science exam sem 2 year 10 physics, energy, and a bit of chemistry
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
76 Terms
what is scalar
a physical quantity described by size
what is vector
a physical quantity described by a size and direction
what is distance
total length of a given path travelled between two points, scalar quantity. usually measured in metres
what is displacement
straight-line distance and direction between the start and finish of a motion, vector quantity. usually measured in metres
what is speed
rate of change of distance over time, scalar. usually measured in metres per second
what is velocity
rate of change of displacement over time, vector. usually measured in metres per second
explain the difference between distance and displacement
distances the total amount travelled and displacement is how far away the object is from it’s starting point
explain the difference between speed and velocity
speed has no direction and is a scalar quantity.
velocity has direction and is a vector quantity
what’s the formula for speed and velocity, (use triangle)
(d = distance for speed and displacement for velocity)
so d is on top, then bottom left is Vav(average velocity or speed) then bottom right is time
what is acceleration
change in velocity over time, usually measured in m/s2
what is acceleration due to gravity
objects have a downwards acceleration due to a planet’s gravitational field. g is the symbol for it. on earth, g ≈ 9.8m/s2 at sea lvl
what does v and u mean
v is final velocity and u is initial velocity
what’s the formula for calculating acceleration (use triangle)
change in velocity on top, a acceleration on bottom left, and change in time on bottom right
The Greek letter ∆ means
change
what can happen when a force is applied to an object
start moving
stop moving
speed up
slow down
change direction
change shape
start/stop spinning
what is force
a push or a pull
can change an object’s motion
symbol is F and is measured in N(newtons)
not required to keep an object moving, friction slows it down
vector quantities
what is net force
resultant force from the addition or subtraction of forces
how to calculate net force
Fnet=m×a
If there’s more than one force, find the difference (biggest minus smallest)
The direction is always that of the larger force
what is inertia
a property of matter by which it continues in its existing state of uniform motion unless acted on by an external force
what’s newtons first law of motion
law of inertia
an object will remain at rest or in constant motion in a. straight line unless acted on by a net unbalanced force
explain how seatbelts work using Newton’s first law of motion
describe motion before change: if a car is travelling 100km/h, so are the passengers
describe motion during change: when car suddenly stops, a force is exerted on the car, but not passengers. the passengers will continue moving 100km/h
explain how/why the motion of the object changes: if the passengers r wearing seatbelts, the seatbelts will exert a force to stop the passenger
what is newton’s second law
an object will accelerate in the direction of an unbalanced force acting on it
acceleration depends on mass and size of net force
we can write the law as: F = m x a
force and acceleration r both vector quantities, and will act in the same direction
how to calculate newtons second law triangle
Fnet(net force) on top, m (mass) on left, a(acceleration) on right
what’s newtons third law
for every action, there’s an equal and opposite reaction on the other object
action-reaction pairs act on different objects, so do not cancel each other out
the reaction force will be equal in size, but opposite in direction to the action force
e.g. when u step forward, pushing back on the ground gives a reaction force of the ground pushing forward on us, without friction the foot will just slide and you won’t move forward
