Dermatology Lecture 4 - Last half
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
73 Terms
What is another term for herpes zoster?
Shingles
What viral infection is caused by the decline of T cell mediated immunity to VSV (probably VZV, varicella-zoster virus, basically meaning what disease is causes by the weaking of immunity against it)?
Herpes Zoster
What is the more common name for the varicella virus?
Chicken pox
The varicella virus (chicken pox) reactivates due to cold, stress, age, and medical conditions, leading to herpes zoster
True or False
True
Symptoms of herpes zoster include unilateral (one-sided) pain and vesicular lesions limited to a dermatome
True or False?
True
Pain, burning, and/or itching often precedes what in herpes zoster 1-5 days later
Rash
Herpes Zoster is presented as a cluster of vesicles of varying sizes
True or False?
True
What do lesions not cross on the body when involving herpes zoster?
Midline
Lesions continue to develop for how many days and then scab over in approximately how many days in herpes zoster
True or False?
3-5 and 10
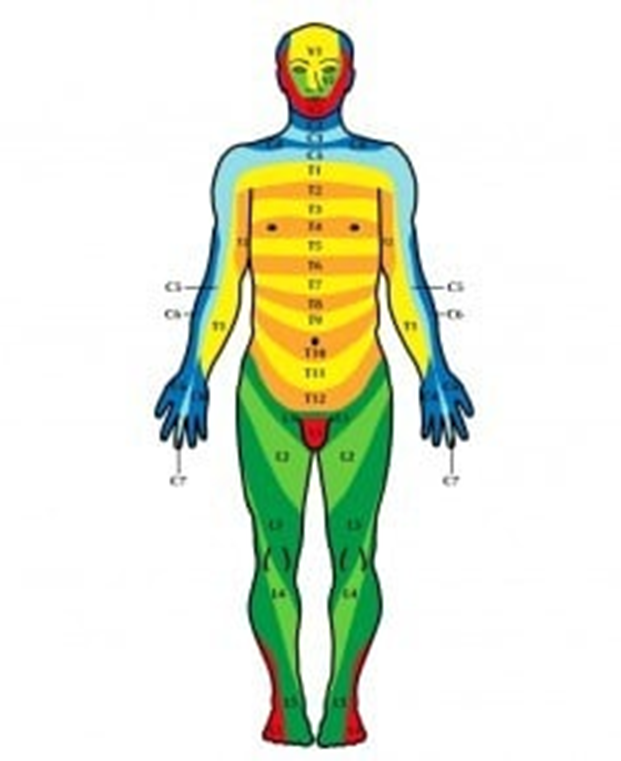
What is this a map of (This is also the lines that herpes zoster are limited to)
Dermatome
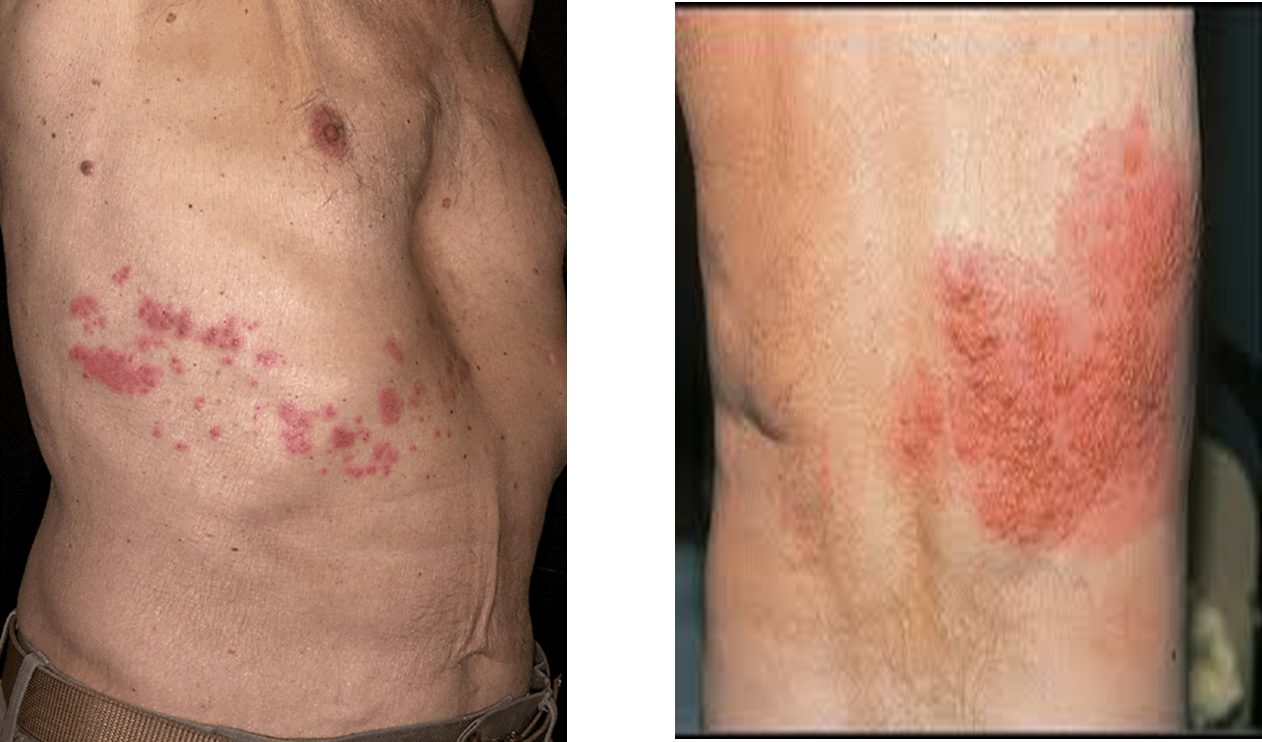
What is the infection?
Herpes zoster
What mediations are used to treat herpes zoster (the slides are wrong with spelling and I have the correct spelling, but the first one is correctly spelled by me and slides)?
Acyclovir, valacyclovir, and famciclovir
What is the strength, frequency, and for how long are medication used for herpes zoster?
800 mg 5 times a day x 7 days
What is herpetic neuralgia?
