MC7 - Induction and resonance
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
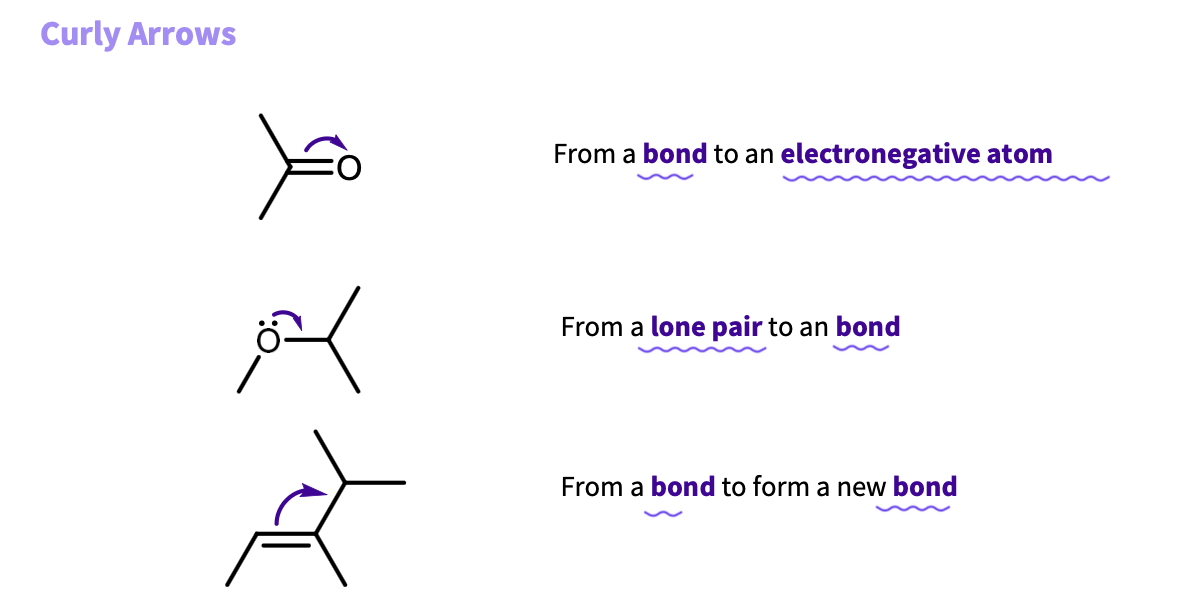
What are the two types of curly arrows?
double headed represent the movement of a pair of electrons
single headed (fishhook) represent the movement of one electron ( matters for radicals
note- arrows only move form a negative ( electron rich ) area to a positive( electron poor) area

Where can curly arrows move from ?
a bond
lone pair
negative charge
Never form + all in one direction
Where must the head of the arrow be directed to?
Head must be directed to an electron deficient area:
-positive charge
-positive end of a polarized bond
-an electronegative atom that can accept a pair of electrons
How do reactions start ?
interactions between electron rich atoms or molecules and electron deficient atoms or molecules
can categorise functional groups into being nucleophiles or electrophiles
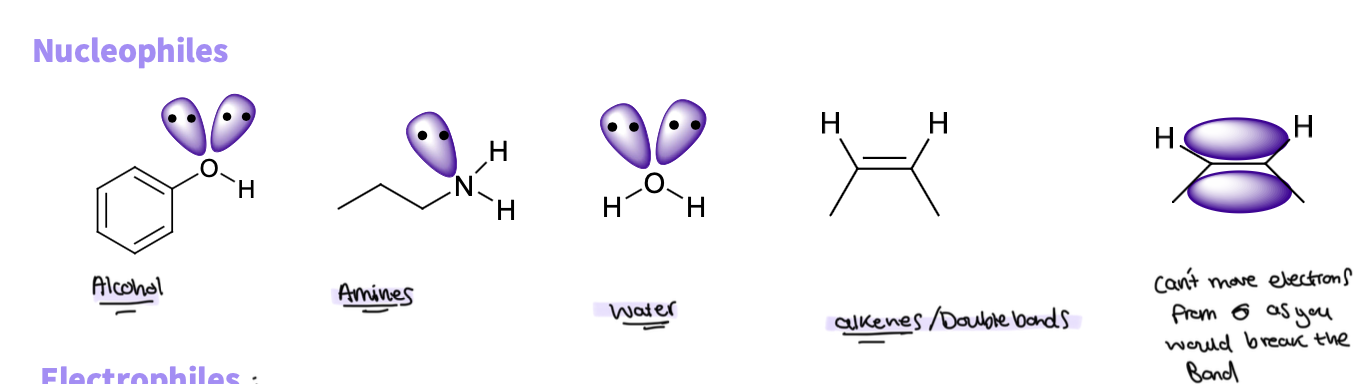
What is a nucleophile ?
