Dermatology - Systemic diseases
1/96
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
97 Terms
Autosomal dominant
Neurofibromatosis is inherited by which type of pattern?
3 multiple choice options
neurofibromin
A defect in the ___ gene causes neurofibromatosis
childhood
In neurofibromatosis when is NF1 diagnosed?
- greater than 6 cafe au lait macules
- two or more neurofibromas
- axillary or inguinal freckling
- optic glioma
- two or more lisch nodules (on iris)
- first degree relative with NF
- skeletal deformity
(must have two for diagnosis)
What are the diagnostic criteria for neurofibromatosis?
Neurofibromatosis
What is the diagnosis?
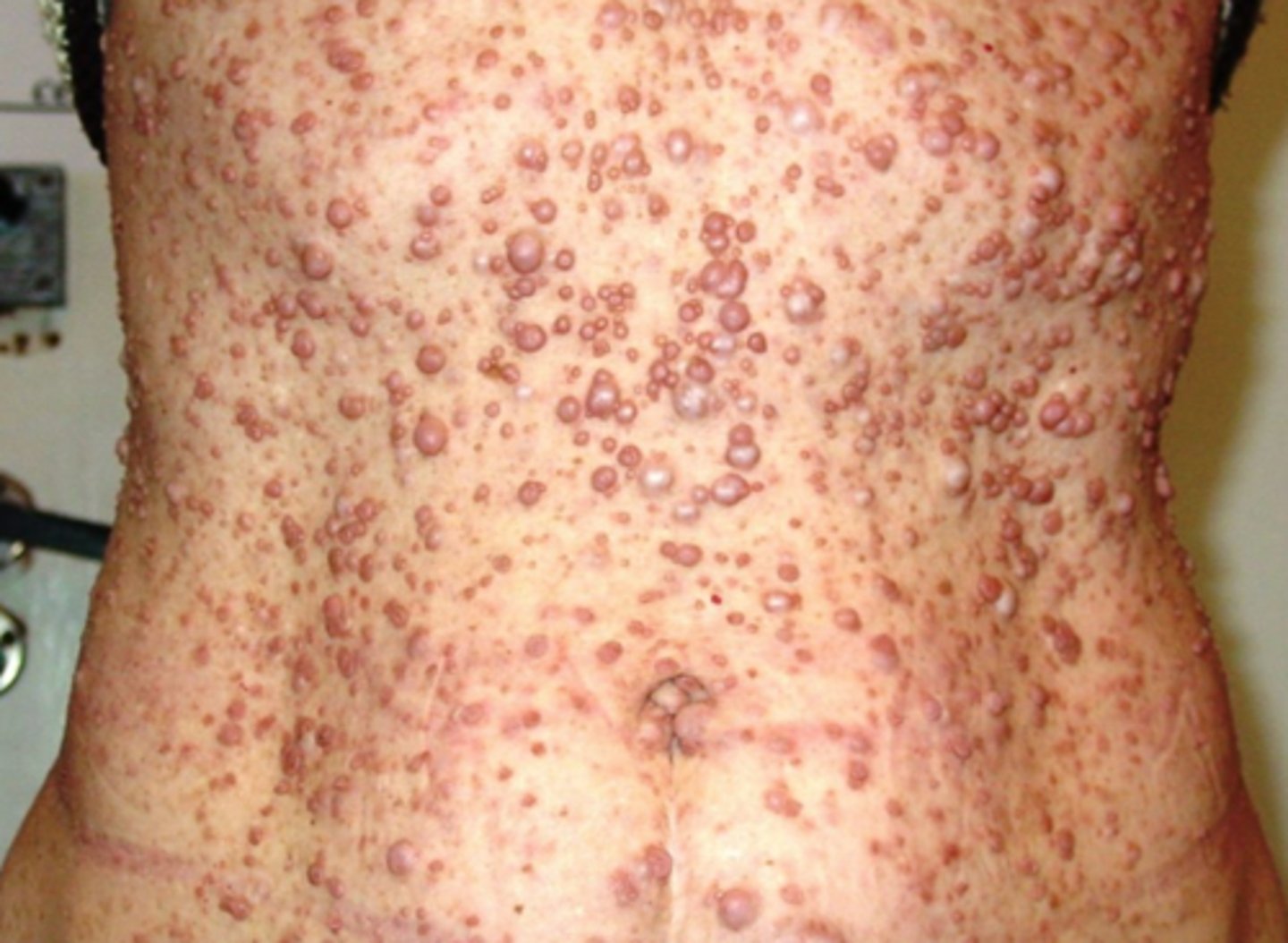
Plexiform neurofibroma
What is the diagnosis?
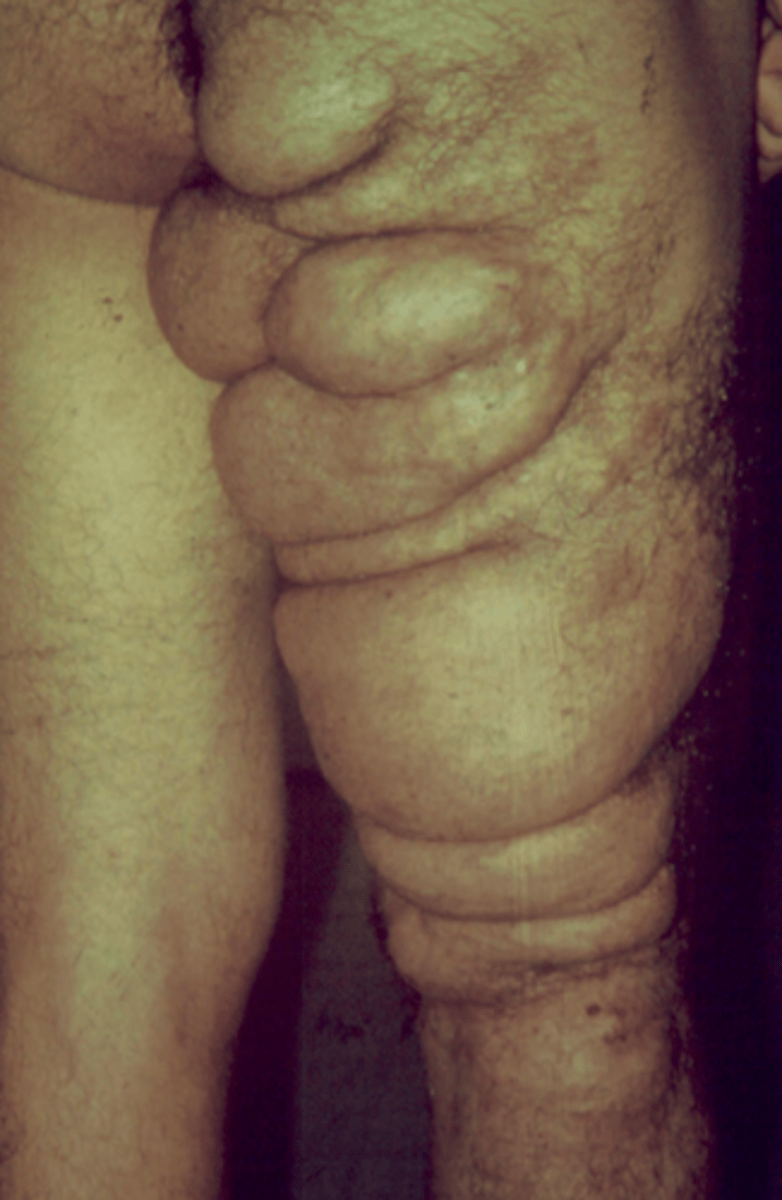
- ophthalmology, neurology, orthopedics, and derm
Which referrals should be given for an NF patient?
Dermatitis herpetiformis
Which type of dermatitis is associated with gluten insensitivity?
- children
- asians and African americans
Dermatitis herpetiformis is rare in which demographics?
Dermatitis herpetiformis
clustered vesicles (often destroyed by scratching) and excoriations on elbows, knees, back
Skin biopsy with DIF
Which diagnostic test is appropriate if dermatitis herpetiformis is suspected?
thyroid disease and T cell lymphoma
In DH there is an increased risk of ___ and ___
- gluten avoidance
- dapsone orally (G6PD deficiency screening and CBC monitoring)
Tx for dermatitis herpetiformis?
sunlight and medications
Cutaneous lupus is exacerbated by ___
Acute cutaneous lupus
Which form of cutaneous lupus has the strongest association with SLE?
3 multiple choice options
Chronic cutaneous
Which form of cutaneous lupus is the most common?
3 multiple choice options
Acute cutaneous
A malar rash is indicative of which type of cutaneous lupus?
3 multiple choice options
Annular and papulosquamous
Subacute cutaneous lupus has two presentations, what are they?
Chronic cutaneous lupus
Discoid lupus is the most common form of ___
3 multiple choice options
discoid lupus
Epidermal atrophy with adherent scaling and follicular plugging is indicative of ___
Acute cutaneous lupus
What is the diagnosis?
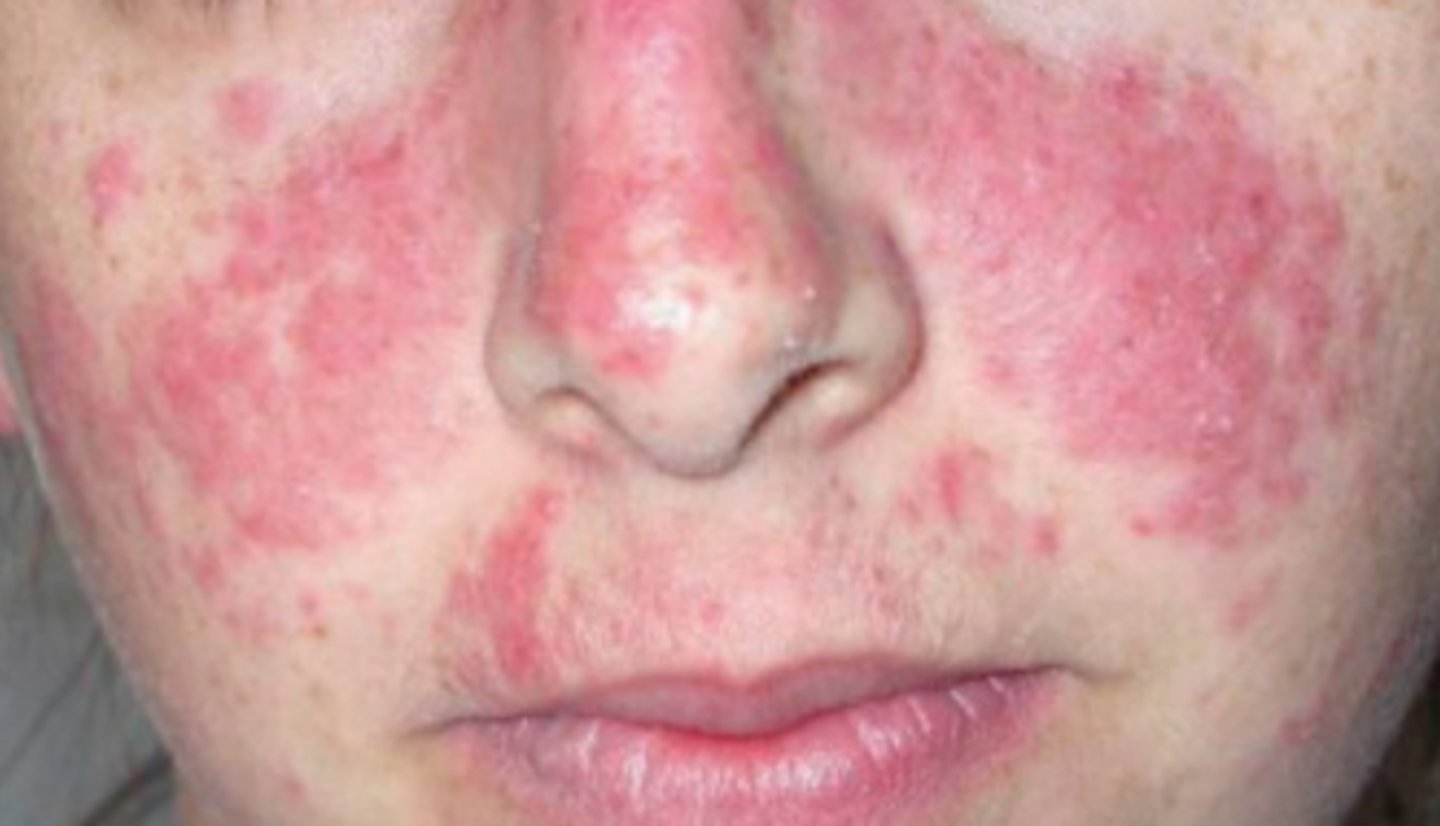
Subacute cutaneous lupus (annular)
What is the diagnosis?