Pain along the nerve
Medications should be given for herpes zoster within 72 hours to prevent post-herpetic neuralgia and shorten the course
Ture or False?
True
Topical cream, Tylenol, Advil, and narcotics are used for pain management for herpes zoster
True or False?
True
When herpes zoster effects the nerves leading to the eye what is it called?
Herpes zoster ophthalmicus
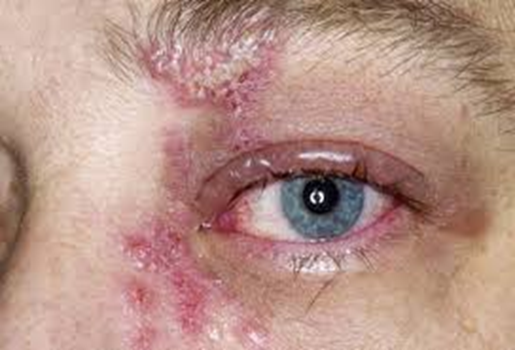
What specific kind of herpes zoster is this?
Herpes zoster ophthalmicus
What does Ramsay-hunt syndrome mean the herpes zoster virus affected?
Facial nerve
How long can post herpetic neuralgia pain (the most common complication of herpes zoster) last after lesions resolve?
Over 3 months
What increases the risks of herpes zoster?
Age
When herpes zoster effects the brain and spinal cord what is the term?
Encephalitis
What is another name for Ramsay-Hunt syndrome?
Herpes Zoster Oticus
Ramsay-Hunt syndrome (Herpes zoster oticus) can cause paralysis and hearing loss in the affected ear
True or False?
True
What shows a 91% prevention rate against herpes zoster (the slides say strigntax, which is the old )?
Shingrix
What is recommended by CDC for patients over 60 for routine immunization (what shingrix is)?
Shingles vaccine
The shingles vaccine (shingrix) helps reduce the risk of developing shingles and post-herpetic neuralgia
True or False
True
Vaccination against what other disease helps prevent herpes zoter?
Varicella
What is the name of the superficial fungal infection?
Fungal skin disease
Superficial fungal infections (Fungal skin disease) are the most common of mucocutaneous infections
True or False?
