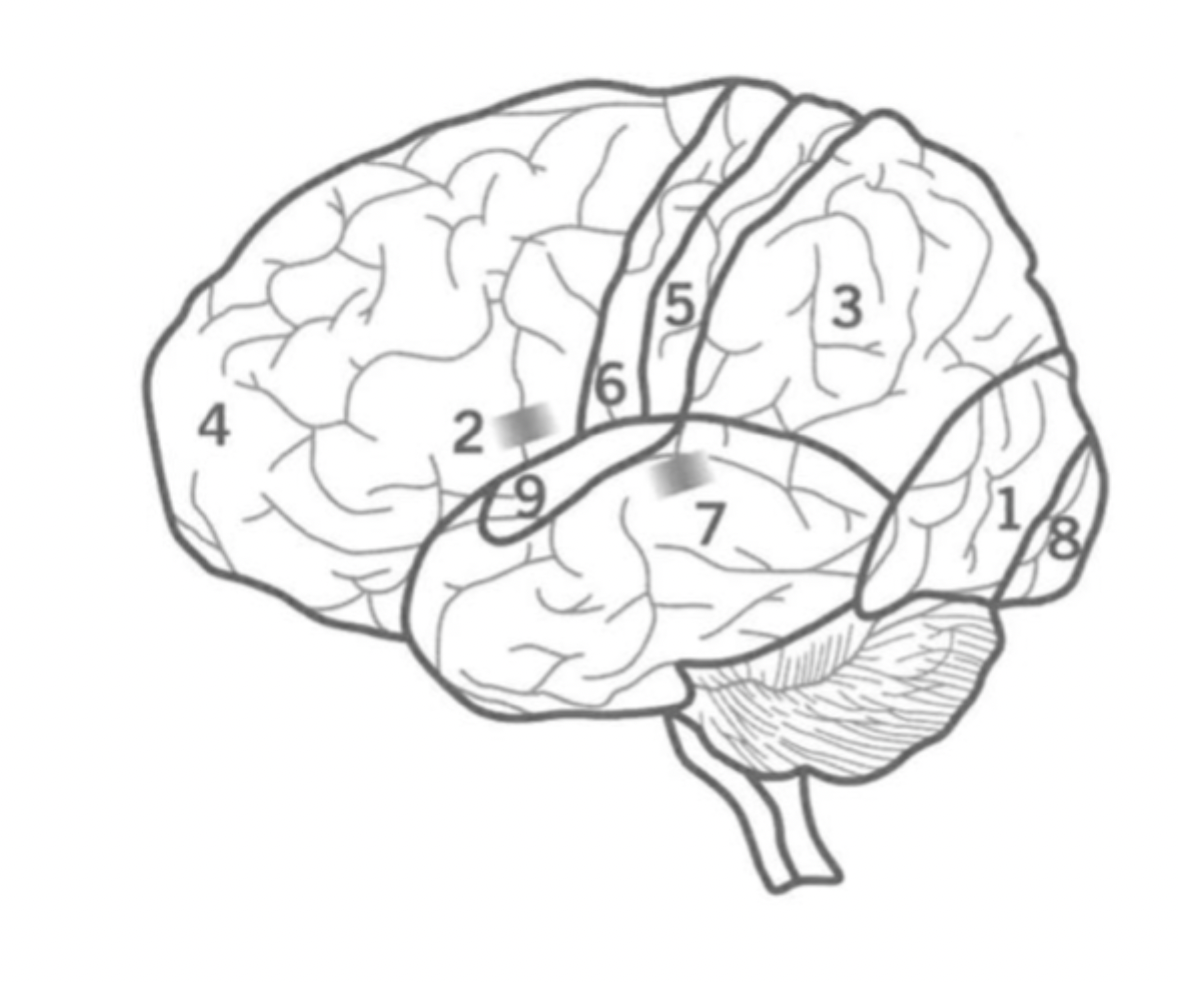
What is the Primary Sensory cortex?
Where is it?
5
Responsible for Somatic sensory information processing, including touch, temperature, pain, and proprioception.