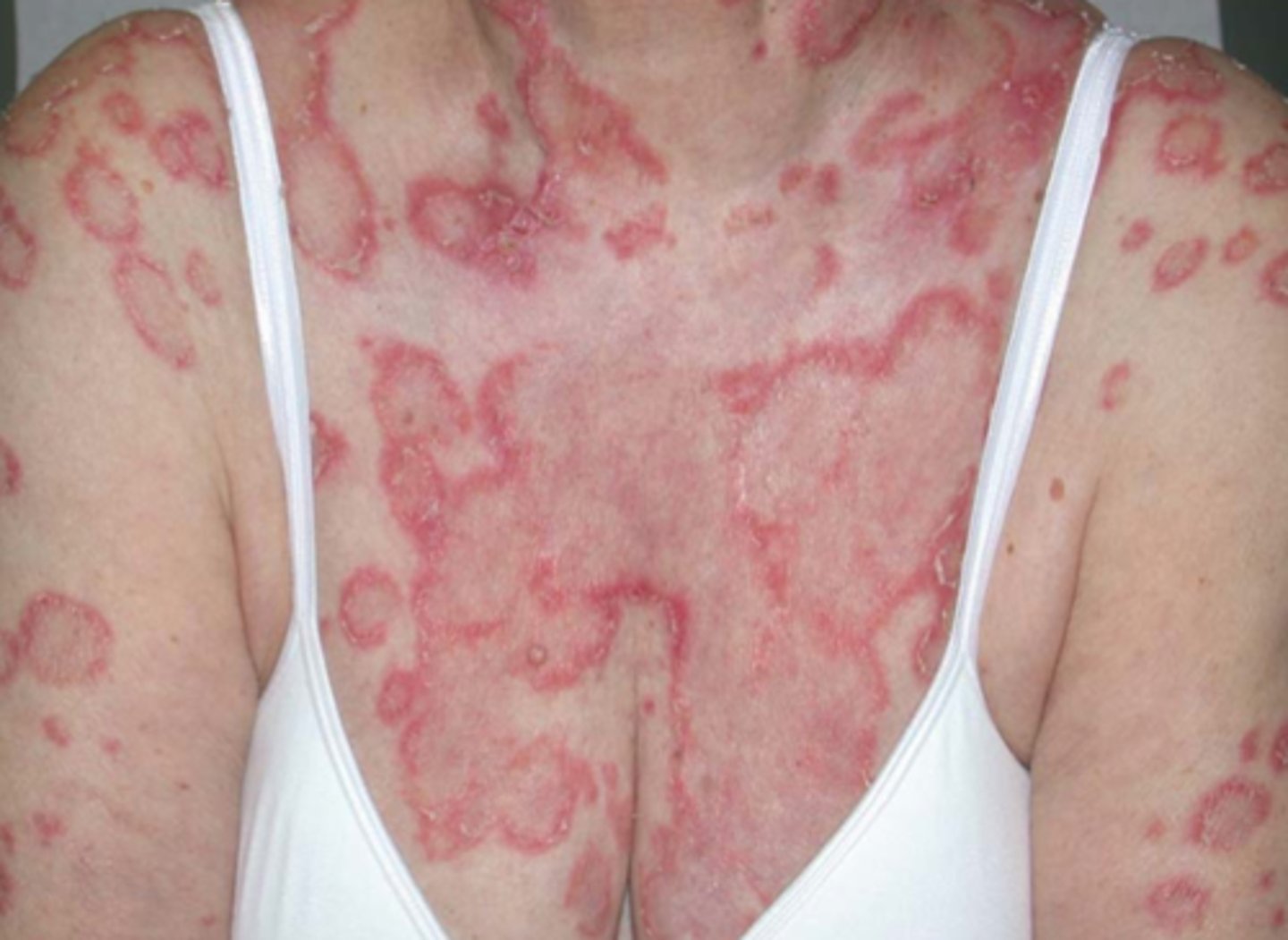
Subacute cutaneous lupus (papulosquamous)
What is the diagnosis?
Discoid lupus
What is the diagnosis?
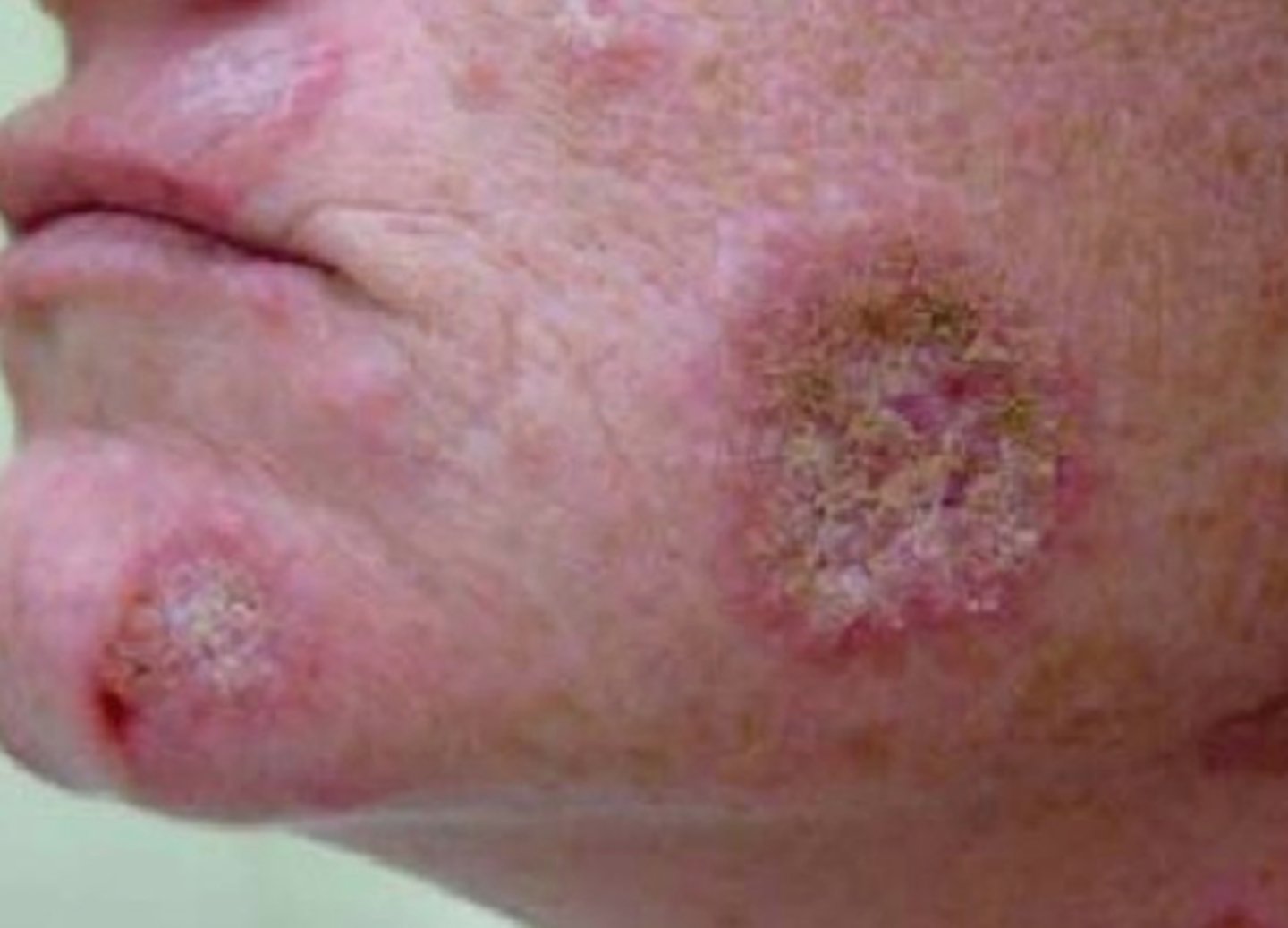
Discoid lupus
What is the diagnosis?
- Skin biopsy
- CBC
- CMP (renal fxn)
- Urinalysis (renal fxn)
- ANA with reflex to ENA
Workup for suspected cutaneous lupus?
- strict sun avoidance
- anti-inflammatory treatment (topical steroids, calcineurin inhibitors, and intralesional steroids)
- systemic immunosuppressants (prednisone, chloroquine, methotrexate, azathioprine, benlysta)
- Rheumatology ref if systemic invovlement
Tx of cutaneous lupus?
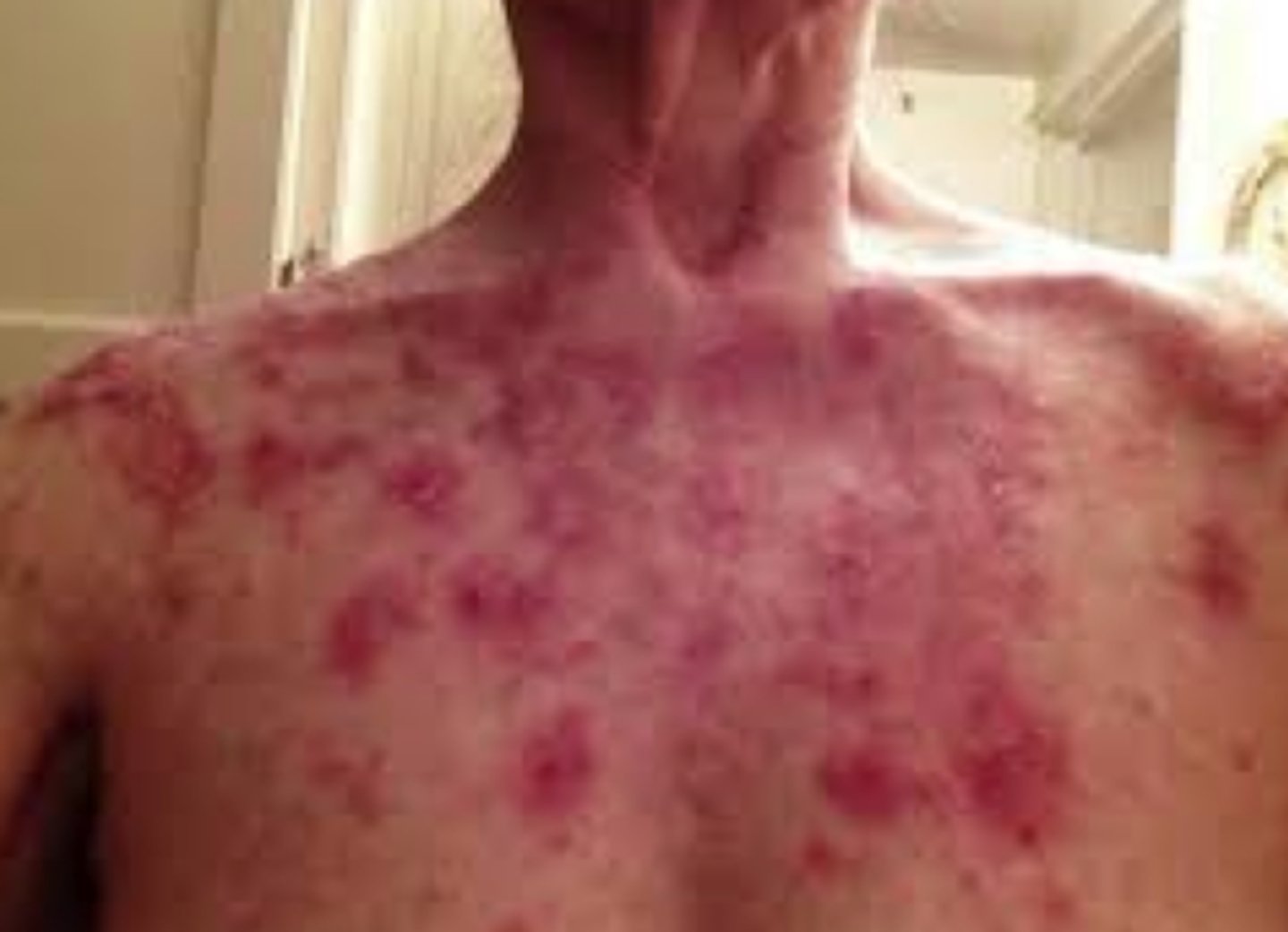
Dermatomyositis
Autoimmune connective tissue disease characterized by extensor myopathy, violaceous cutaneous eruptions and pathogenic autoantibodies
- cutaneous lupus
- scleroderma
- dermatomyositis
Periungal telangectasias are commonly found in which diagnoses?