True
What are the 2 common groups of fungal skin disease?
Dermatophytes and Candida
What type of fungal skin disease is characterized by a unique fungi that infects nonviable keratinized cutaneous structures?
Dermatophytes
What is another name for dermatophytes?
Tinea
Dermatophytes (Tinea) are classified by their site of infection
True or False?
True
What type of dermatophytes (tinea) presents as irregular shaped scaly patches and plaques, often with a raised erythematous border and central clearing?
tinea corporis
Tinea corporis occurs on the trunk, arms, and legs
True or False?
True
Tinea corporis may be a single lesion or multiple lesions
True or False?
True
Tinea corporis and tinea capitis is more commonly referred to as what?
Ringworm
How do you treat tinea corporis?
Topical antifungals
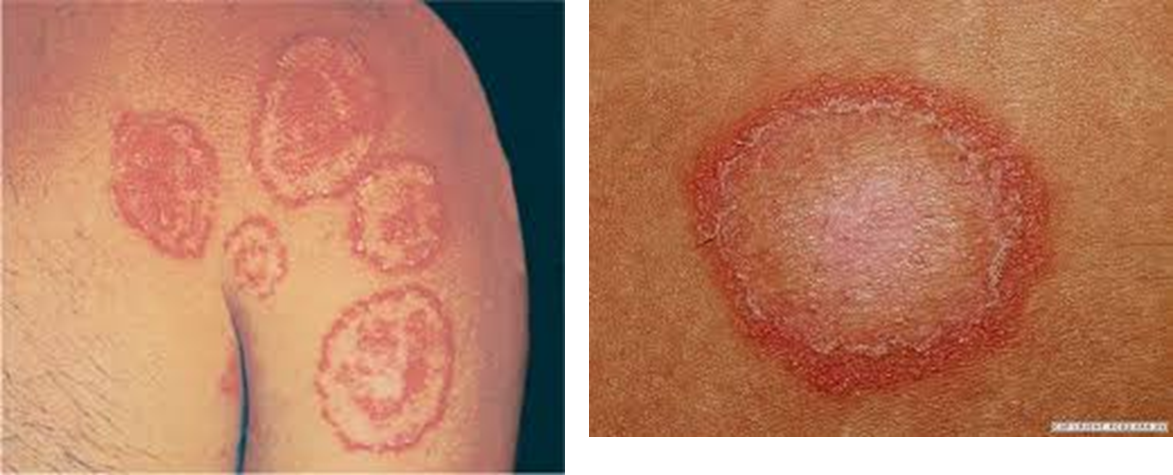
What is this a picture of?
Tinea corporis
Tinea capitis impacts what part of the body?
Scalp
Tinea corporis impacts what part of the body?
Trunk, arms, and legs
Tinea capitis usually effects children from what years?
2-10
Tinea capitis has a wide range of presentation including scaling, broken hair, painful inflammation, and possible scarring alopecia
Ture or False?
True
Alopecia is what?
Hair loss
What is the major treatment for tinea capitis?
Oral antifungals
Topical antifungals are only given if hair is short with small areas affected in tinea capitis
True or False?