An electron rich atom - pair of electrons not involved in bonding which can be shared to form a new bond - alone pair
An electron rich molecule - a bond with high electron density
Give some examples of an nucleophile
alcohol
amines
water
alkenes
What is an electrophile ?
An electron deficient atom-
Can accept a pair of electrons to make up a stable octet of electrons
Name two effects that affect how good a nucleophile is ?
Induction
Resonance
Nucleophiles can be enhanced or reduced in activity -affected by neighbouring atoms ( the rest of the atom)
These two effects:
-can operate together, or compete with each other
Give a brief description of induction
Induction:
-Occurs through sigma bonds
-Based on electronegativities
-Weak in effect
Give a brief description of resonance ?
Resonance:
-Occurs through pi bonds
-Based on ability to share electron and conjugation
-Strong in effect
-If a group has opposing inductive and resonance effects – RESONANCE WINS ( only if competing - one will withdraw one will donate)
What are the 2 types of inductive affects ?
I - = electron withdrawing by induction
I+ = electron donating by induction
what is the effect between carbons and electron rich atoms?
most common effect - electron withdrawing by induction
can be represented in different ways ( arrows )
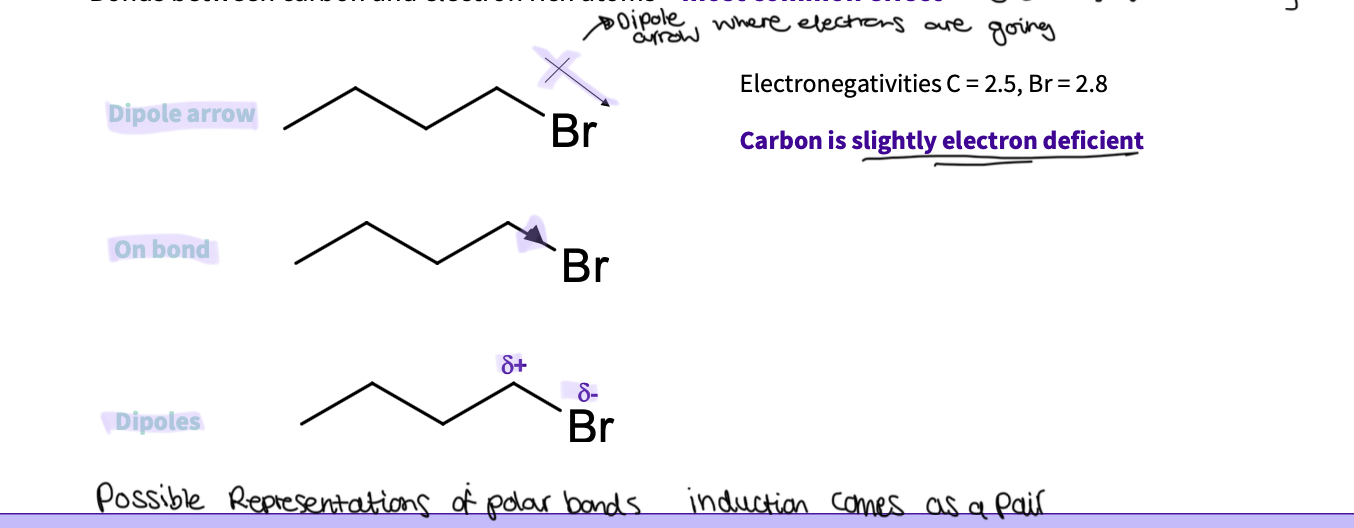
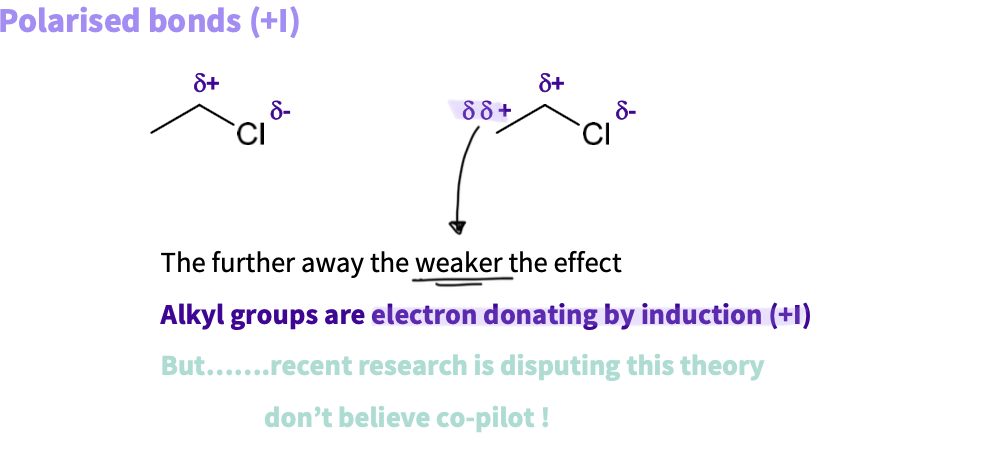
When does electron donating by induction occur?
dipoles can occur between carbon atoms with one being more electron rich
carbon is electron donating
alkyl groups are electron donating by induction ( I+)
What are the 2 Resonance effects ?
Resonance Effects (+M, -M)
Also known as mesomeric effects