when asked to describe a situation using newtons third law of motion, you need to:
state the direction of the action force
state the direction of the reaction force
explain how a fish is able to swim through water using newtons third law of motion
the fish’s fins push backwards against the water, the water pushes forwards against the fish with the same force
are products formed every time molecules of reactants collide
not necessarily, molecules must collide with enough energy and with the correct alignment
how can the rate of a chemical reaction be slowed down
reduce the surface area of particles reacting
reduce the concentration of the reactants
reduce the temperature of the reactants
why does increasing the surface area increase the rate of reaction
increases the number of molecules exposed to other reactant
increases number of collisions
increases likelihood of successful collisions
why does diluting a solution decrease the rate of reaction
diluting reduces concentration, so reduces number of molecules in the same volume
less particles means less collisions
less chance of successful collisions, so slower reaction rate
define momentum
the product of mass and velocity, usually measured in kg m/s. all moving objects possess momentum. momentum is passed from one object to another in a collision
what’s the formula for momentum using triangle
p(momentum) on top, m(mass) on left, v(velocity) on right
what’s the law of conservation of momentum
in an isolate system, the total momentum does not change in a collision, this means the initial momentum is equal to the final momentum
what is a synthesis reaction
a + b → ab
what is a decomposition reaction
ab → a + b
what is an acid and base reaction
acid + base (metal hydroxide) → water + metal salt
what is an acid and metal reaction
acid + metal → salt + hydrogen
what is an acid and metal oxide
acid + metal oxide → salt + water
what is an acid and metal carbonate
acid + metal carbonate → salt + water + carbon dioxide
what is a displacement-time graph
the displacement of an object (vertical axis)
depends on the time taken for the motion (horizontal axis)
the gradient shows the velocity (measured in m/s)
a straight line indicates a constant velocity
a flat line represents a velocity of 0m/s; the object is stationary

what does this show
the objects motion is moving forward (positive direction) at a constant speed
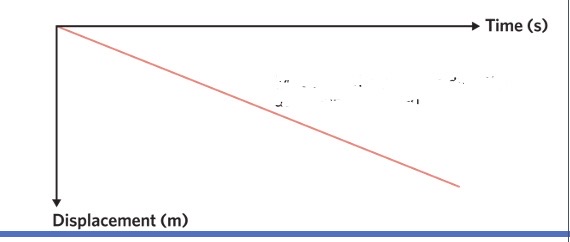
what does this show
the object is moving in the negative direction at a constant speed
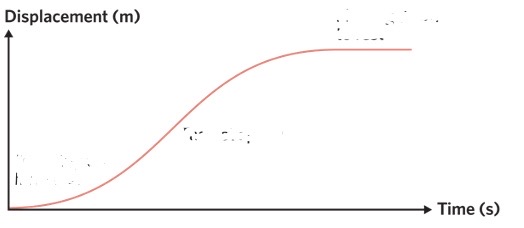
what does this show
the first third is speeding up from rest, 2nd third shows its going the fastest speed, and last third is slowing down to rest
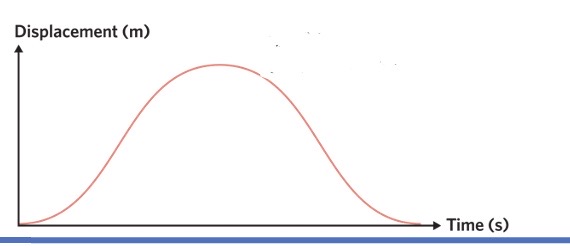
what does this show
the object is moving away, then returning to the starting point
what does a velocity-time graph show
shows how the velocity of an object (vertical axis) depends on the time taken for the motion (horizontal axis)
the gradient shows the acceleration (measured in m/s2)
a straight line indicates a constant acceleration
a flat liner represents a constant velocity
the shaded area under the graph represents the displacement (measured in m)
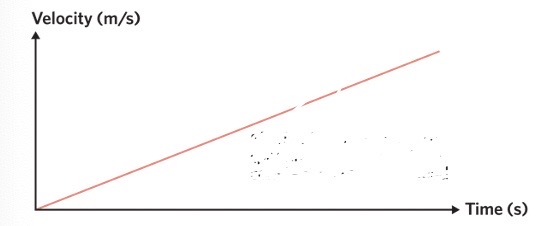
what does this mean
the objects motion is moving forward from rest in a. positive direction with a constant increase of speed
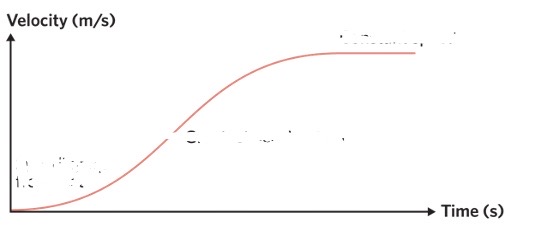
what does this mean
the object is speeding up from rest in 1/3, 2/3 the object has the greatest acceleration, and 3/3 there is a constant speed
what does this mean
the object is moving forward to stop (positive direction) with a constant decrease of speed
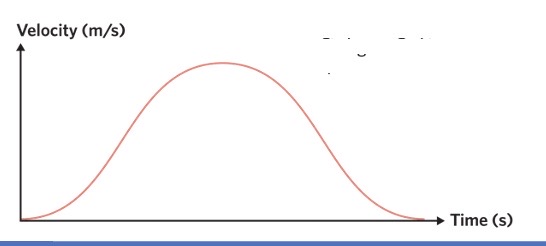
what does this show
the object is starting, speeding up, then slowing down to a stop
what is potential energy
the energy something has because of its position or height or stored condition — not because it’s moving.