dermatomyositis
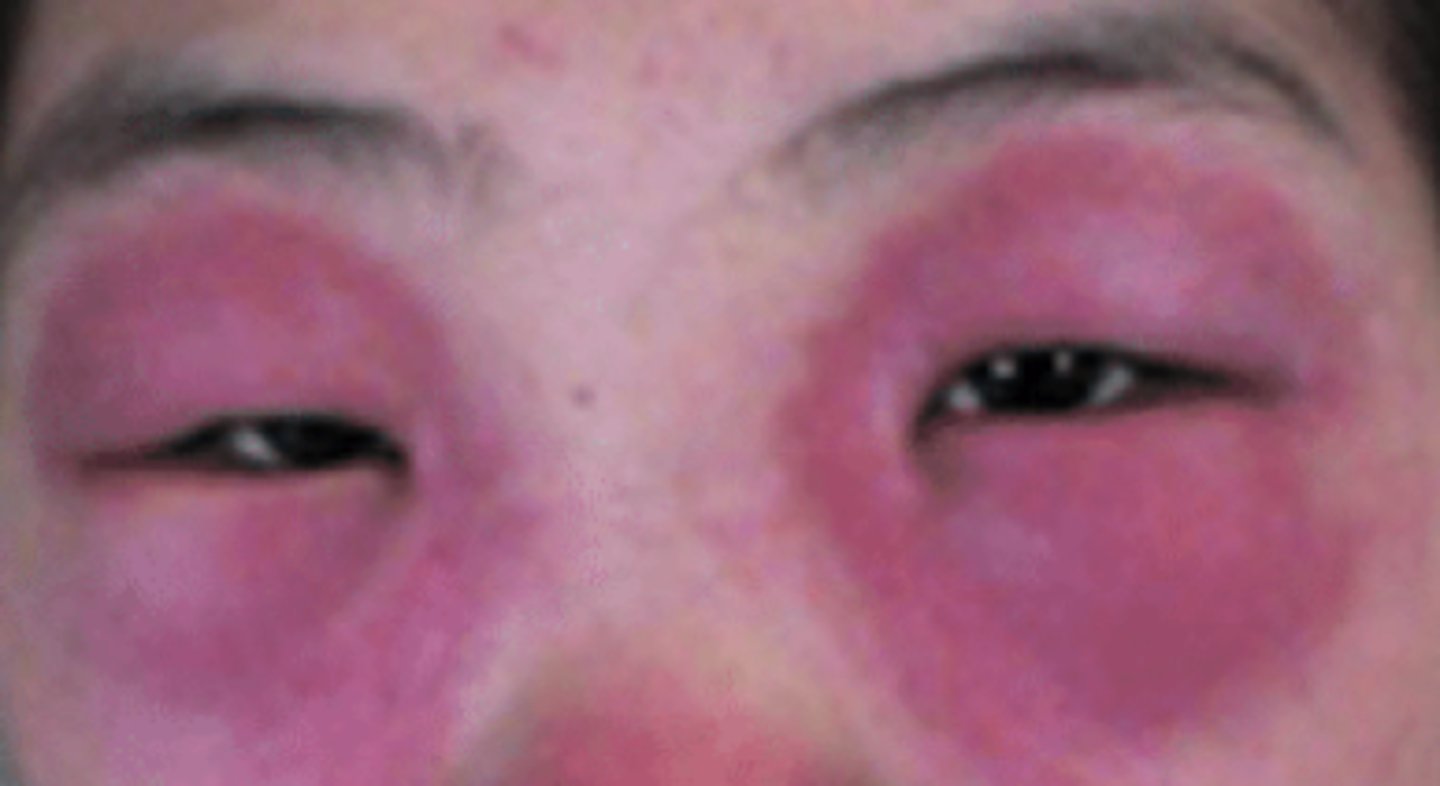
Heliotrope rash is seen in ___
dermatomyositis
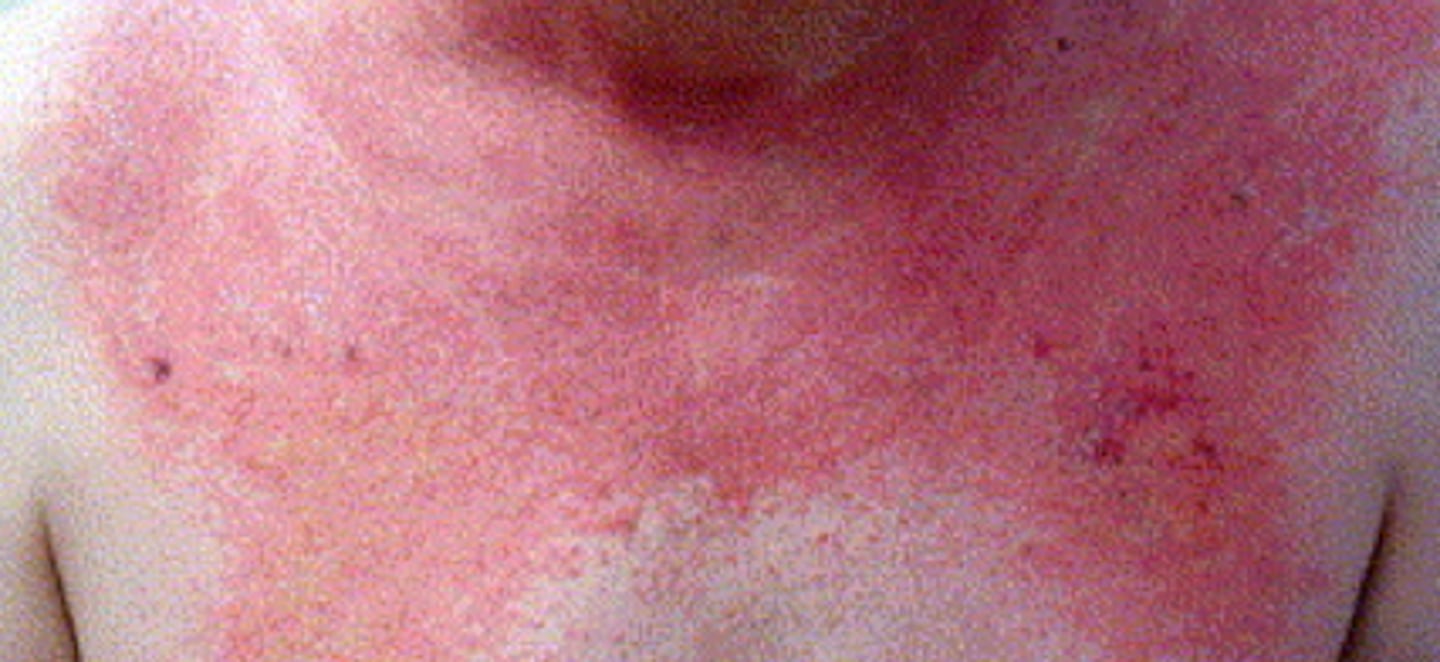
Shawls sign is photosensitive violaceous eruptions on the shoulders neck and chest seen in ___
dorsal hands and knuckles
Atrophic dermal papules of dermatomyositis can be found on the ___
ADPDM (dermatomyositis)
What is the diagnosis?
Dermatomyositis
What is the diagnosis?
Dermatomyositis
What is the diagnosis?
- skin biopsy
- Anti Jo-1 antibodies
- Check for proximal muscle weakness (CK?)
- Screen for occult malignancy
Workup for dermatomyositis?
- sun avoidance
- topical corticosteroids
- systemic immunosuppressants (methotrexate, cyclosporine, mycophenolate mofetil, azathioprine)
Tx of dermatomyositis?
lungs and skin
In sarcoidosis the ___ and ___ are most commonly affected
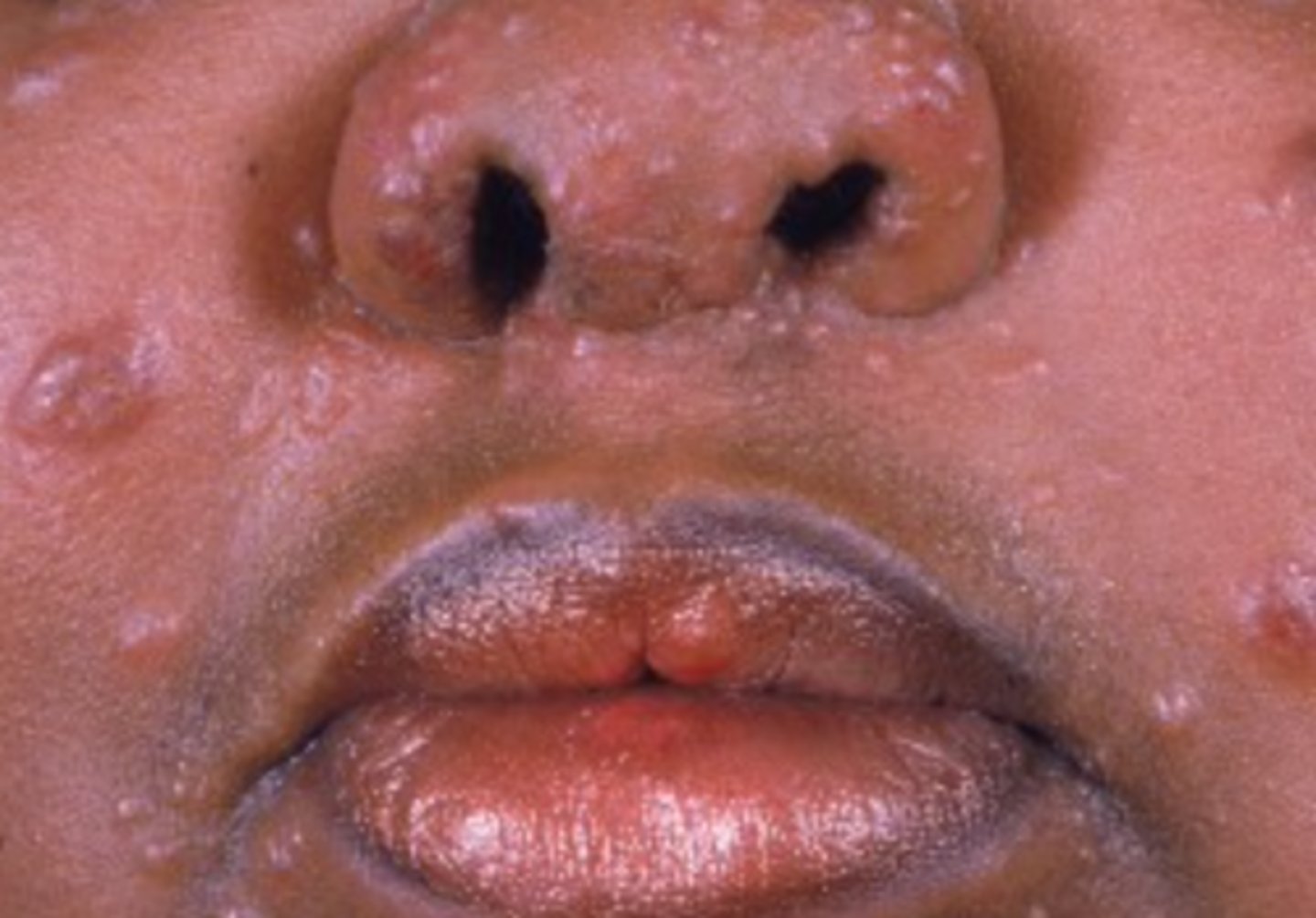
Sarcoidosis
noncaseating granulomas develop in which disease?
Face (m/c), neck, arms and upper trunk
Sarcoidosis is most commonly found on which areas?
Sarcoidosis
What is the diagnosis?
Sarcoidosis
What is the diagnosis?
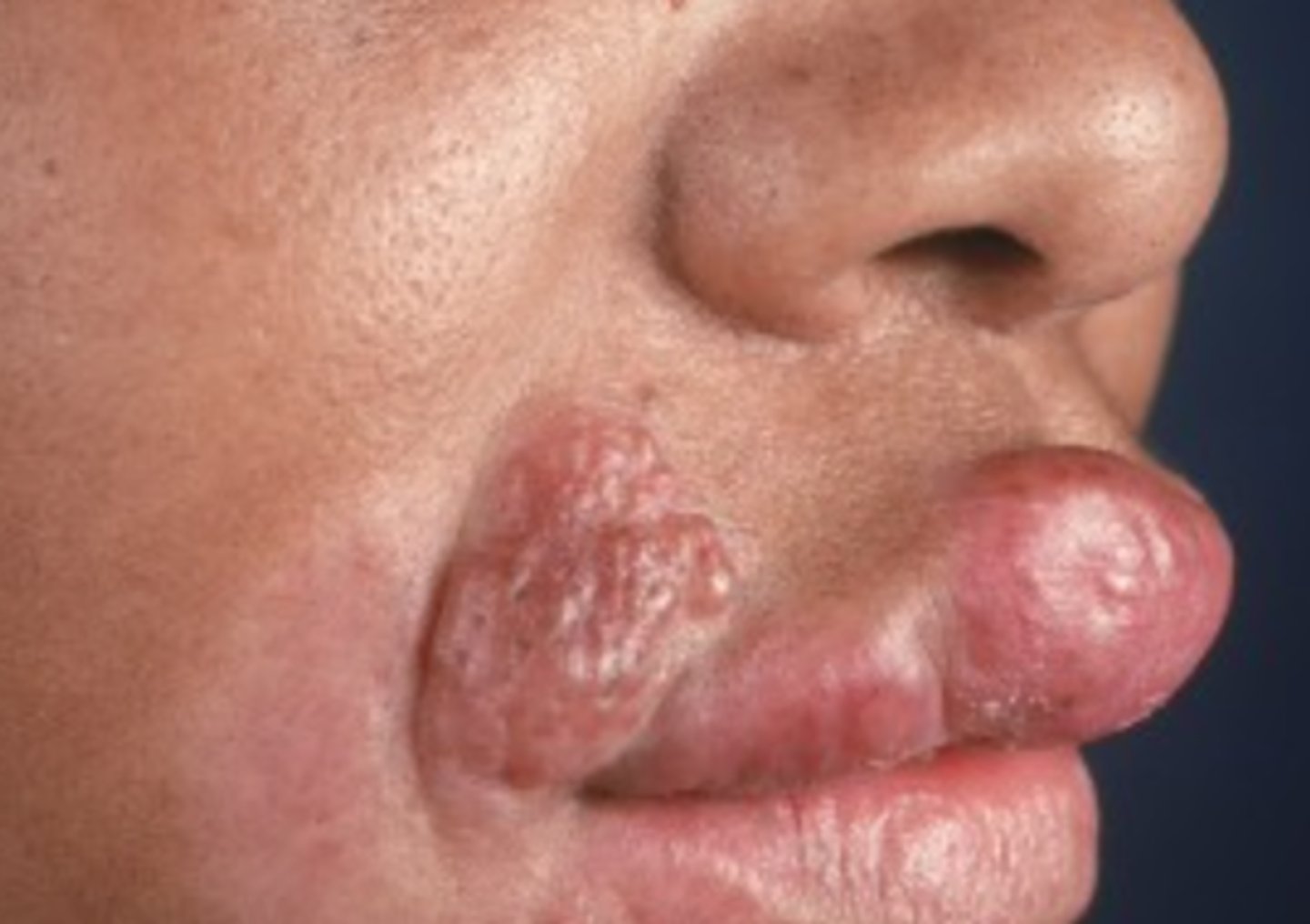
Sarcoidosis
What is the diagnosis?
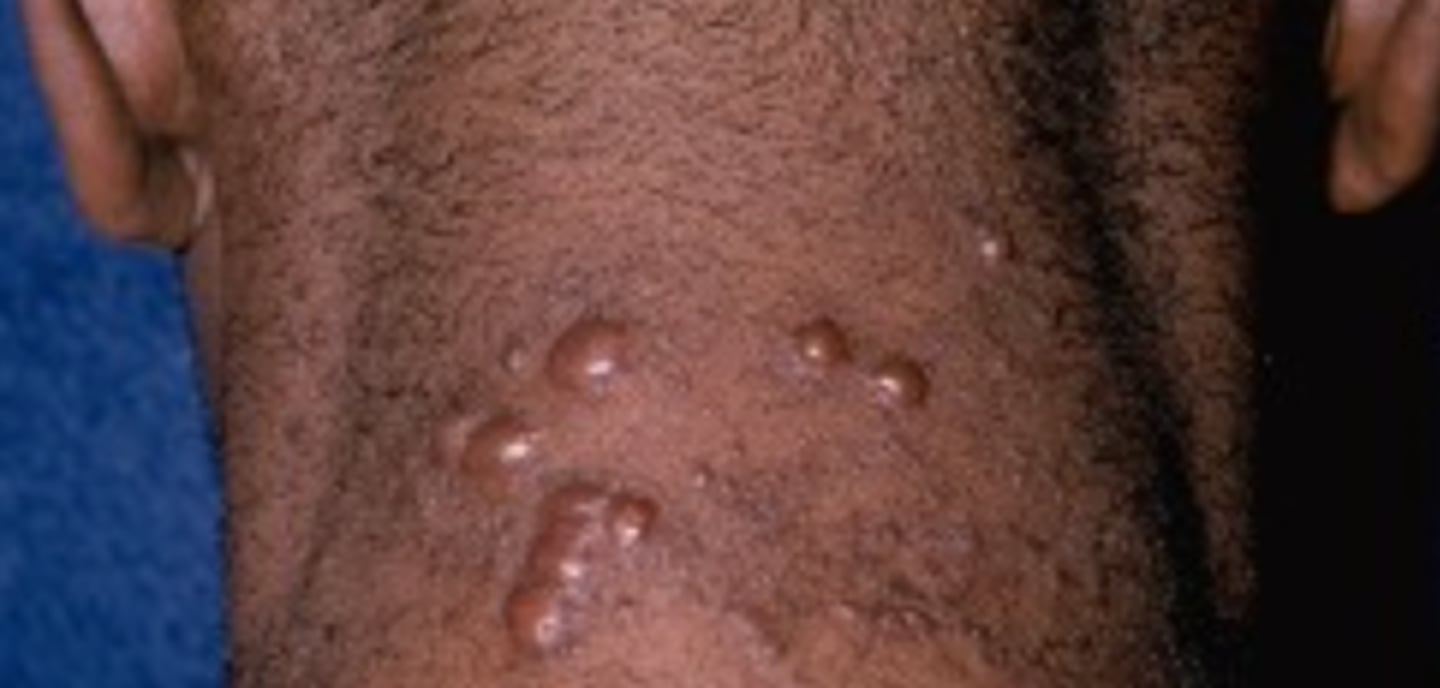
Erythema nodosum
Sarcoidosis PE can also show which other skin condition?