True
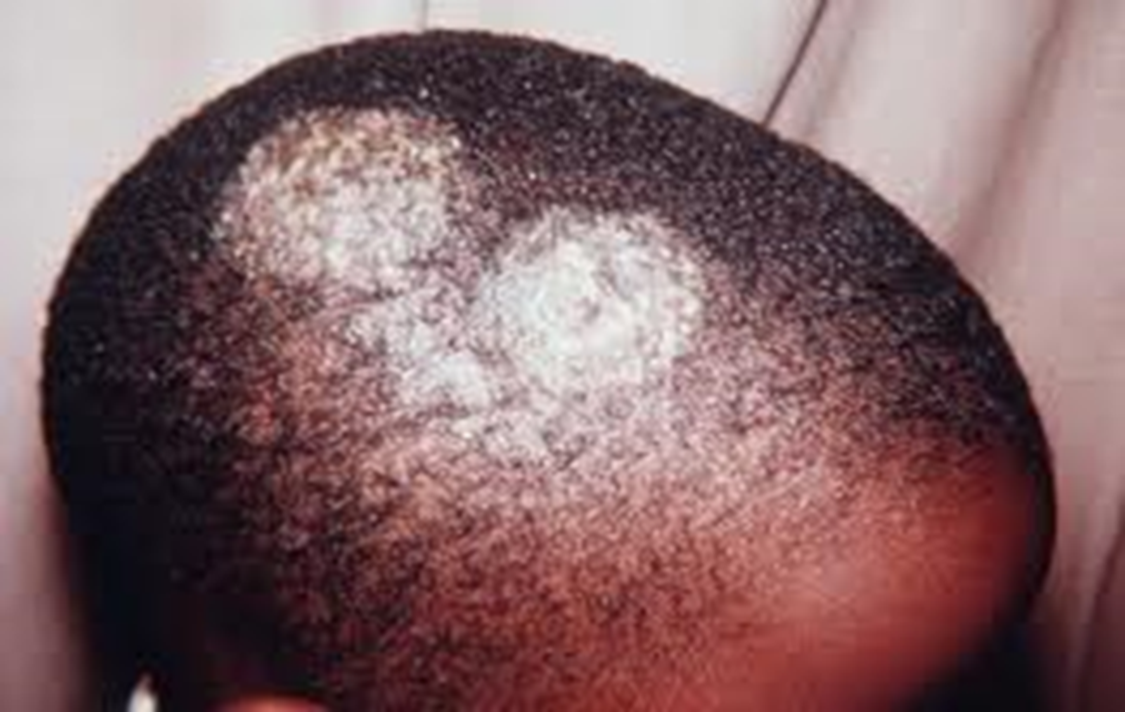
What is this?
Tinea capitis
Tinea pedis effects what?
Feet
Tinea pedis is more commonly known as what?
Athlete’s foot
Tinea pedis (athlete’s foot) is shown by erythema, scaling, erosions, maceration, and/or bullae
True or False?
True
Tinea pedis (athlete’s foot) is asymptomatic, but may be associated with itching
True or False?
True
How do you prevent tinea pedis (athlete’s foot)?
Keep feet dry and shower shoes in public facilities
How do you treat tinea pedis (athlete’s foot)
Topical antifungals
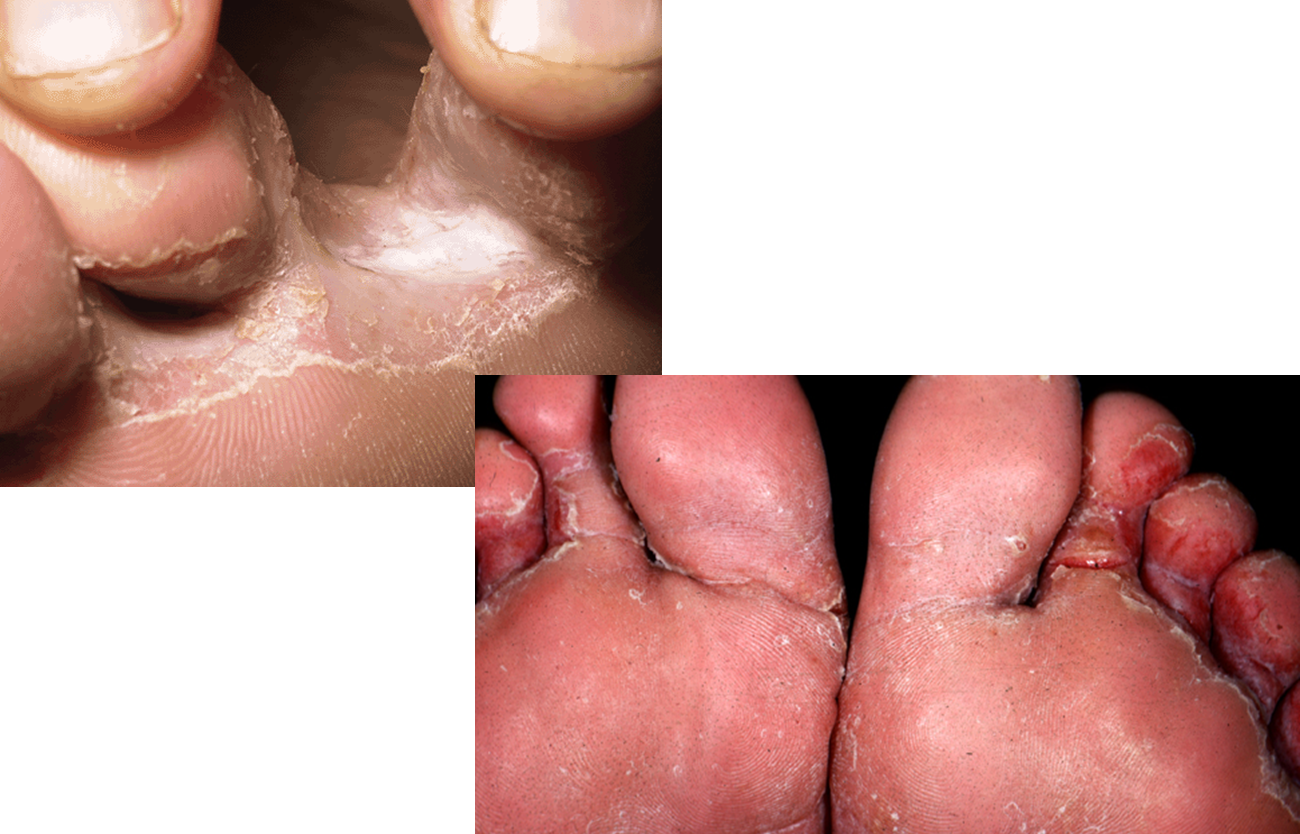
What is this?