can result in electron withdrawing (-M) or electron donating (+M) effects
Where do these resonance effects result from ?
from conjugation within a pi system
The electron density is shared between a number of atoms - delocalised in a single orbital
how are they represented- RESONANCE FORMS
( extreme examples of the effect )
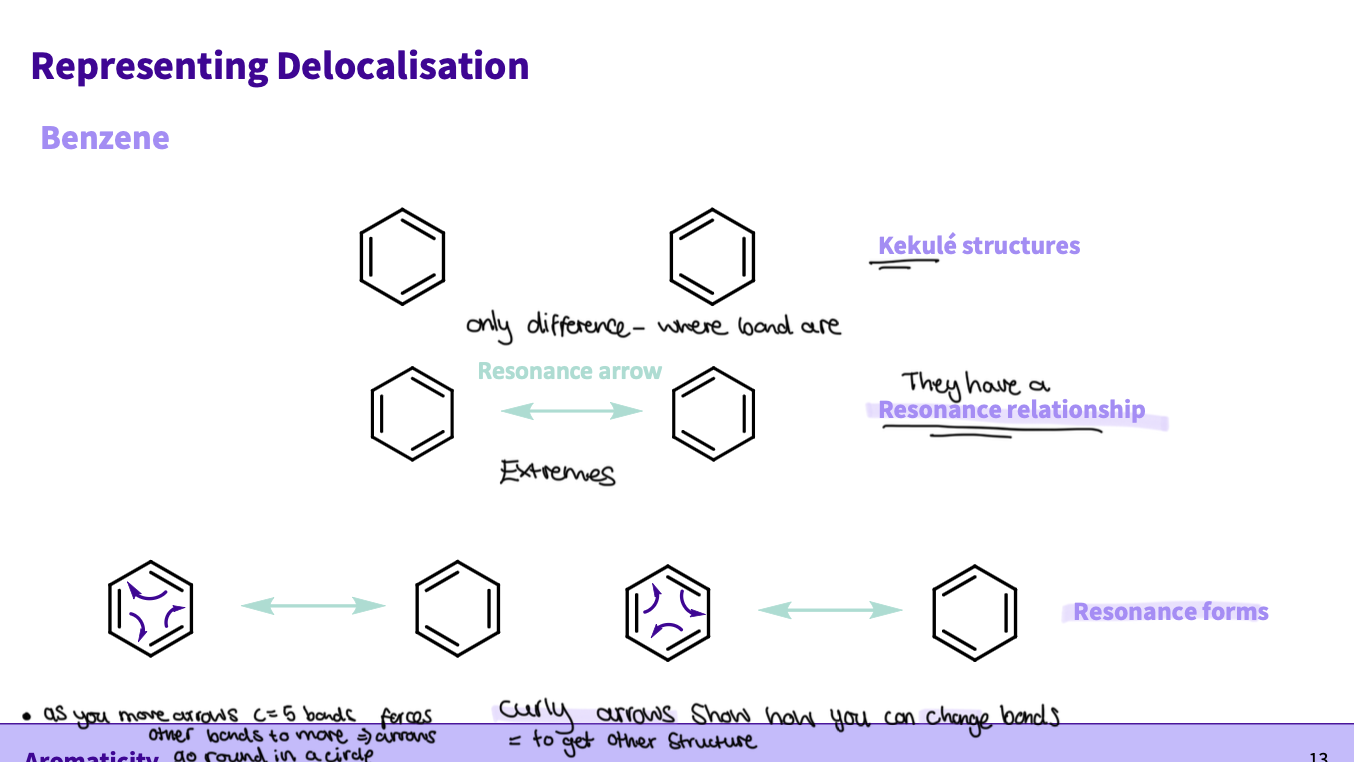
Describe resonance in benzene
benzene structure: 6 cs, 3 sigma, π bonds ,sp2 hybridized, delocalisation - the π electrons overlap
How do we represent its delocalisation?
-the bonds rotate bonds are in different places
-use a resonance arrow to represent they have a resonance relationship
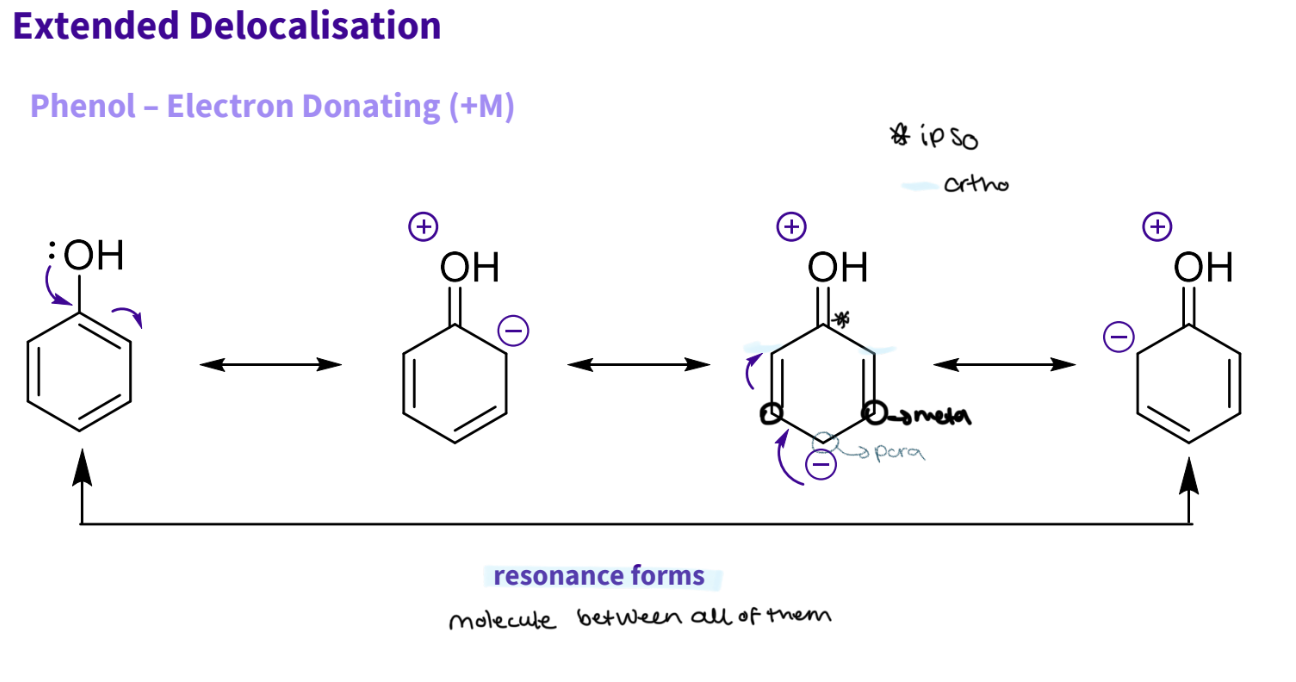
What happens to the resonance when we add a phenol to benzene?
phenol is electron donating ( M+)
the lone pair of oxygen can feed into the ring and be stabilised by conjugation= larger=better