Located in the parietal lobe.
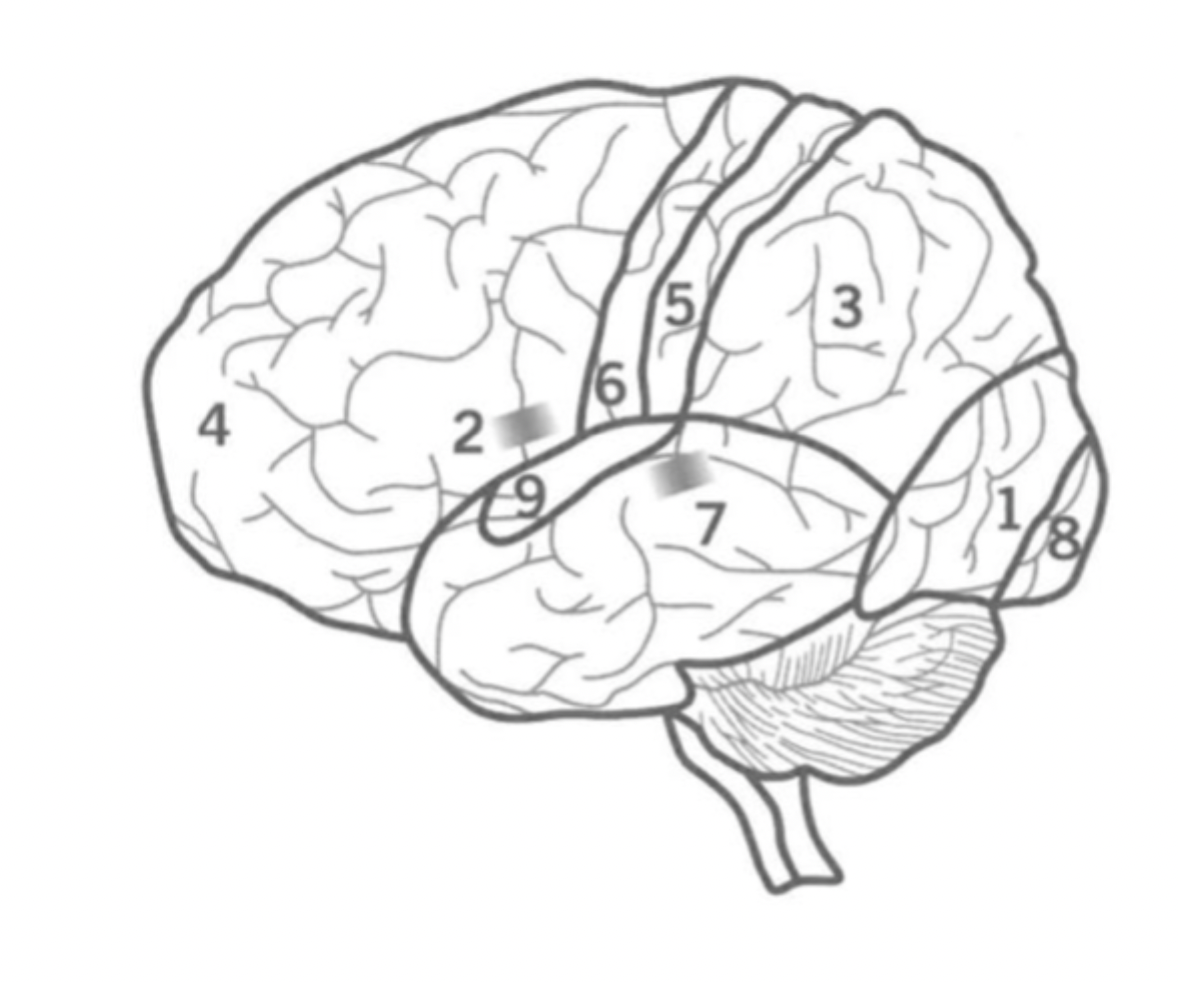
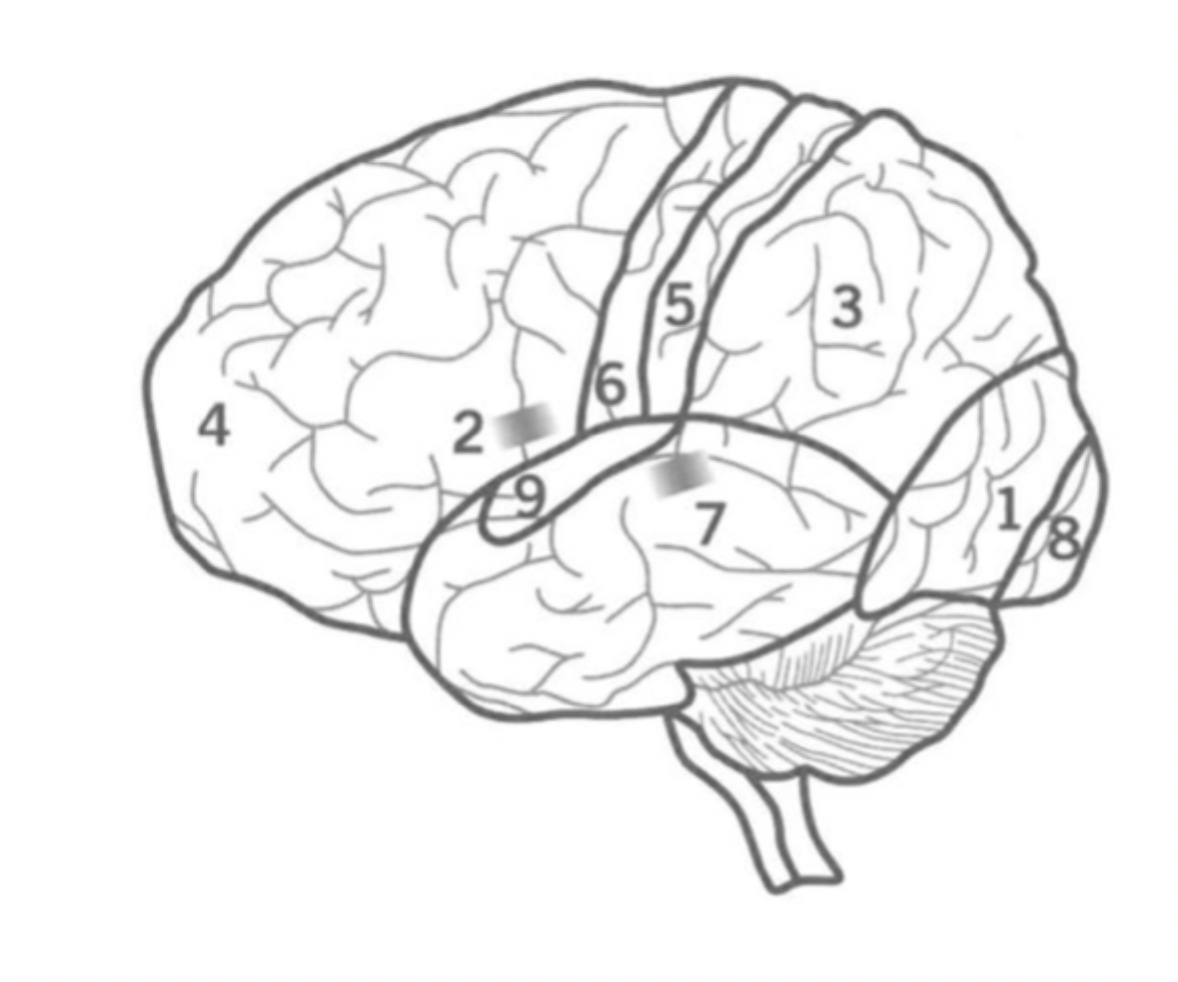
What is the Primary motor cortex?
Where is it?
6
Initiates motor signals and controls fine motor skills.