its stored energy that has the potential to do work
stored in objects, which can have more than one type of potential energy depending on their position or strucutre
what r some types of potential energy and explain
gravitational: energy stored when something is stored above the ground
chemical: energy stored in chemical bonds
elastic: energy stored when something is stretched or compressed
electrical: energy stored due to charged particles being separated
nuclear: energy stored within the nucleus of an atom
magnetic: energy stored in magnetic fields
what is kinetic energy
the energy a moving object has due to its motion
what does the amount of kinetic energy depend on
the objects mass (heavier objects have more kinetic energy if they’re moving at the same speed) and velocity (Faster objects have way more kinetic energy — because velocity is squared in the formula. velocity affects KE the most)
how does potential energy turn into kinetic energy
when an object starts high up, it has max PE and 0 KE (bc its not moving yet)
the object begins to fall, gravity pulls it downward so it accelerates, the PE decreases and KE increases, the energy is transferring from GPE → KE
just before hitting the ground, the object has max KE bc its moving the fastest, its potential energy is almost 0 (height is almost 0)
so, as height decreases, pe turns into ke and as speed increases ke increases
what are the types of kinetic energy
sound
heat
light
motion
what r the conditions for a chemical reaction to take place
particles collide with energy greater than the activation energy and particles collide at the correct orientation
use collision theory to describe the relationship between temperature and the rate of a chemical reaction
at low temp, a higher fraction of collisions have low energy, so the rate is slower
what is mechanical energy
the energy of an object in motion or the energy that is stored in an object due to its position
define work
the change in mechanical energy of an object, calculated by multiplying force and displacement
what is energy transfer
energy is moved from one place to another without changing form, e.g. placing an ice cube in water transfers thermal energy to the ice cube
what is energy transformation
a change in the form of energy, e,g, rollercoasters work bc of a continuous change between kinetic energy and gravitational potential energy (GPE)
explain energy transformation in a heater
when u turn on an electrical heater, it takes electrical energy from the wall and transforms it into thermal energy to warm up ur room. it also produces some light energy, which is why you can see parts of it glowing
how to draw an energy flowchart
list the energy types present in a given situation
write the starting energy
draw an arrow pointing away from the starting energy
write the ending energy (or energies)
Consider a falling soft drink can. It starts with some gravitational potential energy, which is converted into kinetic energy as it falls.
Draw an energy flowchart for this situation
gravitational potential energy → kinetic energy
how to find the efficiency of an energy transformation
useful output energy (J) divided by input energy (J) x 100%
can a system be more than 100% efficient
no
what does a sankey diagram represent
the ratio of efficiency.
the height of each section represents the proportions of energy forms
the total amount of energy is equal at every stage of the transformation
when a question asks “type/method of energy transfer” what do y talk about and explain
it asks about how the energy moves, the main ones are
conduction(energy transferred through direct contact like spoon to hand)
convection (energy transferred by movement of fluids like liquid or air)
radiation (energy transferred by electromagnetic waves which means no contact needed eg sun and firelight)
what is the suffix ide reserved for
ionic compounds (metal and non metal conjoined) or simple covalent compounds. only the non-metal element whose always written second ends with ide
what are the suffixes ate and ite reserved for
polyatomic ions, when a polyatomic ion loses an oxygen, their suffix changes from ate to ite
what is nitrate
NO3-
what is sulfate
SO4 2-
what is carbonate
CO3 2-
what is phosphate
PO 4 3-
what is hydroxide
OH-
ammonium
NH4+