- skin biopsy
- CXR (Pilar lymphadenopathy)
- pulmonary fxn tests
- cardiac eval
- ophthalmology
- labs: TB, serum CA2+, ACE, ANA
Sarcoidosis workup?
- topical corticosteroids
- calcineurin inhibitors
- oral prednisone
- hydroxychloroquine
- methotrexate
- azathiopine
- infliximab
Tx of sarcoidosis?
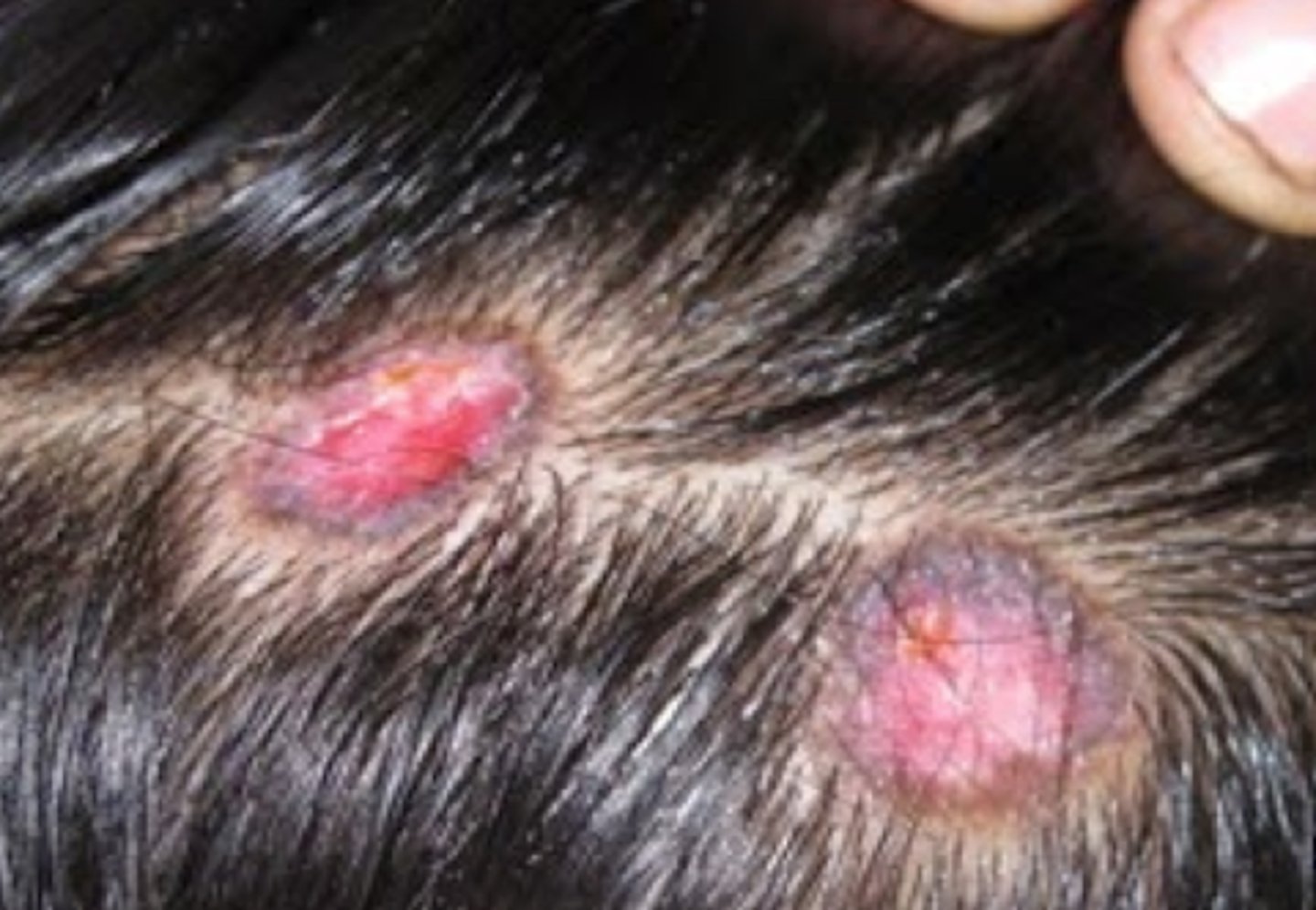
Pyoderma gangrenosum
What is the diagnosis?
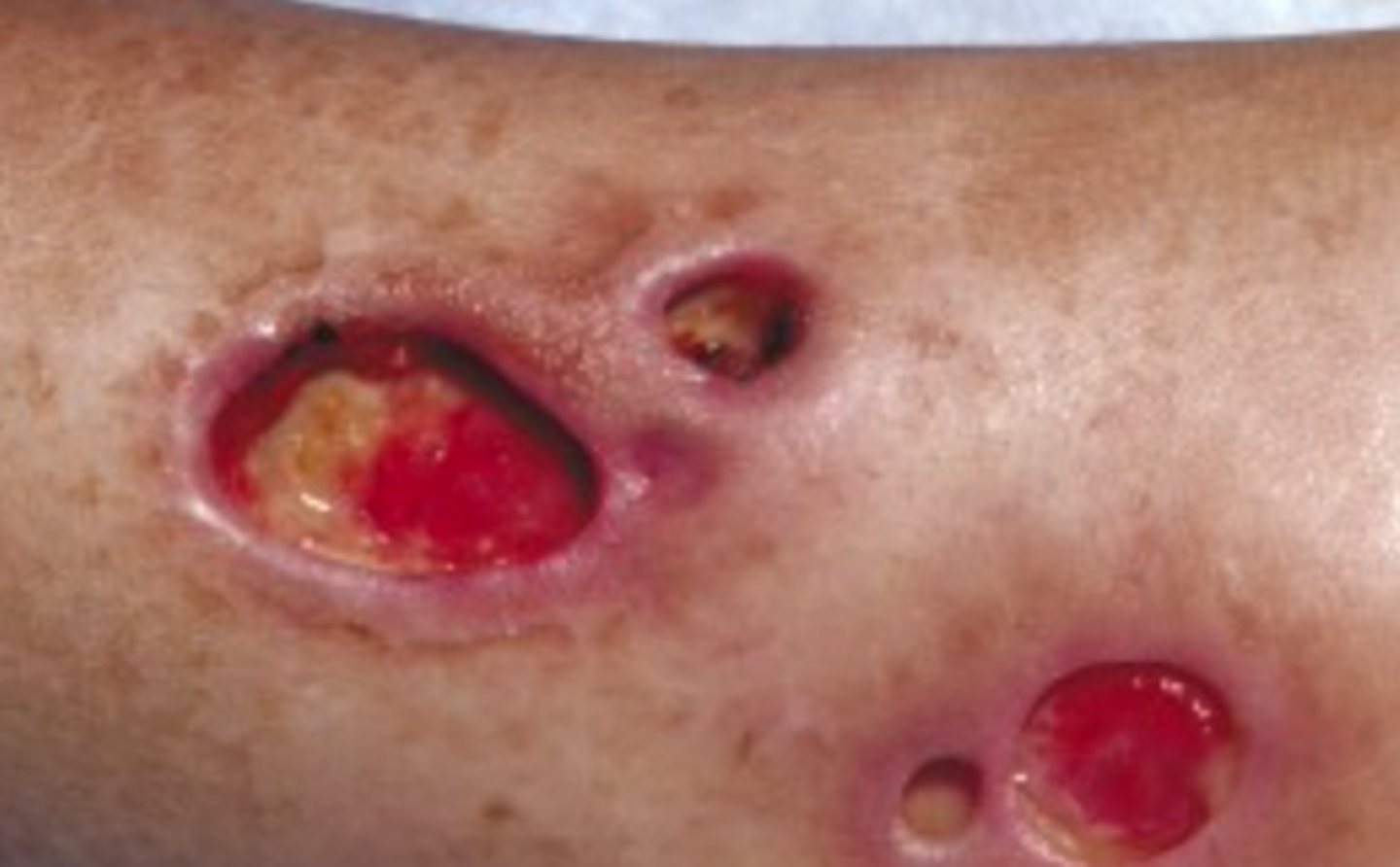
Pyoderma gangrenosum
What is the diagnosis?
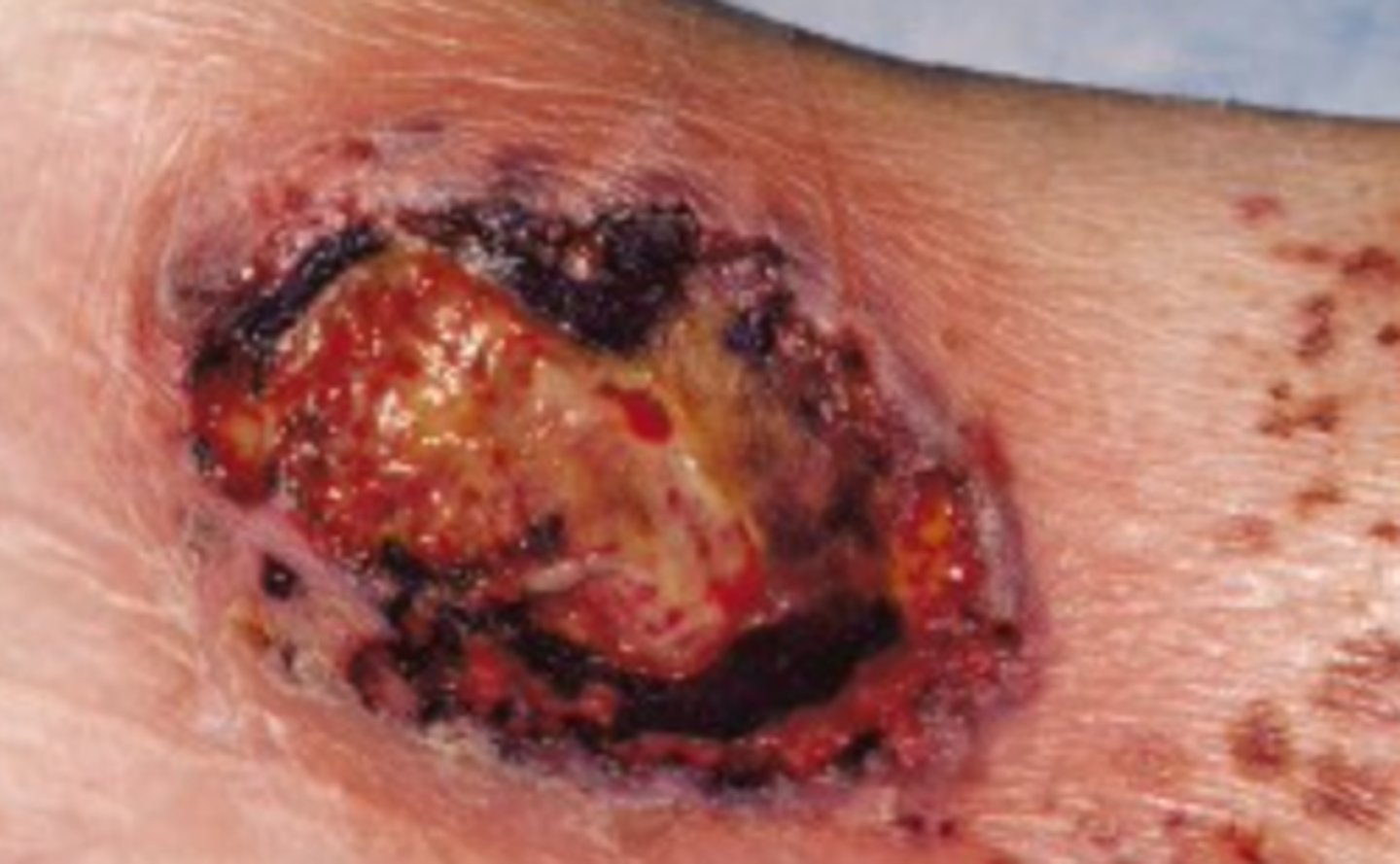
Pyoderma gangrenosum
Neutrophilic infiltration of tissue, destruction and ulceration
Pyoderma gangrenosum
___ appears infected but has no microbial etiology
Pyoderma gangrenosum
___ occurs in association with IBD, arthritis, hematologic dyscrasia and malignancy
Pyoderma gangrenosum
painful, irregular, boggy, blue-red ulcers with violaceous undermined borders and a purulent necrotic base
- avoid debridement
- treat underlying pathology
- topical steroids
- calcineurin inhibitors
- intralesional steroids
- high dose oral steroids
- sulfasalazine, cyclosporine
- infliximab, etanercept, adalimumab
Tx of pyoderma gangrenosum?
Necrobiosis lipoidica
Inflammatory condition of collagen degeneration more common in women
Anterior shins
M/C site of necrobiosis lipoidica?
50
More than ___% of people with necrobiosis lipoidica will develop diabetes
Necrobiosis lipoidica
Round, violaceous patches which turn orange with time on anterior shins with central atrophy, shiny waxy surface, and prominent telangectasias
Necrobiosis lipoidica
What is the diagnosis?