Located in the Frontal lobe.
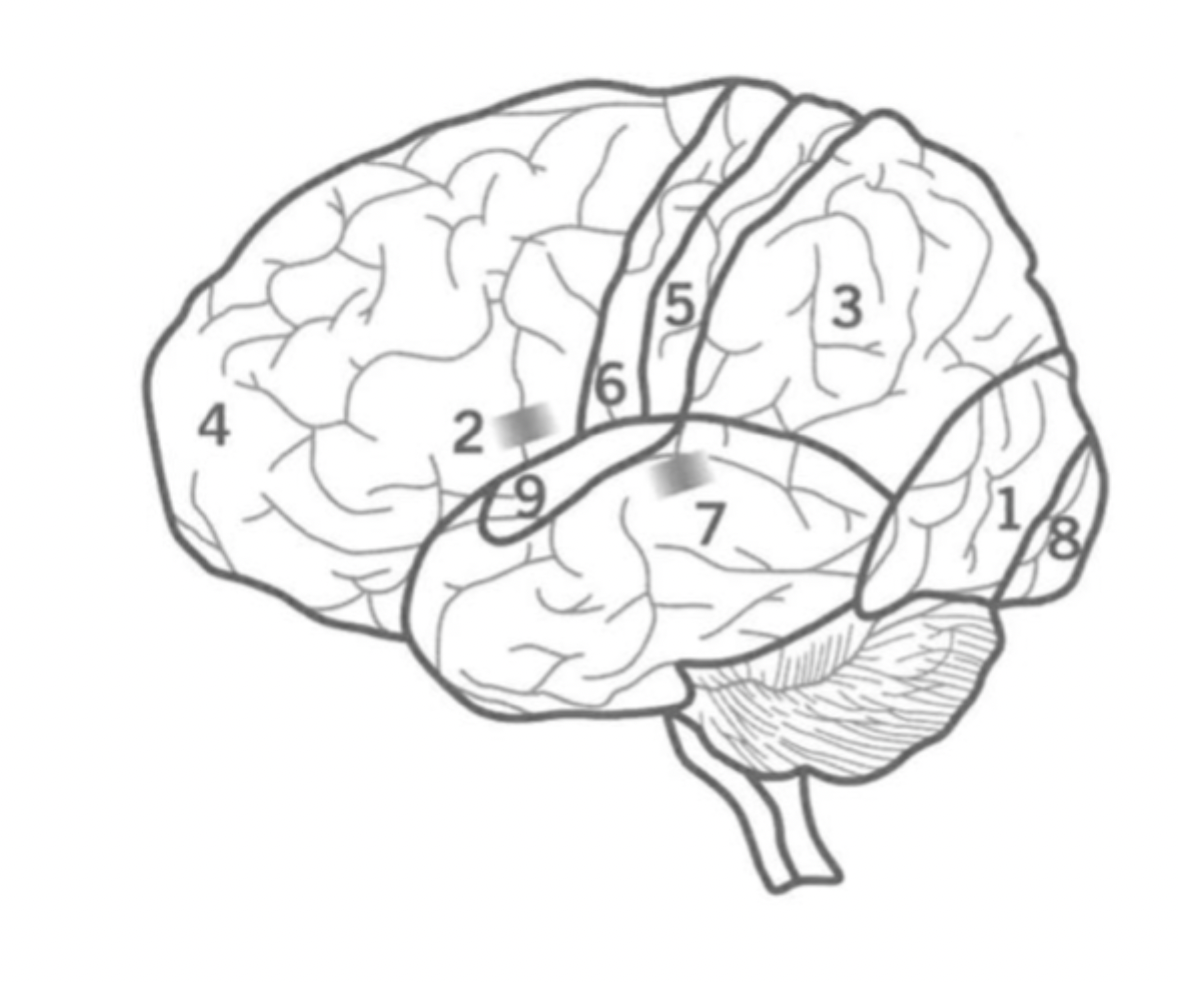
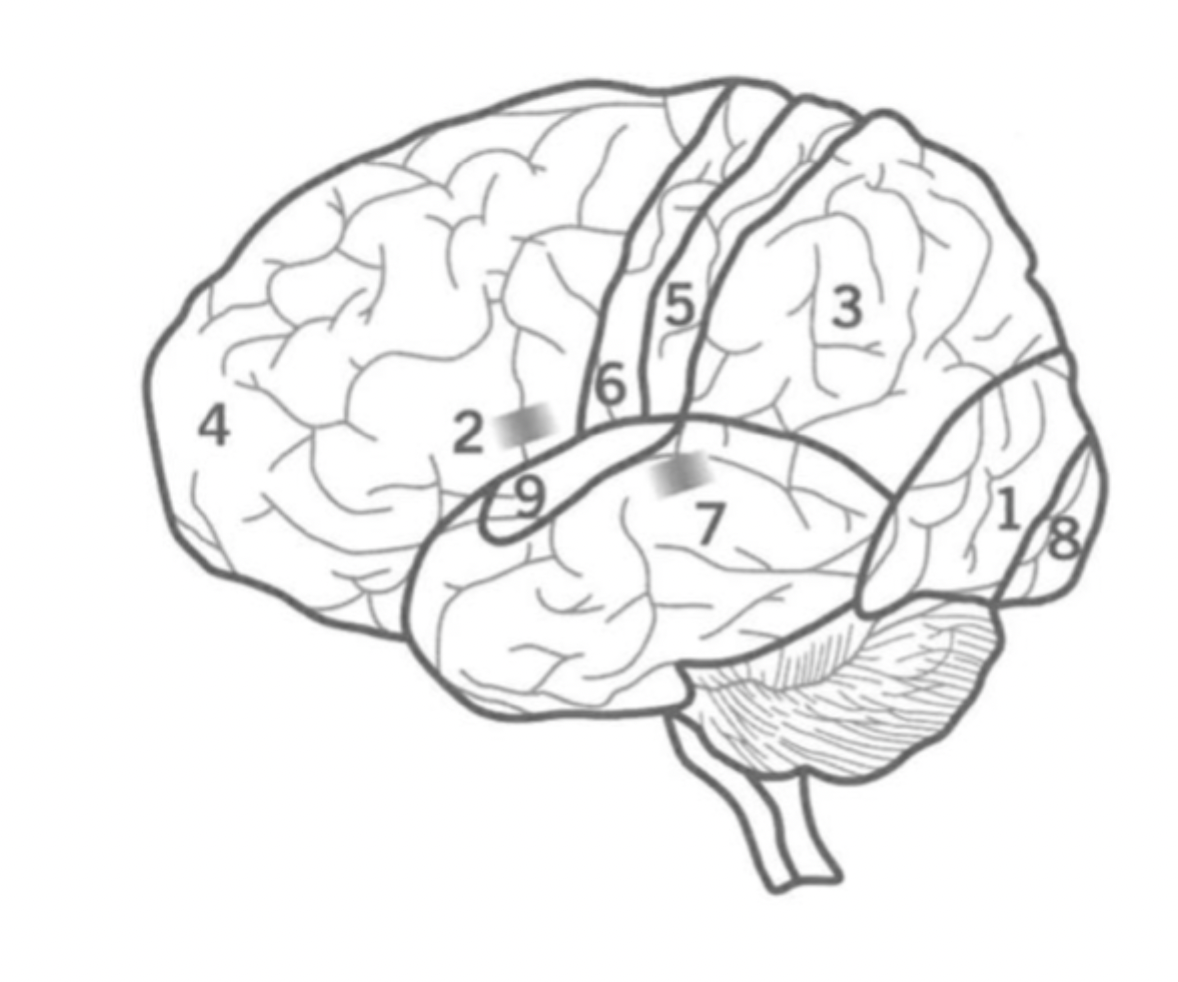
What is Wernick’s Area?
Where is it?
7
