Paper 1: Judicial Precedent (ELS)
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
Judicial
Judges

Precedent
Case that sets a rule
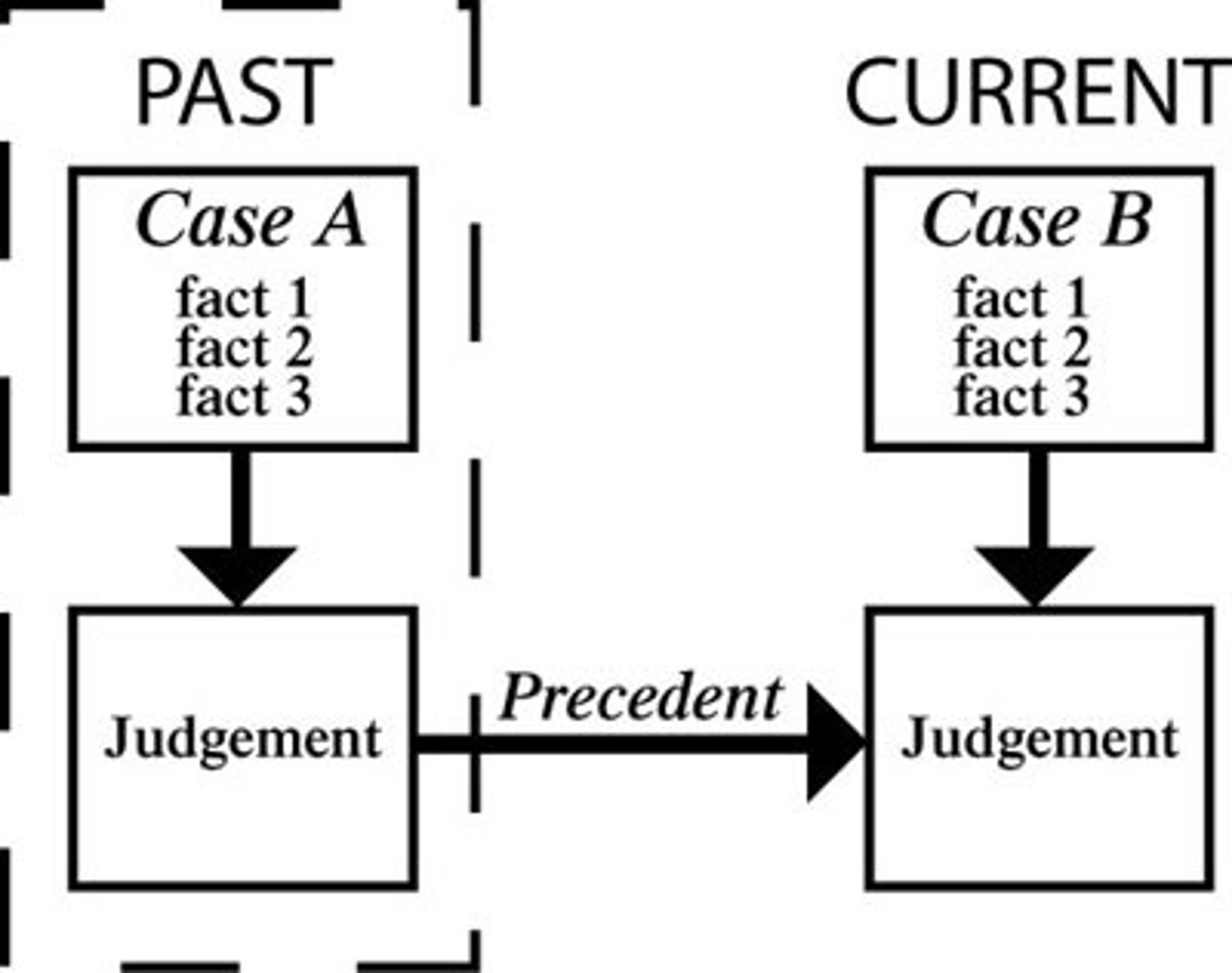
Binding
Permanent link

Reversing
Going back to
Overruling
When a higher court overturns the precedent made by a lower court.
Distinguishing
When a judge in a lower court distinguishes how their case is different from a precedent, so they do not have to follow it.
Doctrine
Theories/Rules/Ideas
What is a law report?
Written records of the judgements at the end of an appeal case, which creates new law.

When and where were law reports introduced?
England and Wales, 1865

Why do we need law reports ?
They explain the rules/law that courts must follow.
Ratio Decidendi Latin meaning
"The reason for the decision"
Ratio decidendi
Legal principle/rationale that underpins a court's judgement.

How is case law a major source of law?
Many more cases than there are acts of parliament.
Stare Decisis: Advantage
Fairness, treats everyone with the same equality and consistency.

Stare Decisis: Disadvantage
Judge may have got it wrong

Which courts are inferior courts?
All courts below Court of Appeal
Can inferior courts create precedents?
No

What does the Supreme Court not have to follow?
Precedents set by Court of Appeal
Types of precedent
- Original
- Binding
- Persuasive
Original Precedent
If a point of law has never been decided before, the decision forms a new precedent (original precedent).

Binding precedent
A previous court ruling that must be followed by courts when deciding a case with similar facts / legal issues.

Case with binding precedent
Donoghue v Stevenson

Persuasive precedent
A judge need not follow this type of precedent, but can be choose to be bound by it.

Ways in which persuasive precedent could happen
- Case from another country
- Case from a lower court
- Dissenting judgment from a lower court
- Choosing to follow judge's speculation in a previous case
Case from another country
E.g. Australia

Case from a lower court
E.g. Supreme Court chooses to follow Court of Appeal

Dissenting judgement from a lower court
E.g. Supreme Court choosing to follow dissenting judge in (Schweppes Ltd).

Choosing to follow the judge's speculation in a previous case
E.g. "This is what I would have done if the situation had been different."

Obiter Dicta Latin meaning
"Other things said"
Obiter Dicta
Everything else said in the judgement

Is Obiter Dicta binding or not binding?
Not binding
1966 Practice Statement
Allows the Supreme Court / House of Lords to depart from a decision "where it appears right to do so."
What court has the same powers as the House of Lords?
Supreme Court

How can the Supreme Court change its previous decisions ?
Using their powers under the 1966 Practice Statement when they think it is "right to do so".
When can the Court of Appeal change its previous decisions ?
If there was an error in a previous case.

Advantages of Judicial Precedent
- Flexibility
- Consistency/fairness

Judicial Precedent Advantage: Flexibility
- 1966 Practice Statement gives SC power to overrule their own past decisions.
- Persuasive Precedent gives judges the choice to be bound by a precedent.

Judicial Precedent Advantage: Consistency/Fairness
Stare decisis reinforces court hierarchy as lower courts must follow the ratio decidendi of precedents set by higher courts.

Where is the Ratio Decidendi found ?
Law Reports