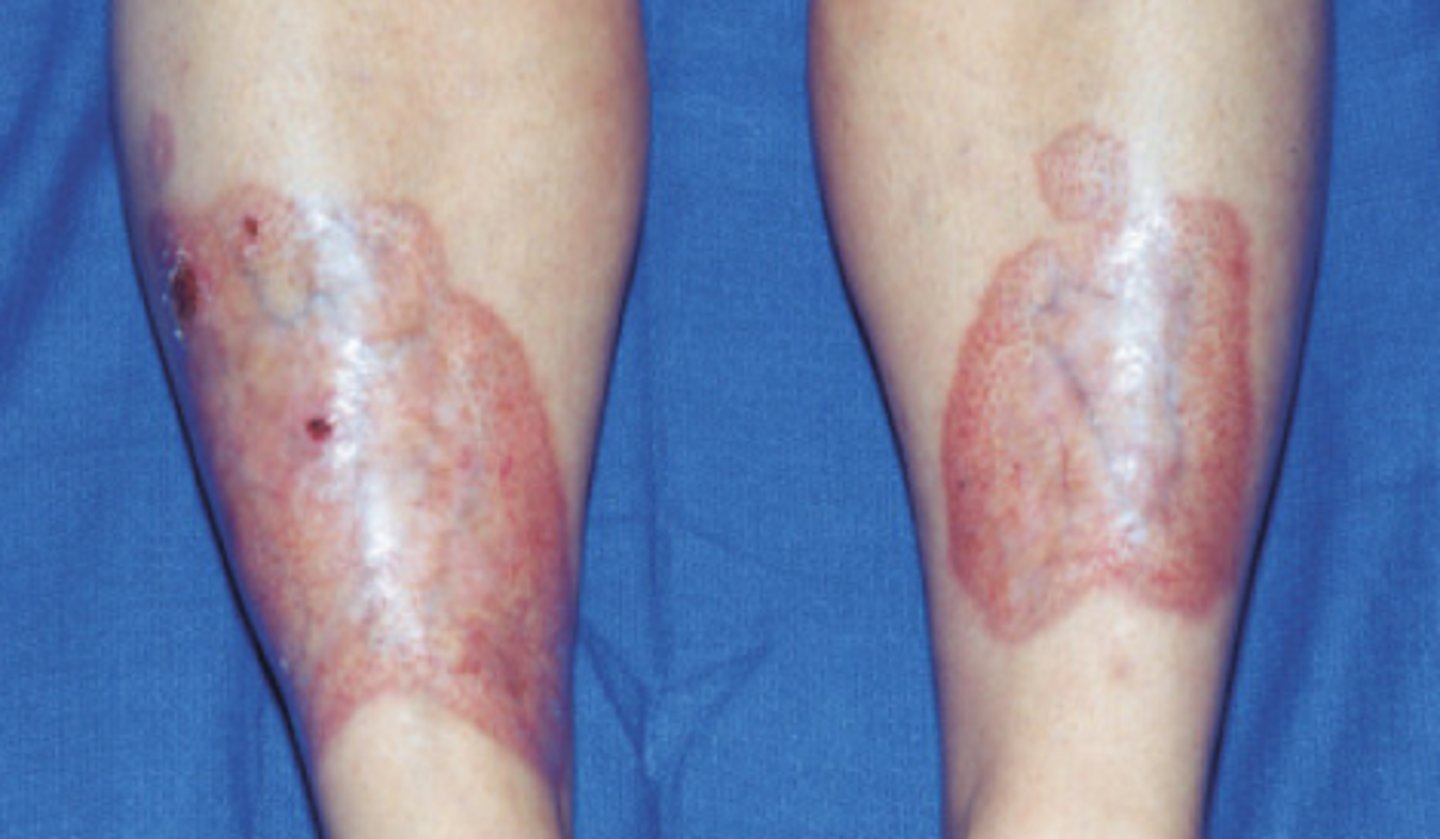
Necrobiosis lipoidica
What is the diagnosis?
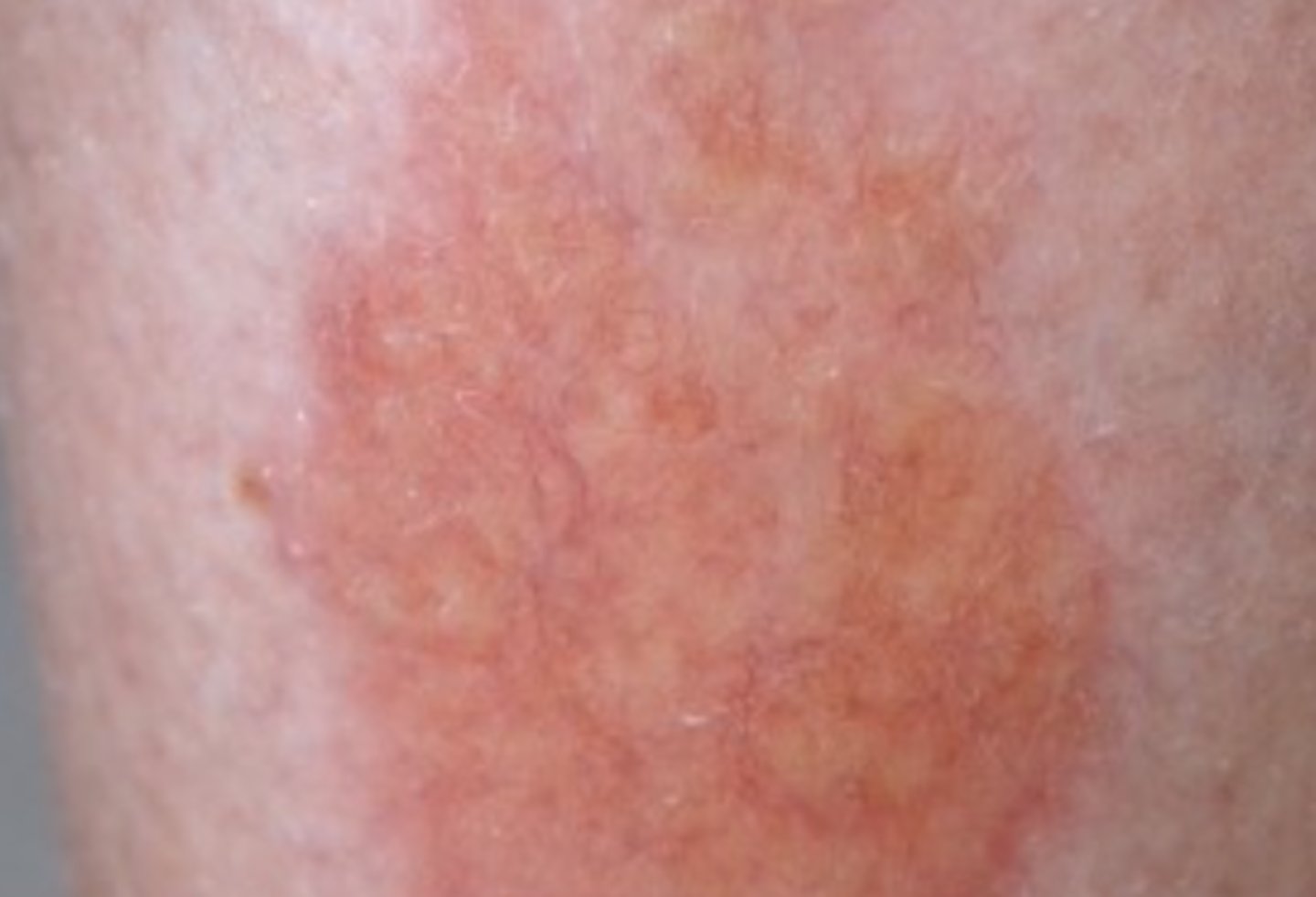
Necrobiosis lipoidica
What is the diagnosis?
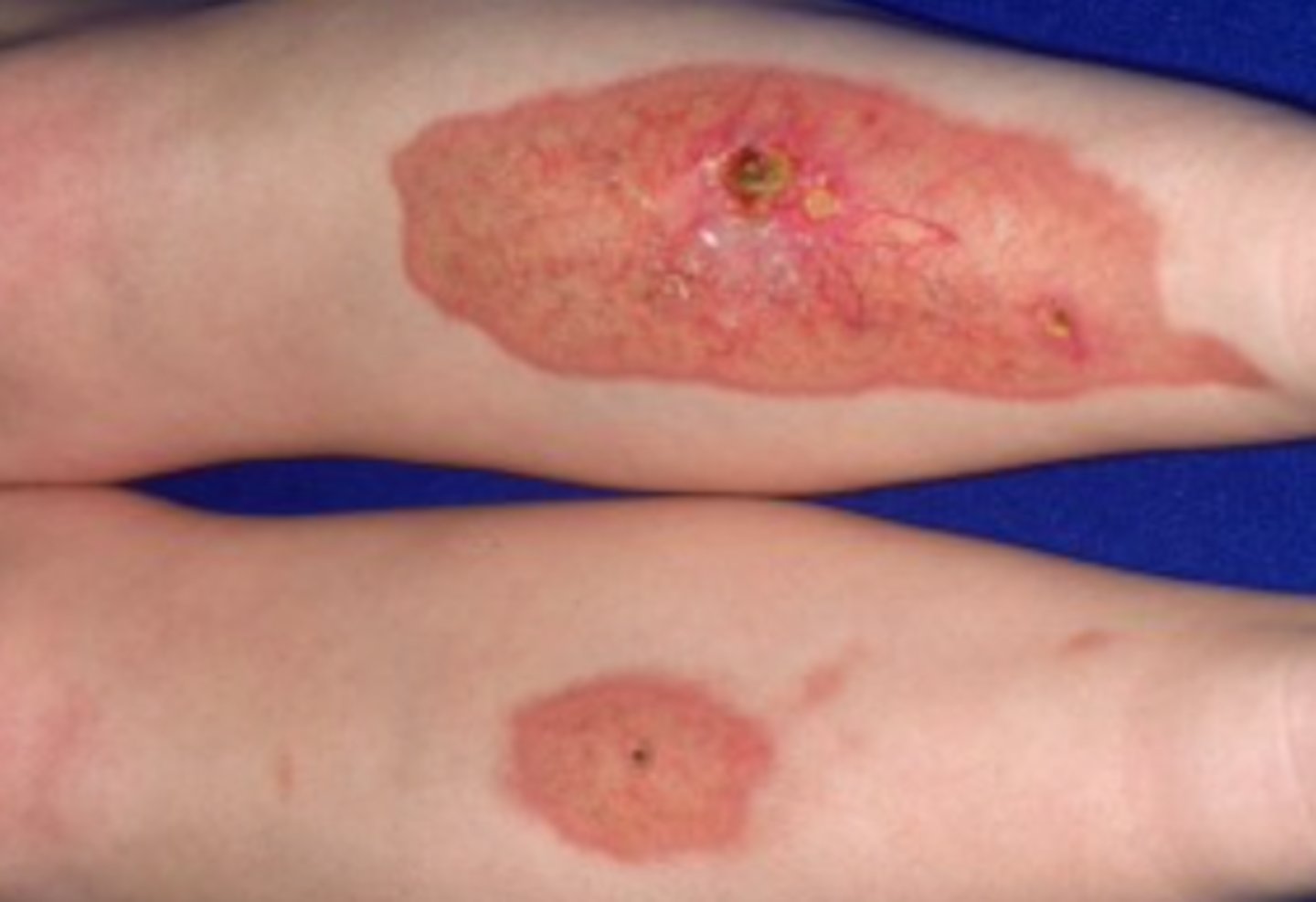
Necrobiosis lipoidica
What is the diagnosis?
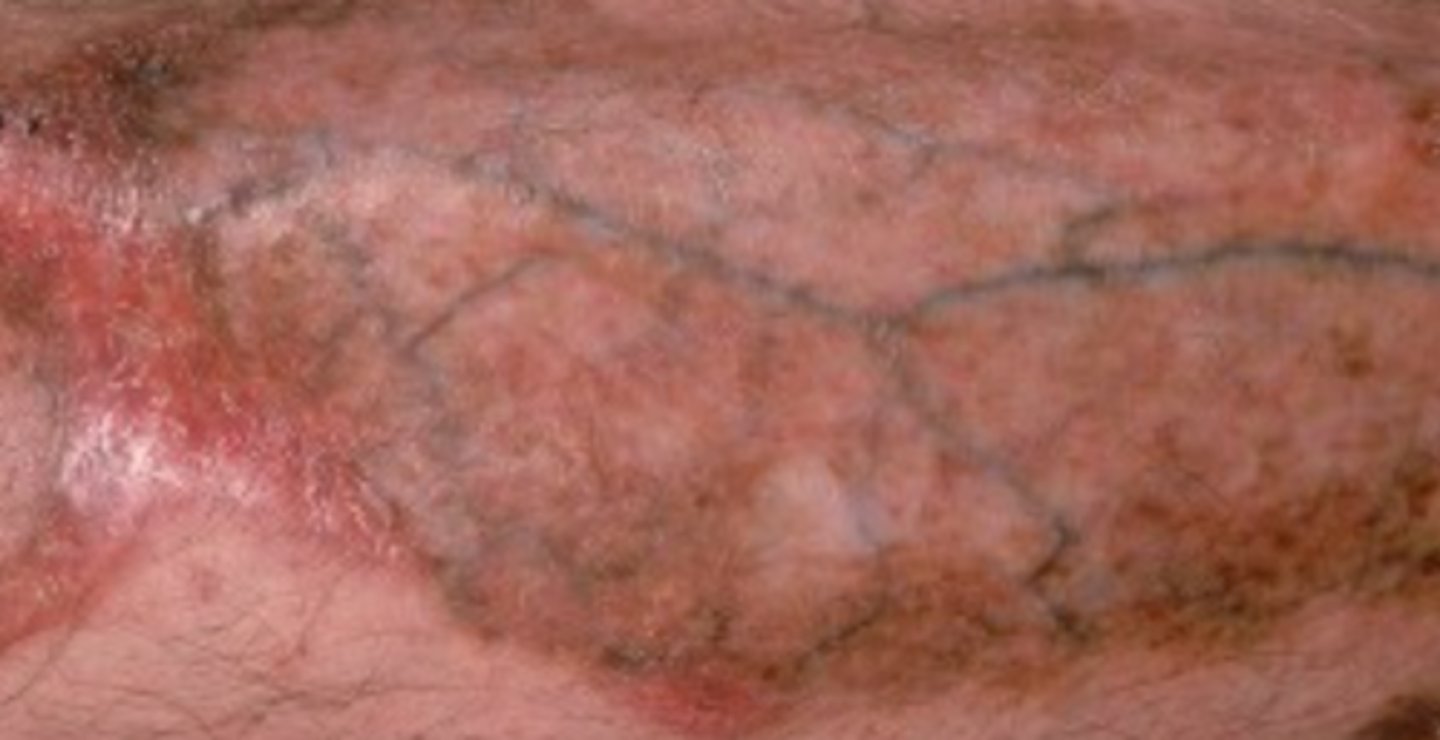
- topical and intralesional steroid
- pentoxifylline (Trental)
- diabetes screening
Tx of necrobiosis lipoidica?