Responsible for the comprehension of human speech.
in the Temporal lobe nex to the Parietal lobe.
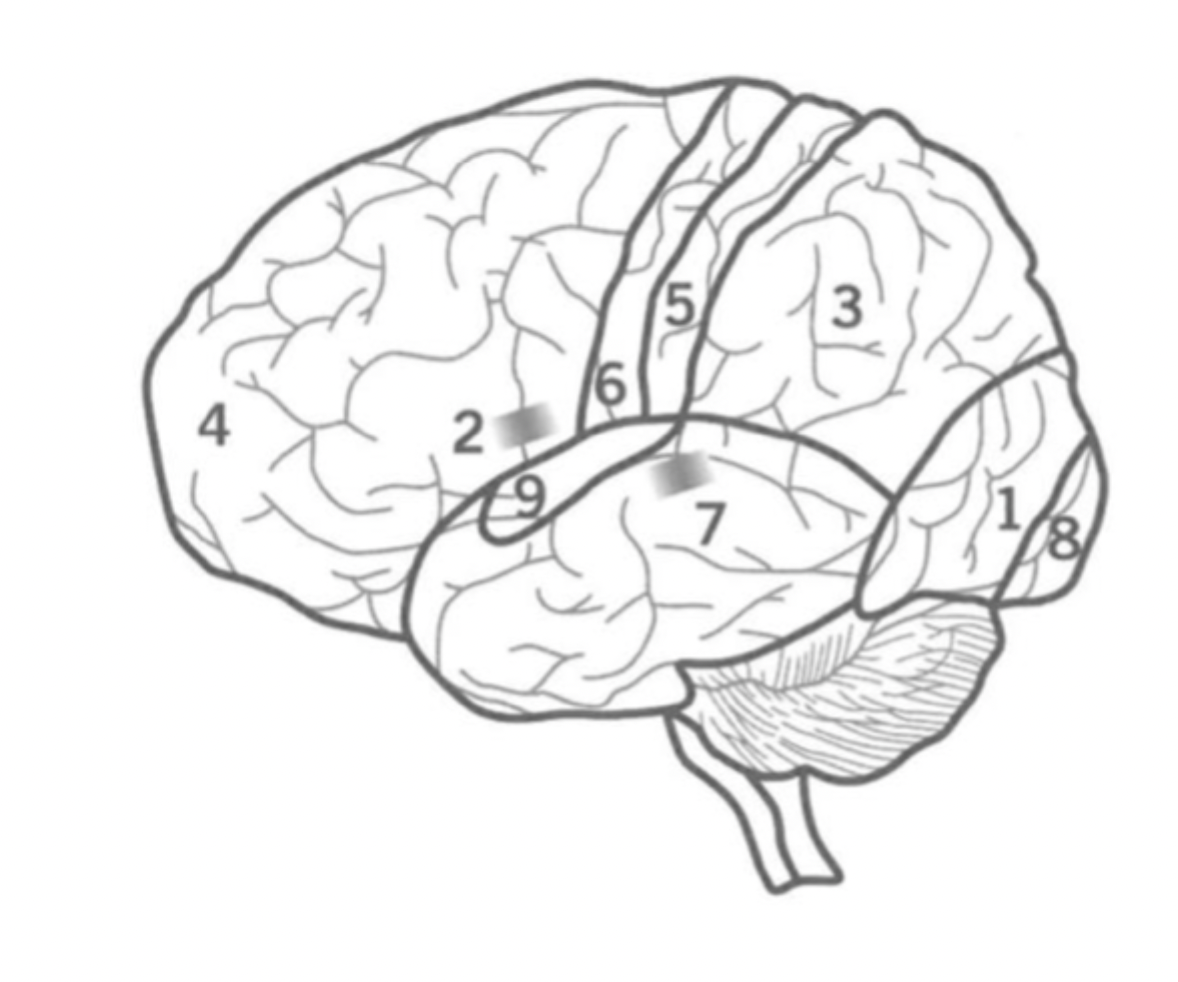
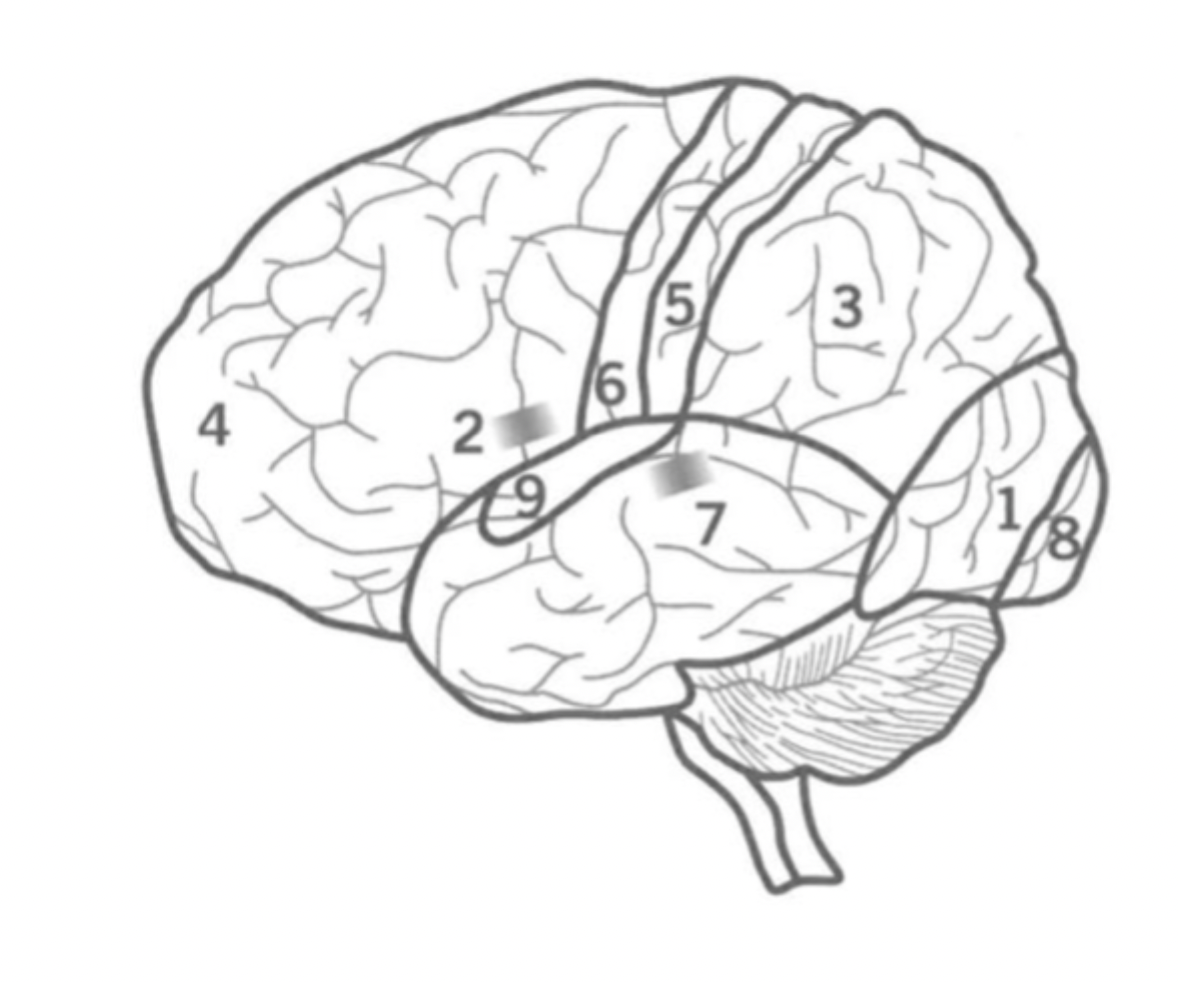