4 resonance forms - actual structure is an average of them all
resonance forms:
1- normal ,arrow from lone pair to bond the double bond in ring breaks
2- this results in oxygen gains a + charge - 2 bonds, - ve charge on carbon because it like 4 bonds ,the negative charge then moves round and. the π bond breaks
3- now a - ve charge on that carbon 4 ,and π bonds at c2 ,c5
4-now negative charge moves around to bond the then the π bond breaks and there is now a negative charge on carbon 6 and a double bond on c4
note - resonance works by forming ,then breaking a bond to form the the bond - goes round in a circle
What happens when there is competing effects ?
An alcohol group is electron withdrawing by Induction (-I)- weaker
An alcohol group on an aromatic ring is electron donating by resonance (+M)
What happens?- RESONANCE WINS
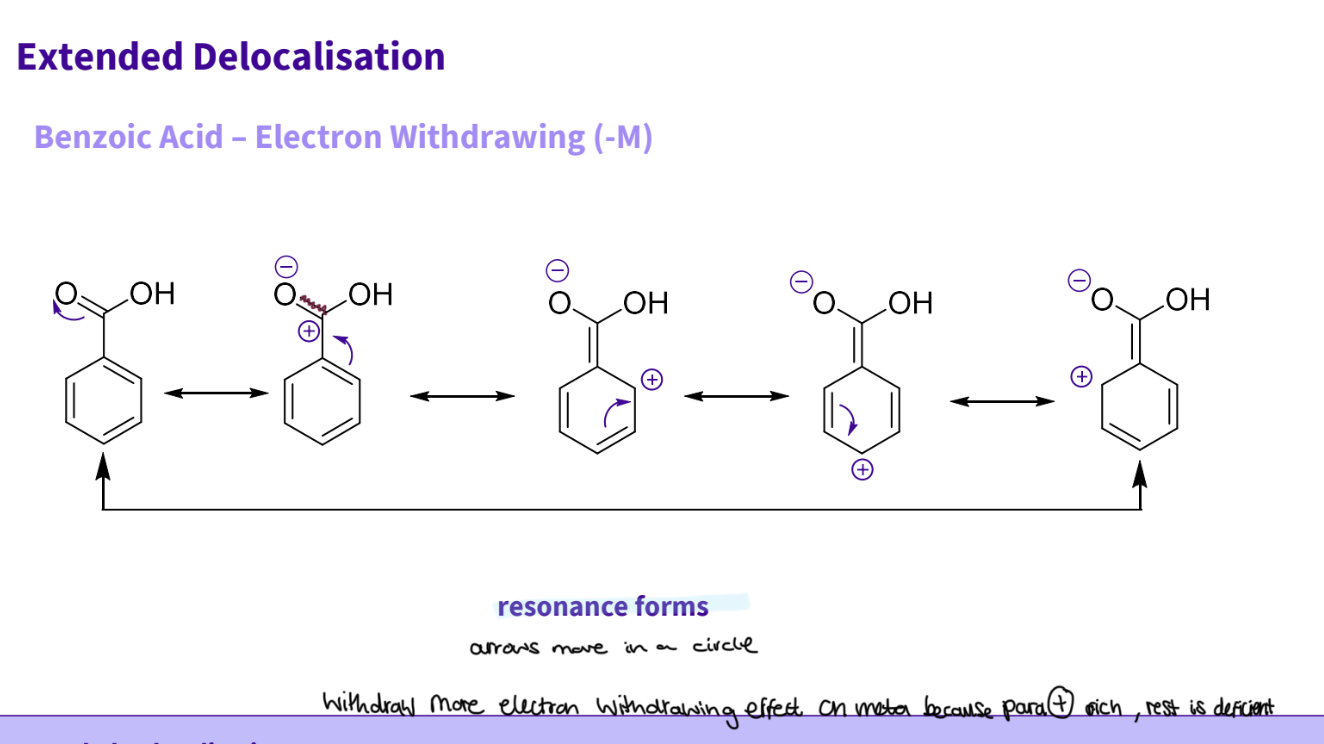
What happens to resonance when you add a carboxylic acid to benzene
( benzoic acid ) ?
Benzoic acid- electron withdrawing ( M-)
carbonyl group is part of extended conjugated system , electrons can be shared from the ring to the substituent
this results in 5 resonance forms
Resonance forms:
1- the oxygen π bond breaks arrow outwards
2- results in -ve charge on oxygen and + ve on the carbon , the double bond breaks to squash positive charge
3- there is now a π bond between the ring and chain and a + ve charge on the c2 ,the double bond on carbon 4 breaks to squash + ve charge
4- now a + ve charge on the c4 - and π bonds at c2 ,c5 ,the π bond at c5 - breaks
5- there is now a π bond on c4 and a + ve charge on. c6
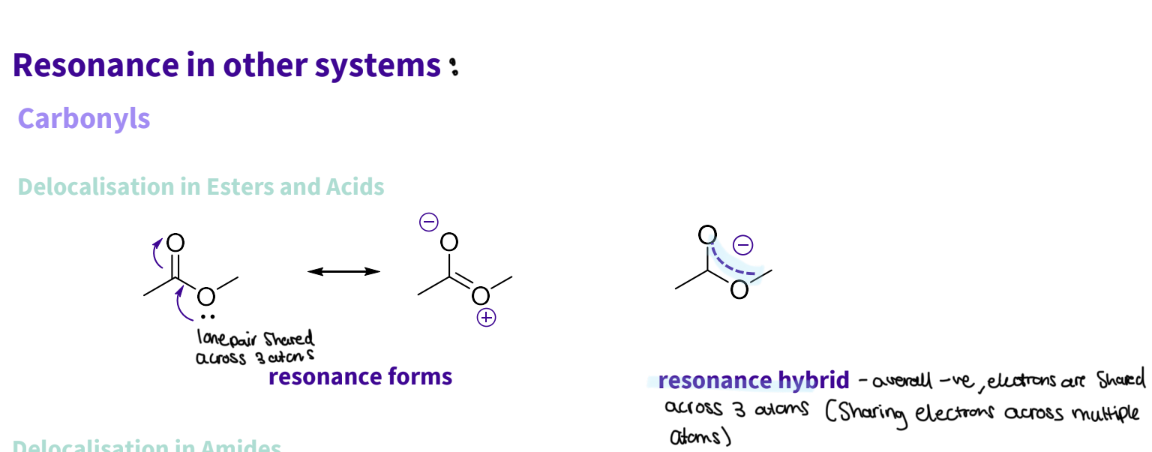
What is the delocalisation /resonance in Carbonyls ?