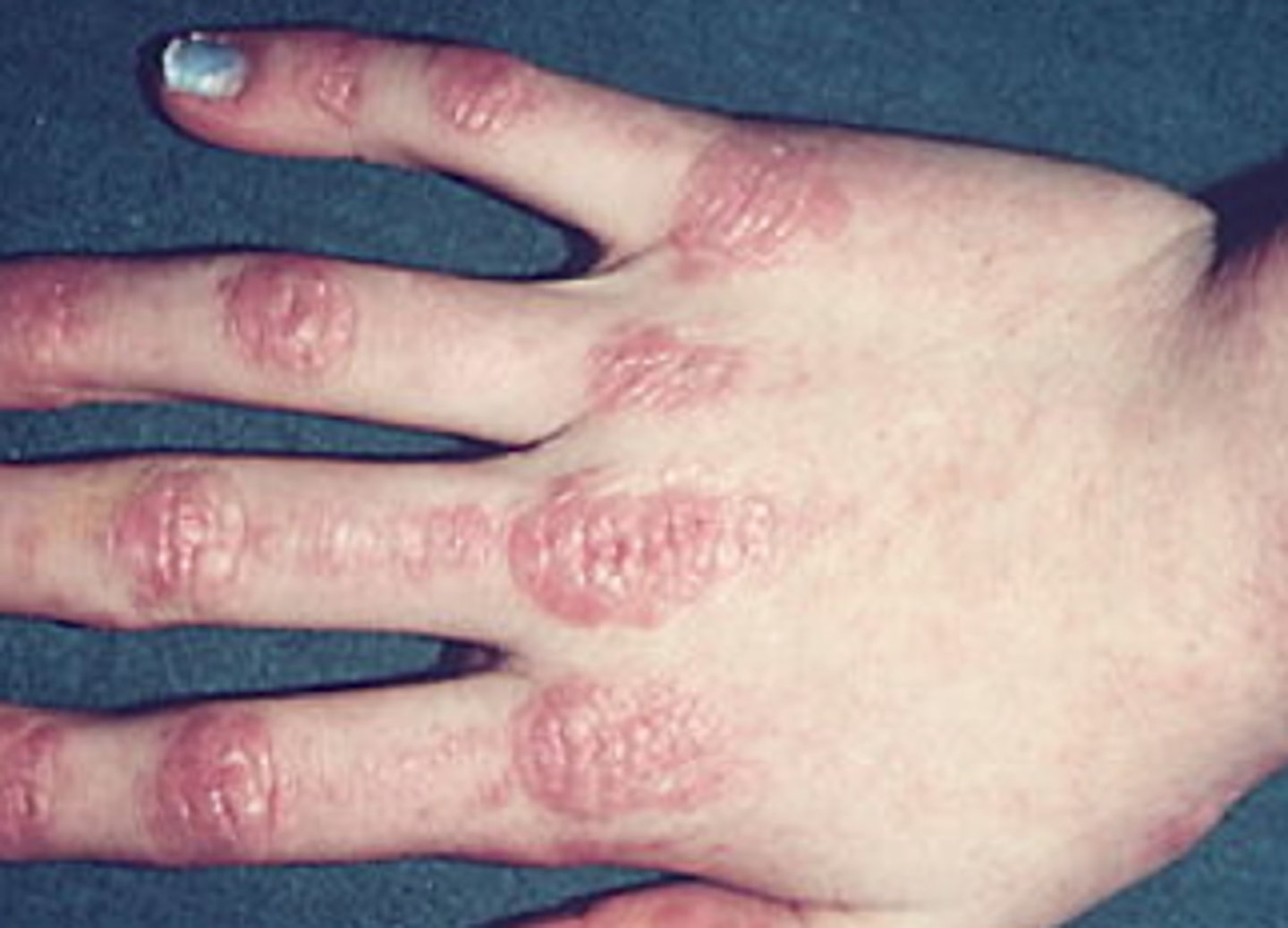
Acanthosis nigricans
asymptomatic velvety rash of flexural skin, neck, axilla and groin
insulin resistance
Onset of acanthosis nigricans is associated with ___
internal malignancy
Sudden onset, extensive or atypical distribution (perioral, mucosal, palms) acanthosis nigricans should have evaluation for ___
- not required
- 12% lactic acid cream
- urea cream
- tretinoin
- salicylic acid
Tx for acanthosis nigricans?
Puetz-Jeghers syndrome
What is caused by a mutation of the STK11/LKB1 gene?
Puetz-Jeghers sydrome
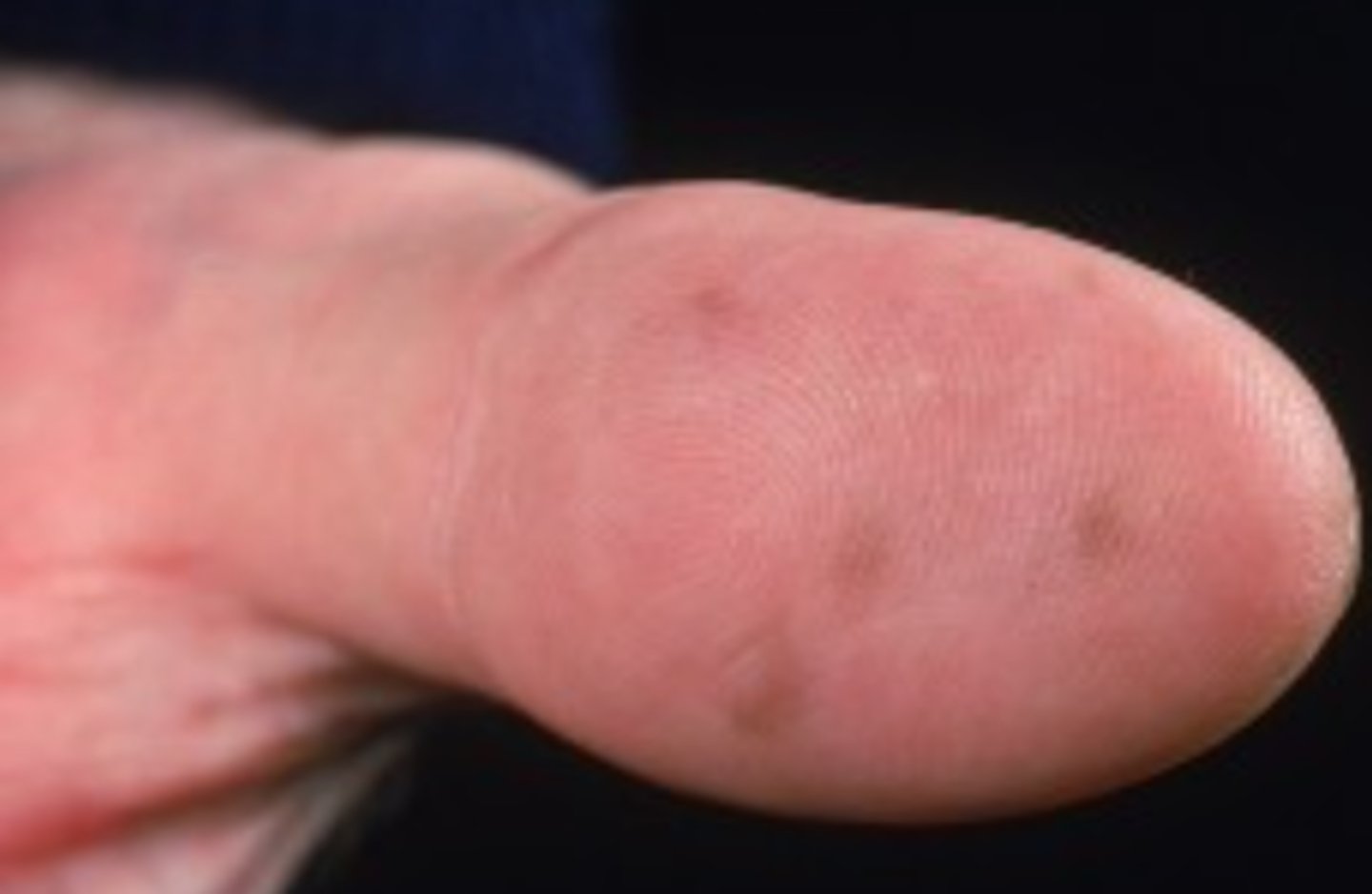
Mucocutaneous pigmented macule of the mouth, lips, eyes, nose, hands, feet and anus
Puetz-Jeghers syndrome
What is the diagnosis?
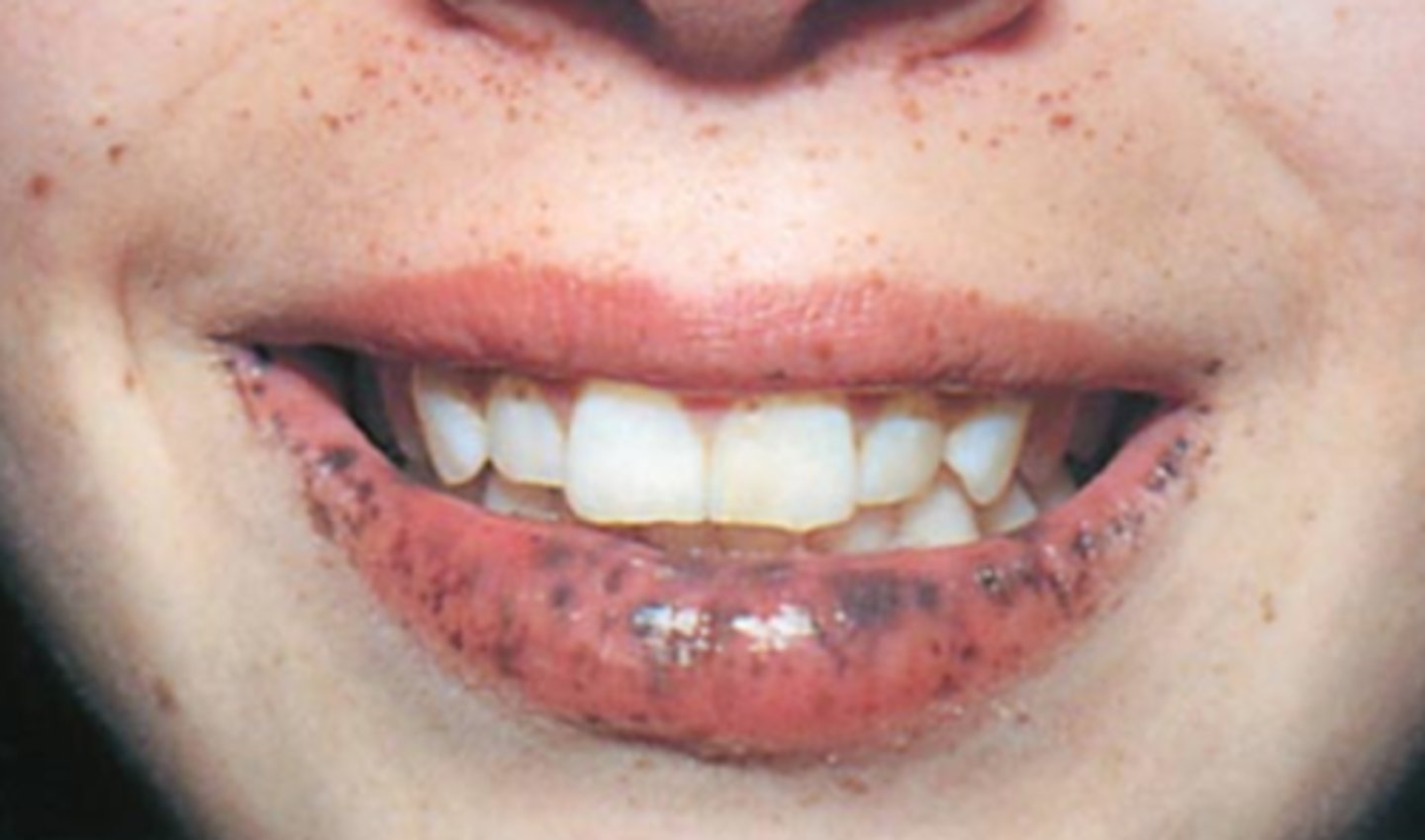
Puetz-Jeghers syndrome
What is the diagnosis?