What is the primary visual cortex?
Where is it?
8
initial stage of visual processing - sees light, colour, shape, motion.
located in the back of the Occipital lobe.
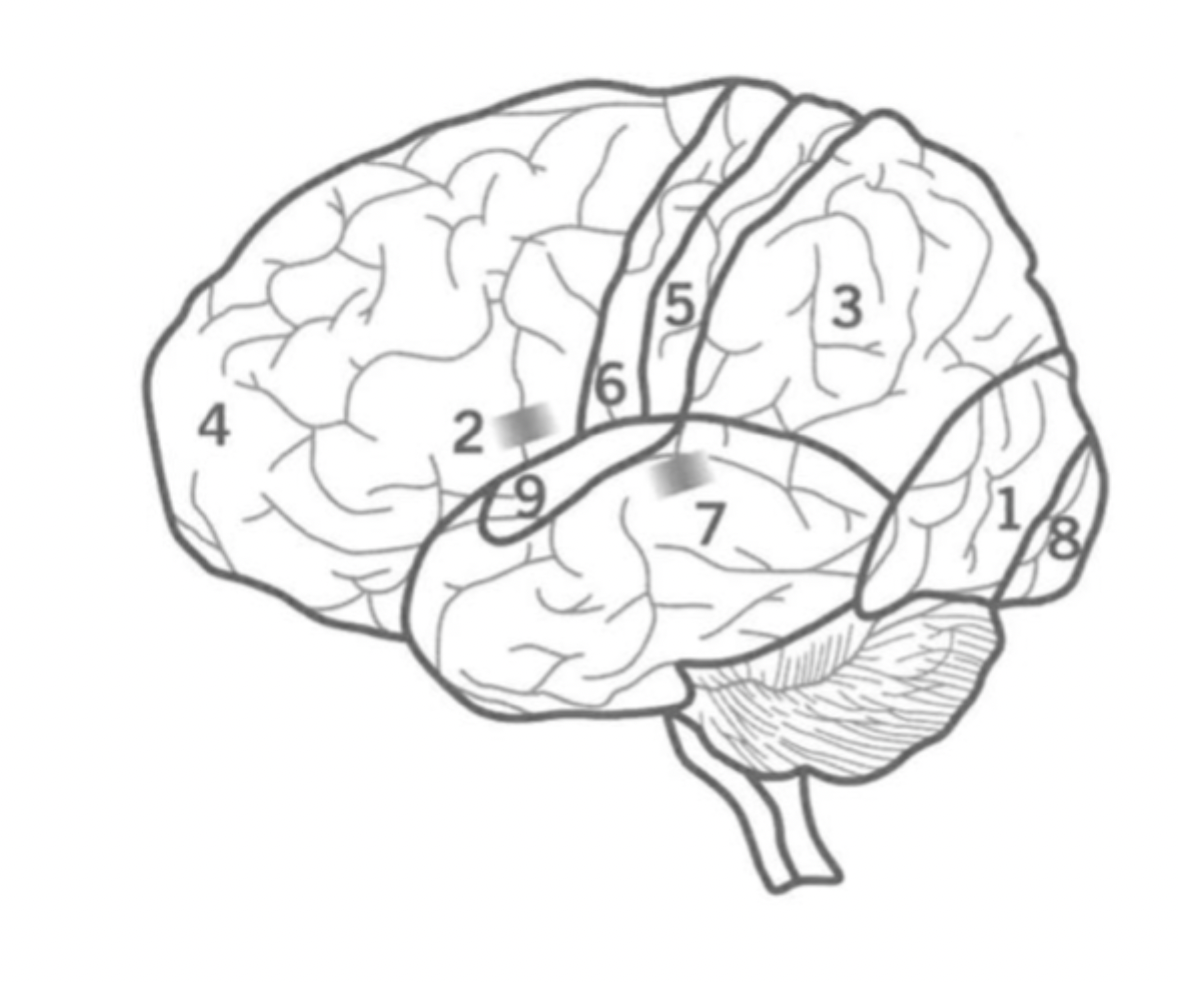