Tinea pedis
Tinea cruris (jock itch) effects what?
Groin, pubic regions, and thighs
Tinea cruris is better known as?
Jock itch
In tinea cruris (jock itch), lesions are large, scaling, well-demarcated, and dull red to brown plaques
True or False?
True
Tinea cruris (jock itch) is asymptomatic, but may have mild itching
True or False?
True
Some factors that increase your chance of getting tinea cruris (jock itch) are humidity, tight clothing, and obesity
True or False?
True
What do you use to treat tinea cruris (jock itch)
Topical antifungals
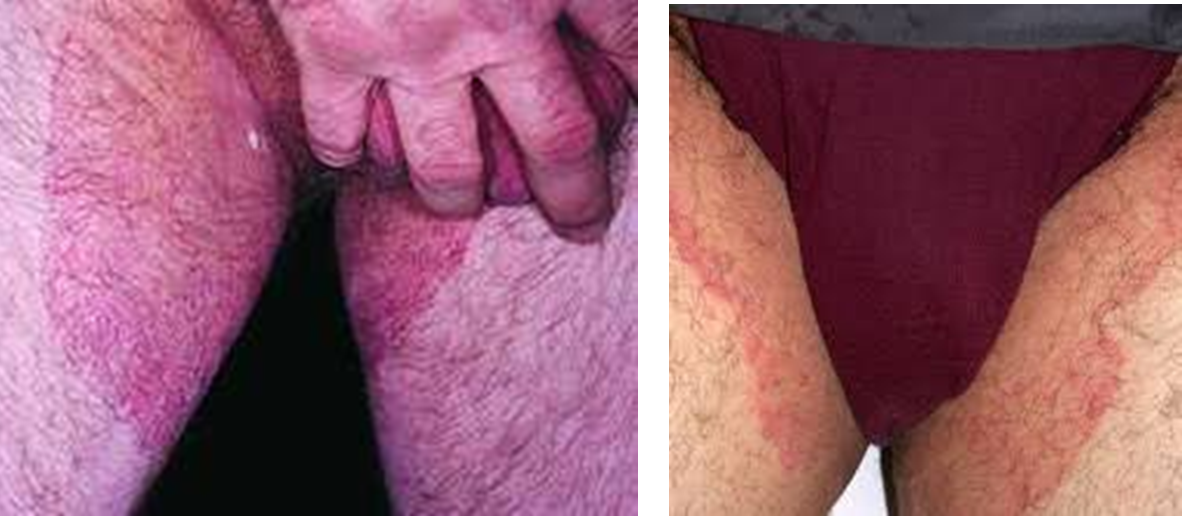
What is this?
