Heavy Metals - Mercury
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
What is mercury pollution?
Mercury is a persistent, bioaccumulative, toxic pollutant.

Mercury Properties
• Neurotoxicity.
• Liposolubility.
• Bioaccumulation.
• Biomagnification
How is mercury released into the environment?
- Disposal of items containing mercury, like batteries, thermometers, etc
- Chemical plants that produce chlorine using mercury electrodes
- Combustion of coal
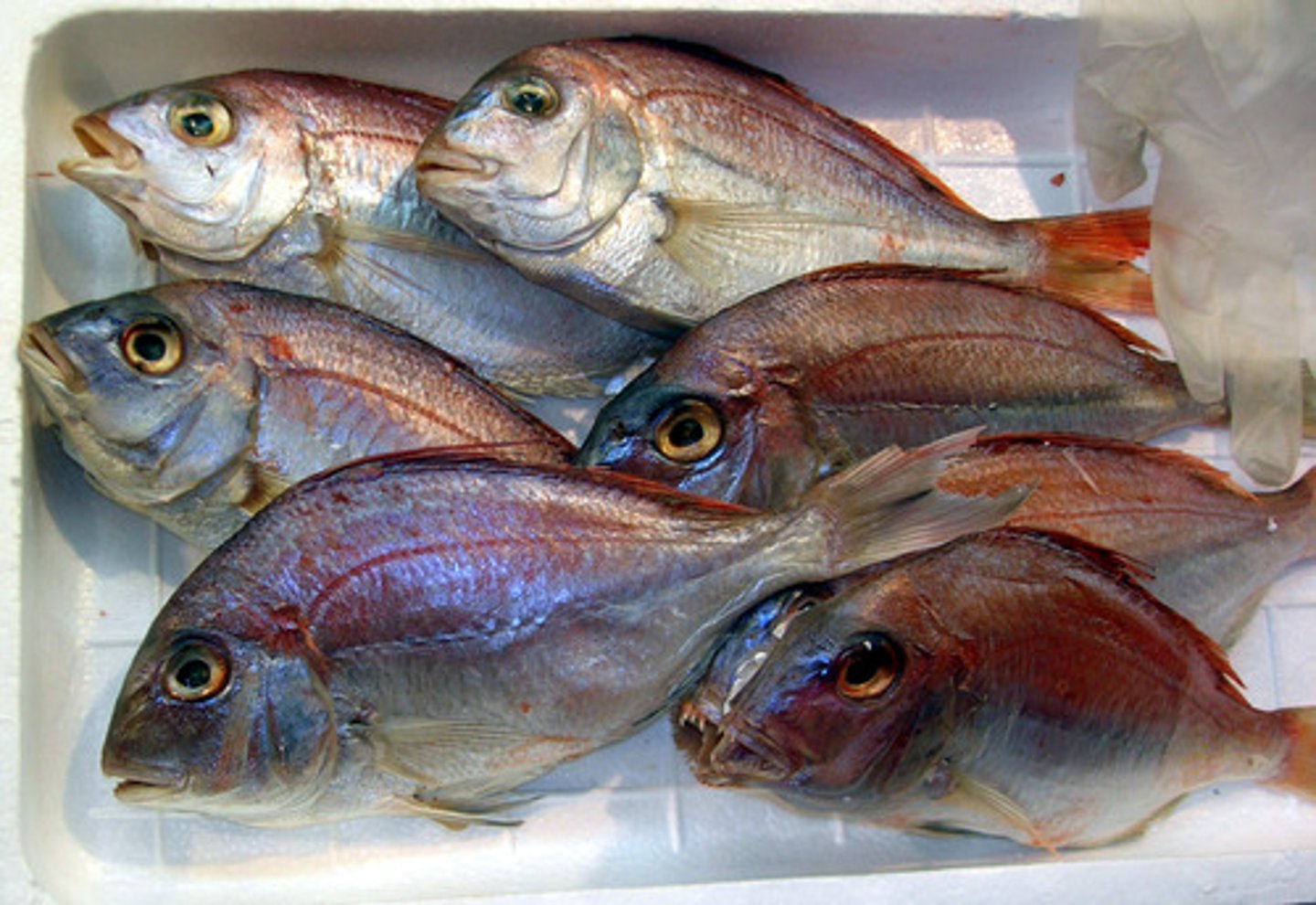
Types of Chemical forms of Mercury
- Elemental mercury
- Inorganic mercury
- Organic mercury
Example of an Inorganic Mercury compound
Mercury Oxide
Example of an Organic Mercury compound
Methyl Mercury
Liquid (elemental) Mercury