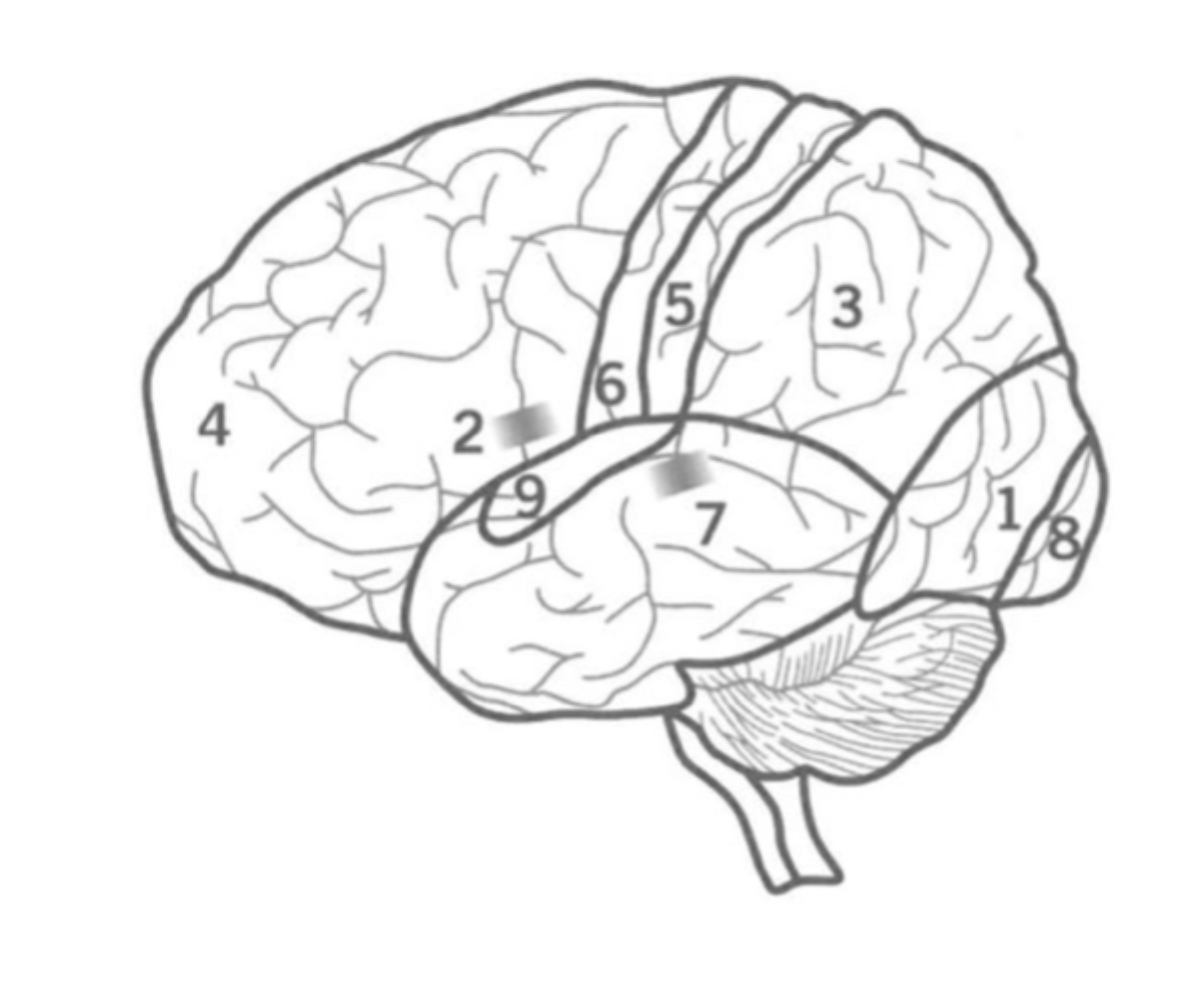
What is the primary auditory cortex?
Where is ti?
9
Initial auditory processing.
located in the Temporal lobe.