Tinea cruris
What is the last five letter for any topical antifungal?
azole
In cases where lesions are large, numerous, or resistant to topical treatment what can be given for Dermatophytosis (tinea)?
Oral antifungals with griseofulvin
Fungal infection caused by yeast are most commonly known as what?
Candida albicans
Candida infection can affect any anatomical structure
True or False?
True
Who is the most susceptible to candida (this is involving those who are very young and very old)?
People with a compromised immune system
What is it called when a candida infection is in an intertriginous area?
Intertrigo
What is an intertriginous area?
Where 2 skin surfaces run together
In intertrigo, a rash begins with vesiculopustular (vesicles and pustules), which rupture, causing maceration
True or False?
True
What medicines are used to treat intertrigo topically?
Nystatin and clotrimazole
What is used to treat candida orally?
Fluconazole (Diflucan)
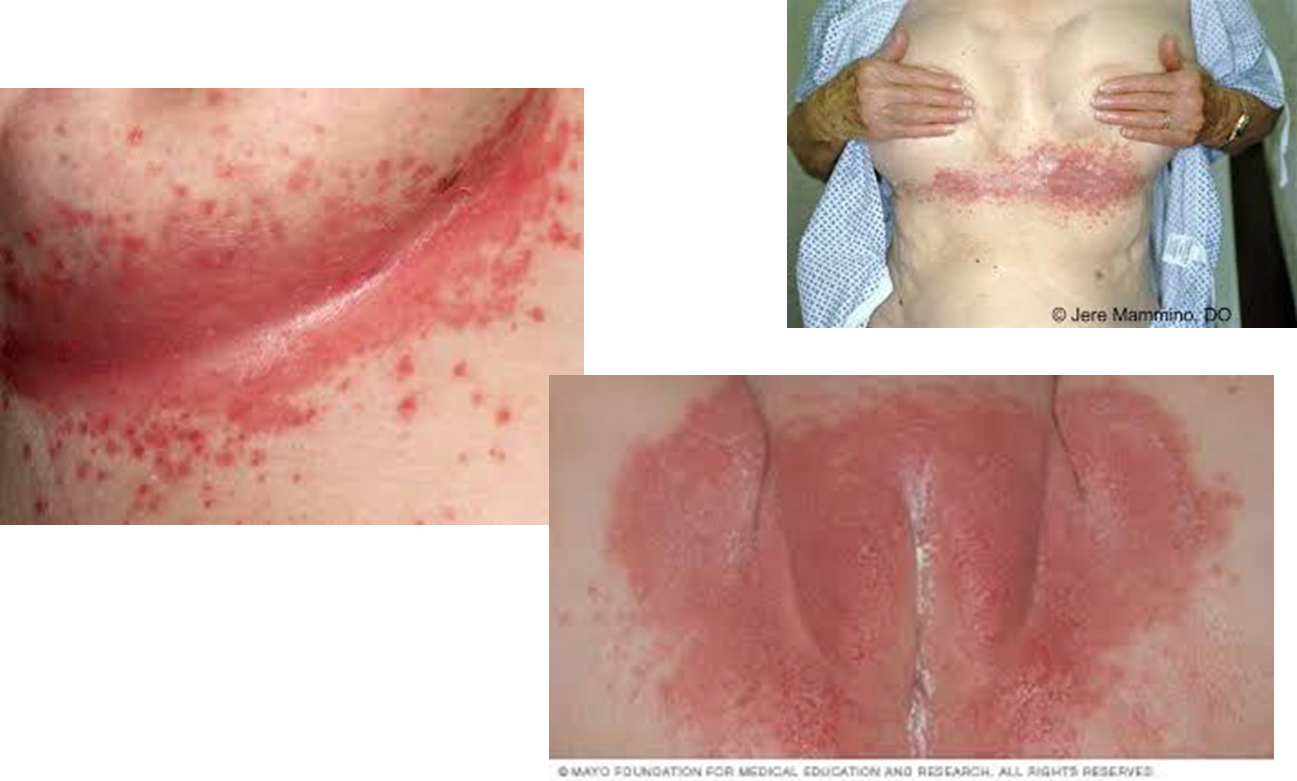
What is this?
Candida