Delocalisation in Esters and Acids
the lone pair is shared across the 3 atoms - oxygen ,carbon ,oxygen
resonance hybrid - overall -ve electrons are shared across three atoms
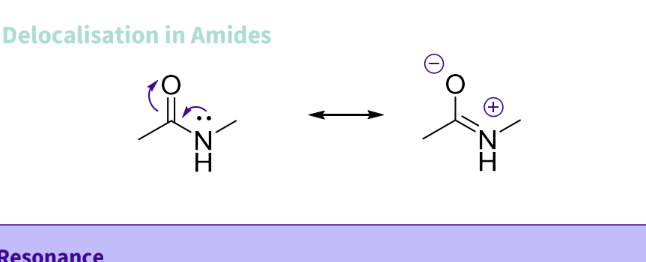
What is the delocalisation of amides/resonance ?
lone -pair on nitrogen forms double n=bond and oxygen double bond breaks
+ ve charbe on the nitrogen , ,-ve charge on oxygen
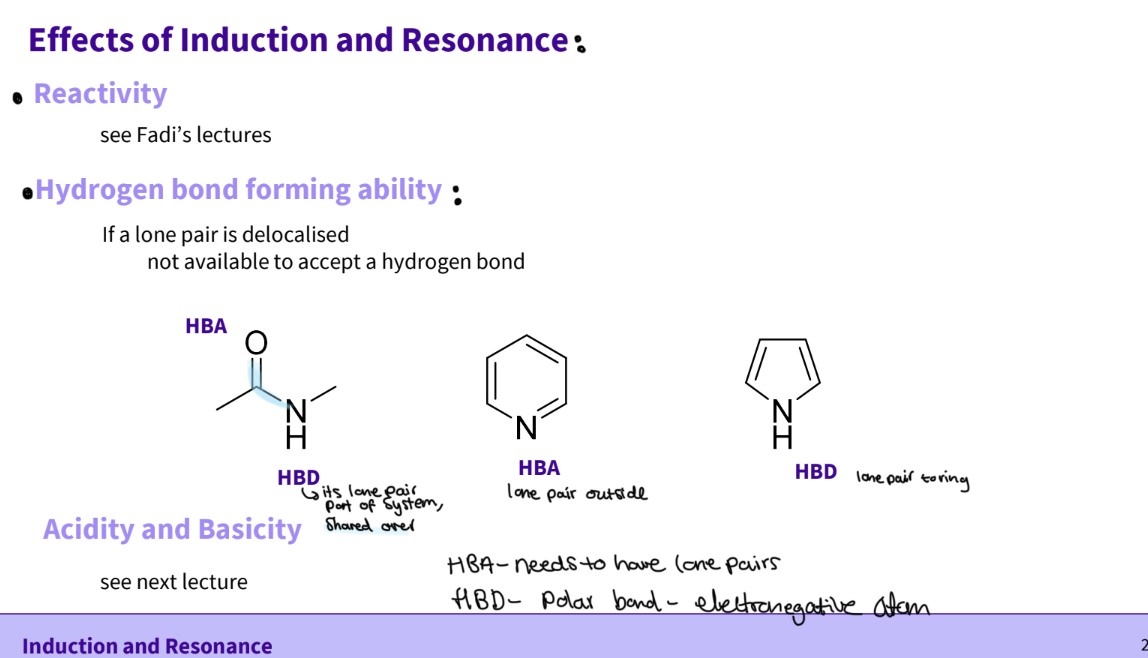
What is the effect of induction and resonance ?
reactivity
hydrogen bond forming ability
acidity and basicity