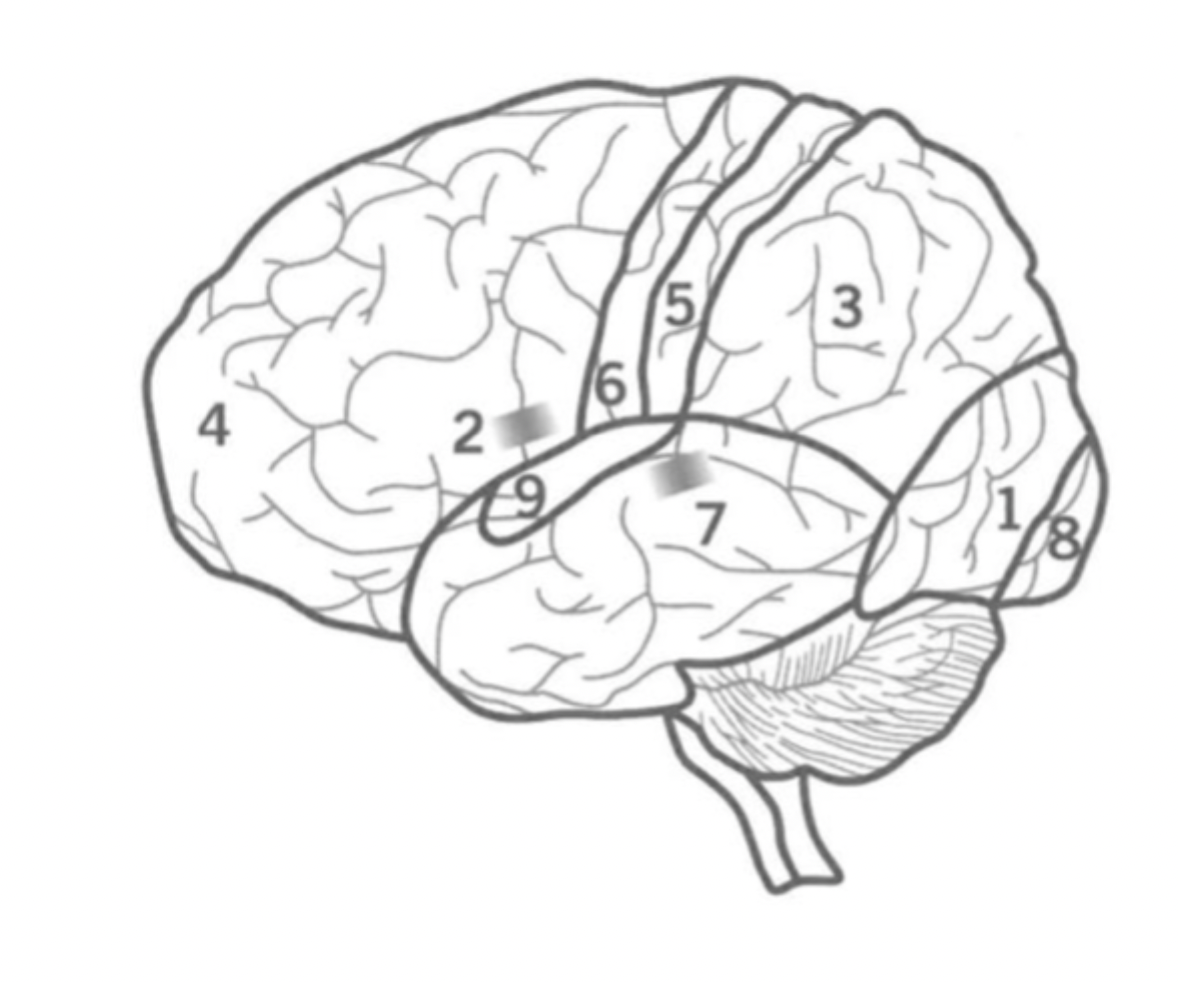
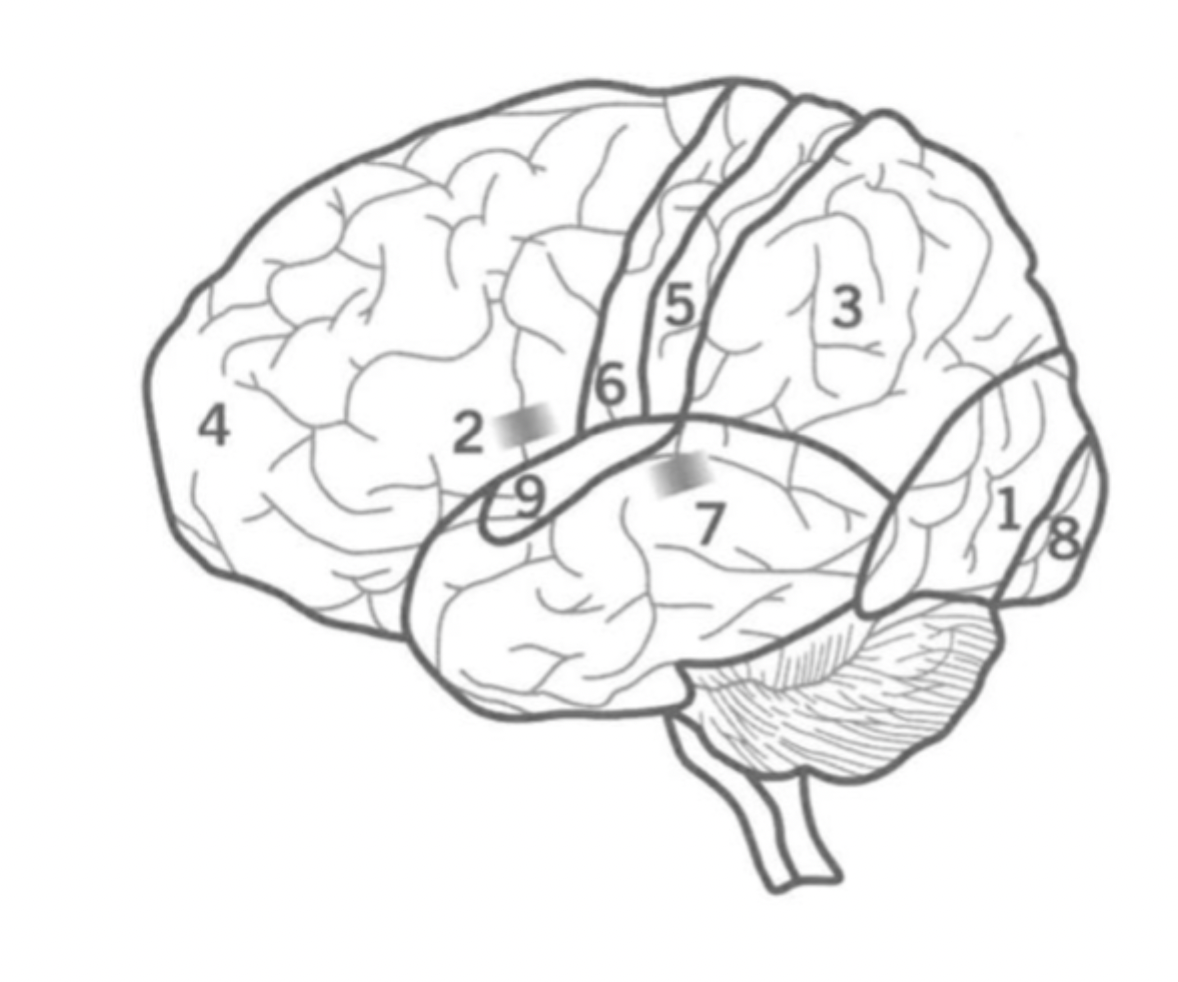
What is the frontal lobe?
