Orgo I: Chapter 8: Alkenes: Reactions and Synthesis
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
How are alkenes usually prepared
Elimination forming alkene and X-Y
dehydrohalogenation
loss of HX from alkyl halide usually by reaction of an alkyl halide with a strong base like potassium hydroxide
dehydration
loss of water from an alcohol, treatment of an alcohol with a strong acid, in tetrahydrofuran (THF)
halogenation
rapid addition of halogens to alkenes to yield 1,2-dihalides (Br & Cl)
bromonium ion
Intermediate formed during bromination of alkenes. R2Br+
why is trans product formed for halogenation
when the bromonium ion forms, the bromine acts as a shield to one side making the second bromide attach at the opposite side
halohydrin reaction
C=C —> (NBS/DMSO) bromonium ion, h2o added, Br-C-C-OH2+ second h2o forms hydronium leaving halohydrin Br-C-C-OH
What are the usual solvents and reagents for bromohydrin formation?
CH3SOCH3 (DMSO) solvent, N-bromosuccinimide (NBS) reagent is the source of Br2
hydration
C=C —> (H3O+) double bond donates to H, H donates to O +C-C-H —>(H2O) +OH2-C-C-H —> (H2O) O donates to H H donates to O HO-C-C-H + H3O+ (markovnikov)
oxymercuration-demercuration reaction
C=C —> (Hg(OAc)2) Mercurinium ion (HgOAc+) —> (H2O) HO-C-C-HgOAc —> (NaBH4) HO-C-C-H (markovnikov)
hydroboration is the alternative to?
complementary method to oxymercuration-demercuration that produces a non-markonikov alcohol
what are the intermediates in hydroboration?
C=C —> (BH3/THF) --> organoborane intermediate H-C-C-BH2 —> (H2O2/ OH-) --> H-C-C-OH (non-markovnikov’s alcohol)
syn stereochemistry
addition to the same side of the double or triple bond
hydrogenation
C=C —> (H2, PtO2/CH3O2H) H3-C-C-H3 (cis)
epoxide
oxirane, cyclic ether with an oxygen atom in a 3 membered ring
epoxidation reaction
C=C —> (H-O-O-(C=O)-R) Epoxide + H-O-(C=O)
diol formation via epoxide
C=C —> (H-O-O-(C=O)-R) Epoxide (+ H-O-(C=O)) —> (H3O+) Epoxide-H+ —> (H2O) HO-C-C-OH2+ —> HO-C-C-OH (trans)
diol formation with only one intermediate
C=C —> (OsO4) cyclic osmate intermediate —> (NaHSO3/H2O) HO-C-C-OH (cis)
ozonolysis reaction
C=C —> (O3/CH3Cl2) molozonide (clockwise, -O-O-O-C-C-) —> ozonide (clockwise, -O-O-C-O-C-) —> (Zn/CH3CO2H/H2O) C=O C=O
what will potassium manganate produce and how
carboxylic acids and CO2 if H are present H3C-C=C-H2 —> (KMnO4/H3O+) H2C-(C=O)-OH + CO2
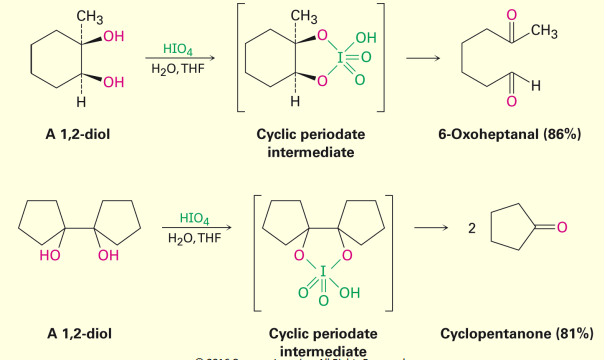
HIO4 reaction
simplest way to generate a carbene
treat CHCl3 with strong base like KOH
is the product of the reaction between dichlorocarbene and alkene stereospecific
yes cis with cis and trans with trans