- It is not easily absorbed through the skin or gut
- Vapours may be absorbed in the lungs if they are inhaled

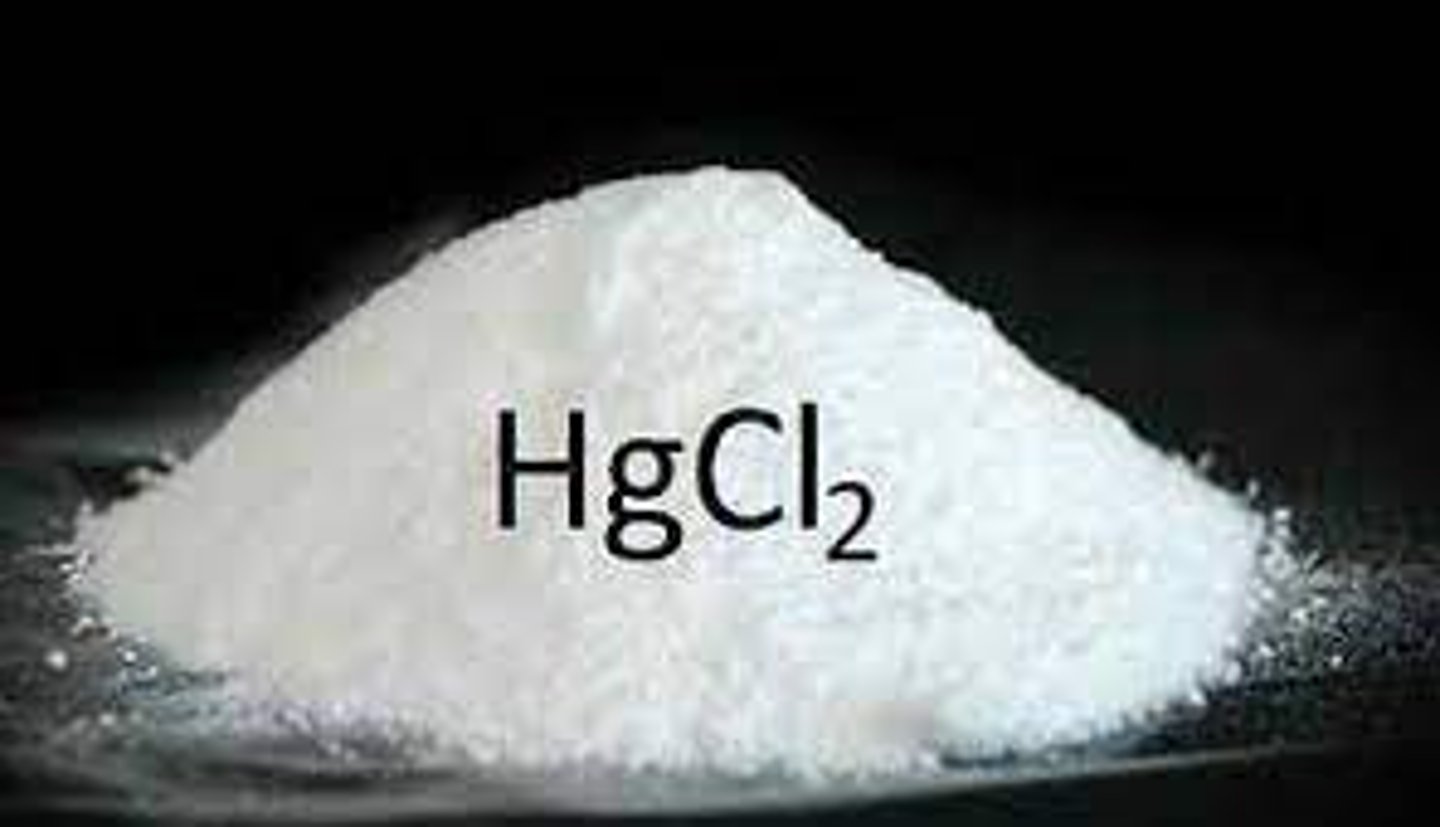
Inorganic Mercury Compounds
- An example would be Mercury Oxide (HgO)
- They are absorbed moderately well in the gut

Organic Mercury Compounds
- An example would be Methyl Mercury (CH₃Hg)
- Are easily absorbed through the skin, by the gut, and as vapours if inhaled
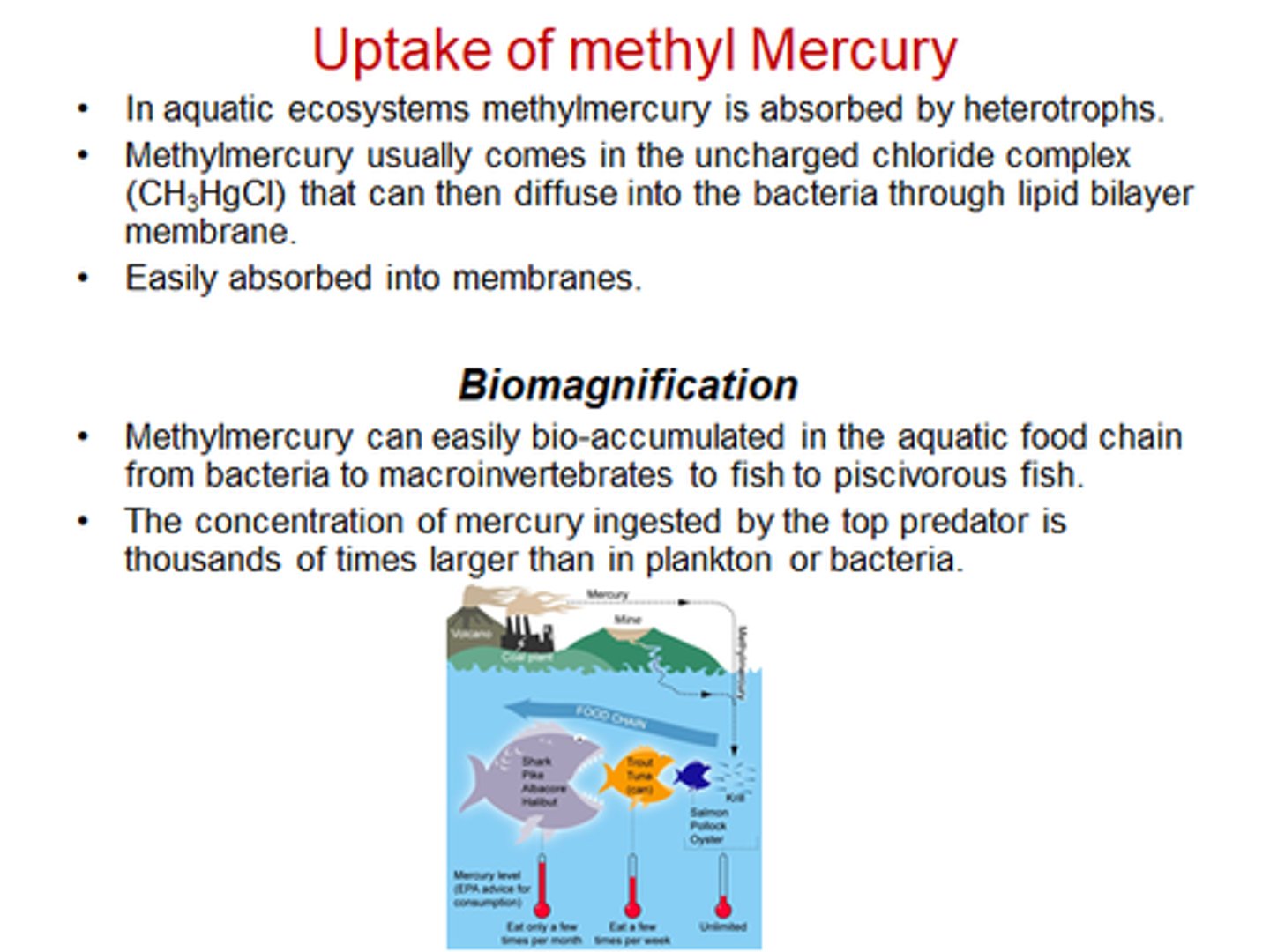
Why are organic mercury compounds dangerous?
They are liposoluble, so can pass through cell membranes easily, including through the blood-brain barrier into the brain, where the impacts can be more serioues.
It can also cross the placenta and harm unborn babies.
Also causes kidney damage.
Why are even low toxicity inorganic mercury compounds still having severe pollution impacts?
1) Relatively low toxicity inorganic mercury compounds enter anaerobic sediments in lakes or the sea
2) They may then be changed into organic compounds (such as methyl mercury) by anaerobic microbes.
3) The mercury then bioaccumulated and biomagnifies along food chains
4) It often reaches concentrations that are much higher than when it was released into the environment.
How to control mercury pollution?
- Replacing mercury thermometers with electronic thermometers
- Using reverse osmosis or activated carbon filters to remove mercury from effluents
- Ion exchange filters
- Disposal at high pH to reduce solubility