Where is it?
responsible for motor control, decision making, attention, memory.
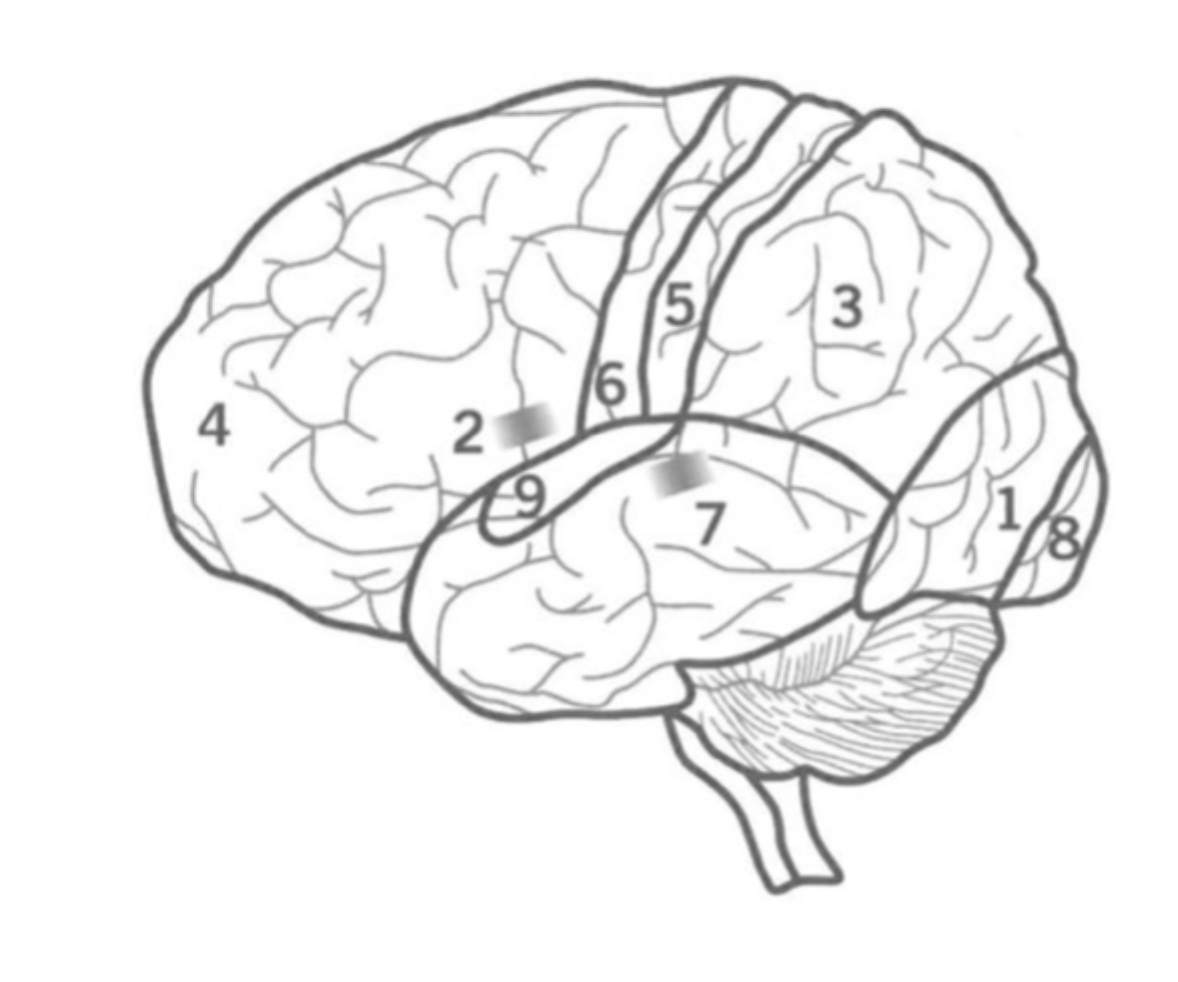
What is the temporal lobe?
Where is it?
Auditory processing, speech and learning through memory formation,
bottom behind.
What is the reticular formation and where is it?
a network of interconnected neurons that go through the brain stem and is in the midbrain.
pain modulation, autonomic functions, Motor control, sensory filtering