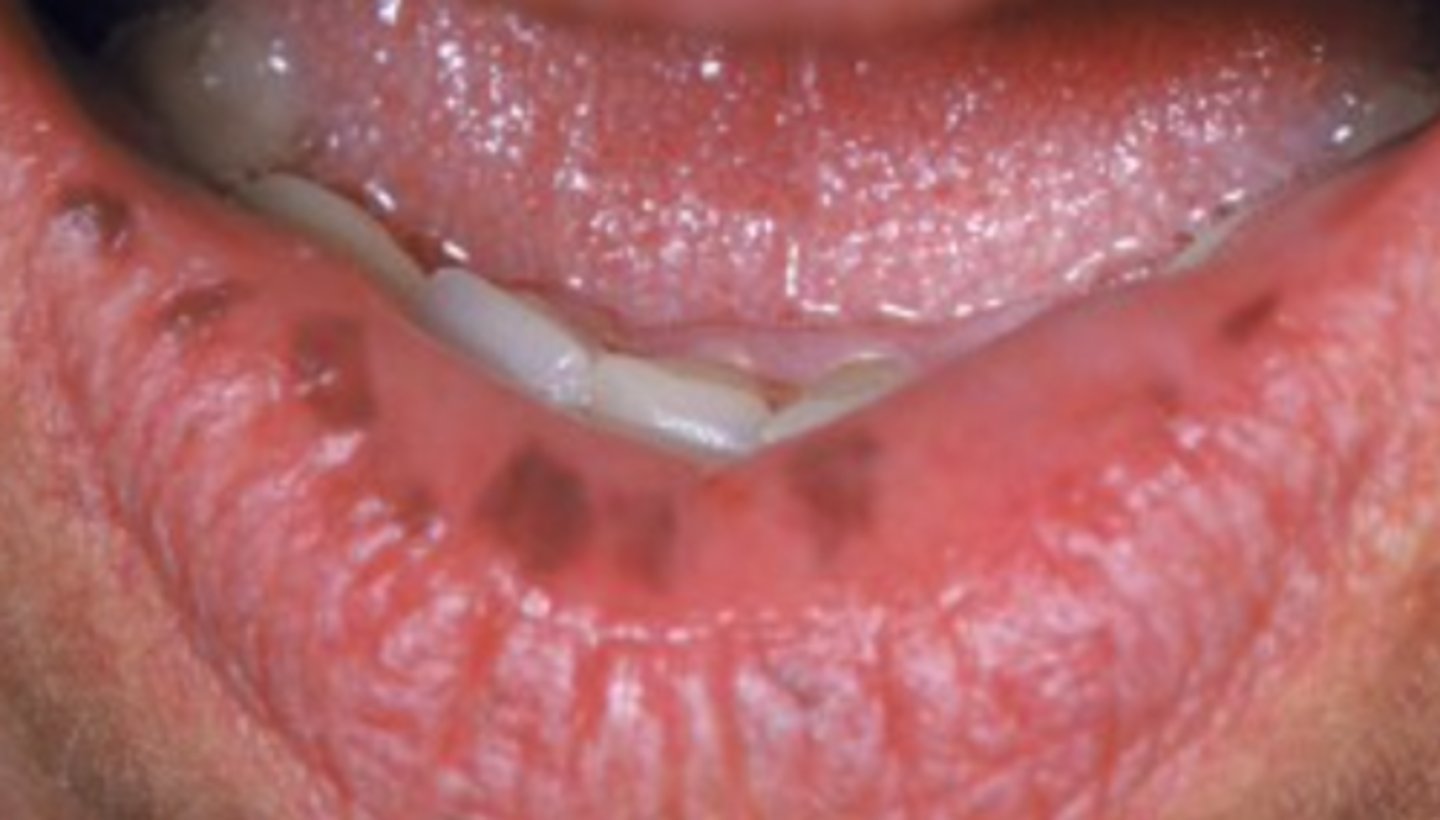
Puetz-Jeghers syndrome
What is the diagnosis?
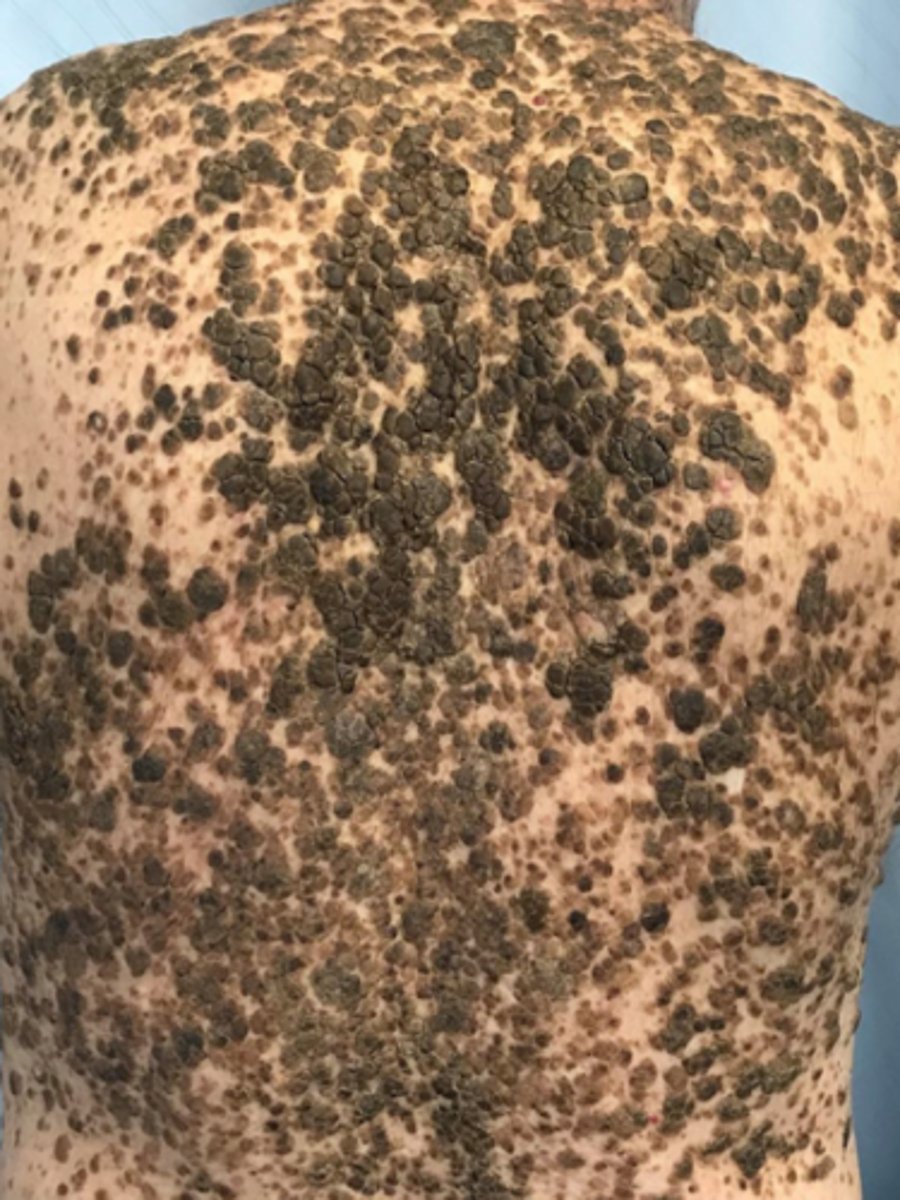
Sign of leser trelat
Sudden appearance or sudden increase of seborrheic keratosis
Gastrointestinal adenocarcinoma
Which diagnosis is most common in sign of leser trelat?
Colon, ovaries, cervix, breast, lung, pancreas, and stomach
Patients with Puetz-Jegher are more at risk for which types of cancer?
Sign of leser trelat
What is the diagnosis?
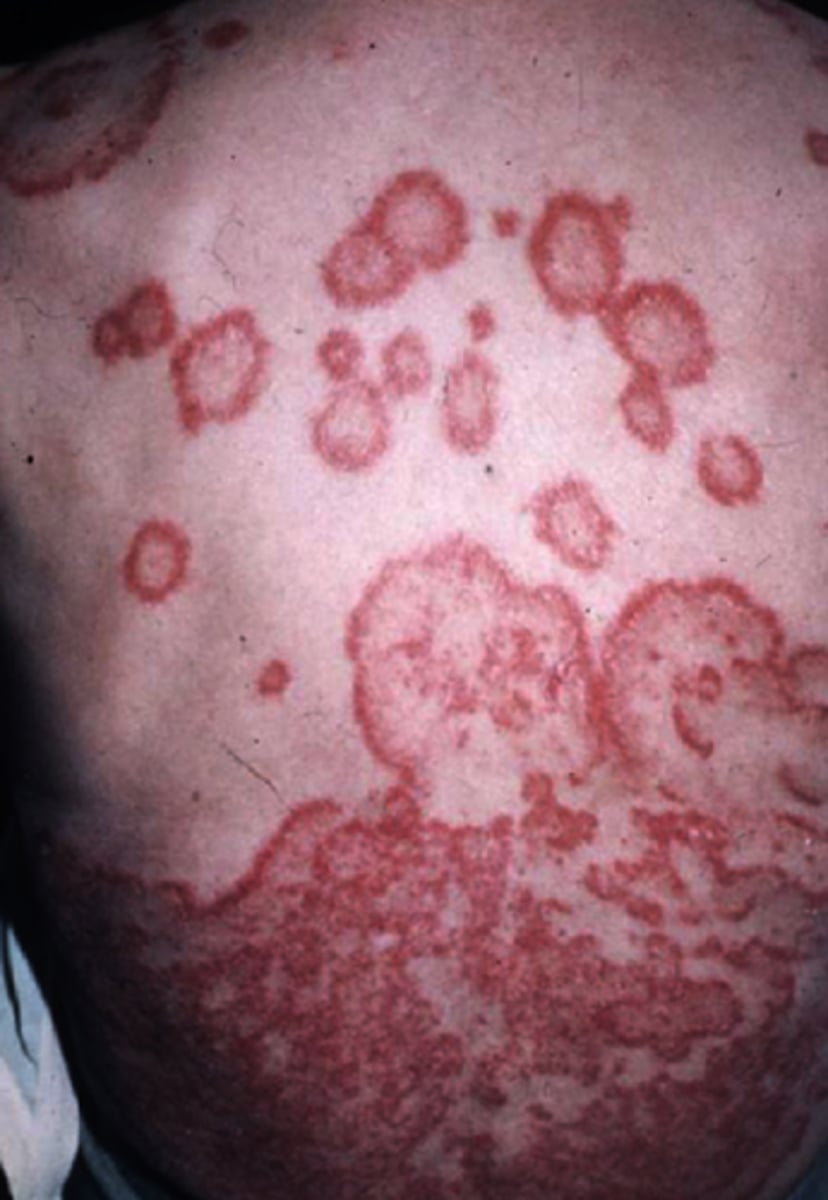
Erythema Repens Gyratum
Pruritic, erythematous, annular eruption with edges that advance at a rapid rate (~1cm)
erythema repens gyratum
Around 70-90% of people with ___ have underlying malignancy (lung cancer m/c)
Erythema repens gyratum
What is the diagnosis?
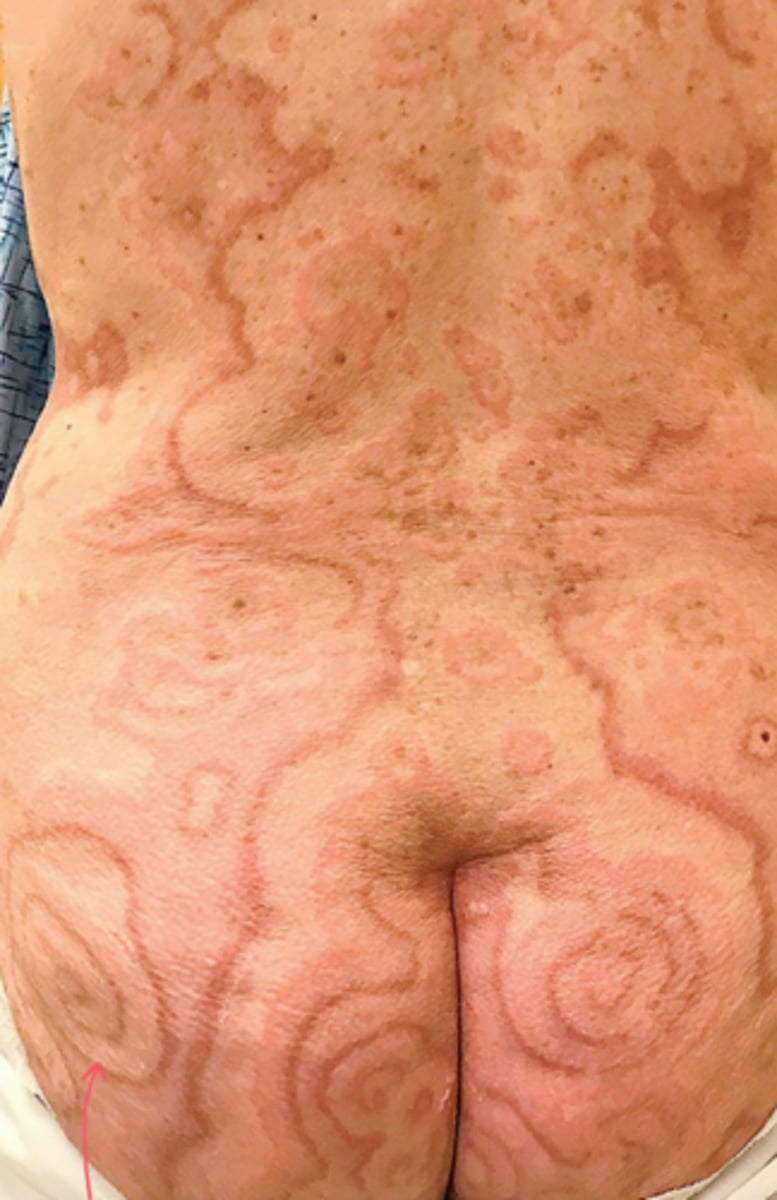
Erythema repens gyratum
What is the diagnosis?
Essential pruritis
Generalized idiopathic itching without any primary lesions
Essential pruritis
Incidence of ___ is often exacerbated by harsh soaps and lack of moisturization
subclinical primary dermatitis
If topical steroids alleviate essential pruritis, it is suggestive of ___
- young with well moisturized skin
- failing to respond to gentle skin care and topical steroids
Underlying systemic issues should be suspected in essential pruritis if patient is ___
- liver disease/biliary obs
- renal disease
- thyroid disease
- anemia
- viral disease
- hematologic malignancy
Common etiologies of essential pruritis?
neurological cause
Focal pruritis without primary lesions is indicative of ___
lymphoma
Genital pruritis without a known cause can be a sign of ___
- CBC
- CMP
- TSH
- Iron studies
- Vit D
Workup for essential pruritis?
HIV/AIDS
Dermatoses with unusual or severe presentations or failure to respond to typical therapies should raise suspicion for___
viremia and can have visceral involvement
disseminated herpes zoster suggests
HIV/AIDS infection
Severe/erythrodermic or recalcitrant psoriasis is suggestive of ___
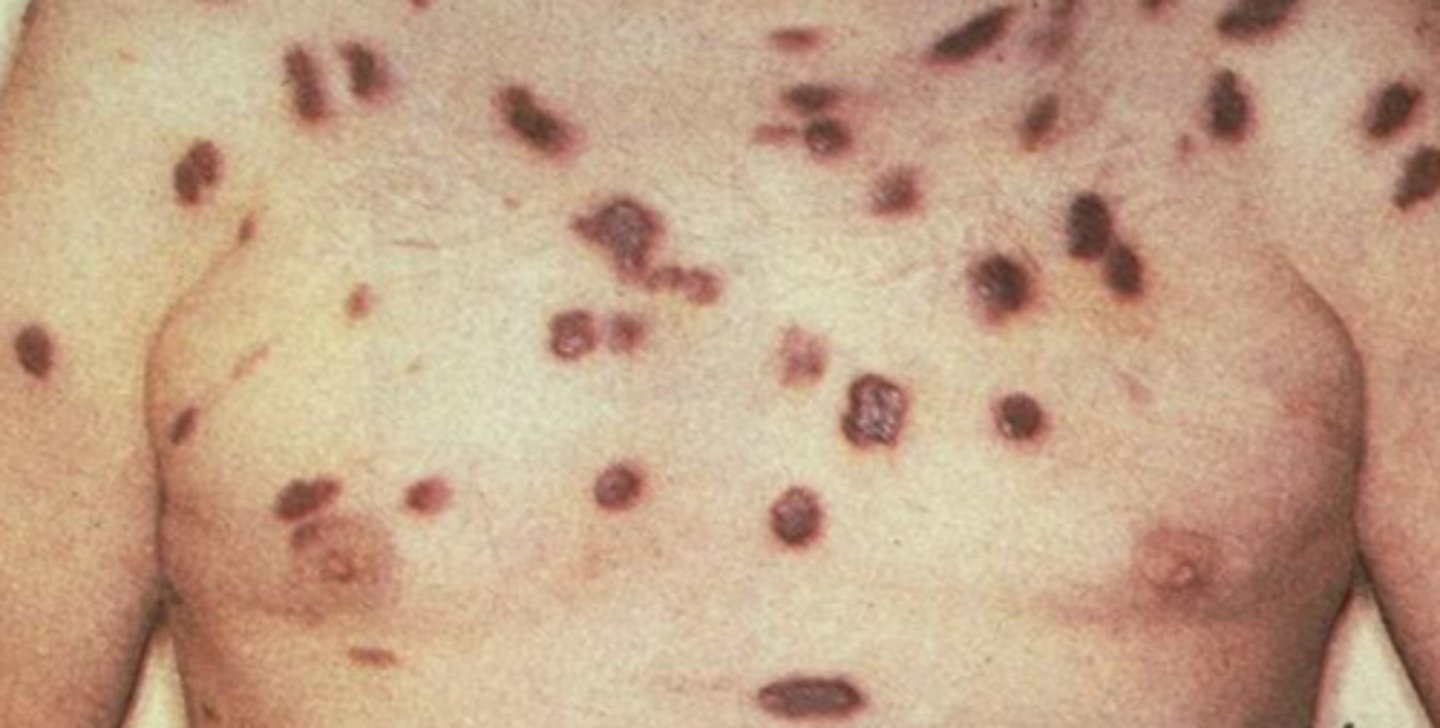
HHV 8
What causes Kaposi Sarcoma?
Kaposi Sarcoma
40% of men with aids develop ___
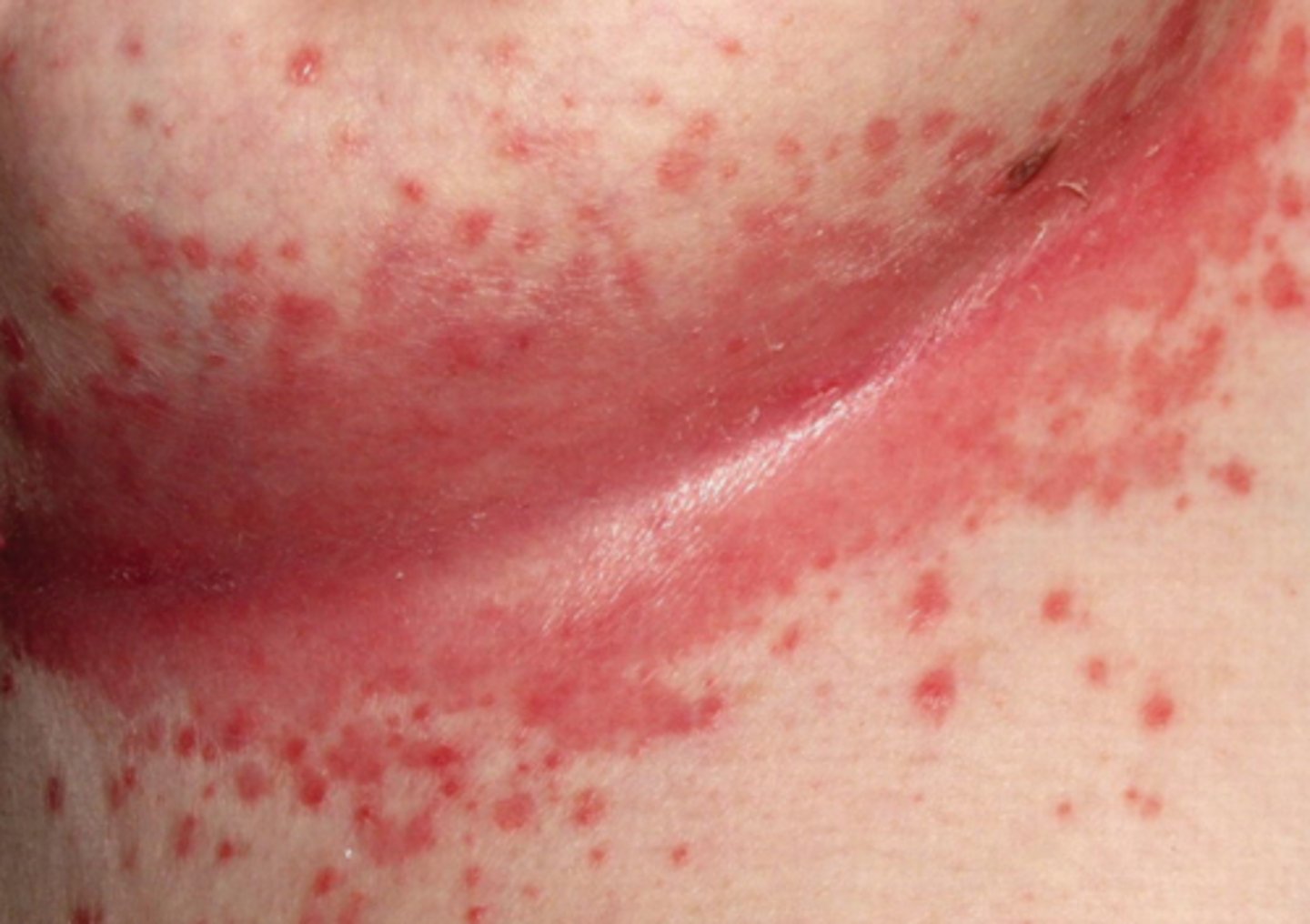
Candidal intertrigo
What is the diagnosis?
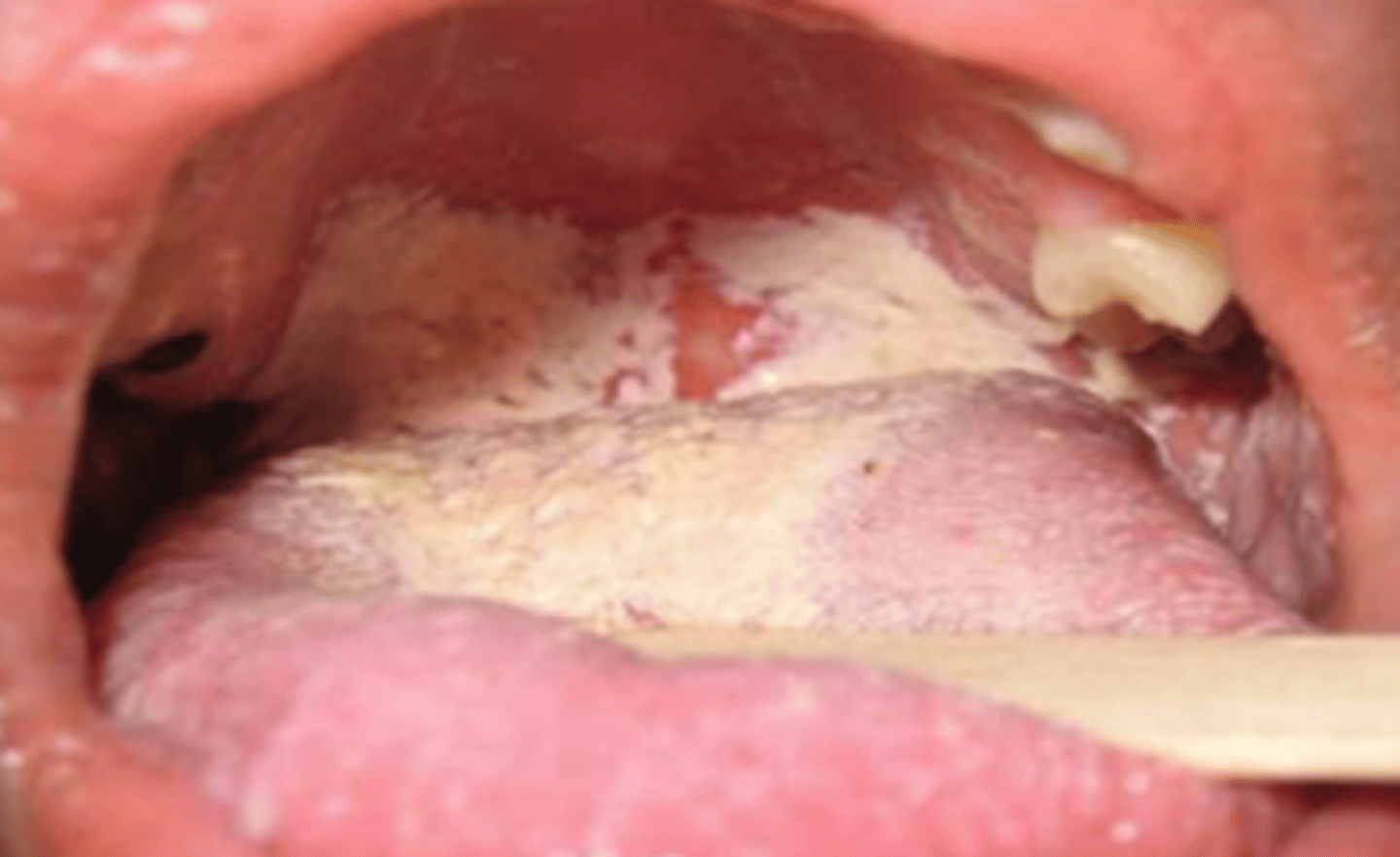
Thrush
What is the diagnosis?
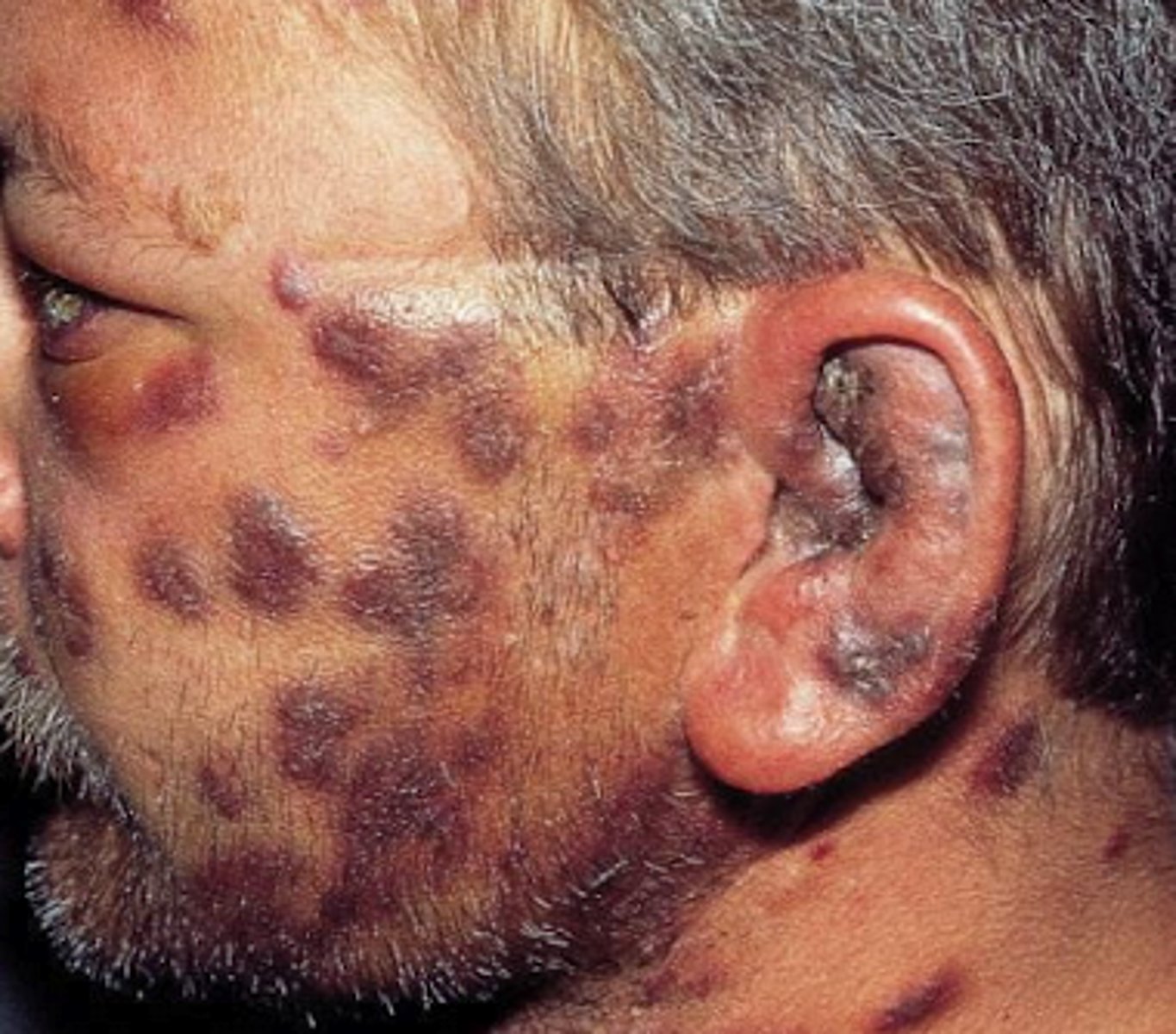
Kaposi Sarcoma
What is the diagnosis?
Kaposi Sarcoma
What is the diagnosis?
- punch biopsy
- HIV testing
- oncology and infectious disease
Tx of Kaposi Sarcoma